weight FORD SUPER DUTY 2017 4.G Owners Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: FORD, Model Year: 2017, Model line: SUPER DUTY, Model: FORD SUPER DUTY 2017 4.GPages: 636, PDF Size: 10.56 MB
Page 7 of 636
Bed Ramps....................................................265
Towing
Towing a Trailer............................................268
Trailer Reversing Aids
.................................269
Trailer Sway Control
....................................277
Recommended Towing Weights............277
Essential Towing Checks...........................281
Towing the Vehicle on Four Wheels......289
Driving Hints
Breaking-In....................................................290
Economical Driving
.....................................290
Driving Through Water................................291
Floor Mats........................................................291
Snowplowing................................................292
Roadside Emergencies
Roadside Assistance..................................295
Hazard Warning Flashers
.........................296
Fuel Shutoff - 6.2L/6.8L
...........................296
Fuel Shutoff - 6.7L Diesel.........................297
Jump Starting the Vehicle........................298
Post-Crash Alert System.........................300
Transporting the Vehicle
..........................300
Towing Points................................................301
Customer Assistance
Getting the Services You Need
..............303
In California (U.S. Only)............................304
The Better Business Bureau (BBB) Auto Line Program (U.S. Only).....................305
Utilizing the Mediation/Arbitration Program (Canada Only)
......................306
Getting Assistance Outside the U.S. and Canada.......................................................306
Ordering Additional Owner's Literature....................................................307
Reporting Safety Defects (U.S. Only)............................................................308 Reporting Safety Defects (Canada
Only)............................................................308
Fuses
Fuse Specification Chart...........................310
Changing a Fuse
...........................................318
Maintenance
General Information...................................320
Opening and Closing the Hood..............320
Under Hood Overview - 6.2L....................321
Under Hood Overview - 6.8L...................322
Under Hood Overview - 6.7L Diesel
......323
Engine Oil Dipstick
......................................324
Engine Oil Check - 6.2L/6.8L..................324
Engine Oil Check - 6.7L Diesel................325
Changing the Engine Oil and Oil Filter..............................................................326
Changing the Coalescer Filter Element.......................................................327
Oil Change Indicator Reset......................328
Engine Coolant Check - 6.2L/6.8L........329
Engine Coolant Check - 6.7L Diesel......333
Automatic Transmission Fluid Check............................................................337
Transfer Case Fluid Check.......................340
Brake Fluid Check
.......................................340
Power Steering Fluid Check......................341
Washer Fluid Check
.....................................341
Draining the Fuel Filter Water Trap - 6.7L Diesel............................................................342
Fuel Filter - 6.2L/6.8L................................343
Changing the 12V Battery.........................343
Checking the Wiper Blades.....................345
Changing the Wiper Blades.....................345
Adjusting the Headlamps........................346
Changing a Bulb
...........................................347
Bulb Specification Chart
..........................350
Changing the Engine Air Filter - 6.2L/ 6.8L...............................................................353
4
Super Duty (TFE) Canada/United States of America, enUSA, First Printing Table of Contents
Page 20 of 636

GENERAL INFORMATION
See the following sections for directions
on how to properly use safety restraints
for children.
WARNINGS
Always make sure your child is
secured properly in a device that is
appropriate for their height, age and
weight. Child safety restraints must be
bought separately from your vehicle.
Failure to follow these instructions and
guidelines may result in an increased risk
of serious injury or death to your child. All children are shaped differently.
The National Highway Traffic Safety
Administration and other safety
organizations, base their recommendations
for child restraints on probable child height,
age and weight thresholds, or on the
minimum requirements of the law. We
recommend that you check with a NHTSA
Certified Child Passenger Safety WARNINGS
Technician (CPST) to make sure that you
properly install the child restraint in your
vehicle and that you consult your
pediatrician to make sure you have a child
restraint appropriate for your child. To
locate a child restraint fitting station and
CPST, contact NHTSA toll free at
1-888-327-4236 or go to
www.nhtsa.dot.gov. In Canada, contact
Transport Canada toll free at
1-800-333-0371 or go to www.tc.gc.ca to
find a Child Car Seat Clinic in your area.
