run flat FORD MONDEO 1993 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 1993, Model line: MONDEO, Model: FORD MONDEO 1993Pages: 279, PDF Size: 12.71 MB
Page 12 of 279
0•12
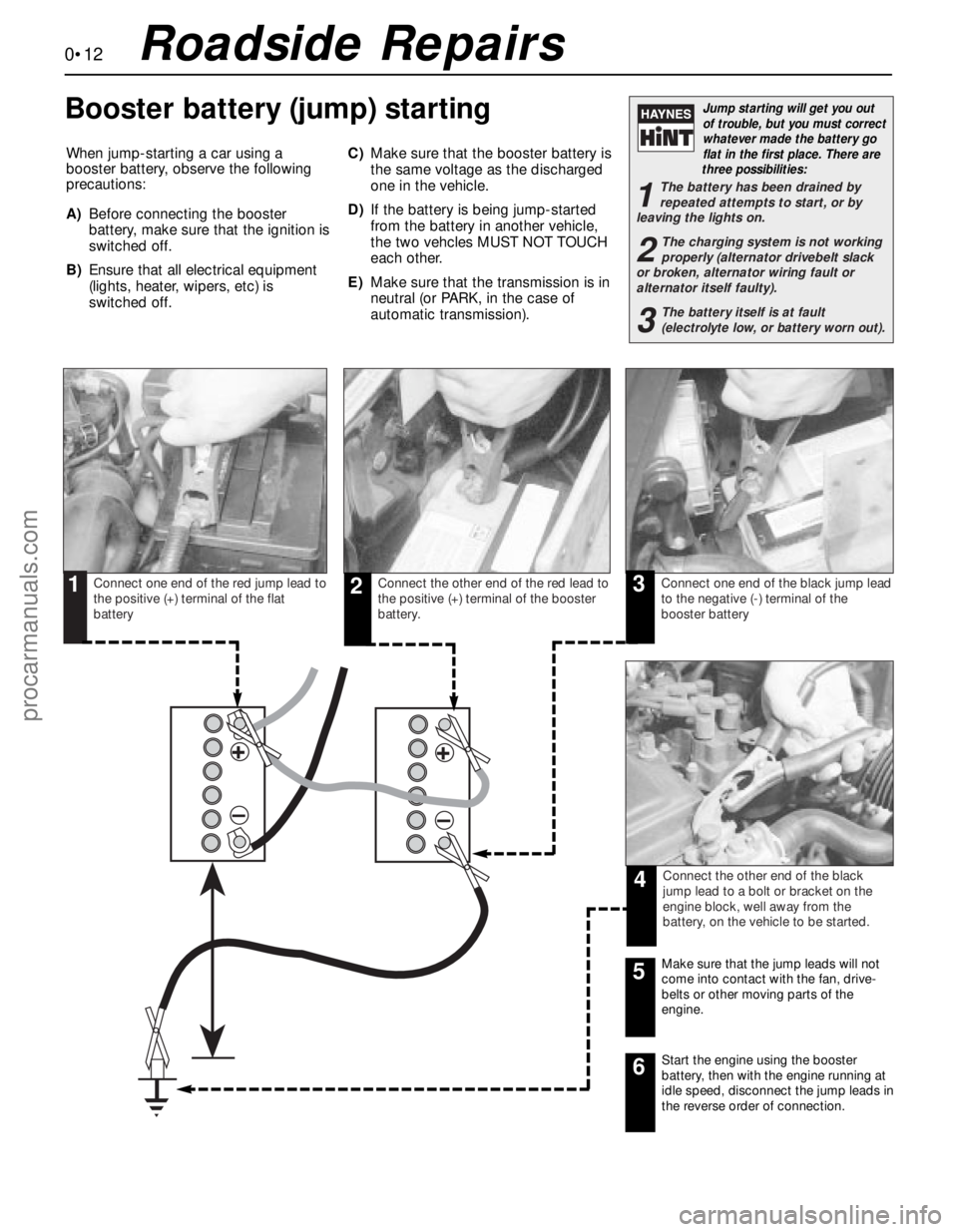
When jump-starting a car using a
booster battery, observe the following
precautions:
A)Before connecting the booster
battery, make sure that the ignition is
switched off.
B)Ensure that all electrical equipment
(lights, heater, wipers, etc) is
switched off.C)Make sure that the booster battery is
the same voltage as the discharged
one in the vehicle.
D)If the battery is being jump-started
from the battery in another vehicle,
the two vehcles MUST NOT TOUCH
each other.
E)Make sure that the transmission is in
neutral (or PARK, in the case of
automatic transmission).
Jump starting will get you out
of trouble, but you must correct
whatever made the battery go
flat in the first place. There are
three possibilities:
1The battery has been drained by
repeated attempts to start, or by
leaving the lights on.
2The charging system is not working
properly (alternator drivebelt slack
or broken, alternator wiring fault or
alternator itself faulty).
3The battery itself is at fault
(electrolyte low, or battery worn out).
Connect one end of the red jump lead to
the positive (+) terminal of the flat
batteryConnect the other end of the red lead to
the positive (+) terminal of the booster
battery.Connect one end of the black jump lead
to the negative (-) terminal of the
booster battery
Connect the other end of the black
jump lead to a bolt or bracket on the
engine block, well away from the
battery, on the vehicle to be started.
123
4
Make sure that the jump leads will not
come into contact with the fan, drive-
belts or other moving parts of the
engine.5
Start the engine using the booster
battery, then with the engine running at
idle speed, disconnect the jump leads in
the reverse order of connection.6
Roadside Repairs
Booster battery (jump) starting
procarmanuals.com
Page 24 of 279
the tyre to cause deflation. If removal of a nail
reveals that the tyre has been punctured, refit
the nail, so that its point of penetration is
marked. Then immediately change the wheel,
and have the tyre repaired by a tyre dealer. Do
not drive on a tyre in such a condition. If in any
doubt as to the possible consequences of any
damage found, consult your local tyre dealer
for advice.
8General tyre wear is influenced to a large
degree by driving style - harsh braking and
acceleration, or fast cornering, will all produce
more rapid tyre wear. Interchanging of tyres
may result in more even wear; however, it is
worth bearing in mind that if this is completely
effective, the added expense is incurred of
replacing simultaneously a complete set of
tyres, which may prove financially restrictive
for many owners.
9Front tyres may wear unevenly as a result of
wheel misalignment. The front wheels should
always be correctly aligned according to the
settings specified by the vehicle
manufacturer.10Don’t forget to check the spare tyre for
condition and pressure.
11Legal restrictions apply to many aspects
of tyre fitting and usage, and in the UK this
information is contained in the Motor Vehicle
Construction and Use Regulations. It is
suggested that a copy of these regulations is
obtained from your local police, if in doubt as
to current legal requirements with regard to
tyre type and condition, minimum tread depth,
etc.
