Engine assembly HONDA CR-V 1999 RD1-RD3 / 1.G Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: HONDA, Model Year: 1999, Model line: CR-V, Model: HONDA CR-V 1999 RD1-RD3 / 1.GPages: 1395, PDF Size: 35.62 MB
Page 519 of 1395

Description
General Operation
The Automatic transmission is a 3-element torque converter and triple-shaft electronically controlled unit which provides 4
speeds forward and 1 reverse speed The unit is positioned in line with the engine'
There are two tvoes of automatic transmission on CR-V; the four-wheel drive (4WD) model ('97 - 00)' and the front-wheel
drive (2WD) model ('98 - 00).
Toroue Converter, G€ars, and Clutches
The torque converter consists of a pump. turbine. and stator assembly in a single unit. The torque converter is connected to
the engine crankshatt. These parts turn together as a unit as the engine turns. Around the outside of the torque converter is
a ring gear which meshes with the starter pinion when the engine is started. The torque converter assembly serves as a fly-
wheel while transmitting power to the transmission mainshaft.
The transmission has three parallel shafts: the mainshaft. the countershaft, and the sub-shaft. The mainshaft is in line with
the engine crankshaft. The mainshaft includes the 1st, 2nd. and 4th clutches, and gears lor 3rd,2nd,4th. reverse and 1st
(3rd gear is integral with the mainshaft, while reverse gear is integral with the 4th gear). The countershaft includes the 3rd
clutch and gears for 3rd,2nd, 4th, reverse, 1st, and park. Reverse and 4th gears can be locked to the countershaft at its cen-
ter, providing 4th gear or reverse, depending on which way the selector is moved. The sub-shaft includes the lst-hold
clutch and gears for lst and 4th.
The gears on the mainshaft are in constant mesh with those on the countershaft and sub-shaft. When certain combinations
of gears are engaged by the ctutches, power is transmitted from the mainshaft to the countershaft to provide E, D!, tr, tr,
and E position ('97 - 98 models). and E. E, E, and E position ('99 - 00 models)'
Electlonic Control
The electronic controt system consists of the Powenrain Control Module (PCM), sensors, a linear solenoid, and four
solenoid valves. Shifting and lock-up are electronically controlled for comfortable driving under all conditions. The PCM is
located below the dashboard, under the kick panel on the passenger's side.
Hydraulic Control
The valve bodies include the main valve body, the secondary valve body, the regulator valve body, the servo body, and
the lock up valve body. They are bolted to the torque converter housing. The main valve body contains the manual valve,
the 1-2 shift valve, the 2nd orifice control valve. the CPB {Clutch Pressure Back-up) valve, the modulator valve, the servo
control valve. the relief valve, and ATF pump gears. The secondary valve body contains the 2-3 shift valve, the 3-4 shift
valve, the 3,4 orifice control valve. the 4th exhaust valve and the CPC (Clutch Pressure Control) valve. The regulator valve
bodv contains the pressure regulator valve, the torque converter check valve, the cooler relief valve, and the lock-up con-
trol valve. The servo body contains the servo valve which is integrated with the reverse shift tork, and the accumulators
The lock-up valve body contains the lock-up shift valve and the lock-up timing valve. The linear solenoid and the shift con-
trol solenoid valve Ay'B are bolted to the outside of the transmission housing, and the lock-up control solenoid valve Ay'B is
bolted to the outside of the torque converter housing. Fluid trom the regulator passes through the manual valve to the
various control valves. The clutches receive fluid from their respective feed pipes or internal hydraulic circuit
ShiftControl Mechanism
input from various sensors located throughout the vehicle determines which shift control solenoid valve the PCM will acti-
vate. Activating a shift control solenoid valve changes modulator pressure, causing a shift valve to move. This pressurizes
a line to one of the clutches. engaging that clutch and its corresponding gear. The shift control solenoid valves A and B are
controlled by the PCM.
Lock-up Mechanism
tn E! position (,97 - 98 modets) and in E position ('99 - O0 models), in 3rd and 4th, and in Del position in 3rd ('97 - 98
models) and in El position with Over,Drive (O/D) is OFF (by pressing rhe O/D switchl in 3rd ('99 - 00 models), pressurized
fluid is drained from the back of the torque converter through a fluid passage, causing the lock-up piston to be held
against the torque converter cover, As this takes place, the mainshaft rotates at the same speed as the engine crankshaft.
Together with hydraulic control, the PcM optimizes the timing of the lock-up mechanism The lock-up valves control the
range of lock-up according to lock-up control solenoid valves A and B, and the linear solenoid. When lock-up control
solenoid valves A and B activate, the modulator pressure changes. The lock-up control solenoid valves A and B and the
linear solenoid are controlled by the PCM.
{cont'd)
14-3
www.emanualpro.com
Page 520 of 1395

Description
General Operation (cont'dl
Gsar Selection'97 - 98 Models
The shift lever has seven positions; El PARK, ts REVERSE, N NEUTRAL, Ell 1st through 4th ranges, lpq 1st th.ough 3rdranges, P 2nd gear, and [ 1st gear
'99 - 00 Models
The shitt lever has six positions; El PARK, E REVERSE, E NEUTRAL. E ,lst through 4th ranges, and 1st through 3rd(when Over-Drive (O/D) is OFF) ranges. @ 2nd gear, and E 1st gear.
