spark plugs FORD SIERRA 1983 1.G Reference Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 1983, Model line: SIERRA, Model: FORD SIERRA 1983 1.GPages: 26, PDF Size: 0.57 MB
Page 3 of 26
Buying spare parts
Spare parts are available from many
sources, including maker’s appointed
garages, accessory shops, and motor factors.
To be sure of obtaining the correct parts, it
will sometimes be necessary to quote the
vehicle identification number. If possible, it
can also be useful to take the old parts along
for positive identification. Items such as
starter motors and alternators may be
available under a service exchange scheme -
any parts returned should always be clean.
Our advice regarding spare part sources is
as follows.
Officially-appointed garages
This is the best source of parts which are
peculiar to your car, and which are not
otherwise generally available (eg badges,
interior trim, certain body panels, etc). It is
also the only place at which you should buy
parts if the vehicle is still under warranty.
Accessory shops
These are very good places to buy
materials and components needed for themaintenance of your car (oil, air and fuel
filters, spark plugs, light bulbs, drivebelts, oils
and greases, brake pads, touch-up paint, etc).
Components of this nature sold by a
reputable shop are of the same standard as
those used by the car manufacturer.
Besides components, these shops also sell
tools and general accessories, usually have
convenient opening hours, charge lower
prices, and can often be found not far from
home. Some accessory shops have parts
counters where the components needed for
almost any repair job can be purchased or
ordered.
Motor factors
Good factors will stock all the more
important components which wear out
comparatively quickly, and can sometimes
supply individual components needed for the
overhaul of a larger assembly (eg brake seals
and hydraulic parts, bearing shells, pistons,
valves, alternator brushes). They may also
handle work such as cylinder block reboring,
crankshaft regrinding and balancing, etc.
Tyre and exhaust specialists
These outlets may be independent, or
members of a local or national chain. They
frequently offer competitive prices when
compared with a main dealer or local garage,
but it will pay to obtain several quotes before
making a decision. When researching prices,
also ask what “extras” may be added - for
instance, fitting a new valve and balancing the
wheel are both commonly charged on top of
the price of a new tyre.
Other sources
Beware of parts or materials obtained from
market stalls, car boot sales or similar outlets.
Such items are not invariably sub-standard,
but there is little chance of compensation if
they do prove unsatisfactory. In the case of
safety-critical components such as brake
pads, there is the risk not only of financial loss
but also of an accident causing injury or death.
Second-hand components or assemblies
obtained from a car breaker can be a good
buy in some circumstances, but this sort of
purchase is best made by the experienced
DIY mechanic.
Vehicle identification numbers
Modifications are a continuing and
unpublicised process in vehicle manufacture,
quite apart from major model changes. Spareparts lists are compiled upon a numerical
