gear shift HONDA CIVIC 1997 6.G Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: HONDA, Model Year: 1997, Model line: CIVIC, Model: HONDA CIVIC 1997 6.GPages: 2189, PDF Size: 69.39 MB
Page 690 of 2189
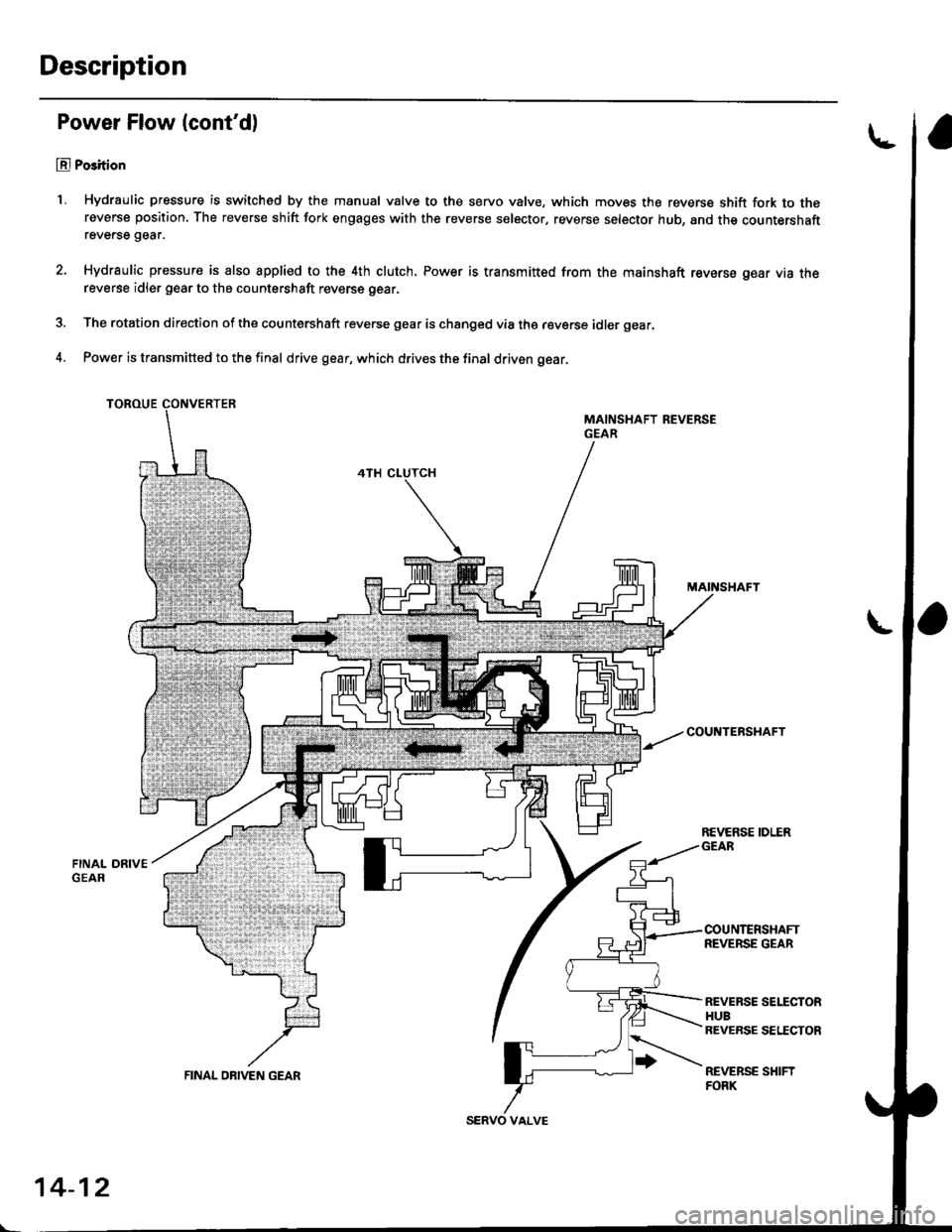
Description
Power Flow (cont'd)
El Po3ition
1, Hydraulic pressure is switched by the manual valve to the servo valve, which moves the reverse shift fork to thereverse position. The reverse shift fork engages with the reverse selector, reverse selector hub, and the countershaftreverse gear.
Hydraulic pressure is also applied to the 4th clutch. Power is transmitt€d from the mainshaft reverse gear via thereverse idler gear to the countershaft reverse gear.
The rotation direction of the countershaft reverse gear is changed via the reverse idler gear,
Power is transmitted to the final drive gear, which drives the final driven gear.
TOROUE
MAINSHAFT
COU TERSHAFT
REVERSE SELECTORHUBREVERSE SETICTOR
REVERSE SHIFTFORK
REVERSE IDLER
14-12
FINAL ON|VEN GEAR
Page 692 of 2189
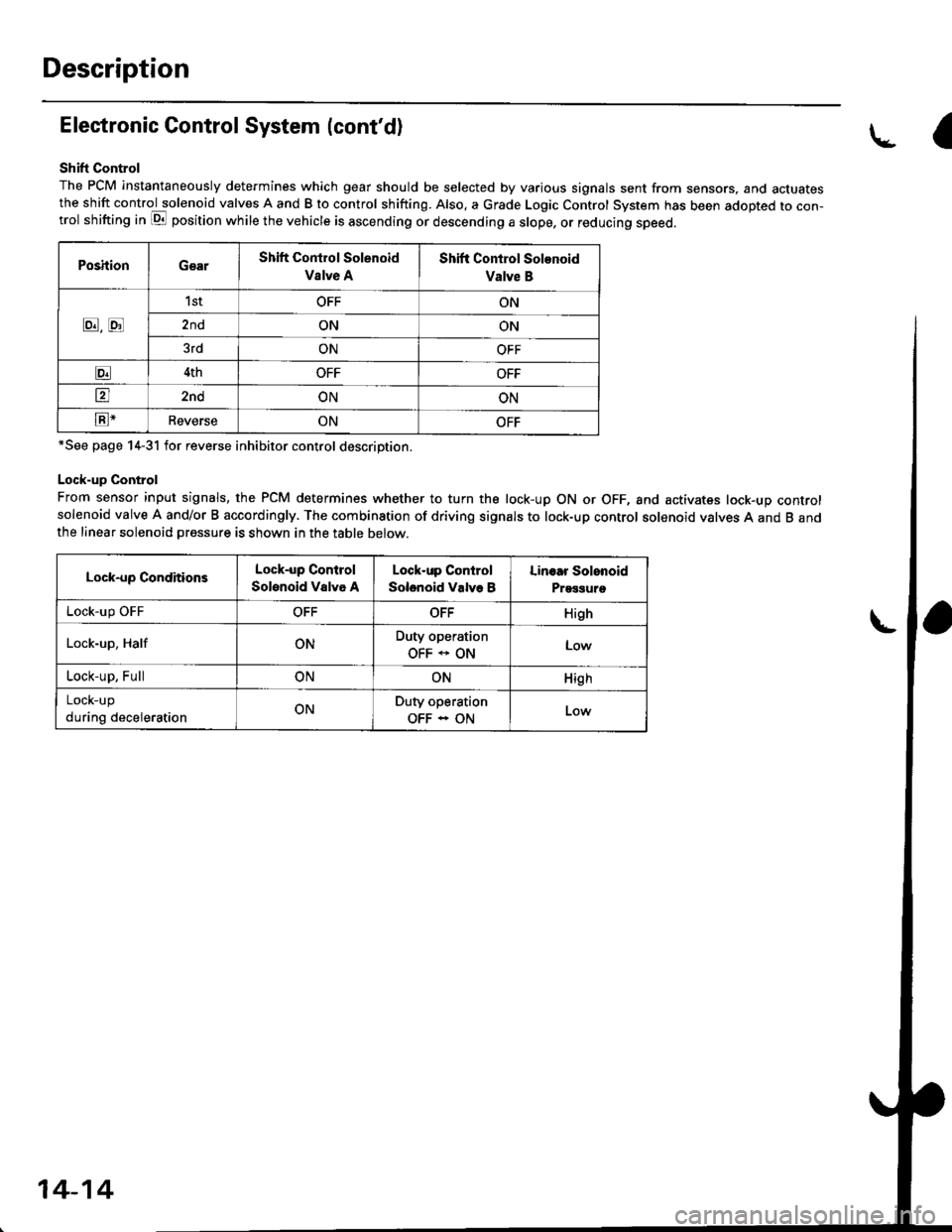
Description
Electronic Control System (cont'd)
Shift Control
The PCM instantaneously determines which gear should be selected by various signals sent from sensors, and actuatesthe shift control solenoid valves A and B to control shifting. Also. a Grade Logic Control System has been adopted to con-trol shifting in E position while the vehicle is ascending or descending a slope, or reducing speed.
