change wheel GMC SIERRA DENALI 2003 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: GMC, Model Year: 2003, Model line: SIERRA DENALI, Model: GMC SIERRA DENALI 2003Pages: 428, PDF Size: 20.35 MB
Page 228 of 428

Getting Familiar with Off-Road Driving
It’s a good idea to practice in an area that’s safe and
close to home before you go into the wilderness.
Off-road driving does require some new and different
driving skills. Heres’s what we mean.
Tune your senses to different kinds of signals. Your
eyes, for example, need to constantly sweep the terrain
for unexpected obstacles. Your ears need to listen
for unusual tire or engine sounds. With your arms,
hands, feet and body, you’ll need to respond to
vibrations and vehicle bounce.
Controlling your vehicle is the key to successful off-road
driving. One of the best ways to control your vehicles
is to control your speed. Here are some things to keep in
mind. At higher speeds:
e
e
e
e
you approach things faster and you have less time
to scan the terrain for obstacles.
you have less time to react.
you have more vehicle bounce when you drive over
obstacles.
you’ll need more distance for braking, especially
since you’re on an unpaved surface. When you’re driving off-road,
bouncing and
quick changes in direction can easily throw
you out of position. This could cause you to
lose control and crash.
So, whether you’re
driving on or
off the road, you and your
passengers should wear safety belts.
Scanning the Terrain
Off-road driving can take you over many different kinds
of terrain. You need to be familiar with the terrain
and its many different features. Here are some things to
consider.
Surface Conditions: Off-roading can take you over
hard-packed dirt, gravel, rocks, grass, sand, mud, snow
or ice. Each of these surfaces affects the steering,
acceleration and braking of your vehicle in different
ways. Depending upon the kind of surface you are on,
you may experience slipping, sliding, wheel spinning,
delayed acceleration, poor traction and longer braking
distances.
4-1 9
Page 229 of 428

Surface Obstacles: Unseen or hidden obstacles can
be hazardous. A rock, log, hole, rut or bump can startle
you
if you’re not prepared for them. Often these
obstacles are hidden by grass, bushes, snow or even
the rise and fall of the terrain itself. Here are some
things to consider:
Is the path ahead clear?
Will the surface texture change abruptly up ahead?
Does the travel take you uphill or downhill?
(There’s more discussion of these subjects later.)
Will you have to stop suddenly or change direction
quickly?
When you drive over obstacles or rough terrain, keep a
firm grip on the steering wheel. Ruts, toughs or other
surface features can jerk the wheel out of your hands
if
you’re not prepared.
When you drive over bumps, rocks, or other obstacles,
your wheels can leave the ground. If this happens,
even with one or two wheels, you can’t control
the vehicle as well or at all. Because you
will be on an unpaved surface, it’s
especially important to avoid sudden acceleration,
sudden turns or sudden braking.
In a way, off-road driving requires a different kind of
alertness from driving on paved roads and highways.
There are no road signs, posted speed limits or
signal lights. You have to use your own good judgment
about what is safe and what isn’t.
Drinking and driving can be very dangerous on any
road. And this is certainly true for off-road driving. At the
very time you need special alertness and driving
skills, your reflexes, perceptions and judgment can be
affected by even
a small amount of alcohol. You
could have a serious
- or even fatal - accident if you
drink and drive or ride with a driver who has been
drinking. See
Drunken Driving on page 4-2.
4-20
Page 236 of 428

be crushed or ki 1. 1 rays c_ out on L--,
uphill (high9 side of the vehicle and stay well
clear of the rollover path.
Driving in Mud, Sand, Snow or Ice
When you drive in mud, snow or sand, your wheels
won’t get good traction. You can’t accelerate as quickly,
turning
is more difficult, and you’ll need longer braking
distances.
It’s best to use a low gear when you’re in mud
- the
deeper the mud, the lower the gear. In really deep mud,
the idea is to keep your vehicle moving
so you don’t
get stuck.
When you drive on sand, you’ll sense a change in
wheel traction. But it
will depend upon how loosely
packed the sand is. On loosely packed sand (as
on beaches or sand dunes) your tires will tend to sink
into the sand. This will improve traction. Drive at a
reduced speed and avoid sharp turns or abrupt
maneuvers. Hard
packed snow and ice offer the worst tire traction.
On these surfaces, it’s very easy to lose control.
On
wet ice, for example, the traction is so poor that you will
have difficulty accelerating. And
if you do get moving,
poor steering and difficult braking can cause you to slide
out of control.
Driving on frozen lakes, ponds or rivers can be
dangerous. Underwater springs, currents
under the ice, or sudden thaws can weaken the
ice. Your vehicle could fall through the ice and
you and your passengers could drown. Drive
your vehicle on safe surfaces only.
Driving in Water
Heavy rain can mean flash flooding, and flood waters
demand extreme caution.
Find out how deep the water is before you drive through
it.
If it’s deep enough to cover your wheel hubs, axles
or exhaust pipe, don’t try
it - you probably won’t
get through.
,41so, water that deep can damage your
axle and other vehicle parts.
4-27
Page 266 of 428