basis, the individual vehicle identification
numbers being essential to correct
identification of the component concerned.
When ordering spare parts, always give as
much information as possible. Quote the car
model, year of manufacture, body and engine
numbers, as appropriate.
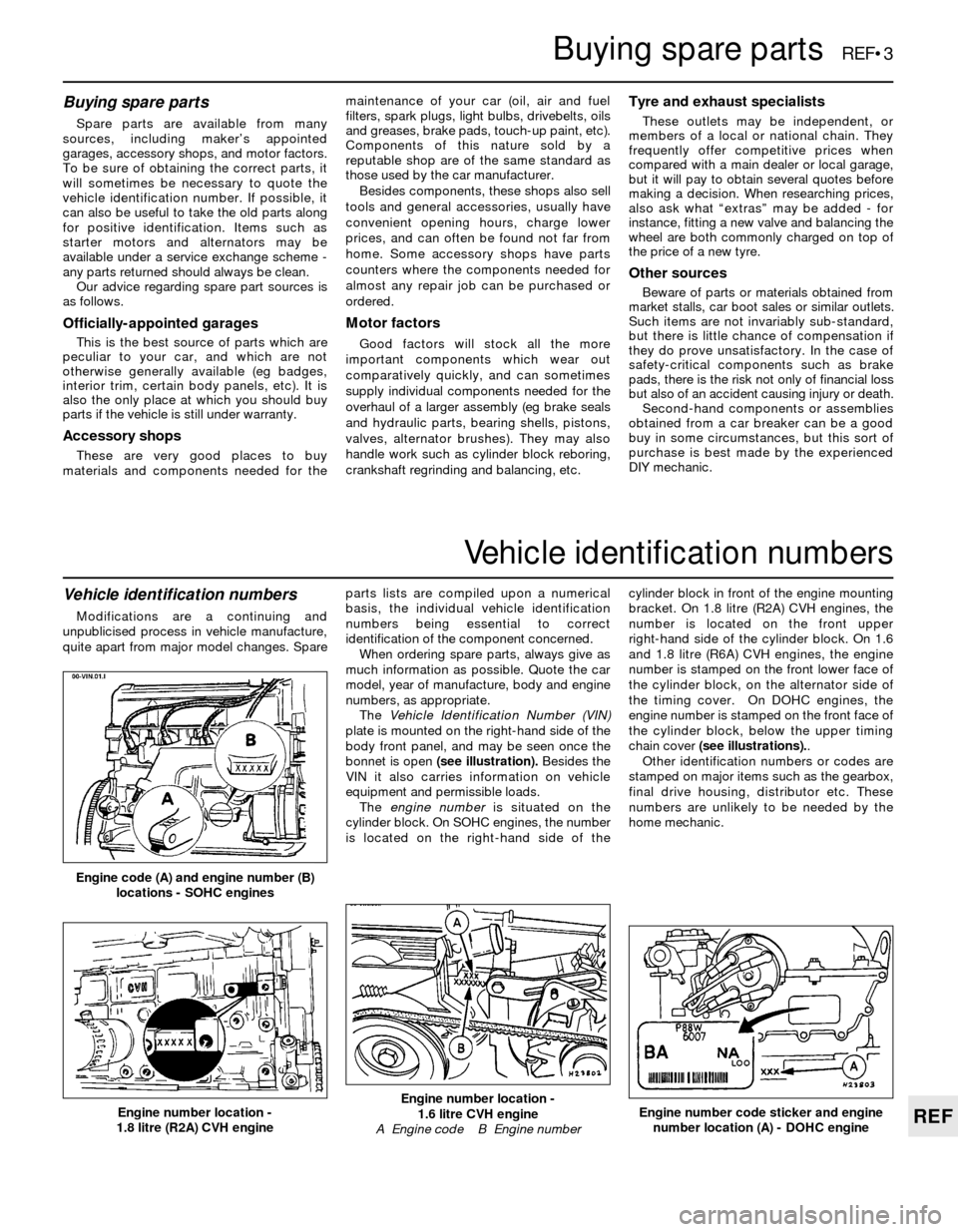
The Vehicle Identification Number (VIN)
plate is mounted on the right-hand side of the
body front panel, and may be seen once the
bonnet is open (see illustration).Besides the
VIN it also carries information on vehicle
equipment and permissible loads.
The engine numberis situated on the
cylinder block. On SOHC engines, the number
is located on the right-hand side of thecylinder block in front of the engine mounting
bracket. On 1.8 litre (R2A) CVH engines, the
number is located on the front upper
right-hand side of the cylinder block. On 1.6
and 1.8 litre (R6A) CVH engines, the engine
number is stamped on the front lower face of
the cylinder block, on the alternator side of
the timing cover. On DOHC engines, the
engine number is stamped on the front face of
the cylinder block, below the upper timing
chain cover (see illustrations)..
Other identification numbers or codes are
stamped on major items such as the gearbox,
final drive housing, distributor etc. These
numbers are unlikely to be needed by the
home mechanic.
Buying spare parts REF•3
Engine code (A) and engine number (B)
locations - SOHC engines
Engine number location -
1.8 litre (R2A) CVH engineEngine number code sticker and engine
number location (A) - DOHC engineEngine number location -
1.6 litre CVH engine
A Engine code B Engine number
REF
Vehicle identification numbers
Page 11 of 26

The vehicle owner who does his or her own maintenance according
to the recommended service schedules should not have to use this
section of the manual very often. Modern component reliability is such
that, provided those items subject to wear or deterioration are
inspected or renewed at the specified intervals, sudden failure is
comparatively rare. Faults do not usually just happen as a result of
sudden failure, but develop over a period of time. Major mechanical
failures in particular are usually preceded by characteristic symptoms
over hundreds or even thousands of miles. Those components which
do occasionally fail without warning are often small and easily carried
in the vehicle.
With any fault-finding, the first step is to decide where to begin
investigations. Sometimes this is obvious, but on other occasions, alittle detective work will be necessary. The owner who makes half a
dozen haphazard adjustments or replacements may be successful in
curing a fault (or its symptoms), but will be none the wiser if the fault
recurs, and ultimately may have spent more time and money than was
necessary. A calm and logical approach will be found to be more
satisfactory in the long run. Always take into account any warning
signs or abnormalities that may have been noticed in the period
preceding the fault - power loss, high or low gauge readings, unusual
smells, etc - and remember that failure of components such as fuses or
spark plugs may only be pointers to some underlying fault.