Starting is possible only in @ and @ positions. using a slide-type. neutral-safety switch.
Automatic Transaxle (A/T) Gear Position IndicatorThis indicator in the instrument panel shows which gear has been selected.
Transler Mochanism {4WD}
The transfer mechanism consists of the transfer shaft drive gear. the transfer shaft. the transfer drive gear, the transfer driv-en gear shaft, and the companion flange, The transfer mechanism assembly is on the rear side ot the transmission. besidethe differential. The transfer shaft drive gear on the final driven gear drives the transfer shaft driven qear. power is transmit-ted to the rear differential via the transfer shaft and the Drooeller shaft.
Clutches
The four-speed automatic transmission uses hydraulically-actuated clutches to engage or disengage the transmission gears.When the hydraulic pressure is introduced into the clutch drum, the clutch piston moves. This presses the friction discs andsteel plates together, locking them so they don't slip. Power is then transmifted through the engaged clutch pack to its hu$mounted gear. When hydraulic pressure is bled from the clutch pack, the piston releases the friction discs and steel plates, andthey are free to slide past each other. This allows the gearto spin independently on its shaft, transmitting no power.
lst Clutch
The 1st clutch engages/disengages lst gear, and is located at the end ofthe mainshaft, just behind the end cover.The 1st clutch is supplied hydraulic pressure by its ATF feed pipe within the mainshaft.
lst-hold Clutch
The 1st-hold clutch engages/disengages 1st-hold or E position, and is located at the middle of the sub-shaft. The 1st-holdclutch is supplied hydraulic pressure by its ATF feed pipe within the sub-shaft.
2nd Clutch
The znd ciutch engages/disengages 2nd gear, and is located at the middle of the mainshaft. The 2nd clutch is joined back-to-back to the 4th clutch. The 2nd clutch is supplied hydraulic pressure through the mainshaft by a circuit connected to theinternal hydraulic circuit.
PositionDescription
Reverse; reverse selector engaged with countershaft reverse gear and 4th clutch locked.
Allclutches released.
General driving; starts off in 1st, shifts automatically to 2nd, 3rd, then 4th, depending on vehicle speedand throftle position. Downshifts through 3rd,2nd, and lst on deceleration to stop.The lock-up mechanism operates;n 3rd and 4th gear.
used for rapid €cceleration at highway speeds and general driving; stans off in 1st, shifts automatically to2nd_then 3rd, dejending on vehicle speed and throttle position. Downshifts through lower gears on decel-eration to stop. The lock-up mechanism comes into operation in 3rd gear.
Driving in 2nd_gear; stays in 2nd gear, does not shift up and down. For engine braking or better trac_tion starting off on loose or slippery surfaces.
Driving in 1st gear; stays in 1st gear, does not shift up. For engine braking.
tll PARK
t!!l l|EvEn>E
E NEUTRAL
Ell DRrvE ('97 - sB)E DRrvE ('ss - oo)(1st through 4th )
E DRrvE {'97 - s8)O DRTVE with over-Drive (O/D) is OFF('99 - 00)(1st through 3rd)
E SECOND
E FIRST
14-4
www.emanualpro.com
Page 525 of 1395
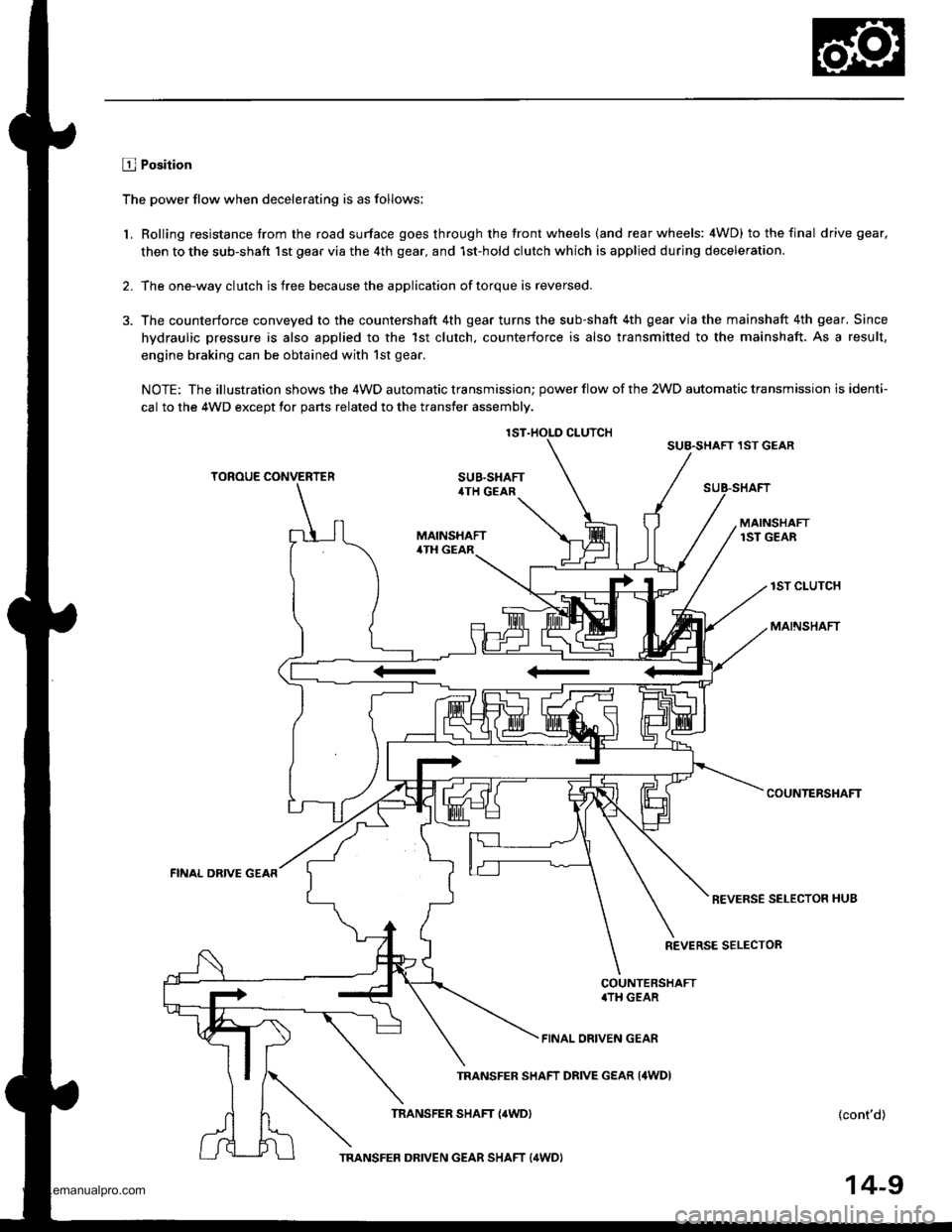
2.
