engine HONDA PRELUDE 1990 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: HONDA, Model Year: 1990, Model line: PRELUDE, Model: HONDA PRELUDE 1990Pages: 143, PDF Size: 2.07 MB
Page 117 of 143
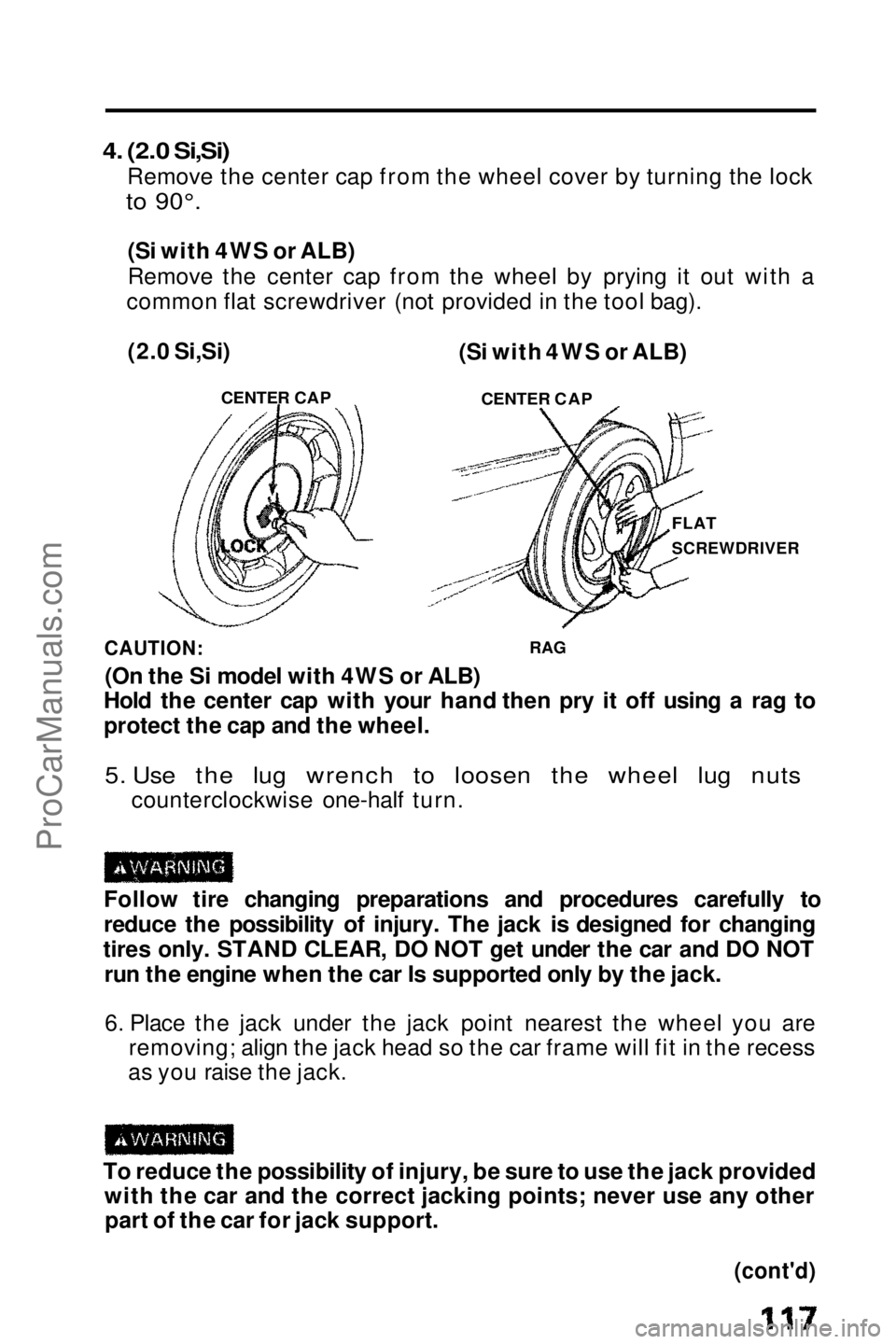
4. (2.0 Si,Si)
Remove the center cap from the wheel cover by turning the lock
to 90°.