Failure to properly restrain children in child
restraints made especially for their height,
age and weight, may result in an increased
risk of serious injury or death to your child. On hot days, the temperature inside
the vehicle can rise very quickly.
Exposure of people or animals to
these high temperatures for even a short
time can cause death or serious heat
related injuries, including brain damage.
Small children are particularly at risk. 17
Super Duty (TFE) Canada/United States of America, enUSA, First Printing Child Safety
Page 21 of 636
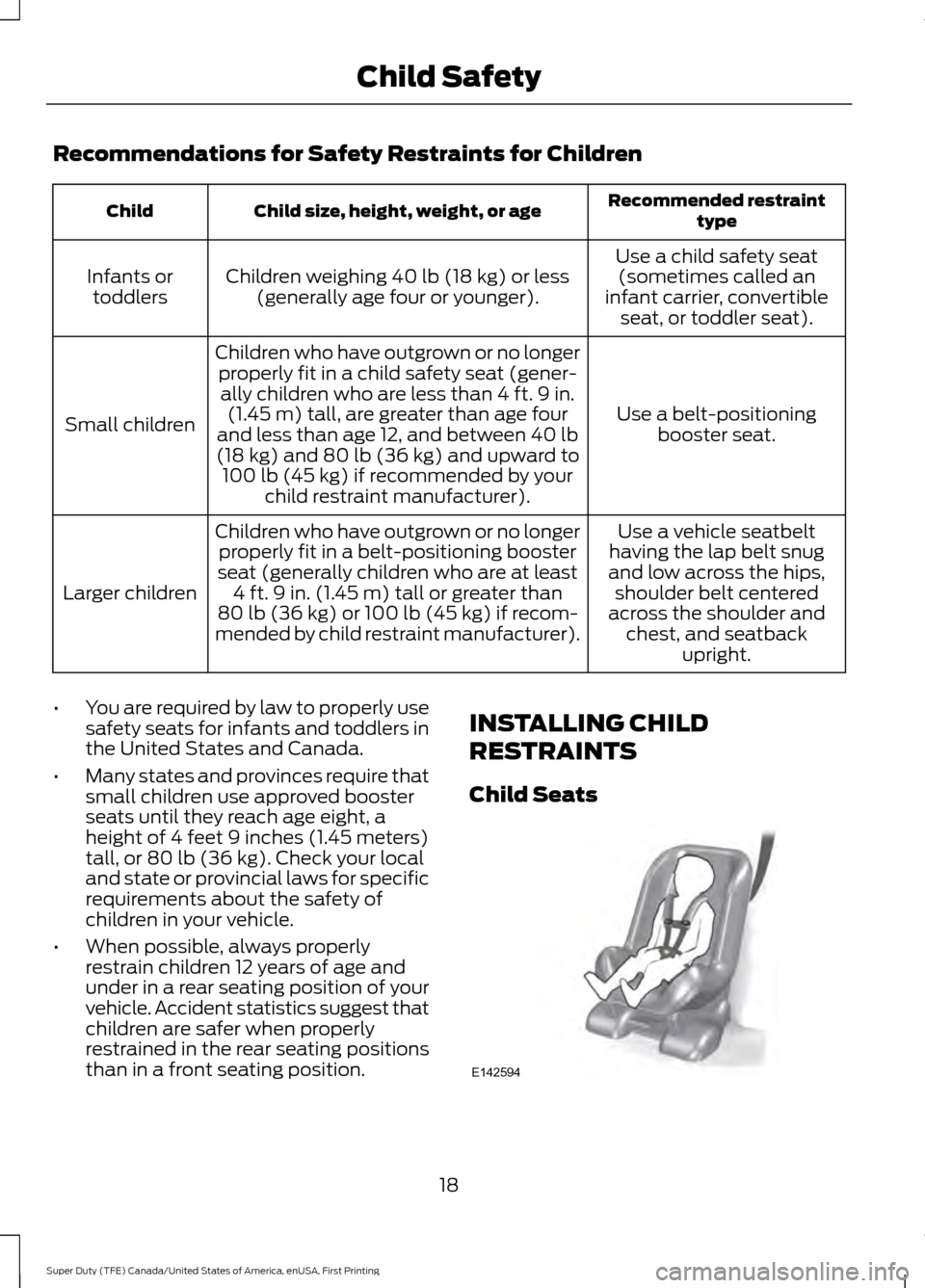
Recommendations for Safety Restraints for Children
Recommended restraint
type
Child size, height, weight, or age
Child
Use a child safety seat(sometimes called an
infant carrier, convertible seat, or toddler seat).
