trailer GMC SAVANA 2009 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: GMC, Model Year: 2009, Model line: SAVANA, Model: GMC SAVANA 2009Pages: 404, PDF Size: 2.35 MB
Page 205 of 404

Your Driving, the Road, and the Vehicle............4-2
Defensive Driving...........................................4-2
Drunk Driving.................................................4-2
Control of a Vehicle........................................4-3
Braking.........................................................4-4
Antilock Brake System (ABS)...........................4-5
Braking in Emergencies...................................4-5
StabiliTrak
®System........................................4-6
Locking Rear Axle..........................................4-8
All-Wheel Drive (AWD) System.........................4-8
Steering........................................................4-8
Off-Road Recovery.......................................4-10
Passing.......................................................4-10
Loss of Control.............................................4-10Driving at Night............................................4-12
Driving in Rain and on Wet Roads..................4-12
Before Leaving on a Long Trip.......................4-13
Highway Hypnosis........................................4-14
Hill and Mountain Roads................................4-14
Winter Driving..............................................4-15
If Your Vehicle is Stuck in Sand, Mud,
Ice, or Snow.............................................4-17
Rocking Your Vehicle to Get It Out.................4-18
Loading the Vehicle......................................4-18
Towing..........................................................4-24
Towing Your Vehicle.....................................4-24
Recreational Vehicle Towing...........................4-24
Towing a Trailer...........................................4-26
Section 4 Driving Your Vehicle
4-1
Page 224 of 404

Steps for Determining Correct Load Limit
1.Locate the statement “The combined weight of
occupants and cargo should never exceed
XXX kg or XXX lbs” on your vehicle’s placard.
2.Determine the combined weight of the driver
and passengers that will be riding in your
vehicle.
3.Subtract the combined weight of the driver
and passengers from XXX kg or XXX lbs.
4.The resulting figure equals the available
amount of cargo and luggage load capacity.
For example, if the “XXX” amount equals
1400 lbs and there will be five 150 lb
passengers in your vehicle, the amount of
available cargo and luggage load capacity is
650 lbs (1400−750 (5 x 150) = 650 lbs).
5.Determine the combined weight of luggage
and cargo being loaded on the vehicle. That
weight may not safely exceed the available
cargo and luggage load capacity calculated in
Step 4.
6.If your vehicle will be towing a trailer, the load
from your trailer will be transferred to your
vehicle. Consult this manual to determine how
this reduces the available cargo and luggage
load capacity of your vehicle. SeeTowing a
Trailer on page 4-26for important information
on towing a trailer, towing safety rules and
trailering tips.
4-20
Page 228 of 404

Towing
Towing Your Vehicle
To avoid damage, the disabled vehicle should be towed
with all four wheels off the ground. Consult your
dealer/retailer or a professional towing service if the
disabled vehicle must be towed. SeeRoadside
Assistance Program on page 7-7.
To tow the vehicle behind another vehicle for
recreational purposes (such as behind a motorhome),
see “Recreational Vehicle Towing” following.
Recreational Vehicle Towing
Recreational vehicle towing means towing the vehicle
behind another vehicle – such as behind a motorhome.
The two most common types of recreational vehicle
towing are known as “dinghy towing” — towing the
vehicle with all four wheels on the ground) and “dolly
towing” — towing the vehicle with two wheels on the
ground and two wheels up on a device known as a
“dolly”.Here are some important things to consider before
recreational vehicle towing:
•What is the towing capacity of the towing vehicle?
Be sure to read the tow vehicle manufacturer’s
recommendations.
•What is the distance that will be travelled? Some
vehicles have restrictions on how far and how
long they can tow.
•Is the proper towing equipment going to be used?
See your dealer/retailer or trailering professional
for additional advice and equipment
recommendations.
•Is the vehicle ready to be towed? Just as preparing
the vehicle for a long trip, make sure the vehicle is
prepared to be towed. SeeBefore Leaving on a
Long Trip on page 4-13.
4-24
Page 229 of 404

Dinghy Towing
Two-Wheel-Drive Vehicles
Notice:If the vehicle is towed with all four wheels
on the ground, the drivetrain components could
be damaged. The repairs would not be covered by
the vehicle warranty. Do not tow the vehicle with
all four wheels on the ground.
