parking brake GREAT WALL HOVER 2006 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: GREAT WALL, Model Year: 2006, Model line: HOVER, Model: GREAT WALL HOVER 2006Pages: 425, PDF Size: 26.05 MB
Page 17 of 425

Brake system
The front wheel brake is ventilation coil type, the rear wheel brake is disk and drum type. The service brake type is that the double-
loop vacuum assist hydraulic brake is applied on the front and rear disc brake. The parking brake is mechanical dragline acting on the
drum brake of the rear wheel.
The free stroke of brake pedal is 20mm
30mm, and the operating stroke of the pedal is 120mm. The operating stroke of the brake
handle is 17
(3 teeth)30(8 teeth).
1. The adjustment of brake pedal
Measure the operating stroke of the brake pedal, the standard value is 120mm. When the eighth is no in compliance with the
requirement, make adjustment according to the following procedures:
a. Separate the brake lamp switch wire connector, loosen the blocking nut, and turn the brake lamp switch to the position that the
stopper is not touched;
b. Unscrew the blocking nut of the operation connecting rod, use the thinnose pliers to turn the operation connecting rod, adjust
the brake pedal height to standard value, after reaching the standard value, tighten the lock nut;
c. Turn the brake lamp switch to the position that the stopper of brake pedal is just touched, continue the turning for 1/2
1 circle,
and tighten the blocking nut;
d. Connect the brake lamp switch wire connector;
e. The brake lamp should not be light when the brake pedal is in release status.
2. Standard value of brake pedal free stroke: 20-30 mm
a. Under the stopping status of the engine, step on the brake pedal for 2
3 times, clear the influence of brake assistor, then use
hand to push the brake pedal to the position that there is resistance, measure the amount of movement (free stroke). It shall
be in compliance with the regulation of standard value;
b. If the gap is less than the regulation value, check to see whether the gap between the carrier rod of brake lamp switch and the
brake pedal is in compliance with the regulation. If this gap is exceeding the regulation, it means that the gap between the drive
rod clevis pin and the brake pedal arm is exceeding the regulated value.
3. Start the engine, step down the brake pedal with a force of about 700N,ehck the main brake pump, whether there is oil
leakage on the connection positions of the brake pipeline. If there is, maintain it.
4. Operating status test of brake assistor
Conduct the operation status test of the brake assistor according to the following methods:
a. Start the engine, stop if after operating for 1
2 minutes. Step on the brake pedal for several times with normal force. Expect
that the pedal can be fully stepped down a the first stepping, the height of the brake pedal shall be raised on and on with the
stepping, thus means that the brake assistor operates normally, if the height of the pedal is not changed, it means that the brake
assistor is damaged;
b. Under the stopping status of the engine, step on the brake pedal for several times, confirms that the height of brake pedal is
elevated on and on, under the status that the brake pedal is stepped down, start the engine. At this time, the brake pedal will
move down a bit, it means that the brake assistor is working normally. If the brake pedal is moving upwards, it means that the
brake assistor is damaged;
c. Under the operation status of the engine, step down the brake pedal to stop the operation of the engine. AT this time, the there
shall be no change of the height of brake pedal within 30 seconds, it means that the brake assistor is working normally. If the
brake pedal is moving upwards, it means that the brake pedal assistor is damaged.
5. Adjustment of the parking brake system:
a.For positioning, pull the brake bar to the limit position for over 3 times, use a force of about 400N to pull the brake parking
lever, count the number of knocking teeth. The standard value of stroke of parking brake : 17
(3 teeth) 30(8 teeth);
b.If the stroke of brake parking lever is too big and not in compliance with the requirement, adjust it with the following methods:
Loosen the brake parking lever, unscrew the adjusting nut.
Remove the adjuster hole cap from the brake assembly, use screwdriver to turn the adjustor in the arrow direction to the limit
that the brake drum cannot turn.
Rotate 5 teeth in the counter arrow direction.
Rotate the adjusting nut, adjust the brake parking lever stroke to the standard value.
c. If the stroke is less than the standard value, unscrew the adjusting nut to make it reach the standard value.
d. Check to see whether the adjusting nut and the rod are loosened, whether the adjusting nut is fixed in the fixed seat.
e. After adjustment, jack up the rear part of the car. Loosen the brake parking lever, the brake disc shall not be dragged when
checking the rear wheel.
f. The breaking in of the parking brake: use the force of about 200-250N to pull the brake parking lever,drive the car for about
400m with a speed of about 60km/h, repeat for 2-3 times, then test on the slope of 30%, the car shall be able to be parked.