Children weighing 40 lb (18 kg) or less
(generally age four or younger).
Infants or
toddlers
Use a belt-positioningbooster seat.
Children who have outgrown or no longer
properly fit in a child safety seat (gener-ally children who are less than 4 ft. 9 in. (1.45 m) tall, are greater than age four
and less than age 12, and between
40 lb
(18 kg) and 80 lb (36 kg) and upward to
100 lb (45 kg) if recommended by your
child restraint manufacturer).
Small children
Use a vehicle seatbelt
having the lap belt snug
and low across the hips, shoulder belt centered
across the shoulder and chest, and seatback upright.
Children who have outgrown or no longer
properly fit in a belt-positioning booster
seat (generally children who are at least 4 ft. 9 in. (1.45 m) tall or greater than
80 lb (36 kg)
or 100 lb (45 kg) if recom-
mended by child restraint manufacturer).
Larger children
• You are required by law to properly use
safety seats for infants and toddlers in
the United States and Canada.
• Many states and provinces require that
small children use approved booster
seats until they reach age eight, a
height of 4 feet 9 inches (1.45 meters)
tall, or
80 lb (36 kg). Check your local
and state or provincial laws for specific
requirements about the safety of
children in your vehicle.
• When possible, always properly
restrain children 12 years of age and
under in a rear seating position of your
vehicle. Accident statistics suggest that
children are safer when properly
restrained in the rear seating positions
than in a front seating position. INSTALLING CHILD
RESTRAINTS
Child Seats
18
Super Duty (TFE) Canada/United States of America, enUSA, First Printing Child SafetyE142594
Page 24 of 636