Two-wheel-drive vehicles should not be towed with
all four wheels on the ground. Two-wheel-drive
transmissions have no provisions for internal
lubrication while being towed.
All-Wheel-Drive Vehicles
The vehicle was not designed to be towed with all four
wheels on the ground. To properly tow these vehicles,
they should be placed on a platform trailer with all
four wheels off the ground.
Notice:Towing an all-wheel-drive vehicle with all
four wheels on the ground, or even with only two of
its wheels on the ground, will damage drivetrain
components. Do not tow an all-wheel-drive vehicle
with any of its wheels on the ground.
Dolly Towing
Rear Towing (Rear Wheels Off the Ground)
Two-Wheel-Drive Vehicles
Use the following procedure to tow the vehicle from
the rear:
1. Attach the dolly to the tow vehicle following the
dolly manufacturer’s instructions.
2. Drive the rear wheels onto the dolly.
3. Firmly set the parking brake. SeeParking Brake on
page 2-26for more information.
4. Put the transmission in P (Park).
5. Secure the vehicle to the dolly following the
manufacturer’s instructions.
6. Use an adequate clamping device designed for
towing to ensure that the front wheels are locked
into the straight position.
7. Turn the ignition to LOCK/OFF.
If the tow vehicle will not be started or driven for
six weeks or more, remove the battery cable
from the negative terminal (post) of the battery to
prevent the battery from draining while towing.
4-25
Page 230 of 404

All-Wheel-Drive Vehicles
The vehicle was not designed to be towed with two
wheels on the ground. To properly tow these vehicles,
they should be placed on a platform trailer with all
four wheels off the ground.
Notice:Towing an all-wheel-drive vehicle with all
four wheels on the ground, or even with only two of
its wheels on the ground, will damage drivetrain
components. Do not tow an all-wheel-drive vehicle
with any of its wheels on the ground.
Towing a Trailer
If the vehicle has a diesel engine, see the DURAMAX®
Diesel manual for more information.
{CAUTION:
The driver can lose control when pulling a trailer if
the correct equipment is not used or the vehicle is
not driven properly. For example, if the trailer is
too heavy, the brakes may not work well — or
even at all. The driver and passengers could be
CAUTION: (Continued)
CAUTION: (Continued)
seriously injured. The vehicle may also be
damaged; the resulting repairs would not be
covered by the vehicle warranty. Pull a trailer only
if all the steps in this section have been followed.
Ask your dealer/retailer for advice and information
about towing a trailer with the vehicle.
Notice:Pulling a trailer improperly can damage the
vehicle and result in costly repairs not covered
by the vehicle warranty. To pull a trailer correctly,
follow the advice in this section and see your
dealer/retailer for important information about
towing a trailer with the vehicle.
To identify the trailering capacity of the vehicle, read the
information in “Weight of the Trailer” that appears
later in this section.
Trailering is different than just driving the vehicle by itself.
Trailering means changes in handling, acceleration,
braking, durability and fuel economy. Successful, safe
trailering takes correct equipment, and it has to be used
properly.
4-26
Page 231 of 404

The following information has many time-tested,
important trailering tips and safety rules. Many of these
are important for your safety and that of your passengers.
So please read this section carefully before pulling a
trailer.
Pulling A Trailer
Here are some important points:
•There are many different laws, including speed limit
restrictions, having to do with trailering. Make sure
the rig will be legal, not only where you live but
also where you will be driving. A good source for
this information can be state or provincial police.
•Consider using a sway control. See “Hitches” later
in this section.
•Do not tow a trailer at all during the first 500 miles
(800 km) the new vehicle is driven. The engine,
axle or other parts could be damaged.
•Then, during the first 500 miles (800 km) that a
trailer is towed, do not drive over 50 mph (80 km/h)
and do not make starts at full throttle. This helps
the engine and other parts of the vehicle wear in at
the heavier loads.
•Vehicles with an automatic transmissions can tow
in D (Drive). Shift the transmission to a lower gear
if the transmission shifts too often under heavy
loads and/or hilly conditions.Three important considerations have to do with weight:
•The weight of the trailer
•The weight of the trailer tongue
•The weight on the vehicle’s tires
Also see Tow/Haul later in this section for information
about the Tow/Haul button and the Tow/Haul indicator
light.