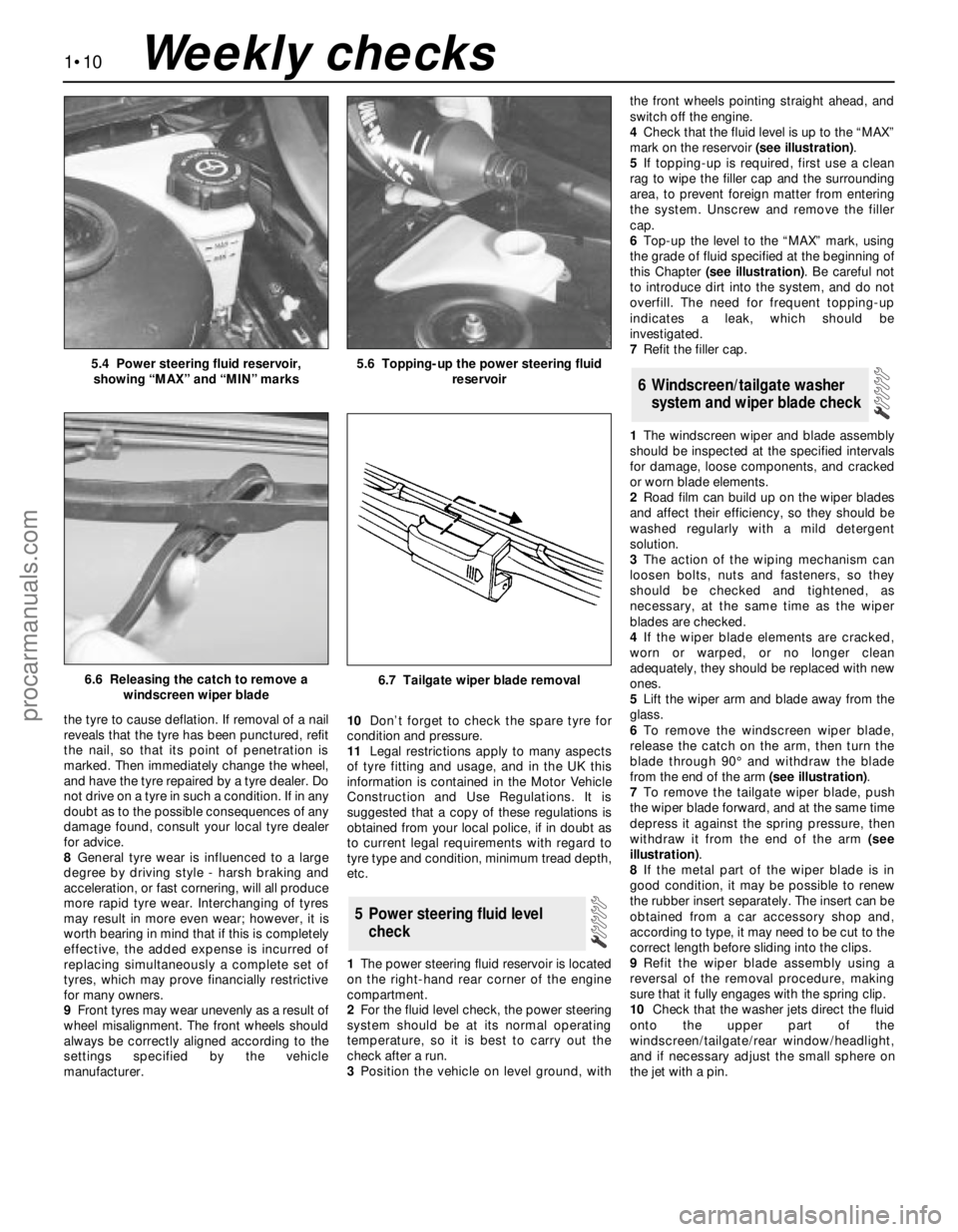
1The power steering fluid reservoir is located
on the right-hand rear corner of the engine
compartment.
2For the fluid level check, the power steering
system should be at its normal operating
temperature, so it is best to carry out the
check after a run.
3Position the vehicle on level ground, withthe front wheels pointing straight ahead, and
switch off the engine.
4Check that the fluid level is up to the “MAX”
mark on the reservoir (see illustration).
5If topping-up is required, first use a clean
rag to wipe the filler cap and the surrounding
area, to prevent foreign matter from entering
the system. Unscrew and remove the filler
cap.
6Top-up the level to the “MAX” mark, using
the grade of fluid specified at the beginning of
this Chapter (see illustration). Be careful not
to introduce dirt into the system, and do not
overfill. The need for frequent topping-up
indicates a leak, which should be
investigated.
7Refit the filler cap.
1The windscreen wiper and blade assembly
should be inspected at the specified intervals
for damage, loose components, and cracked
or worn blade elements.
2Road film can build up on the wiper blades
and affect their efficiency, so they should be
washed regularly with a mild detergent
solution.
3The action of the wiping mechanism can
loosen bolts, nuts and fasteners, so they
should be checked and tightened, as
necessary, at the same time as the wiper
blades are checked.
4If the wiper blade elements are cracked,
worn or warped, or no longer clean
adequately, they should be replaced with new
ones.
5Lift the wiper arm and blade away from the
glass.
6To remove the windscreen wiper blade,
release the catch on the arm, then turn the
blade through 90° and withdraw the blade
from the end of the arm (see illustration).
7To remove the tailgate wiper blade, push
the wiper blade forward, and at the same time
depress it against the spring pressure, then
withdraw it from the end of the arm (see
illustration).
8If the metal part of the wiper blade is in
good condition, it may be possible to renew
the rubber insert separately. The insert can be
obtained from a car accessory shop and,
according to type, it may need to be cut to the
correct length before sliding into the clips.
9Refit the wiper blade assembly using a
reversal of the removal procedure, making
sure that it fully engages with the spring clip.
10Check that the washer jets direct the fluid
onto the upper part of the
windscreen/tailgate/rear window/headlight,
and if necessary adjust the small sphere on
the jet with a pin.
6 Windscreen/tailgate washer
system and wiper blade check
5 Power steering fluid level
check
1•10
5.4 Power steering fluid reservoir,
showing “MAX” and “MIN” marks5.6 Topping-up the power steering fluid
reservoir
6.7 Tailgate wiper blade removal6.6 Releasing the catch to remove a
windscreen wiper blade
Weekly checks
procarmanuals.com
Page 27 of 279

amperage charger, but don’t use one rated
more than 1/10th the amp/hour rating of the
battery (ie no more than 5 amps, typically).
Rapid boost charges that claim to restore the
power of the battery in one to two hours are
hardest on the battery, and can damage
batteries not in good condition. This type of
charging should only be used in emergency
situations.
14The average time necessary to charge a
battery should be listed in the instructions that
come with the charger. As a general rule, a
trickle charger will charge a battery in 12 to
16 hours.
1Check the seat belts for satisfactory
operation and condition. Inspect the webbing
for fraying and cuts. Check that they retract
smoothly and without binding into their reels.
2Check that the seat belt mounting bolts are
tight, and if necessary tighten them to the
specified torque wrench setting.
General
1The auxiliary drivebelt is of the flat, multi-
ribbed (or “polyvee”) type, and is located on
the right-hand end of the engine. It drives the
alternator, water pump, power steering pump
and (when fitted) the air conditioning
compressor from the engine’s crankshaft
pulley.
