height HONDA CIVIC COUPE 1999 Owners Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: HONDA, Model Year: 1999, Model line: CIVIC COUPE, Model: HONDA CIVIC COUPE 1999Pages: 269, PDF Size: 2.42 MB
Page 30 of 269
Protecting Children
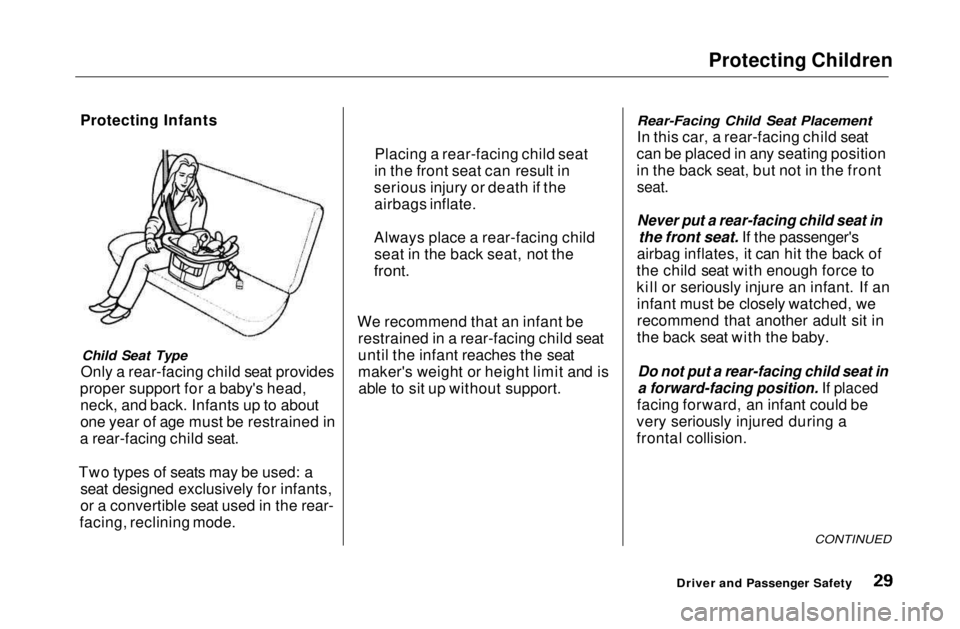
Protecting Infants
Child Seat Type
Only a rear-facing child seat provides
proper support for a baby's head, neck, and back. Infants up to about
one year of age must be restrained in
a rear-facing child seat.
Two types of seats may be used: a seat designed exclusively for infants,
or a convertible seat used in the rear-
facing, reclining mode. We recommend that an infant be
restrained in a rear-facing child seat
until the infant reaches the seat
maker's weight or height limit and isable to sit up without support.
Rear-Facing Child Seat Placement
In this car, a rear-facing child seat
can be placed in any seating position
in the back seat, but not in the front
seat.
Never put a rear-facing child seat in
the front seat. If the passenger's
airbag inflates, it can hit the back of
the child seat with enough force to
kill or seriously injure an infant. If an infant must be closely watched, we
recommend that another adult sit in
the back seat with the baby.
Do not put a rear-facing child seat in
a forward-facing position. If placed
facing forward, an infant could be
very seriously injured during a
frontal collision.
CONTINUED
Driver and Passenger Safety
Placing a rear-facing child seat
in the front seat can result in
serious injury or death if the airbags inflate.
Always place a rear-facing child seat in the back seat, not the
front.Main Menu Table of Contents s t
Page 34 of 269
Protecting Children
Additional Precautions for Infants Never hold an infant on your lap.
If you are not wearing a seat belt
in a crash, you could be thrown
forward into the dashboard and crush the infant.
If you are wearing a seat belt, the
infant can be torn from your arms.For example, if your car crashes
into a parked vehicle at 30 mph (48 km/h), a 20-lb (9 kg) infant
will become a 600-lb (275 kg) force, and you will not be able to hold on.
