Reverse HONDA CR-V 2000 RD1-RD3 / 1.G Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: HONDA, Model Year: 2000, Model line: CR-V, Model: HONDA CR-V 2000 RD1-RD3 / 1.GPages: 1395, PDF Size: 35.62 MB
Page 529 of 1395
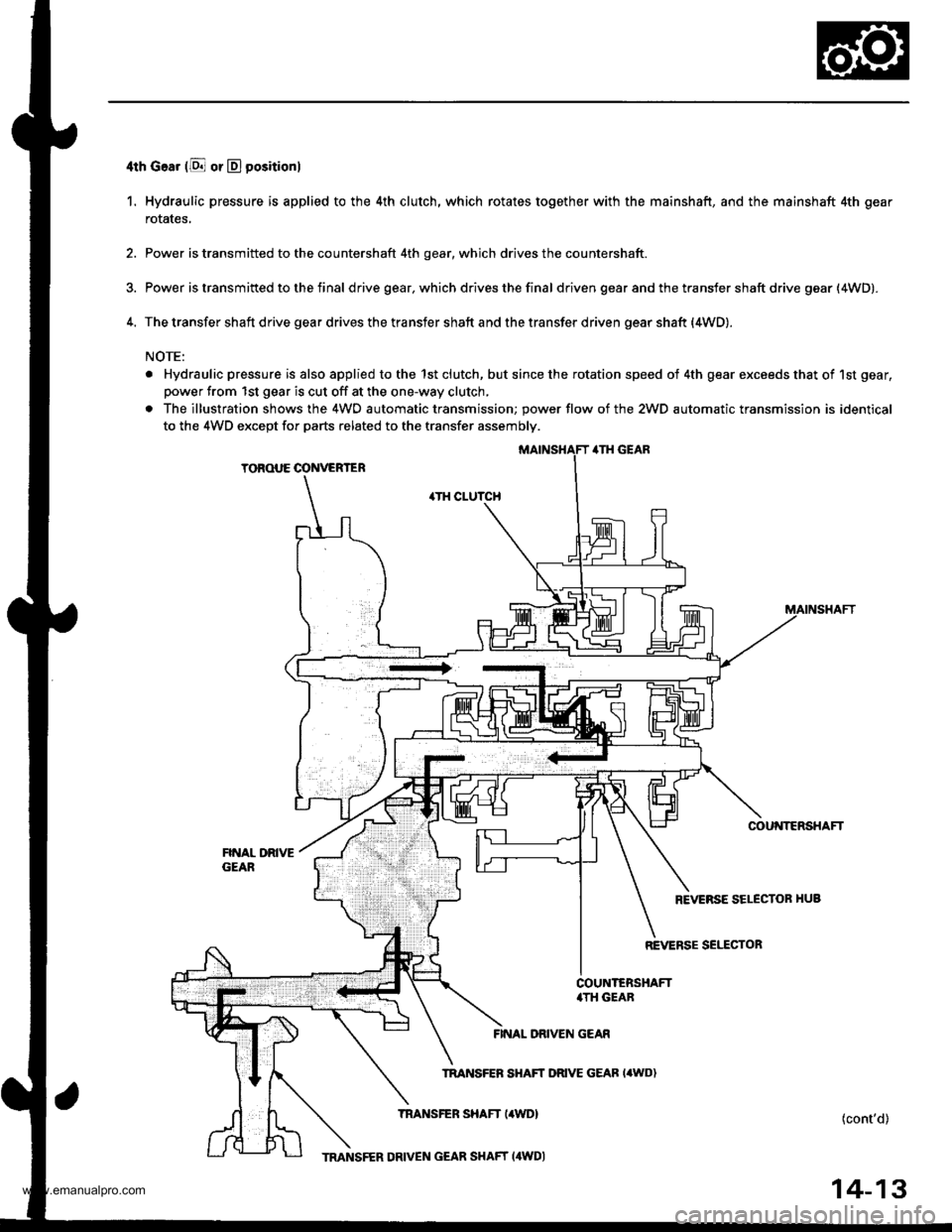
4th Goar (E or D positionl
1. Hydraulic pressure is applied to the 4th clutch, which rotates together with the mainshaft, and the mainshaft 4th gear
rotates,
2. Power is transmitted to the countershaft 4th gear, which drives the countershaft.
3. Power is transm ifted to the f inal d rive gear, which drives the fina I driven gear and the transfer shaft drive gear (4WD).
4. The transfer shaft drive gear drives the transfer shaft and the transfer driven gear shaft {4WD).
NOTE:
. Hydraulic pressure is also applied to the 1st clutch, but since the rotation speed of 4th gear exceeds that of 1st gear,
power from 1st gear is cut off at the one-way clutch,
. The illustration shows the 4WO automatic transmission; power flow of the 2WD automatic transmission is identical
to the 4WD except for parts related to the transfer assembly.
