light ISUZU TROOPER 1998 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 1998, Model line: TROOPER, Model: ISUZU TROOPER 1998Pages: 3573, PDF Size: 60.36 MB
Page 1671 of 3573
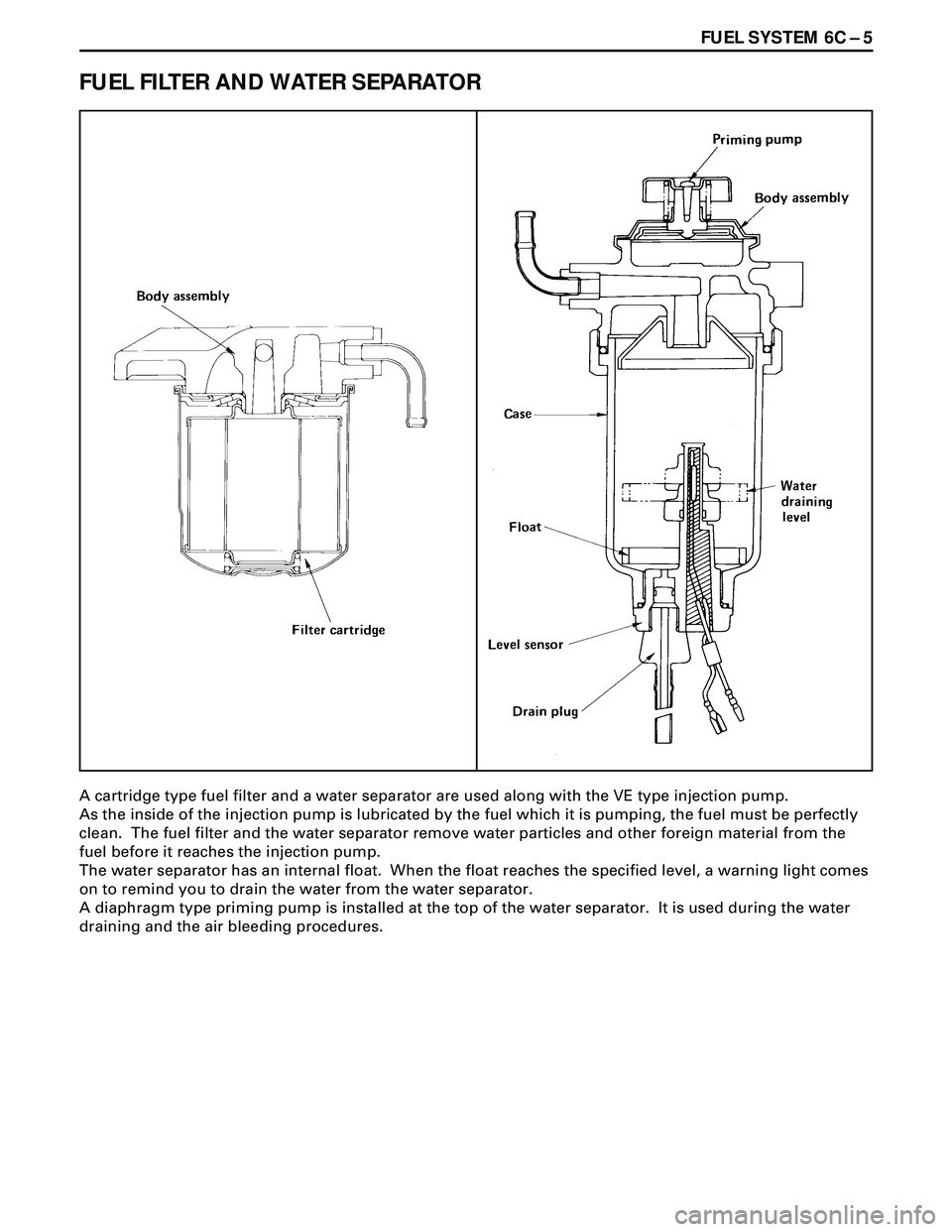
FUEL SYSTEM 6C Ð 5
FUEL FILTER AND WATER SEPARATOR
A cartridge type fuel filter and a water separator are used along with the VE type injection pump.