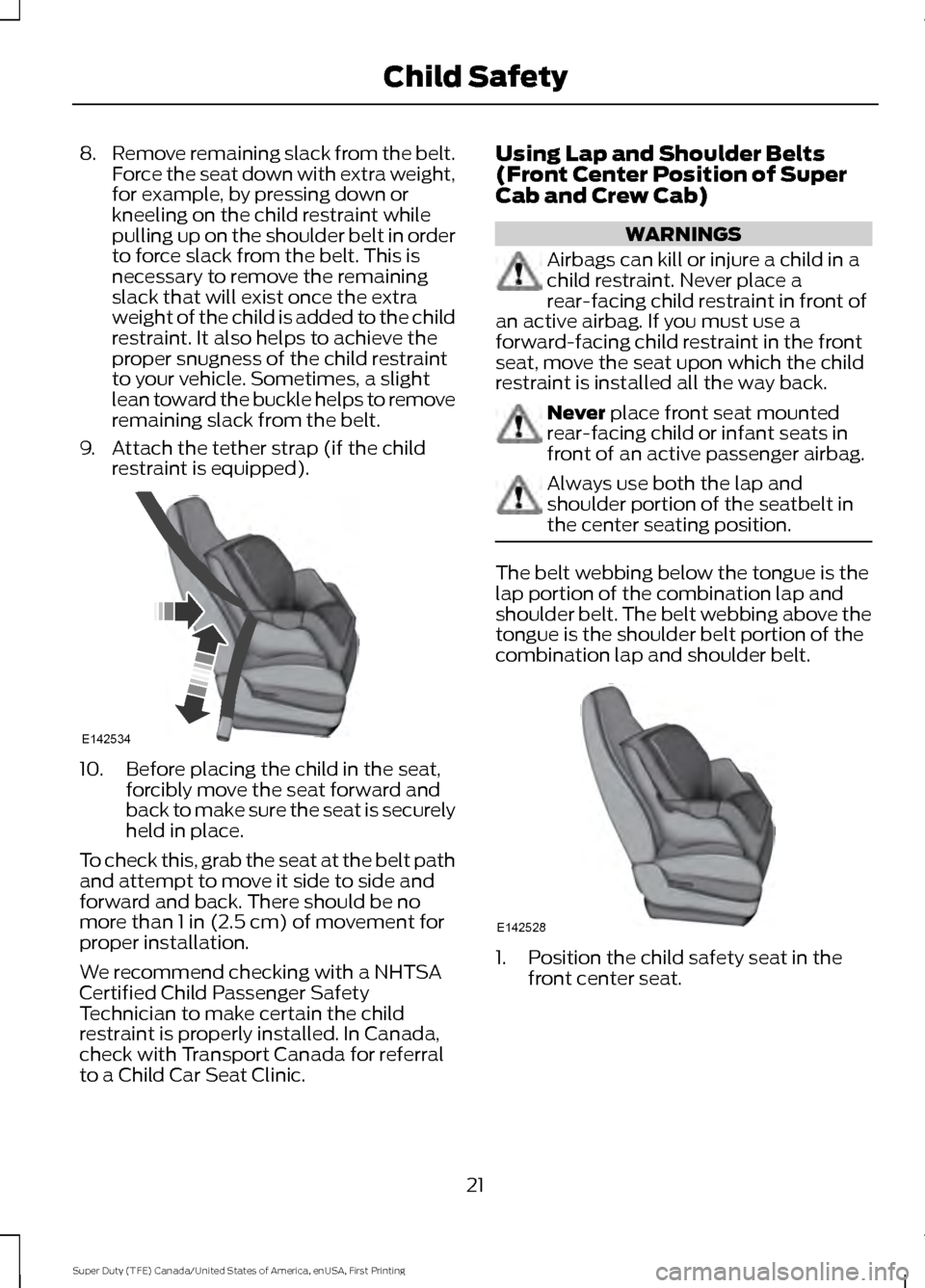
8.
Remove remaining slack from the belt.
Force the seat down with extra weight,
for example, by pressing down or
kneeling on the child restraint while
pulling up on the shoulder belt in order
to force slack from the belt. This is
necessary to remove the remaining
slack that will exist once the extra
weight of the child is added to the child
restraint. It also helps to achieve the
proper snugness of the child restraint
to your vehicle. Sometimes, a slight
lean toward the buckle helps to remove
remaining slack from the belt.
9. Attach the tether strap (if the child restraint is equipped). 10. Before placing the child in the seat,
forcibly move the seat forward and
back to make sure the seat is securely
held in place.
To check this, grab the seat at the belt path
and attempt to move it side to side and
forward and back. There should be no
more than 1 in (2.5 cm) of movement for
proper installation.
We recommend checking with a NHTSA
Certified Child Passenger Safety
Technician to make certain the child
restraint is properly installed. In Canada,
check with Transport Canada for referral
to a Child Car Seat Clinic. Using Lap and Shoulder Belts
(Front Center Position of Super
Cab and Crew Cab) WARNINGS
Airbags can kill or injure a child in a
child restraint. Never place a
rear-facing child restraint in front of
an active airbag. If you must use a
forward-facing child restraint in the front
seat, move the seat upon which the child
restraint is installed all the way back. Never
place front seat mounted
rear-facing child or infant seats in
front of an active passenger airbag. Always use both the lap and
shoulder portion of the seatbelt in
the center seating position.