ilTH GEAR
TOROUE CONVERTER
.TH CLUTCH
COU'{TERSHAFT
REVERSE SELECTOR HUB
REVERSE SELECTOR
FINAL DRIVEN GEAR
TRANSFEB SHAFT DRIVE GEAB I'WD)
TNANSFER SHAFT I4WDI{cont'd)
14-13
TMNSFER DRIVEN GEAR SHAFT (4WDI
www.emanualpro.com
Page 530 of 1395
Description
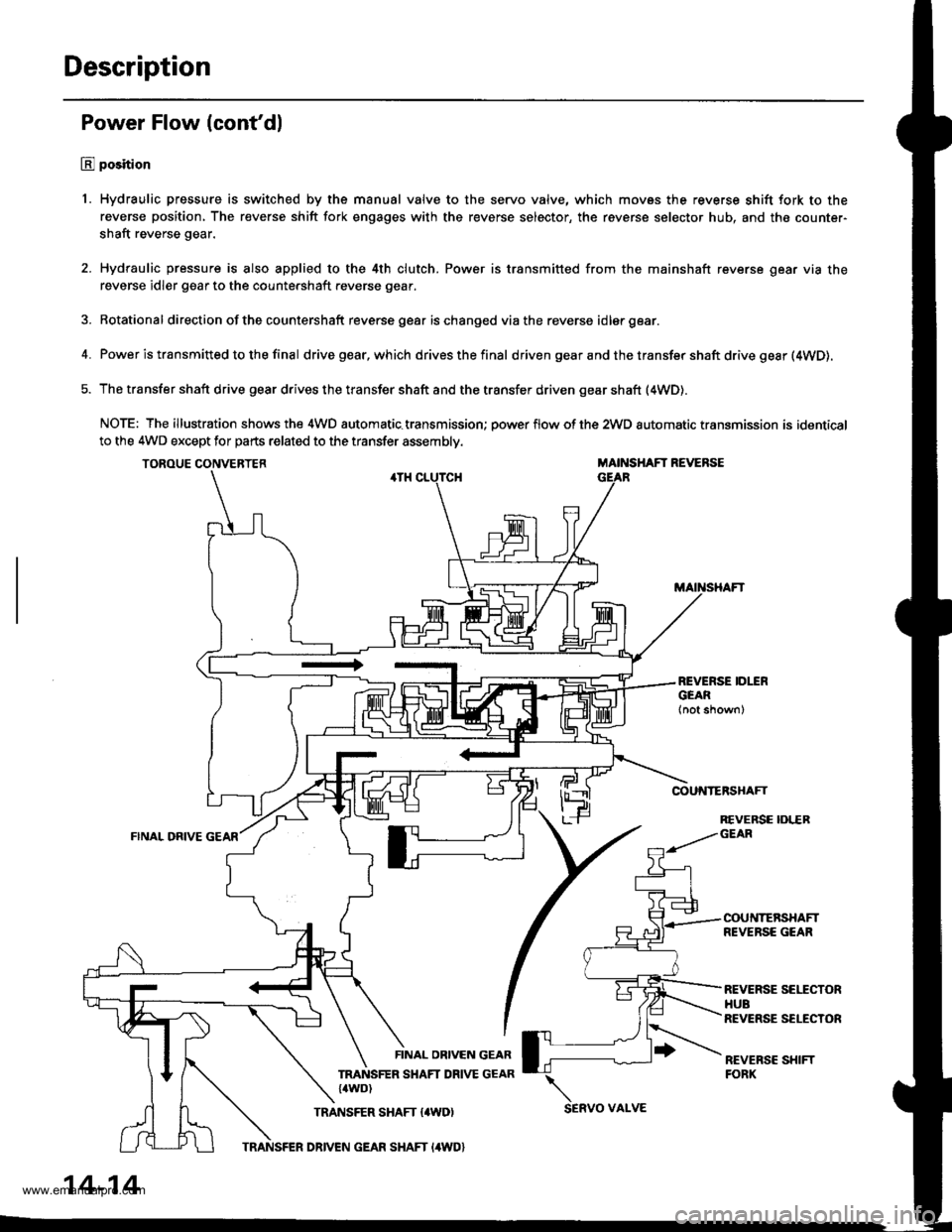
Power Flow (cont'dl
E position
1. Hydraulic pressure is switched by the manual valve to the servo valve, which movss the reverse shift fork to the
reverse position, The reverse shift fork engages with the reverse selector, the reverse selector hub, and the counter-
shaft reverse gear.
2. Hydraulic pressure is also applied to the 4th clutch. Power is transmitted from the mainshaft reverse gear via the
reverse idler gear to the countershaft reverse gear.
3. Rotational direction ofthe countershaft reverse gear ischanged viathe reverse idlergear.
4. Power is transmitted to the final drivegear,which drivesthefinal d riven gear a nd the transfer shaft drive gesr (4WD).
5. The transfer shaft drive gear drives the transfer shaft and the transfer driven gear shaft (4WD).
NOTE: The illustration shows the 4WD automatic.transmission; power flow of the 2wD automatic transmission is identical
to the 4WD except for parts related to the transfer assembly.
