brake FORD SUPER DUTY 2009 2.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 2009, Model line: SUPER DUTY, Model: FORD SUPER DUTY 2009 2.GPages: 418, PDF Size: 3.55 MB
Page 305 of 418

WARNING:If the parking brake is fully released, but the brake
warning lamp remains illuminated, the brakes may not be
working properly. See your authorized dealer.
4WD Systems
4WD (when you select a 4WD mode), uses all four wheels to power the
vehicle. This increases traction, enabling you to drive over terrain and
road conditions that a conventional two-wheel drive vehicle cannot.
Power is supplied to all four wheels through a transfer case. On 4WD
vehicles, the transfer case allows you to select 4WD when necessary.
Information on transfer case operation and shifting procedures can be
found in theDrivingchapter. Information on transfer case maintenance
can be found in theMaintenance and Specificationschapter. You
should become thoroughly familiar with this information before you
operate your vehicle.
Normal characteristics
On some 4WD models, the initial shift from two-wheel drive to 4x4 while
the vehicle is moving can cause some momentary clunk and ratcheting
sounds. This is the front drivetrain coming up to speed and the
automatic locking hubs engaging and is not cause for concern.
Sand
When driving over sand, try to keep all four wheels on the most solid
area of the trail. Avoid reducing the tire pressures but shift to a lower
gear and drive steadily through the terrain. Apply the accelerator slowly
and avoid spinning the wheels.
Avoid excessive speed because vehicle momentum can work against you
and cause the vehicle to become stuck to the point that assistance may
be required from another vehicle. Remember, you may be able to back
out the way you came if you proceed with caution.
Note:If air is released from your tires, the Tire Pressure Monitoring
System (TPMS) indicator light may illuminate (if equipped).
2009 F-250/350/450/550(f23)
Owners Guide, 1st Printing
USA(fus)
Driving
305
Page 306 of 418

Mud and water
If you must drive through high
water, drive slowly. Traction or
brake capability may be limited.
When driving through water,
determine the depth; avoid water
higher than the bottom of the hubs
(if possible) and proceed slowly. If
the ignition system gets wet, the
vehicle may stall.
Once through water, always try the brakes. Wet brakes do not stop the
vehicle as effectively as dry brakes. Drying can be improved by moving
your vehicle slowly while applying light pressure on the brake pedal.
Be cautious of sudden changes in vehicle speed or direction when you
are driving in mud. Even 4WD vehicles can lose traction in slick mud. As
when you are driving over sand, apply the accelerator slowly and avoid
spinning your wheels. If the vehicle does slide, steer in the direction of
the slide until you regain control of the vehicle.
If the transmission, transfer case or front axle are submerged in water,
their fluids should be checked and changed, if necessary.
Driving through deep water may damage the transmission.
Refer toTransmission temperature gaugein theInstrument Cluster
chapter for transmission fluid temperature information.
If the front or rear axle is submerged in water, the axle lubricant should
be replaced.
After driving through mud, clean off residue stuck to rotating driveshafts
and tires. Excess mud stuck on tires and rotating driveshafts causes an
imbalance that could damage drive components.
“Tread Lightly” is an educational
program designed to increase public
awareness of land-use regulations
and responsibilities in our nations
wilderness areas. Ford Motor
Company joins the U.S. Forest Service and the Bureau of Land
Management in encouraging you to help preserve our national forest and
other public and private lands by “treading lightly.”
Driving on hilly or sloping terrain
Although natural obstacles may make it necessary to travel diagonally up
or down a hill or steep incline, you should always try to drive straight up
2009 F-250/350/450/550(f23)
Owners Guide, 1st Printing
USA(fus)
Driving
306
Page 307 of 418

or straight down.Avoid driving crosswise or turning on steep
slopes or hills. A danger lies in losing traction, slipping sideways and
possibly rolling over. Whenever driving on a hill, determine beforehand
the route you will use. Do not drive over the crest of a hill without
seeing what conditions are on the other side. Do not drive in reverse
over a hill without the aid of an observer.
When climbing a steep slope or hill,
start in a lower gear rather than
downshifting to a lower gear from a
higher gear once the ascent has
started. This reduces strain on the
engine and the possibility of stalling.
If you do stall out, do not try to
turn around because you might roll
over. It is better to back down to a
safe location.