The belt webbing below the tongue is the
lap portion of the combination lap and
shoulder belt. The belt webbing above the
tongue is the shoulder belt portion of the
combination lap and shoulder belt.
1. Position the child safety seat in the
front center seat.
21
Super Duty (TFE) Canada/United States of America, enUSA, First Printing Child SafetyE142534 E142528
Page 27 of 636

4. Insert the belt tongue into the proper
buckle (the buckle closest to the
direction the tongue is coming from)
for that seating position until you hear
a snap and feel the latch engage. Make
sure the tongue is latched securely by
pulling on it. 5. To put the retractor in the automatic
locking mode, grasp the lap portion of
the inflatable seatbelt and pull upward
until you pull all of the belt out.
Note: The automatic locking mode is
available on the front passenger and rear
seats. Note:
Unlike the standard seatbelt, the
inflatable seatbelt's unique lap portion locks
the child restraint for installation. The ability
for the shoulder portion of the belt to move
freely is normal, even after the lap belt has
been put into the automatic locking mode.
Note: The lock-off device on some child
restraints may not accommodate the
shoulder portion of the inflatable seatbelt.
Follow all instructions provided by the
manufacturer of the child restraint regarding
the necessary and proper use of the lock-off
device. In some instances, these devices
have been provided only for use in vehicles
with seatbelt systems that would otherwise
require a locking clip.
6. Allow the belt to retract to remove slack. The belt clicks as it retracts to
indicate it is in the automatic locking
mode.
7. Try to pull the belt out of the retractor to make sure the retractor is in the
automatic locking mode (you should
not be able to pull more belt out). If the
retractor is not locked, unbuckle the
belt and repeat Steps 5 and 6. 8.
Remove remaining slack from the belt.
Force the seat down with extra weight,
for example, by pressing down or
kneeling on the child restraint while
pulling down on the lap belt in order to
force slack from the belt. This is
24
Super Duty (TFE) Canada/United States of America, enUSA, First Printing Child SafetyE146523 E146524 E146525
Page 28 of 636

necessary to remove the remaining
slack that will exist once the extra
weight of the child is added to the child
restraint. It also helps to achieve the
proper snugness of the child restraint
to your vehicle. Sometimes, a slight
lean toward the buckle will additionally
help to remove remaining slack from
the belt.
9. Attach the tether strap (if the child restraint is equipped). 10. Before placing the child in the seat,
forcibly move the seat forward and
back to make sure the seat is securely
held in place. To check this, grab the
seat at the belt path and attempt to
move it side to side and forward and
back. There should be no more than
1 in (2.5 cm) of movement for proper
installation.
We recommend checking with a NHTSA
Certified Child Passenger Safety
Technician to make certain the child
restraint is properly installed. In Canada,
check with Transport Canada for referral
to a Child Car Seat Clinic. Using Lower Anchors and Tethers
for CHildren (LATCH) WARNINGS
Do not attach two child safety
restraints to the same anchor. In a
crash, one anchor may not be strong
enough to hold two child safety restraint
attachments and may break, causing
serious injury or death. Depending on where you secure a
child restraint, and depending on the
child restraint design, you may block
access to certain seatbelt buckle
assemblies and LATCH lower anchors,
rendering those features potentially
unusable. To avoid risk of injury, make sure
occupants only use seating positions
where they are able to be properly
restrained. The LATCH system is composed of three
vehicle anchor points: two lower anchors
where the vehicle seatback and seat
cushion meet (called the seat bight) and
one top tether anchor behind that seating
position.
LATCH compatible child safety seats have
two rigid or webbing mounted
attachments that connect to the two lower
anchors at the LATCH equipped seating
positions in your vehicle. This type of
attachment method eliminates the need
to use seatbelts to attach the child
restraint. However, you can still use the
seatbelt to attach the child restraint if the
lower anchors are not used. For
forward-facing child restraints, you must
also attach the top tether strap to the
proper top tether anchor if a top tether
strap has been provided with your child
restraint.