TOROUE CONVERTERMAINSHAFT REVERSE
COUNTERSHAFT
FINAL ORIVE
REVERSE IDLERGEAR
COUNTERSHAFTREVERSE GEAR
REVERSE SEITCTORHUBREVERSE SELECTOR
REVEBSC SHIFTFORK
FINAL OBIVEN GEAR
TRANSFER SHAFT DRIVE GEAR{4WD)
TRANSFER SHAFT {4WD)SERVO VAI-VE
14-14
TRANSFER DRIVEN GEAR SHAFT I4WD}
www.emanualpro.com
Page 533 of 1395
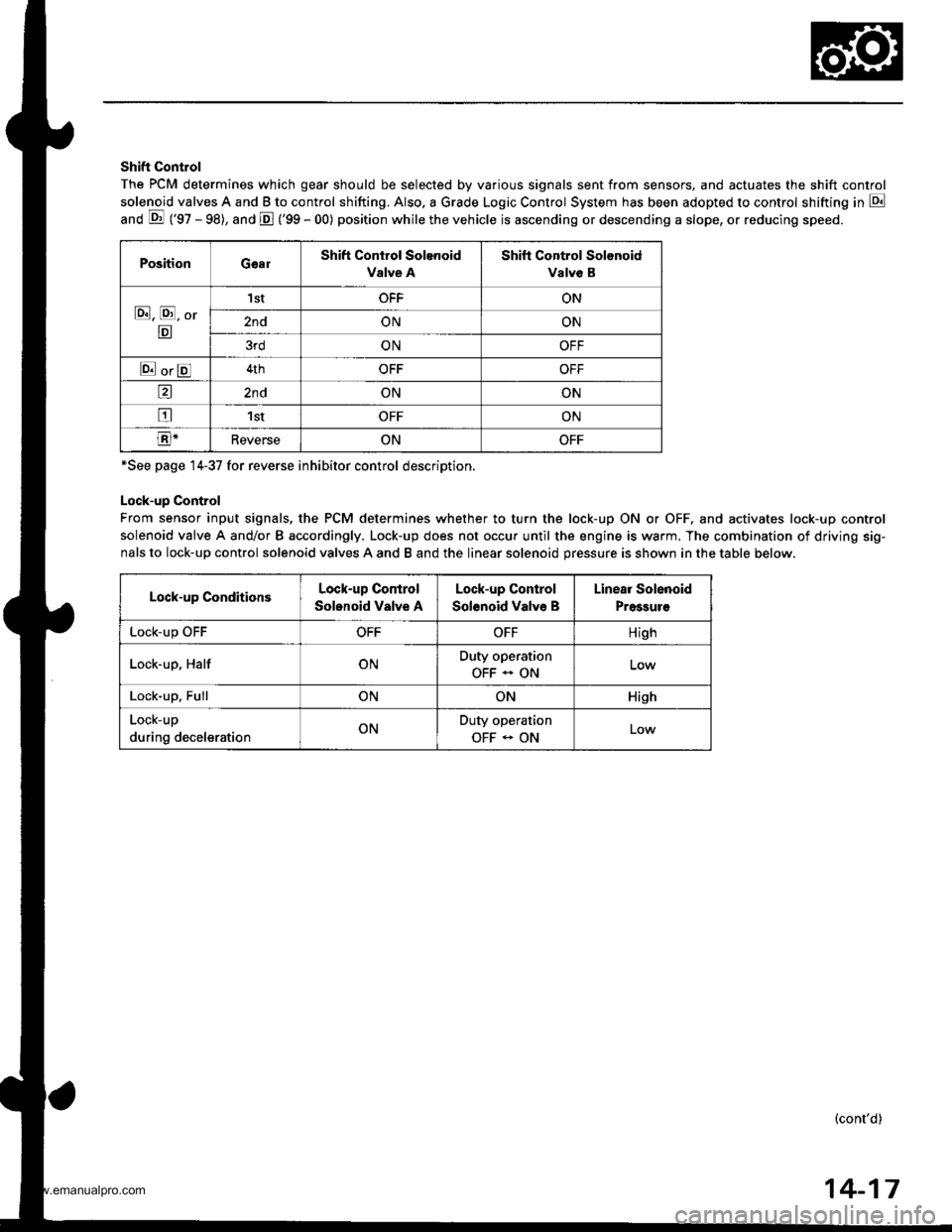
Shift Control
The PCM determines which gear should be selected by various signals sent from sensors, and actuates the shift control
solenoid valves A and B to control shifting. Also. a Grade Logic Control System has been adopted to control shifting in E
anO E ('gZ - gg), and E ('99 - 00) position while the vehicle is ascending or descending a slope, or reducing speeo.
PositionGearShift Control Solenoid
Valve A
Shift Control Solonoid
Valve B
E, E, Or
E
'I stOFFON
2ndONON
3rdONOFF
E orE4thOFFOFF
a2ndONON
tr1stOFFON
E-ReverseONOFF
*See page 14-37 for reverse inhibitor control description.
Lock-up Control
From sensor input signals, the PCM determines whether to turn the lock-up ON or OFF, and activates lock-up control
solenoid valve A and/or B accordingly. Lock-up does not occur until the engine is warm. The combination of driving sig-
nals to lock-up control solenoid valves A and B and the linear solenoid pressure is shown in the table below.
Lock-up ConditionsLock-up Control