Making Turns
Stay at least twice as far behind the vehicle ahead as
you would when driving your vehicle without a trailer.
This can help you avoid situations that require
heavy braking and sudden turns.
Passing
You’ll need more passing distance up ahead when
you’re towing a trailer. And, because you’re a good deal
longer, you’ll need to go much farther beyond the
passed vehicle before you can return to your lane.
Backing Up
Hold the bottom of the steering wheel with one hand.
Then, to move the trailer to the left, just move that hand
to the left. To move the trailer to the right, move your
hand to the right. Always back up slowly and,
if possible,
have someone guide you.
Your vehicle is equipped with four-wheel steering and
if
you use it while backing your trailer the same rules
apply. However, with four-wheel steering your rig will
respond more quickly and it may take additional practice
to get used to backing up with four-wheel steering.
Notice: Making very sharp turns while trailering
could cause the trailer to come in contact with the
vehicle. Your vehicle could be damaged. Avoid
making very sharp turns while trailering.
When you’re turning with a trailer, make wider turns
than normal.
Do this so your trailer won’t strike
soft shoulders, curbs, road signs, trees or other objects.
Avoid jerky or sudden maneuvers. Signal well in
advance.
Turn Signals When Towing a Trailer
The arrows on your instrument panel will flash whenever
you signal a turn or lane change. Properly hooked up,
the trailer lamps will also flash, telling other drivers
you’re about to turn, change lanes or stop.
When towing a trailer, the arrows on your instrument
panel will flash for turns even
if the bulbs on the trailer
are burned out. Thus, you may think drivers behind
you are seeing your signal when they are not. It’s
important to check occasionally to be sure the trailer
bulbs are still working.
4-57
Page 332 of 428
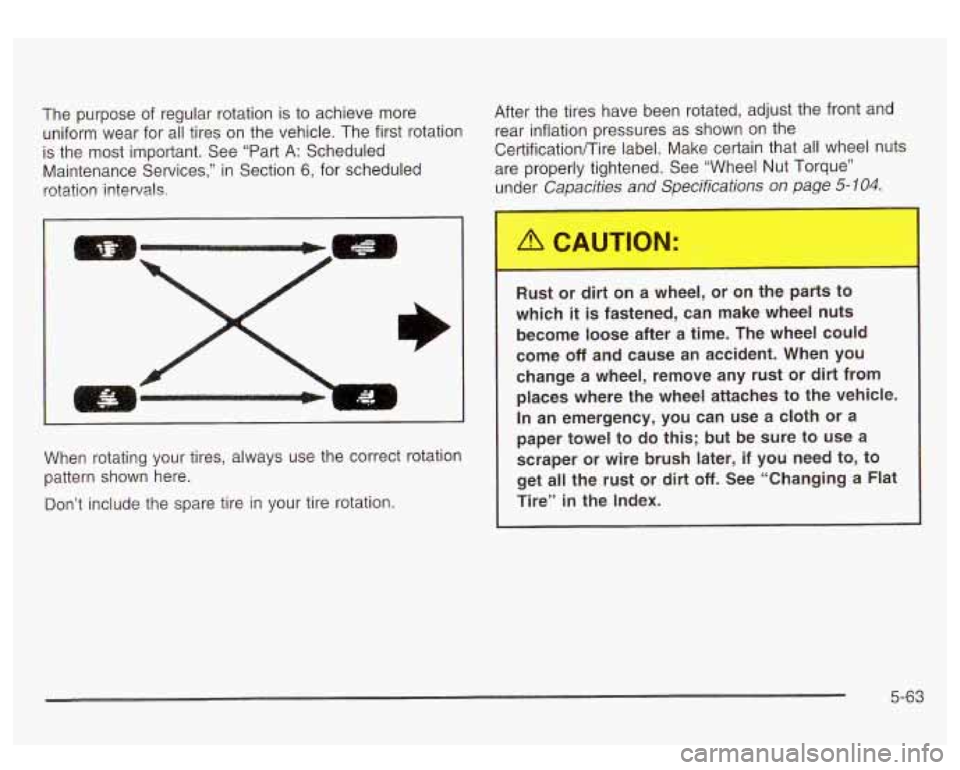
The purpose of regular rotation is to achieve more
uniform wear for all tires on the vehicle. The first rotation
is the most important. See “Part A: Scheduled
Maintenance Services,” in Section
6, for scheduled
rotation
intervals;
After the tires have been rotated, adjust the front and
rear inflation pressures as shown on the
CertificationEire label. Make certain that all wheel nuts
are properly tightened. See “Wheel Nut Torque”
under
Capacities and Specificatiol on ge 5-104.
When rotating your tires, always use the correct rotation
pattern shown here.
Don’t include the spare tire in your tire rotation. Rust or dirt on a
wheel, or on the parts to
which
it is fastened, can make wheel nuts
become loose after a time. The wheel could
come
off and cause an accident. When you
change a wheel, remove any rust or dirt from
places where the wheel attaches to the vehicle,
In an emergency, you can use a cloth or a
paper towel to do
this; but be sure to use a
scraper or wire brush later,
if you need to, to
get all the rust or dirt
off. See “Changing a Flal
Tire”
in the Index.
5-63
Page 338 of 428

