pump HONDA CIVIC 1999 6.G Owners Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: HONDA, Model Year: 1999, Model line: CIVIC, Model: HONDA CIVIC 1999 6.GPages: 2189, PDF Size: 69.39 MB
Page 558 of 2189
\
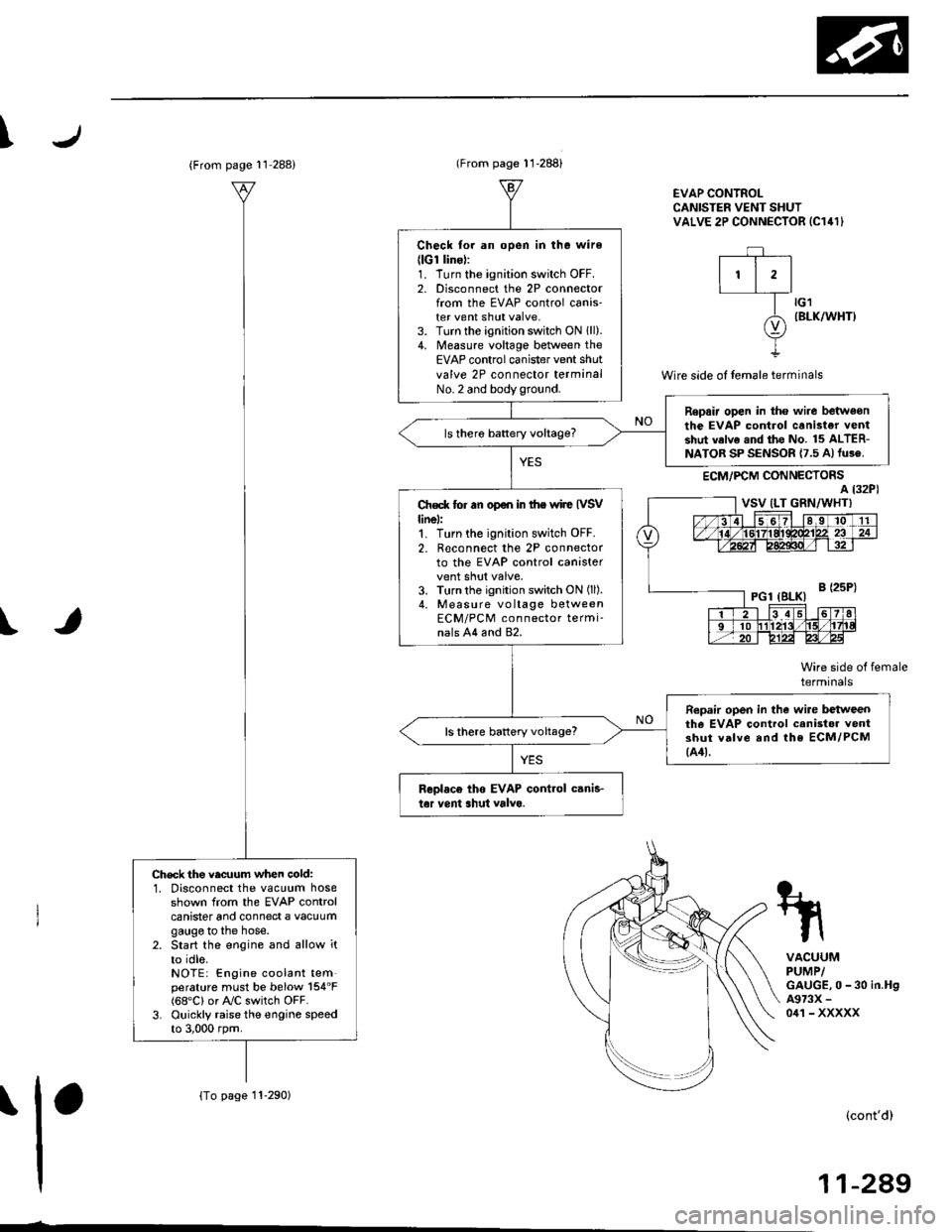
EVAP CONTROLCANISTER VENT SHUTVALVE 2P CONNECTOR IC141I
Wire side of temale terminals
ECM,/PCM CONNECTORS
tG1IBLK/WHT}
A973X -
0/r1 - XXXXX
Wire side of femaletermrnats
\
?,T-t
fl
VACUUMPUMP/GAUGE, 0 -30 in.Hg
\(cont'd)
11-289
{From page l1 288}
{To page 11-290)
Ch€ck the vac[um when cold:1, Disconnect the vacuum hoseshown from the EVAP controlcanister and connect a vacuumgauge to the hose.2. Start the engine and allow it
to idle.NOTEi Engine coolant temperature must be below 154"F(68'C) or Ay'C switch OFF.3. Ouickly raise the engine speedto 3,000 rpm.
(From page 11-288)
Check for an open in tha wire(lGt linol:1. Turn the ignition switch OFF.2. Disconnect the 2P connectorfrom the EVAP control canis-ter vent shut valve.3. Turn the ignition switch ON lll).4. Measure voltage between theEVAP control canister vent shut
valve 2P connector terminalNo.2 and bodyground.
Repair open in the wire betweenthe EVAP control canister ventshut valve .nd the No. 15 ALTER-NATOR SP SENSOR {7.5 A)fu3e.
ls there battery voltage?
Ch€d( for an op€n in the wiie IVSVlinel:1. Turn the ignition switch OFF.
2. R€connect the 2P connectorto the EVAP control canistervent shut valve,3. Turn the ignition switch ON (ll).
4. Measure vo ltage betweenECM/PCM connector termi-nals A4 and 82.
Repair open in the wire bctweenthe EVAP control canistor ventshut valve and lhe ECM/PCM{44t.
ls there battery voltage?