Page 19 of 425
Electrical system
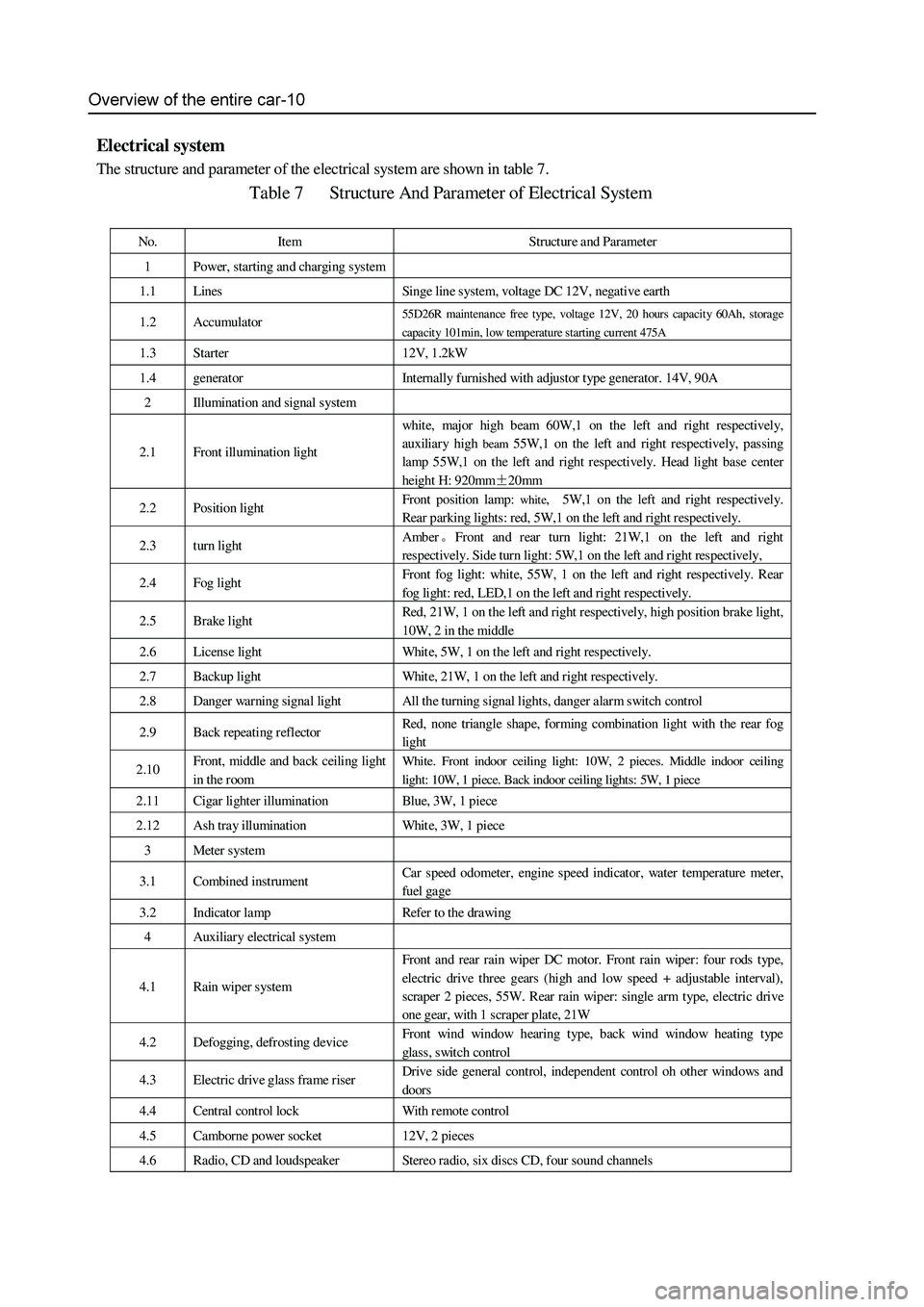
The structure and parameter of the electrical system are shown in table 7.
Table 7 Structure And Parameter of Electrical System
No. Item Structure and Parameter
1 Power, starting and charging system
1.1 Lines Singe line system, voltage DC 12V, negative earth
1.2 Accumulator 55D26R maintenance free type, voltage 12V, 20 hours capacity 60Ah, storage
capacity 101min, low temperature starting current 475A
1.3 Starter 12V, 1.2kW
1.4 generator Internally furnished with adjustor type generator. 14V, 90A
2 Illumination and signal s ystem
2.1 Front illumination light
white, major high beam 60W,1 on the left and right respectively,
auxiliary high
beam 55W,1 on the left and right respectively, passing
lamp 55W,1 on the left and right respectively. Head light base center
height H: 920mm±20mm
2.2 Position light Front position lamp: white, 5W,1 on the left and right respectively.
Rear parking lights: red, 5W,1 on the left and right respectively.
2.3 turn light Amber。Front and rear turn light: 21W,1 on the left and right
respectively. Side turn light: 5W,1 on the left and right respectively,
2.4 Fog light Front fog light: white, 55W, 1 on the left and right respectively. Rear
fog light: red, LED,1 on the left and right respectively.
2.5 Brake light Red, 21W, 1 on the left and right respectively, high position brake light,
10W, 2 in the middle
2.6 License light White, 5W, 1 on the left and right respectively.
2.7 Backup light White, 21W, 1 on the left and right respectively.
2.8 Danger warning signal light All the turning signal lights, danger alarm switch control
2.9 Back repeating reflector Red, none triangle shape, forming combination light with the rear fog
light
2.10 Front, middle and back ceiling light
in the room White. Front indoor ceiling light: 10W, 2 pieces. Middle indoor ceiling
light: 10W, 1 piece. Back indoor ceiling lights: 5W, 1 piece
2.11 Cigar lighter illumination Blue, 3W, 1 piece
2.12 Ash tray illumination White, 3W, 1 piece
3 Meter system
3.1 Combined instrument Car speed odometer, engine speed indicator , water t emperature met er,
fuel gage
3.2 Indicator lamp Refer to the drawing
4 Auxiliary electrical system
4.1 Rain wiper system Front and rear rain wiper DC motor. Front rain wiper: four rods type,
electric drive three gears (high and low speed + adjustable interval),
scraper 2 pieces, 55W. Rear rain wiper: single arm type, electric drive
one gear, with 1 scraper plate, 21W
4.2 Defogging, defrosting device Front wind window hearing type, back wind window heating type
glass, switch control
4.3 Electric drive glass frame riser Drive side general control, independent control oh other windows and
doors
4.4 Central control lock With r emote control
4.5 Camborne power socket 12V, 2 pieces
4.6 Radio, CD and loudspeaker Stereo radio, six discs CD, four sound channels
Page 81 of 425

Automatic transmission-5
Table 2.1 Gear selection and its function
Gear selection function
1st-Gear
(manual 1
st-Gear ) The first gear is using for climbing and braking. It is a function which limits the speed of
the car. The speed limitation by engine is realized by reduce the opening degree of
throttle position.