The pages which follow provide an easy-reference guide to the more
common problems which may occur during the operation of the
vehicle. These problems and their possible causes are grouped under
Fault diagnosisREF•11
REF
Engine
MEngine fails to rotate when attempting to start
MStarter motor turns engine slowly
MEngine rotates, but will not start
MEngine difficult to start when cold
MEngine difficult to start when hot
MStarter motor noisy or excessively-rough in engagement
MEngine starts, but stops immediately
MEngine idles erratically
MEngine misfires at idle speed
MEngine misfires throughout the driving speed range
MEngine hesitates on acceleration
MEngine stalls
MEngine lacks power
MEngine backfires
MOil pressure warning light illuminated with engine running
MEngine runs-on after switching off
MEngine noises
Cooling system
MOverheating
MOvercooling
MExternal coolant leakage
MInternal coolant leakage
MCorrosion
Fuel and exhaust systems
MExcessive fuel consumption
MFuel leakage and/or fuel odour
MExcessive noise or fumes from exhaust system
Clutch
MPedal travels to floor - no pressure or very little resistance
MClutch fails to disengage (unable to select gears)
MClutch slips (engine speed increases; no increase in vehicle speed)
MJudder as clutch is engaged
MNoise when depressing or releasing clutch pedal
Manual gearbox
MNoisy in neutral with engine running
MNoisy in one particular gear
MDifficulty engaging gears
MJumps out of gear
MVibration
MLubricant leaks
Automatic transmission
MFluid leakage
MTransmission fluid brown, or has burned smellMGeneral gear selection problems
MTransmission will not downshift (kickdown) with acceleration
MEngine will not start in any gear, or starts in gears other than Park
or Neutral
MTransmission slips, shifts roughly, is noisy, or has no drive in forward
or reverse gears
Propeller shaft
MClunking or knocking noise when taking up drive
MVibration when accelerating or decelerating
Final drive and driveshafts
MExcessive final drive noise
MOil leakage from final drive
MGrating, knocking or vibration from driveshafts
Braking system
MVehicle pulls to one side under braking
MNoise (grinding or high-pitched squeal) when brakes applied
MExcessive brake pedal travel
MBrake pedal feels spongy when depressed
MExcessive brake pedal effort required to stop vehicle
MJudder felt through brake pedal or steering wheel when braking
MPedal pulsates when braking hard
MBrakes binding
MRear wheels locking under normal braking
Suspension and steering systems
MVehicle pulls to one side
MWheel wobble and vibration
MExcessive pitching and/or rolling around corners, or during braking
MWandering or general instability
MExcessively-stiff steering
MExcessive play in steering
MLack of power assistance
MTyre wear excessive
Electrical system
MBattery will not hold a charge for more than a few days
MIgnition/no-charge warning light remains on with engine running
MIgnition/no-charge warning light fails to come on
MLights inoperative
MInstrument readings inaccurate or erratic
MHorn inoperative, or unsatisfactory in operation
MWindscreen/tailgate wipers inoperative, or unsatisfactory in operation
MWindscreen/tailgate washers inoperative, or unsatisfactory in
operation
MElectric windows inoperative, or unsatisfactory in operation
MCentral locking system inoperative, or unsatisfactory in operation
Introduction
Page 12 of 26

headings denoting various components or systems, such as Engine,
Cooling system, etc. The Chapter and/or Section which deals with the
problem is also shown in brackets. Whatever the fault, certain basic
principles apply. These are as follows:
Verify the fault. This is simply a matter of being sure that you know
what the symptoms are before starting work. This is particularly
important if you are investigating a fault for someone else, who may
not have described it very accurately.
Don’t overlook the obvious. For example, if the vehicle won’t start, is
there fuel in the tank? (Don’t take anyone else’s word on this particular
point, and don’t trust the fuel gauge either!) If an electrical fault is
indicated, look for loose or broken wires before digging out the test
gear.Cure the disease, not the symptom. Substituting a flat battery with a
fully-charged one will get you off the hard shoulder, but if the
underlying cause is not attended to, the new battery will go the same
way. Similarly, changing oil-fouled spark plugs for a new set will get
you moving again, but remember that the reason for the fouling (if it
wasn’t simply an incorrect grade of plug) will have to be established
and corrected.