L
E Position
The power flow when decelerating is as follows:
Rolling resistance trom the road surface goes through the tront wheels (and rear wheels: 4WD) to the final drive gear.
then to the sub-shaft lst gear via the 4th gear. and 1st-hold clutch which is applied during deceleration.
The one-way clutch is free because the application of torque is reversed.
The counterforce conveyed to the countershaft 4th gear turns the sub-shaft 4th gear via the mainshaft 4th gear. Since
hydraulic pressure is also applied to the 1st clutch. counterforce is also transmitted to the mainshaft. As a result,
engine braking can be obtained with'lst gear.
NOTE: The illustration shows the 4WD automatic transmission; power flow of the 2WD automatic transmission is identi-
cal to the 4WD except tor parts related to the transfer assembly.
J.
SUB.SHAFT 1ST GEAR
TOROUE CONVERTER
FINAL DRIVE GEAR
SUB.SHAFT{TH GEAR
MAINSHAFTlST GEAR
lST CLUTCH
MAINSHAFT
COUNTERSHAFT
REVERSE SELECTOR HUB
REVERSE SELECTOR
COUNTERSHAFTIITH GEAR
FINAL ORIVEN GEAR
TRANSFER SHAFT DRIVE GEAR {4WDI
TRANSFEB SHAFT {{WD){cont'd}
lST.HOLD CLUTCH
TRANSFER DRIVEN GEAR SHAFT {,lWDl
14-9
www.emanualpro.com
Page 526 of 1395
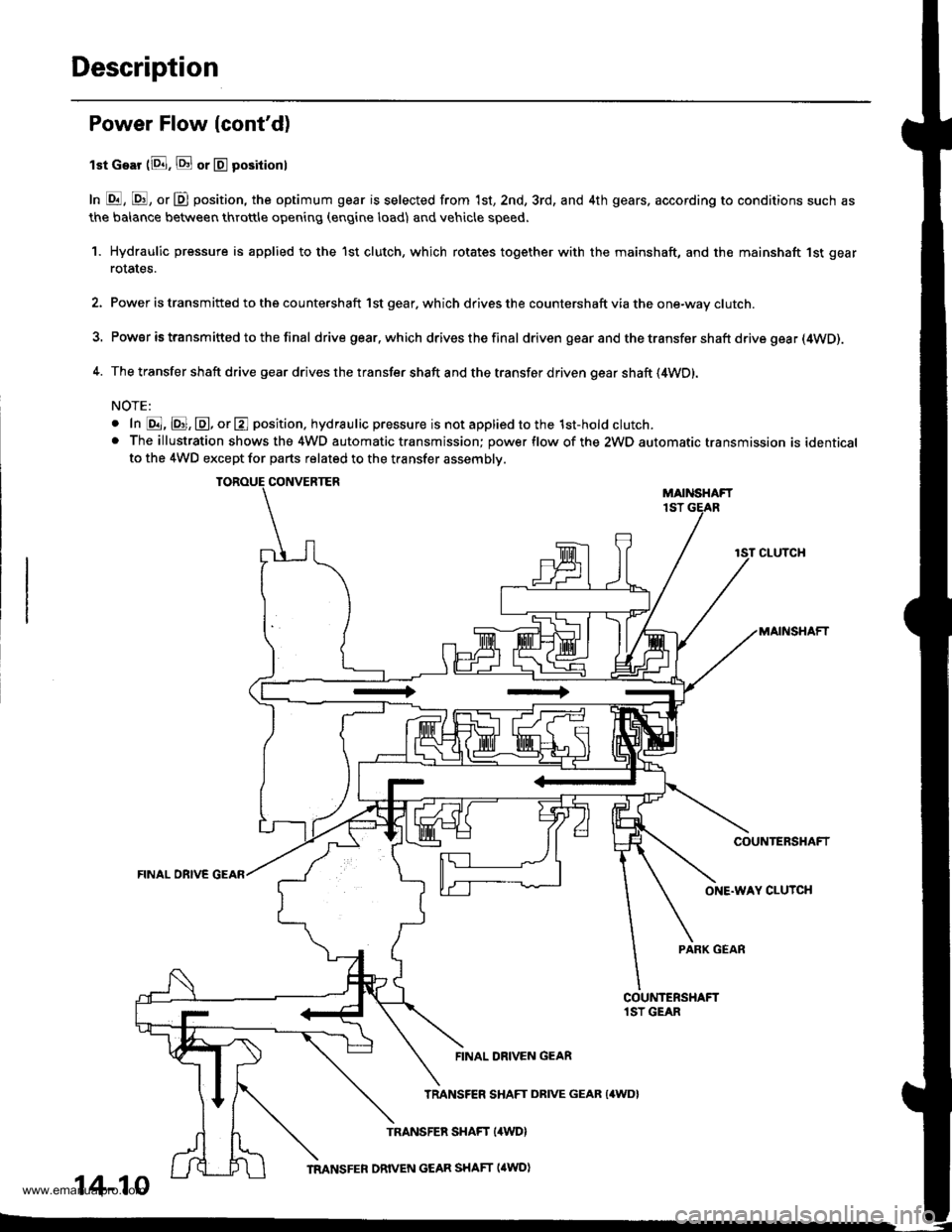
Description
Power Flow lcont'd)
lst Gear (8. E or E positionl