2nd-Gear (automatic, manual
2
nd-Gear) In economic mode, it can process the 1
st and 2nd shifting operation when engage the 2nd
–Gear. The limitation of vehicle speed by engine is realized through reducing the
opening of throttle position. in 4WD 4 high, , the transmission will maintain 2
nd-Gear
position The manual mode and winter-Mode will only maintain 2nd-Gear 。
3rd-Gear
(automatic, manual 3rd-Gea) In economic mode and dynamic mode, it can process the shifting operation of 1
st, 2nd
and 3rd-Gear when engage the 3rd-Gear, and can reaches the very high vehicle speed. At
this time the locking clutch can process the locking action, refer to vehicle user manual.
The limitation of vehicle speed by engine is realized by reduce the opening of throttle
position. In 4WD 4 low, the transmission should be maintained in 3
rd –Gear position.
Under manual mode, the transmission will be kept in 3rd-Gear.
D-gear
(drive) It can process the 1
st, 2nd, 3rd and 4th –Gear position operation and gear-shifting operation
of (1-2), (1-3), (2-3), (2-4), (3-4), (4-3), (4-2), (3-1) and (2-1). This shifting operation is
processed by taking the vehicle speed, throttle position, throttle position switching
frequency (or forced Gear-decreasing) as the parameter. The locking clutch can process
the locking action in 3rd –Gear, 4
th-Gear according to the type of vehicle. Refer to user
manual of vehicle.
N-Gear
(neutral gear) Only the rear brake belt is engaged at this time. It determines whether the function can
be realized according to the vehicle speed, engine speed and throttle position. But the
gear-position sensor allows the starting of engine. Allow the slide of N-Gear.
R-Gear
(reverse gear) Set the anti-misoperation in forward function according to the vehicle speed, engine
speed and throttle position opening to realize the reverse operation. The gear-position
sensor can start the revers e lamp.
P-gear
(parking gear) Only the rear brake belt is engaged at this time. The function can be determined
according to the vehicle speed, engine speed and throttle position. The output shaft of
transmission is locked. The gear-position sensor can start the engine.
Page 82 of 425
Automatic transmission-6
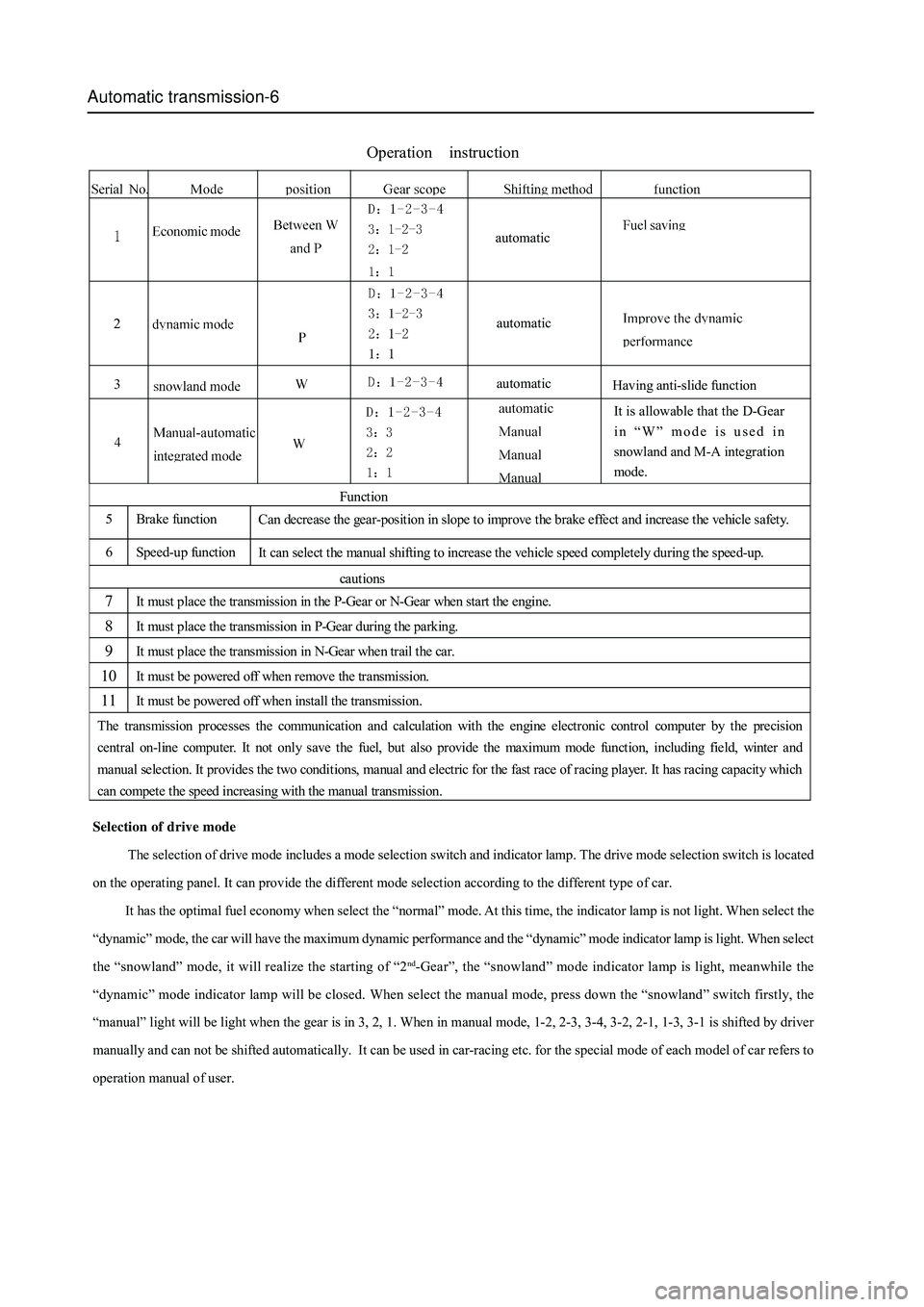
Selection of drive mode
The selection of drive mode includes a mode selection switch and indicator lamp. The drive mode selection switch is located
on the operating panel. It can provide the different mode selection according to the different type of car.
