traction 4 GMC SIERRA 2010 Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: GMC, Model Year: 2010, Model line: SIERRA, Model: GMC SIERRA 2010Pages: 630, PDF Size: 4.65 MB
Page 383 of 630

Scanning the Terrain
Off-road driving can take you over many different kinds
of terrain. Be familiar with the terrain and its many
different features.
Surface Conditions :Off-roading surfaces can be
hard-packed dirt, gravel, rocks, grass, sand, mud, snow,
or ice. Each of these surfaces affects the vehicle's
steering, acceleration, and braking in different ways.
Depending on the surface, slipping, sliding, wheel
spinning, delayed acceleration, poor traction, and longer
braking distances can occur.
Surface Obstacles : Unseen or hidden obstacles can
be hazardous. A rock, log, hole, rut, or bump can startle
you if you are not prepared for them. Often these
obstacles are hidden by grass, bushes, snow, or even
the rise and fall of the terrain itself.
Some things to consider:
.Is the path ahead clear?
.Will the surface texture change abruptly up ahead?
.Does the travel take you uphill or downhill?
.Will you have to stop suddenly or change direction
quickly?
When driving over obstacles or rough terrain, keep a
firm grip on the steering wheel. Ruts, troughs, or other
surface features can jerk the wheel out of your hands. When driving over bumps, rocks, or other obstacles, the
wheels can leave the ground. If this happens, even with
one or two wheels, you cannot control the vehicle as
well or at all.
Because you will be on an unpaved surface, it is
especially important to avoid sudden acceleration,
sudden turns, or sudden braking.
Off-roading requires a different kind of alertness from
driving on paved roads and highways. There are no
road signs, posted speed limits, or signal lights. Use
good judgment about what is safe and what is not.
Driving on Hills
Off-road driving often takes you up, down, or across a
hill. Driving safely on hills requires good judgment and
an understanding of what the vehicle can and cannot
do. There are some hills that simply cannot be driven,
no matter how well built the vehicle.
{WARNING:
Many hills are simply too steep for any vehicle.
If you drive up them, you will stall. If you drive
down them, you cannot control your speed. If you
drive across them, you will roll over. You could be
seriously injured or killed. If you have any doubt
about the steepness, do not drive the hill.
5-15
Page 384 of 630

Approaching a Hill
When you approach a hill, decide if it is too steep to
climb, descend, or cross. Steepness can be hard to
judge. On a very small hill, for example, there may be a
smooth, constant incline with only a small change in
elevation where you can easily see all the way to the
top. On a large hill, the incline may get steeper as you
near the top, but you might not see this because the
crest of the hill is hidden by bushes, grass, or shrubs.
Consider this as you approach a hill:
.Is there a constant incline, or does the hill get
sharply steeper in places?
.Is there good traction on the hillside, or will the
surface cause tire slipping?
.Is there a straight path up or down the hill so you
will not have to make turning maneuvers?
.Are there obstructions on the hill that can block
your path, such as boulders, trees, logs, or ruts?
.What is beyond the hill? Is there a cliff, an
embankment, a drop-off, a fence? Get out and
walk the hill if you do not know. It is the smart way
to find out.
.Is the hill simply too rough? Steep hills often have
ruts, gullies, troughs, and exposed rocks because
they are more susceptible to the effects of erosion.
Driving Uphill
Once you decide it is safe to drive up the hill:
.Use a low gear and get a firm grip on the
steering wheel.
.Get a smooth start up the hill and try to maintain
speed. Not using more power than needed can
avoid spinning the wheels or sliding.
{WARNING:
Turning or driving across steep hills can be
dangerous. You could lose traction, slide
sideways, and possibly roll over. You could be
seriously injured or killed. When driving up hills,
always try to go straight up.
.Try to drive straight up the hill if at all possible.
If the path twists and turns, you might want to find
another route.
.Ease up on the speed as you approach the top
of the hill.
.Attach a flag to the vehicle to be more visible to
approaching traffic on trails or hills.
5-16
Page 389 of 630