Never put a seat belt over yourself
and an infant. During a crash, the
belt could press deep into the infant and cause very serious
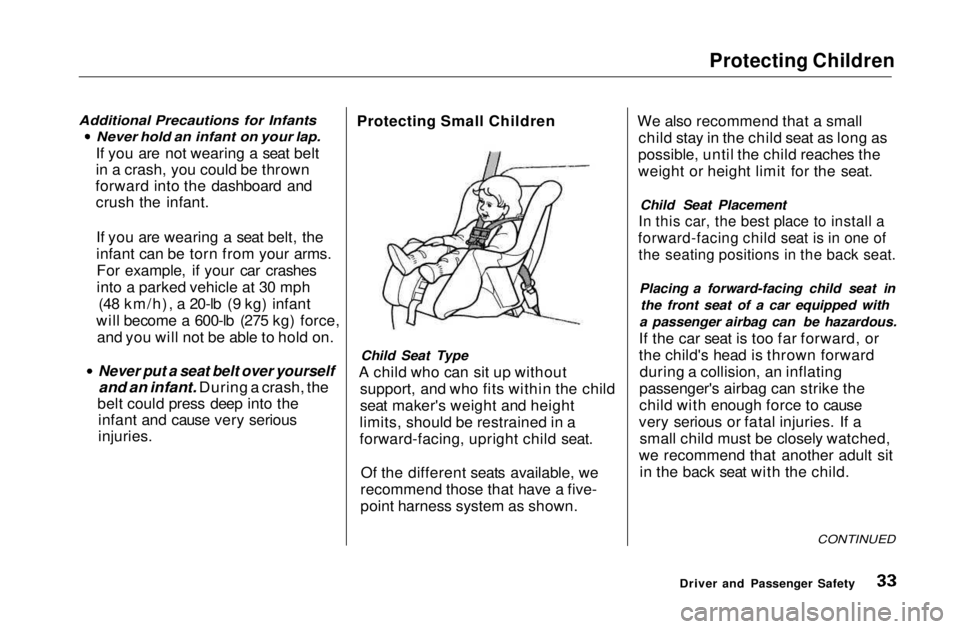
injuries. Protecting Small Children
Child Seat Type
A child who can sit up without support, and who fits within the child
seat maker's weight and height
limits, should be restrained in a
forward-facing, upright child seat.
Of the different seats available, we
recommend those that have a five-
point harness system as shown. We also recommend that a small
child stay in the child seat as long as
possible, until the child reaches the
weight or height limit for the seat.
Child Seat Placement
In this car, the best place to install a
forward-facing child seat is in one of
the seating positions in the back seat.
Placing a forward-facing child seat in the front seat of a car equipped with
a passenger airbag can be hazardous.
If the car seat is too far forward, or
the child's head is thrown forward during a collision, an inflating
passenger's airbag can strike the
child with enough force to cause
very serious or fatal injuries. If a small child must be closely watched,
we recommend that another adult sit in the back seat with the child.
CONTINUED
Driver and Passenger SafetyMain Menu Table of Contents s t
Page 38 of 269
Protecting Children
Protecting Larger Children
When a child reaches the recommended weight or height limit
for a forward-facing child seat, the child should sit in one of the outer
back seats and wear a lap/shoulder belt. The lap/shoulder belt provides
better protection than the lap belt.
If a child is too short for the shoulder
part of the belt to properly fit, we
recommend that the child use a
booster seat until they are tall enough to use the seat belt without a
booster.
The following pages give instructions on how to check properseat belt fit, what kind of booster
seat to use if one is needed, and
important precautions for children
who must sit in the front seat.
Checking Seat Belt Fit
To determine if a lap/shoulder belt properly fits a child, have the child
put on the seat belt. Follow theinstructions on page 13 . Then check
how the belt fits.
CONTINUED
Driver and Passenger Safety
Allowing a larger child to sit
improperly in the front seat canresult in injury or death if the
airbags inflate.
If a larger child must sit in front,
make sure the child moves the
seat as far back as possible
and wears the seat belt properly.Main Menu Table of Contents s t
Page 40 of 269

Protecting Children
Using a Booster Seat
If a child needs a booster seat, we
recommend choosing a style that
allows the child to use the lap/
shoulder belt directly, without a
shield, as shown.
Whichever style you select, follow the booster seat maker's instructions. A child may continue using a booster
seat until the tops of the ears are
even with the top of the seat-back. A
child of this height should be tall
enough to use the lap/shoulder belt
without a booster.
When Can a Larger Child Sit in Front
The National Highway Traffic Safety
Administration and Transport Canada recommend that all children
ages 12 and under be properly
restrained in the back seat.