It has the optimal fuel economy when select the “normal” mode. At this time, the indicator lamp is not light. When select the
“dynamic” mode, the car will have the maximum dynamic performance and the “dynamic” mode indicator lamp is light. When select
the “snowland” mode, it will realize the starting of “2
nd-Gear”, the “snowland” mode indicator lamp is light, meanwhile the
“dynamic” mode indicator lamp will be closed. When select the manual mode, press down the “snowland” switch firstly, the
“manual” light will be light when the gear is in 3, 2, 1. When in manual mode, 1-2, 2-3, 3-4, 3-2, 2-1, 1-3, 3-1 is shifted by driver
manually and can not be shifted automatically. It can be used in car-racing etc. for the special mode of each model of car refers to
operation manual of user.
Operation instruction
Function
5 Brake function
Can decrease the gear-position in slope to improve the brake effect and increase the vehicle safety.
6 Speed-up function
It can select the manual shifting to increase the vehicle speed completely during the speed-up.
cautions
7 It must place the transmission in the P-Gear or N-Gear when start the engine.
8 It must place the transmission in P-Gear during the parking.
9 It must place the transmission in N-Gear when trail the car.
10 It must be powered off when remove the transmission.
11 It must be powered off when install the transmission.
The transmission processes the communication and calculation with the engine electronic control computer by the precision
central on-line computer. It not only save the fuel, but also provide the maximum mode function, including field, winter and
manual selection. It provides the two conditions, manual and electric for the fast race of racing player. It has racing capacity wh i ch
can compete the speed increasing with the manual transmission.
automatic
Having anti-slide function
It is allowable that the D-Gear
in “W” mode is used in
snowland and M-A integration
mode. automatic
automatic
Page 98 of 425
Automatic transmission-22
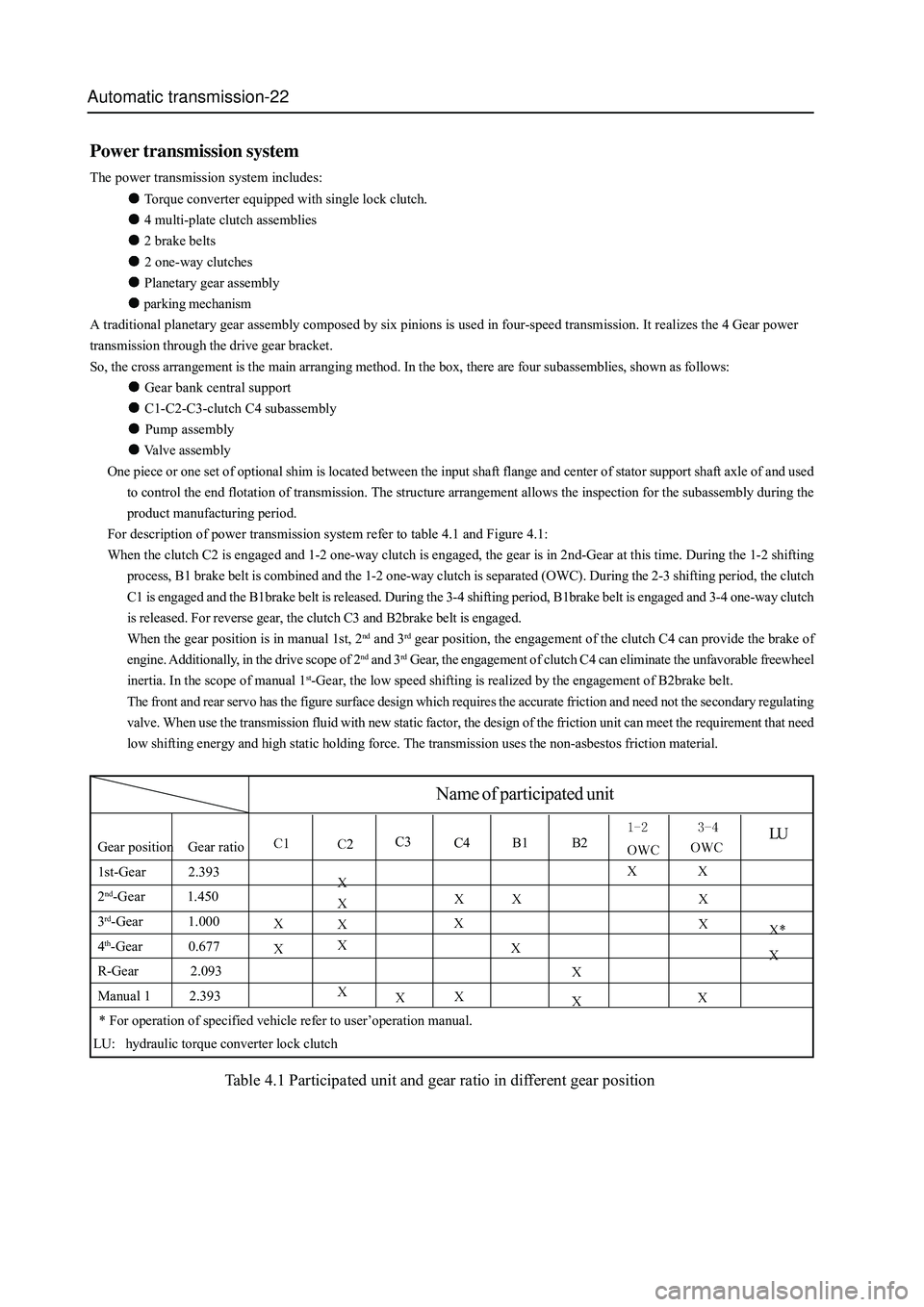
Power transmission system
The power transmission system includes:
Torque converter equipped with single lock clutch.
