coolant level FORD SIERRA 1991 2.G Cooling And Air Conditioning Systems Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 1991, Model line: SIERRA, Model: FORD SIERRA 1991 2.GPages: 12, PDF Size: 0.62 MB
Page 1 of 12

System type
SOHC models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Pressurised, with belt-driven coolant pump, crossflow radiator,
thermo-viscous fan, thermostat, and expansion tank
CVH and DOHC models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Pressurised, with belt-driven coolant pump, crossflow radiator,
electric fan, thermostat, and expansion tank
Thermostat
Nominal temperature rating (fully open):
SOHC models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88ºC (190º F)
CVH models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100ºC (212ºF)
DOHC models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102ºC (216ºF)
Opening temperature:
SOHC models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85 to 89ºC (185 to 192ºF)
CVH models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88ºC (190ºF)
CVH (R6A type) models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85 to 89ºC (185 to 192ºF)
DOHC models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85 to 89ºC (185 to 192ºF)
Expansion tank cap opening pressure
SOHC models:
Up to 1987 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.85 to 1.1 bar (12 to 16 lbf/in2)
From 1987 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.0 to 1.25 bar (15 to 18 lbf/in2)
CVH models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.0 to 1.25 bar (15 to 18 lbf/in2)
DOHC models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.0 to 1.4 bar (15 to 20 lbf/in2)
Coolant mixture . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1 Specifications
System capacity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1 Specifications
Drivebelt tensions
Air conditioning system compressor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10.0 mm (0.4 in) deflection at the midpoint of the belt’s longest run
under firm thumb pressure
Coolant pump/alternator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10.0 mm (0.4 in) deflection midway between coolant pump and
alternator (or power steering pump) pulleys under firm thumb pressure
Chapter 3
Cooling, heating and air conditioning systems
Air conditioning system - component renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Coolant pump - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
Coolant pump/alternator drivebelt(s) - checking, renewal and
tensioning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
Coolant pump/alternator drivebelt tensioner (DOHC models with
power steering) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Cooling fan switch - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Cooling system - draining . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
Cooling system - filling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4
Cooling system - flushing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3
Electric cooling fan - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Expansion tank and coolant level sensor - removal and refitting . . . .15General information and precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1
Heater controls - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
Heater motor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Heater unit - overhaul . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
Heater unit - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
Radiator - inspection and cleaning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6
Radiator - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
Temperature gauge sender - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
Thermostat - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
Thermostat - testing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
Thermo-viscous cooling fan (SOHC models) - removal and refitting .12
3•1
Specifications Contents3
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanic
Difficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert
DIY or professional
Degrees of difficulty
Page 2 of 12

Torque wrench settingsNmlbf ft
Radiator upper mounting nuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21 to 2515 to 18
Radiator lower mounting bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8 to 126 to 9
Coolant pump bolts:
SOHC models:
M8 bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17 to 2113 to 15
M10 bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35 to 4226 to 31
CVH models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8 to 116 to 8
CVH (R6A type) models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7 to 105 to 7
DOHC models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21 to 2815 to 21
Thermostat housing bolts:
SOHC/DOHC models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17 to 2013 to 15
CVH models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8 to 116 to 8
CVH (R6A type) models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8 to 126 to 9
Cooling fan shroud-to-radiator nuts/bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8 to 116 to 8
Coolant pump pulley bolts:
SOHC models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21 to 2815 to 21
DOHC models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20 to 2515 to 18
Coolant pump/alternator drivebelt tensioner bolt:
CVH models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23 to 3017 to 22
DOHC models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .70 to 9752 to 72
Cooling fan blades-to-fan hub bolts (SOHC models) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8 to 106 to 7
Air conditioning compressor-to-bracket bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .65 to 7548 to 55
Air conditioning compressor bracket-to-engine bolts:
M10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .85 to 9263 to 68
M12 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .110 to 12081 to 89
Air conditioning condenser fan assembly-to-condenser bolts:
Models up to 1987 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2 to 31 to 2
Models from 1987 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8 to 116 to 8
Air conditioning condenser securing bolts (models from 1987) . . . . . . .27 to 3320 to 24
General information
The cooling system is of pressurised type,
and consists of a front mounted radiator,
coolant pump, cooling fan, wax type
thermostat, and an expansion tank.