In E, E, or D position, the optimum gear is selected from 1st, 2nd, 3rd, and 4th gears, according to conditions such as
the balance between throttle opening (engine load) and vehicle speed.
1. Hydraulic pressure is applied to the 1st clutch, which rotates together with the mainshaft, and the mainshaft 1st gear
rotates.
2. Power is transmitted to the countershaft 1st gear. which drives the countershaft via the one-way clutch.
3. Power is transm itted to the final drive gear.which drives the final driven gear and the transfer shaft drive gea r (4WD).
4. The transfer shaft drive gear drives the transfer shaft and the transfer driven gear shaft (4WD).
NOTE:
o In @, @, @, or E position. hydraulic pressure is not applied to the 1st-hold clutch.. The illustration shows the 4WD automatic transmission; power flow of the 2WD automatic transmission is identicalto the 4WD except for parts related to the transfer assembly.
CONVERTERMAIiISHAFT1ST
CLUTCH
MAINSHAFT
COUNTERSHAFT
FINAL OBIVE GEAR
ONE.WAY CLUTCH
PARK GEAR
FINAL DRIVEN GEAR
14-10
TRANSFER SHAFT DRIVE GEAR {4WD}
www.emanualpro.com
Page 540 of 1395
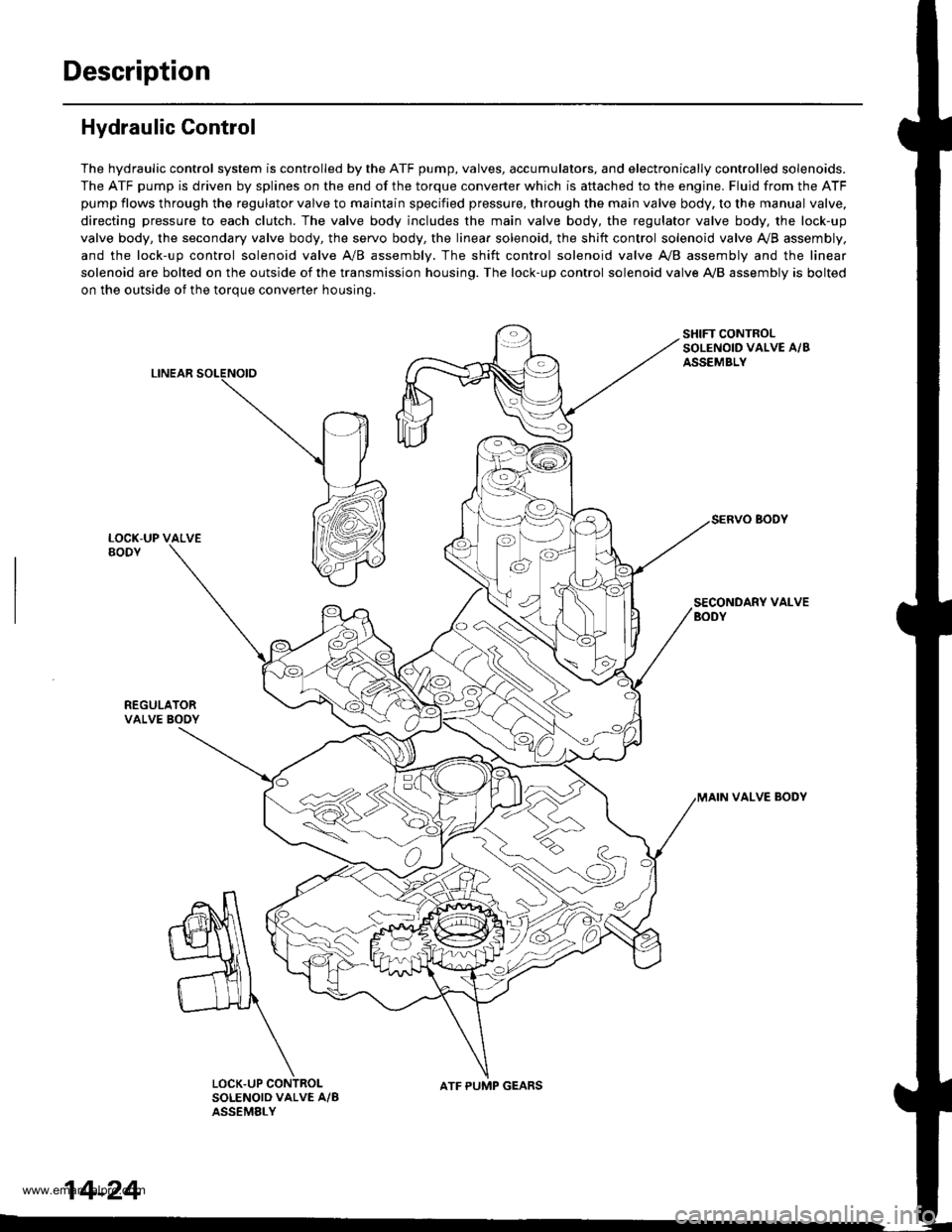
Description
Hydraulic Control
The hydraulic control system is controlled by the ATF pump, valves, accumulators, and electronically controlled solenoids.