4 multi-plate clutch assemblies
2 brake belts
2 one-way clutches
Planetary gear assembly
parking mechanism
A traditional planetary gear assembly composed by six pinions is used in four-speed transmission. It realizes the 4 Gear power
transmission through the drive gear bracket.
So, the cross arrangement is the main arranging method. In the box, there are four subassemblies, shown as follows:
Gear bank central support
C1-C2-C3-clutch C4 subassembly
Pump assembly
Valve assembly
One piece or one set of optional shim is located between the input shaft flange and center of stator support shaft axle of and used
to control the end flotation of transmission. The structure arrangement allows the inspection for the subassembly during the
product manufacturing period.
For description of power transmission system refer to table 4.1 and Figure 4.1:
When the clutch C2 is engaged and 1-2 one-way clutch is engaged, the gear is in 2nd-Gear at this time. During the 1-2 shifting
process, B1 brake belt is combined and the 1-2 one-way clutch is separated (OWC). During the 2-3 shifting period, the clutch
C1 is engaged and the B1brake belt is released. During the 3-4 shifting period, B1brake belt is engaged and 3-4 one-way clutch
is released. For reverse gear, the clutch C3 and B2brake belt is engaged.
When the gear position is in manual 1st, 2
nd and 3rd gear position, the engagement of the clutch C4 can provide the brake of
engine. Additionally, in the drive scope of 2
nd and 3rd Gear, the engagement of clutch C4 can eliminate the unfavorable freewheel
inertia. In the scope of manual 1
st-Gear, the low speed shifting is realized by the engagement of B2brake belt.
The front and rear servo has the figure surface design which requires the accurate friction and need not the secondary regulating
valve. When use the transmission fluid with new static factor, the design of the friction unit can meet the requirement that need
low shifting energy and high static holding force. The transmission uses the non-asbestos friction material.
LUGear position Gear ratio
1st-Gear 2.393
2
nd-Gear 1.450
3
rd-Gear 1.000
4
th-Gear 0.677
R-Gear 2.093
Manual 1 2.393
C3C4 B1 B2
Name of participated unit
* For operation of specified vehicle refer to user’operation manual.
LU: hydraulic torque converter lock clutch
Table 4.1 Participated unit and gear ratio in different gear position
Page 100 of 425
Automatic transmission-24
Front servo and brake belt Rear servo and brake belt
Figure 4.4 brake belt
One-way clutch
The transmission has two one-way clutches, 1-2 one-way clutch and 3-4 one-way clutch (notice that the third one-way clutch is
located on torque converter, also called as retainer)
1-2 one-way clutch is located between the planet carrier assembly and central shaft. The structure makes the planet carrier only
can rotate in single direction around the central shaft. The one-way clutch is only engaged in automatic 1
st-Gear.
3-4 one-way clutch is located between the clutch C4 and clutch C2.The structure makes the clutch C2 drive the front planetary
gear in 1
st, 2nd and 3rd –Gear, but is disengaged in 4th-Gear and overspeed.
Planetary gear assembly
The planetary gear block used in transmission is the traditional lavena gear block consisted of6 pinions.
Parking mechanism
When select the parking-Gear, the steering column will move the parking lever backwardly to engage with the parking ratch
(refer to Figure 4.5). The ratchet is engaged with the tooth of external gear ring fear to lock the output shaft axle in the
transmission. When it is not in parking-gear, the return spring will release the parking ratchet and unlock the output shaft to
prevent the occurrence of accident parking action.