Rcolaco tho EVAP control canis.t6r vent shut valvo.
a t32P)
-
Page 560 of 2189
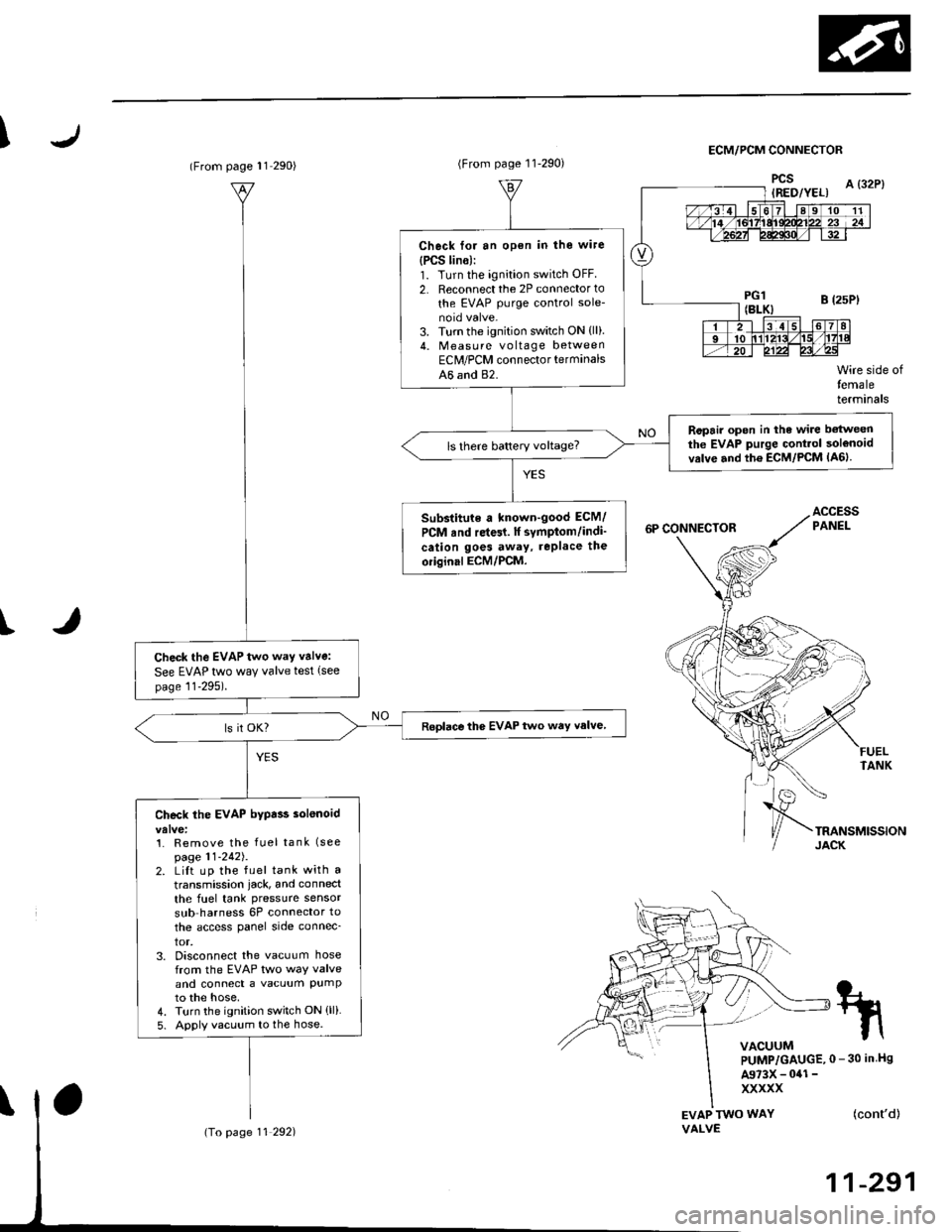
IECM/PCM CONNECTOR
I
EVAP TWO WAYVALVE
Wire side oftemaleterminals
FUELTANK
(cont'd)
11-291
tn
VACUUMPUMP/GAUGE,0 - 30 in Hs
A973X - 041 -
xxxxx
(From page l1 290)
Check the EVAP two way valve:
See EVAP two way valve test (see
page 11-295).
Roplace the EVAP two way valve
Check the EVAP bypa$ solenoid
1. Remove the fuel tank (see
page 11-242J.2. LiIt up the fuel tank with a
transmission iack, and connect
the fuel tank pressure sensor
sub harness 6P connector to
the access panel side connec_
tor,3. Disconnect the vacuum hosefrom the EVAP two way valveand connect a vacuum PumPto the hose,4. Turn the ignition switch ON (ll)
5. Apply vacuum to the hose.
(To page 11 292)
(From page 11-290)
Check for an open in the wire
{PCS lin6):1. Turn the ignition switch OFF
2. Reconnect the 2P connector to
the EVAP purge control sole-
3. Turn the ignition switch ON {ll).4. Measu re voltage betweenEClr/PCM connector terminals
A6 and 82.
Ropair open in the wire betweenthe EVAP purge Gontrol solenoidvrlve and th6 ECM/PCM lA6lls there battery voltage?
Substitute a known-good ECM/
PCM rnd re{61. lf symptom/indi'
cation goes away, rePlace the
oiiginal ECM/PCM.
Page 563 of 2189
Emission Control System
Evaporative Emission (EVAPI Controls (cont'd)
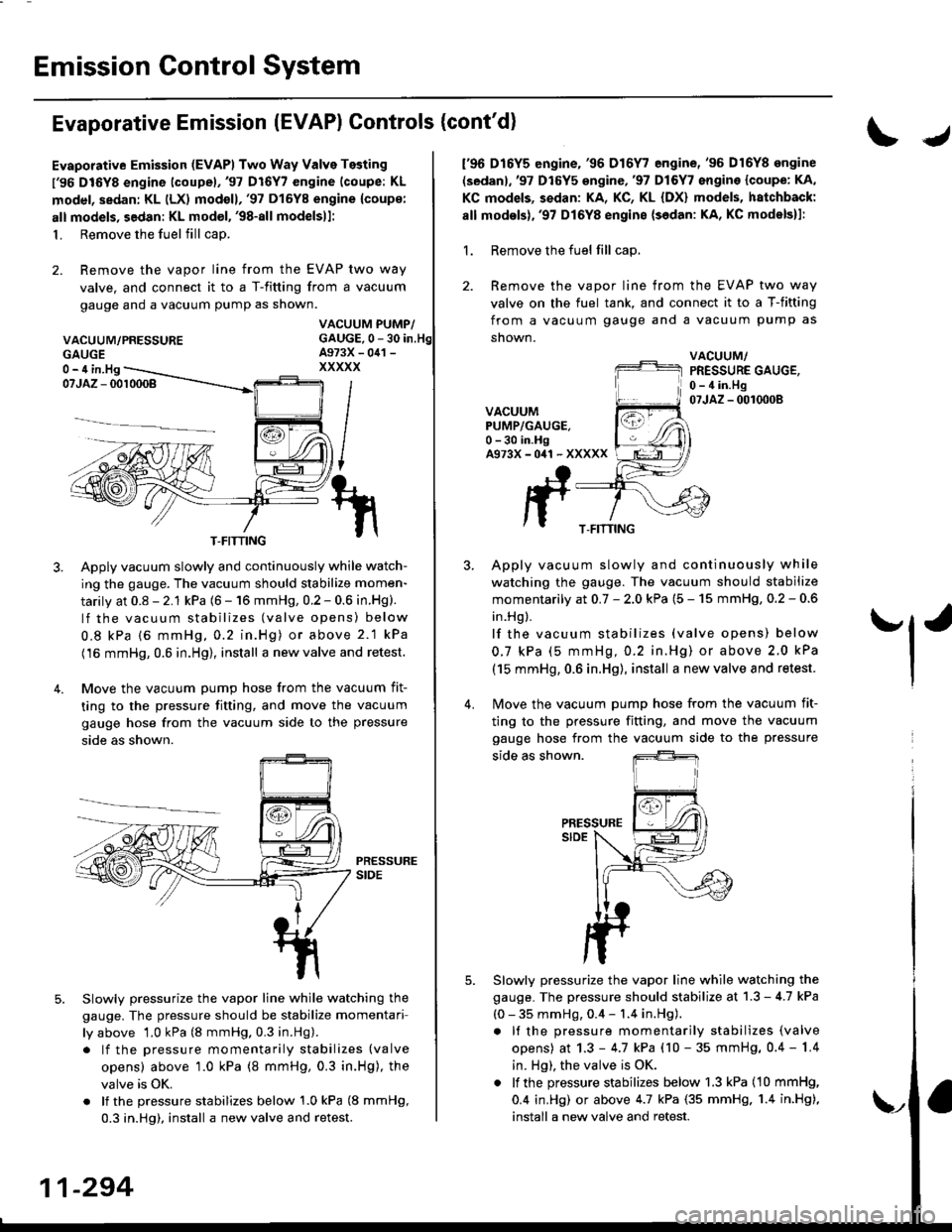
Evaporative Emission (EVAPI Two Way Valve Testing
l'96 DIGYS engine lcoupel,'97 Dl6Y7 engine (coupe: KL
model, sedan: KL (LX) modoll,'97 Dl6Y8 engine {coup€:
alt models, sedan: KL model, '98-all modelsll:
1. Remove the fuel fill cap.
2. Remove the vapor line from the EVAP two way
valve. and connect it to a T-fitting from a vacuum
gauge and a vacuum pump as shown.
VACUUM/PRESSURE
IJ
f96 D16Y5 engine,'96 D16Y7 engine,'96 D16Y8 ongine
(sedanl,'97 D16Y5 engine,'97 Dl6Y7 engine {coupe: KA,
KC models, sedan: KA, KC, KL {DX} models, hatchback:
all modsls),'97 D16Y8 engine {sedan: KA, KC models}l:
1. Remove the fuel fill cap,
2. Remove the vapor line from the EVAP two way
valve on the fuel tank, and connect it to a T-fitting
from a vacuum gauge and a vacuum pump as
snown.
VACUUM/PRESSURE GAUGE,0 - 4 in.Hg07JAZ - 0010008VACUUMPUMP/GAUGE.0 -30 in.HgA973X-041 -XXXXX
Apply vacuum slowly and continuously while watch-
ing the gauge. The vacuum should stabilize momen-
tarily at 0.8 - 2.1 kPa (6 - 16 mmHg, 0.2 - 0.6 in.Hg).
lf the vacuum stabilizes (valve opens) below
0.8 kPa {6 mmHg, 0.2 in.Hg) or above 2.1 kPa
(16 mmHg, 0.6 in.Hg), install a new valve and retest.
Move the vacuum pump hose from the vacuum fit-
ting to the pressure fitting, and move the vacuum
gauge hose from the vacuum side to the pressure
side as shown.
Slowlv pressurize the vapor line while watching the
gauge. The pressure should be stabilize momentari
ly above 1.0 kPa (8 mmHg. 0.3 in.Hg).
. lf the pressure momentarily stabilizes (valve
opens) above '1.0 kPa (8 mmHg, 0.3 in.Hg), the
valve is OK.
. lf the pressure stabilizes below 1.0 kPa (8 mmHg,
0.3 in.Hg), install a new valve and retest.
Apply vacuum slowly and continuously while
watching the gauge. The vacuum should stabilize
momentarily at 0.7 - 2.0 kPa (5 - 15 mmHg, 0.2 - 0.6
in.Hg ).
lf the vacuum stabilizes (valve opens) below
0.7 kPa (5 mmHg,0.2 in.Hg) or above 2.0 kPa
(15 mmHg, 0.6 in.Hg), install a new valve and retest.
Move the vacuum pump hose from the vacuum fit-
'l'
4.
5.
ting to the pressure fitting, and move the
gauge hose from the vacuum side to the
side as shown.
PRESSURESIDE
Slowly pressurize the vapor line while watching the
gauge. The pressure should stabilize at 1.3 - 4.7 kPa
(0 - 35 mmHg, 0.4 - 1.4 in.Hg).
. It the pressure momentarily stabilizes (valve
opens) at 1.3 - 4.7 kPa (10 - 35 mmHg, 0.4 - 1.4
in. Hg), the valve is OK.
. lf the pressure stabilizes below 1.3 kPa (10 mmHg,
0.4 in.Hg) or above 4.7 kPa (35 mmHg. 1.4 in.Hg),
install a new valve and retest.