As the inside of the injection pump is lubricated by the fuel which it is pumping, the fuel must be perfectly
clean. The fuel filter and the water separator remove water particles and other foreign material from the
fuel before it reaches the injection pump.
The water separator has an internal float. When the float reaches the specified level, a warning light comes
on to remind you to drain the water from the water separator.
A diaphragm type priming pump is installed at the top of the water separator. It is used during the water
draining and the air bleeding procedures.
Page 1674 of 3573
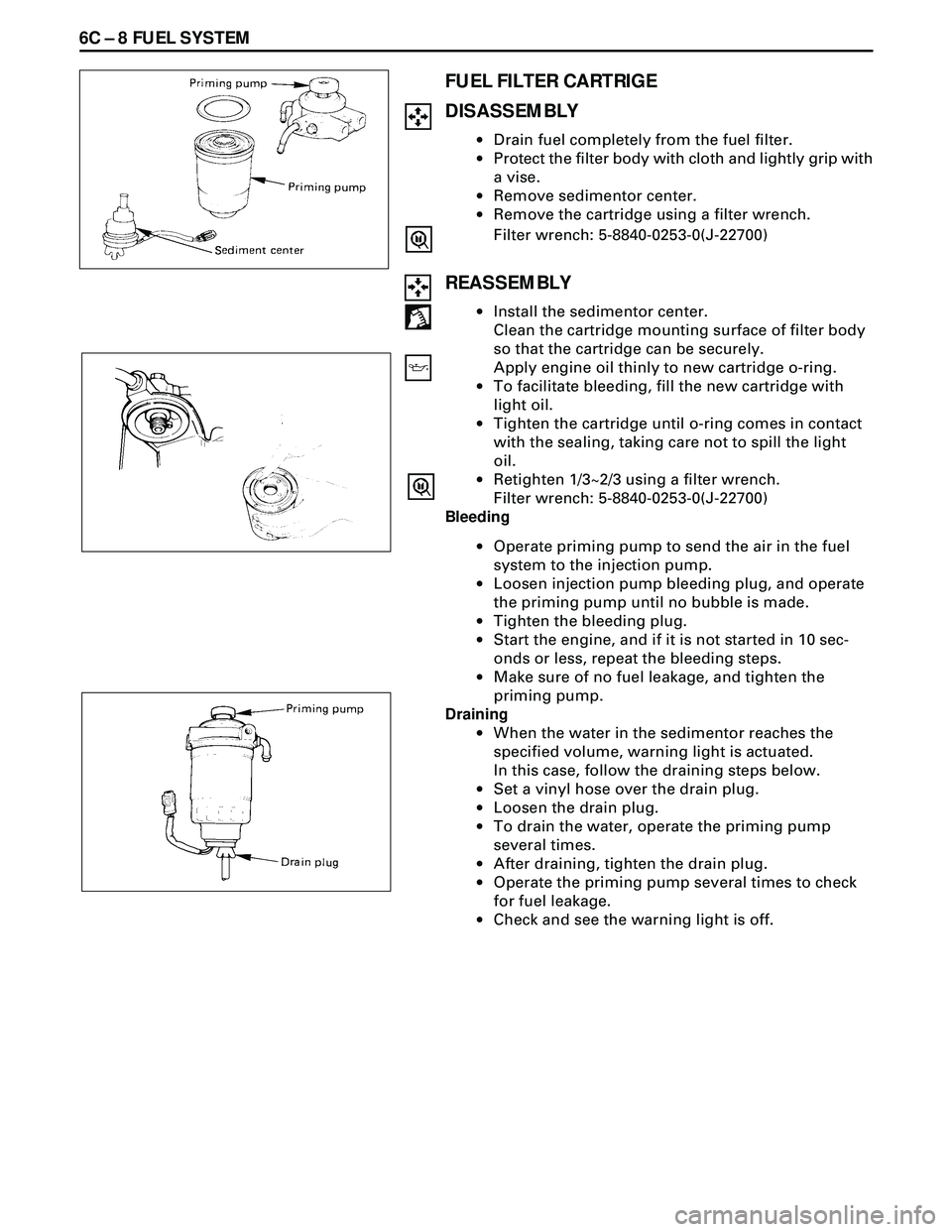
6C Ð 8 FUEL SYSTEM
FUEL FILTER CARTRIGE
DISASSEMBLY
·Drain fuel completely from the fuel filter.