The radiator matrix is manufactured from
honeycombed metal, and the end tanks are
made of plastic. On automatic transmission
models, the right-hand end tank incorporates
the transmission fluid cooler.
The coolant pump is located on the front
face of the engine block, and is belt-driven.
The pump is of the impeller type.
The cooling fan draws cold air over the
radiator matrix to assist the cooling process
when the forward speed of the vehicle is too
low to provide sufficient cooling airflow, or the
ambient temperature is unusually high. SOHC
models have a thermo-viscous fan, whereas
CVH and DOHC models have an
electrically-operated fan.
The thermo-viscous fan is controlled by the
temperature of the air behind the radiator.
When the air temperature reaches a
predetermined level, a bi-metallic coil
commences to open a valve within the unit,
and silicon fluid is fed through a system of
vanes. Half the vanes are driven directly by
the coolant pump, and the remaining half are
connected to the fan blades. The vanes are
arranged so that drive is transmitted to the fan
blades in relation to the viscosity of the silicon
fluid, and this in turn depends on ambienttemperature and engine speed. The fan is
therefore only operating when required, and
compared with direct-drive type fans
represents a considerable improvement in fuel
economy, drivebelt wear and fan noise.
The electrically-operated fan is switched on
by a temperature sensor mounted in the
thermostat housing when the temperature
reaches a predetermined level. The fan is
therefore only operating when required, and like
the thermo-viscous fan, offers a considerable
advantage over direct-drive type fans.
A thermostat is fitted. Its purpose is to
ensure rapid engine warm-up by restricting
the flow of coolant to the engine when cold
and also to assist in regulating the normal
operating temperature of the engine.
The expansion tank incorporates a pressure
cap which effectively pressurises the cooling
system as the coolant temperature rises,
thereby increasing the boiling point of the
coolant. The tank also has a further degas
function. Any accumulation of air bubbles in the
coolant is returned to the tank and released in
the air space, thus maintaining the efficiency of
the coolant. The pressure cap also incorporates
a vacuum relief valve which prevents a vacuum
forming in the system as it cools.
The system functions as follows. Cold
coolant in the bottom of the radiator circulates
through the bottom hose to the coolant pump
where the pump impeller pushes the coolant
through the passages within the cylinder
block, cylinder head and inlet manifold. After
cooling the cylinder bores, combustion
chambers and valve seats, the coolant
reaches the underside of the thermostat
which is initially closed. A small proportion ofthe coolant passes from the thermostat
housing to the expansion tank, but the main
circulation is through the inlet manifold,
automatic choke (where applicable), and
heater matrix, finally returning to the coolant
pump. When the coolant reaches a
predetermined temperature, the thermostat
opens and hot water passes through the top
hose to the top of the radiator. As the coolant
circulates through the radiator, it is cooled by
the flow of air to the vehicle’s forward motion,
supplemented by the action of the cooling fan
where necessary. By the time it reaches the
bottom of the radiator the coolant is cooled,
and the cycle is repeated. Circulation of
coolant continues through the expansion
tank, inlet manifold, automatic choke (where
applicable) and heater at all times, the heater
temperature being controlled by an air flap.
An air conditioning system is available as
an optional extra on certain models. In
conjunction with the heater, the system
enables any reasonable air temperature to be
achieved inside the vehicle; it also reduces
the humidity of the incoming air, aiding
demisting even when cooling is not required.