The back seat is the safest place for a child of any age or size.
In addition, the passenger's airbag
poses serious risks to children. If theseat is too far forward, or the child's
head is thrown forward during a collision, or the child is unrestrained
or out of position, an inflating airbag
can kill or seriously injure the child.
Of course, children vary widely. And
while age may be one indicator of
when a child can safely ride in the front, there are other important
factors you should consider.
CONTINUED
Driver and Passenger SafetyMain Menu Table of Contents s t
Page 77 of 269
Seat Adjustments
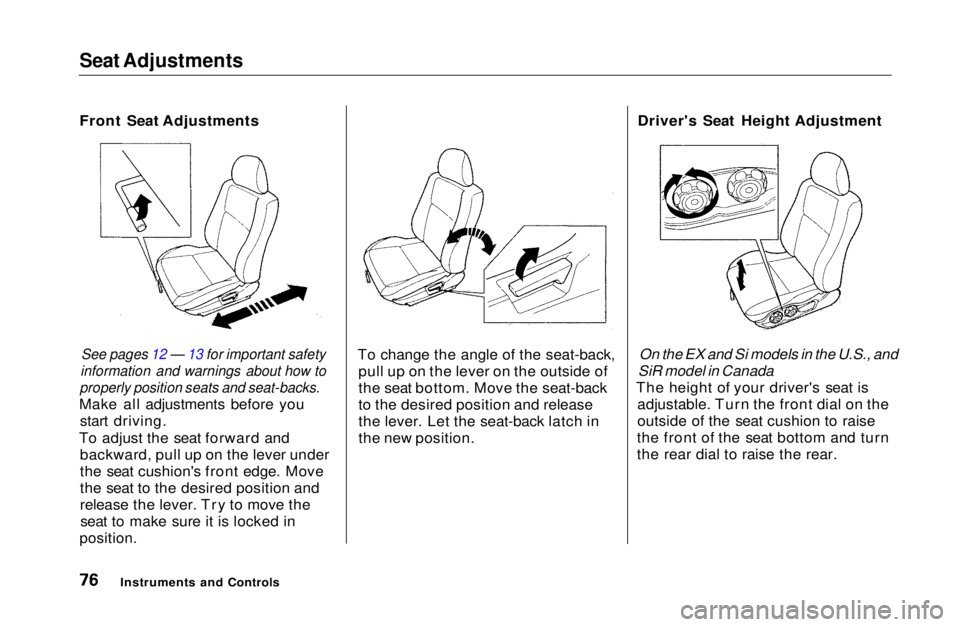
Front Seat Adjustments
See pages 12 — 13 for important safety
information and warnings about how to
properly position seats and seat-backs.
Make all adjustments before you start driving.
To adjust the seat forward and backward, pull up on the lever under
the seat cushion's front edge. Move
the seat to the desired position and
release the lever. Try to move theseat to make sure it is locked in
position.
To change the angle of the seat-back,
pull up on the lever on the outside of
the seat bottom. Move the seat-back
to the desired position and release
the lever. Let the seat-back latch in
the new position. Driver's Seat Height Adjustment
On the EX and Si models in the U.S., and
SiR model in Canada
The height of your driver's seat is adjustable. Turn the front dial on the
outside of the seat cushion to raise
the front of the seat bottom and turn
the rear dial to raise the rear.
Instruments and ControlsMain Menu Table of Contents s t
Page 79 of 269
Seat Adjustments, Folding Rear Seat
The front head restraints adjust for height. You need both hands to
adjust the restraint. Do not attempt
to adjust it while driving. To raise it, pull upward. To lower the restraint,
push the release button sideways and push the restraint down.