·Protect the filter body with cloth and lightly grip with
a vise.
·Remove sedimentor center.
·Remove the cartridge using a filter wrench.
Filter wrench: 5-8840-0253-0(J-22700)
REASSEMBLY
·Install the sedimentor center.
Clean the cartridge mounting surface of filter body
so that the cartridge can be securely.
Apply engine oil thinly to new cartridge o-ring.
·To facilitate bleeding, fill the new cartridge with
light oil.
·Tighten the cartridge until o-ring comes in contact
with the sealing, taking care not to spill the light
oil.
·Retighten 1/3~2/3 using a filter wrench.
Filter wrench: 5-8840-0253-0(J-22700)
Bleeding
·Operate priming pump to send the air in the fuel
system to the injection pump.
·Loosen injection pump bleeding plug, and operate
the priming pump until no bubble is made.
·Tighten the bleeding plug.
·Start the engine, and if it is not started in 10 sec-
onds or less, repeat the bleeding steps.
·Make sure of no fuel leakage, and tighten the
priming pump.
Draining
·When the water in the sedimentor reaches the
specified volume, warning light is actuated.
In this case, follow the draining steps below.
·Set a vinyI hose over the drain plug.
·Loosen the drain plug.
·To drain the water, operate the priming pump
several times.
·After draining, tighten the drain plug.
·Operate the priming pump several times to check
for fuel leakage.
·Check and see the warning light is off.
Page 1676 of 3573

6C Ð 10 FUEL SYSTEM
DISASSEMBLY
·Grip nozzle holder with a vise, loosen retaining nut
and disassemble.
·Loosen holder nut and remove the nozzle.
CAUTION
·Be careful not to damage the needle valve.
·Remove spacer, positioning pin, and push rod.
·Remove spring and adjusting shim.
CAUTION
·Wash all the parts removed and arrange them on a
cylinder basis, care should be taken not to miss any
parts.
·Soak the nozzle assembly in a parts receptacle filled
with light oil.
·Care should be taken not to miss shim, if used.
INSPECTION
Nozzle
·Soak the nozzle removed in clean light oil, wash
nozzle body and needle valve separately, and check
and see that the needle valve slide smoothly in the
nozzle body.