2The good condition and proper tension of
the auxiliary drivebelt is critical to the
operation of the engine. Because of their
composition and the high stresses to which
they are subjected, drivebelts stretch anddeteriorate as they get older. They must,
therefore, be regularly inspected.
Check
3With the engine switched off, open and
support the bonnet, then locate the auxiliary
drivebelt on the right-hand end of the engine,
under the engine right-hand mounting
bracket. (Be very careful, and wear protective
gloves to minimise the risk of burning your
hands on hot components, if the engine has
recently been running.) For improved access,
jack up the front right-hand side of the
vehicle, support it securely on an axle stand,
remove the roadwheel, then remove the
auxiliary drivebelt cover (two fasteners) from
inside the wheel arch (see illustration).
4Using an inspection light or a small electric
torch, and rotating the engine when necessary
with a spanner applied to the crankshaft
pulley bolt, check the whole length of the
drivebelt for cracks, separation of the rubber,
and torn or worn ribs (see illustration). Also
check for fraying and glazing, which gives the
drivebelt a shiny appearance. Both sides of
the drivebelt should be inspected, which
means you will have to twist the drivebelt to
check the underside. Use your fingers to feel
the drivebelt where you can’t see it. If you are
in any doubt as to the condition of the
drivebelt, renew it (go to paragraph 7).
Drivebelt tension
5The auxiliary drivebelt is tensioned by an
automatic tensioner; regular checks are not
required, and manual “adjustment” is not
possible.
6If you suspect that the drivebelt is slipping
and/or running slack, or that the tensioner is
otherwise faulty, it must be renewed. To do
this, remove the drivebelt as described below,
then unbolt the tensioner (two Torx-type
screws accessible from underneath, via the
wheel arch) from the alternator mounting
bracket (see illustration). On fitting the new
tensioner, ensure it is aligned correctly on its
mountings, and tighten the screws to the
specified torque wrench setting.
Renewal
7Open the bonnet. Jack up the front right-
hand side of the vehicle and support it
securely on an axle stand, remove the
roadwheel, then remove the auxiliary drivebelt
cover (two fasteners) from inside the wheel
arch.
8If the existing drivebelt is to be refitted,
mark it, or note the maker’s markings on its
flat surface, so that it can be installed the
same way round.
9Reaching up between the body and the
engine (above and to the rear of the
crankshaft pulley), apply a spanner to the
hexagon in the centre of the automatic
tensioner’s pulley. Rotate the tensioner pulley
clockwise to release its pressure on the
drivebelt, then slip the drivebelt off the
crankshaft pulley, and release the tensioner
again (see illustration). Working from the
wheel arch or engine compartment as
necessary, and noting its routing, slip the
drivebelt off the remaining pulleys and
withdraw it.
10Check all the pulleys, ensuring that their
grooves are clean, and removing all traces of
oil and grease. Check that the tensioner
works properly, with strong spring pressure
11 Auxiliary drivebelt check and
renewal
10 Seat belt check
1•13
1
11.9 Rotate the tensioner pulley clockwise
to release its pressure on the drivebelt,
then slip the drivebelt off the crankshaft
pulley
11.3 Removing the auxiliary drivebelt
cover - it is secured by a fastener at each
end (arrowed) - from inside the right-hand
front wheel arch
11.4 Check the auxiliary drivebelt for signs
of wear like these. Very small cracks across
the drivebelt ribs are acceptable. If the
cracks are deep, or if the drivebelt looks
worn or damaged in any other way, renew it
11.6 The auxiliary drivebelt is tensioned by
an automatic tensioner; Torx screws
(arrowed) secure it to alternator mounting
bracket
Every 10 000 miles
procarmanuals.com
Page 28 of 279
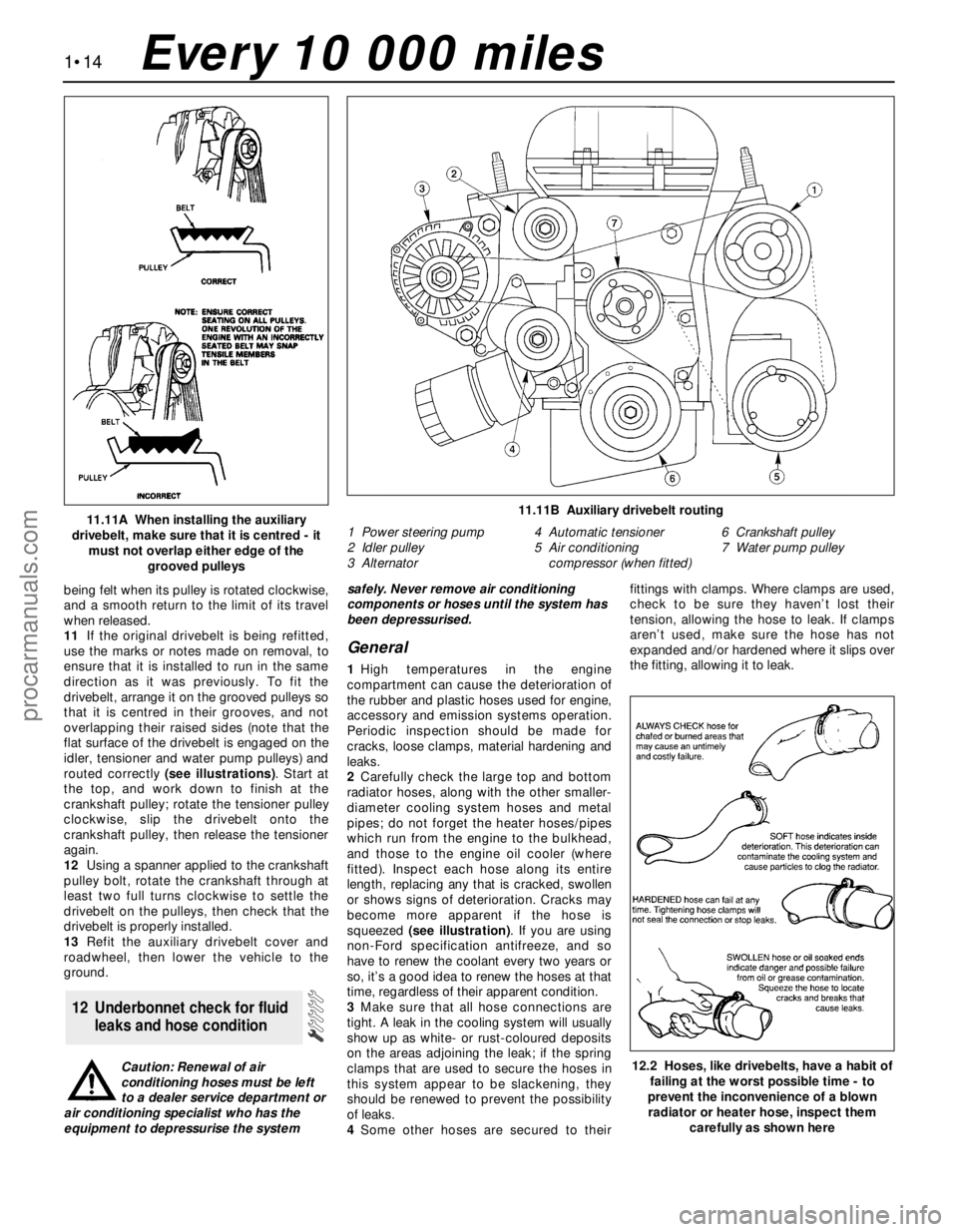
being felt when its pulley is rotated clockwise,
and a smooth return to the limit of its travel
when released.