A rear blowout, particularly on a curve, acts much like a Changing a Flat Tire
skid and may require the same correction you’d use
in a skid. In any rear blowout, remove your foot from the
If a tire goes flat, avoid further tire and wheel damage
accelerator pedal. Get the vehicle under control by by driving slowly
to a level place. Turn on your
steering
the way you want the vehicle to go. it may be hazard warning flashers.
very bumpy and noisy, but you can still steer. Gently
brake
to a stop - well off the road if possible.
If a tire goes flat, the next part shows how
to use your
jacking equipment to change a flat tire safely.
C..-nging a tire can cause
an injury. The
vehicle can slip
off the jack and roll over you
or other people. You and they could be badly
injured. Find a level place to change your tire.
To help prevent the vehicle from moving:
1. Set the parking brake firmly.
2. Put the shift lever in PARK (P).
3. Turn off the engine.
4. Put the wheel blocks at the front and rear
of the tire farthest away from the one
being changed. That
would be the tire on
the other side of the vehicle, at the
opposite end.
5-69
Page 348 of 428
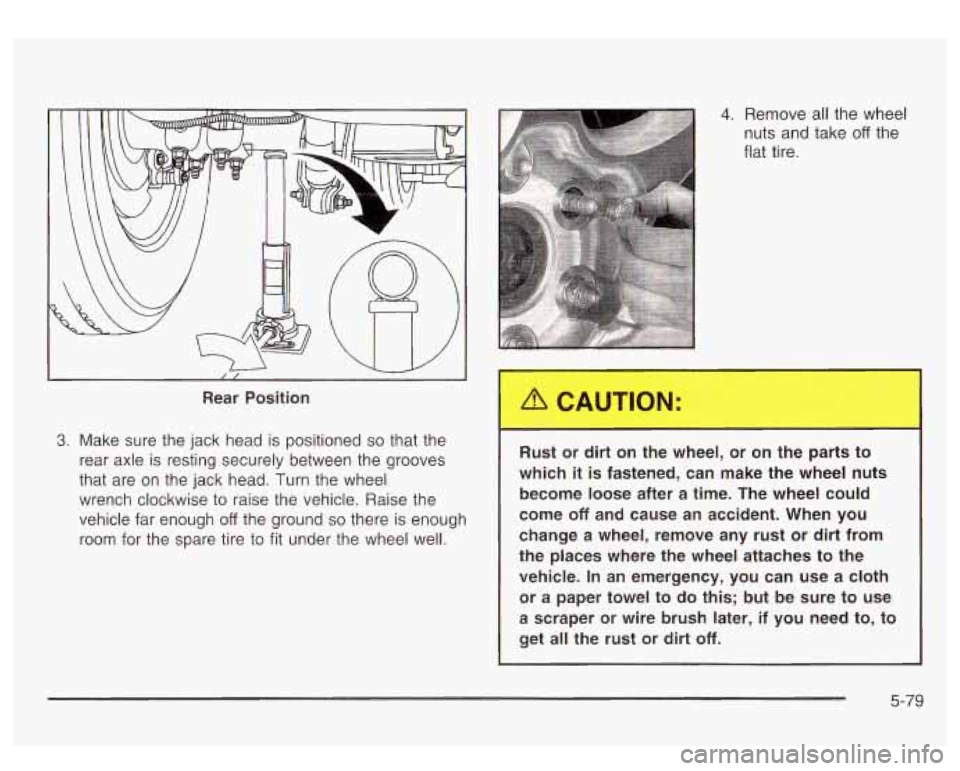
Rear Position
3. Make sure the jack head is positioned so that the
rear axle
is resting securely between the grooves
that are on the jack head. Turn the wheel
wrench clockwise to raise the vehicle. Raise the
vehicle far enough
off the ground so there is enough
room for the spare tire to
fit under the wheel well.
4. Remove all the wheel
nuts and take
off the
flat tire.
Rust or dirt on the wheel, or on the parts to
which
it is fastened, can make the wheel nuts
become loose after a time. The wheel could
come
off and cause an accident. When you
change
a wheel, remove any rust or dirt from
the places where the wheel attaches to the
vehicle. In an emergency, you can use a cloth
or
a paper towel to do this; but be sure to use
a scraper or wire brush later, if you need to, to
get all the rust
or dirt off.
5-79
Page 379 of 428

