Oil leak HONDA CIVIC 1997 6.G Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: HONDA, Model Year: 1997, Model line: CIVIC, Model: HONDA CIVIC 1997 6.GPages: 2189, PDF Size: 69.39 MB
Page 1468 of 2189
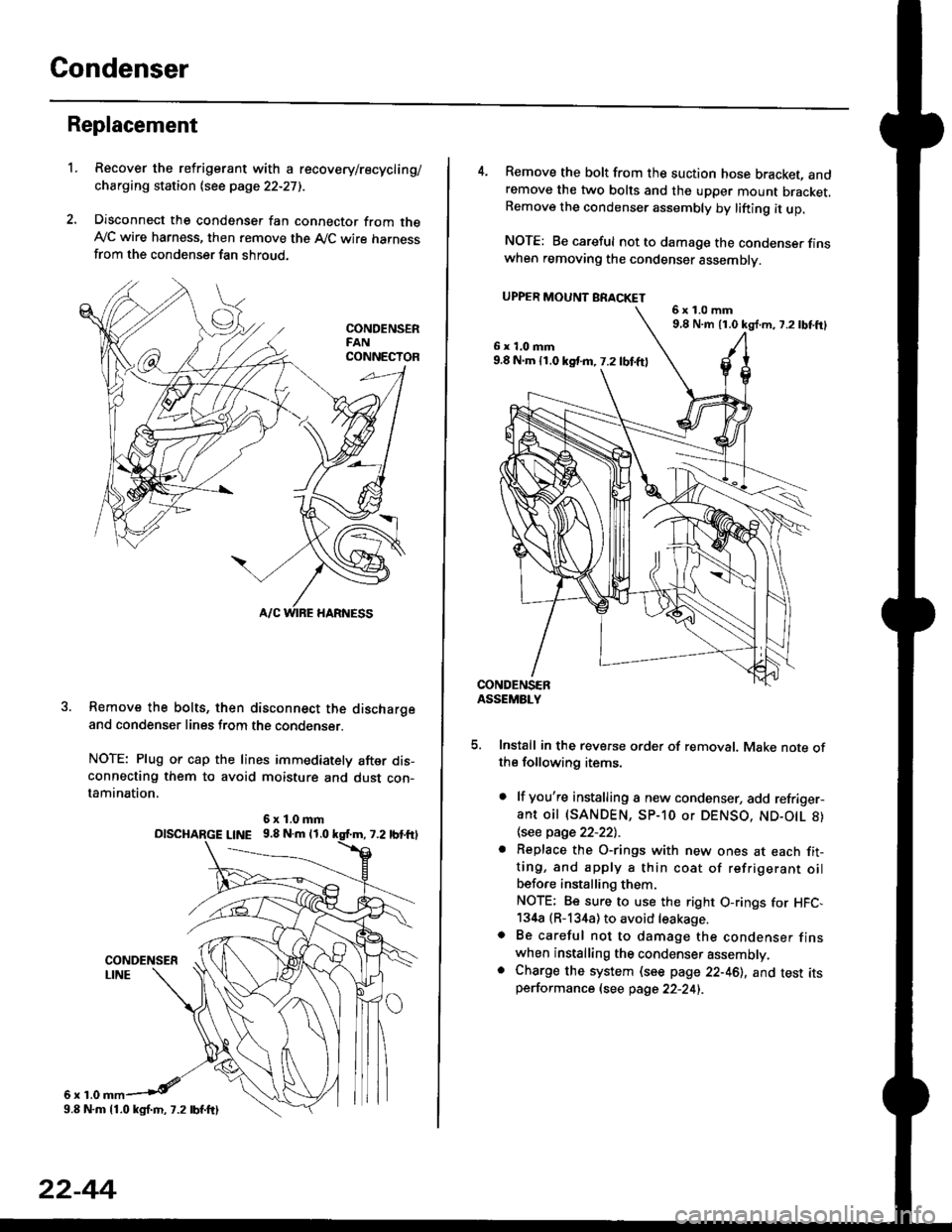
Condenser
Replacement
1.Recover the refrigerant with a recovery/recycling/
charging station lsee page 22-271.
Disconnect the condenser fan connector from theAy'C wire harness, then remove the A,/C wire harnessfrom the condenser fan shroud.