PoshionGearShift Control Solenoid
Vslve A
Shift Control Solenoid
Valve B
8,tr
1stOFFON
2ndONON
3rdONOFF
E4thOFFOFF
tr2ndONON
E-ReverseONOFF
*See page 14-31 for reverse inhibitor control description.
Lock-up Control
From sensor input signals, the PCM determines whether to turn the lock-up ON or OFF, and activates lock-up controlsolenoid valve A and/or B accordingly. The combination of driving signals to lock-up control solenoid valves A and B andthe linear solenoid pressure is shown in the table below.
Lock-up ConditionsLock-up Control
Solenoid Valvo A
Lock-up Control
Solenoid Valve B
Linoar Solonoid
Prggguro
Lock-up OFFOFFOFFHigh
Lock-up, HalfONDuty operation
OFF * ONLow
Lock-up, FullONONHigh
LOCK-Up
during decelerationONDuty operation
OFF - ON
a
14-14
Page 694 of 2189
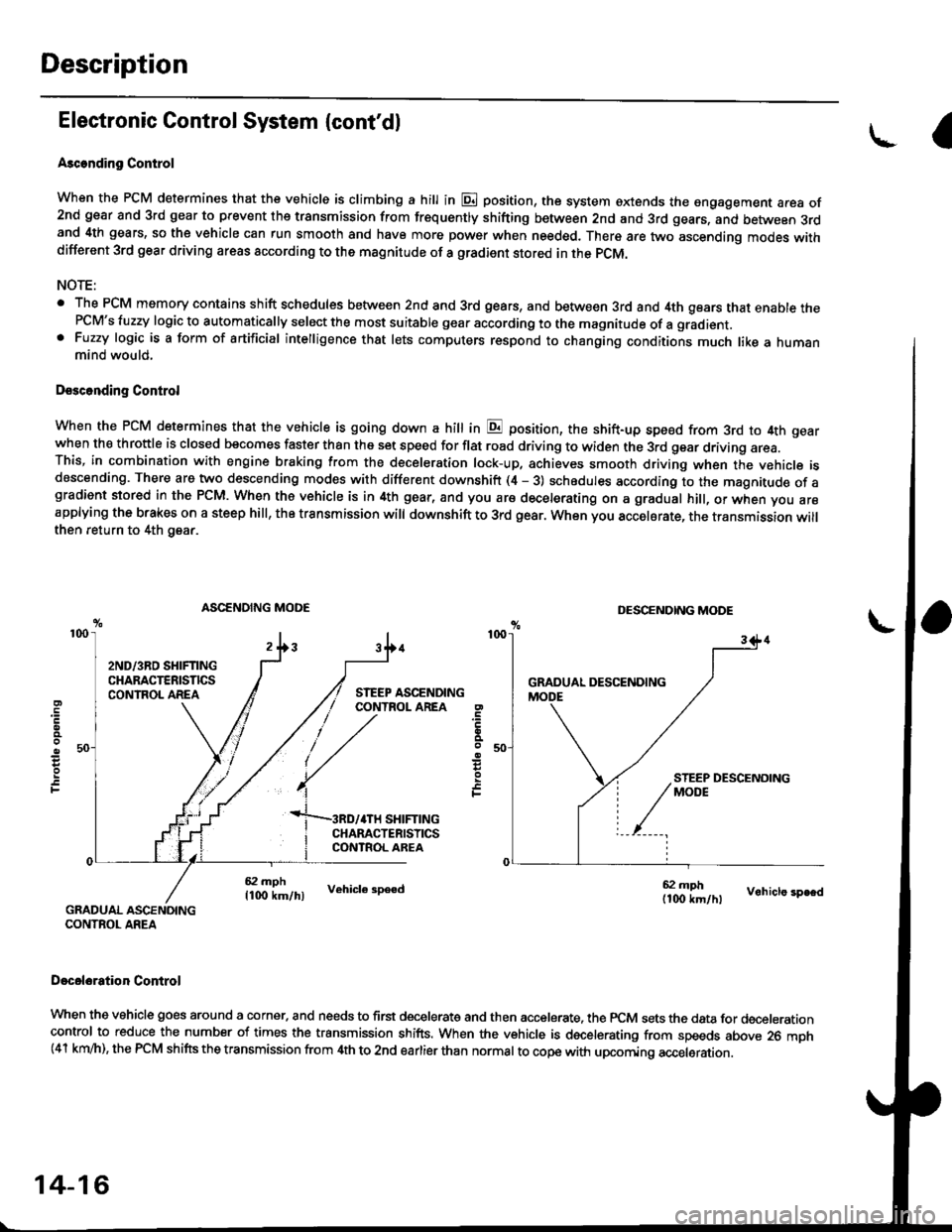
Description
Electronic Control System {cont'dl
Ascending Control
When the PCM determines that the vehicle is climbing a hill in E position, the system oxtends the sngagement area of2nd gear and 3rd gear to prevent ths transmission from fr€quently shifting between 2nd and 3rd gears, and between 3rdand 4th gears, so the vehicle can run smooth and have more power when needed. There are two ascending modes withdifferent 3rd gear driving areas according to the magnitude of a gradient stored in the pCM.