Stalling on an Incline
{WARNING:
Getting out on the downhill (low) side of a vehicle
stopped across an incline is dangerous. If the
vehicle rolls over, you could be crushed or killed.
Always get out on the uphill (high) side of the
vehicle and stay well clear of the rollover path.
If the vehicle stalls when crossing an incline, be sure
you, and any passengers, get out on the uphill side,
even if the door there is harder to open. If you get out
on the downhill side and the vehicle starts to roll over,
you will be right in its path.
If you have to walk down the slope, stay out of the path
the vehicle will take if it does roll over.
Driving in Mud, Sand, Snow, or Ice
When you drive in mud, snow, or sand, the wheels do
not get good traction. Acceleration is not as quick,
turning is more difficult, and braking distances
are longer. It is best to use a low gear when in mud
—the deeper
the mud, the lower the gear. In really deep mud, keep
the vehicle moving so it does not get stuck.
When driving on sand, wheel traction changes. On
loosely packed sand, such as on beaches or sand
dunes, the tires will tend to sink into the sand. This
affects steering, accelerating, and braking. Drive at a
reduced speed and avoid sharp turns or abrupt
maneuvers.
Hard packed snow and ice offer the worst tire traction.
On these surfaces, it is very easy to lose control. On
wet ice, for example, the traction is so poor that you will
have difficulty accelerating. And, if the vehicle does get
moving, poor steering and difficult braking can cause it
to slide out of control.
{WARNING:
Driving on frozen lakes, ponds, or rivers can be
dangerous. Underwater springs, currents under
the ice, or sudden thaws can weaken the ice. Your
vehicle could fall through the ice and you and your
passengers could drown. Drive your vehicle on
safe surfaces only.
5-21
Page 390 of 630

Driving in Water
{WARNING:
Driving through rushing water can be dangerous.
Deep water can sweep your vehicle downstream
and you and your passengers could drown. If it is
only shallow water, it can still wash away the
ground from under your tires, and you could lose
traction and roll the vehicle over. Do not drive
through rushing water.
Heavy rain can mean flash flooding, and flood waters
demand extreme caution.
Find out how deep the water is before driving through
it. Do not try it if it is deep enough to cover the wheel
hubs, axles, or exhaust pipe —you probably will not
get through. Deep water can damage the axle and
other vehicle parts. If the water is not too deep, drive slowly through it. At
faster speeds, water splashes on the ignition system
and the vehicle can stall. Stalling can also occur if you
get the tailpipe under water. If the tailpipe is under
water, you will never be able to start the engine. When
going through water, remember that when the brakes
get wet, it might take longer to stop. See
Driving in Rain
and on Wet Roads on page 5‑23.
After Off-Road Driving
Remove any brush or debris that has collected on the
underbody, chassis, or under the hood. These
accumulations can be a fire hazard.
After operation in mud or sand, have the brake linings
cleaned and checked. These substances can cause
glazing and uneven braking. Check the body structure,
steering, suspension, wheels, tires, and exhaust system
for damage and check the fuel lines and cooling system
for any leakage.
The vehicle requires more frequent service due to
off-road use. Refer to the Maintenance Schedule for
additional information.
5-22
Page 391 of 630

Driving at Night
Night driving is more dangerous than day driving
because some drivers are likely to be impaired—by
alcohol or drugs, with night vision problems, or by
fatigue.
Night driving tips include:
.Drive defensively.
.Do not drink and drive.
.Reduce headlamp glare by adjusting the inside
rearview mirror.
.Slow down and keep more space between you and
other vehicles because headlamps can only light
up so much road ahead.
.Watch for animals.
.When tired, pull off the road.
.Do not wear sunglasses.
.Avoid staring directly into approaching headlamps.
.Keep the windshield and all glass on your vehicle
clean —inside and out.
.Keep your eyes moving, especially during turns
or curves.
No one can see as well at night as in the daytime.
But, as we get older, these differences increase.
A 50-year-old driver might need at least twice as much
light to see the same thing at night as a 20-year-old.
Driving in Rain and on Wet Roads
Rain and wet roads can reduce vehicle traction and
affect your ability to stop and accelerate. Always drive
slower in these types of driving conditions and avoid
driving through large puddles and deep‐standing or
flowing water.
{WARNING:
Wet brakes can cause crashes. They might not
work as well in a quick stop and could cause
pulling to one side. You could lose control of
the vehicle.
After driving through a large puddle of water or a
car/vehicle wash, lightly apply the brake pedal
until the brakes work normally.
Flowing or rushing water creates strong forces.
Driving through flowing water could cause your
vehicle to be carried away. If this happens, you
and other vehicle occupants could drown. Do not
ignore police warnings and be very cautious about
trying to drive through flowing water.
5-23
Page 394 of 630
Winter Driving
Driving on Snow or Ice
Drive carefully when there is snow or ice between the
tires and the road, creating less traction or grip. Wet ice
can occur at about 0°C (32°F) when freezing rain
begins to fall, resulting in even less traction. Avoid
driving on wet ice or in freezing rain until roads can be
treated with salt or sand.
Drive with caution, whatever the condition. Accelerate
gently so traction is not lost. Accelerating too quickly
causes the wheels to spin and makes the surface under
the tires slick, so there is even less traction.
Try not to break the fragile traction. If you accelerate too
fast, the drive wheels will spin and polish the surface
under the tires even more.
TheStabiliTrak
®Systemon page 5‑6improves the
ability to accelerate on slippery roads, but slow down
and adjust your driving to the road conditions. When
driving through deep snow, turn off the traction control
part of the StabiliTrak
®System to help maintain vehicle
motion at lower speeds.
The Antilock Brake System (ABS)
on page 5‑4improves vehicle stability during hard stops on slippery
roads, but apply the brakes sooner than when on
dry pavement. Allow greater following distance on any slippery road
and watch for slippery spots. Icy patches can occur on
otherwise clear roads in shaded areas. The surface
of a curve or an overpass can remain icy when the
surrounding roads are clear. Avoid sudden steering
maneuvers and braking while on ice.
Turn off cruise control, if equipped, on slippery surfaces.
Blizzard Conditions
Being stuck in snow can be in a serious situation. Stay
with the vehicle unless there is help nearby. If possible,
use the
Roadside Assistance Program
on page 8‑7.
To get help and keep everyone in the vehicle safe:
.Turn on the Hazard Warning Flasherson
page 4‑3.
.Tie a red cloth to an outside mirror.
{WARNING:
Snow can trap engine exhaust under the vehicle.
This may cause exhaust gases to get inside.
Engine exhaust contains carbon monoxide (CO)
which cannot be seen or smelled. It can cause
unconsciousness and even death.
(Continued)
5-26
Page 396 of 630