Remove the bolts, then disconnect the dischargeand condenser lines from the condenser.
NOTE: Plug or cap the lines immediately after dis-connecting them to avoid moisture and dust con-tamination,
6r1.0
6x1.0mmolscHARGE L|NE 9.8 N.m 11.0
9.8 N.m 11.0 kgl.m, 7.2 lbf.ftl
22-44
4. Remove the bolt from the suction hose bracket, andremove the two bolts and the upper mount bracket.Remove the condenser assembly by lifting it up.
NOTE: Be careful not to damage the condenser finswhen removing the condenser assembly.
UPPER MOUNT BRACKET
5. Install in the reverse order of removal. Make note ofthe following items.
. lf you're installing a new condenser, add refriger-ant oil (SANDEN, SP-10 or DENSO, ND-O|L 8)
\see page 22-22l.-
. Replace the O-rings with new ones at each fit-ting, and apply a thin coat of refrigerant oilbefo.e installing them.
NOTE; Be sure to use the right O-rings for HFC,134a (R-134a) to avoid leakage.o Be careful not to damage the condenser finswhen installing the condenser assembly.. Charge the system (see page 22-46), and test itsperformance (see page 22-24i.
6x1.0mm9,8 N.m 11.0 kg{.m, 7.2lbtft}
6x1.0mm9.8 N.m 11.0 kst m, 7.2 lbf.ftl
Page 1470 of 2189
A/C System Service
Charging
Use only service equipment that is U.L.-listed and is cer-
tified to meet the requirements of SAE J2210 to remove
HFC-134a (R-134a) from the air conditioner system.
CAUTION: Exposure to air conditioner refrigerant and
lubricant vapor or mist can irritale eyes, nose and
throat. Avoid breathing the air conditioner retrigerant
and lubricant vaoor or mist,
lf accidental system discharge occurs, ventilate workarea before resuming service, Additional health and
safety information may be obtained from the refrigerant
and lubricant manufacturers.
Refrigerant capacityt 600 - 650 g 121.1 - 22.9 ozl
CAUnON: Do not overcharg€ the system; the comprcssor
will be damaged.
Connect a R-134a refrigerant recovery/recycling/charging
station to the vehicle, as shown, following the equipment
manufacturer's instructions.
Recovery/Recycling/Charging Station
22-46
Leak Test
Use only service equipment that is U.L,-listed and is cer-
tified to meet the requirements of SAE J2210 to remove
HFC-134a (R-134a) from the air conditioner system.
CAUTION: Exposure io air conditioner refrigerant and
lubricant vapot or mist can itritats eyes, no36 and thtoat.
Avoid breathing the air conditioner refrigeranl and lubri-
cant vapor or mist,
lf accidental system discharge occurs, ventilate workarea betore resuming service.
R-134a service equipment or vehicle air conditioner sys-
tems should not be pressure tested or leak tested with
comoressed air.
@ some mixtures of air and R-134a have
been shown to be combugtibls at elevatgd prossures
and can result in tire or explosion causing iniuly orplopgrty damage. Nev€r usc compre33od air to pressure
test R-13'la servica oquipment or yohiclo air conditionor
systems.
Additional health and safety information may be obtained
from the refrigerant and lubricant manufacturers.
1. Connect a R-134a refrigerant recove rylrecycling/
charging station to the vehicle, as shown in the pre-
vious column, following the equipment manufactur-
er's instructions.
NOTE; Be sure to install the same amount of new
refrigerant oil back into the A,/C system before charg-In9.
Open the high-pressure valve to charge the system
to the specified capacity, then close the supply
valve, and remove the charging system couplers.
Rofrigerant capacity: 600 - 650 g (21.1 - 22.9 oz)
Check the system for leaks using a R-134a refriger-
ant leak detector with an accuracy of 14 9 10.5 ozlper yea. or better.
lf you find leaks that require the system to be opened(to repair or replace hoses. fittings. etc.), recover the
system according to the Recovery Procedure on page
22-27.
After checking and repairing leaks. the system must
be evacuated (see System Evacuation on page 22-451.