Apply just enough power to the
wheels to climb the hill. Too much
power will cause the tires to slip,
spin or lose traction, resulting in
loss of vehicle control.
Descend a hill in the same gear you
would use to climb up the hill to
avoid excessive brake application
and brake overheating. Do not
descend in neutral; instead,
manually shift to a lower gear. Your
vehicle has anti-lock brakes, apply
the brakes steadily. Do not “pump”
the brakes.
Driving on snow and ice
4WD vehicles have advantages over 2WD vehicles in snow and ice but
can skid like any other vehicle.
Should you start to slide while driving on snowy or icy roads, turn the
steering wheel in the direction of the slide until you regain control.
2009 F-250/350/450/550(f23)
Owners Guide, 1st Printing
USA(fus)
Driving
307
Page 308 of 418

Avoid sudden applications of power and quick changes of direction on
snow and ice. Apply the accelerator slowly and steadily when starting
from a full stop.
Avoid sudden braking as well. Although a 4WD vehicle may accelerate
better than a two-wheel drive vehicle in snow and ice, it won’t stop any
faster, because as in other vehicles, braking occurs at all four wheels. Do
not become overconfident as to road conditions.
Make sure you allow sufficient distance between you and other vehicles
for stopping. Drive slower than usual and consider using one of the lower
gears. In emergency stopping situations, avoid locking of the wheels. Use
a “squeeze” technique, push on the brake pedal with a steadily increasing
force which allows the wheels to brake yet continue to roll so that you
may steer in the direction you want to travel. If you lock the wheels,
release the brake pedal and repeat the squeeze technique. If your vehicle
is equipped with a Four Wheel Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS), apply the
brake steadily. Do not “pump” the brakes. Refer to theBrakessection of
this chapter for additional information on the operation of the anti-lock
brake system.
Never drive with chains on the front tires of 4WD vehicles without also
putting them on the rear tires. This could cause the rear to slide and
swing around during braking.
Maintenance and Modifications
The suspension and steering systems on your vehicle have been designed
and tested to provide predictable performance whether loaded or empty
and durable load carrying capability. For this reason, Ford Motor
Company strongly recommends that you do not make modifications such
as adding or removing parts (such as lift kits or stabilizer bars) or by
using replacement parts not equivalent to the original factory equipment.
Any modifications to a vehicle that raise the center of gravity can make
it more likely the vehicle will roll over as a result of a loss of control.
Ford Motor Company recommends that caution be used with any vehicle
equipped with a high load or device (such as ladder racks or pickup box
cover).
Failure to maintain your vehicle properly may void the warranty, increase
your repair cost, reduce vehicle performance and operational capabilities
and adversely affect driver and passenger safety. Frequent inspection of
vehicle chassis components is recommended if the vehicle is subjected to
heavy off-road usage.
2009 F-250/350/450/550(f23)
Owners Guide, 1st Printing
USA(fus)
Driving
308
Page 309 of 418

VEHICLE USED AS A STATIONARY POWER SOURCE
Auxiliary equipment called power take-off, or PTO, is often added to the
engine or transmission to operate utility equipment. Examples include a
wheel-lift for tow trucks, cranes, tools for construction or tire service,
and pumping fluids. PTO applications draw auxiliary horsepower from
the powertrain, often while the vehicle is stationary. In this condition,
there is limited cooling air flow through the radiator and around the
vehicle that normally occurs when a vehicle is moving. The aftermarket
PTO system installer, having the most knowledge of the final application,
is responsible for determining whether additional chassis heat protection
or powertrain cooling is required, and alerting the user to the safe and
proper operation.
Ford Super Duty Vehicles are qualified for use as a stationary power
source, within limits detailed in theFord Truck Body Builders Layout
Book,found at www.fleet.ford.com/truckbbas, and through the Ford
Truck Body Builders Advisory Service.
Gas engine vehicles are qualified for up to 10 minutes of continuous
operation as a stationary power source, due to the potential for the
normal venting of fuel vapors. For stationary PTO operation of extended
duration (beyond 10 minutes), diesel engine is recommended. Further
consult your aftermarket PTO installer, since the duration of operation
limit for the aftermarket PTO may be less than the vehicle is capable of.