Solonoid Valve A
Lock-up Control
Solenoid Valve B
Linear Solenoid
Pressuro
LOCK-Up \JrrOFFOFFHigh
Lock-up, HalfONDuty operation
OFF - ON
Lock-up, FullONONHish
Lock-up
during decelerationONDuty operation
OFF - ONLow
(cont'd)
14-17
www.emanualpro.com
Page 544 of 1395
Description
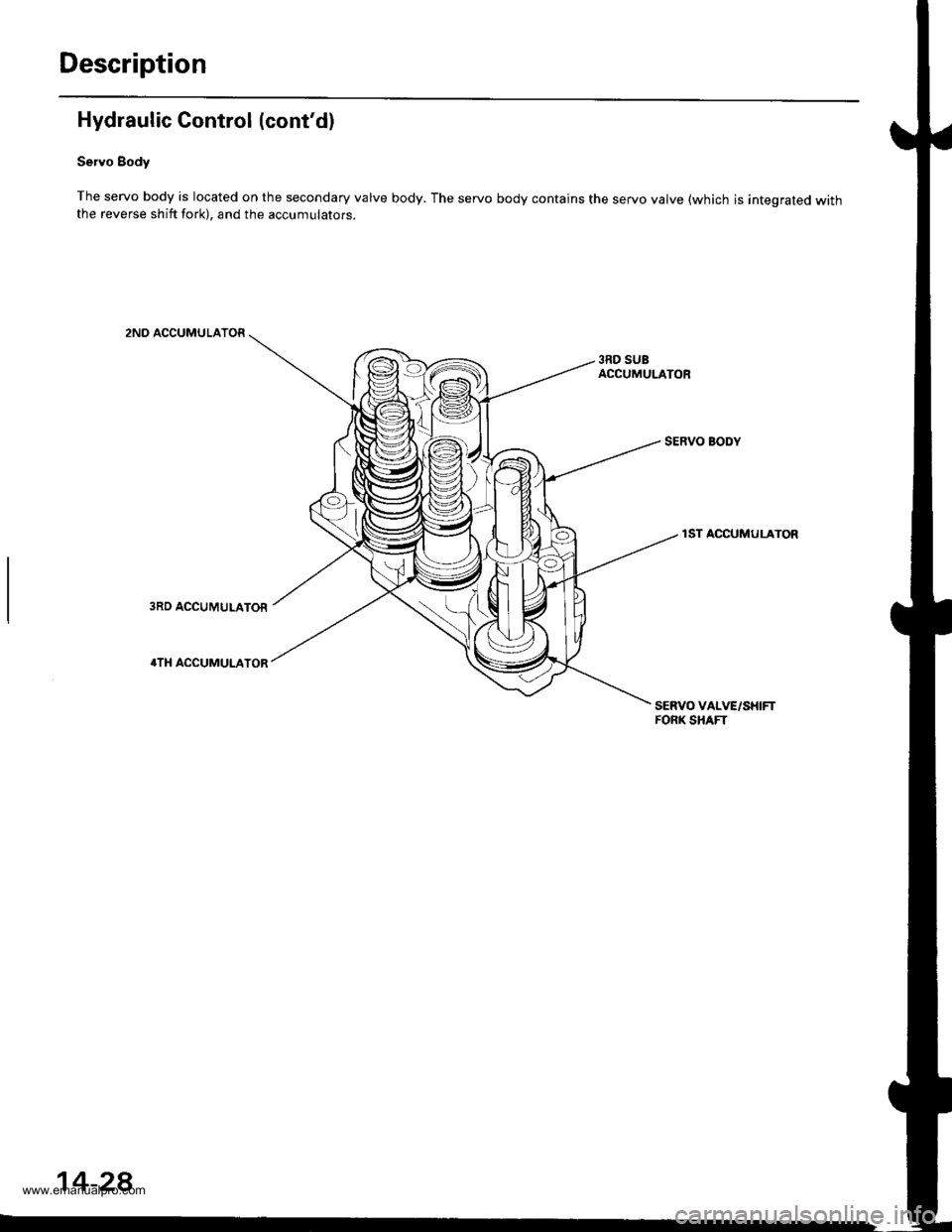
Hydraulic Control (cont'd)
Servo Body
The servo body is located on the secondary valve body. The servo body contains the servo valve (which is integrated withthe reverse shift fork), and the accumulators.
2ND ACCUMULATOR
3RD SUBACCUMULATOR
SERVO BODY
1ST ACCUMULATOR
SERVO VALVE/SHIFTFORK SHAFT
14-28
www.emanualpro.com
Page 553 of 1395
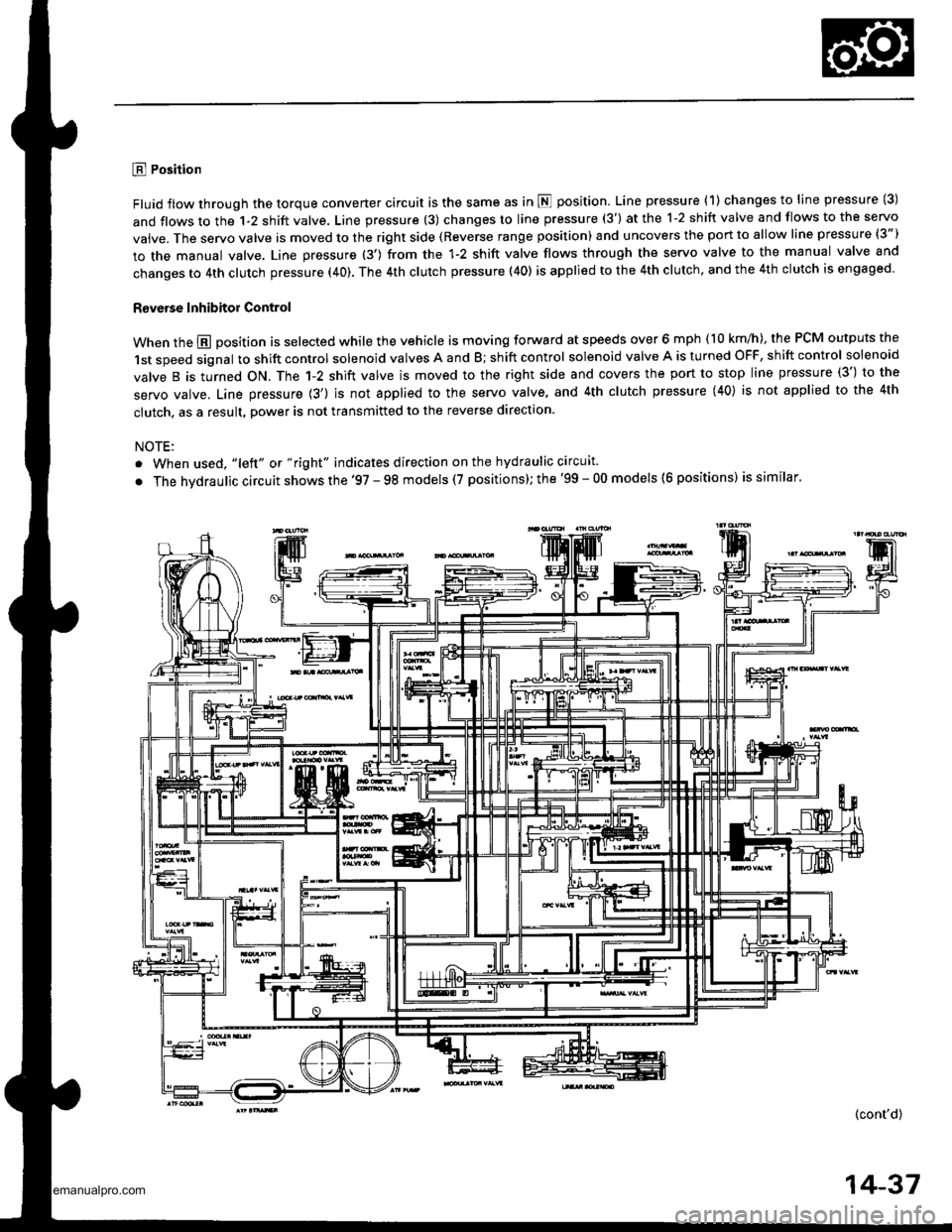
E Position
Fluid flow through the torque converter circuit is the same as in N position. Line pressure (1) changes to line pressure (3)
and flows to the 1-2 shift valve. Line pressure (3) changes to line pressure (3') at the 1-2 shift valve and flows to the servo
vaive. The servo valve is moved to the right side (Reverse range position) and uncovers the port to allow line pressure (3")
to the manual valve. Line pressure (3') from the 1-2 shift valve flows through the servo valve to the manual valve and
changes to 4th clutch pressure (40). The 4th clutch pressure (40) is applied to the 4th clutch, and the 4th clutch is engaged.