Don’t take anything for granted. Particularly, don’t forget that a
“new” component may itself be defective (especially if it’s been rattling
around in the boot for months), and don’t leave components out of a
fault diagnosis sequence just because they are new or recently-fitted.
When you do finally diagnose a difficult fault, you’ll probably realise
that all the evidence was there from the start.
Engine fails to rotate when attempting to start
MBattery terminal connections loose or corroded (Chapter 1).
MBattery discharged or faulty (Chapter 5).
MBroken, loose or disconnected wiring in the starting circuit (Chapter 5).
MDefective starter solenoid or switch (Chapter 5).
MDefective starter motor (Chapter 5).
MStarter pinion or flywheel/driveplate ring gear teeth loose or broken
(Chapters 2 or 5).
MEngine earth strap broken or disconnected.
Starter motor turns engine slowly
MPartially-discharged battery (recharge, use jump leads, or push start)
(Chapter 5).
MBattery terminals loose or corroded (Chapter 1).
MBattery earth to body defective (Chapter 5).
MEngine earth strap loose.
MStarter motor (or solenoid) wiring loose (Chapter 5).
MStarter motor internal fault (Chapter 5).
Engine rotates, but will not start
MFuel pump inertia switch tripped (electric pump) (Chapter 4).
MFuel tank empty.
MBattery discharged (engine rotates slowly) (Chapter 5).
MBattery terminal connections loose or corroded (Chapter 1).
MIgnition components damp or damaged (Chapters 1 and 5).
MBroken, loose or disconnected wiring in the ignition circuit (Chapters 1
and 5).
MWorn, faulty or incorrectly-gapped spark plugs (Chapter 1).
MFuel injection system fault (Chapter 4).
MMajor mechanical failure (eg broken timing chain) (Chapter 2).
Engine difficult to start when cold
MBattery discharged (Chapter 5).
MBattery terminal connections loose or corroded (Chapter 1).
MWorn, faulty or incorrectly-gapped spark plugs (Chapter 1).
MFuel injection system fault (Chapter 4).
MOther ignition system fault (Chapters 1 and 5).
MLow cylinder compressions (Chapter 2).
Engine difficult to start when hot
MAir filter element dirty or clogged (Chapter 1).
MFuel injection system fault (Chapter 4).
MLow cylinder compressions (Chapter 2).
Starter motor noisy or excessively-rough in
engagement
MStarter pinion or flywheel/driveplate ring gear teeth loose or broken
(Chapters 2 or 5).
MStarter motor mounting bolts loose or missing (Chapter 5).
MStarter motor internal components worn or damaged (Chapter 5).
Engine starts, but stops immediately
MLoose or faulty electrical connections in the ignition circuit
(Chapters 1 and 5).
MVacuum leak at the throttle body or inlet manifold (Chapter 4).
MFuel injection system fault (Chapter 4).
Engine idles erratically
MIncorrectly-adjusted idle speed (Chapter 4).
MAir filter element clogged (Chapter 1).
MVacuum leak at the throttle body, inlet manifold or associated
hoses (Chapter 4).
MWorn, faulty or incorrectly-gapped spark plugs (Chapter 1).
MUneven or low cylinder compressions (Chapter 2).
MCamshaft lobes worn (Chapter 2).
MFuel injection system fault (Chapter 4).
Engine misfires at idle speed
MWorn, faulty or incorrectly-gapped spark plugs (Chapter 1).
MFaulty spark plug HT leads (Chapter 5).
MVacuum leak at the throttle body, inlet manifold or associated
hoses (Chapter 4).
MFuel injection system fault (Chapter 4).
MDistributor cap cracked or tracking internally, where applicable
(Chapter 5).
MUneven or low cylinder compressions (Chapter 2).
MDisconnected, leaking, or perished crankcase ventilation hoses
(Chapter 4).
Engine misfires throughout the driving speed range
MFuel filter choked (Chapter 1).
MFuel pump faulty, or delivery pressure low (Chapter 4).
MFuel tank vent blocked, or fuel pipes restricted (Chapter 4).
MVacuum leak at the throttle body, inlet manifold or associated
hoses (Chapter 4).
MWorn, faulty or incorrectly-gapped spark plugs (Chapter 1).
MFaulty spark plug HT leads (Chapter 5).
MDistributor cap cracked or tracking internally, where applicable
(Chapter 5).
MFaulty ignition coil (Chapter 5).