The refrigeration side of the air conditioning
system functions in a similar way to a
domestic refrigerator. A compressor, belt-
driven from the crankshaft pulley, draws
refrigerant in its gaseous phase from an
evaporator. The compressed refrigerant
passes through a condenser where it loses
heat and enters its liquid phase. After passing
through the dehydrator, which acts as a
reservoir and filter to extract moisture from
the circuit, the refrigerant returns to the
evaporator where it absorbs heat from the air
1General information and
precautions
3•2Cooling, heating and air conditioning systems
Page 3 of 12
passing over the evaporator fins on its way to
the vehicle interior. The refrigerant becomes a
gas again and the cycle is repeated.
Various subsidiary controls and sensors
protect the system against excessive
temperature and pressures. Additionally,
engine idle speed is increased when the
system is in use to compensate for the
additional load imposed by the compressor.
Precautions
Air conditioning refrigerant
Although the refrigerant is not itself toxic, in
the presence of a naked flame (or a lighted
cigarette) it forms a highly toxic gas. Liquid
refrigerant spilled on the skin will cause
frostbite. If refrigerant enters the eyes, rinse
them with a dilute solution of boric acid and
seek medical advice immediately.
In view of the above points, and of the need
for specialised equipment for evacuating and
recharging the system, any work which
requires the disconnection of a refrigerant line
must be left to a specialist.
Do not allow refrigerant lines to be exposed
to temperatures above 230°F (110°C) - eg
during welding or paint drying operations and
do not operate the air conditioning system if it
is known to be short of refrigerant, or further
damage may result.
Antifreeze mixture
Antifreeze mixture is poisonous. Keep it out
of reach of children and pets. Wash splashes
off skin and clothing with plenty of water.
Wash splashes off vehicle paintwork to avoid
discolouration.
Antifreeze/water mixture must be renewed
at the specified intervals to preserve its anti-
corrosive properties. In climates where
antifreeze protection is unnecessary, a
corrosion inhibitor may be used instead -
consult a Ford dealer. Never run the engine
for long periods with plain water as coolant.
