ABS GMC ACADIA 2010 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: GMC, Model Year: 2010, Model line: ACADIA, Model: GMC ACADIA 2010Pages: 444, PDF Size: 2.58 MB
Page 251 of 444
Driving and Operating 9-1
Driving and
Operating
Driving Information
Defensive Driving . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-2
Drunk Driving . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-2
Control of a Vehicle . . . . . . . . . . . 9-3
Braking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-3
Steering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-4
Off-Road Recovery . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-5
Loss of Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-5
Driving on Wet Roads . . . . . . . . . 9-6
Highway Hypnosis . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-7
Hill and Mountain Roads . . . . . . 9-7
Winter Driving . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-8
If the Vehicle is Stuck . . . . . . . . 9-10
Vehicle Load Limits . . . . . . . . . . 9-10
Starting and Operating
New Vehicle Break-In . . . . . . . . 9-15
Ignition Positions . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-16
Retained AccessoryPower (RAP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-17
Starting the Engine . . . . . . . . . . 9-17
Engine Heater . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-18 Shifting Into Park . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-19
Shifting Out of Park . . . . . . . . . . 9-20
Parking Over Things
That Burn . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-21
Engine Exhaust
Engine Exhaust . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-21
Running the Vehicle WhileParked . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-22
Automatic Transmission
Automatic Transmission . . . . . 9-22
Manual Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-24
Tow/Haul Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-25
Drive Systems
All-Wheel Drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-25
Brakes
Antilock BrakeSystem (ABS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-26
Parking Brake . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-27
Brake Assist . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-27
Ride Control Systems
StabiliTrak System . . . . . . . . . . . 9-28
Cruise Control
Cruise Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-30
Object Detection Systems
Ultrasonic Parking Assist . . . . 9-32
Rear Vision Camera (RVC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-34
Fuel
Fuel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-39
Recommended Fuel . . . . . . . . . 9-40
Gasoline Specifications . . . . . . 9-40
California FuelRequirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-40
Fuels in Foreign Countries . . . 9-40
Fuel Additives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-41
Filling the Tank . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-42
Filling a Portable Fuel Container . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-43
Towing
General TowingInformation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-44
Driving Characteristics and Towing Tips . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-44
Trailer Towing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-49
Towing Equipment . . . . . . . . . . . 9-53
Conversions and Add-Ons
Add-On Electrical Equipment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-55
Page 256 of 444
9-6 Driving and Operating
tires to slip and lose cornering force.
And in the acceleration skid, too
much throttle causes the driving
wheels to spin.
If the vehicle starts to slide, ease
your foot off the accelerator pedal
and quickly steer the way you want
the vehicle to go. If you start
steering quickly enough, the vehicle
may straighten out. Always be ready
for a second skid if it occurs.
Of course, traction is reduced when
water, snow, ice, gravel, or other
material is on the road. For safety,
slow down and adjust your driving to
these conditions. It is important to
slow down on slippery surfaces
because stopping distance is longer
and vehicle control more limited.
While driving on a surface with
reduced traction, try your best to
avoid sudden steering, acceleration,
or braking, including reducing
vehicle speed by shifting to a lowergear. Any sudden changes could
cause the tires to slide. You might
not realize the surface is slippery
until the vehicle is skidding. Learn to
recognize warning clues
—such as
enough water, ice, or packed snow
on the road to make a mirrored
surface —and slow down when you
have any doubt.
Remember: Any Antilock Brake
System (ABS) helps avoid only the
braking skid.
Driving on Wet Roads
Rain and wet roads can reduce
vehicle traction and affect your
ability to stop and accelerate.
Always drive slower in these types
of driving conditions and avoid
driving through large puddles and
deep-standing or flowing water.
{WARNING
Wet brakes can cause crashes.
They might not work as well in a
quick stop and could cause
pulling to one side. You could
lose control of the vehicle.
After driving through a large
puddle of water or a car/vehicle
wash, lightly apply the brake
pedal until the brakes work
normally.
Flowing or rushing water creates
strong forces. Driving through
flowing water could cause your
vehicle to be carried away. If this
happens, you and other vehicle
occupants could drown. Do not
ignore police warnings and be
very cautious about trying to drive
through flowing water.
Page 258 of 444
9-8 Driving and Operating
{WARNING
Coasting downhill in N (Neutral)
or with the ignition off is
dangerous. The brakes will have
to do all the work of slowing down
and they could get so hot that
they would not work well. You
would then have poor braking or
even none going down a hill. You
could crash. Always have the
engine running and the vehicle in
gear when going downhill.