R€verse Inhibitor Control
When the @ position is selected while the vehicle is moving forward at speeds over 6 mph (10 km/h), the PCM outputs the
1st speed signal to shift control solenoid valves A and B; shift control solenoid valve A is turned OFF, shift control solenoid
valve B is turned ON. The 1-2 shift valve is moved to the right side and covers the port to stop line pressure (3') to the
servo valve. Line pressure {3') is not applied to the servo valve, and 4th clutch pressure (40} is not applied to the 4th
clutch, as a result, power is not transmitted to the reverse direction.
NOTE:
. When used, "lelt" ot " right" indicates direction on the hydraulic circuit.
. The hvdraulic circuit shows the '97 - 98 models (7 positions); the '99 - 00 models (6 positions) is similar'
(cont'd)
14-37
www.emanualpro.com
Page 554 of 1395
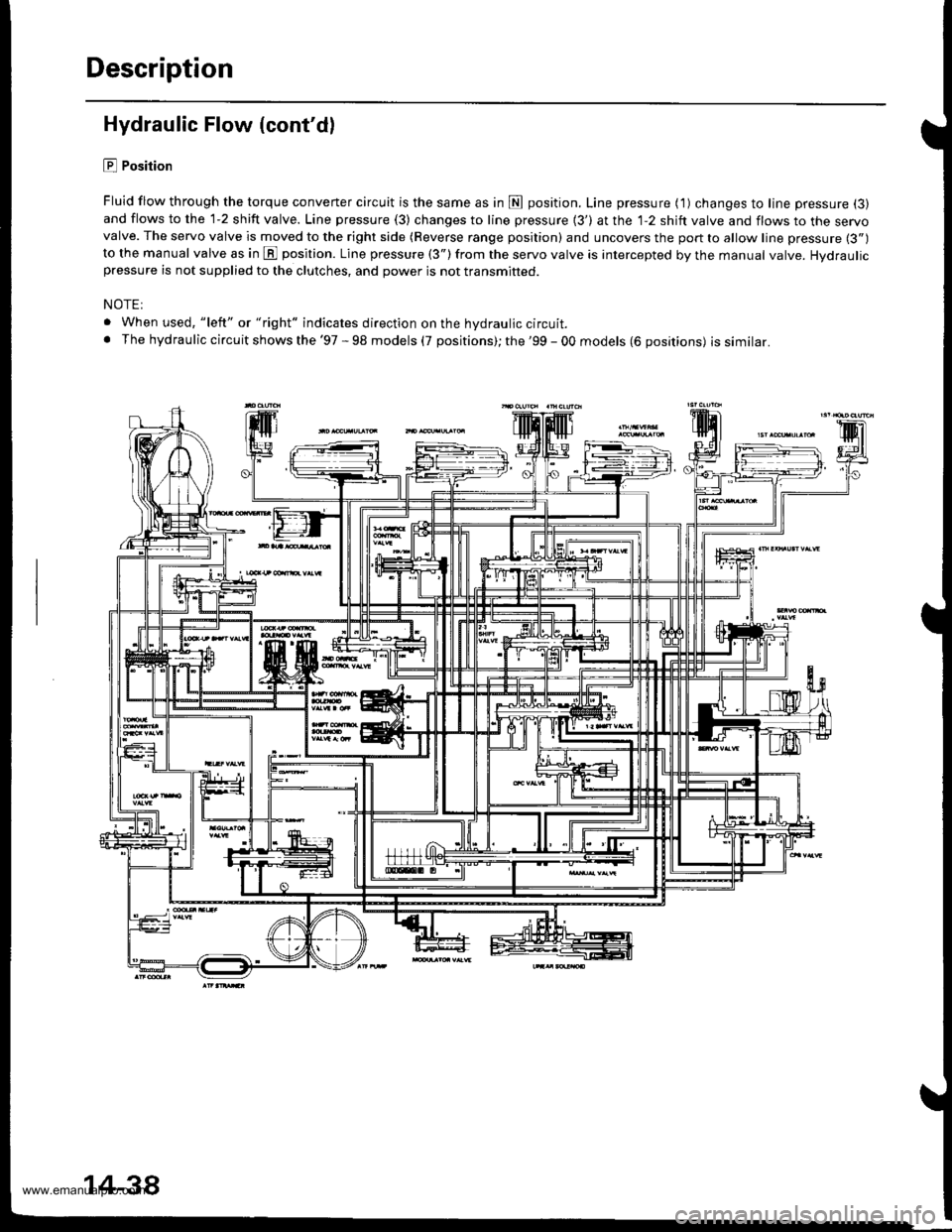
Description
Hydraulic Flow (cont'dl
E Position
Fluid flow through the torque converter circuit is the same as in fl position. Line pressure ( 1) changes to line pressure (3)
and flows to the 1-2 shift valve. Line pressure (3) changes to line pressure {3') at the 1-2 shift valve and flows to the servovalve. The servo valve is moved to the right side (Reverse range position) and uncovers the port to allow line pressure (3")
to the manual valve as in E position. Line pressure (3") from the servo valve is intercepted by the manual valve. Hydraulicpressure is not supplied to the clutches, and power is not transmitted.