Only use the specified antifreeze as inferior
brands may not contain the necessary
corrosion inhibitors, or may break down at
high temperatures. Antifreeze containing
methanol is particularly to be avoided, as the
methanol evaporates.
The specified mixture is 45 to 50%
antifreeze and 50 to 55% clean soft water (by
volume). Mix the required quantity in a clean
container.
Refer to Chapter 1, Section 46.
Refer to Chapter 1, Section 46.
Refer to Chapter 1, Section 46.
Removal
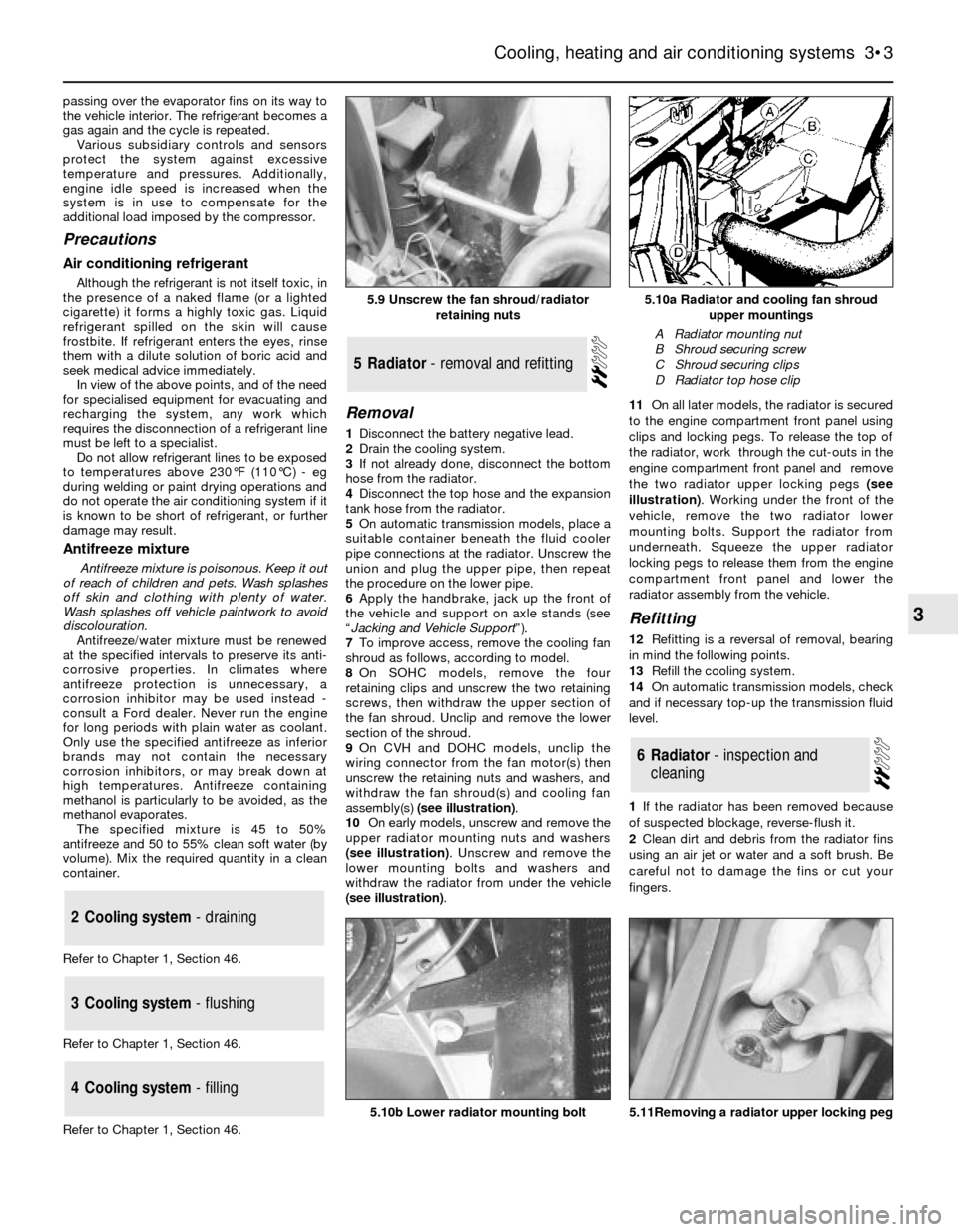
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Drain the cooling system.
3If not already done, disconnect the bottom
hose from the radiator.
4Disconnect the top hose and the expansion
tank hose from the radiator.
5On automatic transmission models, place a
suitable container beneath the fluid cooler
pipe connections at the radiator. Unscrew the
union and plug the upper pipe, then repeat
the procedure on the lower pipe.
6Apply the handbrake, jack up the front of
the vehicle and support on axle stands (see
“Jacking and Vehicle Support”).
7To improve access, remove the cooling fan
shroud as follows, according to model.
8On SOHC models, remove the four
retaining clips and unscrew the two retaining
screws, then withdraw the upper section of
the fan shroud. Unclip and remove the lower
section of the shroud.
9On CVH and DOHC models, unclip the
wiring connector from the fan motor(s) then
unscrew the retaining nuts and washers, and
withdraw the fan shroud(s) and cooling fan
assembly(s) (see illustration).
10On early models, unscrew and remove the
upper radiator mounting nuts and washers
(see illustration). Unscrew and remove the
lower mounting bolts and washers and
withdraw the radiator from under the vehicle
(see illustration).11On all later models, the radiator is secured
to the engine compartment front panel using
clips and locking pegs. To release the top of
the radiator, work through the cut-outs in the
engine compartment front panel and remove
the two radiator upper locking pegs (see
illustration). Working under the front of the
vehicle, remove the two radiator lower
mounting bolts. Support the radiator from
underneath. Squeeze the upper radiator
locking pegs to release them from the engine
compartment front panel and lower the
radiator assembly from the vehicle.