.Stay in your own lane. Do not
swing wide or cut across the
center of the road. Drive at
speeds that let you stay in your
own lane.
.Top of hills: Be
alert—something could be in
your lane (stalled car, accident).
.Pay attention to special road
signs (falling rocks area, winding
roads, long grades, passing or
no-passing zones) and take
appropriate action.
Winter Driving
Driving on Snow or Ice
Drive carefully when there is snow
or ice between the tires and the
road, creating less traction or grip.
Wet ice can occur at about 0°C
(32°F) when freezing rain begins to
fall, resulting in even less traction.
Avoid driving on wet ice or in
freezing rain until roads can be
treated with salt or sand.
Drive with caution, whatever the
condition. Accelerate gently so
traction is not lost. Accelerating too
quickly causes the wheels to spin
and makes the surface under the
tires slick, so there is even less
traction.
Try not to break the fragile traction.
If you accelerate too fast, the drive
wheels will spin and polish the
surface under the tires even more. The
Antilock Brake System (ABS)
on page 9‑26improves vehicle
stability during hard stops on
slippery roads, but apply the brakes
sooner than when on dry pavement.
Allow greater following distance on
any slippery road and watch for
slippery spots. Icy patches can
occur on otherwise clear roads in
shaded areas. The surface of a
curve or an overpass can remain icy
when the surrounding roads are
clear. Avoid sudden steering
maneuvers and braking while
on ice.
Turn off cruise control, if equipped,
on slippery surfaces.
Page 276 of 444

9-26 Driving and Operating
Brakes
Antilock Brake
System (ABS)
This vehicle has the Antilock Brake
System (ABS), an advanced
electronic braking system that helps
prevent a braking skid.
When the engine is started and the
vehicle begins to drive away, ABS
checks itself. A momentary motor or
clicking noise might be heard while
this test is going on, and it might
even be noticed that the brake
pedal moves a little. This is normal.
If there is a problem with ABS, this
warning light stays on. SeeAntilock
Brake System (ABS) Warning Light
on page 5‑19. If driving safely on a wet road and it
becomes necessary to slam on the
brakes and continue braking to
avoid a sudden obstacle, a
computer senses that the wheels
are slowing down. If one of the
wheels is about to stop rolling, the
computer will separately work the
brakes at each wheel.
ABS can change the brake pressure
to each wheel, as required, faster
than any driver could. This can help
the driver steer around the obstacle
while braking hard.
As the brakes are applied, the
computer keeps receiving updates
on wheel speed and controls
braking pressure accordingly.
Remember: ABS does not change
the time needed to get a foot up to
the brake pedal or always decrease
stopping distance. If you get too
close to the vehicle in front of you,
there will not be enough time to
apply the brakes if that vehicle
suddenly slows or stops. Always
leave enough room up ahead to
stop, even with ABS.
Using ABS
Do not pump the brakes. Just hold
the brake pedal down firmly and let
ABS work. The ABS pump or motor
might be heard operating, and the
brake pedal might be felt to pulsate,
but this is normal.
Braking in Emergencies
ABS allows the driver to steer and
brake at the same time. In many
emergencies, steering can help
more than even the very best
braking.
Page 277 of 444
Driving and Operating 9-27
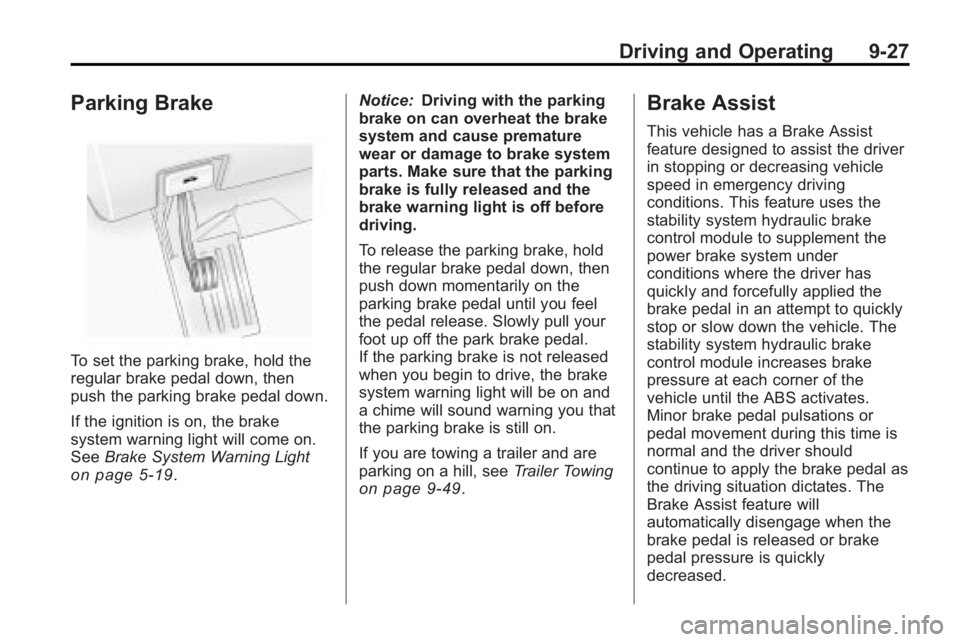
Parking Brake
To set the parking brake, hold the
regular brake pedal down, then
push the parking brake pedal down.