Weight of the Trailer
How heavy can a trailer safely be?
It depends on how the rig is used. For example, speed,
altitude, road grades, outside temperature and how
much the vehicle is used to pull a trailer are all
important. It can depend on any special equipment on
the vehicle, and the amount of tongue weight the vehicle
can carry. See “Weight of the Trailer Tongue” later in
this section for more information.
Maximum trailer weight is calculated assuming only the
driver is in the tow vehicle and it has all the required
trailering equipment. The weight of additional optional
equipment, passengers and cargo in the tow vehicle
must be subtracted from the maximum trailer weight.
4-27
Page 232 of 404
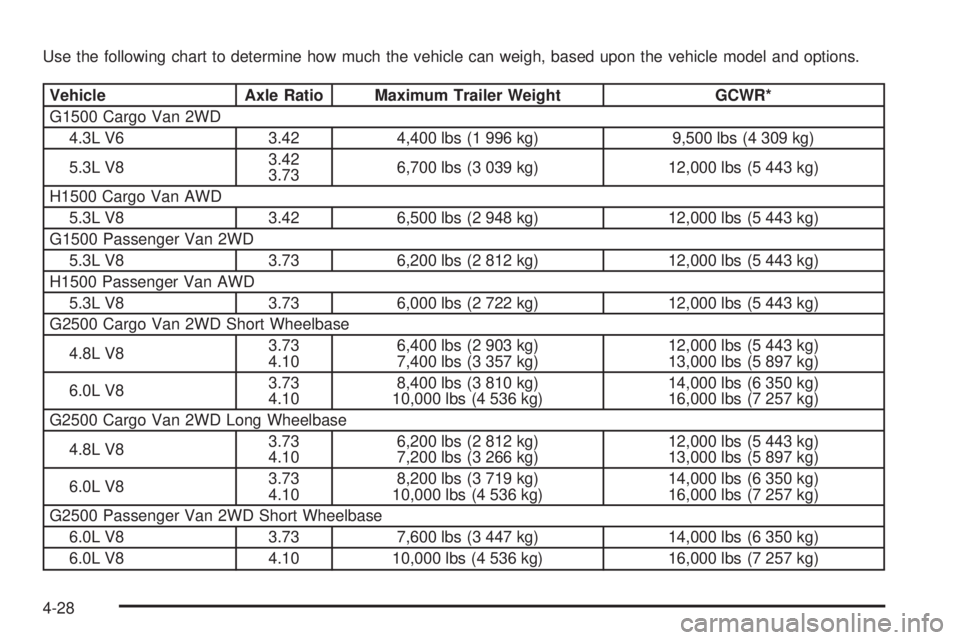
Use the following chart to determine how much the vehicle can weigh, based upon the vehicle model and options.
Vehicle Axle Ratio Maximum Trailer Weight GCWR*
G1500 Cargo Van 2WD
4.3L V6 3.42 4,400 lbs (1 996 kg) 9,500 lbs (4 309 kg)
5.3L V83.42
3.736,700 lbs (3 039 kg) 12,000 lbs (5 443 kg)
H1500 Cargo Van AWD
5.3L V8 3.42 6,500 lbs (2 948 kg) 12,000 lbs (5 443 kg)
G1500 Passenger Van 2WD
5.3L V8 3.73 6,200 lbs (2 812 kg) 12,000 lbs (5 443 kg)
H1500 Passenger Van AWD
5.3L V8 3.73 6,000 lbs (2 722 kg) 12,000 lbs (5 443 kg)
G2500 Cargo Van 2WD Short Wheelbase
4.8L V83.73
4.106,400 lbs (2 903 kg)
7,400 lbs (3 357 kg)12,000 lbs (5 443 kg)
13,000 lbs (5 897 kg)
6.0L V83.73
4.108,400 lbs (3 810 kg)