Refitting
12Refitting is a reversal of removal, bearing
in mind the following points.
13Refill the cooling system.
14On automatic transmission models, check
and if necessary top-up the transmission fluid
level.
1If the radiator has been removed because
of suspected blockage, reverse-flush it.
2Clean dirt and debris from the radiator fins
using an air jet or water and a soft brush. Be
careful not to damage the fins or cut your
fingers.
6Radiator -inspectionand
cleaning
5Radiator - removal and refitting
4Cooling system - filling
3Cooling system - flushing
2Cooling system - draining
Cooling, heating and air conditioning systems 3•3
3
5.10a Radiator and cooling fan shroud
upper mountings
A Radiator mounting nut
B Shroud securing screw
C Shroud securing clips
D Radiator top hose clip
5.11Removing a radiator upper locking peg5.10b Lower radiator mounting bolt
5.9 Unscrew the fan shroud/radiator
retaining nuts
Page 8 of 12
DOHC models
6Disconnect the battery negative lead.
7To provide additional clearance when
removing the cooling fan shroud assembly
(which is removed from below the vehicle),
apply the handbrake, then jack up the front of
the vehicle and support it securely on axle
stands (see “Jacking and Vehicle Support”).
8Disconnect the wiring plug(s) from the
motor(s), and where applicable, unclip the
wiring from the fan shroud.
9Unclip the expansion tank hose from the
fan shroud.
10Unscrew the two nuts securing the fan
shroud to the top of the radiator, then tilt the
top of the shroud away from the radiator, and
lift the shroud to release the lower securing
clips. Withdraw the assembly from below the
vehicle.
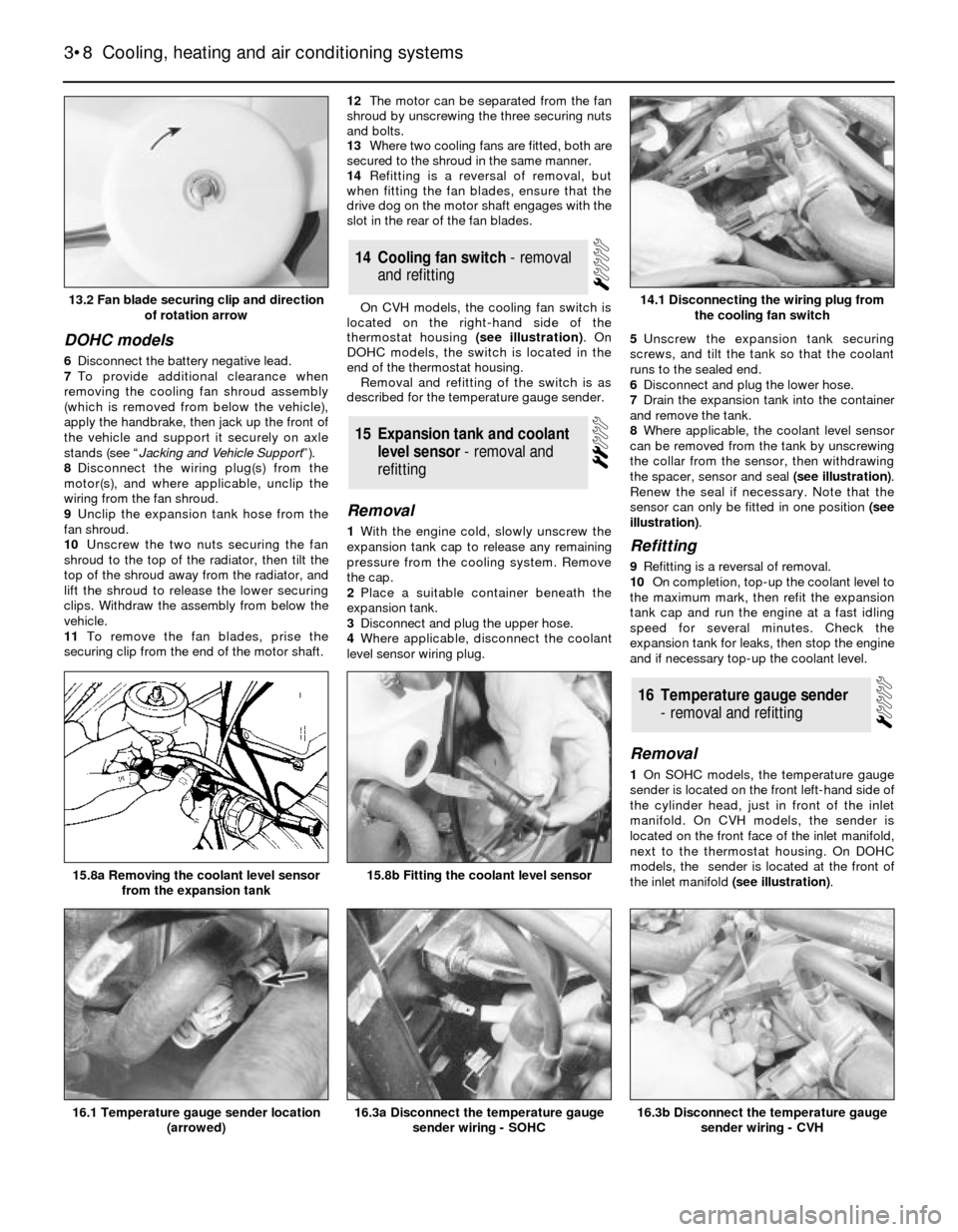
11To remove the fan blades, prise the
securing clip from the end of the motor shaft.12The motor can be separated from the fan
shroud by unscrewing the three securing nuts
and bolts.
13Where two cooling fans are fitted, both are
secured to the shroud in the same manner.