The ATF pump is driven by splines on the end of the torque converter which is aftached to the engine. Fluid from the ATF
pump flows through the regulator valve to maintain specified pressure, through the main valve body, to the manual valve,
directing pressure to each clutch. The valve body includes the main valve body, the regulator valve body, the lock-up
valve body, the secondary valve body, the servo body, the linear solenoid, the shift control solenoid valve Ay'B assembly,
and the lock-up control solenoid valve A/B assembly. The shift control solenoid valve A,/B assembly and the linear
solenoid are bolted on the outside of the transmission housing. The lock-up control solenoid valve A,/B assembly is bolted
on the outside of the torque converter housing.
LINEAR
SHIFT CONTROLSOLENOID VALVE A/BASSEMBLY
SECONDARY VALVEBODY
REGULATORVALVE BOOY
VALVE BODY
SOLENOID VALVE A/BASSEMELY
N
ATF PUMP GEARS
14-24
www.emanualpro.com
Page 599 of 1395

From page 14 82
Replace the Lock-up ControlSolenoid Valve Assembly andRecheck:1. Replace the lock-up controlsolenoid valve A/B assembly(see page 14-'135).2. Turn the ignition switch OFFand reset the PCM by remov-ing the BACK uP (7.5 A) fusein the under-hood fuse/relaybox for more than 10 seconds.3. lJsing the scan tool, check tobe sure that the engine coolanttemperature is 176"F 180'C) orabove,4. Drive the vehicle at 55 mph(88 km/h) constantly for moretnan one mrnute.5. Recheck for code P0740 (40).
Does the OBD ll scan tool indicatecode PO74O or doesthe El indicator light indicate code 40?The svstem is OK ai this time.
Replace the Linear Sol€noidA$embly and Recheck:'1. Beplace the linear solenoidassembly {see page 14-138).2. Turn the ignition switch OFFand reset the PCM memory byremoving the BACK UP (7.5 A)fuse in the underhood fuse/relay box for more than 10seconds.3. Using the scan tool, check tobe sure that the engine coolanttemperature is 176"F (80'C) orabove.4. Drive the vehicle at 55 mph (88
km/h) constantly for more thanone minute,5. Recheck for code P0740 {40).
Does the OBD ll scan toolindicate code P0740 or doesthe E indicator light indicate code 40?
The svsteo is OK at this tim€.
Replace the transmission andtorque convertor assembly.
www.emanualpro.com
Page 636 of 1395

Electrical Troubleshooting ('98 - 00 Models)
Troubleshooting Flowchart - Lock-up Control System (cont'd)
From page 14-119
Replace the Lock-up ControlSolenoid Valve A/B Assomblyand Recheck:1. Replace the lock-up controlsolenoid valve A,/B assembly(see page 14-!35).2. Turn the ignition switch OFFand reset the PCM memory byremoving the BACK UP (7.5 A)fuse in the undeFdash fuse/relay box for more than 10seconds.3. Using the scan tool, check tobe sure that the engine coolanttemperature is 176"F {80'C) orabove.4. Drive the vehicle at 55 mph(88 km/h) constantly tor morethan one minute.5. Recheck {or code P0740 (40i.
Does the OBD ll scan tool indicatecode P0740 or does the [9i] or Eindicator light indicate code 40?The system is OK at this time.