NOTE:
. The PCM memory contains shift schedules between 2nd and 3rd gears, and between 3rd and 4th gears that enable thePCM's fuzzy logic to automatically select the most suitable gear according to the magnitude of a gradient. Fuzzy logic is a form of artificial intelligence that lets computers respond to changing conditions much like a humanmind would,
Dssconding Control
When the PCM determines that the vehicle is going down a hilt in E position, the shift-up speed from 3rd to 4th gearwhen th€ throftle is closed becomes faster than the set speed for flat road driving to widen the 3rd gear driving area.This, in combination with engine braking from the deceleration lock-up, achieves smooth driving when the vehicle isdescending. There are two descending modes with different downshift (4 - 3) schedules according to the magnitude of agradient stored in the PCM. When the vehicle is in 4th gear, and you are decelerating on a gradual hill, or when you areapplying the brakes on a steep hill, the transmission will downshift to 3rd gear. When you accel6rate, the transmission willthen return to 4th gear.
ASCENDING MODEDESCENDING MODE
4TH SHIFTING
L.
F
CHARACTERISIICSCONTROL AREA
ff.1"11", vehicr. 3pe€dff;Tlr., vohicre speed
GRADUAL ASCENOINGCONTROL AREA
Docel6ration Control
When the vehicle goes around a corner. and needs to first decelerate and then accelerate. the rcM sets the data for decelerationcontrol to reduce the number of times the transmission shifts. When the vehicle is decelerating from speeds above 26 mph(41 km/h), the rcM shifts the transmission from 4th to 2nd earlier than normal to cope with upcoming acceleration.
14-16
Page 697 of 2189
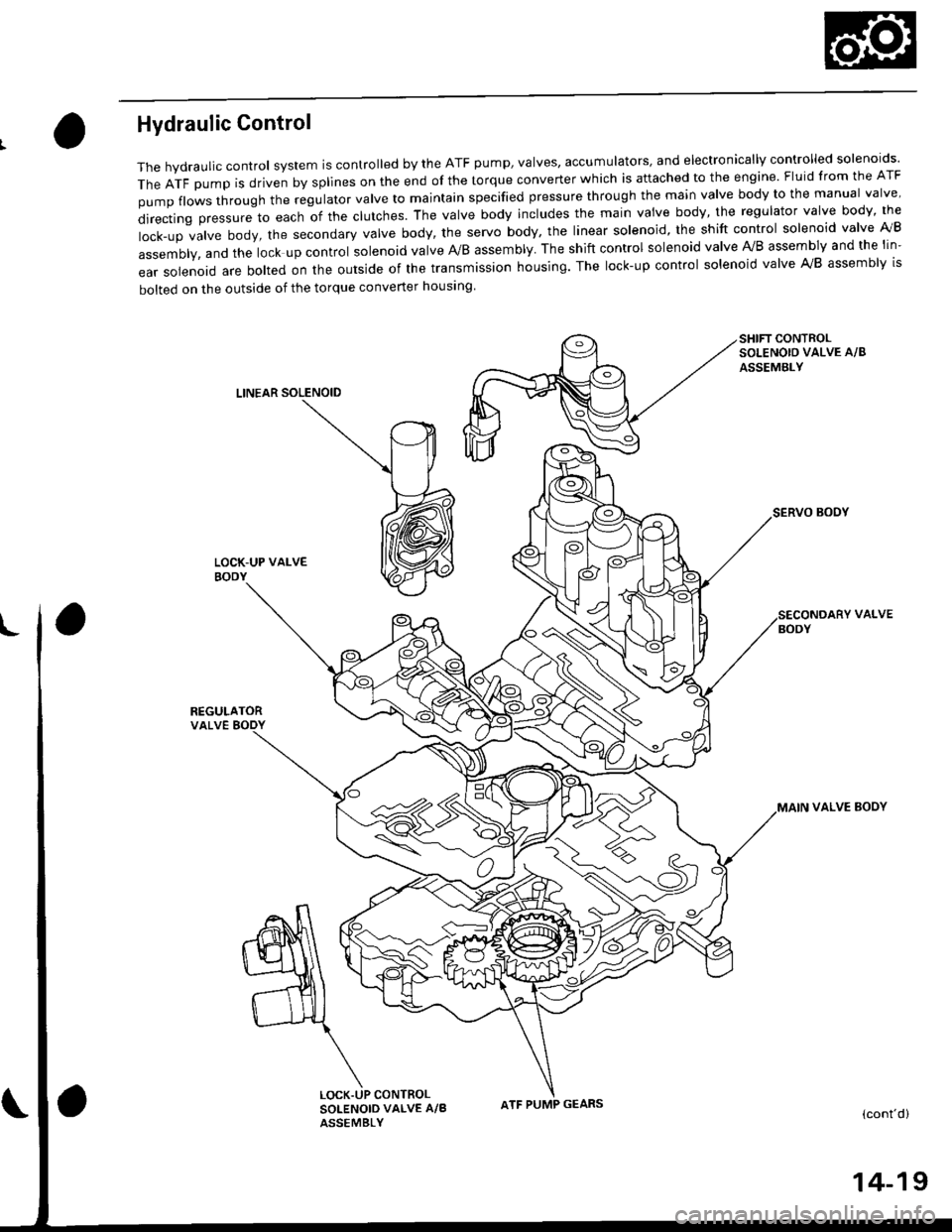
Hydraulic Control