10,000 lbs (4 536 kg)14,000 lbs (6 350 kg)
16,000 lbs (7 257 kg)
G2500 Cargo Van 2WD Long Wheelbase
4.8L V83.73
4.106,200 lbs (2 812 kg)
7,200 lbs (3 266 kg)12,000 lbs (5 443 kg)
13,000 lbs (5 897 kg)
6.0L V83.73
4.108,200 lbs (3 719 kg)
10,000 lbs (4 536 kg)14,000 lbs (6 350 kg)
16,000 lbs (7 257 kg)
G2500 Passenger Van 2WD Short Wheelbase
6.0L V8 3.73 7,600 lbs (3 447 kg) 14,000 lbs (6 350 kg)
6.0L V8 4.10 10,000 lbs (4 536 kg) 16,000 lbs (7 257 kg)
4-28
Page 233 of 404
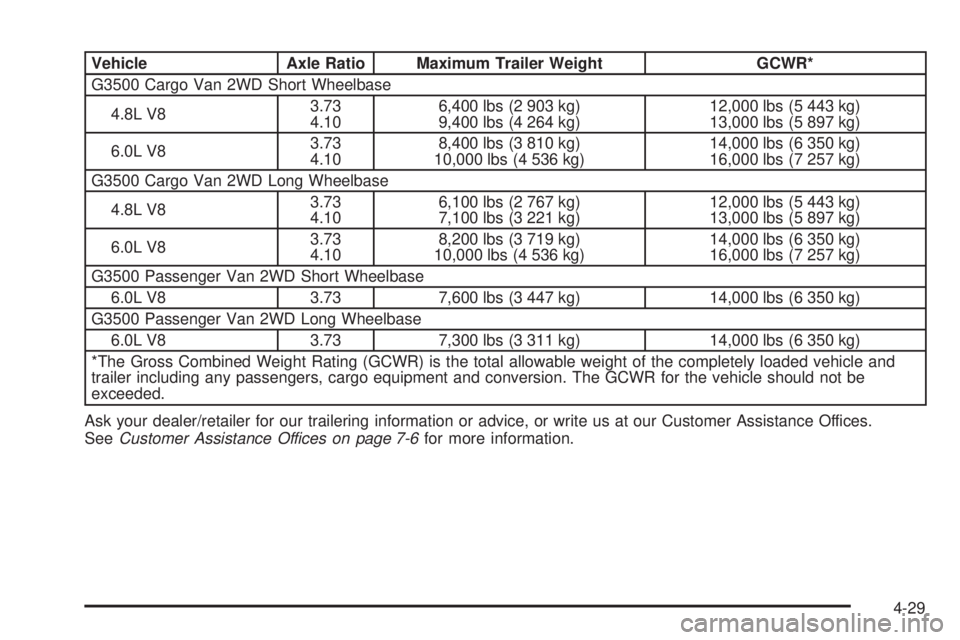
Vehicle Axle Ratio Maximum Trailer Weight GCWR*
G3500 Cargo Van 2WD Short Wheelbase
4.8L V83.73
4.106,400 lbs (2 903 kg)
9,400 lbs (4 264 kg)12,000 lbs (5 443 kg)
13,000 lbs (5 897 kg)
6.0L V83.73
4.108,400 lbs (3 810 kg)
10,000 lbs (4 536 kg)14,000 lbs (6 350 kg)
16,000 lbs (7 257 kg)
G3500 Cargo Van 2WD Long Wheelbase
4.8L V83.73
4.106,100 lbs (2 767 kg)
7,100 lbs (3 221 kg)12,000 lbs (5 443 kg)
13,000 lbs (5 897 kg)
6.0L V83.73
4.108,200 lbs (3 719 kg)
10,000 lbs (4 536 kg)14,000 lbs (6 350 kg)
16,000 lbs (7 257 kg)
G3500 Passenger Van 2WD Short Wheelbase
6.0L V8 3.73 7,600 lbs (3 447 kg) 14,000 lbs (6 350 kg)
G3500 Passenger Van 2WD Long Wheelbase
6.0L V8 3.73 7,300 lbs (3 311 kg) 14,000 lbs (6 350 kg)
*The Gross Combined Weight Rating (GCWR) is the total allowable weight of the completely loaded vehicle and
trailer including any passengers, cargo equipment and conversion. The GCWR for the vehicle should not be
exceeded.