Your vehicle has LATCH lower anchors for
child restraint installation at the following
seating positions (LATCH is not available
on Regular Cab):
25
Super Duty (TFE) Canada/United States of America, enUSA, First Printing Child SafetyE142534
Page 35 of 636

If the booster seat slides on the vehicle
seat upon which it is being used, placing a
rubberized mesh sold as shelf or carpet
liner under the booster seat may improve
this condition. Do not introduce any item
thicker than this under the booster seat.
Check with the booster seat
manufacturer's instructions.
CHILD RESTRAINT
POSITIONING
WARNINGS
Airbags can kill or injure a child in a
child seat. Never place a rear-facing
child seat in front of an active airbag.
If you must use a forward-facing child seat
in the front seat, move the vehicle seat
upon which the child seat is installed all
the way back. When possible, all children
age 12 and under should be properly
restrained in a rear seating position. If all
children cannot be seated and restrained
properly in a rear seating position, properly
restrain the largest child in the front seat. Always carefully follow the
instructions and warnings provided
by the manufacturer of any child
restraint to determine if the restraint device
is appropriate for your child's size, height,
weight, or age. Follow the child restraint
manufacturer's instructions and warnings WARNINGS
provided for installation and use in
conjunction with the instructions and
warnings provided by your vehicle
manufacturer. A safety seat that is
improperly installed or utilized, is
inappropriate for your child's height, age,
or weight or does not properly fit the child
may increase the risk of serious injury or
death. Never let a passenger hold a child on
his or her lap while your vehicle is
moving. The passenger cannot
protect the child from injury in a crash,
which may result in serious injury or death. Never use pillows, books, or towels
to boost a child. They can slide
around and increase the likelihood
of injury or death in a crash. Always restrain an unoccupied child
seat or booster seat. These objects
may become projectiles in a crash or
sudden stop, which may increase the risk
of serious injury. Never place, or allow a child to place,