(Si with 4WS or ALB)
Remove the center cap from the wheel by prying it out with a
common flat screwdriver (not provided in the tool bag).
(2.0 Si,Si)
CAUTION:
(On the Si model with 4WS or ALB)
Hold the center cap with your hand then pry it off using a rag to
protect the
cap and the wheel.
5. Use the lug wrench to loosen the wheel lug nuts
counterclockwise one-half turn.
Follow tire changing preparations and procedures carefully to
reduce the possibility of injury. The jack
is designed for changing
tires only.
STAND CLEAR, DO NOT get under the car and DO NOT
run the engine when the car Is supported only by the jack.
6. Place the jack under the jack point nearest the wheel you are removing; align the jack head so the car frame will fit in the recess
as you raise the jack.
To reduce the possibility of injury, be sure to use the jack provided with the car and the correct jacking points; never use any otherpart of the car for jack support.
RAG
(cont'd)
CENTER CAP
CENTER CAP
(Si with 4WS or ALB)
FLAT
SCREWDRIVERProCarManuals.comMain Menu t s
Page 119 of 143
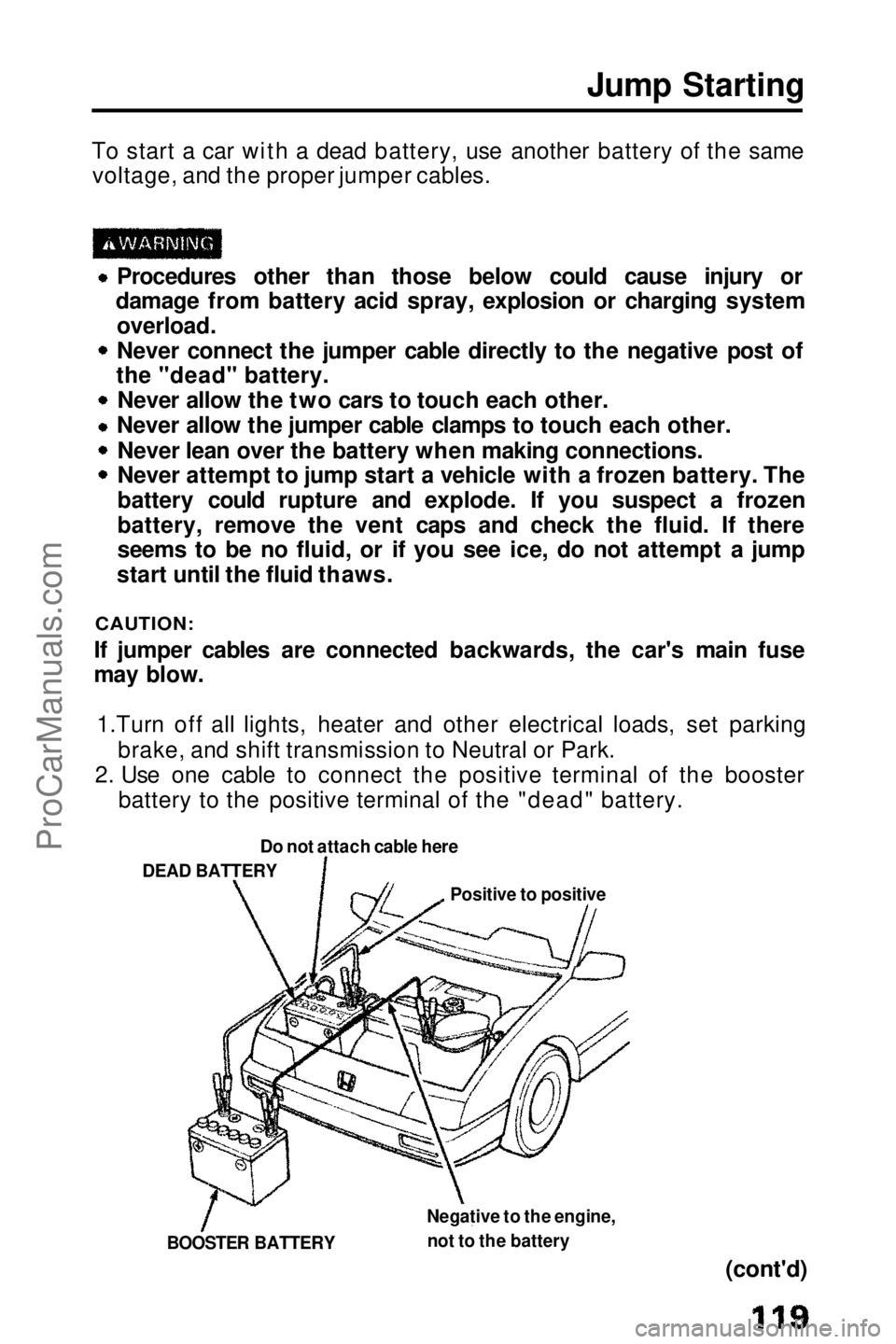
Jump Starting
To start a car with a dead battery, use another battery of the same voltage, and the proper jumper cables. Procedures other than those below could cause injury or
damage from battery acid spray, explosion or charging system
overload.