MUneven or low cylinder compressions (Chapter 2).
MFuel injection system fault (Chapter 4).
Engine hesitates on acceleration
MWorn, faulty or incorrectly-gapped spark plugs (Chapter 1).
MVacuum leak at the throttle body, inlet manifold or associated
hoses (Chapter 4).
MFuel injection system fault (Chapter 4).
Engine stalls
MVacuum leak at the throttle body, inlet manifold or associated
hoses (Chapter 4).
REF•12Fault diagnosis
Engine
Page 13 of 26

MFuel filter choked (Chapter 1).
MFuel pump faulty, or delivery pressure low (Chapter 4).
MFuel tank vent blocked, or fuel pipes restricted (Chapter 4).
MFuel injection system fault (Chapter 4).
Engine lacks power
MFuel filter choked (Chapter 1).
MFuel pump faulty, or delivery pressure low (Chapter 4).
MUneven or low cylinder compressions (Chapter 2).
MWorn, faulty or incorrectly-gapped spark plugs (Chapter 1).
MVacuum leak at the throttle body, inlet manifold or associated
hoses (Chapter 4).
MFuel injection system fault (Chapter 4).
MBrakes binding (Chapters 1 and 10).
MClutch slipping (Chapter 6).
Engine backfires
MVacuum leak at the throttle body, inlet manifold or associated
hoses (Chapter 4).
MFuel injection system fault (Chapter 4).
Oil pressure warning light illuminated with engine
running
MLow oil level, or incorrect oil grade (Chapter 1).
MFaulty oil pressure sensor (Chapter 2).
MWorn engine bearings and/or oil pump (Chapter 2).
MExcessively high engine operating temperature (Chapter 3).
MOil pressure relief valve defective (Chapter 2).
MOil pick-up strainer clogged (Chapter 2).
Note:Low oil pressure in a high-mileage engine at tickover is not
necessarily a cause for concern. Sudden pressure loss at speed is far
more significant. In any event, check the gauge or warning light sender
before condemning the engine.
Engine runs-on after switching off
MExcessive carbon build-up in engine (Chapter 2).
MExcessively high engine operating temperature (Chapter 3).
Engine noises
Pre-ignition (pinking) or knocking during acceleration or
under load
MIgnition timing incorrect/ignition system fault (Chapters 1 and 5).
MIncorrect grade of spark plug (Chapter 1).
MIncorrect grade of fuel (Chapter 1).
MVacuum leak at throttle body, inlet manifold or associated hoses
(Chapter 4).
MExcessive carbon build-up in engine (Chapter 2).
MFuel injection system fault (Chapter 4).
Whistling or wheezing noises
MLeaking inlet manifold or throttle body gasket (Chapter 4).
MLeaking exhaust manifold gasket (Chapter 4).
MLeaking vacuum hose (Chapters 4 and 10).
MBlowing cylinder head gasket (Chapter 2).
Tapping or rattling noises
MWorn valve gear, timing chain, camshaft or hydraulic tappets
(Chapter 2).
MAncillary component fault (water pump, alternator, etc) (Chapters 3, 5)
Knocking or thumping noises
MWorn big-end bearings (regular heavy knocking, perhaps less
under load) (Chapter 2).
MWorn main bearings (rumbling and knocking, perhaps worsening
under load) (Chapter 2).
MPiston slap (most noticeable when cold) (Chapter 2).
MAncillary component fault (water pump, alternator, etc) (Chapters 3, 5)
Overheating
MAuxiliary drivebelt broken or incorrectly adjusted (Chapter 1).
MInsufficient coolant in system (Chapter 1).
MThermostat faulty (Chapter 3).
MRadiator core blocked, or grille restricted (Chapter 3).
MElectric cooling fan or thermostatic switch faulty (Chapter 3).
MViscous-coupled fan faulty (Chapter 3).
MIgnition timing incorrect, or ignition system fault (Chapters 1 and 5).
MInaccurate temperature gauge sender unit (Chapter 3).
MAirlock in cooling system (Chapter 3).
Overcooling
MThermostat faulty (Chapter 3).
MInaccurate temperature gauge sender unit (Chapter 3).
External coolant leakage
MDeteriorated or damaged hoses or hose clips (Chapter 1).
MRadiator core or heater matrix leaking (Chapter 3).
MPressure cap faulty (Chapter 3).
MWater pump internal seal leaking (Chapter 3).
MWater pump-to-block seal leaking (Chapter 3).
MBoiling due to overheating (Chapter 3).