11If the original drivebelt is being refitted,
use the marks or notes made on removal, to
ensure that it is installed to run in the same
direction as it was previously. To fit the
drivebelt, arrange it on the grooved pulleys so
that it is centred in their grooves, and not
overlapping their raised sides (note that the
flat surface of the drivebelt is engaged on the
idler, tensioner and water pump pulleys) and
routed correctly (see illustrations). Start at
the top, and work down to finish at the
crankshaft pulley; rotate the tensioner pulley
clockwise, slip the drivebelt onto the
crankshaft pulley, then release the tensioner
again.
12Using a spanner applied to the crankshaft
pulley bolt, rotate the crankshaft through at
least two full turns clockwise to settle the
drivebelt on the pulleys, then check that the
drivebelt is properly installed.
13Refit the auxiliary drivebelt cover and
roadwheel, then lower the vehicle to the
ground.
Caution: Renewal of air
conditioning hoses must be left
to a dealer service department or
air conditioning specialist who has the
equipment to depressurise the systemsafely. Never remove air conditioning
components or hoses until the system has
been depressurised.
General
1High temperatures in the engine
compartment can cause the deterioration of
the rubber and plastic hoses used for engine,
accessory and emission systems operation.
Periodic inspection should be made for
cracks, loose clamps, material hardening and
leaks.
2Carefully check the large top and bottom
radiator hoses, along with the other smaller-
diameter cooling system hoses and metal
pipes; do not forget the heater hoses/pipes
which run from the engine to the bulkhead,
and those to the engine oil cooler (where
fitted). Inspect each hose along its entire
length, replacing any that is cracked, swollen
or shows signs of deterioration. Cracks may
become more apparent if the hose is
squeezed (see illustration). If you are using
non-Ford specification antifreeze, and so
have to renew the coolant every two years or
so, it’s a good idea to renew the hoses at that
time, regardless of their apparent condition.
3Make sure that all hose connections are
tight. A leak in the cooling system will usually
show up as white- or rust-coloured deposits
on the areas adjoining the leak; if the spring
clamps that are used to secure the hoses in
this system appear to be slackening, they
should be renewed to prevent the possibility
of leaks.
4Some other hoses are secured to theirfittings with clamps. Where clamps are used,
check to be sure they haven’t lost their
tension, allowing the hose to leak. If clamps
aren’t used, make sure the hose has not
expanded and/or hardened where it slips over
the fitting, allowing it to leak.
12 Underbonnet check for fluid
leaks and hose condition
1•14
11.11A When installing the auxiliary
drivebelt, make sure that it is centred - it
must not overlap either edge of the
grooved pulleys11.11B Auxiliary drivebelt routing
1 Power steering pump
2 Idler pulley
3 Alternator4 Automatic tensioner
5 Air conditioning
compressor (when fitted)6 Crankshaft pulley
7 Water pump pulley
12.2 Hoses, like drivebelts, have a habit of
failing at the worst possible time - to
prevent the inconvenience of a blown
radiator or heater hose, inspect them
carefully as shown here
Every 10 000 miles
procarmanuals.com
Page 34 of 279

brake shoes is not less than the
recommendation given in the Specifications.
14If it is difficult to determine the exact
thickness of the brake shoe linings, or if you
are at all concerned about the condition of the
shoes, then remove the rear drums for a more
comprehensive inspection (refer to Chapter 9)
(see illustration).
15With the drum removed, check the shoe
return and hold-down springs for correct
installation, and check the wheel cylinders for
leakage of brake fluid. Check the friction
surface of the brake drums for scoring and
discoloration. If excessive, the drum should
be resurfaced or renewed.
16Before refitting the wheels, check all
brake lines and hoses (refer to Chapter 9). On
completion, apply the handbrake and check
that the rear wheels are locked. The
handbrake is self-adjusting, and no manual
adjustment is possible.
1Check that the doors, bonnet and
tailgate/boot lid close securely. Check that
the bonnet safety catch operates correctly.
Check the operation of the door check straps.
2Lubricate the hinges, door check straps,
the striker plates and the bonnet catch
sparingly with a little oil or grease.1Apply the handbrake.
2Remove the wheel covers, using the flat
end of the wheelbrace supplied in the tool kit
(on models with the RS trim kit, it will be
necessary to unscrew the retaining bolts with
the special key).
3Check that the roadwheel nuts are tightened
to the specified torque wrench setting.
4Refit the wheel covers.
Check the operation and
performance of the braking
system
1Make sure that the vehicle does not pull to
one side when braking, and that the wheels
do not lock prematurely when braking hard.
2Check that there is no vibration through the
steering when braking.
3Check that the handbrake operates
correctly, without excessive movement of the
lever, and that it holds the vehicle stationary
on a slope.
4With the engine switched off, test the
operation of the brake servo unit as follows.
Depress the footbrake four or five times to
exhaust the vacuum, then start the engine. As
the engine starts, there should be a noticeable
“give” in the brake pedal as vacuum builds
up. Allow the engine to run for at least two
minutes, and then switch it off. If the brake
pedal is now depressed again, it should be
possible to detect a hiss from the servo as the
pedal is depressed. After about four or five
applications, no further hissing should be
heard, and the pedal should feel considerably
harder.
Steering and suspension
5Check for any abnormalities in the steering,
suspension, handling or road “feel”.
6Drive the vehicle, and check that there are
no unusual vibrations or noises.
7Check that the steering feels positive, with
no excessive sloppiness or roughness, andcheck for any suspension noises when
cornering and driving over bumps.
Drivetrain
8Check the performance of the engine,
transmission and driveshafts.
9Check that the engine starts correctly, both
when cold and when hot.
10Listen for any unusual noises from the
engine and transmission.
11Make sure that the engine runs smoothly
when idling, and that there is no hesitation
when accelerating.
12On manual transmission models, check
that all gears can be engaged smoothly
without noise, and that the gear lever action is
not abnormally vague or “notchy”.
13On automatic transmission models, make
sure that all gearchanges occur smoothly
without snatching, and without an increase in
engine speed between changes. Check that
all the gear positions can be selected with the
vehicle at rest. If any problems are found, they
should be referred to a Ford dealer.
14Listen for a metallic clicking sound from
the front of the vehicle as the vehicle is driven
slowly in a circle with the steering on full-lock.
Carry out this check in both directions. If a
clicking noise is heard, this indicates wear in a
driveshaft joint, in which case renew the joint
if necessary.
Clutch
15Check that the clutch pedal moves
smoothly and easily through its full travel, and
that the clutch itself functions correctly, with
no trace of slip or drag. If the movement is
uneven or stiff in places, check that the cable
is routed correctly, with no sharp turns.