Never connect the jumper cable directly to the negative post of
the "dead" battery.
Never allow the two cars to touch each other.
Never allow the jumper cable clamps to touch each other.
Never lean over the battery when making connections.
Never attempt to jump start a vehicle with a frozen battery. The
battery could rupture and explode. If you suspect a frozen
battery, remove the vent caps and check the fluid. If there
seems to be no fluid, or if you see ice, do not attempt a jump
start until the fluid thaws.
CAUTION:
If jumper cables are connected backwards, the car's main fuse
may blow.
1.Turn off all lights, heater and other electrical loads, set parking
brake, and
shift transmission to Neutral or Park.
2. Use one cable to connect the positive terminal of the booster battery to the positive terminal of the "dead" battery.
(cont'd)
Do not attach cable here
DEAD BATTERY
Positive to positive
Negative to the engine, not to the battery
BOOSTER BATTERYProCarManuals.comMain Menu t s
Page 120 of 143

Jump Starting (cont'd)
3. Use the other cable to connect the negative terminal of the booster battery to the engine at the ground cable as shown.
4.To remove the cables, reverse the above procedures exactly.
DO NOT push or tow a car to start it. The forward surge when the
engine starts could cause a collision. Also, under some conditions,
the catalytic converter could be damaged. A car equipped with an
automatic transmission cannot be started by pushing or towing.
NOTE:
After jump-starting the car, there is a possibility that the ALB
warning light may come on due to insufficient battery voltage. After
the battery is sufficiently recharged and the engine is turned off and restarted, the ALB warning light should indicate that the ALB
system is OK, by coming on for a few seconds each time the engine is started. If the light remains on after recharging, have it checked
by a Honda dealer.ProCarManuals.comMain Menu t s
Page 121 of 143
If towing is necessary, contact a professional towing service. Your
authorized Honda dealer can assist you with detailed towing
instructions.
Never use tow chains or rope to tow a car; your ability to safety
control the car may be adversely affected.
We recommend the following:
Flat Bed Equipment — Entire car is winched on a flat bed vehicle.
This is the best way of transporting your Honda.
Wheel Lift Type — Tow with the front wheels off the ground.
If the
car can only be towed with the front wheels on the ground:
make sure the transmission is full of fluid (see page 86 — 87)
and tow with the transmission in neutral (N) and the ignition key in
the I position.
CAUTION:
To avoid serious damage on automatic transmission cars, first start the engine and shift to D, then to N and shut the engine off. If
the engine does not run or the transmission cannot be shifted
while the engine is running, the car must be transported on flatbed equipment.
Check local regulations for towing.
CAUTION:
Do not exceed 35 mph (55 km/h) or tow for distances of more
than 50 miles (80 km). If a Sling Type tow is used, the tow truck driver should position
wood spacer blocks between your car's frame and the chains
and lift straps to avoid damaging the bumper and the body. Do not use the bumpers to lift the car or to support the car's
weight while towing.