If the ignition is on, the brake
system warning light will come on.
SeeBrake System Warning Light
on page 5‑19. Notice:
Driving with the parking
brake on can overheat the brake
system and cause premature
wear or damage to brake system
parts. Make sure that the parking
brake is fully released and the
brake warning light is off before
driving.
To release the parking brake, hold
the regular brake pedal down, then
push down momentarily on the
parking brake pedal until you feel
the pedal release. Slowly pull your
foot up off the park brake pedal.
If the parking brake is not released
when you begin to drive, the brake
system warning light will be on and
a chime will sound warning you that
the parking brake is still on.
If you are towing a trailer and are
parking on a hill, see Trailer Towingon page 9‑49.
Brake Assist
This vehicle has a Brake Assist
feature designed to assist the driver
in stopping or decreasing vehicle
speed in emergency driving
conditions. This feature uses the
stability system hydraulic brake
control module to supplement the
power brake system under
conditions where the driver has
quickly and forcefully applied the
brake pedal in an attempt to quickly
stop or slow down the vehicle. The
stability system hydraulic brake
control module increases brake
pressure at each corner of the
vehicle until the ABS activates.
Minor brake pedal pulsations or
pedal movement during this time is
normal and the driver should
continue to apply the brake pedal as
the driving situation dictates. The
Brake Assist feature will
automatically disengage when the
brake pedal is released or brake
pedal pressure is quickly
decreased.
Page 279 of 444
Driving and Operating 9-29
Traction control can be turned on by
pressing and releasing the traction
control disable button if not
automatically shut off for any other
reason.
When the traction control system is
turned off, the StabiliTrak light and
the appropriate traction control off
message will be displayed on the
DIC to warn the driver. The vehicle
will still have brake-traction control
when traction control is off, but will
not be able to use the engine speed
management system. See“Traction
Control Operation” next for more
information.
When the traction control system
has been turned off, system noises
may be heard and felt as a result of
the brake-traction control working.
It is recommended to leave the
system on for normal driving
conditions, but it may be necessary
to turn the system off if the vehicle
is stuck in sand, mud, ice or snow, and you want to
“rock”the vehicle to
attempt to free it. It may also be
necessary to turn off the system
when driving in extreme off-road
conditions where high wheel spin is
required. See If the Vehicle is Stuck
on page 9‑10.
Traction Control Operation
The traction control system is part of
the StabiliTrak system. Traction
control limits wheel spin by reducing
engine power to the wheels (engine
speed management) and by
applying brakes to each individual
wheel (brake-traction control) as
necessary.
The traction control system is
enabled automatically when the
vehicle is started. It will activate and
the StabiliTrak light will flash if it
senses that any of the wheels are
spinning or beginning to lose
traction while driving. If traction
control is turned off, only the
brake-traction control portion of
traction control will work. The
engine speed management will be disabled. In this mode, engine
power is not reduced automatically
and the driven wheels can spin
more freely. This can cause the
brake-traction control to activate
constantly.
Notice:
If the wheel(s) of one axle
is allowed to spin excessively
while the StabiliTrak, ABS and
brake warning lights and any
relevant DIC messages are
displayed, the transfer case could
be damaged. The repairs would
not be covered by the vehicle
warranty. Reduce engine power
and do not spin the wheel(s)
excessively while these lights and
messages are displayed.
The traction control system may
activate on dry or rough roads or
under conditions such as heavy
acceleration while turning or abrupt
upshifts/downshifts of the
transmission. When this happens, a
reduction in acceleration may be
noticed, or a noise or vibration may
be heard. This is normal.
Page 298 of 444
9-48 Driving and Operating
The vehicle can tow in D (Drive).