14-120
www.emanualpro.com
Page 672 of 1395
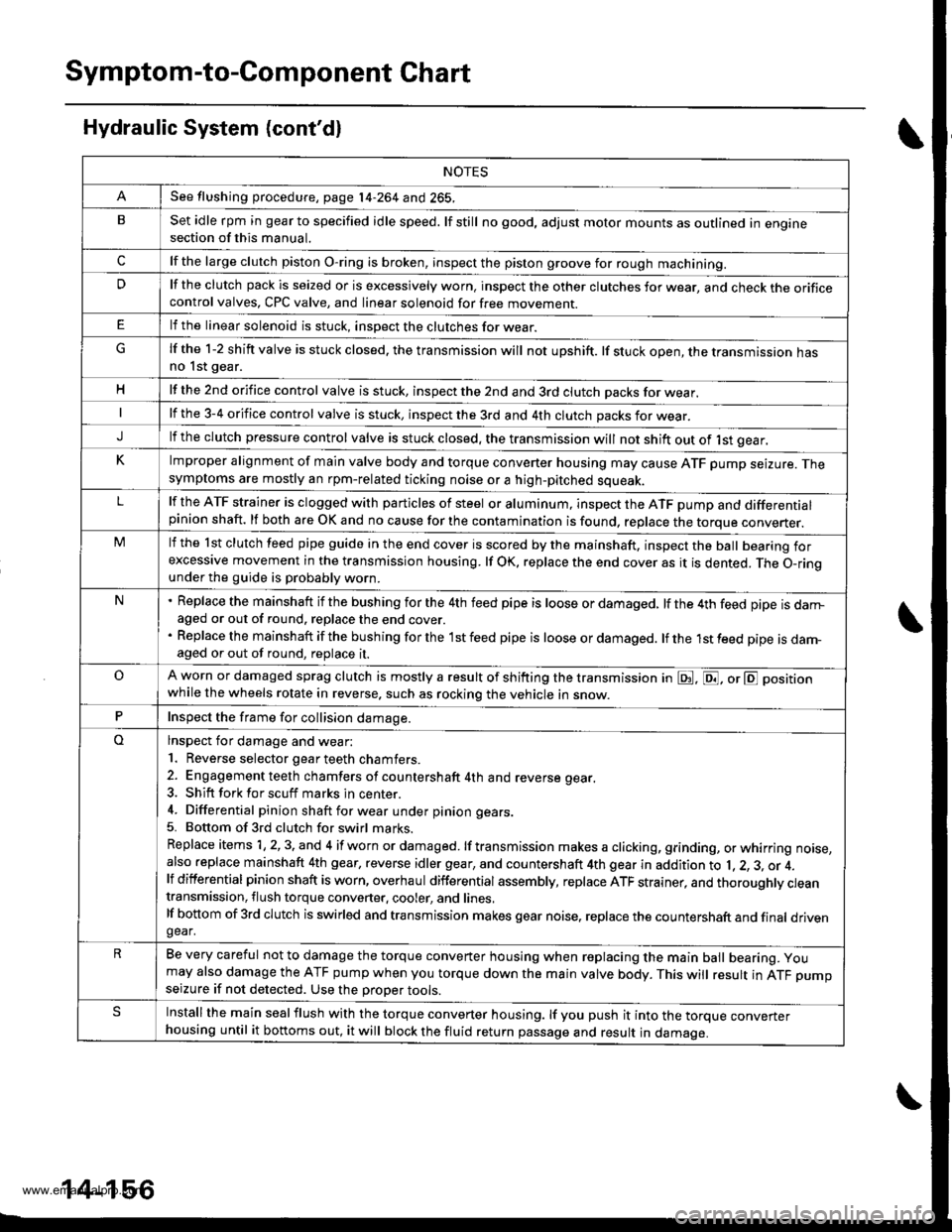
Symptom-to-Com ponent Chart
Hydraulic System (cont'd)
NOTES
See flushing procedure, page l4-264 and 265,
BSet idle rpm in gear to specified idle speed. lf still no good, adjust motor mounts as outlined in enginesection of this manual.
clf the large clutch piston O-ring is broken, inspect the piston groove for rough machining.
Dlf the clutch pack is seized or is excessively worn. inspect the other clutches fot wear, and check the orificecontrol valves, CPC valve, and linear solenoid for free movement.
lf the linear solenoid is stuck, inspect the clutches for wear.
lf the 1-2 shift valve is stuck closed. the transmission will not upshift. lf stuck open, the transmission hasno lst gear.
Hlf the 2nd orifice control valve is stuck, inspect the 2nd and 3rd clutch Dacks for wear.
lf the 3-4 orifice control valve is stuck, inspect the 3rd and 4th clutch packs for wear.
Jlf the clutch pressure control valve is stuck closed. the transmission will not shift out of lst gear.
Klmproper alignment of main valve body and torque converter housing may cause ATF pump seizure. Thesymptoms are mostly an rpm-related ticking noise or a high-pitched squeak.
Llf the ATF strainer is clogged with particles of steel or aluminum, inspect the ATF pump and differentialpinion shaft. lf both are OK and no cause for the contamination is found, replace the torque converter.
Mlf the lst clutch feed pipe guide in the end cover is scored by the mainshaft. inspect the ball bearing forexcessive movement in the transmission housing. lf oK, replace the end cover as it is dented. The o-rinounder the guide is probably worn.
N' Replace the mainshaft if the bushing for the 4th feed pipe is loose or damaged, lf the 4th feed pipe is darrFaged or out of round. replace the end cover.' Replace the mainshaft if the bushing for the l st feed pipe is loose or damaged. lf the 1st feed pipe is dam-aged or out of round, replace it.
oA worn or damaged sprag clutch is mostly a result of shifting the transmission in E!. E, or E positionwhile the wheels rotate in reverse. such as rocking the vehicle in snow.
PInspect the frame for collision damage.
lnspect for damage and wear:
l. Reverse selector gear teeth chamfers.