When towing a car with 4WS even with the front wheels off the ground, turn the wheels straight ahead and tie the steering wheel in place. TowingProCarManuals.comMain Menu s t
Page 122 of 143

If Your Car Gets Stuck
If your car gets stuck in sand, mud, or snow, call a professional
towing service for assistance in getting your car out,
CAUTION:
Do not rev up the engine and allow the wheels to spin freely at
high speed. Severe transmission damage may result if the wheels are allowed to spin for more than a few seconds. DO NOT try to free a car with automatic transmission from
snow etc. by rocking the car alternately between forward and
reverse gears. Severe transmission damage may result from
shifting into gear with the wheels moving.ProCarManuals.comMain Menu s t
Page 123 of 143
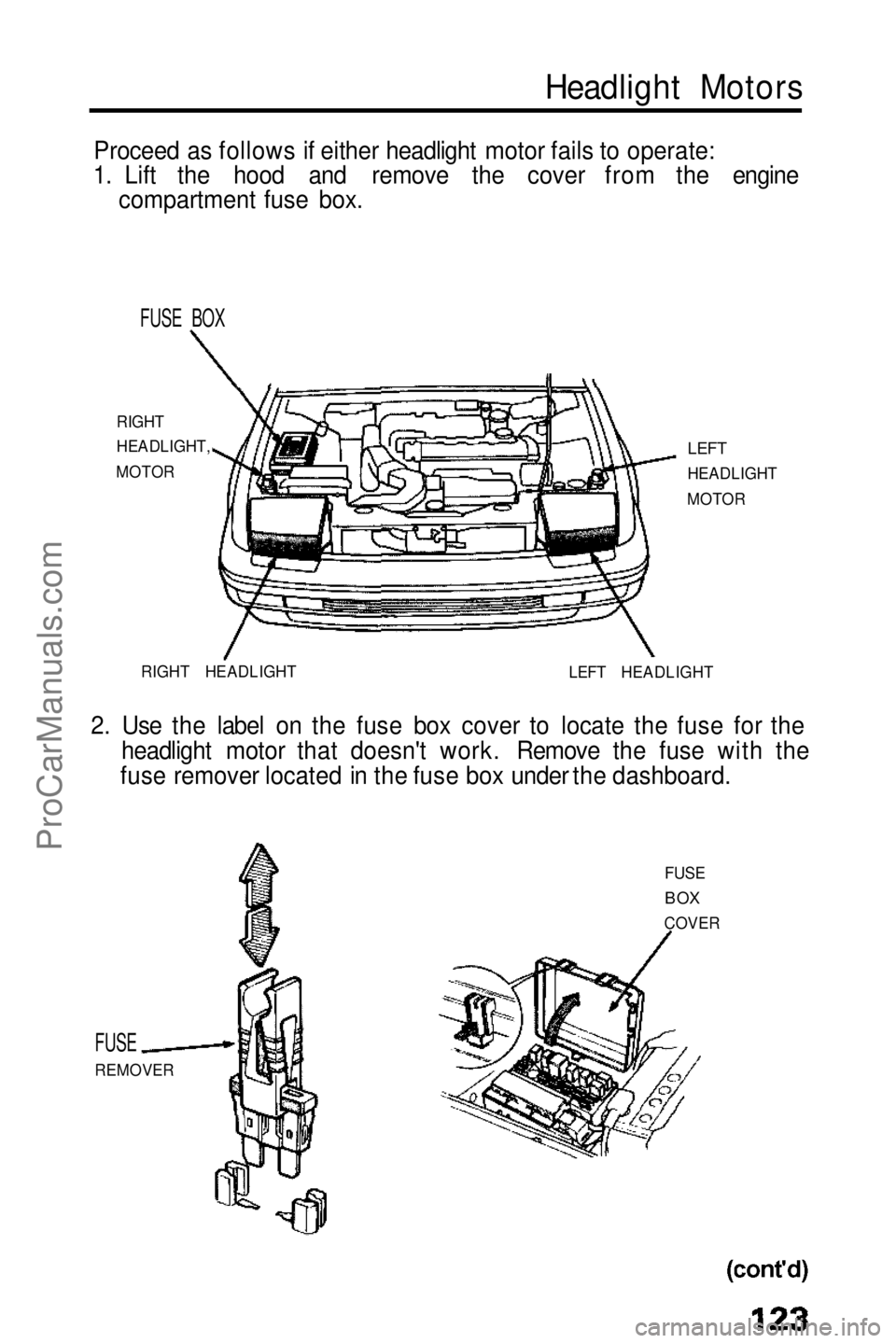
Headlight Motors
Proceed as follows if either headlight motor fails to operate:
1. Lift the hood and remove the cover from the engine compartment fuse box.
FUSE BOX
RIGHT
HEADLIGHT,
MOTOR
LEFT
HEADLIGHT
MOTOR
RIGHT HEADLIGHT LEFT HEADLIGHT
2. Use the label on the fuse box cover to locate the fuse for the headlight motor that doesn't work. Remove the fuse with the
fuse remover located in the fuse box under the dashboard.
FUSE
REMOVER FUSE
BOX
COVERProCarManuals.comMain Menu s t
Page 125 of 143
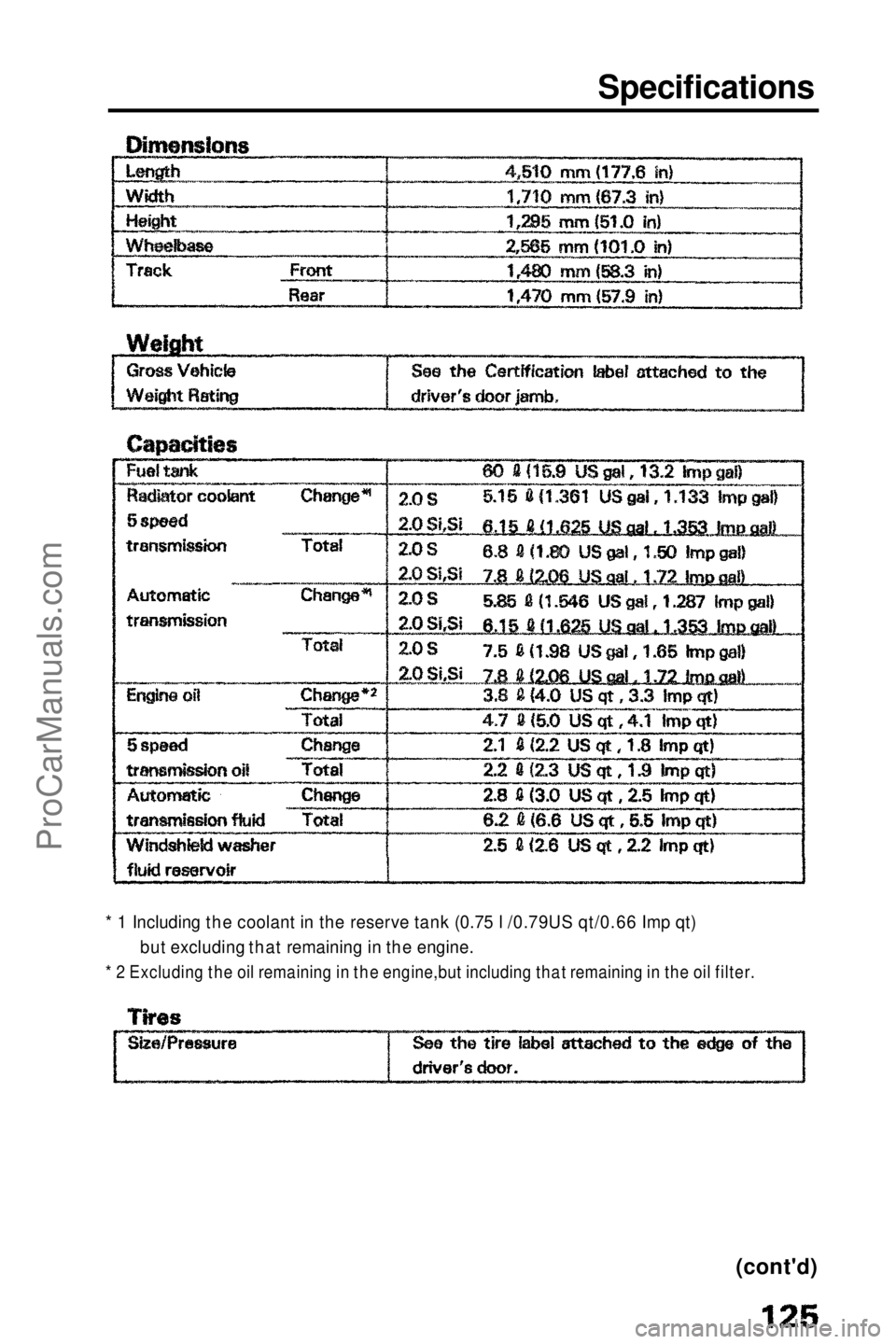
Specifications
* 1 Including the coolant in the reserve tank (0.75 l /0.79US qt/0.66 Imp qt) but excluding that remaining in the engine.