DRIVING THROUGH WATER
If driving through deep or standing
water is unavoidable, proceed very
slowly especially when the depth is
not known. Never drive through
water that is higher than the bottom
of the wheel rims (for cars) or the
bottom of the hubs (for trucks).
When driving through water, traction or brake capability may be limited.
Also, water may enter your engine’s air intake and severely damage your
engine or your vehicle may stall.Driving through deep water where
the transmission vent tube is submerged may allow water into the
transmission and cause internal transmission damage.
Once through the water, always dry the brakes by moving your
vehicle slowly while applying light pressure on the brake pedal.
Wet brakes do not stop the vehicle as quickly as dry brakes.
2009 F-250/350/450/550(f23)
Owners Guide, 1st Printing
USA(fus)
Driving
309
Page 318 of 418
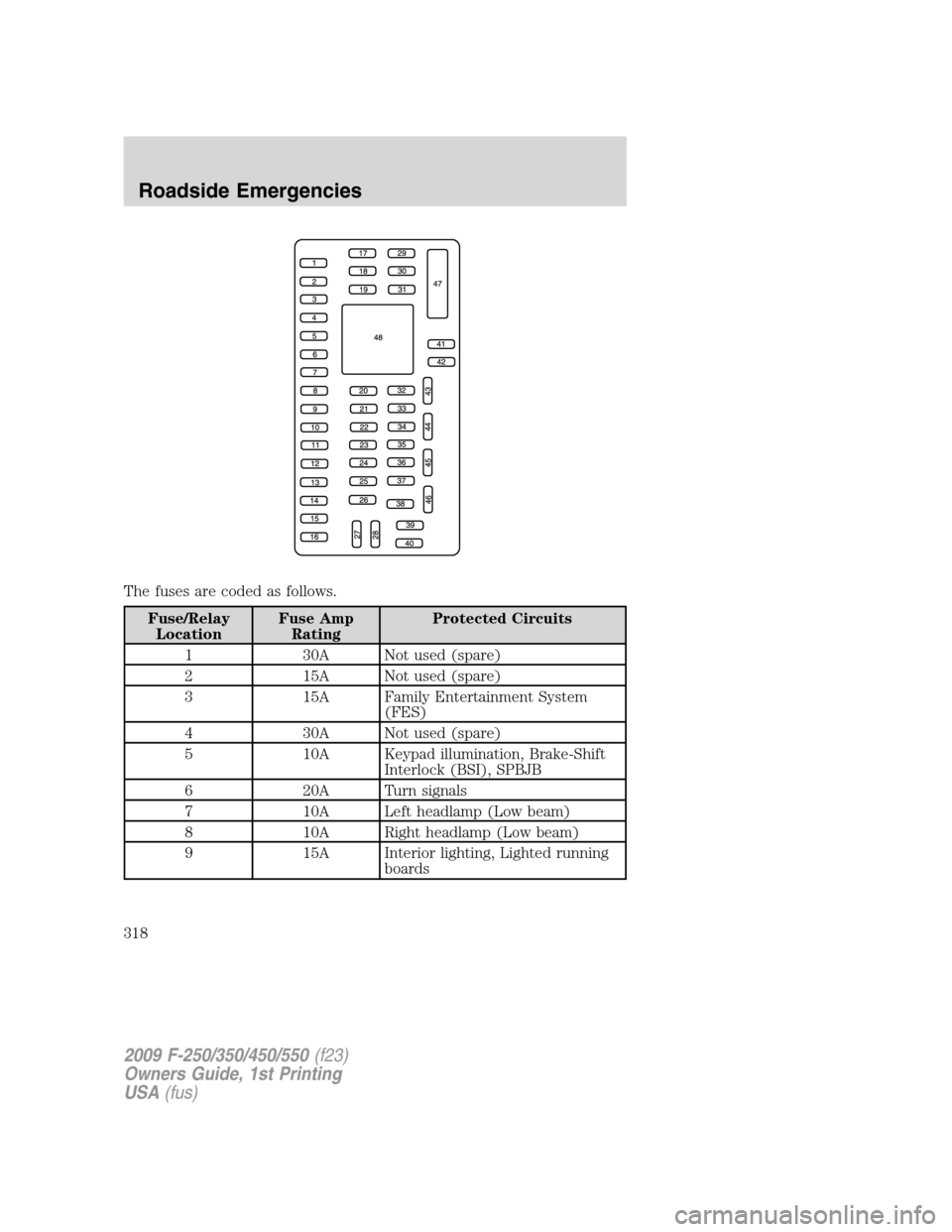
The fuses are coded as follows.