The hydraulic control system is controlled by the ATF pump, valves, accumulators, and electronically controlled solenoids'
TheATFpUmpisdrivenbysp||nesontheendofthetorqueconverterWhichisattachedtotheengine.F|uidfromtheATF
pumpf|owsthroughtheregu|atorva|vetomajntainspecifiedpressurethroughthemainva|vebodytothemanuaIva|ve'
directingpressuretoeachofthec|utches.Theva|vebodyinc|udesthemainvaivebody,theregu|atorvalvebody,the
|ock-upva|vebody,thesecondaryVa|vebody,theservobody,theIinearso|enoid,theshiftcontro|so|enoidva|velVB
assembly, and the lock up control solenoid valve A/B assembly. The shift control solenoid valve Ay'B assembly and the lin-
ear solenoid are bolted on the outside of the transmission housing. The lock-up control solenoid valve A,/B assembly is
bolted on the outside of the torque converter housing
SHIFT CONTROLSOLENOIO VALVE A/8
ASSEMBLY
LINEAR SOLENOID
SERVO BOOY
REGULATORVALVE BODY
VALVE
VALVE BOOY
(cont'd)
CONTROLSOLENOID VALVE A/BASSEMBLY
ATF PUMP GEARS
14-19
Page 705 of 2189
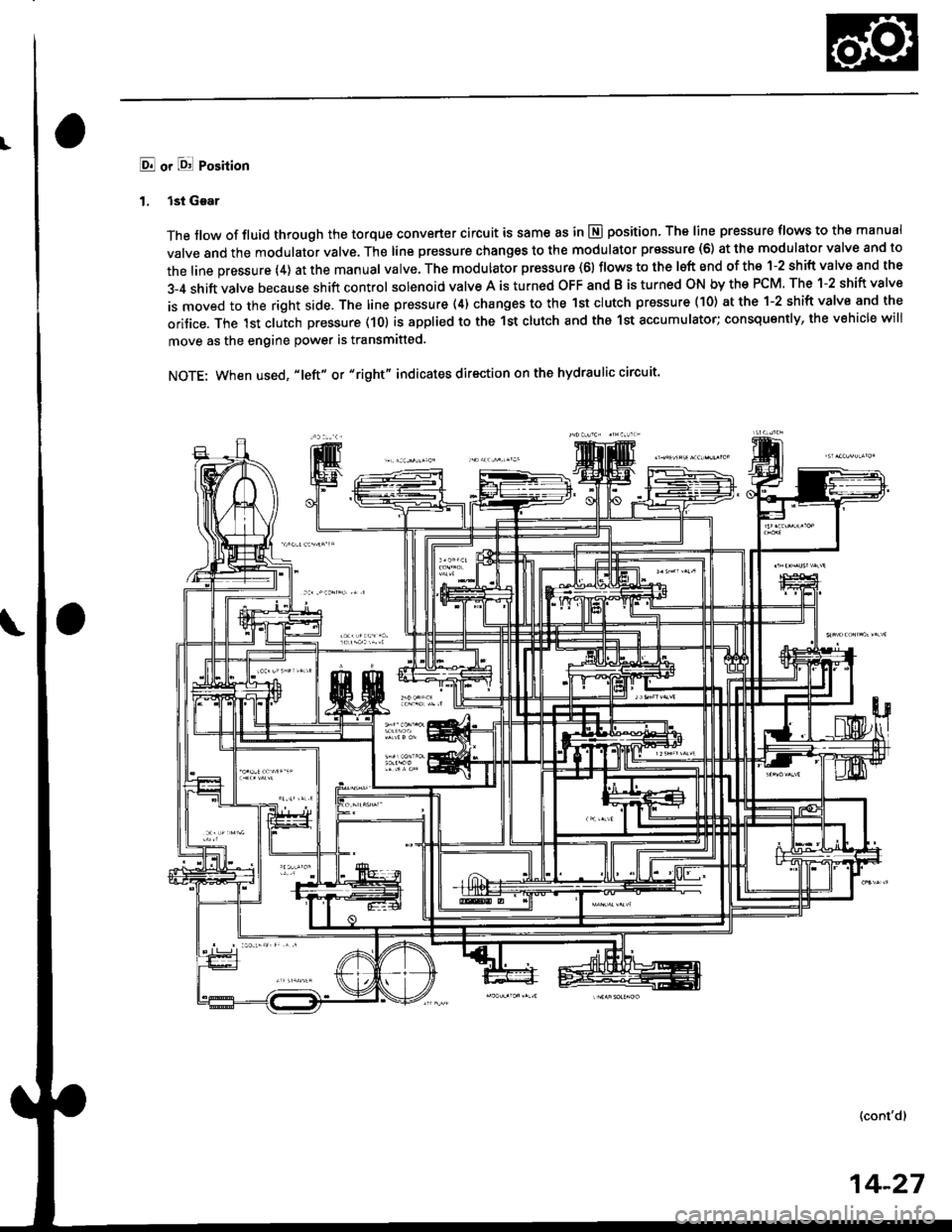
E! or l8! Position
1. lst Gear
The flow of fluid through the torque converter circuit is same as in E position, The line pressure tlows to the manual
valve and the modulator valve. The line pressure changes to the modulator pr€ssure (6) at the modulator valve and to
the line pressure (4) at the manual valve. The modulator pressure (61 flows to the lsft end of the 1-2 shift valve and the
3-4 shift valve because shift control solenoid valve A is turned OFF and B is turned ON by the PCM. The 1-2 shift valve
is moved to the right side. The line pressure (4) changes to the lst clutch pressure (10) at the 1-2 shift valve and the
oritice. The lst clutch pressure (10) is applied to the 1st clutch and tho 1st accumulator; consquently, the vehicle will
move as the engine power is transmitted.