* 2 Excluding the oil remaining in the engine,but including that remaining in the oil filter.
(cont'd)ProCarManuals.comMain Menu t s
Page 127 of 143
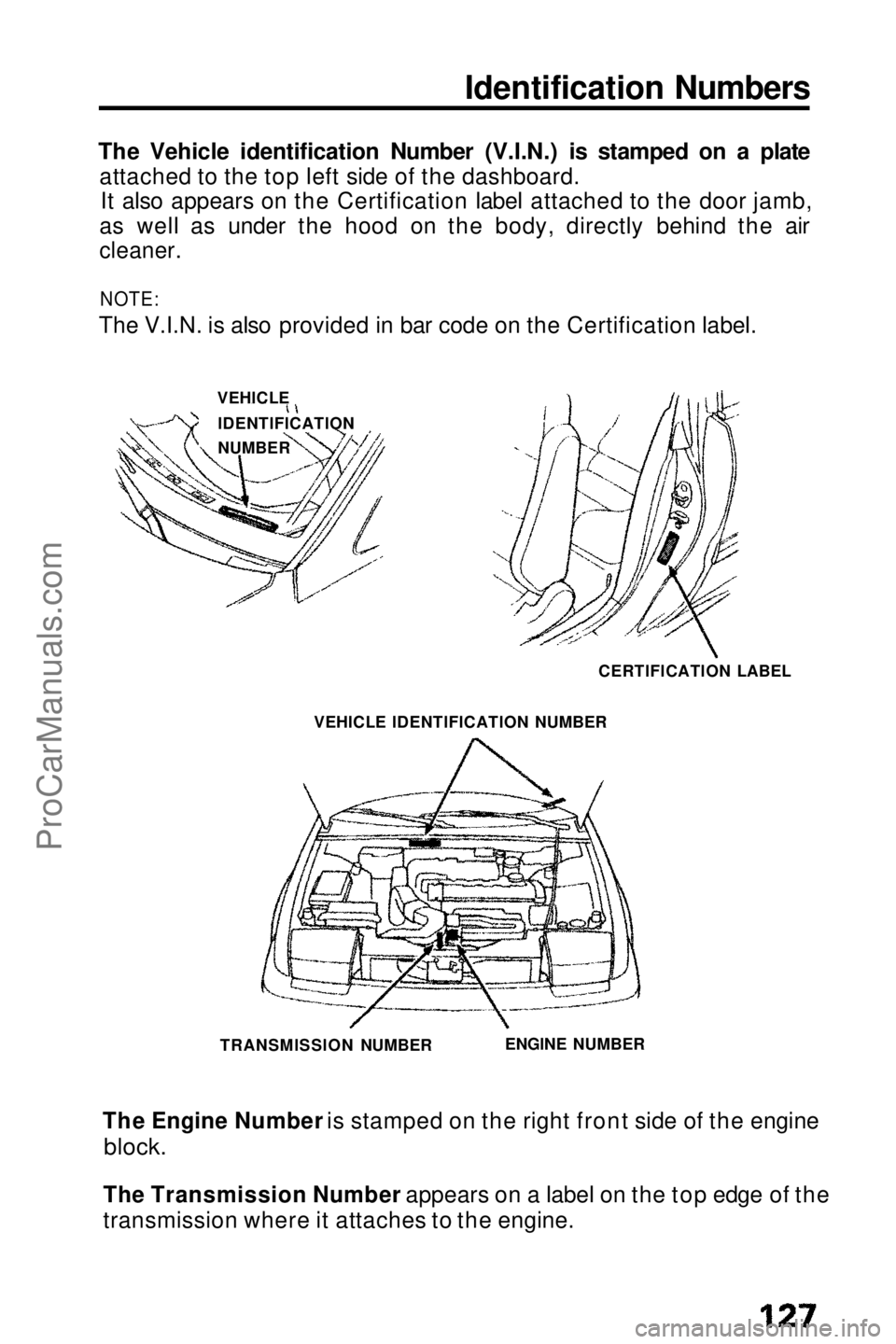
Identification Numbers
The Vehicle identification Number (V.I.N.) is stamped on a plate attached to the top left side of the dashboard.It also appears on the Certification label attached to the door jamb,
as well as under the hood on the body, directly behind the air
cleaner.