If Your Vehicle is Stuck in Sand,
Mud, Ice, or Snow
Slowly and cautiously spin the wheels to free the
vehicle when stuck in sand, mud, ice, or snow. See
Rocking Your Vehicle to Get It Out on page 5‑28.
If the vehicle has a traction system, it can often help
to free a stuck vehicle. Refer to the vehicle's traction
system in the Index. If stuck too severely for the traction
system to free the vehicle, turn the traction system off
and use the rocking method.
{WARNING:
If the vehicle's tires spin at high speed, they can
explode, and you or others could be injured.
The vehicle can overheat, causing an engine
compartment fire or other damage. Spin the
wheels as little as possible and avoid going above
55 km/h (35 mph) as shown on the speedometer.
For information about using tire chains on the vehicle,
see Tire Chains on page 6‑89.
Rocking Your Vehicle to Get It Out
Turn the steering wheel left and right to clear the
area around the front wheels. For four-wheel-drive
vehicles, shift into Four‐Wheel High. For vehicles with
StabiliTrak
®, turn the traction control part of the system
off. Shift back and forth between R (Reverse) and a
forward gear, spinning the wheels as little as possible.
To prevent transmission wear, wait until the wheels stop
spinning before shifting gears. Release the accelerator
pedal while shifting, and press lightly on the accelerator
pedal when the transmission is in gear. Slowly spinning
the wheels in the forward and reverse directions causes
a rocking motion that could free the vehicle. If that does
not get the vehicle out after a few tries, it might need
to be towed out. Recovery hooks can be used, if the
vehicle has them. If the vehicle does need to be towed
out, see Towing Your Vehicle on page 5‑43.
5-28
Page 450 of 630