NOTE:
. When used, "left" or "right" indicates direction on the hydraulic circuit.. The hydraulic circuit shows the '97 - 98 models (7 positions); the '99 - 00 models (6 positions) issimilar.
14-38
www.emanualpro.com
Page 556 of 1395
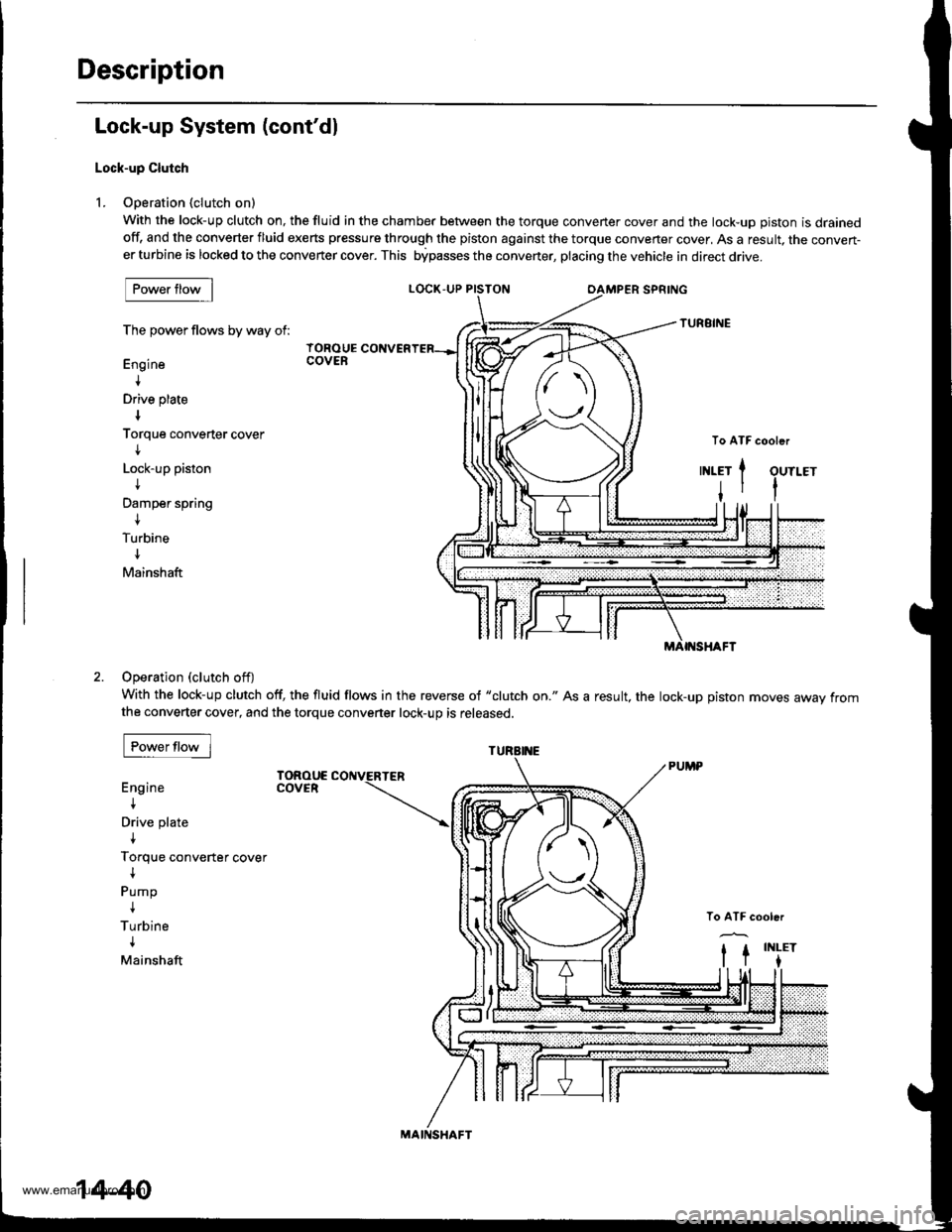
Description
Lock-up System (cont'dl
Lock-up Clutch
L Ooeration (clutch on)
With the lock-up clutch on, the fluid in the chamber between the torque convener cover and the lock-uD oiston is drainedoff, and the converter fluid exerts pressure through the piston against the torque converter cover, As a result, the conven-er turbine is locked to the converter cover. This bipasses the converter, placing the vehicle in direct drive.
LOCK,UP PISTON
The power flows by way of:
Engine
+
Drive plate
Torque converter cover
I
Lock-up piston
t
Damper spring
{
Turbine
Mainshaft
IOROUECOVER
Operation (clutch off)
With the lock-up clutch off, the fluid flows in the reverse of "clutch on." As a result, the lock-up piston moves away fromthe converter cover, and the torque converter lock-up is released.