Fuse/Relay
LocationFuse Amp
RatingProtected Circuits
1 30A Not used (spare)
2 15A Not used (spare)
3 15A Family Entertainment System
(FES)
4 30A Not used (spare)
5 10A Keypad illumination, Brake-Shift
Interlock (BSI), SPBJB
6 20A Turn signals
7 10A Left headlamp (Low beam)
8 10A Right headlamp (Low beam)
9 15A Interior lighting, Lighted running
boards
2009 F-250/350/450/550(f23)
Owners Guide, 1st Printing
USA(fus)
Roadside Emergencies
318
Page 320 of 418
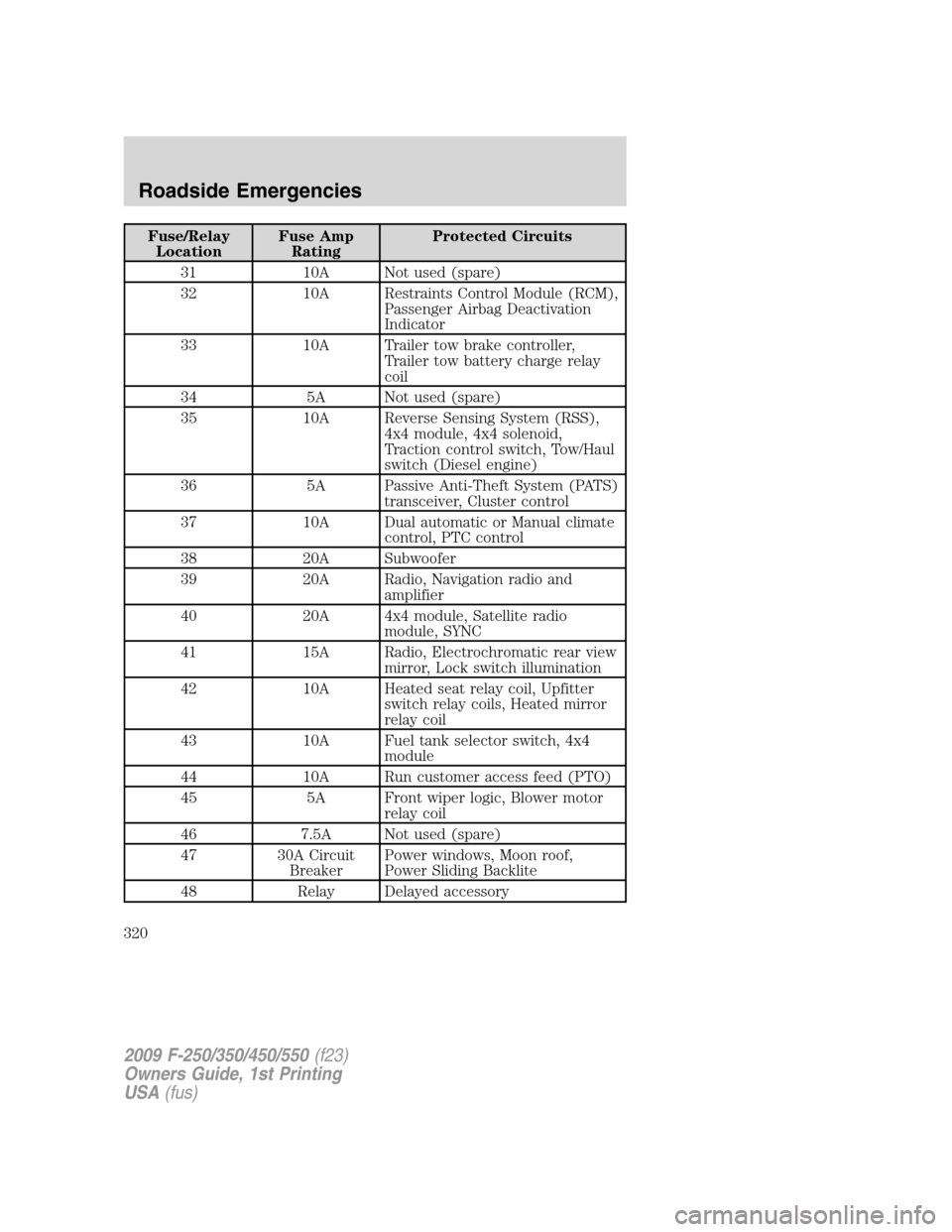
Fuse/Relay
LocationFuse Amp
RatingProtected Circuits
31 10A Not used (spare)
32 10A Restraints Control Module (RCM),
Passenger Airbag Deactivation
Indicator
33 10A Trailer tow brake controller,
Trailer tow battery charge relay
coil
34 5A Not used (spare)
35 10A Reverse Sensing System (RSS),
4x4 module, 4x4 solenoid,
Traction control switch, Tow/Haul
switch (Diesel engine)
36 5A Passive Anti-Theft System (PATS)
transceiver, Cluster control
37 10A Dual automatic or Manual climate
control, PTC control
38 20A Subwoofer