vacuum
pressure
GAUGE0- 4 in.Hg
T-FITTINGT-FITTING
11-294
\,
Page 564 of 2189
\
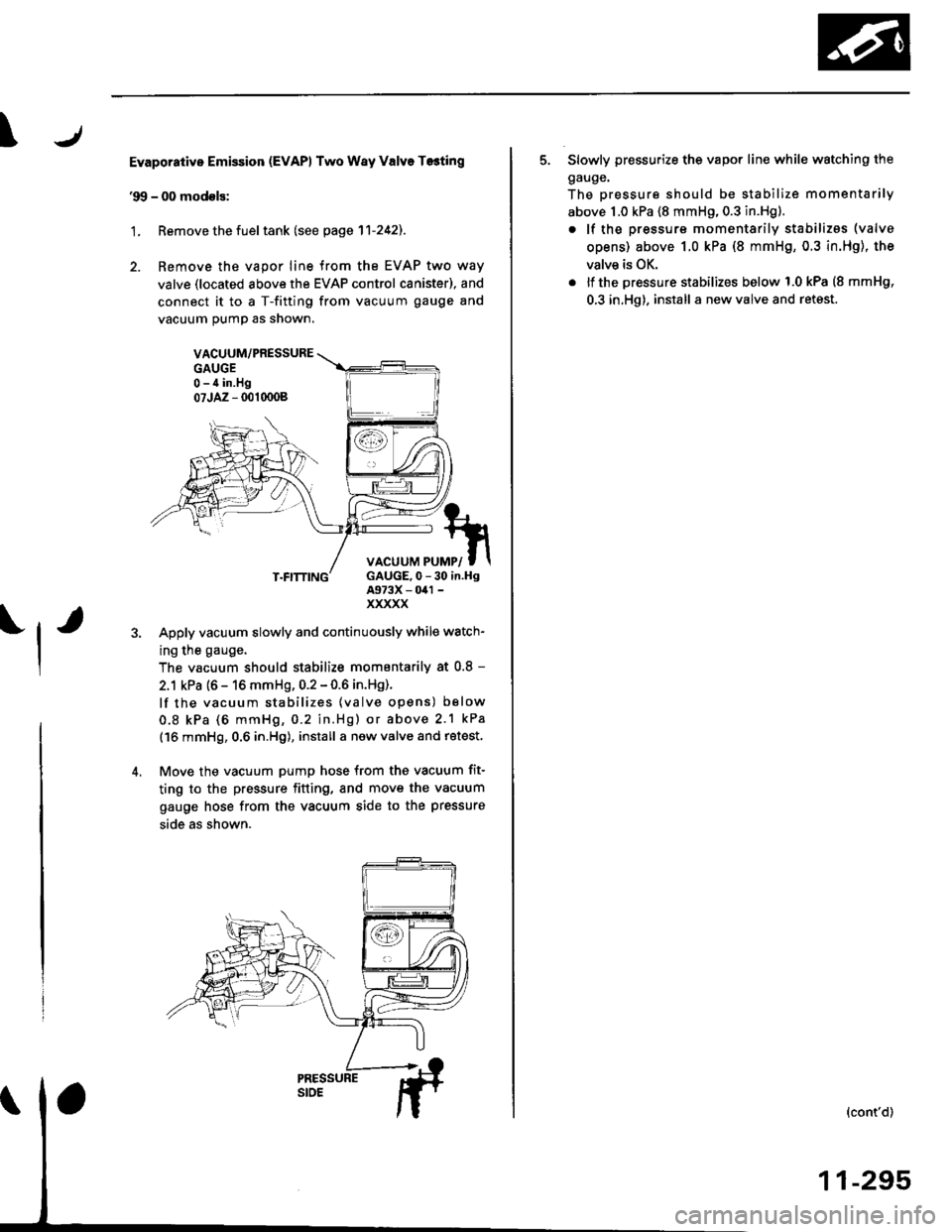
Evaporative Emission (EvAPl Two Way Valve T6ting
'99 - 00 modols:
'L Remove the fuel tank (see page 11-242).
2. Remove the vapor line {rom the EVAP two way
valve (located above the EVAP control canister), and
connect it to a T-fitting from vacuum gauge and
vacuum pumo as snown,
VACUUM/PRESSUREGAUGE0 - il in.Hg07JAZ - 001(x)08
ry(L
"*'"""_,";f1
T.FITTING
Apply vacuum slowly and continuously while watch-
ing the gauge.
The vacuum should stabilize momentarily at 0.8 -
2.1 kPa {6 - 16 mmHg, 0.2 - 0.6 in.Hg).
lf the vacuum stabilizes (valve opens) below
0.8 kPa (6 mmHg, 0.2 in.Hg) or above 2.1 kPa
(16 mmHg, 0.6 in.Hg), install a nsw valve and retest.
Move the vacuum pump hose from the vacuum fit-
ting to the pressure fitting, and move the vacuum
gauge hose from the vacuum side to the pressure
side as shown.
GAUGE,0 - 30 in.Hg4973X - (Xl -
xxxxx
J.
5. Slowly pressurize the vapor lin€ while watching the
gauge.
The pressure should be stabilize momentarily
above 1.0 kPa (8 mmHg, 0.3 in.Hg).
. lf the pressure momentarily stabilizes (valve
opens) above 1.0 kPa (8 mmHg, 0.3 in.Hg), the
valve is OK.
. ll the pressure stabilizes below 1.0 kPa (8 mmH9,
0,3 in,Hg), install a new valve and retsst.
(cont'd)