14Refitting is a reversal of removal, but
when fitting the fan blades, ensure that the
drive dog on the motor shaft engages with the
slot in the rear of the fan blades.
On CVH models, the cooling fan switch is
located on the right-hand side of the
thermostat housing (see illustration). On
DOHC models, the switch is located in the
end of the thermostat housing.
Removal and refitting of the switch is as
described for the temperature gauge sender.
Removal
1With the engine cold, slowly unscrew the
expansion tank cap to release any remaining
pressure from the cooling system. Remove
the cap.
2Place a suitable container beneath the
expansion tank.
3Disconnect and plug the upper hose.
4Where applicable, disconnect the coolant
level sensor wiring plug. 5Unscrew the expansion tank securing
screws, and tilt the tank so that the coolant
runs to the sealed end.
6Disconnect and plug the lower hose.
7Drain the expansion tank into the container
and remove the tank.
8Where applicable, the coolant level sensor
can be removed from the tank by unscrewing
the collar from the sensor, then withdrawing
the spacer, sensor and seal (see illustration).
Renew the seal if necessary. Note that the
sensor can only be fitted in one position (see
illustration). Refitting
9Refitting is a reversal of removal.
10On completion, top-up the coolant level to
the maximum mark, then refit the expansion
tank cap and run the engine at a fast idling
speed for several minutes. Check the
expansion tank for leaks, then stop the engine
and if necessary top-up the coolant level.
Removal
1On SOHC models, the temperature gauge
sender is located on the front left-hand side of
the cylinder head, just in front of the inlet
manifold. On CVH models, the sender is
located on the front face of the inlet manifold,
next to the thermostat housing. On DOHC
models, the sender is located at the front of
the inlet manifold (see illustration).