Use a lower gear if the transmission
shifts too often.
When towing at high altitude on
steep uphill grades, engine coolant
will boil at a lower temperature than
at normal altitudes. If the engine is
turned off immediately after towing
at high altitude on steep uphill
grades, the vehicle may show
signs similar to engine overheating.
To avoid this, let the engine run
while parked, preferably on level
ground, with the transmission in
P (Park) for a few minutes before
turning the engine off. If the
overheat warning comes on, see
Engine Overheating on page 10‑19.
On a long uphill grade, shift down
and reduce the vehicle speed to
around 88 km/h (55 mph) to reduce
the possibility of the engine and the
transmission overheating.Parking on Hills
{WARNING
Parking the vehicle on a hill with
the trailer attached can be
dangerous. If something goes
wrong, the rig could start to move.
People can be injured, and both
the vehicle and the trailer can be
damaged. When possible, always
park the rig on a flat surface.
If parking the rig on a hill:
1. Press the brake pedal, but do not shift into P (Park) yet. Turn
the wheels into the curb if facing
downhill or into traffic if facing
uphill.
2. Have someone place chocks under the trailer wheels. 3. When the wheel chocks are in
place, release the brake pedal
until the chocks absorb the load.
4. Reapply the brake pedal. Then apply the parking brake and shift
into P (Park).
5. Release the brake pedal.
Leaving After Parking on a Hill
1. Apply and hold the brake pedal while you:
.Start the engine.
.Shift into a gear.
.Release the parking brake.
2. Let up on the brake pedal.
3. Drive slowly until the trailer is clear of the chocks.
4. Stop and have someone pick up and store the chocks.
Page 338 of 444
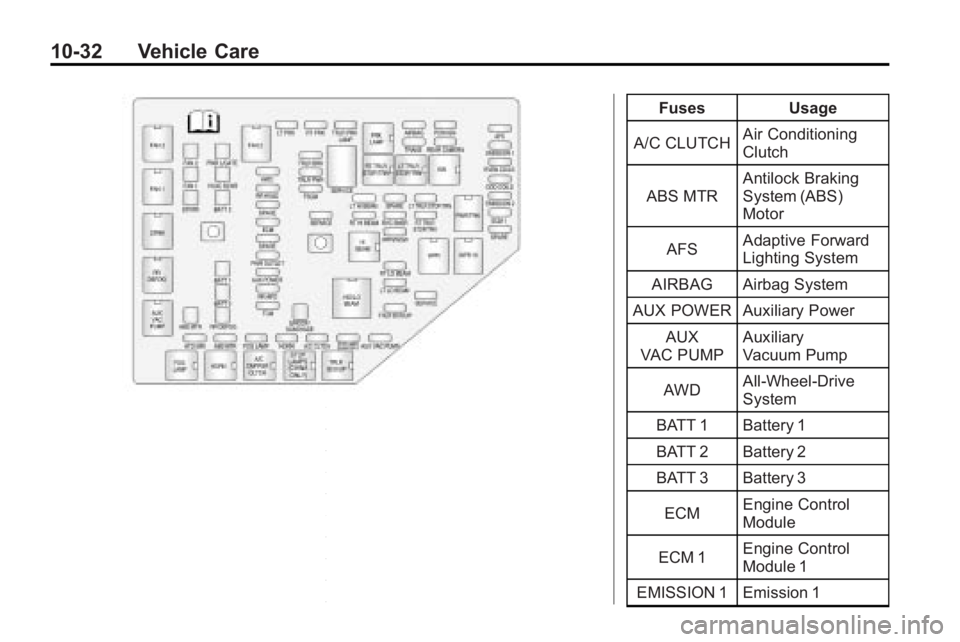
10-32 Vehicle Care
FusesUsage
A/C CLUTCH Air Conditioning
Clutch
ABS MTR Antilock Braking
System (ABS)
Motor
AFS Adaptive Forward
Lighting System
AIRBAG Airbag System
AUX POWER Auxiliary Power
AUX
VAC PUMP Auxiliary
Vacuum Pump
AWD All-Wheel-Drive
System
BATT 1 Battery 1
BATT 2 Battery 2
BATT 3 Battery 3
ECM Engine Control
Module
ECM 1 Engine Control
Module 1
EMISSION 1 Emission 1
Page 371 of 444
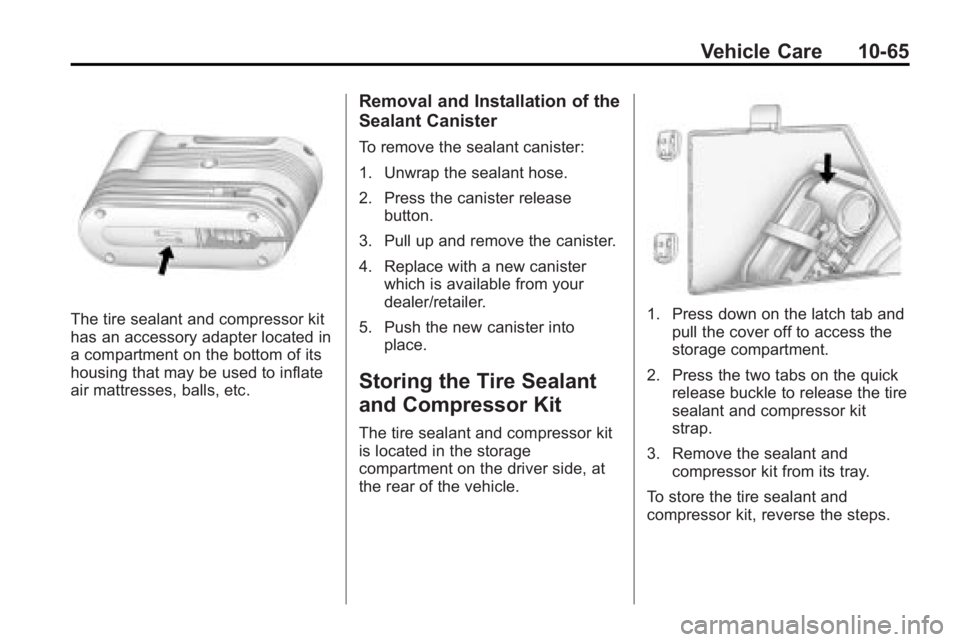
Vehicle Care 10-65
The tire sealant and compressor kit
has an accessory adapter located in
a compartment on the bottom of its
housing that may be used to inflate
air mattresses, balls, etc.
Removal and Installation of the
Sealant Canister
To remove the sealant canister:
1. Unwrap the sealant hose.
2. Press the canister releasebutton.