11-295
Page 565 of 2189
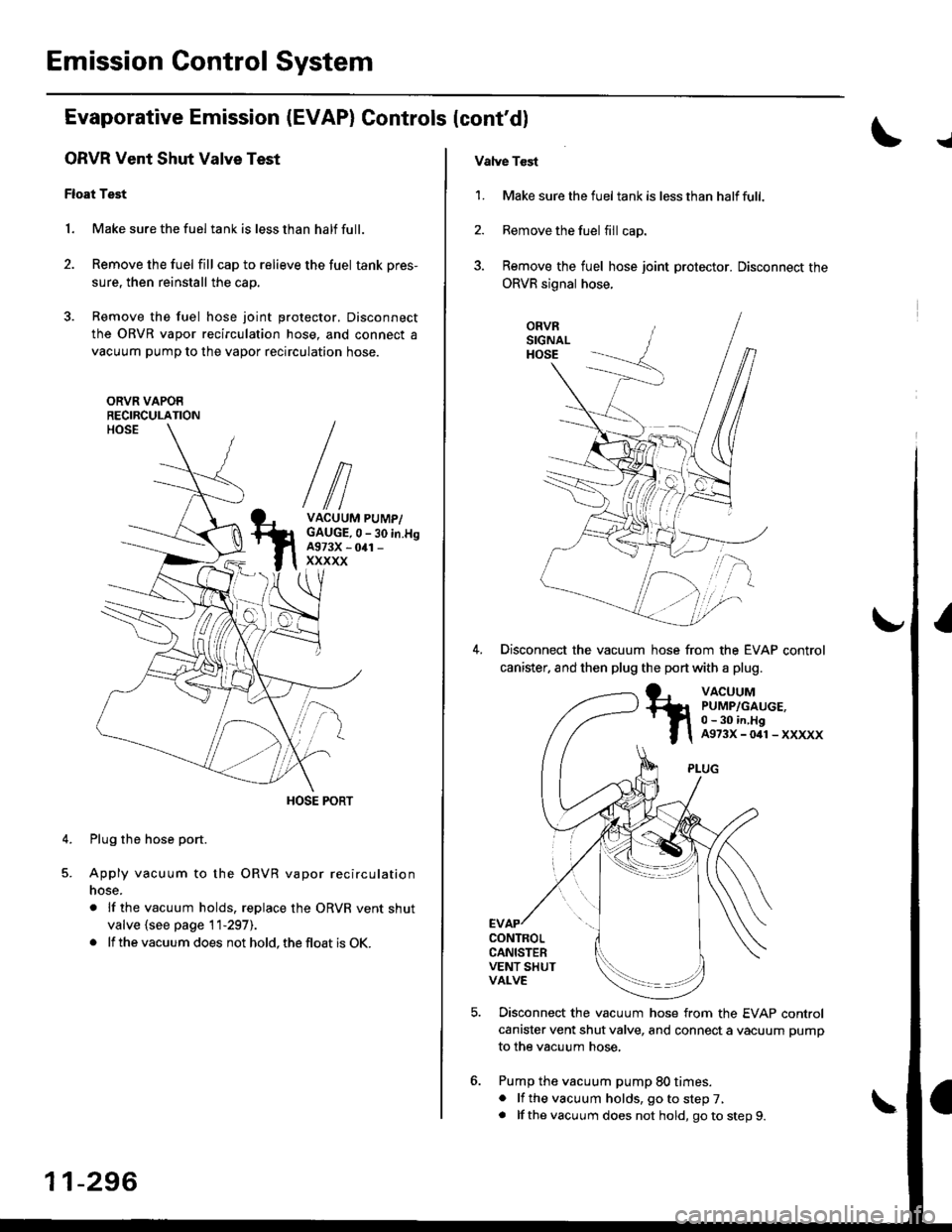
Emission Gontrol System
Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Controls (cont'dl
ORVR Vent Shut Valve Test
Float Test
1. Make sure the fuel tank is less than half full.
2. Remove the fuel fill cap to relieve the fuel tank pres-
sure, then reinstall the cap.
3. Remove the fuel hose joint protector. Disconnect
the ORVR vapor recirculation hose, and connect a
vacuum pump to the vapor recirculation hose.
ORVR VAPOERECIRCULATION
VACUUM PUMP/GAUGE,0 - 30 in.H9A973X - 041 -
xxxxx
Plug the hose port.
Apply vacuum to the ORVR vapor recirculation
nose.
. lf the vacuum holds, replace the ORVR vent shut
valve {see page 11-297).
. lf the vacuum does not hold, the float is OK.
4.
11-296
Vatve Tcst
1. Make sure the fueltank is lessthan halffull.
2. Remove the fuel fill cap.
3. Remove the fuel hose joint protector. Disconnect the
ORVR signal hose.
ORVRSIGNALHOSE
Disconnect the vacuum hose from the EVAP control
canister. and then plug the port with a plug.
VACUUMPUMP/GAUGE,0 - 30 in,HgA973X-041-XXXXX
CONTROLCANISTERVENT SHUTVALVE
Disconnect the vacuum hose from the EVAP control
canister vent shut valve, and connect a vacuum pump
to the vacuum hose,
Pump the vacuum pump 80 times.. lf the vacuum holds, go to step 7,. lf thevacuum does not hold, goto step9.
Page 566 of 2189
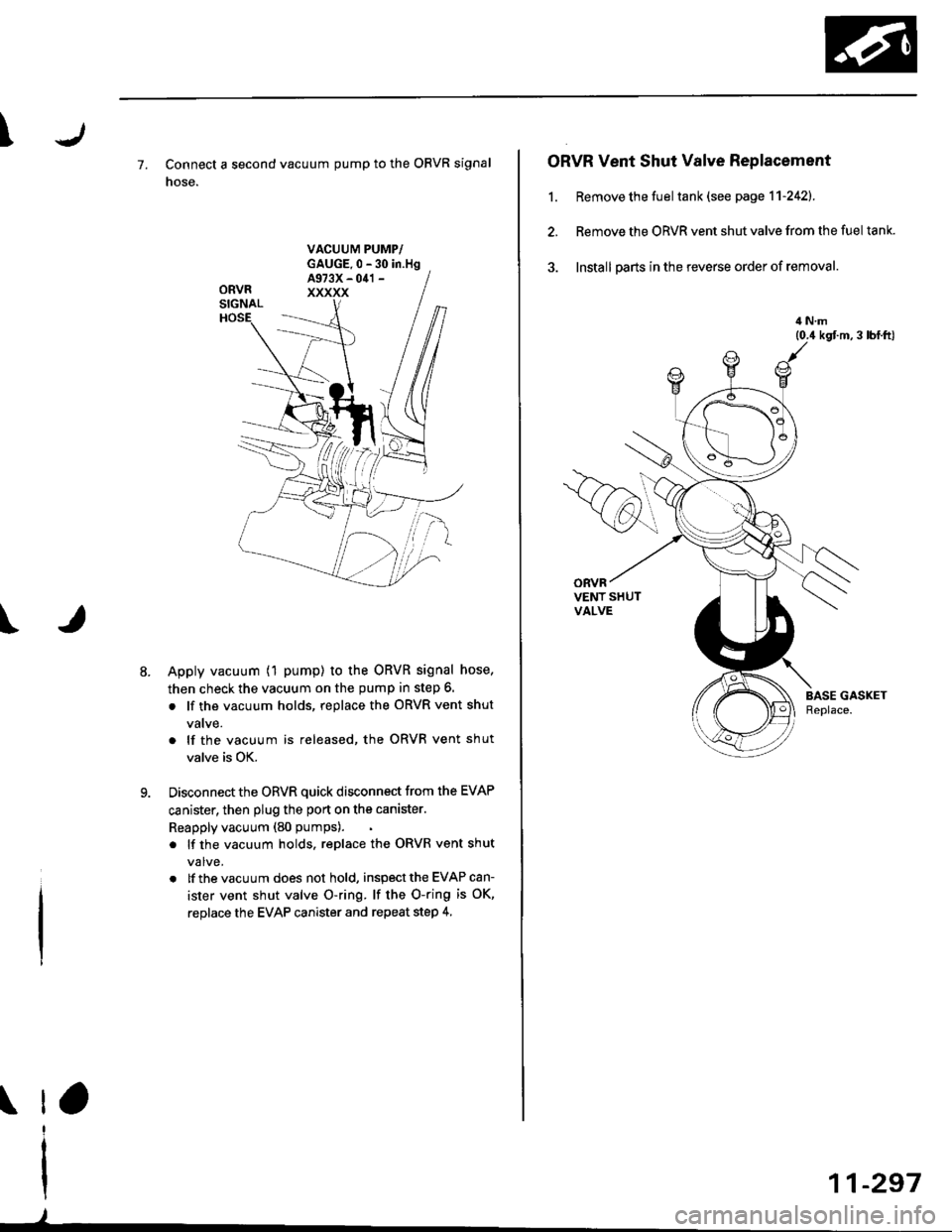
\
\
7. Connect a second vacuum pump to the OBVR signal
nose.
VACUUM PUMP/GAUGE.0 - 30 in.HgA973X - 041 -
xxxxx
Apply vacuum (1 pump) to the ORVR signal hose,
then check the vacuum on the pump in step 6.
. lf the vacuum holds, replace the ORVR vent shut
valve.
. lf the vacuum is released, the ORVR vent shut
valve is OK.