2. Engagement teeth chamfers of countershaft 4th and reverse gear.
3. Shift fork for scuff marks in center.
4. Differential pinion shaft for wear under pinion gears.
5. Bottom of 3rd clutch for swirl marks.
Replace items 1, 2, 3. and 4 if worn or damaged. lf transmission makes a clicking, grinding, or whirring noise,also replace mainshaft 4th gear, reverse idler gear, and countershaft 4th gear in addition to 1,2, 3, or 4.lf differential pinion shaft is worn, overhaul differential assembly, replace ATF strainer, and thoroughly cjeantransmission, flush torque converter. cooler, and lines,lf bottom of 3rd clutch is swirled and transmission makes gear noise. replace the countershaft and final drivenoear,
Be very careful not to damage the torque converter housing when replacing the main ball bearing. you
may also damage the ATF pump when you torque down the main valve body. This will result in ATF pumpseizure if not detected. Use the Drooer tools.
SInstall the main seal flush with the torque converter housing. lf you push it into the torque converterhousing until it bottoms out, it will block the fluid return passage and result in damage.
www.emanualpro.com
Page 678 of 1395
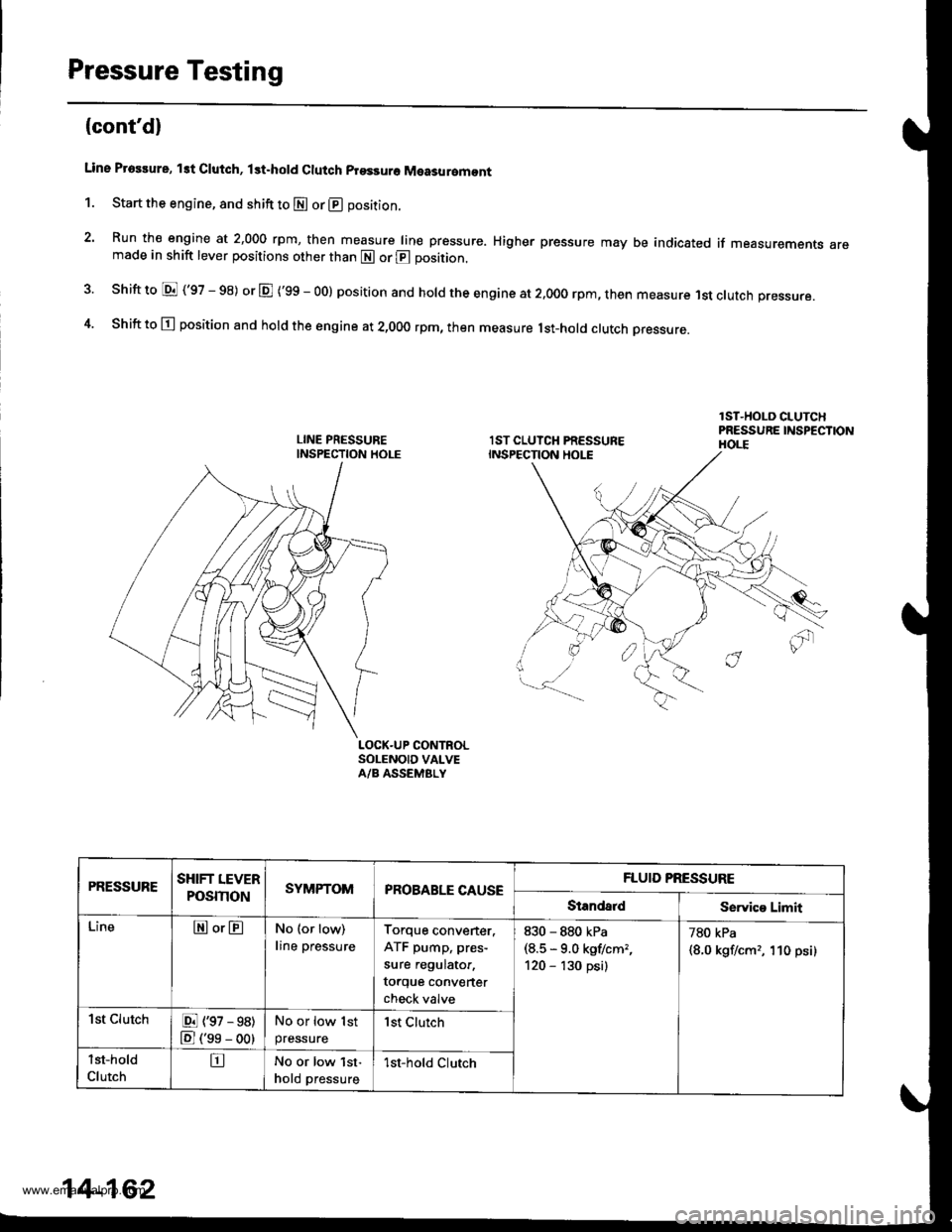
Pressure Testing
(cont'd)
Line Proslure, lst Clutch, lst.hold Clutch prsssuro Measuromont
1. Start the engine, and shift to E or @ position.
2. Run the engine at 2,000 rpm, then measure line pressure. Higher pressure may be indicated if measurements aremade in shift lever positions other than E or @ position.
shift to E ('97 - 98) or E ('99 - oo) position and hold the engine at 2.ooo rpm, then measure 1st clutch pressure.
Shift to E position and hold the engine at 2,000 rpm, then measure lst-hotd ctutch Dressure.
LOCK.UP CONTROLSOLENOID VALVEA/B ASSEMBLY
4.