NOTE:
The V.I.N. is also provided in bar code on the Certification label.
VEHICLE IDENTIFICATION NUMBER
TRANSMISSION NUMBER
ENGINE NUMBERThe Engine Number is stamped on the right front side of the engine
block.
The Transmission Number appears on a label on the top edge of the
transmission where
it attaches to the engine.CERTIFICATION LABEL
VEHICLE
IDENTIFICATION
NUMBERProCarManuals.comMain Menu t s
Page 131 of 143

Evaporative Emission Control System
The Evaporative Emission Control System is designed to prevent
fuel vapors from escaping into the atmosphere.
(2.0 Si,Si)
Fuel vapors from the fuel tank are directed into the charcoal
canister where they are adsorbed and stored while the engine is
stopped or idling. When the coolant temperature rises to a certain
value, the vapors are drawn into the engine through the throttle body and the intake manifold during normal engine operation.
(2.0 S)Fuel vapors from the fuel tank and carburetor are directed into the
charcoal canister where they are adsorbed and stored while the
engine is stopped.
When the engine is running and engine coolant temperature is above
the set temperature of the thermo sensor, the purge control diaphragm valve is open so that fuel vapors in the charcoal canister may be drawn into the engine through the carburetor and the intake
manifold.
Engine Exhaust Controls
The engine exhaust emission control systems are designed to
control combustion during idle, acceleration, cruise, and deceleration.
These systems are entirely separate from the crankcase and evaporative emission control systems described previously. HONDA PGM-FI System (2.0 Si,Si)
The PGM-FI system consists of three independent sub-systems; Air intake, Electronic Control and Fuel Control, thus allowing moreaccurate control of air/fuel ratios under all operating conditions.
The Electronic Control Unit (ECU) detects the amount of air
drawn into the cylinders and determines the amount of fuel to be injected to provide the optimum air/fuel ratio for all engine needs.
(cont'd)ProCarManuals.comMain Menu t s
Page 132 of 143

Emission Controls (cont'd)
Intake Air Temperature Control System (2.0 S)The air control valve mounted inside the air cleaner snorkel
automatically opens and closes according to the intake air
temperature. The carburetor then receives air of constant
temperature which results in lower exhaust emissions.
Carburetor Controls (2.0 S)—Throttle controller — This system controls the throttle during
gear shifting, reducing the amount of HC caused by unburned
fuel mixture.
— Choke opener — When starting a cold engine, this device
opens the choke slightly. This reduces the amount of HC and
CO.
— Altitude Compensation devices — The Air Jet Controller (AJC)
has an atmospheric pressure sensing bellows. The AJC is
designed to control the amount of additional air fed to the
carburetor jets to maintain good driveability at any altitude. Ignition Timing Control System
This system automatically controls the ignition timing to reduce
the amount of HC and NOx.
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) [Except California 2.0 S models]
The EGR system is designed to control the formation of oxides of nitrogen (NOx) caused when fuel mixture burns at high
temperature. It works by recirculating exhaust gas through the EGR valve and intake manifold into the combustion chambers
where it reduces peak temperature by diluting the air/fuel mixture.
Catalytic Converter
The catalyst is used to convert hydrocarbons (HC), carbon monoxide (CO) and oxides of nitrogen (NOx) in the exhaust gas,
to carbon dioxide (CO 2
), dinitrogen (N 2
) and water vapor.
ProCarManuals.comMain Menu t s