Engine
I
Drive plate
{
Torque converter cover
{
Pump
I
Turbine
{
Mainshaft
TOROUECOVER
To ATF cooler{(1\\n1INLET
t
Jtl
ort
MAIf{SHAFT
MAII{SHAFT
14-40
www.emanualpro.com
Page 663 of 1395
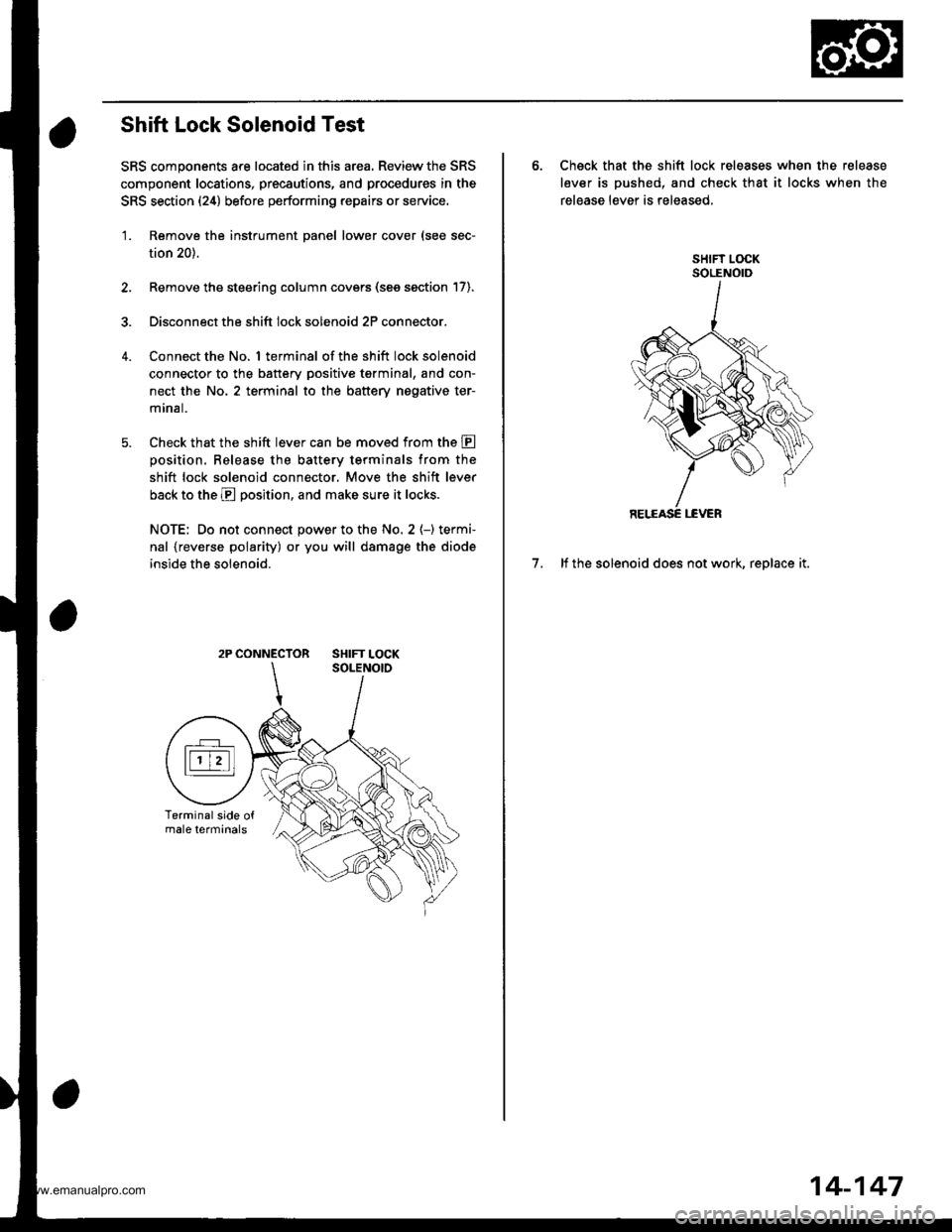
Shift Lock Solenoid Test
SRS components are located in this area. Review the SRS
component locations, precautions, and procedures in the
SRS section (24) before performing repairs or service,
'1. Remove the instrument panel lower cover (see sec-
tion 20).
2. Remove the steering column covers (see section 17).
3. Disconnect the shift lock solenoid 2P connector.
Connect the No. 1 terminal of the shift lock solenoid
connector to the battery positive tgrminal, and con-
nect the No. 2 terminal to the battery nogative ter-
mrnal.
Check that the shift lever can be moved from the E
oosition. Release the batterv terminals from the
shift lock solenoid connector. Move the shift lever
back to the E position, and make sure it locks.
NOTE: Do not connect power to the No. 2 (-) termi-
nal {reverse polarity) or you will damage the diode
inside the solenoid.
2P CONNECTOR SHIFT LOCK
6. Check that the shift lock releases when the release
lever is pushed, and check that it locks when the
release lever is released,
7. lf the solenoid does not work, replace it.