Page 1678 of 3573
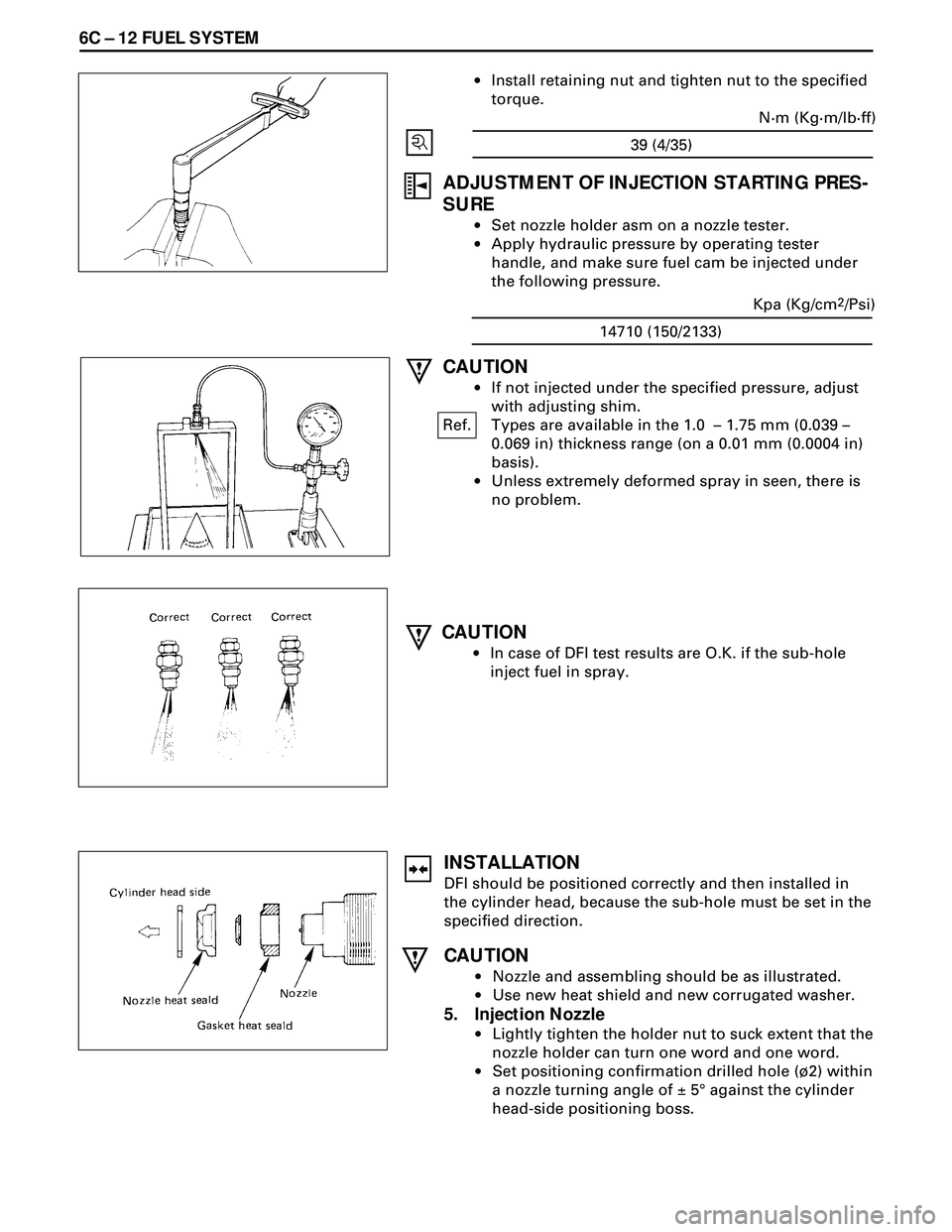
6C Ð 12 FUEL SYSTEM
·Install retaining nut and tighten nut to the specified
torque.
ADJUSTMENT OF INJECTION STARTING PRES-
SURE
·Set nozzle holder asm on a nozzle tester.
·Apply hydraulic pressure by operating tester
handle, and make sure fuel cam be injected under
the following pressure.
CAUTION
·In case of DFI test results are O.K. if the sub-hole
inject fuel in spray.
14710 (150/2133)Kpa (Kg/cm
2/Psi)
CAUTION
·If not injected under the specified pressure, adjust
with adjusting shim.
Ref. Types are available in the 1.0 Ð 1.75 mm (0.039 Ð
0.069 in) thickness range (on a 0.01 mm (0.0004 in)
basis).
·Unless extremely deformed spray in seen, there is
no problem.
INSTALLATION
DFI should be positioned correctly and then installed in
the cylinder head, because the sub-hole must be set in the
specified direction.
CAUTION
·Nozzle and assembling should be as illustrated.