39 20A Radio, Navigation radio and
amplifier
40 20A 4x4 module, Satellite radio
module, SYNC
41 15A Radio, Electrochromatic rear view
mirror, Lock switch illumination
42 10A Heated seat relay coil, Upfitter
switch relay coils, Heated mirror
relay coil
43 10A Fuel tank selector switch, 4x4
module
44 10A Run customer access feed (PTO)
45 5A Front wiper logic, Blower motor
relay coil
46 7.5A Not used (spare)
47 30A Circuit
BreakerPower windows, Moon roof,
Power Sliding Backlite
48 Relay Delayed accessory
2009 F-250/350/450/550(f23)
Owners Guide, 1st Printing
USA(fus)
Roadside Emergencies
320
Page 321 of 418
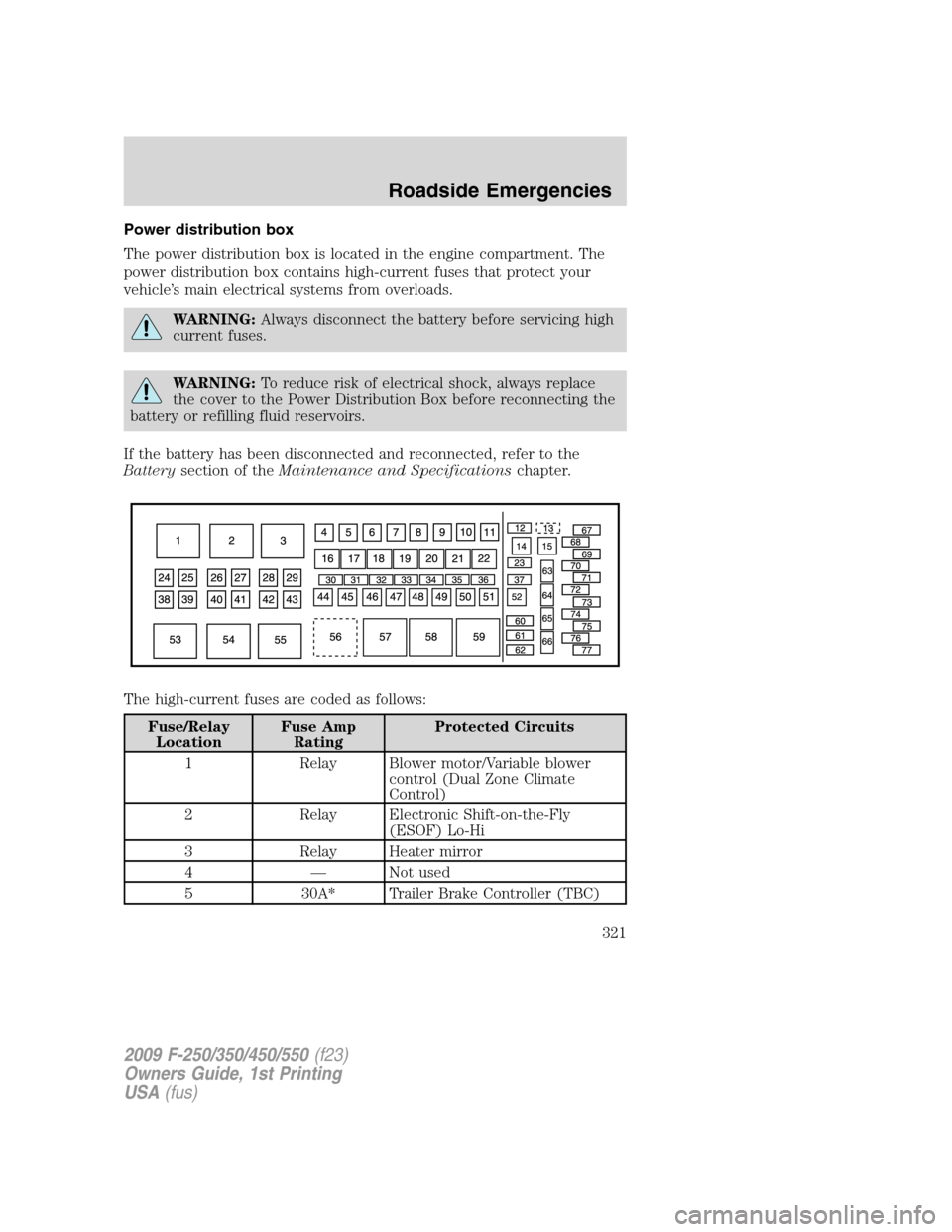
Power distribution box
The power distribution box is located in the engine compartment. The
power distribution box contains high-current fuses that protect your
vehicle’s main electrical systems from overloads.
WARNING:Always disconnect the battery before servicing high
current fuses.
WARNING:To reduce risk of electrical shock, always replace
the cover to the Power Distribution Box before reconnecting the