Figure 4.3 Clutch assembly
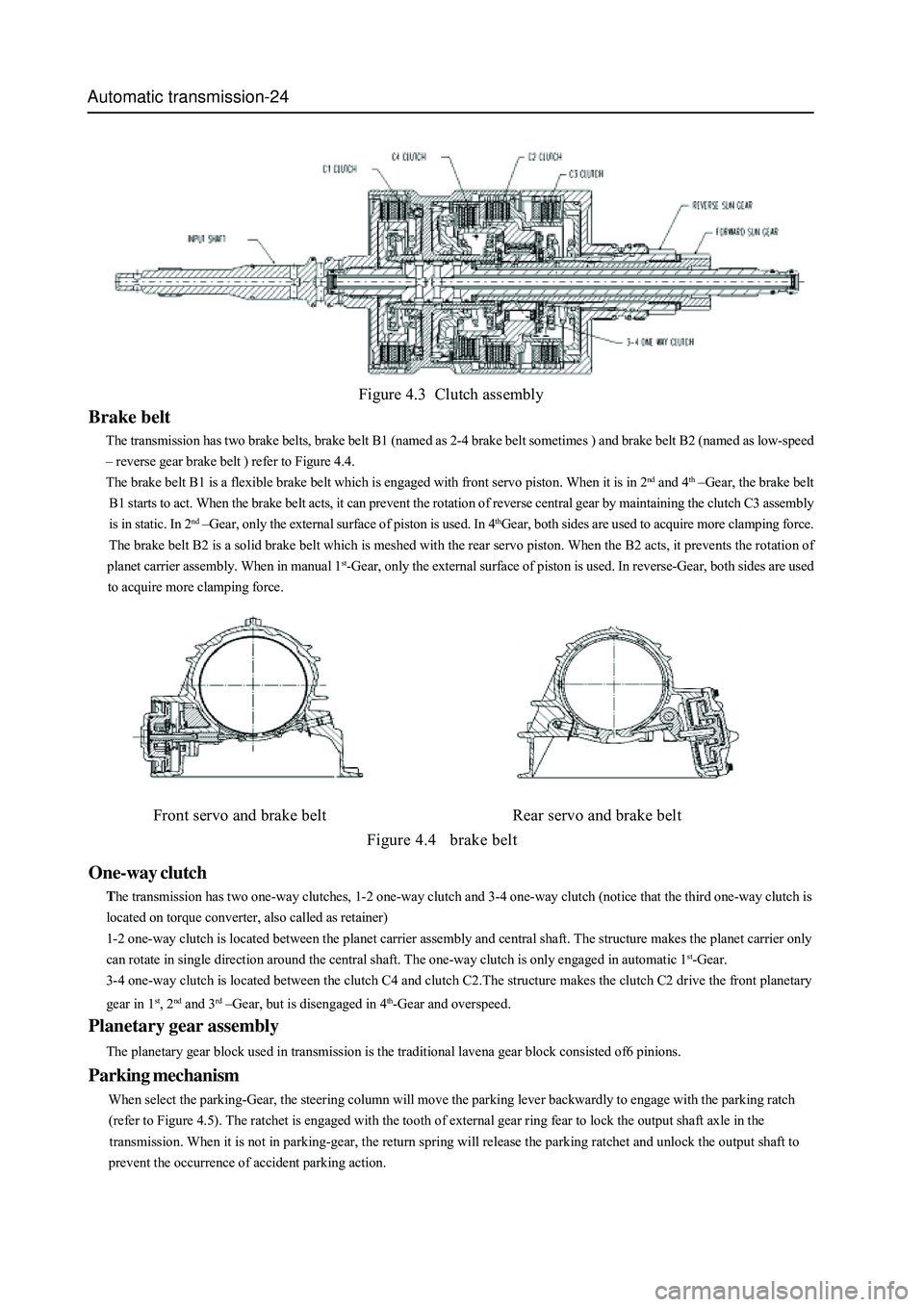
Brake belt
The transmission has two brake belts, brake belt B1 (named as 2-4 brake belt sometimes ) and brake belt B2 (named as low-speed
– reverse gear brake belt ) refer to Figure 4.4.
The brake belt B1 is a flexible brake belt which is engaged with front servo piston. When it is in 2
nd and 4th –Gear, the brake belt
B1 starts to act. When the brake belt acts, it can prevent the rotation of reverse central gear by maintaining the clutch C3 assembly
is in static. In 2
nd –Gear, only the external surface of piston is used. In 4thGear, both sides are used to acquire more clamping force.
The brake belt B2 is a solid brake belt which is meshed with the rear servo piston. When the B2 acts, it prevents the rotation of
planet carrier assembly. When in manual 1
st-Gear, only the external surface of piston is used. In reverse-Gear, both sides are used
to acquire more clamping force.
Page 102 of 425
Automatic transmission-26
Power transmission
Introduction
It has the following power transmission pointed to different Gear-position:
power transmission N-Gear and P-Gear
power transmission R-Gear
power transmission manual 1
power transmission Automatic 1st-Gear
power transmission Automatic 2nd -Gear
power transmission Automatic 3rd -Gear
power transmission Automatic 3rd-Gear locking
power transmission Automatic 4th -Gear (overspeed -gear)
power transmission Automatic 4th -Gear locking
For description of each kind of power transmission condition, refer to following parts.