the shoulder belt under a child's arm
or behind the back because it
reduces the protection for the upper part
of the body and may increase the risk of
injury or death in a crash.
32
Super Duty (TFE) Canada/United States of America, enUSA, First Printing Child SafetyE142597
Page 36 of 636
WARNINGS
To avoid risk of injury, do not leave WARNINGS
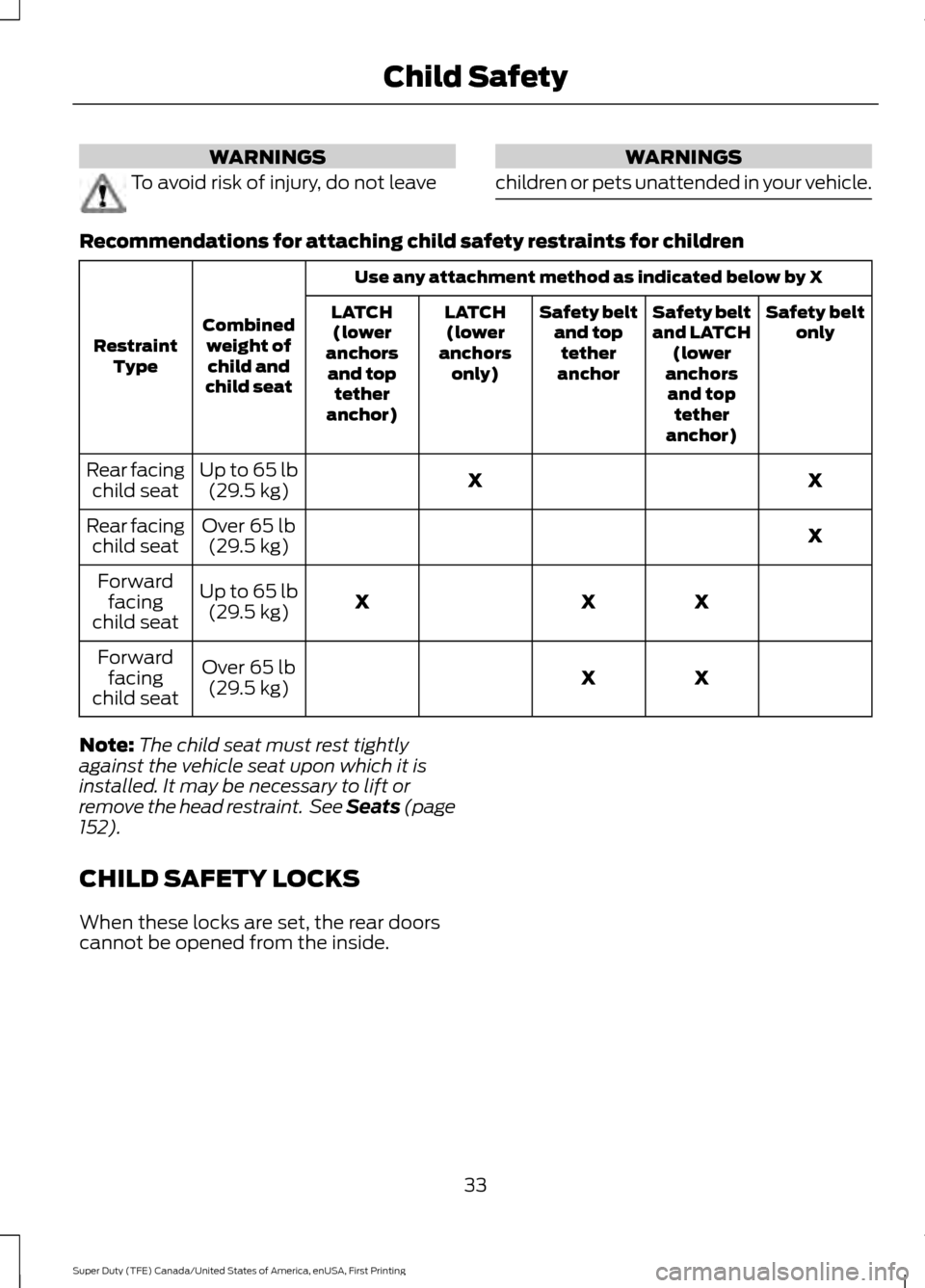
children or pets unattended in your vehicle. Recommendations for attaching child safety restraints for children
Use any attachment method as indicated below by X
Combined weight ofchild and
child seat
Restraint
Type Safety belt
only
Safety belt
and LATCH
(lower
anchors and top tether
anchor)
Safety belt
and toptether
anchor
LATCH
(lower
anchors only)
LATCH
(lower
anchors and top tether
anchor)
X
X
Up to 65 lb
(29.5 kg)
Rear facing
child seat
X
Over
65 lb
(29.5 kg)
Rear facing
child seat
X
X
X
Up to
65 lb
(29.5 kg)
Forward
facing
child seat
X
X
Over
65 lb
(29.5 kg)
Forward
facing
child seat
Note: The child seat must rest tightly
against the vehicle seat upon which it is
installed. It may be necessary to lift or
remove the head restraint. See Seats (page
152
).
CHILD SAFETY LOCKS
When these locks are set, the rear doors
cannot be opened from the inside.
33
Super Duty (TFE) Canada/United States of America, enUSA, First Printing Child Safety
Page 155 of 636

SITTING IN THE CORRECT
POSITION
WARNINGS
Sitting improperly, out of position or
with the seatback reclined too far
can take weight off the seat cushion
and affect the decision of the passenger
sensing system, resulting in serious injury
or death in the event of a crash. Always sit
upright against your seat back, with your
feet on the floor. Do not recline the seatback as this
can cause the occupant to slide
under the safety belt, resulting in
serious injury in the event of a crash. Do not place objects higher than the
seatback to reduce the risk of serious
injury in the event of a crash or during
heavy braking. When you use them properly, the seat,
head restraint, safety belt and airbags will
provide optimum protection in the event
of a crash. We recommend that you follow these
guidelines:
•
Sit in an upright position with the base
of your spine as far back as possible.