16Temperature gauge sender
- removal and refitting
15Expansion tank and coolant
level sensor - removal and
refitting
14Cooling fan switch -removal
andrefitting
3•8Cooling, heating and air conditioning systems
13.2 Fan blade securing clip and direction
of rotation arrow
15.8a Removing the coolant level sensor
from the expansion tank
16.3a Disconnect the temperature gauge
sender wiring - SOHC16.1 Temperature gauge sender location
(arrowed)16.3b Disconnect the temperature gauge
sender wiring - CVH
15.8b Fitting the coolant level sensor
14.1 Disconnecting the wiring plug from
the cooling fan switch
Page 9 of 12
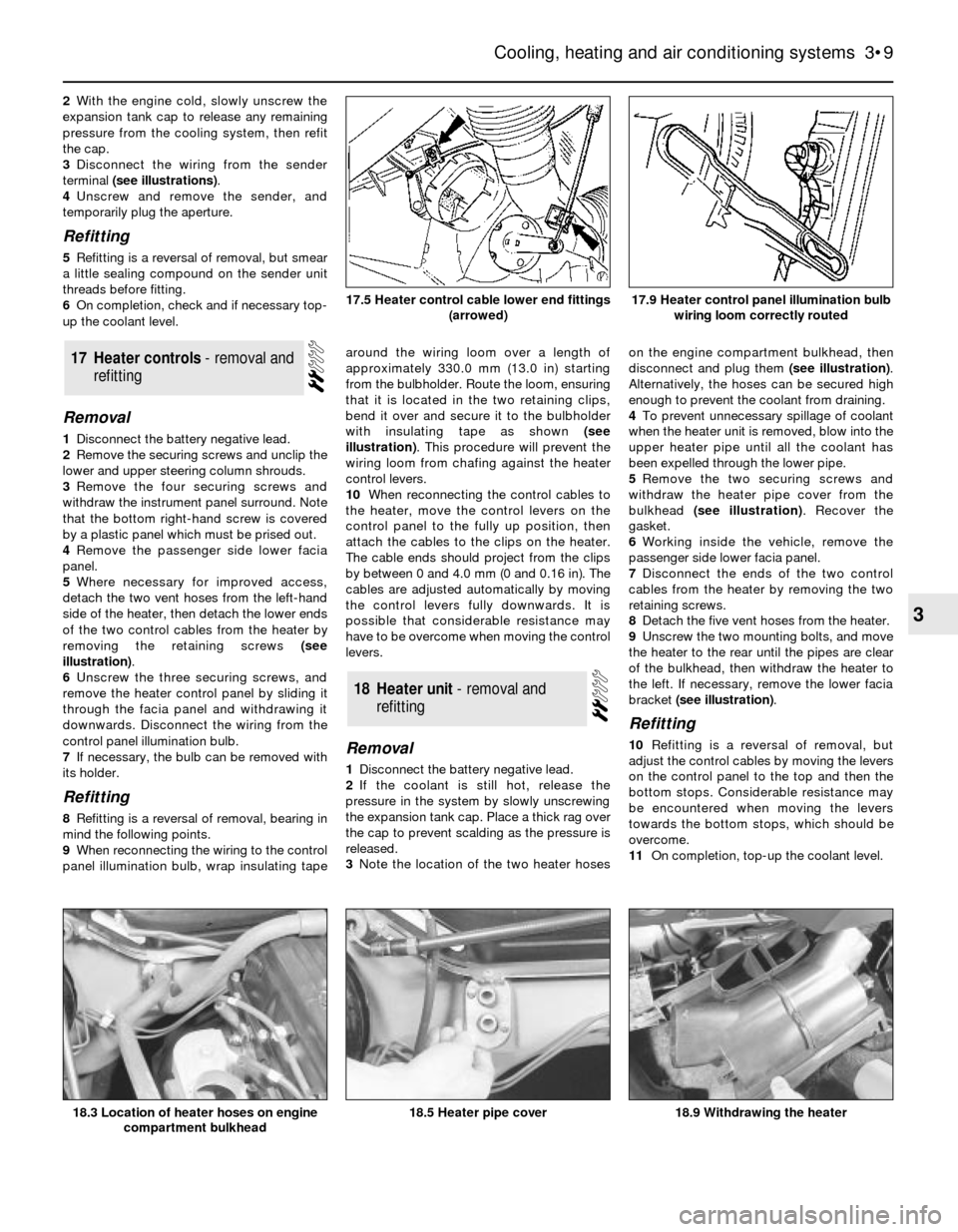
2With the engine cold, slowly unscrew the
expansion tank cap to release any remaining
pressure from the cooling system, then refit
the cap.