NOTE: When used, "|eft" or "right" indicates direction on the hydraulic circuit'
(cont'd)
14-27
Page 707 of 2189
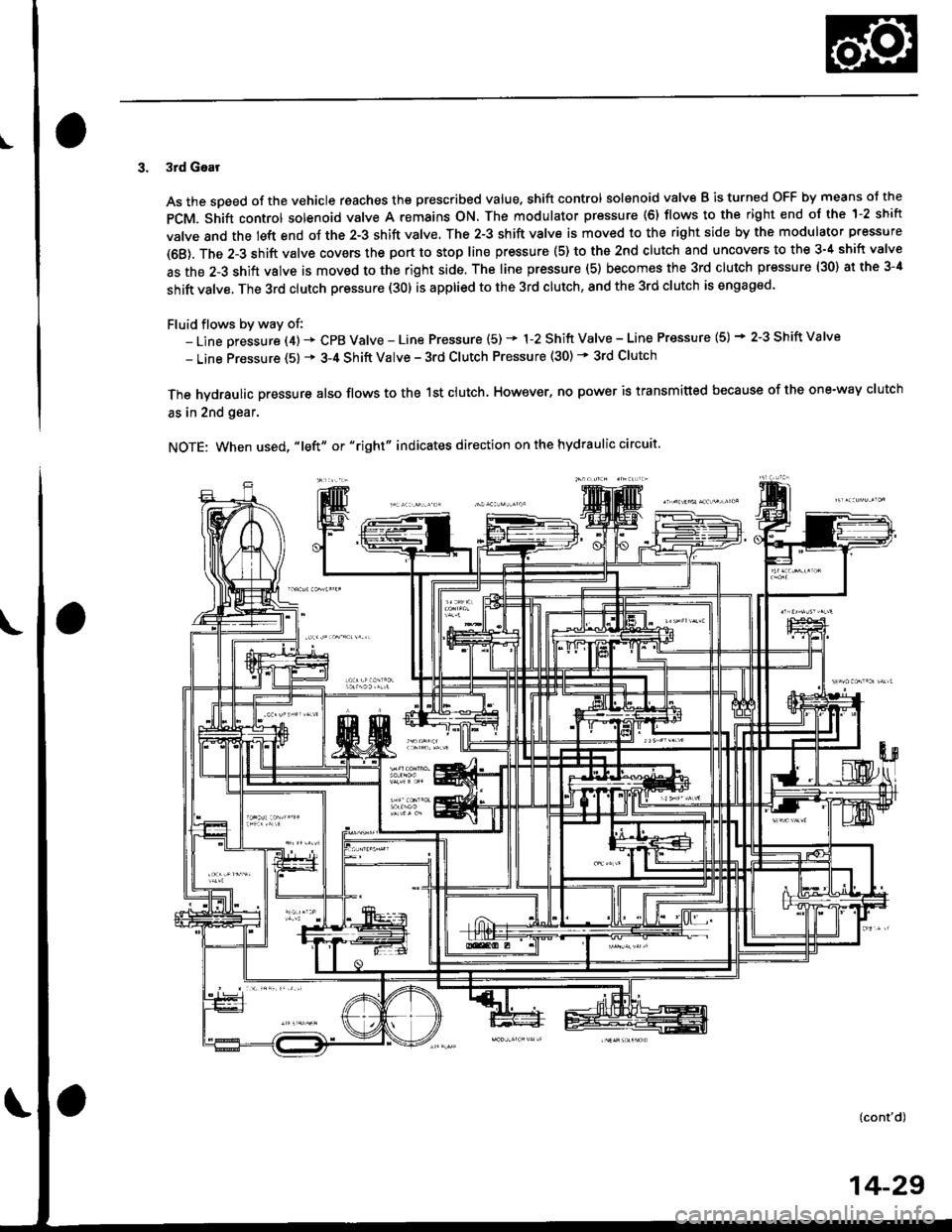
I
3. 3rd Gear
As the soeed of the vehicle reaches the prescribed value, shift control solenoid valve B is turned OFF by means ol the
pCM. Shift control solenoid valve A remains ON. The modulator pressure (6) flows to the right end of the 1-2 shift
valve and the left end oJ the 2-3 shift valve. The 2-3 shift valve is moved to the right side by the modulator pressure
(68). The 2-3 shift valve covers the port to stop line pressure (5) to the 2nd clutch and uncovers to the 3-4 shift valve
as the 2-3 shift valve is moved to the right side. The line pressure (5) becomes the 3rd clutch pressure (30) at the 3-4
shift valve. The 3rd clutch pressure (30) is applied to the 3rd clutch, and the 3rd clutch is engaged'
Fluid flows by way of:- Line Dressure (4) * CPB Valve - Line Pressure (5) * 1-2 Shift Valve - Line Pressure (5) * 2-3 Shift Valve
- Line Pressure (5) * 3-4 Shift Valve - 3rd Clutch Pressure (30) - 3rd Clutch
The hvdraulic pressure also flows to the 1st clutch. However, no power is transmitted because of the one-way clutch
as in 2nd gear.
NOTE: When used, "|eft" or "right" indicates direction on the hydraulic circuit.
14-29
Page 708 of 2189
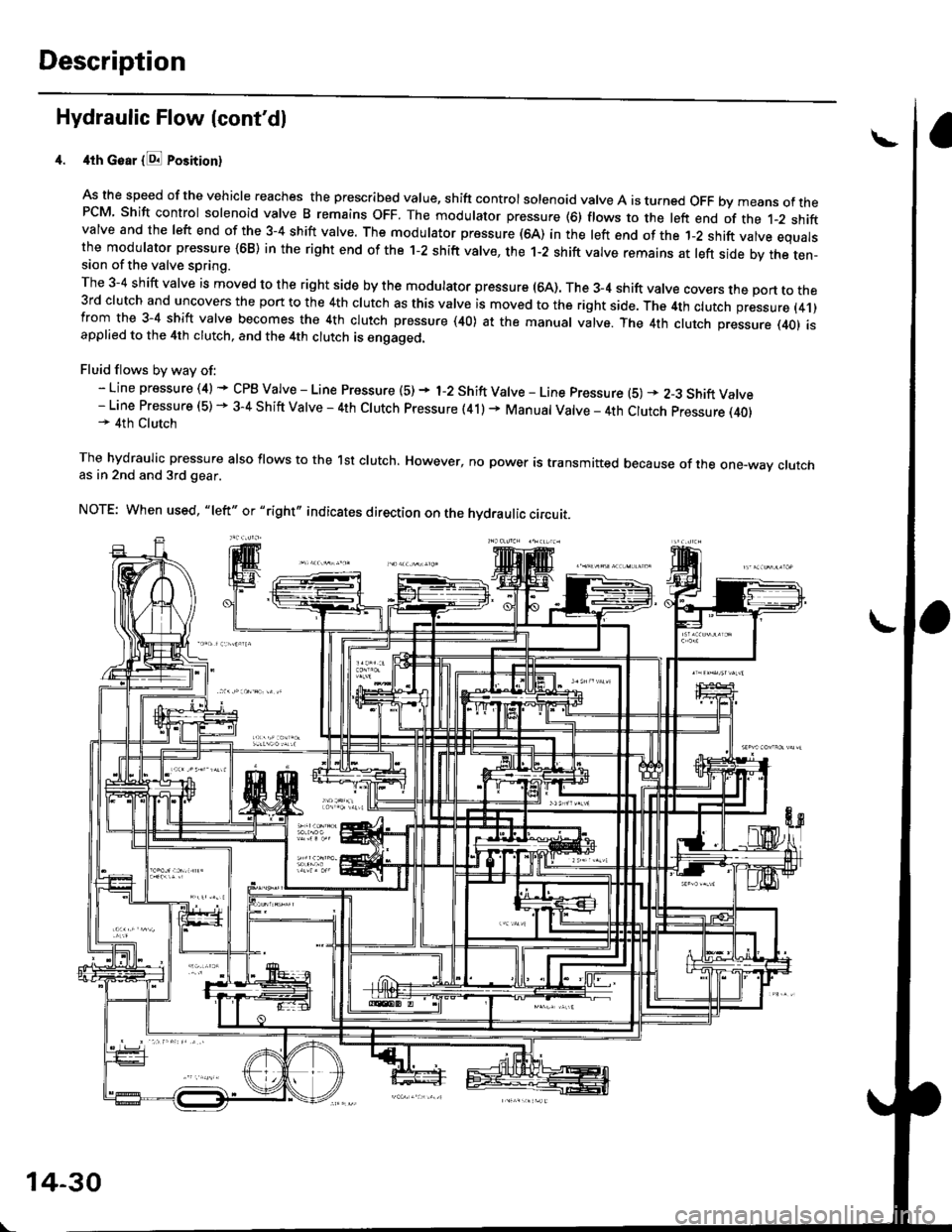
Description
Hydraulic Flow lcont'dl
4th Goar {E Position}
As the speed of the vehicle reaches the prescribed value, shift controlsolenoid valve A is turned OFF bymeans ofthePCM Shift control solenoid valve B remains oFF. The modulator pressure (6) flows to the left end of the t-2 shiftvalve and the left end of the 3-4 shift valve. The modulator pressure (64) in the left end of the 1-2 shift valve equalsthe modulator pressure {68) in the right end of the 1-2 shift valve, the 1-2 shift valve remains at left side by the ten-sion of the valve spring.