Disconnect the ORVR quick disconnect from the EVAP
canister, then plug the port on the canister.
Reapply vacuum (80 pumps).
. lf the vacuum holds, reDlace the ORVR vent shut
valve,
. lf the vacuum does not hold, inspect the EVAP can-
ister vent shut valve O-ring. lf the O-ring is OK,
replace the EVAP canister and repeat step 4.
\
I
11-297
ORVR Vent Shut Valve Replacement
1. Remove the fuel tank (see page 1 1-242).
2. Remove the ORVR vent shut valve from the fuel tank.
3. lnstall oarts in the reverse order of removal.
Page 573 of 2189
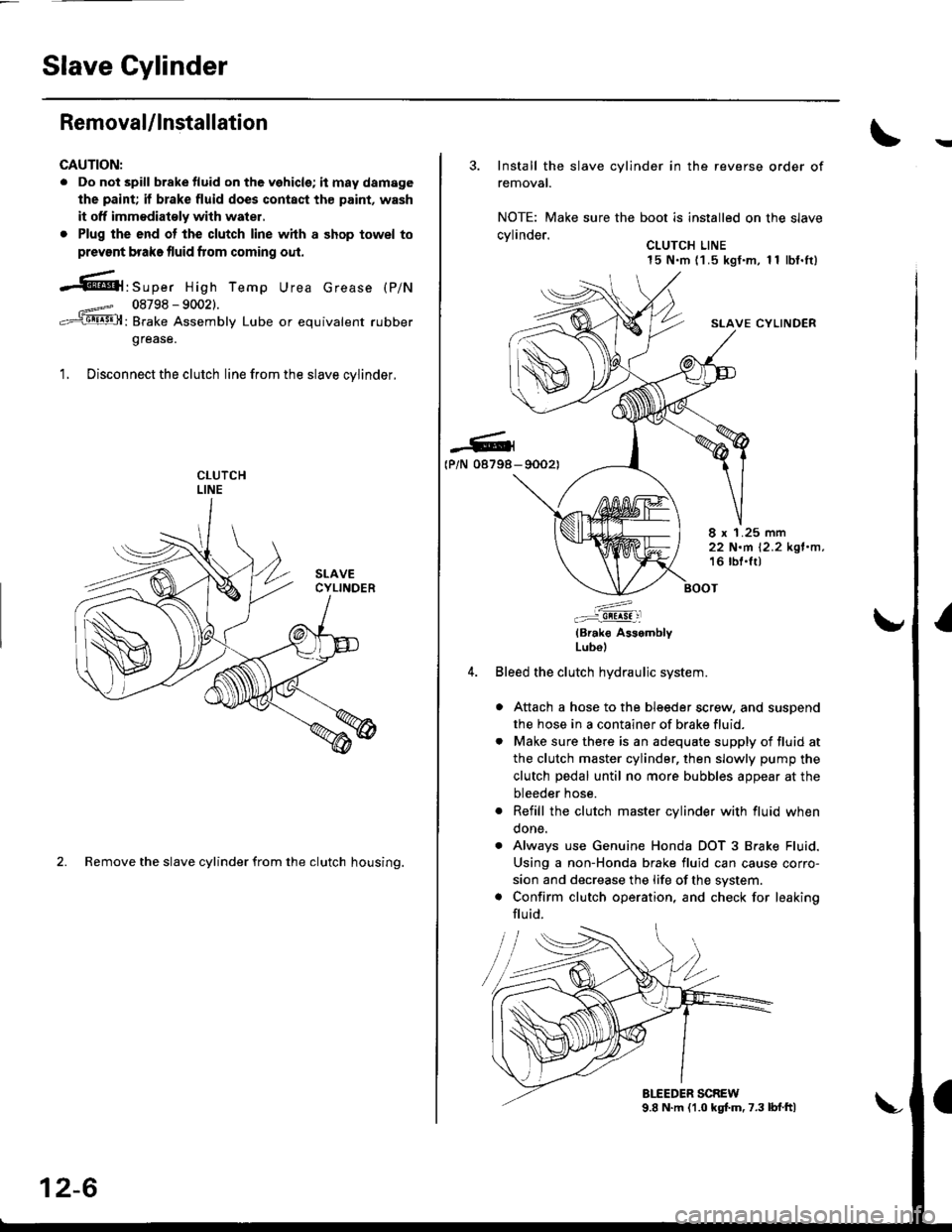
Slave Gylinder
Removal/lnstallation
CAUTION:
. Do not spill brake tluid on the vehicle; it may damage
the paint; if brake fluid does contact th€ paint, wash
it off immodiatoly with water,
. Plug the end ot the clutch line with a shop towel to
prevsnt brake fluid from coming oul.
-61'srp", High Temp Urea crease (p/N
08798 - 90021.
: Brake Assembly Lube or equivalent rubber
grease.
1. Disconnect the clutch line from the slave cvlinder.
2. Remove the slave cylinder from the clutch housing.
12-6
3. Install the slave cylinder in the reverse order of
removal.
NOTE: Make sure the boot is installed on the slave
cvlinder.. CLUTCH LINE15 N.m (1 .5 kgf.m, 1 1 lbf.It)
SLAVE CYLINDER
-G4(P/N 08798- 90021
8 x 1.25 mm22 N.m 12.2 kgl.n,16 lbl.lt)
:^..:i!!!!! :l
(Brak€ AssemblyLubol
Bleed the clutch hydraulic system.
a Attach a hose to the bleeder screw, and suspend
the hose in a container of brake fluid.
. Make sure there is an adequate supply of fluid at
the clutch master cylinder, then slowly pump the
clutch pedal until no more bubbles appear at the
bleeder hose.
. Refill the clutch master cylinder with fluid when
done.
. Always use Genuine Honda DOT 3 Brake Fluid.
Using a non-Honda brake fluid can cause corro-
sion and decrease the life of the system.
. Confirm clutch operation, and check for leaking
flu id.
Page 679 of 2189

Automatic Transmission
Special Tools ......... .....'."".'-.-.' 14'2
Description .,....................-...... 14-3
power Flow ......,................. 14"6
Elestronic Control System .... . ................'..'.'.. 14-13
Hvdraulic Control .....'......" 1'l-19
Hydraulic F|ow...... .'.'.".'....11-21
Lock-up System '............ ... t/t'33
Electrical System
Component Locations....,.............'......'.............'.,. 14'39
PCM Circuit Diagram
lA/T Control Syst€m: '96 - 98 Models) .........'.. 1/t-40
PCM Tarminal Volt8ge/Measuring Condhions
{'96 - 98 ModeblA/T Control System ............