·Use new heat shield and new corrugated washer.
5. Injection Nozzle
·Lightly tighten the holder nut to suck extent that the
nozzle holder can turn one word and one word.
·Set positioning confirmation drilled hole (¿2) within
a nozzle turning angle of ± 5¡ against the cylinder
head-side positioning boss.
39 (4/35)N·m (Kg·m/lb·ff)
Page 1691 of 3573

ENGINE ELECTRICAL 6D1 Ð 1
SECTION 6D
ENGINE ELECTRICAL
CONTENTS
Battery................................................................................................................................... Section 6D1
Starting System ................................................................................................................... Section 6D2
Charging System.................................................................................................................. Section 6D3
QOS-IIIPreheating System ................................................................................................. Section 6D6
SECTION 6D1
BATTERY
CONTENTS
General Description ......................................... 6D1Ð1
Diagnosis .......................................................... 6D1Ð1
On-Vehicle Service........................................... 6D1Ð3
Battery Charging .......................................... 6D1Ð3Jump Starting .............................................. 6D1Ð3
Removal and Installation of Battery .......... 6D1Ð4
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
There are six battery fluid caps at the top of the
battery. These are covered by a paper label.
The battery is completely sealed except for the six
small vent holes at the side. These vent holes per-
mit the escape of small amounts of gas generated
by the battery.
This type of battery has the following advantages
over conventional batteries:1. There is no need to add water during the entire
service life of the battery.
2. The battery protects itself against overcharging.
The battery will refuse to accept an excessive
charge.
(A conventional battery will accept an excessive
charge, resulting in gassing and loss of battery
fluid.)
3. The battery is much less vulnerable to self-
discharge than a conventional type battery.
DIAGNOSIS
1. VISUAL INSPECTION
Inspect the battery for obvious physical damage,
such as a cracked or broken case, which would
permit electrolyte loss.
Replace the battery if obvious physical damage is
discovered during inspection.
Check for any other physical damage and correct it
as necessary. If not, proceed to Step 2.
2. HYDROMETER CHECK
There is a built-in hydrometer (Charge test indica-
tor) at the top of the battery. It is designed to be
used during diagnostic procedures.Before trying to read the hydrometer, carefully
clean the upper battery surface.
If your work area is poorly lit, additional light may
be necessary to read the hydrometer.
a. BLUE RING OR DOT VISIBLE Ð Go to Step
4.
b. BLUE RING OR DOT NOT VISIBLE Ð Go to
Step 3.
Page 1693 of 3573

ENGINE ELECTRICAL 6D1 Ð 3
BATTERY CHARGING
Observe the following safety precautions when
charging the battery:
1. Never attempt to charge the battery when the
fluid level is below the lower level line on the
side of the battery. In this case, the battery
must be replaced.
2. Pay close attention to the battery during the
charging procedure.
Battery charging should be discontinued or the
rate of charge reduced if the battery feels hot to
the touch.
Battery charging should be discontinued or the
rate of charge reduced if the battery begins to
gas or spew electrolyte from the vent holes.
3. In order to more easily view the hydrometer
blue dot or ring, it may be necessary to jiggle or
tilt the battery.
4. Battery temperature can have a great effect on
battery charging capacity.
5. The sealed battery used on this vehicle may be
either quick-charged or slow-charged in the
same manner as other batteries.
Whichever method you decide to use, be sure
that you completely charge the battery. Never
partially charge the battery.
JUMP STARTING
JUMP STARTING WITH AN AUXILIARY
(BOOSTER) BATTERY
CAUTION:
Never push or tow the vehicle in an attempt to
start it. Serious damage to the emission system
as well as other vehicle parts will result.
Treat both the discharged battery and the
booster battery with great care when using
jumper cables. Carefully follow the jump
starting procedure, being careful at all times to
avoid sparking.