16Inspect both ends of the clutch inner
cable, both at the gearbox end and inside the
car, for signs of wear and fraying.
17Check the pedal stroke as described in
Chapter 8, Section 3, and adjust if necessary.
Instruments and electrical
equipment
18Check the operation of all instruments
and electrical equipment.
19Make sure that all instruments read
correctly, and switch on all electrical
equipment in turn, to check that it functions
properly.
26 Road test
25 Roadwheel nut tightness
check
24 Door and bonnet check and
lubrication
1•20
23.14 If the lining is bonded to the brake
shoe, measure the lining thickness from
the outer surface to the metal shoe, as
shown here; if the lining is riveted to the
shoe, measure from the lining outer
surface to the rivet head
Every 20 000 miles
Every 20 000 miles or 2 years
1The air entering the vehicle’s ventilation
system is passed through a very fine pleated-
paper air filter element, which removes
particles of pollen, dust and other airborne
foreign matter. To ensure its continued
effectiveness, this filter’s element must be
renewed at regular intervals.2Remove the left-hand side windscreen
wiper arm (Chapter 12).
3Prise off their trim caps, then unscrew the two
screws securing the windscreen edge of the cowl
grille panel; open the bonnet and remove the
remaining three retaining screws (see illustration).
4Peel back the rubber seal and withdraw the
cowl grille panel.
5Releasing the clip at each end, lift out the
pollen filter housing, and withdraw the
element (see illustrations).6Wipe out the ventilation system intake and
the filter housing, removing any leaves, dead
insects etc.
7If carrying out a routine service, the element
must be renewed regardless of its apparent
condition. If you are checking the element for
any other reason, inspect its front surface; if it
is very dirty, renew the element. If it is only
moderately dusty, it can be re-used by
blowing it clean from the rear to the front
surface with compressed air. Because it is a
27 Ventilation system pollen
filter renewal
procarmanuals.com
Page 49 of 279

9Remove the nuts and detach the manifold
and gasket (see illustration). Take care not
to damage vulnerable components such as
the EGR pipe as the manifold assembly is
manoeuvred out of the engine compartment.
When removing the manifold with the engine
in the vehicle, additional clearance can be
obtained by unscrewing the studs from the
cylinder head; a female Torx-type socket will
be required (see illustration).
10Always fit a new gasket on reassembly, to
carefully-cleaned components (see below).
Do notattempt to re-use the original gasket.
Inspection
11Use a scraper to remove all traces of old
gasket material and carbon deposits from the
manifold and cylinder head mating surfaces. If
the gasket was leaking, have the manifold
checked for warpage at an automotive
machine shop, and have it resurfaced if
necessary.
Caution: When scraping, be very
careful not to gouge or scratch
the delicate aluminium alloy
cylinder head.
12Provided both mating surfaces are clean
and flat, a new gasket will be sufficient to
ensure the joint is gas-tight. Do notuse any
kind of exhaust sealant upstream of the
catalytic converter.
13Note that the downpipe is secured to the
manifold by two bolts, with a coil spring,
spring seat and self-locking nut on each. On
refitting, tighten the nuts until they stop on thebolt shoulders; the pressure of the springs will
then suffice to make a leakproof joint (see
illustrations).
14Do not overtighten the nuts to cure a leak
- the bolts will shear; renew the gasket and
the springs if a leak is found. The bolts
themselves are secured by spring clips to the
manifold, and can be renewed easily if
damaged (see illustration).
Refitting
15Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure, noting the following points:
(a) Position a new gasket over the cylinder
head studs, and fit a new plastic guide
sleeve to the stud nearest to the
thermostat housing, so that the manifold
will be correctly located (see illustration).
Do notrefit the manifold without this
sleeve.
(b) Refit the manifold, and finger-tighten the
mounting nuts.
(c) Working from the centre out, and in three
or four equal steps, tighten the nuts to the
torque wrench setting given in the
Specifications Section of this Chapter.
(d) Refit the remaining parts in the reverse
order of removal. Tighten all fasteners to
the specified torque wrench settings.
(e) Refill the cooling system (see Chapter 1).
(f) Run the engine, and check for exhaust
leaks. Check the coolant level when fully
warmed-up to normal operating
temperature.1Remove the auxiliary drivebelt - either
remove the drivebelt completely, or just
secure it clear of the crankshaft pulley,
depending on the work to be carried out (see
Chapter 1).
2If necessary, rotate the crankshaft until the
timing marks align (see Section 4).
3The crankshaft must now be locked to
prevent its rotation while the pulley bolt is
unscrewed. Proceed as follows:
(a) If the engine/transmission is still installed
in the vehicle:
(1) If the vehicle is fitted with manual
transmission, select top gear, and have an
assistant apply the brakes hard.
(2) If the vehicle is fitted with automatic
transmission, unbolt the small metal cover
plate from the sump, and use a large
screwdriver or similar to lock the
driveplate ring gear teeth while an
assistant slackens the pulley bolt; take
care not to damage the teeth or the
surrounding castings when using this
method.
(b) If the engine/transmission has been
removed but not yet separated:
(1) If the vehicle is fitted with manual
transmission, remove the starter motor
(see Chapter 5) and lock the flywheel
8 Crankshaft pulley -
removal and refitting
In-car engine repair procedures 2A•9
2A
7.13B Renew exhaust system downpipe-
to-manifold gasket to prevent leaks7.14 Release spring clip to extract
securing bolt from manifold, when required7.15 Fit plastic guide sleeve to stud
arrowed when refitting exhaust manifold
7.9A Unscrew nuts (arrowed) to remove
exhaust manifold . . .
7.9B . . . studs can be unscrewed also, if
required, to provide additional working
space7.13A Showing exhaust downpipe-to-
manifold securing bolts - note coil spring,
and shoulder on bolt
procarmanuals.com
Page 69 of 279

How to use this Chapter
This Part of Chapter 2 is devoted to
engine/transmission removal and refitting, to
those repair procedures requiring the removal
of the engine/transmission from the vehicle,
and to the overhaul of engine components. It
includes only the Specifications relevant to
those procedures. Refer to Part A for
additional Specifications, if required.
General information
The information ranges from advice
concerning preparation for an overhaul and
the purchase of replacement parts, to detailed
step-by-step procedures covering removal
and installation of internal engine components
and the inspection of parts.
The following Sections have been written
based on the assumption that the engine has
been removed from the vehicle. For
information concerning in-vehicle engine
repair, as well as removal and installation of
the external components necessary for the
overhaul, see Part A of this Chapter and
Section 5 of this Part.
When overhauling this engine, it is essential
to establish first exactly what replacement
parts are available. At the time of writing,
components such as the piston rings are not
available separately from the
piston/connecting rod assemblies; pistons,
gudgeon pins and valve guides are not
available separately, and very few under- or
oversized components are available for
engine reconditioning. In most cases, it would
appear that the easiest and most
economically-sensible course of action is to
replace a worn or damaged engine with an
exchange unit.
It’s not always easy to determine when, or
if, an engine should be completely
overhauled, as a number of factors must be
considered.