PCM Circuit Disgram(A/T Conlrol System: '99 - 00 Modsls) '..........' 14-44
PCM Terminal Voltage/Measuring Conditions('99 - 00 Models)A/T Control System ...
Troubleshooting Proceduros ....
Symptom-to-ComPonent Chari
Efectricaf SFiem - '96 - 98 Models '..-.-..."'.'..11-52
Eloqtrical System -'99 - 00 Modols ... .........". 1+54
EleclricatTroubl$hooting ('96 - 98 Models)
Valve Body
Repair .................... ........'.... 14-139
Valve
Assembly
ATF Pump
1,1-1i10
Inspection ...........'.......... 14-141
Main Valvs Body
Disass€mbf y/lnspoction/R.sssembly .'.'.'.'.. -. -. 1 1-1 12
Secondsry Valve BodY
Disa$embfy/lnspoction/Rsassembly ......'.'.'.'. 11-111
Regulator Valve Body
Disa$embly/lnspoction/Rea3sembly ..........'... 14-1{5
Servo Body
Disassombly/lnsp€ction/Reassembly .".'........ 14-146
Lock-up Valv6 Body
Dis$s.mbf y/ln3poction/Rea$embly .'.. -. -..'.'.' 1 1-1 17
Mainsh!ft
Dkassembly/lnep€ction Reassembly ..'...'........ 14'148
Inspoction .............'..........'. l it-149
Countsrshaft
Disa$embly/lnspeqtion/Rea3sembly .......'...'.. 1a-l51
Dba$ombly/Re$s.mblY11-152
til-46
I rl-48
Troubleshooting Flowcharts
Electrical Troubleshooting ('9!t - 00 Models)
Troublsshooting Flowchart3
Lock-up Control Solenoid vslvo A/B AssemblY
RePlacoment
Shift Cont.ol Solenoid Valve A/B A3sembly
Inspestion
Ona-way Clutch
Disassembh/lrupoction/Rca$embly .. "'........ l4-155
Clutch
lllustlttcd Ind.x {A48A, B4RA Transmlssion) ..' 14-156
tustr.tod Index (MrnA Transmi$ionl ............ til-158
...................... 14-153
L
14-56
1+81'
14-105
1+105
Replacoment ......
Mainshaft/Countorshaft Spo€d Sonsors
Replacemsnt ......'."'........... lit'108
Hydraulic System
Symptom-to-Componeni Chart
Hydraulic Sydemr+109
t4-113
1+116
11-117
Rea$emblY
14-106 Difforrr ial
llhdraied Index........ t4-156
B.ckhrh ln3poction. 14-167
Boaring Roplacemont..-..........11-167
..... 14-108 Diftrrsniial Carrior Repl8cemeni .'.-.............'...' lil-168
Oil Sall Romovalt4-t 59
Oil Soal ln3tallstion/Sidc Clearance'......'.....'... 1'l'169
Torqua Convertcr Housing Boarings
Mlin3haft Besring/Oil Scal Roplac.ment ."..'.. lil-172
Counio6hatt Betring R.plscem.nt ..'...... ....... 14-173
Test.....,......14-106
14-107
14-160
11-162
11-171
11-175
Replacement
Test .....,.,..........
Road Te3t
Linear Solenoid AsssmblY
Stall Speed
lllustrated Indax
Transmission/End Cover'. ....
Transmission Hou3ing,.............'.'......'....""..-.-.. 11-128
Torque Conve.ter Housing/Valvo Body ........... 14-130
End Cover
14-itB Park Stop
1+119 In3pection/Adiustmsnt...'......'.'............'...."""'14-175
Transmbgion
Reassombly
11-122 Torquo Convertet/Drivr Plsie ............'.'............'.. . l4-182
Transmission
11.726 Inrtallation
Tranlmission Housing Boarings
Msinsh.ft /CounteEhaft Bearings
B!pltcomgnt
Rcvo.3s ldlor Gear
lnrtallation
Cooler Flushing ..
Shift Cabls
Test
Fluid Level
Checkin9 .........."..'.'.....
Changing
Pressure Testing
Transmission
Transmission
Rgmoval ..
lil-176
.'..........'.'.'..... 1'l-183
.... lil-187
11-132Adiustmont
RemovaUlnttallation1,1-190
lit-191Transmisgion Housing
Removal ... '.'...... ......'..... 14-l3il
Tolque Convgrter Housing/valvs Body
Rsmoval .........,...... ............. 14-136
Valve CaDs
Description .......'................. t 4'138
Shift lndicator Panel
Adiu3tmant ..'.................. 14-192
ATF Coolor Hoses
Connection ..,............,.,....... l'l-192
Shift Lever .,........
Page 681 of 2189

Description
The automatic transmission is a 3-element torque converter and a dual-shaft electronically controlled unit which provides
4 soeeds forward and 1 reverse.
Torque Convertel, Geats, and Clutches
The torque converter consists of a pump, turbine and stator, assembled in a single unit. They are connected to the engine
crankshaft so they turn together as a unit as the engine turns. Around the outside of the torque converter is a ring gear
which meshes with the starter pinion when the engine is being started. The entire torque converter assembly seryes as a
flywheel while transmiuing power to the transmission mainshaft.
The transmission has two parallel shafts: the mainshaft and the countershaft. The mainshaft is in Iine with the engine
crankshaft. The mainshaft includes the 1st, 2nd and 4th clutches, gears tor 2nd, 4th, reverse and lst (3rd gear is integral
with the mainshaft, while the reverse gear is integral with the 4th gear). The countershaft includes the 3rd clutch, and
gears for 3rd,2nd, 4th, reverse. 1st and park. The gears on the mainshaft are in constant mesh with those on the counter-
shaft. When certain combinations of gears in transmission are engaged by clutches. power is transmitted from the main-
shaft to the countershaft to provide E, ld, E, and E positions.