To remove a head restraint for cleaning or repair, pull it up as far as
it will go. Push the release button
and pull the restraint out of the seat-
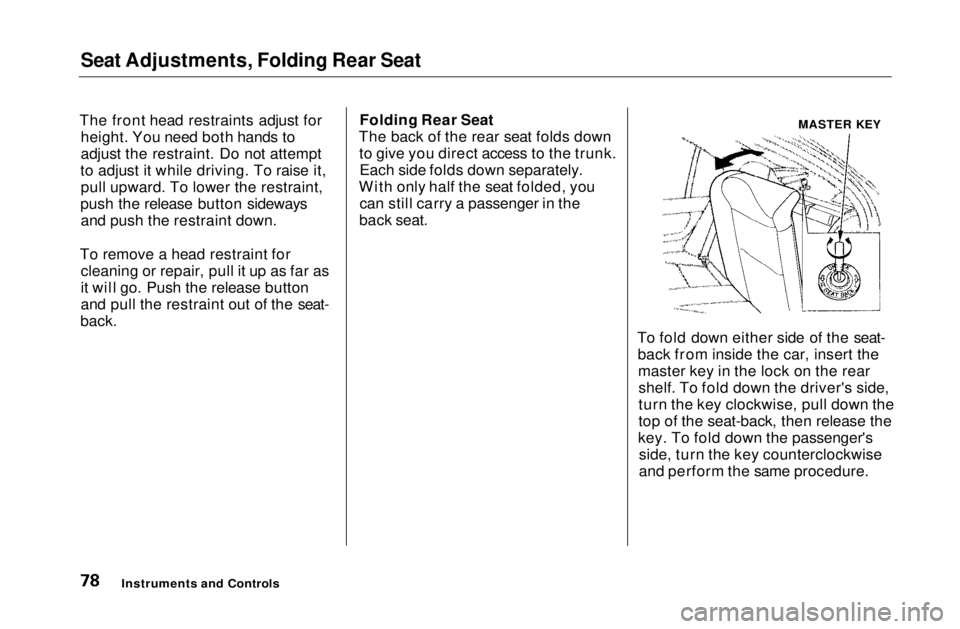
back. Folding Rear Seat
The back of the rear seat folds down to give you direct access to the trunk.Each side folds down separately.
With only half the seat folded, you can still carry a passenger in the
back seat.
To fold down either side of the seat-back from inside the car, insert themaster key in the lock on the rearshelf. To fold down the driver's side,
turn the key clockwise, pull down the
top of the seat-back, then release the
key. To fold down the passenger's side, turn the key counterclockwise
and perform the same procedure.
Instruments and Controls
MASTER KEYMain Menu Table of Contents s t
Page 131 of 269
Accessories and Modifications
Modifications Do not remove any original
equipment or modify your car in any
way that would alter its design or operation. This could make your car
unsafe and illegal to drive.
For example, do not make any
modifications that would change the
ride height of your car, or install
wheels and tires with a different overall diameter.
Such modifications can adversely
affect handling, and interfere with
the operation of the car's anti-lock
brakes and other systems. In addition, any modifications that
decrease ground clearance increase
the chance of undercarriage parts striking a curb, speed bump, or other
raised object, which could cause
your airbags to deploy.
Do not modify your steering wheelor any other part of your
Supplemental Restraint System.
Modifications could make the
system ineffective. Additional Safety Precaution
Do not attach or place objects on the
airbag covers. Any object attached to
or placed on the covers marked "SRS
AIRBAG," in the center of the steering wheel and on top of the
dashboard, could interfere with the
proper operation of the airbags. Or,
if the airbags inflate, the objects
could be propelled inside the car and
hurt someone.
Before DrivingMain Menu Table of Contents s t
Page 248 of 269

Tire Information
Tire Size Designation A tire's sidewall is marked with a tire size designation. You will need this
information when selecting replace-
ment tires for your vehicle. The
following explains what the letters and numbers in the tire size
designation mean.
(Example tire size designation)
P185/65R14 85S
P — Applicable vehicle type (tires
marked with the prefix "P" are
intended for use on passenger cars;
however, not all tires have this
marking).
185 — Tire width in millimeters.
65 — Aspect ratio. The tire's section
height as a percentage of its width.
R — Tire construction code (Radial). 14 — Rim diameter in inches. 85 — Load Index, a numerical code
associated with the maximum load
the tire can carry.
S — Speed Symbol. See the speed
rating chart in this section for additional information.
Wheel Size Designation Wheels are also marked with important information that you need
if you ever have to replace one. The
following explains what the letters and numbers in the wheel size
designation mean.
(Example wheel size designation)
14x5J
14 — Rim diameter in inches.
5 — Rim width in inches.
J — Rim contour designation. Tire Speed Ratings
The chart below shows many of the different speed ratings currently
being used for passenger vehicle
tires. The speed symbol is part of the tire size designation on the sidewallof the tire. This symbol corresponds
to that tire's designed maximum safe
operating speed.
Technical InformationMain Menu Table of Contents s t