WARNING:
Failure to carefully follow the jump starting
procedure could result in the following:
1. Serious personal injury, particulaly to
your eyes.
2. Property damage from a battery explo-
sion, battery acid, or an electrical fire.
3. Damage to the electronic components of
one or both vehicles particularly. Never expose the battery to an open flame or elec-
trical spark. Gas generated by the battery may catch
fire or explode.
Remove any rings, watches, or other jewelry before
working around the battery. Protect your eyes by
wearing an approved set of goggles.
Never allow battery fluid to come in contact with
your eyes or skin.
Never allow battery fluid to come in contact with
fabrics or painted surfaces.
Battery fluid is a highly corrosive acid.
Should battery fluid come in contact with your
eyes, skin, fabric, or a painted surface, immediately
and thoroughly rinse the affected area with clean
tap water.
Never allow metal tools or jumper cables to come
in contact with the positive battery terminal, or any
other metal surface of the vehicle. This will protect
against a short circuit.
Always keep batteries out of the reach of young
children.
JUMP STARTING PROCEDURE
1. Set the vehicle parking brake.
If the vehicle is equipped with an automatic
transmission, place the selector lever in the
ÒPARKÓ position.
If the vehicle is equipped with a manual trans-
mission place the shift lever in the ÒNEUTRALÓ
position.
Turn ÒOFFÓ the ignition.
Turn ÒOFFÓ all lights and any other accessory
requiring electrical power.
2. Look at the built-in hydrometer.
If the indication area of the built-in hydrometer
is completely clear, do not try to jump start.
3. Attach the end of one jumper cable to the posi-