The 3-4 shift valve is moved to the right side by the modulator pressure (64). The 3_4 shift valve covers the port to the3rd clutch and uncovers the port to the 4th clutch as this valve is moved to the right side. The 4th clutch pressure (4.1)from the 3-4 shift valve becomes the 4th clutch pressure (40) at the manual valve. The 4th clutch pressure (401 isapplied to the 4th clutch, and the 4th clutch is engaged.
Fluid flows by way of:- Line pressure (4) * CPB Valve - Line Pressure (5) + 1-2 Shift Valve - Line pressure (5) * 2-3 Shift Valve- Line Pressure (5) - 3-4 Shift Valve - 4th Clutch pressure (41) + Manual Valve _ 4th Clutch pressure (40)* 4th Clutch
The hydraulic pressure also flows to the lst clutch. However, no power is transmitted because of the one-way crutchas in 2nd and 3rd gear.
NOTE: When used, "|eft" or "right,, indicates direction on the hydraulic circuit.
\
14-30
Page 721 of 2189
I
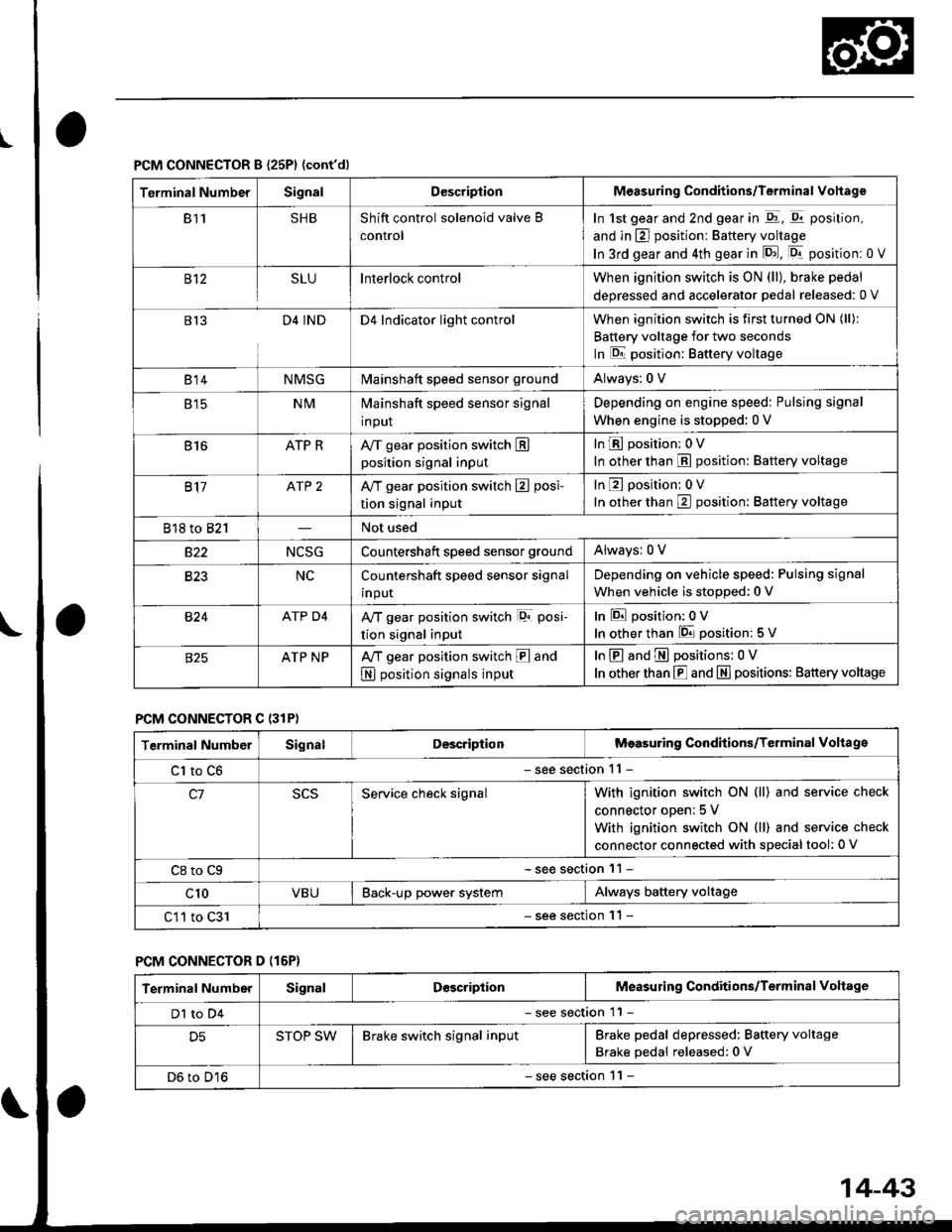
PCM CONNECTOR B {25P1 {cont'dl
Terminal NumberSignalDescriptionMeasuring Conditions/Terminal Vohage
811SHBShift control solenoid valve B
control
In 1st gear and 2nd gear in -q1, q11 position,
and in E] position: Battery voltage
In 3rd gear and 4th gear in lD.J, [Dr- position: 0 V
B't2SLUInterlock controlWhen ignition switch is ON (ll), brake pedal
deoressed and accelerator Dedal released: 0 V
813D4 INDD4 Indicator light controlWhen ignition switch is first turned ON (ll):
Battery voltage for two seconds
In E position: Baftery voltage
B't 4NMSGMainshaft speed sensor groundAlways: 0 V
E tcNMMainshaft speed sensor signal
input
Depending on engine speed: Pulsing signal
When engine is stopped: 0 V
816ATP RAy'T gear position switch Eposition signal input
InE position: 0V
In other than E position: Battery voltage
817ATP 2A/T gear position switch E posi-
tion signal input
InE position: 0V
In orher than E position: Battery voltage
818 to 821Not used
s22NCSGCountershatt speed sensor groundAlwaysr 0 V