Electronic Control
The electronic control svstem consists of the Powertrain Control Module {PCM), sensors, a linear solenoid and four
solenojd valves. Shifting and lock-up are electronically controlled for comtonable driving under all conditions. The PCM is
located below the dashboard, under the front lower panel on the passenger's side
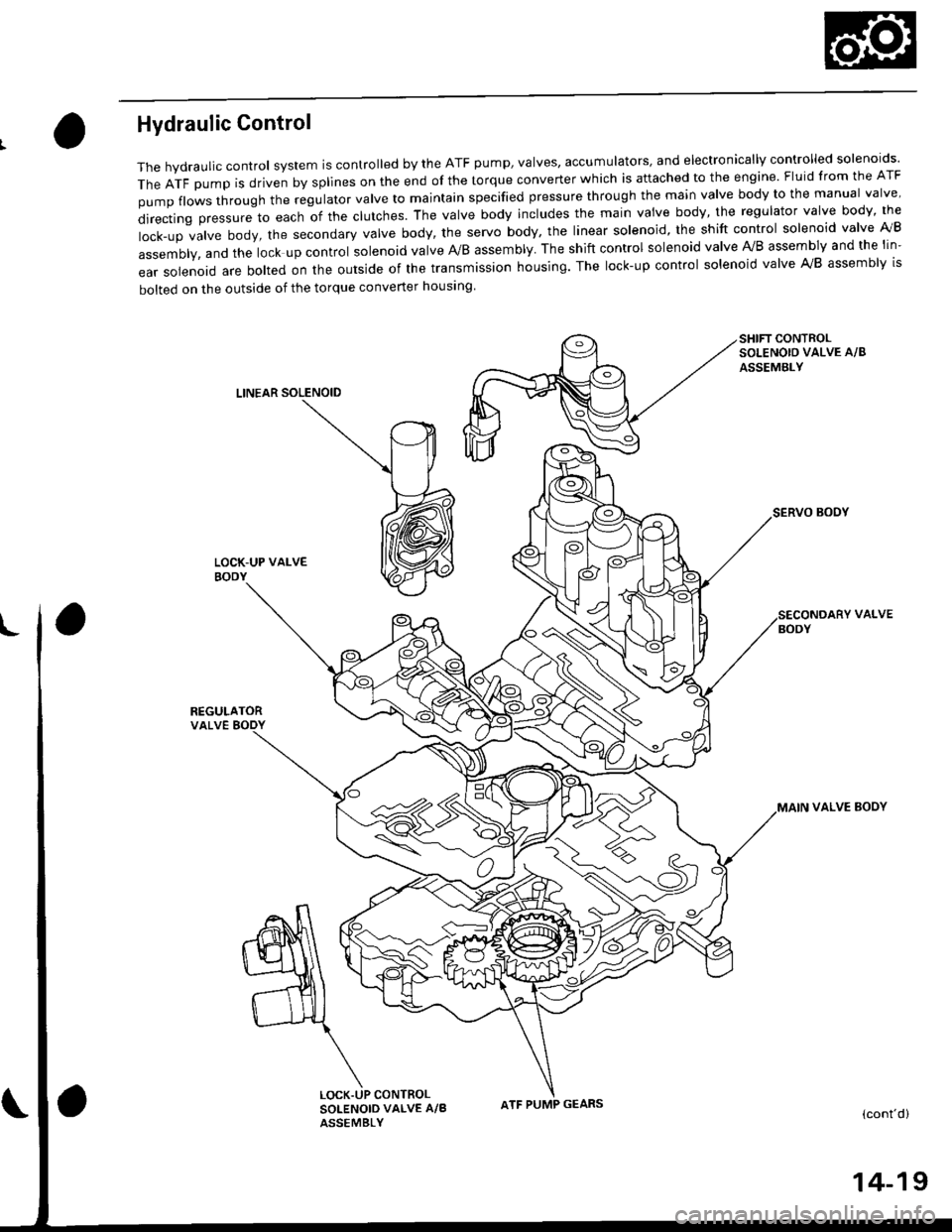
Hydraulic Control
The valve bodies include the main vatve body, the secondary valve body, the regulator valve body, the servo body and the
lock-up valve body through the respective separator plates, They are bolted on the torque converter housang
The main valve body contains the manual valve, the 1-2 shift valve. the 2nd orifice control valve, the CPB {Clutch Pressure
Back-up) valve, the modulator valve. the servo control valve, the relief valve, and ATF pump gears The secondary valve
body contains the 2-3 shift valve. the 3-4 shift valve, the 3-4 orifice control valve, the 4th exhaust valve and the CPC (Clutch
pressure Control) valve. The regulator valve body contains the pressure regulator valve, the torque converter check valve,
the cooler relief valve, and the lock-up control valve. The servo body contains the servo valve which is integrated with the
reverse shift fork, and the accumulators. The lock-up valve body contains the lock-up shift valve and the lock-up timing
valve. The linear solenoid and the shift control solenoid valve Ay'B are bolted on the outside of the transmission housing,
and the lock-up control solenoid valve Ay'B is bolted on the outside of the torque converter housing. Fluid from regulator
passes through the manual valve to the various control valves. The clutches receive fluid from their respective teed pipes
or internal hydraulic circuit.
Shift Control Mechanism
Input from various sensors located throughout the car determines which shift control solenoid valve the PCM will activate
Activating a shift control solenoid valve changes modulator pressure, causing a shift valve to move. This pressurizes a line
to one of the clutches, engaging that clutch and its corresponding gear, The shift control solenoid valves A and B are con-
trolled by the PCM.
Lock-up Mechanism
In ,Dt1 position, in 3rd and 4th. and in E position in 3rd, pressurized fluid is drained from the back of the torque converter
through a fluid passage, causing the lock-up piston to be held against the torque converter cover. As this takes place, the
mainshaft rotates at the same as the engine crankshaft. Together with hydraulic control, the PCM optimizes the timing of
the lock-up mechanism. The lock-up valves control the range of lock-up according to lock-up control solenoid valves A and
B, and linear solenoid. When lock-up control solenoid valves A and B activate, the modulator pressure changes The lock-
up control solenoid valves A and B and the linear solenoid are controlled by the PCM.
(cont'd)
14-3
Page 697 of 2189
Hydraulic Control
The hydraulic control system is controlled by the ATF pump, valves, accumulators, and electronically controlled solenoids'
TheATFpUmpisdrivenbysp||nesontheendofthetorqueconverterWhichisattachedtotheengine.F|uidfromtheATF
pumpf|owsthroughtheregu|atorva|vetomajntainspecifiedpressurethroughthemainva|vebodytothemanuaIva|ve'
directingpressuretoeachofthec|utches.Theva|vebodyinc|udesthemainvaivebody,theregu|atorvalvebody,the
|ock-upva|vebody,thesecondaryVa|vebody,theservobody,theIinearso|enoid,theshiftcontro|so|enoidva|velVB
assembly, and the lock up control solenoid valve A/B assembly. The shift control solenoid valve Ay'B assembly and the lin-
ear solenoid are bolted on the outside of the transmission housing. The lock-up control solenoid valve A,/B assembly is
bolted on the outside of the torque converter housing
SHIFT CONTROLSOLENOIO VALVE A/8
ASSEMBLY
LINEAR SOLENOID
SERVO BOOY
REGULATORVALVE BODY
VALVE
VALVE BOOY
(cont'd)
CONTROLSOLENOID VALVE A/BASSEMBLY
ATF PUMP GEARS
14-19