Page 1579 of 2189
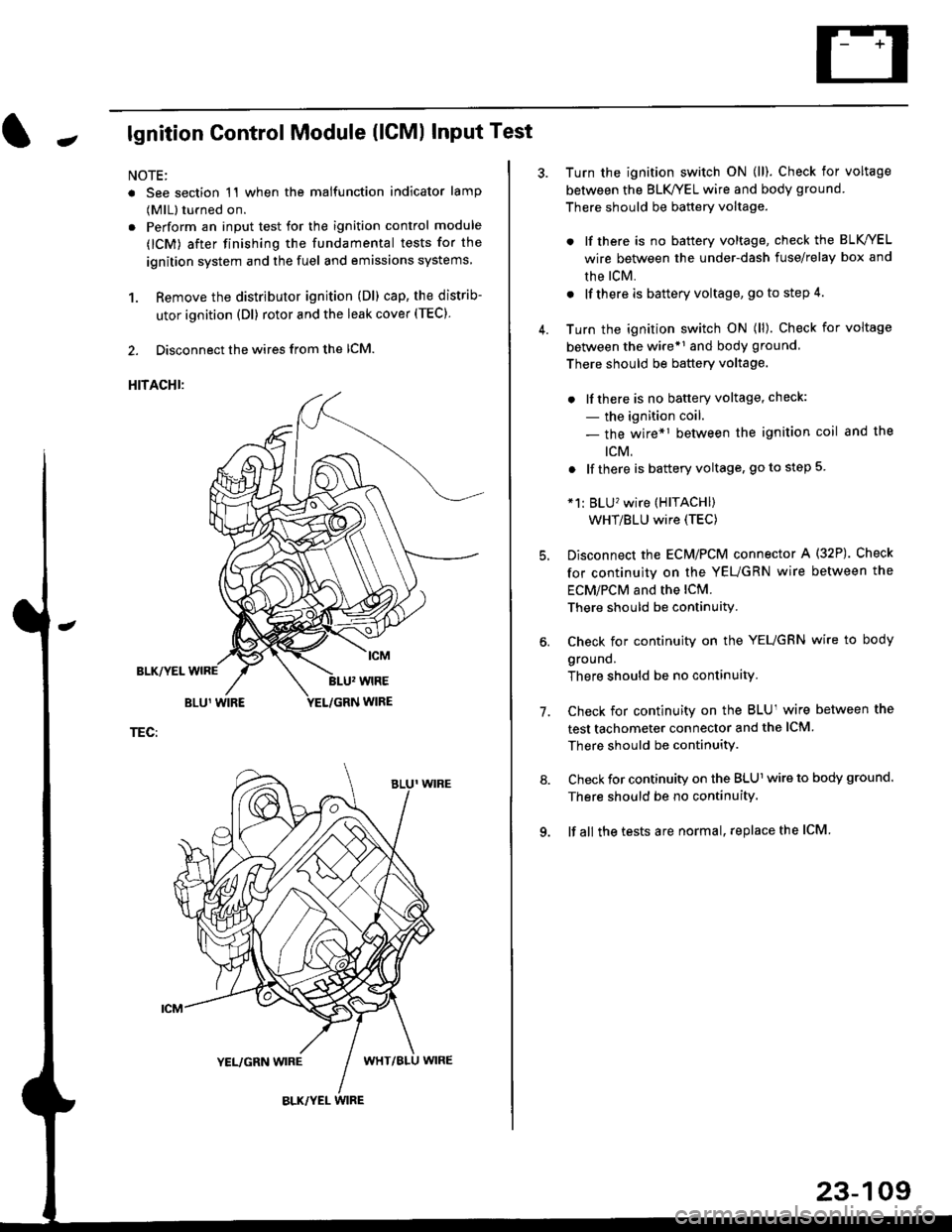
Jlgnition Control Module (lCMl Input Test
NOTE:
. See section 1'l when the malfunction indicator lamp
(MlL) turned on.
. Perform an input test for the ignition control module
(lCM) after finishing the fundamental tests for the
ignition system and the fuel and emissions systems
1. Remove the distributor ignition (Dl) cap, the distrib-
utor ignition (Dl) rotor and the leak cover (TEC).
2. Disconnect the wires from the lCM.
HITACHI:
BLK/YEL
TEC:
Turn the ignition switch ON (ll). Check for voltage
between the BLK/YEL wire and body ground.
There should be battery voltage.