High mileage is not necessarily an
indication that an overhaul is needed, while
low mileage doesn’t preclude the need for an
overhaul. Frequency of servicing is probably
the most important consideration. An engine
that’s had regular and frequent oil and filter
changes, as well as other required
maintenance, will most likely give many
thousands of miles of reliable service.
Conversely, a neglected engine may require
an overhaul very early in its life.
Excessive oil consumption is an indication
that piston rings, valve seals and/or valve
guides are in need of attention. Make surethat oil leaks aren’t responsible before
deciding that the rings and/or guides are
worn. Perform a cylinder compression check
(Part A of this Chapter, Section 3) to
determine the extent of the work required.
Loss of power, rough running, knocking or
metallic engine noises, excessive valve train
noise and high fuel consumption rates may
also point to the need for an overhaul,
especially if they’re all present at the same
time. If a full service doesn’t remedy the
situation, major mechanical work is the only
solution.
An engine overhaul involves restoring all
internal parts to the specification of a new
engine. Note:Always check first what
replacement parts are available before
planning any overhaul operation; refer to
Section 1 of this Part. Ford dealers, or a good
engine reconditioning specialist/automotive
parts supplier may be able to suggest
alternatives which will enable you to overcome
the lack of replacement parts.
During an overhaul, it is usual to renew the
piston rings, and to rebore and/or hone the
cylinder bores; where the rebore is done by an
automotive machine shop, new oversize
pistons and rings will also be installed - all
these operations, of course, assume the
availability of suitable replacement parts. The
main and big-end bearings are generally
renewed and, if necessary, the crankshaft
may be reground to restore the journals.
Generally, the valves are serviced as well,
since they’re usually in less-than-perfect
condition at this point. While the engine is
being overhauled, other components, such as
the starter and alternator, can be renewed as
well, or rebuilt, if the necessary parts can be
found. The end result should be an as-new
engine that will give many trouble-free miles.
Note:Critical cooling system components
such as the hoses, drivebelt, thermostat and
water pump MUST be replaced with new
parts when an engine is overhauled. The
radiator should be checked carefully, to
ensure that it isn’t clogged or leaking (see
Chapter 3). Also, as a general rule, the oil
pump should be renewed when an engine is
rebuilt.
Before beginning the engine overhaul, read
through the entire procedure to familiarise
yourself with the scope and requirements of
the job. Overhauling an engine isn’t difficult,
but it is time-consuming. Plan on the vehicle
being off the road for a minimum of two
weeks, especially if parts must be taken to an
automotive machine shop for repair or
reconditioning. Check on availability of parts,
and make sure that any necessary special
tools and equipment are obtained in advance.
Most work can be done with typical hand
tools, although a number of precision
measuring tools are required, for inspecting
parts to determine if they must be replaced.
Often, an automotive machine shop will
handle the inspection of parts, and will offer
advice concerning reconditioning andreplacement. Note:Always wait until the
engine has been completely dismantled, and
all components, especially the cylinder
block/crankcase, have been inspected, before
deciding what service and repair operations
must be performed by an automotive machine
shop. Since the block’s condition will be the
major factor to consider when determining
whether to overhaul the original engine or buy
a rebuilt one, never purchase parts or have
machine work done on other components
until the cylinder block/crankcase has been
thoroughly inspected.As a general rule, time
is the primary cost of an overhaul, so it
doesn’t pay to install worn or sub-standard
parts.
As a final note, to ensure maximum life and
minimum trouble from a rebuilt engine,
everything must be assembled with care, in a
spotlessly-clean environment.
If you’ve decided that an engine must be
removed for overhaul or major repair work,
several preliminary steps should be taken.
Locating a suitable place to work is
extremely important. Adequate work space,
along with storage space for the vehicle, will
be needed. If a workshop or garage isn’t
available, at the very least, a flat, level, clean
work surface made of concrete or asphalt is
required.
Cleaning the engine compartment and
engine/transmission before beginning the
removal procedure will help keep tools clean
and organized.
The engine can only be withdrawn by
removing it complete with the transmission;
the vehicle’s body must be raised and
supported securely, sufficiently high that the
engine/transmission can be unbolted as a
single unit and lowered to the ground; the
engine/transmission unit can then be
withdrawn from under the vehicle and
separated. An engine hoist or A-frame will
therefore be necessary. Make sure the
equipment is rated in excess of the combined
weight of the engine and transmission. Safety
is of primary importance, considering the
potential hazards involved in removing the
engine/transmission from the vehicle.
If this is the first time you have removed an
engine, a helper should ideally be available.
Advice and aid from someone more
experienced would also be helpful. There are
many instances when one person cannot
simultaneously perform all of the operations
required when removing the engine/
transmission from the vehicle.
Plan the operation ahead of time. Arrange for,
or obtain, all of the tools and equipment you’ll
need prior to beginning the job. Some of the
equipment necessary to perform
engine/transmission removal and installation
3 Engine/transmission removal -
methods and precautions
2 Engine overhaul -
general information
1 General information
Engine removal and general engine overhaul procedures 2B•3
2B
procarmanuals.com
Page 85 of 279

to the engine bearings, the acid attacks and
corrodes the bearing material.
7Incorrect shell refitting during engine
assembly will lead to bearing failure as well.
Tight-fitting shells leave insufficient bearing
running clearance, and will result in oil
starvation. Dirt or foreign particles trapped
behind a bearing shell result in high spots on
the bearing, which lead to failure. Do not
touch any shell’s bearing surface with your
fingers during reassembly; there is a risk of
scratching the delicate surface, or of
depositing particles of dirt on it.
1Before reassembly begins, ensure that all
new parts have been obtained, and that all
necessary tools are available. Read through
the entire procedure, to familiarise yourself
with the work involved, and to ensure that all
items necessary for reassembly of the engine
are at hand. In addition to all normal tools and
materials, suitable sealant will be required for
two of the joint faces (Ford recommend
Hylosil 102 for the cylinder block/crankcase-
to-sump/oil pump/oil seal carrier joints, and
Loctite 518 for the camshaft right-hand
bearing caps). In all other cases, provided the
relevant mating surfaces are clean and flat,
new gaskets will be sufficient to ensure joints
are oil-tight. Do notuse any kind of silicone-
based sealant on any part of the fuel system
or inlet manifold, and neveruse exhaust
sealants upstream of the catalytic converter.
2In order to save time and avoid problems,
engine reassembly can be carried out in the
following order:
(a) Crankshaft (Section 17).
(b) Piston/connecting rod assemblies
(Section 18).
(c) Oil pump (Part A of this Chapter, Section
16).
(d) Sump (Part A of this Chapter, Section 15).
(e) Flywheel/driveplate (Part A of this
Chapter, Section 21).
(f) Cylinder head (Part A of this Chapter,
Section 14).(g) Timing belt inner cover, tensioner and
toothed pulleys, and timing belt (Part A of
this Chapter).
(h) Engine external components.
3At this stage, all engine components should
be absolutely clean and dry, with all faults
repaired; they should be laid out (or in
individual containers) on a completely-clean
work surface.
1Before installing new piston rings, check
the end gaps. Lay out each piston set with a
piston/connecting rod assembly, and keep
them together as a matched set from now on.