MCore plug leaking (Chapter 2).
Internal coolant leakage
MLeaking cylinder head gasket (Chapter 2).
MCracked cylinder head or cylinder block (Chapter 2).
Corrosion
MInfrequent draining and flushing (Chapter 1).
MIncorrect coolant mixture or inappropriate coolant type (Chapter 1).
Fault diagnosisREF•13
REF
Cooling system
Excessive fuel consumption
MAir filter element dirty or clogged (Chapter 1).
MFuel injection system fault (Chapter 4).
MIgnition timing incorrect or ignition system fault (Chapters 1 and 5).
MBrakes binding (Chapter 10).
MTyres under-inflated (Chapter 1).
Fuel leakage and/or fuel odour
MDamaged fuel tank, pipes or connections (Chapters 1 and 4).
Excessive noise or fumes from exhaust system
MLeaking exhaust system or manifold joints (Chapters 1 and 4).
MLeaking, corroded or damaged silencers or pipe (Chapters 1 and 4).
MBroken mountings causing body or suspension contact (Chapter 4).
Fuel and exhaust systems
Page 24 of 26

refitting - 2A•10, 2B•7, 2C•9
removal - 2A•8, 2B•4, 2C•6
SOHC engines- 2A•1et seq
spark plugs - 1•2, 1•14, 5•12
sump - 2A•20, 2B•15, 2C•19
timing belt/chain and sprockets - 2A•12,
2B•8, 2C•10
timing and sprockets - 2A•12, 2B•8, 2C•10
valves - 1•15
Engine electrical systems - 5•1 et seq
Environmental considerations- REF•4
Exhaust gas oxygen sensor (HEGO)- 4B•15
Exhaust gas recirculation valve- 4B•14
Exhaust manifold- 4A•17, 4B•15
Exhaust pressure transducer- 4B•14
Exhaust system- 1•11, 4A•18, 4B•15
Expansion tank/coolant sensor- 3•8
FFacia panel- 12•16
Facia panel switches- 13•4
Fan (radiator)- 3•7
Fault diagnosis- REF•11
automatic transmission - REF•14
braking system - REF•15
clutch - REF•14
cooling system - REF•13
driveshafts - REF•15
electrical system - REF•16
engine - REF•12
final drive - REF•15
fuel and exhaust systems - REF•13
manual gearbox - REF•14
propeller shaft - REF•15
steering - REF•16
suspension - REF•16
Final drive and driveshafts- 9•1 et seq
Final drive fault diagnosis- REF•11, REF•15
Final drive unit- 9•2, 9•3, 9•4
Fluids- 0•17
Flywheel/driveplate- 2A•18, 2B•15, 2C•19
Foglamps- 13•15
Ford VV carburettor- 1•12, 4A•13
Front suspension crossmember- 11•3
Front suspension strut- 11•4
Fuel systems- carburettor - 4A•1 et seq
Fuel systems- fuel injection - 4B•1 et seq
Fuel system:
accelerator cable - 4A•8
accelerator pedal - 4A•8
air cleaner - 1•18, 1•19, 4A•4, 4B•4
airflow meter - 4B•8
catalytic converter - 4B•3, 4B•14
CFI unit- 4B•10
depressurising fuel injection system - 4B•4
dismantling and reassembly - 4A•8
electronic vacuum regulator - 4B•11
exhaust gas recirculation valve - 4B•14
exhaust gas oxygen sensor (HEGO) - 4B•15
exhaust manifold - 4A•17, 4B•15
exhaust pressure transducer - 4B•14
exhaust system - 4A•18, 4B•15
fuel filler cap - 12•14
fuel filter - 1•2, 1•20
fuel level sender unit - 4A•7, 4B•7fuel pressure regulator - 4A•5, 4B•5
fuel pump - 4A•5, 4A•6, 4B•6
fuel tank - 4A•7
fuel vapour separator - 4A•5
fuel gauges - 13•8
idle speed control valve - 4B•7
injector(s) - 4B•8
inlet manifold - 4A•15, 4B•12
mixture adjustment potentiometer - 4B•7
pulse-air - 4B•10
throttle body - 4B•12
throttle control motor - 4B•11
throttle position sensor - 4B•11
throttle valve control motor - 4B•11
Fuses- 13•3
GGear linkage- 7A•4