. lf there is no battery voltage, check the BLK/YEL
wire between the under-dash fuse/relay box and
rhe lcM.
. lf there is battery voltage, go to step 4.
Turn the ignition switch ON (ll). Check for voltage
between the wire*r and body ground
There should be battery voltage.
. lfthere is no battery voltage, check:
- the ignition coil.
- the wire*1 between the ignition coil and the
tcM.
. lf there is battery voltage, go to step 5
*1: BLU'�wire (HITACHI)
WHT/BLU wire (TEC)
Disconnect the EcM/PCM connector A (32P). Check
for continuity on the YEUGRN wire between the
ECM/PCM and the lCM.
There should be continuity.
Check for continuity on the YEUGRN wire to body
ground.
There should be no continuity.
Check for continuity on the BLUl wire between the
test tachometer connector and the ICM
There should be continuitY.
Check for continuity on the BLUl wire to body ground.
There should be no continuity.
lf all the tests are normal, replace the ICM
7.
23-109
Page 1980 of 2189

Gauges (cont'd)
- How the Gircuit Works
When the ignition switch is in ON (ll) or START (lll),
battery voltage is supplied through fuse 25 to the
gauges in the gauge assembly.
Speedometer and Odometer
The odometer and soeedometer drive circuits
receive pulses from the vehicle speed sensor
(VSS). The pulse rate increases as the car
accelerates. The frequency and duration of these
input pulses are measured and displayed by the
speedometer, odometer and tripmeter.
Tachometer
The tachometer drive circuit receives pulses from
the ignition control module (lCM) in the distributor
assembly or the ECM/PCM. The solid-state
lachometer then displays these pulses as engine
speed. For each 200 pulses per minute from the
ignition control modul€ (lCM) or the ECM/PCM, the
tachometer displays 100 RPM.
Engine Coolant Temperature Gauge
The engine coolant temperature gauge has two
intersecting coils wound around a permanent
magnet rotor. Voltage applied to the coils, through
fuse 25, generates a magnetic lield. The magnetic
field, controlled by the coolant temperature sending
unit, causes the rotor to rotate and the gauge
needle to move. As the resistance in the sending
unit varies, current through the gauge coils
changes. The gauge needle moves toward the coil
with the strongest magnetic field.
The 6ngine coolant temperature sending unit's
resistance varies from about 137 ohms at low
engine temperature to between 3H6 ohms at high
temperature (radiator fan running).
Refer to the Service Manual (Section 23, Electrical)
for specific tests or troubleshooting procedures.
81-2
(
Fuel Gauge (All except cX)
The fuel gauge has two intersecting coils wound
around a permanent magnet rotor. Voltage applied
to the coils, through tuse 25, generates a magnetic
field. The magnetic field, controlled by the fuel
gauge sending unit, causes the rotor to rotate and
the gauge needle to move. As the resislance in the
sending unit varies, current through the gauge coils
changes. The gauge needle moves toward the coil
with the strongest magnetic field.
The fuel gauge sending unit's resistance varies
from about 2-5 ohms at full, to about 110 ohms at
empty. When you turn the ignition switch off, the
gauge remains at the last reading until you turn the
ignition switch to ON (ll) or START (lll) again,
Refer to the Service Manual (Section 23, Electrical)
for specific tests or troubleshooting procedures.
Fuel Gauge (GX)
The fuel gauge has two intersecting coils wound
around a permanent magnet rotor. Voltage applied
to the coils, through fuse 25, generates a magnetic
field. The magnetic field, controlled by the PCM,
causes the rotor to rotate and the gauge needle to
move. The PCM calculates the gas quantity in the
fuel tank by using the fuel pressure value detected
by the tuel tank pressure sensor and the fuel
temperature value detected by the fuel tank
temperalure sensor, and outputs the signal to the
gauge assembly. The gauge needle moves toward
the coil with the strongest magnetic field.
When you turn the ignition switch off , the gauge
remains at the last reading until you turn the ignition
switch to ON (ll) or START (lll) again. When the
PCM detects a malfunction with the fuel pressure or
temperature, or detects a gas leak, the PCM
reduces the fuel meter to 0.
Refer to the Service Manual GX Supplement
(Section 11 , Fuel and Emissions) for specific tests
or troubleshooting procedures.
a
a