Part A: Scheduled Maintenance
Services
This part contains engine oil and chassis lubrication scheduled maintenance which explains the engine oil life
system and how it indicates when to change the
engine oil and filter. Lubricate chassis components with
each oil change.
Also, listed are scheduled maintenance
services which are to be performed at the mileage
intervals specified.
Using Your Maintenance Schedule
We at General Motors want to help you keep your
vehicle in good condition. But we don’t know exactly how
you’ll drive it. You may drive very short distances only
a few times a week. Or you may drive long distances in
very hot, dusty weather. You may use your vehicle in
making deliveries. Or yo may drive
it to work, to
do errands or in many other ways.
Because
of all the different ways people use their
vehicles, maintenance needs vary. You may need more
frequent checks and replacements.
So please read
the following and note how you drive.
If you have any
questions on how to keep your vehicle in good condition,
see your dealer. This part tells
you the maintenance services you should
have done and when you should schedule them.
When you go to your dealer for your service needs,
you’ll know that GM-trained and supported service
people will perform the work using genuine
GM parts.
The proper fluids and lubricants
so use are listed in Part
D. Make sure whoever services your vehicle uses
these.
All parts should be replaced and all necessary
repairs done before you or anyone else drives the
vehicle.
This schedule is for vehicles that:
carry passengers and cargo within recommended
limits. You will find these limits on your vehicle’s
Certification/Tire label. See
Loading Your Vehicle on
page 4-45.
are driven on reasonable road surfaces within legal
driving limits.
are driven off-road in the recommended manner.
See
Operating Your All- Wheel-Drive Vehicle Off
Paved Roads on page 4- 16.
use the recommended fuel. See Gasoline Octane
on page 5-5.
6-4
Page 390 of 428

Transfer Case and Front Axle
(All-Wheel Drive) Inspection
Every 12 months, or at engine oil change intervals,
check front axle and transfer case and add lubricant
when necessary.
A fluid loss could indicate a problem.
Check and have it repaired,
if needed. Check vent
hose at transfer case for kinks and proper installation.
Brake System Inspection
Inspect the complete system. Inspect brake lines and
hoses for proper hook-up, binding, leaks, cracks,
chafing, etc; Inspect
disc brake pads for wear and rotors
for surface condition. Inspect other brake parts,
including calipers, parking brake, etc. You may need to
have your brakes inspected more often if your driving
habits or conditions result in frequent braking.
6-1 5
Page 400 of 428

GM Mobility Program for Persons
with Disabilities
This program, available to
qualified applicants, can
reimburse you up to
$1,000 toward aftermarket
driver or passenger
adaptive equipment you
may require for your
vehicle (hand controls,
wheelchair/scooter lifts, etc.).
This program can also provide you with free resource
information, such as area driver assessment centers and
mobility equipment installers. The program is available
for a limited period
of time from the date of vehicle
purchase/lease. See your dealer for more details or call
the GM Mobility Assistance Center at 1-800-323-9935.
Text telephone (TTY) users, call 1-800-833-9935.
GM of Canada also has a Mobility Program. Call
1-800-GM-DRIVE (463-7483) for details. All TTY users
call 1-800-263-3830.
Roadside Assistance Program
GMC’s Roadside Assistance Provides stranded owners
with over-the-phone roadside repairs, location of the
nearest GMC dealer or the following special
services:
Flat Tire Change: Installation of spare tire will be
covered at no charge (customer is responsible for repair
or replacement of tire).
Fuel Delivery: Delivery of enough fuel for the customer
to get to the nearest service station (up to
$5.00)
will be covered.
Jump Start: No-start situations which require a battery
jump start will be covered at
no charge.
Lock Out: Replacement keys or locksmith service will be
covered at no charge
if you are unable to gain entry
into your vehicle. Delivery of the replacement key will be
covered within 10 miles (16 km).
Emergency Towing Sewice: Towing to the nearest GMC
dealer for warranty related disablements will be
covered.
7-5