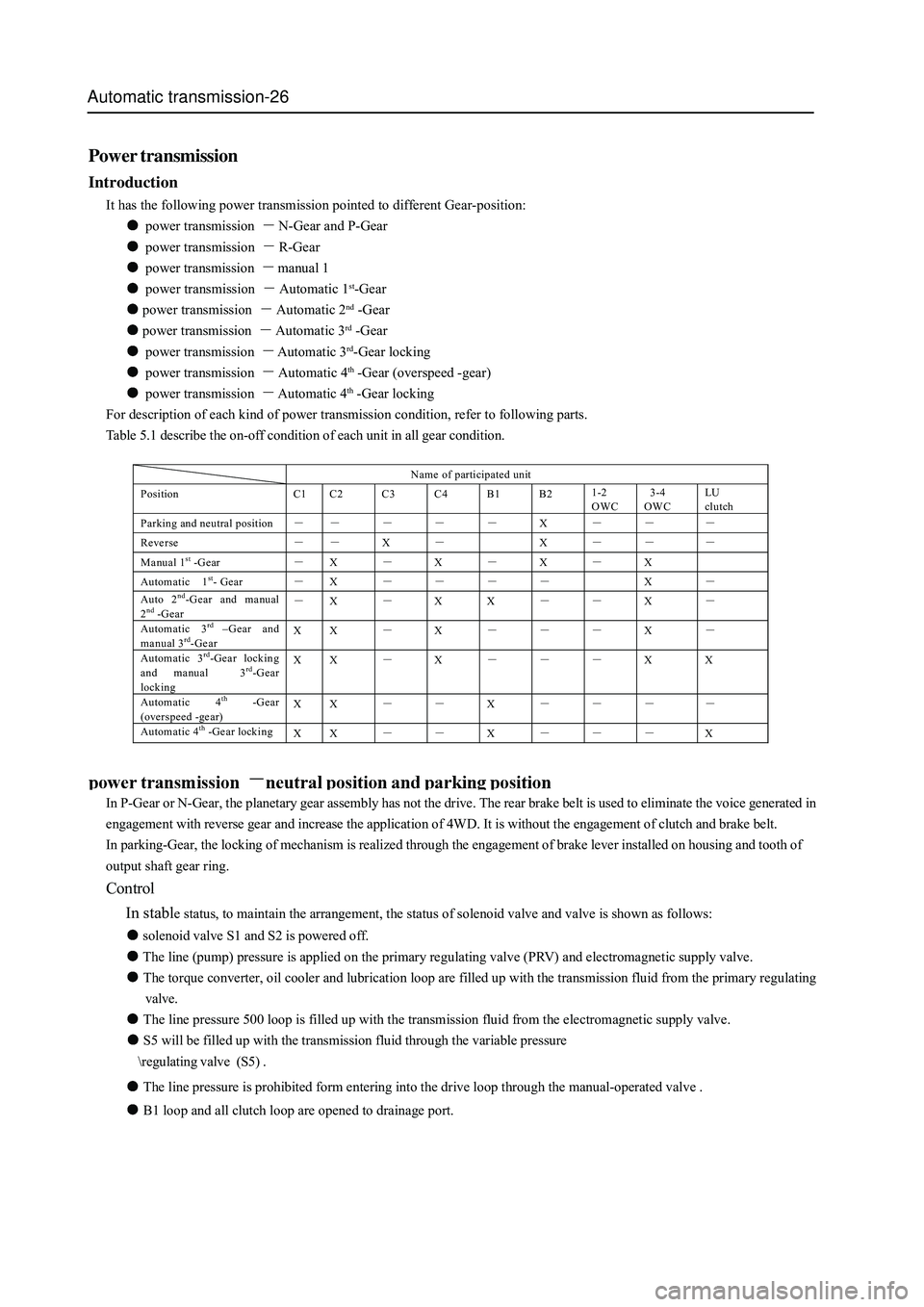
Table 5.1 describe the on-off condition of each unit in all gear condition.
Name of participated unit
Position C1 C2 C3 C4 B1 B2 1-2
OWC 3-4
OWC LU
clutch
Parking and neutral position - - - - - X - - -
Reverse - - X - X - - -
Manual 1st -G ear - X - X - X - X
Automatic 1st- Gear - X - - - - X -
Auto 2nd-Gear and manual
2nd -G ear - X - X X - - X - Automatic 3rd –Gear and
manual 3rd-Gear X X - X - - - X - Automatic 3rd-Gear locking
and manual 3rd-Gear
locking X X - X - - - X X
Automatic 4th -Gear
(overspeed -gear) X X - - X - - - -
Automatic 4th -Gear locking
X X - - X - - - X
In P-Gear or N-Gear, the planetary gear assembly has not the drive. The rear brake belt is used to eliminate the voice generated in
engagement with reverse gear and increase the application of 4WD. It is without the engagement of clutch and brake belt.
In parking-Gear, the locking of mechanism is realized through the engagement of brake lever installed on housing and tooth of
output shaft gear ring.
Control
In stabl
e status, to maintain the arrangement, the status of solenoid valve and valve is shown as follows:
solenoid valve S1 and S2 is powered off.
The line (pump) pressure is applied on the primary regulating valve (PRV) and electromagnetic supply valve.
The torque converter, oil cooler and lubrication loop are filled up with the transmission fluid from the primary regulating
valve.
The line pressure 500 loop is filled up with the transmission fluid from the electromagnetic supply valve.
S5 will be filled up with the transmission fluid through the variable pressure
egulating valve (S5) .
The line pressure is prohibited form entering into the drive loop through the manual-operated valve .
B1 loop and all clutch loop are opened to drainage port.
Page 129 of 425

Adjustment
Hydraulic system
Following parts is the detailed description for self-detection procedure pointed to the condition occurred in chapter
6. including the condition indicated the failure, to point the problem existed in the hydraulic system.
It should select the proper procedure from the following primary detection when adjust the transmission.
Detection process of transmission fluid
Detect the manual linkage adjusting system(refer to factory manual of car)
Detect the engine idle speed
Anchoring test (beyond the scope of the maintenance manual)
On-road test (beyond the scope of the maintenance manual)
Detection procedure of transmission fluid level
1. General
The process is used to detect the level of vehicle transmission fluid. It will cause the failure or delay of transmission shifting if
the level is low than required value and the vehicle does not reach the drive temperature.
Firstly, process the transmission diagnosis information detection for vehicle (refer to chapter 6). If found the failure of sensor,
then it maybe caused by transmission fluid level is less than specified value.
It should detect whether has the abnormal delay and Gear-position condition when select the forward or reverse-gear by driving
the vehicle. One feature of oil level less than normal value is that the vehicle has the gear-position delay and lack condition when
the vehicle is in steering. The previous problem will occur when the transmission fluid temperature is low.
When the oil temperature is medium and vehicle speed failure is recorded, the gear-position lose condition
will not occurs any longer, it means that needs to fill the transmission with the transmission fluid.