B�23NCCountershaft speed sensor signal
input
Depending on vehicle speed: Pulsing signal
When vehicle is stopped: 0 V
B�24ATP D4Ay'T gear position switch lor posi-
tion signal input
InEposition:0V
In other than 6 position: 5 V
ATP NPA,/T gear position switch E and
N position signals input
InE and E positions: 0V
In otherthan E and N] positions: Battery voltage
PCM CONNECTOR C {31P)
Terminal NumberSignalDescriptionMeasuring Conditions/Terminal Voltage
Cl to C6- see section 11 -
c1Service check signalWith ignition switch ON (ll) and service check
connector oDen; 5 V
With ignition switch ON (ll) and service check
connector connected with sDecial tool: 0 V
C8 to Cg- see section 11 -
c10VBUBack-up power systemAlways battery voltage
C11 to C31- see section '11 -
PCM CONNECTOR D (16P}
Terminal NumberSignalDescriptionMeasuring Conditions/Terminal Voltage
Dl to D4- see section 11 -
D5STOP SWBrake switch signal inputBrake pedal depressed: Battery voltage
Brake pedal released: 0 V
D6 to D16- see section 1 l -
14-43
Page 725 of 2189
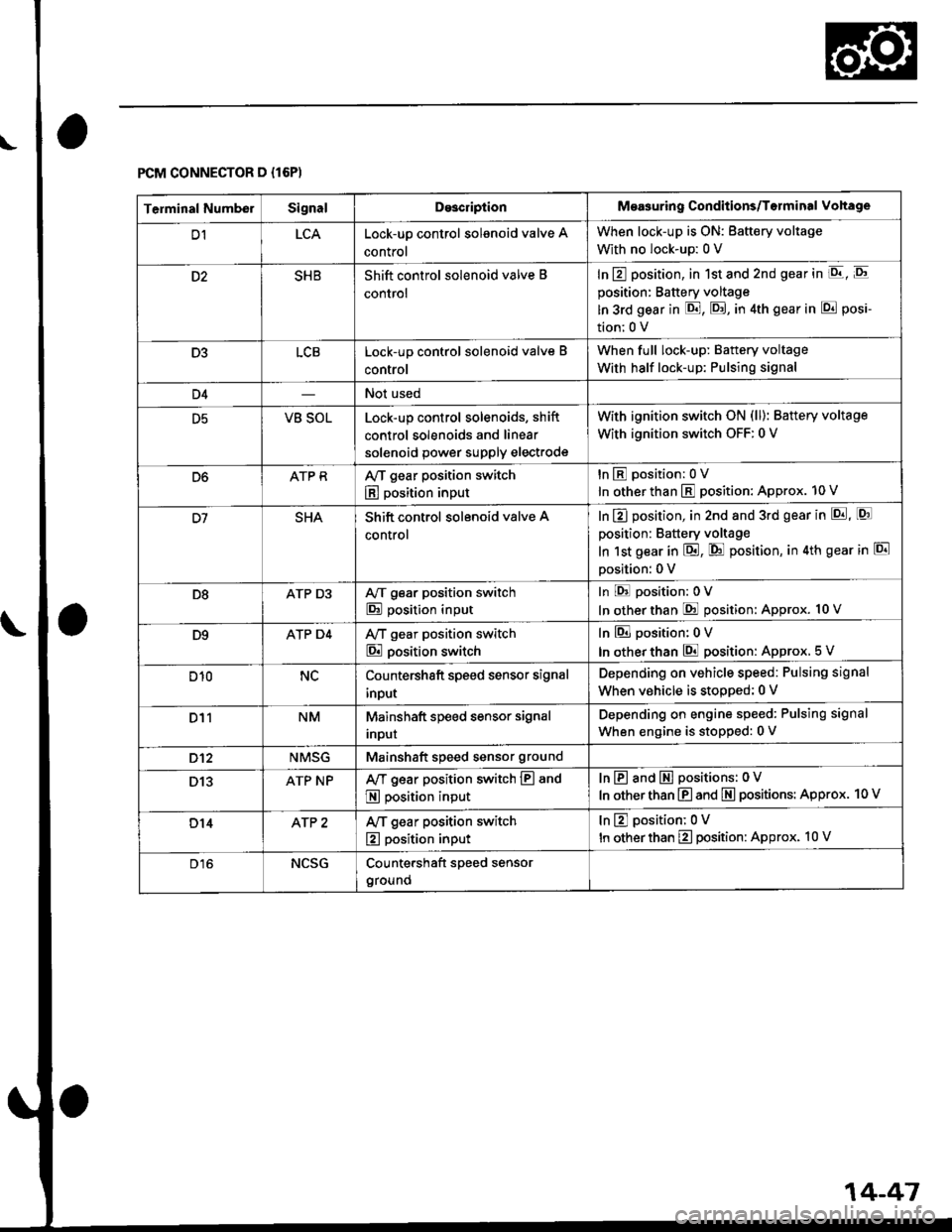
FCM CONNECTOR D {16P)
\o
14-47
Terminal NumberSignalDo3criptionMeasuring Conditions/Torminal Vohage
D1LCALock-up control solenoid valve A
control
When lock-up is ON: Battery voltage
With no lock-up: 0 V
SHBShift control solenoid valve B
control
In E position, in 1st and 2nd gear in E, E
position: Battery voltage
ln 3rd gear in E, E, in 4th gear in E posi-
tion;0 V
D3LCBLock-up control solenoid valve B
control
When full lock-up: Battery voltage
With half lock-up: Pulsing signal
D4Not used
D5VB SOLLock-up control solenoids, shift
control solenoids and linear
solenoid power supply electrode
with ignition switch oN (ll): Battery voltage
With ignition switch OFF: 0 V
D6ATP RAy'T gear position switch
E position input
tnEposition:0V
In other than E position: Approx. 10 V
SHAShift control solenoid valve A
control
In E] position, in 2nd and 3rd gear in p!, [Q]