PRESSURESHIFT LEVER
POSmONSYMPTOMPROBABLE CAUSEFLUID PRESSURE
StandaldService Limit
LineEor@No (or low)
line pressure
Torque converter.
ATF pump, pres-
sure regulator,
torque converter
check valve
830 - 880 kPa(8.5 * 9.0 kgflcm,,
120 - '130 psi)
780 kPa
{8.0 kgf/cm,, 'l10 psi)
1st ClutchE (97 - 98)
E ('se - oo)
No or low 1st
pressurelst Clurch
lst-hold
ClutchtrNo or low lst-
hold pressure1st-hold Clutch
14-162
www.emanualpro.com
Page 684 of 1395
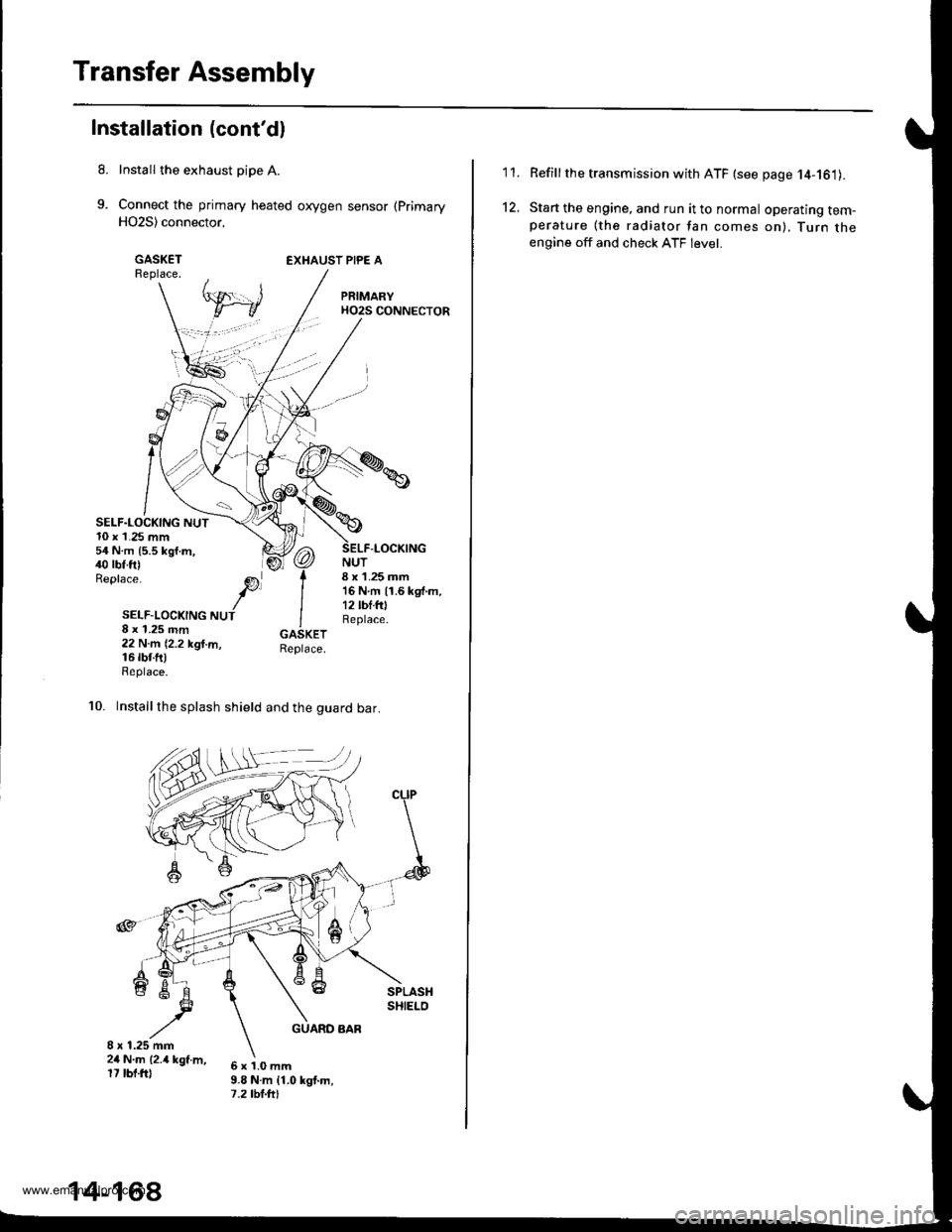
Transfer Assembly
Installation (cont'dl
Install the exhaust pipe A.
Connect the primary heated oxygen sensor (Primary
H02S) connector,
GASKETReplace.EXHAUST PIPE A
SELF.LOCKING NUT10 x 1.25 mm54 N.m {5.5 kgf.m,40 rbf.ft)Replace.
NUT8 x 1.25 mm16Nm11.6kgf.m,12 lbf.fOReplace.
-LOCKING
SELF-LOCKING NUT8 x 1.25 mm22 N.m (2.2 kgl.m,16 rbr.fttReplace.
10. Installthe splash shield and the guard bar.
6x1.0mm9.8 N.m {1.0 kgt.m,7.2 tbt.ftt
14-168
'I '�I.
12.
Refillthe transmission with ATF (see page 14-161).
Start the engine, and run it to normal operating tem-perature (the radiator fan comes on), Turn theengine off and check ATF level.
www.emanualpro.com