2Insert the top compression ring into the first
cylinder, and square it up with the cylinder
walls by pushing it in with the top of the piston
(see illustration). The ring should be near the
bottom of the cylinder, at the lower limit of
ring travel.
3To measure the end gap, slip feeler gauges
between the ends of the ring, until a gauge
equal to the gap width is found (see
illustration). The feeler gauge should slide
between the ring ends with a slight amount of
drag. Compare the measurement to the value
given in the Specifications Section of this
Chapter; if the gap is larger or smaller than
specified, double-check to make sure you
have the correct rings before proceeding. If
you are assessing the condition of used rings,
have the cylinder bores checked and
measured by a Ford dealer or similar engine
reconditioning specialist, so that you can be
sure of exactly which component is worn, and
seek advice as to the best course of action to
take.
4If the end gap is still too small, it must be
opened up by careful filing of the ring ends
using a fine file. If it is too large, this is not as
serious, unless the specified limit is exceeded,
in which case very careful checking is
required of the dimensions of all components,
as well as of the new parts.
5Repeat the procedure for each ring that will
be installed in the first cylinder, and for eachring in the remaining cylinders. Remember to
keep rings, pistons and cylinders matched up.
6Refit the piston rings as follows. Where the
original rings are being refitted, use the marks
or notes made on removal, to ensure that
each ring is refitted to its original groove and
the same way up. New rings generally have
their top surfaces identified by markings
(often an indication of size, such as “STD”, or
the word “TOP”) - the rings must be fitted with
such markings uppermost (see illustration).
Note:Always follow the instructions printed
on the ring package or box - different
manufacturers may require different
approaches. Do not mix up the top and
second compression rings, as they usually
have different cross-sections.
7The oil control ring (lowest one on the
piston) is usually installed first. It is composed
of three separate elements. Slip the
spacer/expander into the groove (see
illustration). If an anti-rotation tang is used,
make sure it is inserted into the drilled hole in
the ring groove. Next, install the lower side
rail. Don’t use a piston ring installation tool on
the oil ring side rails, as they may be
damaged. Instead, place one end of the side
rail into the groove between the
spacer/expander and the ring land, hold it
firmly in place, and slide a finger around the
piston while pushing the rail into the groove
16 Piston rings - refitting
15 Engine overhaul -
reassembly sequence
Engine removal and general engine overhaul procedures 2B•19
2B
16.7A Installing the spacer/expander in
the oil control ring groove
16.2 When checking piston ring end gap,
the ring must be square in the cylinder
bore (this is done by pushing the ring down
with the top of a piston, as shown)
16.3 With the ring square in the bore,
measure the end gap with a feeler
gauge16.6 Look for etched markings (“STD” -
indicating a standard-sized ring - shown
here) identifying piston ring top surface
procarmanuals.com
Page 87 of 279

make sure that no dirt or oil was between the
bearing shells and the caps or block when the
clearance was measured. If the Plastigage is
noticeably wider at one end than the other,
the journal may be tapered (see Section 13).
12Carefully scrape all traces of the
Plastigage material off the main bearing
journals and the bearing surfaces. Be very
careful not to scratch the bearing - use your
fingernail or the edge of a credit card.
Final refitting
13Carefully lift the crankshaft out of the
engine. Clean the bearing surfaces of the
shells in the block, then apply a thin, uniform
layer of clean molybdenum disulphide-based
grease, engine assembly lubricant, or clean
engine oil to each surface (see illustration).
Coat the thrustwasher surfaces as well.
14Lubricate the crankshaft oil seal journals
with molybdenum disulphide-based grease,
engine assembly lubricant, or clean engine oil.
15Make sure the crankshaft journals are
clean, then lay the crankshaft back in place in
the block (see illustration). Clean the bearing
surfaces of the shells in the caps, then
lubricate them. Install the caps in their
respective positions, with the arrows pointing
to the timing belt end of the engine.
16Working on one cap at a time, from the
centre main bearing outwards (and ensuring
that each cap is tightened down squarely and
evenly onto the block), tighten the mainbearing cap bolts to the specified torque
wrench setting.
17Rotate the crankshaft a number of times
by hand, to check for any obvious binding.
18Check the crankshaft endfloat (see
Section 10). It should be correct if the
crankshaft thrust faces aren’t worn or
damaged, and if the No 3 (centre) main
bearing’s upper shell has been renewed.
19Refit the crankshaft left-hand oil seal
carrier, and install a new seal (see Part A of
this Chapter, Section 20).
1Before refitting the piston/connecting rod
assemblies, the cylinder bores must be
perfectly clean, the top edge of each cylinder
must be chamfered, and the crankshaft must
be in place.
2Remove the big-end bearing cap from No 1
cylinder connecting rod (refer to the marks
noted or made on removal). Remove the
original bearing shells, and wipe the bearing
recesses of the connecting rod and cap with a
clean, lint-free cloth. They must be kept
spotlessly-clean!
Big-end bearing running
clearance check
3Clean the back of the new upper bearing
shell, fit it to the connecting rod, then fit the
other shell of the bearing set to the big-end
bearing cap. Make sure the tab on each shell
fits into the notch in the rod or cap recess
(see illustration).
Caution: Don’t hammer the shells
into place, and don’t nick or
gouge the bearing face. Don’t
lubricate the bearing at this time.
4It’s critically important that all mating
surfaces of the bearing components are
perfectly clean and oil-free when they’re
assembled.
5Position the piston ring gaps as described
in Section 16, lubricate the piston and rings
with clean engine oil, and attach a piston ring
compressor to the piston. Leave the skirt
protruding about a quarter-inch, to guide the
piston into the cylinder bore. The rings must
be compressed until they’re flush with the
piston.
6Rotate the crankshaft until No 1 crankpin
(big-end) journal is at BDC (Bottom Dead
Centre), and apply a coat of engine oil to the
cylinder walls.
7Arrange the No 1 piston/connecting rod
assembly so that the arrow on the piston
crown points to the timing belt end of the
engine. The cylinder number (counting from
the timing belt end of the engine) is etched
into the flat-machined surface of the
connecting rod and its cap, and must be
visible from the front (exhaust side) of the
engine (see illustrations 9.5A and 9.5B).
Gently insert the assembly into the No 1
cylinder bore, and rest the bottom edge of the
ring compressor on the engine block.
8Tap the top edge of the ring compressor to
make sure it’s contacting the block around its
entire circumference.
9Gently tap on the top of the piston with the
end of a wooden hammer handle (see
illustration), while guiding the connecting
18 Piston/connecting rod
assemblies-
refitting and big-end bearing
running clearance check
Engine removal and general engine overhaul procedures 2B•21
2B
18.3 Tab on each big-end bearing shell
must engage with notch in connecting rod
or cap18.9 The piston can be driven gently into
the cylinder bore with the end of a wooden
or plastic hammer handle
18.11 The connecting rod and big-end
bearing cap of each assembly must share
the same etched cylinder number, visible
from the same (front/exhaust) side of the
engine
17.13 Ensure bearing shells are absolutely
clean, lubricate liberally . . .17.15 . . . and refit the crankshaft
procarmanuals.com
Page 91 of 279
4If a hose proves stubborn, try to release it
by rotating it on its unions before attempting
to work it off. Gently prise the end of the hose
with a blunt instrument (such as a flat-bladed
screwdriver), but do not apply too much force,
and take care not to damage the pipe stubs or
hoses. Note in particular that the radiator hose
unions are fragile; do not use excessive force
when attempting to remove the hoses. If all
else fails, cut the hose with a sharp knife, then
slit it so that it can be peeled off in two pieces.