position: Battery voltage
In 1st gear in E, @ position, in 4th gear in El
Dosition: 0 V
D8ATP D3A/T gear position switch
E position input
In E position:0V
In otherthan @ position: Approx. 10 V
D9ATP D4Ay'T gear position switch
E position switch
In El position: 0 V
In other than E position: Approx. 5 V
D10NCCountershaft speed sensor signal
input
Depending on vehicle speed: Pulsing signal
When vehicle is stooped: 0 V
D11NMMainshaft speed sensor signal
Inpur
Depending on engine speed: Pulsing signal
When engine is stopped: 0 V
D't2NMSGMainshaft speed sensor ground
D13ATP NPAy'T gear position switch E and
E position input
InE and E positions: 0V
In other than E and E positions: Approx. 10 V
D14AfP 2Ay'T gear position switch
E position input
tnEposition;0V
In other than E position: Approx. 10 V
D16NCSGCountershaft speed sensor
ground
Page 730 of 2189
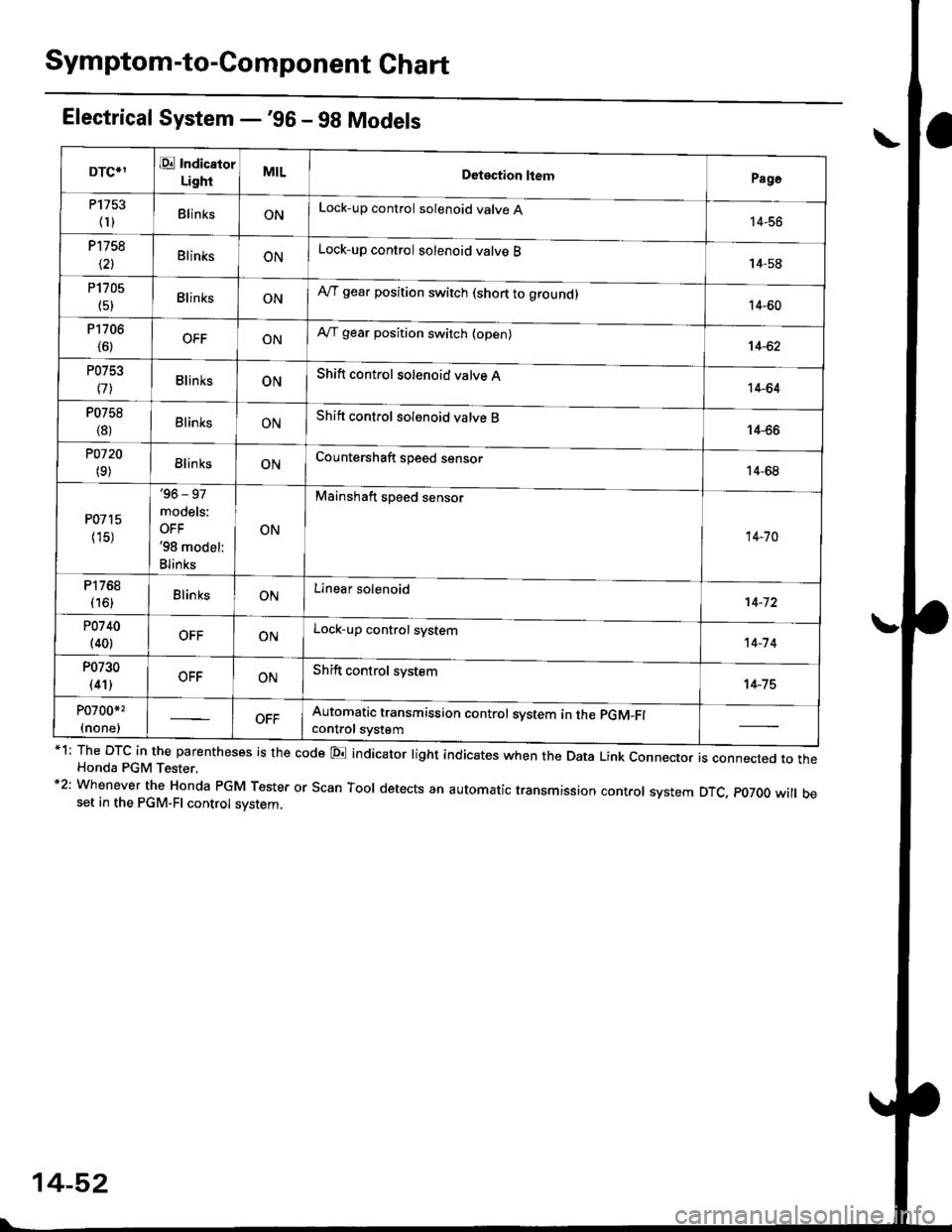
Symptom-to-Component Ghart
Electrical System -'gG - 98 Models
*1: The DTC in the parentheses is the code E indicator light indicates when the Data Link connector is connected to theHonda PGM Tester.*2: Whenever the Honda PGM Tester or Scan Tool detects an automatic transmission control system DTC, p07OO will beset in the PGM-FI control svstem.
DTCIIE Indicaior
LightMILDotection ltemPage
P1753
fl)BlinksONLock-up control solenoid valve A14-56
P1758
\21BlinksONLock-up control solenoid valve B14-58
P1705
(51BlinksONAy'T gear position switch (short to groundl14-60
P1706
(6)OFFONA,/T gear position switch (open)14-62
P0753
l7lBlinksONShift control solenoid valve A14-64
P0758
{8)ElinksONShift control solenoid valve B14-66
POl20
(9)BlinksONCountershaft speed sensor14-68
P0715
{15)
'96 - 97
models:
OFF'98 model:
Blinks
ON
Mainshaft speed sensor
14-70
P1768
{16)BlinksONLinear solenoid't 4-72
P0740
(40)OFFONLock-up control system14-7 4
P0730
(41)OFFONShift control system14-75
P0700*,
(none)Automatic transmission control svstem in the pGM-Fl
control svstem
14-52