3Disconnect the wiring from the sender
terminal (see illustrations).
4Unscrew and remove the sender, and
temporarily plug the aperture.
Refitting
5Refitting is a reversal of removal, but smear
a little sealing compound on the sender unit
threads before fitting.
6On completion, check and if necessary top-
up the coolant level.
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Remove the securing screws and unclip the
lower and upper steering column shrouds.
3Remove the four securing screws and
withdraw the instrument panel surround. Note
that the bottom right-hand screw is covered
by a plastic panel which must be prised out.
4Remove the passenger side lower facia
panel.
5Where necessary for improved access,
detach the two vent hoses from the left-hand
side of the heater, then detach the lower ends
of the two control cables from the heater by
removing the retaining screws (see
illustration).
6Unscrew the three securing screws, and
remove the heater control panel by sliding it
through the facia panel and withdrawing it
downwards. Disconnect the wiring from the
control panel illumination bulb.
7If necessary, the bulb can be removed with
its holder.
Refitting
8Refitting is a reversal of removal, bearing in
mind the following points.
9When reconnecting the wiring to the control
panel illumination bulb, wrap insulating tapearound the wiring loom over a length of
approximately 330.0 mm (13.0 in) starting
from the bulbholder. Route the loom, ensuring
that it is located in the two retaining clips,
bend it over and secure it to the bulbholder
with insulating tape as shown (see
illustration). This procedure will prevent the
wiring loom from chafing against the heater
control levers.
10When reconnecting the control cables to
the heater, move the control levers on the
control panel to the fully up position, then
attach the cables to the clips on the heater.
The cable ends should project from the clips
by between 0 and 4.0 mm (0 and 0.16 in). The
cables are adjusted automatically by moving
the control levers fully downwards. It is
possible that considerable resistance may
have to be overcome when moving the control
levers.
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2If the coolant is still hot, release the
pressure in the system by slowly unscrewing
the expansion tank cap. Place a thick rag over
the cap to prevent scalding as the pressure is
released.
3Note the location of the two heater hoseson the engine compartment bulkhead, then
disconnect and plug them (see illustration).
Alternatively, the hoses can be secured high
enough to prevent the coolant from draining.
4To prevent unnecessary spillage of coolant
when the heater unit is removed, blow into the
upper heater pipe until all the coolant has
been expelled through the lower pipe.
5Remove the two securing screws and
withdraw the heater pipe cover from the
bulkhead (see illustration). Recover the
gasket.
6Working inside the vehicle, remove the
passenger side lower facia panel.
7Disconnect the ends of the two control
cables from the heater by removing the two
retaining screws.
8Detach the five vent hoses from the heater.
9Unscrew the two mounting bolts, and move
the heater to the rear until the pipes are clear
of the bulkhead, then withdraw the heater to
the left. If necessary, remove the lower facia
bracket (see illustration).
Refitting
10Refitting is a reversal of removal, but
adjust the control cables by moving the levers
on the control panel to the top and then the
bottom stops. Considerable resistance may
be encountered when moving the levers
towards the bottom stops, which should be
overcome.
11On completion, top-up the coolant level.
18Heater unit - removal and
refitting
17Heater controls - removal and
refitting
Cooling, heating and air conditioning systems 3•9
3
18.3 Location of heater hoses on engine
compartment bulkhead18.9 Withdrawing the heater18.5 Heater pipe cover
17.9 Heater control panel illumination bulb
wiring loom correctly routed17.5 Heater control cable lower end fittings
(arrowed)