tive terminal of the booster battery.
Attach the other end of the same cable to the
positive terminal of the discharged battery.
Do not allow the vehicles to touch each other.
This will cause a ground connection, effectively
neutralizing the charging procedure.
Be sure that the booster battery has a 12 volt
rating.
4. Attach one end of the remaining cable to the
negative terminal of the booster battery.
Attach the other end of the same cable to a
solid engine ground (such as the A/C com-
pressor bracket or the generator mounting
bracket) of the vehicle with the discharged bat-
tery.
This ground connection must be at least 450
mm (18 in) from the battery of the vehicle
whose battery is being charged.
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
Page 1716 of 3573
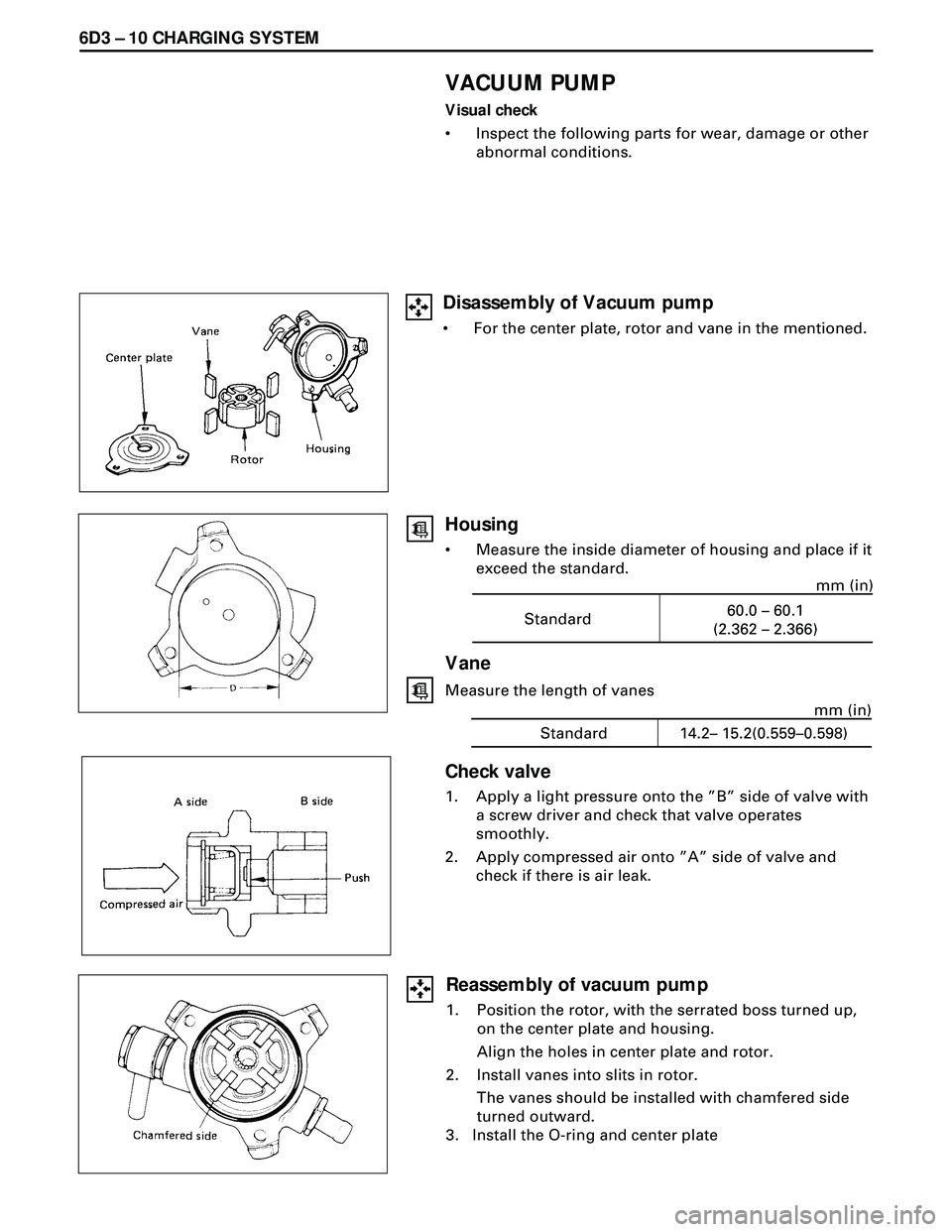
6D3 Ð 10 CHARGING SYSTEM
VACUUM PUMP
Visual check
¥ Inspect the following parts for wear, damage or other
abnormal conditions.
Standard60.0 – 60.1
(2.362 – 2.366)mm (in)
Vane
Measure the length of vanes
Standard 14.2– 15.2(0.559–0.598)mm (in)
Check valve
1. Apply a light pressure onto the ÓBÓ side of valve with
a screw driver and check that valve operates
smoothly.
2. Apply compressed air onto ÓAÓ side of valve and
check if there is air leak.
Housing
¥ Measure the inside diameter of housing and place if it
exceed the standard.
Reassembly of vacuum pump
1. Position the rotor, with the serrated boss turned up,
on the center plate and housing.
Align the holes in center plate and rotor.
2. Install vanes into slits in rotor.
The vanes should be installed with chamfered side
turned outward.
3. Install the O-ring and center plate
Disassembly of Vacuum pump
¥ For the center plate, rotor and vane in the mentioned.