2. Detection of transmission fluid level
When fill up or replace the transmission fluid, it must use the Castrol TQ95 automatic transmission fluid (ATF) or other
permissive oil. It will damage the performance and service life of transmission if use the unpermissive transmission fluid.
Please ensure the transmission fluid level is correct. The transmission also can be damaged if the transmission fluid level is
incorrect.
The setting procedure of transmission fluid level is shown as follows:
Caution:
When the transmission is in operating temperature, the hot transmission fluid may flow out form the
housing if remove the filling plug.
a. If the vehicle is in operating temperature, allow two hours time for cooling before add the transmission fluid, but
it must not more than 4 hours (this will make the transmission locate in the correct temperature range). When the
temperature is overheating, the transmission fluid level will higher than the plug port. Removal of plug will cause
the transmission fluid flows out from the oil filling port, then cause the low level of transmission fluid.
b. The gear-position of transmission is in parking-Gear (P-Gear), shut off the engine.
c. Lifting the vehicle (or parking above the trench).
d. Clean the around of plug when remove it. Then remove and clean the plug and check the O-ring for damage. Install
the oil filling pump in the oil filling hole.
e. Lower the vehicle; the oil filling pump will be connected to the vehicle at this time. Fill the transmission with the
oil partially. Then start the vehicle in P-Gear to rotate the engine in idle speed. Step down the foot brake, pull the
shifting lever in each gear-position in circulation and add the transmission fluid until the action of each gear-
position can be sensed.
f. Shut down the engine; lift the vehicle; ensure the vehicle is always in horizontal.
g. Remove the filling plug 3 minutes after the engine is shut off, but must not be no more than1 hour. At this time, the
correct level position should be in the bottom of oil filling hole. If does not reach the liquid level position, then fill
with few transmission fluid to make it reach the correct level.
h. Replace the transmission; clean the residual transmission fluid on the transmission and
vehicle.
i. Tighten the transmission plug to the specified torque of 30
35Nm.
Page 132 of 425

Caution:
Do not take out the central support by knocking the output shaft , otherwise, it will damage the surface of thrust bearing
permanently
o. Remove the central support, 1-2 one-way clutch and planetary gear block.
p. Use the T40 special tools to remove the parking lever cum disc.
q. Remove the rear brake belt support and rear brake belt.
r. Remove the output shaft assembly.
2. Transmission case
It should follow the following procedure when remove the transmission:
a. Use the tools to take out the fixed pin from one side of cross shaft gear sensor (2WD and 4WD mode).
b. Remove the gear sensor from the case. Use the special tools to take out the cross shaft seal.
c. Take out the circlip from the cross shaft. Pull up the cross shaft and take out the drive pin from the sector gear-position
selection plate.
d. Use the tools, press down the cross-shaft pin and take out the shaft , reset spring and bolt from the housing. Refer to Figure
8.3.
Figure 8.3 Installation and disassembly of cross-axle pinFigure 8.2 central support retainer
i. Use the pump remover to remove the pump, refer to Figure 8.1.
g. Remove the input shaft , front clutch cylinder and overspeed –Gear shaft as an integral. Take it out from the front of housing.
k. Remove the clutch C3 cylinder and central gear .
l. Remove the brake belt support and brake belt.
m. Use the 50 special tools to remove two central support connecting bolts.
n. Remove the central support retainer, refer to Figure 8.2.
Page 133 of 425

e. Take out the manual-operated valve operating lever and parking operating lever.
f. Take out the 10 pin socket connector form the wire bunch bracket adjacent gear sensor.
g. Press down the raised part of 10-pin plug and take out the 10-pin connecting plug from the box.
h. Separate the NO.7 solenoid valve wire bunch form the front end of housing.
i. Remove the brake bar pivot, brake shaft and spring.
j. Remove the shaft and rear servo operating lever.
k. Remove the rear servo cover and piston assembly.
l. Remove the BIR circlip, valve and spring.
m. Remove two brake belt adjusting shims.
n. Check the output shaft bush in box, replace it if necessary.
o. Check the cooler pipeline, replace it if necessary.
p. Check the box for damage.
Caution:
It must not remove the operating lever of parking gear in normal condition.
q. It needs to remove the P-Gear operating lever: take out the circlip from the pivot, knock the external of shaft until it can move
freely in box. Then use a width and thin object to table out the bolt form the box, operating lever and spring.
3. Front clutch cylinder
When take out the front clutch cylinder, please refer to Figure 8.4. The procedure is shown as follows:
Figure 8.4 Assembly of front clutch cylinder
a. Place the assembly on a level surface.
b. Remove the thrust bearing and adjusting shim from the input shaft .
c. Remove the retainer and input shaft form the front end of clutch .
d. Remove the overspeed gear shaft and clutch C1 hub assembly from the clutch cylinder.
e. Take out the clutch disk C1 form the cylinder.
f. Take out the retainer which fix the clutch C3 hub on the rear end of clutch cylinder, then take out the hub.
g. Take out the C2\clutch C4 hub assembly and remove the thrust bearing form the C4 hub.
h. Take out the clutch C2 disc.
i. Reverse the clutch cylinder and take out the clutch C4 sleeve, clutch disk and two wave washers. The 3-4 one-way clutches is
located between the C2 and clutch C4 hub. The other wheel axle can be taken out by rotating a wheel axle in clockwise.
j. Remove the thrust block form the clutch C4 cylinder hub.
Caution
Ensure the spring keeping device does not be clamped in the spring groove and all spring pressure is released.
k. Put end surface of C2\clutch C4 upwardly, connect the clutch cylinder with the tools. Pressed down the piston reset spring,
take out the spring fixing retainer (Refer to Figure 8.5). Remove the tools and take out the ring spring, fixing part and spring.