Service
For service and parts needs, visit your dealer/retailer.
You will receive genuine GM parts and GM-trained and
supported service people.
Genuine GM parts have one of these marks:
Accessories and Modifications
When non‐dealer/non‐retailer accessories are added to
the vehicle, they can affect vehicle performance and
safety, including such things as airbags, braking,
stability, ride and handling, emissions systems,
aerodynamics, durability, and electronic systems like
antilock brakes, traction control, and stability control.
Some of these accessories could even cause
malfunction or damage not covered by the
vehicle warranty.
Damage to vehicle components resulting from the
installation or use of non‐GM certified parts, including
control module modifications, is not covered under the
terms of the vehicle warranty and may affect remaining
warranty coverage for affected parts.
GM Accessories are designed to complement and
function with other systems on the vehicle. Your
GM dealer/retailer can accessorize the vehicle using
genuine GM Accessories. When you go to your
GM dealer/retailer and ask for GM Accessories, you
will know that GM-trained and supported service
technicians will perform the work using genuine
GM Accessories.
Also, seeAdding Equipment to Your Airbag-Equipped
Vehicle on page 2‑91.
6-4
Page 512 of 630
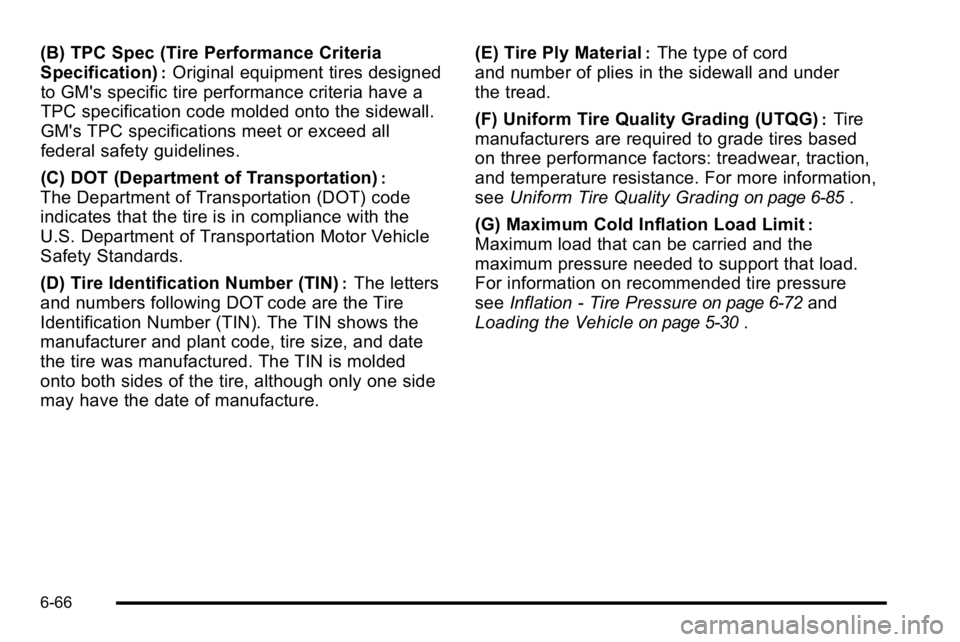

(B) TPC Spec (Tire Performance Criteria
Specification)
:Original equipment tires designed
to GM's specific tire performance criteria have a
TPC specification code molded onto the sidewall.
GM's TPC specifications meet or exceed all
federal safety guidelines.
(C) DOT (Department of Transportation)
:
The Department of Transportation (DOT) code
indicates that the tire is in compliance with the
U.S. Department of Transportation Motor Vehicle
Safety Standards.
(D) Tire Identification Number (TIN)
:The letters
and numbers following DOT code are the Tire
Identification Number (TIN). The TIN shows the
manufacturer and plant code, tire size, and date
the tire was manufactured. The TIN is molded
onto both sides of the tire, although only one side
may have the date of manufacture. (E) Tire Ply Material
:The type of cord
and number of plies in the sidewall and under
the tread.
(F) Uniform Tire Quality Grading (UTQG)
:Tire
manufacturers are required to grade tires based
on three performance factors: treadwear, traction,
and temperature resistance. For more information,
see Uniform Tire Quality Grading
on page 6‑85.
(G) Maximum Cold Inflation Load Limit
:
Maximum load that can be carried and the
maximum pressure needed to support that load.
For information on recommended tire pressure
see Inflation - Tire Pressure
on page 6‑72and
Loading the Vehicle
on page 5‑30.
6-66
Page 518 of 630

Speed Rating:An alphanumeric code assigned
to a tire indicating the maximum speed at which a
tire can operate.
Traction
:The friction between the tire and the
road surface. The amount of grip provided.
Tread
:The portion of a tire that comes into
contact with the road.
Treadwear Indicators
:Narrow bands, sometimes
called wear bars, that show across the tread of a
tire when only 1/16 inch (1.6 mm) of tread
remains. See When It Is Time for New Tires
on
page 6‑82
.
UTQGS (Uniform Tire Quality Grading
Standards)
:A tire information system that
provides consumers with ratings for a tire's
traction, temperature, and treadwear. Ratings are
determined by tire manufacturers using
government testing procedures. The ratings are
molded into the sidewall of the tire. See Uniform
Tire Quality Grading
on page 6‑85.
Vehicle Capacity Weight
:The number of
designated seating positions multiplied by 150 lbs
(68 kg) plus the rated cargo load. See Loading the
Vehicle
on page 5‑30. Vehicle Maximum Load on the Tire
:Load on an
individual tire due to curb weight, accessory
weight, occupant weight, and cargo weight.
Vehicle Placard
:A label permanently attached to
a vehicle showing the vehicle's capacity weight
and the original equipment tire size and
recommended inflation pressure. See “Tire and
Loading Information Label” underLoading the
Vehicle
on page 5‑30.
Inflation - Tire Pressure
Tires need the correct amount of air pressure to
operate effectively.
Notice:Do not let anyone tell you that under‐
inflation or over‐inflation is all right. It is not.
If your tires do not have enough air (under‐
inflation), you can get the following:
.Too much flexing
.Too much heat
.Tire overloading
.Premature or irregular wear
.Poor handling
.Reduced fuel economy
6-72