• Do not recline the seatback more than
30 degrees.
• Adjust the head restraint so that the
top of it is level with the top of your
head and as far forward as possible.
Make sure that you remain
comfortable.
• Keep sufficient distance between
yourself and the steering wheel. We
recommend a minimum of 10 in
(25 cm) between your breastbone and
the airbag cover.
• Hold the steering wheel with your arms
slightly bent.
• Bend your legs slightly so that you can
press the pedals fully.
• Position the shoulder strap of the
safety belt over the center of your
shoulder and position the lap strap
tightly across your hips.
Make sure that your driving position is
comfortable and that you can maintain full
control of your vehicle.
HEAD RESTRAINTS WARNINGS
Fully adjust the head restraint before
you sit in or operate your vehicle. This
will help minimize the risk of neck
injury in the event of a crash. Do not adjust
the head restraint when your vehicle is
moving. The head restraint is a safety device.
Whenever possible it should be
installed and properly adjusted when
the seat is occupied. An improperly
adjusted head restraint may not
adequately protect an occupant during an
impact from the rear.
152
Super Duty (TFE) Canada/United States of America, enUSA, First Printing SeatsE68595
Page 199 of 636

•
The usable capacity of the fuel tank is
the amount of fuel that you can add to
the fuel tank when the fuel gauge
indicates empty, before the first fuel
filler nozzle automatic shutoff event.
• The advertised capacity is equal to the
volumetric difference between actual
fuel fill before the first fuel filler nozzle
automatic shutoff event and the fuel
quantity when the fuel gauge indicates
empty. See Capacities and
Specifications (page 411). It is the
usable capacity minus the empty
reserve.
• Due to the empty reserve, you may be
able to add more fuel than the
advertised capacity of the fuel tank
when the fuel gauge indicates empty.
Filling the Fuel Tank
For consistent results when refueling:
• Turn the ignition off before fueling; an
inaccurate reading results if the engine
is left running.
• Use the same fill rate
(low-medium-high) each time the tank
is filled.
• Allow no more than one automatic
shut-off when refueling.
Results are most accurate when the filling
method is consistent.
Calculating Fuel Economy
Do not measure fuel economy during the
first
1,000 mi (1,600 km) of driving (this is
your engine ’s break-in period). A more
accurate measurement is obtained after
2,000 mi (3,200 km)
to 3,000 mi
(4,800 km). Also, fuel expense, frequency
of fill ups or fuel gauge readings are not
accurate ways to measure fuel economy.
1. Fill the fuel tank completely and record
the initial odometer reading. 2. Each time you fill the fuel tank, record
the amount of fuel added.
3. After at least three fill ups, fill the fuel tank and record the current odometer
reading.
4. Subtract your initial odometer reading from the current odometer reading.
To calculate L/100 km (liters per 100
kilometers) fuel consumption, multiply the
liters used by 100, then divide by kilometers
traveled. To calculate MPG (miles per
gallon) fuel consumption, divide miles
traveled by gallons used.
Keep a record for at least one month and
record the type of driving (city or highway).
This provides an accurate estimate of your
vehicle ’s fuel economy under current
driving conditions. Keeping records during
summer and winter will show how
temperature impacts fuel economy.
Conditions
• Heavily loading your vehicle reduces
fuel economy.
• Carrying unnecessary weight in your
vehicle may reduce fuel economy.
• Adding certain accessories to your
vehicle such as bug deflectors, rollbars
or light bars, running boards and ski
racks may reduce fuel economy.
• Using fuel blended with alcohol may
lower fuel economy.
• Fuel economy may decrease with lower
temperatures.
• Fuel economy may decrease when
driving short distances.
• You will get better fuel economy when
driving on flat terrain than when driving
on hilly terrain.
196
Super Duty (TFE) Canada/United States of America, enUSA, First Printing Fuel and Refueling