Gear selector mechanism- 7B•5
Gearbox - see Manual gearbox or
Automatic transmission
Gearbox oil- 0•17, 1•3
Glass- 12•11
HHandbrake check/adjustment- 1•16, 10•21
Handbrake cables- 10•20, 10•21
Handbrake lever - 10•22
Handbrake warning lamp switch- 13•6
Handles (door)- 12•9
Hazard warning flasher switch- 13•4
Headlamp alignment- 13•14
Headlamp unit- 13•13
Headlamp washers- 13•12
Headlining - 12•19
Heated rear window- 13•20
Heated seat- 13•19
Heater- 3•9
Hinges and locks- 1•14
Horn- 13•11
Horn switch- 13•5
Hose and fluid leak check- 0•8, 1•10,
Hoses brake- 10•19
Hoses power steering- 11•18
HT coil- 5•13
HT leads- 5•12
Hub carrier (front) - 11•5
Hydraulic fluid- 0•17
Hydraulic system (brakes) bleeding- 10•2
Hydraulic unit, pump, motor (ABS)- 10•15,
10•16
IIdle speed control valve- 4B•7
Idle speed/mixture- 1•11, 1•12, see
Specifications in Chapter 4A, and refer to
specific carburettor type
Ignition electronic modules- 5•3, 5•19
Ignition HT coil- 5•13
Ignition switch- 13•4
Ignition system check- 1•20
Ignition timing adjustment- 5•17
Indicator lamps- 13•15Indicator switch/relay- 13•4
Injector(s)- 4B•8
Inlet manifold- 4A•15, 4B•12
Instrument panel- 13•7
Interior trim- 12•15
Introduction to the Ford Sierra- 0•4
JJacking and vehicle support- 0•6
Jump starting- 0•9
KKickdown cable - 7B•3
LLeaf springs- 11•13
Leak, checking- 0•8, 1•10
Lights- 13•14
Locks:
bootlid - 12•5
door - 12•9, 12•10
tailgate - 12•6
Loudspeakers- 13•20
Lower arm (suspension)- 11•4, 11•7, 11•8
Lubricants and fluids- 0•17
Luggage area light switch- 13•5
MMain bearings- 2A•23, 2B•17, 2C•23
Maintenance and servicing - see Routine
maintenance
Manifolds- 4A•15, 4A•17, 4B•12, 4B•15
Manual gearbox- 7A•1 et seq
fault diagnosis - REF•11, REF•14
gear linkage - 7A•4
gearbox oil - 0•17, 1•3
oil level check - 1•13
removal and refitting - 7A•2
Master cylinder (brake)- 10•13
Mirrors- 12•12
Mixture (CO)- see Idle speed/mixture
Mixture adjustment potentiometer- 4B•7
MOT test checks- REF•7
Mountings, engine-2A•11, 2B•7, 2C•9
NNumber plate lamp- 13•16
OOil change/filter- 1•1, 1•9,
Oil pressure warning switch- 13•6
Oil pump- 2A•21, 2B•16, 2C•20
Oil seals- REF •4
Oil seals crankshaft- 2A•19, 2B•15, 2C•19
Oils- engine and gearbox- 0•17, 1•3
PPads (brake) - 10•3
Paintwork damage- 12•2
Parts- REF•3
REF•24Index
Page 25 of 26

Pedals:
accelerator - 4A•8
brake - 10•22
clutch - 6•2
Pierburg 2V carburettor- 1•12, 4A•14
Pipes/hoses (braking system)- 10•19
Pistons- 2A•22, 2B•17, 2C•21
Plastic components- 12•3
Plugs- 1•2, 1•14, 5•12
Power operated windows- 13•18
Power steering fluid- 0•17
Power steering fluid level- 0•14
Power steering fluid hoses-11•18
Power steering pump- 11•18
Power steering system bleeding- 11•18
Pressure switch (hydraulic unit)- 10•17
Propeller shaft- 8•1 et seq
centre bearing - 8•2
fault diagnosis - REF•11, REF•15
front rubber coupling - 8•3
removal and refitting - 8•2
vibration damper - 8•4
Pulse-air system- 4B•10
Punctures- 0•6
RRadiator- 1•16, 3•3
Radiator cooling fan- 3•7
Radiator grille- 12•14
Radio/cassette player- 13•21
Rear axle- 9•7, 9•8, 11•13
Relays- 13•3
Release bearing (clutch)- 6•5
Repair procedures- REF •4
Respraying- 12•2
Reversing lamp switch- 7B•6, 13•4
Roadtest- 1•17
Roadwheel check- 1•11
Roll bars- 11•6, 11•13