battery or refilling fluid reservoirs.
If the battery has been disconnected and reconnected, refer to the
Batterysection of theMaintenance and Specificationschapter.
The high-current fuses are coded as follows:
Fuse/Relay
LocationFuse Amp
RatingProtected Circuits
1 Relay Blower motor/Variable blower
control (Dual Zone Climate
Control)
2 Relay Electronic Shift-on-the-Fly
(ESOF) Lo-Hi
3 Relay Heater mirror
4 — Not used
5 30A* Trailer Brake Controller (TBC)
2009 F-250/350/450/550(f23)
Owners Guide, 1st Printing
USA(fus)
Roadside Emergencies
321
Page 322 of 418
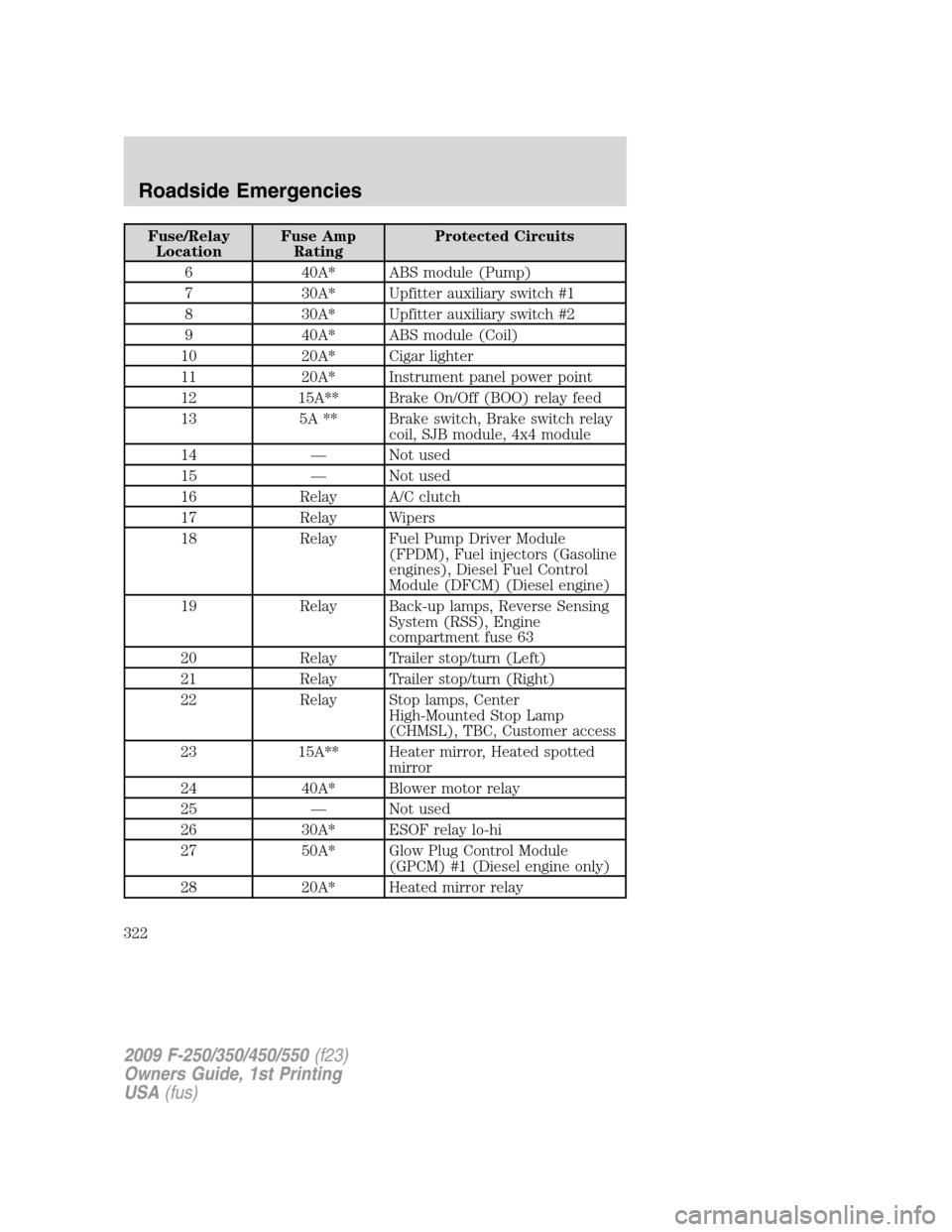
Fuse/Relay
LocationFuse Amp
RatingProtected Circuits
6 40A* ABS module (Pump)
7 30A* Upfitter auxiliary switch #1
8 30A* Upfitter auxiliary switch #2
9 40A* ABS module (Coil)
10 20A* Cigar lighter
11 20A* Instrument panel power point
12 15A** Brake On/Off (BOO) relay feed
13 5A ** Brake switch, Brake switch relay
coil, SJB module, 4x4 module
14 — Not used
15 — Not used
16 Relay A/C clutch
17 Relay Wipers