3. Pull up and remove the canister.
4. Replace with a new canister which is available from your
dealer/retailer.
5. Push the new canister into place.
Storing the Tire Sealant
and Compressor Kit
The tire sealant and compressor kit
is located in the storage
compartment on the driver side, at
the rear of the vehicle.
1. Press down on the latch tab andpull the cover off to access the
storage compartment.
2. Press the two tabs on the quick release buckle to release the tire
sealant and compressor kit
strap.
3. Remove the sealant and compressor kit from its tray.
To store the tire sealant and
compressor kit, reverse the steps.
Page 396 of 444

10-90 Vehicle Care
only be used on floor carpet and
carpeted floor mats. For soils,
always try to remove them first with
plain water or club soda. Before
cleaning, gently remove as much of
the soil as possible using one of the
following techniques:
.For liquids: gently blot the
remaining soil with a paper
towel. Allow the soil to absorb
into the paper towel until no
more can be removed.
.For solid dry soils: remove as
much as possible and then
vacuum.
To clean:
1. Saturate a lint-free, clean white cloth with water or club soda.
2. Remove excess moisture. 3. Start on the outside edge of the
soil and gently rub toward the
center. Continue cleaning, using
a clean area of the cloth each
time it becomes soiled.
4. Continue to gently rub the soiled area.
5. If the soil is not completely removed, use a mild soap
solution and repeat the cleaning
process with plain water.
If any of the soil remains, a
commercial fabric cleaner or spot
lifter may be necessary. Test a small
hidden area for colorfastness before
using a commercial upholstery
cleaner or spot lifter. If the locally
cleaned area gives any impression
that a ring formation may result,
clean the entire surface.
A paper towel can be used to blot
excess moisture from the fabric or
carpet after the cleaning process.
Leather
To remove dust, a soft cloth
dampened with water can be used.
If a more thorough cleaning is
necessary, a soft cloth dampened
with a mild soap solution can be
used. Allow the leather to dry
naturally. Do not use heat, steam,
or spot lifters or spot removers,
or shoe polish on leather. Many
commercial leather cleaners and
coatings that are sold to preserve
and protect leather may
permanently change the
appearance and feel of the leather
and are not recommended. Do not
use silicone or wax-based products,
or those containing organic solvents
to clean the vehicle's interior
because they can alter the
appearance by increasing the gloss
in a non-uniform manner.