Ask your dealer/retailer for our trailering information or advice, or write us at our Customer Assistance Offices.
SeeCustomer Assistance Offices on page 7-6for more information.
4-29
Page 234 of 404

Weight of the Trailer Tongue
The tongue load (A) of any trailer is an important weight
to measure because it affects the total gross weight of the
vehicle. The Gross Vehicle Weight (GVW) includes the
curb weight of the vehicle, any cargo carried in it, and the
people who will be riding in the vehicle. If there are a lot of
options, equipment, passengers or cargo in the vehicle, it
will reduce the tongue weight the vehicle can carry, which
will also reduce the trailer weight the vehicle can tow.
If towing a trailer, the tongue load must be added to the
GVW because the vehicle will be carrying that weight,
too. SeeLoading the Vehicle on page 4-18for more
information about the vehicle’s maximum load capacity.
The trailer tongue weight (A) should be 10 percent to
15 percent of the total loaded trailer weight (B), up to a
maximum of 400 lbs (181 kg) with a weight carrying hitch.The trailer tongue weight (A) should be 10 percent to
15 percent of the total loaded trailer weight (B), up to a
maximum of 1,000 lbs (454 kg) with a weight distributing
hitch.
Do not exceed the maximum allowable tongue weight for
the vehicle. Choose the shortest hitch extension that will
position the hitch ball closest to the vehicle. This will help
reduce the effect of trailer tongue weight on the rear axle.
After loading the trailer, weigh the trailer and then the
tongue, separately, to see if the weights are proper.
If they are not, adjustments might be made by moving
some items around in the trailer.
Trailering may be limited by the vehicle’s ability to carry
tongue weight. Tongue weight cannot cause the vehicle
to exceed the GVWR (Gross Vehicle Weight Rating) or
the RGAWR (Rear Gross Axle Weight Rating). The effect
of additional weight may reduce the trailering capacity
more than the total of the additional weight.
4-30
Page 235 of 404

Consider the following example:
A vehicle model base weight is 5,500 lbs (2 495 kg);
2,800 lbs (1 270 kg) at the front axle and 2,700 lbs
(1 225 kg) at the rear axle. It has a GVWR of 7,200 lbs
(3 266 kg), a RGAWR of 4,000 lbs (1 814 kg) and a
GCWR (Gross Combination Weight Rating) of
14,000 lbs (6 350 kg). The trailer rating should be:
Expect tongue weight to be at least 10 percent of trailer
weight (850 lbs (386 kg)) and because the weight is
applied well behind the rear axle, the effect on the rear
axle is greater than just the weight itself, as much as
1.5 times as much. The weight at the rear axle could be
850 lbs (386 kg) X 1.5 = 1,275 lbs (578 kg). Since the
rear axle already weighs 2,700 lbs (1 225 kg), adding
1,275 lbs (578 kg) brings the total to 3,975 lbs (1 803 kg).
This is very close to, but within the limit for RGAWR as
well. The vehicle is set to trailer up to 8,500 lbs
(3 856 kg).If the vehicle has many options and there is a front seat
passenger and two rear seat passengers with some
luggage and gear in the vehicle as well. 300 lbs (136 kg)
could be added to the front axle weight and 400 lbs
(181 kg) to the rear axle weight. The vehicle now weighs:
Weight is still below 7,200 lbs (3 266 kg) and you
might think 700 additional pounds (318 kg) should be
subtracted from the trailering capacity to stay within
GCWR limits. The maximum trailer would only be
7,800 lbs (3 538 kg). You may go further and think the
tongue weight should be limited to less than 1,000 lbs
(454 kg) to avoid exceeding GVWR. But the effect on the
rear axle must still be considered. Because the rear axle
now weighs 3,100 lbs (1 406 kg), 900 lbs (408 kg) can be
put on the rear axle without exceeding RGAWR. The
effect of tongue weight is about 1.5 times the actual
weight. Dividing the 900 lbs (408 kg) by 1.5 leaves only
600 lbs (272 kg) of tongue weight that can be handled.
Since tongue weight is usually at least 10 percent of total
loaded trailer weight, expect that the largest trailer the
vehicle can properly handle is 6,000 lbs (2 721 kg).
4-31