18 Relay Fuel Pump Driver Module
(FPDM), Fuel injectors (Gasoline
engines), Diesel Fuel Control
Module (DFCM) (Diesel engine)
19 Relay Back-up lamps, Reverse Sensing
System (RSS), Engine
compartment fuse 63
20 Relay Trailer stop/turn (Left)
21 Relay Trailer stop/turn (Right)
22 Relay Stop lamps, Center
High-Mounted Stop Lamp
(CHMSL), TBC, Customer access
23 15A** Heater mirror, Heated spotted
mirror
24 40A* Blower motor relay
25 — Not used
26 30A* ESOF relay lo-hi
27 50A* Glow Plug Control Module
(GPCM) #1 (Diesel engine only)
28 20A* Heated mirror relay
2009 F-250/350/450/550(f23)
Owners Guide, 1st Printing
USA(fus)
Roadside Emergencies
322
Page 325 of 418
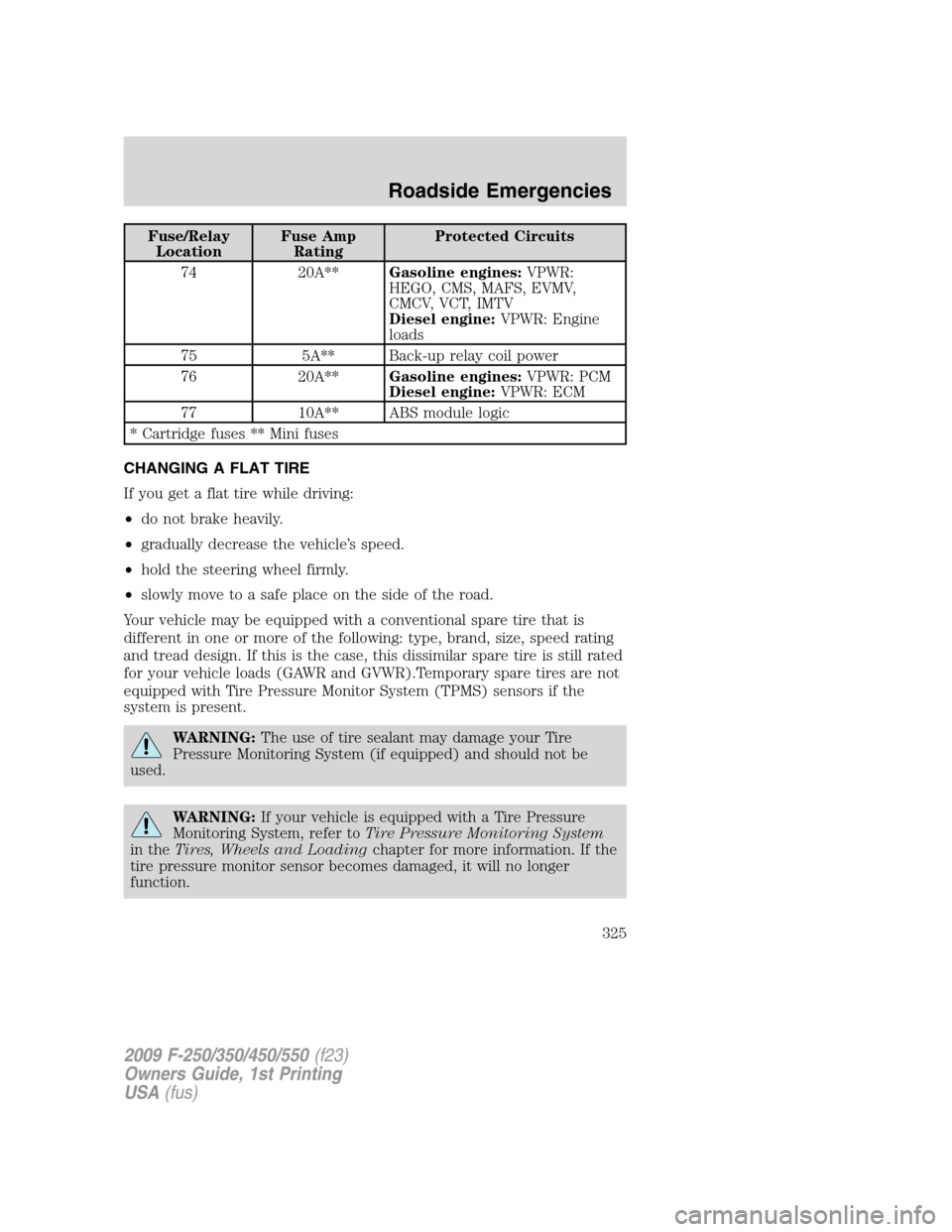
Fuse/Relay
LocationFuse Amp
RatingProtected Circuits
74 20A**Gasoline engines:VPWR:
HEGO, CMS, MAFS, EVMV,
CMCV, VCT, IMTV
Diesel engine:VPWR: Engine
loads
75 5A** Back-up relay coil power
76 20A**Gasoline engines:VPWR: PCM
Diesel engine:VPWR: ECM
77 10A** ABS module logic
* Cartridge fuses ** Mini fuses
CHANGING A FLAT TIRE
If you get a flat tire while driving:
•do not brake heavily.
•gradually decrease the vehicle’s speed.
•hold the steering wheel firmly.
•slowly move to a safe place on the side of the road.
Your vehicle may be equipped with a conventional spare tire that is
different in one or more of the following: type, brand, size, speed rating
and tread design. If this is the case, this dissimilar spare tire is still rated
for your vehicle loads (GAWR and GVWR).Temporary spare tires are not
equipped with Tire Pressure Monitor System (TPMS) sensors if the
system is present.
WARNING:The use of tire sealant may damage your Tire
Pressure Monitoring System (if equipped) and should not be
used.
WARNING:If your vehicle is equipped with a Tire Pressure
Monitoring System, refer toTire Pressure Monitoring System
in theTires, Wheels and Loadingchapter for more information. If the
tire pressure monitor sensor becomes damaged, it will no longer
function.
2009 F-250/350/450/550(f23)
Owners Guide, 1st Printing
USA(fus)
Roadside Emergencies
325