14-147
www.emanualpro.com
Page 664 of 1395
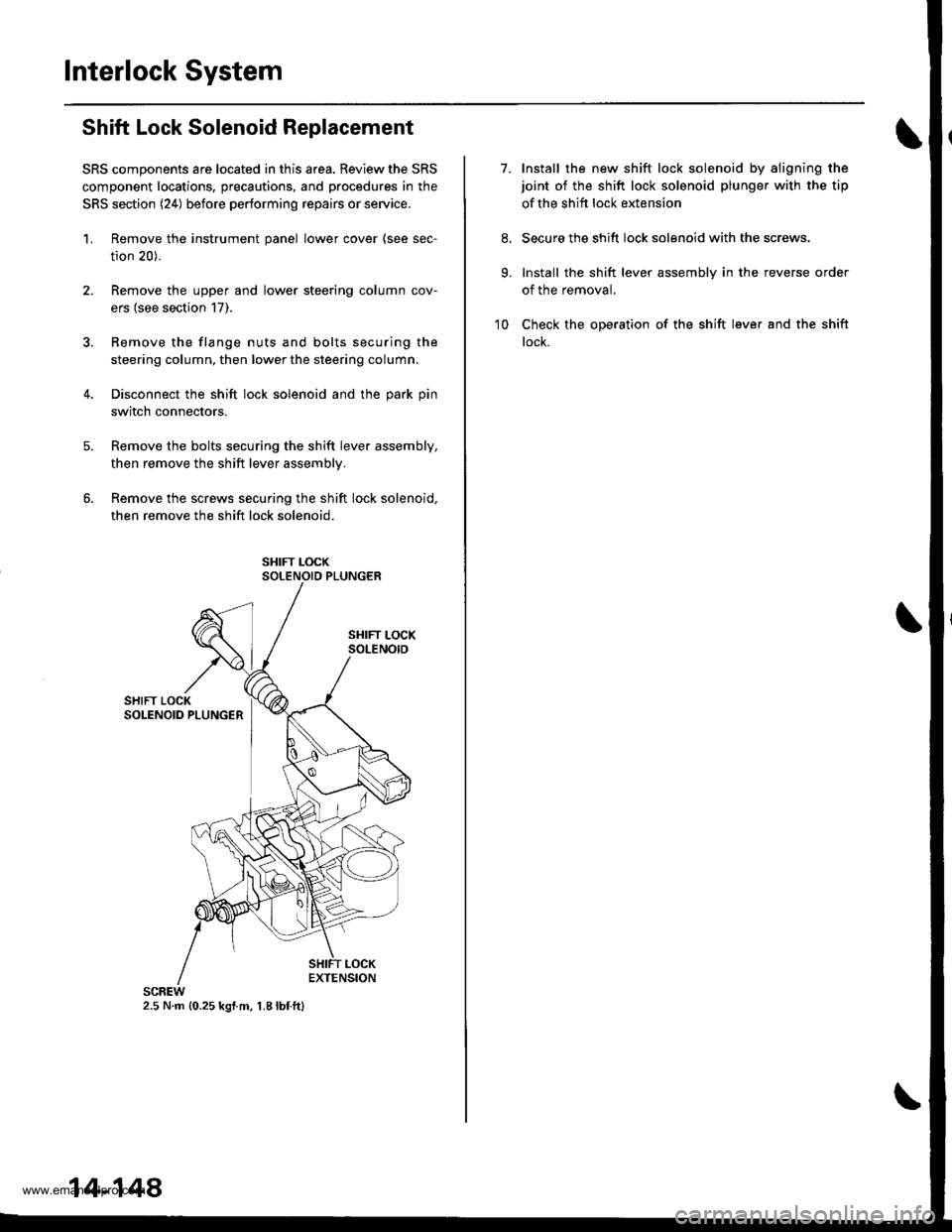
Interlock System
Shift Lock Solenoid Replacement
SRS components are located in this area. Review the SRS
component locations, precautions, and procedures in the
SRS section (24) before performing repairs or service.
'L Remove the instrument panel lower cover (see sec-
tion 20).
2. Remove the upper and lower steering column cov-
ers (see section 17).
3. Bemove the flange nuts and bolts securing the
steering column, then lower the steering column.
4. Disconnect the shift lock solenoid and the park pin
switch connectors.
Remove the bolts securing the shift lever assembly,
then remove the shift lever assemblv.
Remove the screws securing the shift lock solenoid,
then remove the shift lock solenoid.
2.5 N.m {0.25 kgl.m, 1.8lbf.ft}
14-148
7.Install the new shift lock solenoid by aligning the
joint of the shift lock solenoid plunger with the tip
of the shift lock extension
Secure the shift lock solenoid with the screws,
Install the shift lever assembly in the reverse order
of the removal.
Check the operation of the shift lever and the shift
lock.
9.
10
www.emanualpro.com
Page 666 of 1395

Interlock System
Park Pin Switch Replacement -'97 - 98 Models
SRS components are located in this area. Review the SRS component locations, precautions, and procedures in the SRS
section (24) before performing repairs or service.
1. Remove the instrument Danel lower cover (see section 20).
2. Remove the upper and lower steering column covers (see section li,.
3. Remove the flange nuts and bolts securing the steering column. then lower the steering column.4. Disconnect the shift lock solenoid and the park pin switch connectors.
5. Remove the harness clamp bracket.
6. Remove the bolts secu ring the shift lever assembly, then removetheshift lever assembly.
7. Remove the screws securing the shift lock solenoid. then remove the shift lock solenoid,
8. Remove the parkpin switch connector from the shift lever control bracket.
9. Remove the control checker from the shift lever control bracket.
10. Remove the park Din switch from the control checker.
PARK PIN SWITCH
PARK PINSWITCH CONNECTOR
scnEw2.5 N m 10.25 kgt.m, 1.8 lbtftl
9.3 N.m 10.95 kgf.m, 6.9 lbl.ft)
BRACKETCONTROL CHECKER
11. Install the new Dark Din switch on the control checker.
12. lnstall the control checker on the shift lever control bracket.
13. Routethe park pin switch harness through thecutoutofthe shift lever control bracket, then install the park pin switchconnector on the bracket.
14. Install the sh ift lock solenoid by a ligning the joint of the sh ift lock solenoid plu nger with the tip of the shift lock exten-sion.
15. Secure the shift lock solenoid with the screws.
15. Install the shift lever assembly in the reverse order of the removal.'17. Check the operation of the shift lever and the shift lock.
14-150
www.emanualpro.com