Rotor arm- 5•14, 5•15
Routine maintenance and servicing- 1•1 et seq
Routine maintenance procedures- 1•9
Routine maintenance schedule- 1•3
SSafety first!- 0•5
Scratches- 12•2
Seat belts- 1•11, 12•21
Seat heating pad- 13•19
Seats- 12•19
Selector rod- 7B•5
Sender unit fuel level- 4A•7, 4B•7
Sender units coolant temperature- 3•8
Servicing -see Routine maintenance
Servo unit (braking system)- 10•14
Shock absorber- 11•9
Shoes (brake)- 10•6
Short-circuit finding- 13•3
Spare parts- REF•3
Spark plugs- 1•2, 1•14, 5•12
Speakers- 13•20Specifications- see start of relevant Chapter
Speedometer- 13•8
Speedometer cable- 13•11
Spoiler- 12•6
Starter inhibitor switch- 7B•6
Starter motor- 5•8
Steering- 11•1 et seq
check -1•17, 1•18
column/adjustment - 11•15
fault diagnosis - REF•11, REF•16
gear - 11•16, 11•18
hoses - 11•18
power steering system bleeding - 11•18
pump - 11•18
tie-rod end - 11•18
wheel - 11•14
wheel alignment - 11•1, 11•19
Sump- 2A•20, 2B•15, 2C•19
Sunroof- 12•15, 13•6
Support struts (tailgate)- 12•6
Suspension and steering- 11•1 et seq
anti-roll bars - 11•6, 11•13
check - 1•17, 1•18
coil spring (rear) - 11•10
crossmember (front) - 11•3
fault diagnosis - REF•11, REF•16
hub carrier (front) - 11•5
leaf springs - 11•13
lower arm (front/rear) - 11•4, 11•7, 11•8
mountings - 11•12
rear axle assembly - 11•13
shock absorber - 11•9
strut (front) - 11•4
wheel bearings - 11•6, 11•10
Switches:
brake lamp - 13•6
cooling system - 3•8
courtesy lamp - 13•5
direction indicator - 13•4
electric door mirror - 13•5
facia panel - 13•4
handbrake warning lamp - 13•6
hazard warning lamp - 13•4
horn - 13•5
hydraulic pressure (brakes) - 10•17
ignition/lockbarrel - 13•4
luggage area light - 13•5
oil pressure warning - 13•6
reversing - 7B•6, 13•4
starter inhibitor - 7B•6
TTachometer- 13•8
Tailboard- 12•11
Tailgate struts- 12•6
Tailgate/lock- 12•5, 12•6
Temperature gauge and sender unit- 3•8
Thermostat- 3•4
Throttle body- 4B•12
Throttle cable- 4A•8
Throttle position sensor- 4B•11
Throttle valve control motor- 4B•11Tie-rod end- 11•18
Timing adjustment- 5•17
Timing belt/chain and sprockets- 2A•12,
2B•8, 2C•10
Tools and working facilities- REF•5
Towing- 0•7
Transmission housing oil seal- 7B•5
Trim panel (door)- 12•7
Tyre checks and pressures- 0•16, 0•18
UUnderbody- 1•7 1•8, 1•17, 12•2
Underbonnet views -0•10, 1•5
Unleaded petrol- 5•18
Upholstery and carpets- 12•2
VVacuum diaphragm unit- 7B•6
Vacuum servo unit (braking system)- 10•14
Valve block (ABS)- 10•17
Valves- 1•15
Vehicle identification numbers- REF•3
Ventilation system- 3•1 et seq
WWarning system components- 13•9
Washer fluid level- 0•13
Washers- 13•12
Weatherstrip- 12•15
Weber 2V carburettor- 1•12, 4A•14
Weber 2V TLD carburettor- 1•12, 4A•15
Weekly checks- 0•10
Wheel (steering) - 11•14
Wheel alignment- 11•1, 11•19
Wheel arch liners- 12•14
Wheel bearings- 11•6, 11•10
Wheel changing- 0•6
Wheel cylinder- 10•12
Wheel sensor(ABS)- 10•18
Window glass- 12•11
Window regulator- 12•12
Windscreen- 12•11, 12•14
Windscreen washers- 13•12
Windscreen wiper motor- 13•12
Wiper arms- 13•11
Wiper blades- 0•15, 13•11
Wiper motor (headlamp)- 13•13
Wiper motor (rear)- 13•12
Wiper motor (windscreen)- 13•12
Wiring diagrams- WD•1 et seq
Working facilities- REF•5
IndexREF•25
REF