While expensive, this is preferable to buying a
new radiator. Check first, however, that a new
hose is readily available.
5When refitting a hose, first slide the clampsonto the hose, then work the hose onto its
unions. If the hose is stiff, use soap (or
washing-up liquid) as a lubricant, or soften it
by soaking it in boiling water, but take care to
prevent scalding.
6Work each hose end fully onto its union,
then check that the hose is settled correctly
and is properly routed. Slide each clip along
the hose until it is behind the union flared end,
before tightening it securely.
7Refill the system with coolant (see Chap-
ter 1).
8Check carefully for leaks as soon as
possible after disturbing any part of the
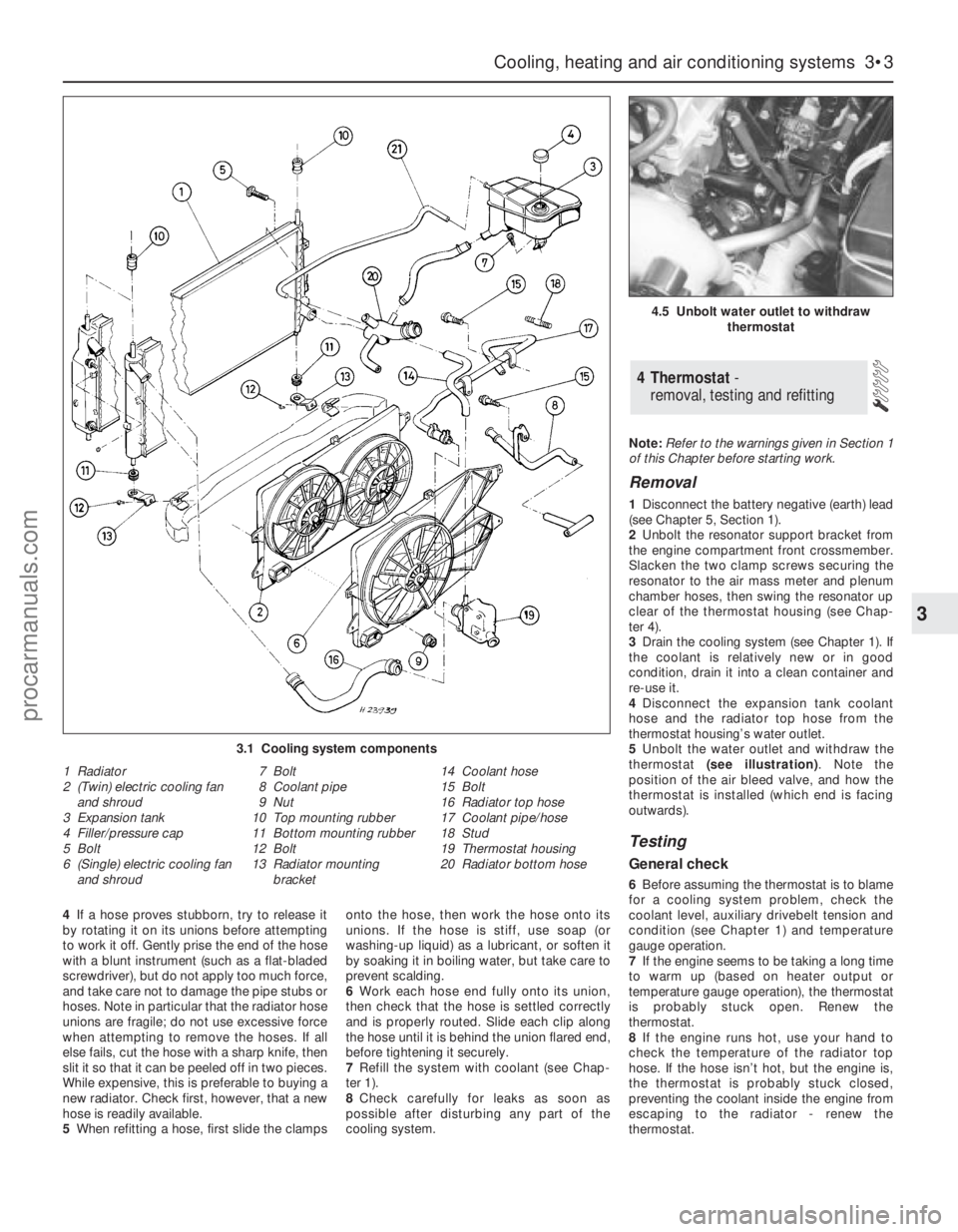
cooling system.Note:Refer to the warnings given in Section 1
of this Chapter before starting work.
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative (earth) lead
(see Chapter 5, Section 1).
2Unbolt the resonator support bracket from
the engine compartment front crossmember.
Slacken the two clamp screws securing the
resonator to the air mass meter and plenum
chamber hoses, then swing the resonator up
clear of the thermostat housing (see Chap-
ter 4).
3Drain the cooling system (see Chapter 1). If
the coolant is relatively new or in good
condition, drain it into a clean container and
re-use it.
4Disconnect the expansion tank coolant
hose and the radiator top hose from the
thermostat housing’s water outlet.
5Unbolt the water outlet and withdraw the
thermostat (see illustration). Note the
position of the air bleed valve, and how the
thermostat is installed (which end is facing
outwards).
Testing
General check
6Before assuming the thermostat is to blame
for a cooling system problem, check the
coolant level, auxiliary drivebelt tension and
condition (see Chapter 1) and temperature
gauge operation.
7If the engine seems to be taking a long time
to warm up (based on heater output or
temperature gauge operation), the thermostat
is probably stuck open. Renew the
thermostat.
8If the engine runs hot, use your hand to
check the temperature of the radiator top
hose. If the hose isn’t hot, but the engine is,
the thermostat is probably stuck closed,
preventing the coolant inside the engine from
escaping to the radiator - renew the
thermostat.
4 Thermostat -
removal, testing and refitting
Cooling, heating and air conditioning systems 3•3
3
4.5 Unbolt water outlet to withdraw
thermostat
3.1 Cooling system components
1 Radiator
2 (Twin) electric cooling fan
and shroud
3 Expansion tank
4 Filler/pressure cap
5 Bolt
6 (Single) electric cooling fan
and shroud7 Bolt
8 Coolant pipe
9 Nut
10 Top mounting rubber
11 Bottom mounting rubber
12 Bolt
13 Radiator mounting
bracket14 Coolant hose
15 Bolt
16 Radiator top hose
17 Coolant pipe/hose
18 Stud
19 Thermostat housing
20 Radiator bottom hose
procarmanuals.com