Page 1720 of 3573
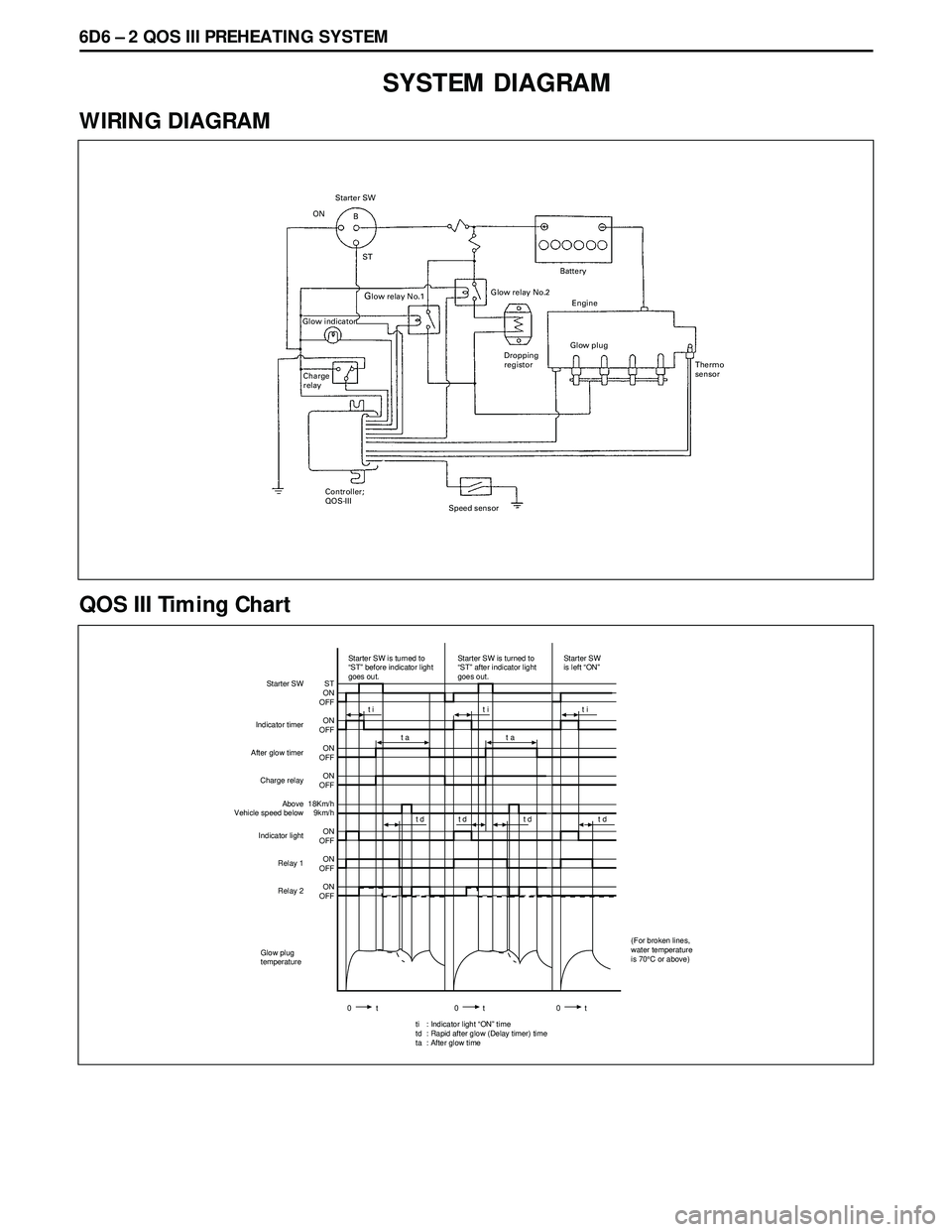
6D6 Ð 2 QOS III PREHEATING SYSTEM
SYSTEM DIAGRAM
WIRING DIAGRAM
ON
B
ST
Glow relay No.1 Starter SW
Battery
Engine Glow relay No.2
Glow indicator
Charge
relayGlow plug
Thermo
sensor
Controller;
QOS-III
Speed sensorDropping
registor
QOS III Timing Chart
ST
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
18Km/h
9km/h
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF Starter SW
Starter SW is turned to
“ST” before indicator light
goes out.Starter SW is turned to
“ST” after indicator light
goes out.Starter SW
is left “ON”
Indicator timer
After glow timer
Charge relay
Indicator light
Relay 1
Relay 2Above
Vehicle speed below
t i t i t i
t a t a
t d t d t d t d
Glow plug
temperature
0t 0t 0t
: Indicator light “ON” time
: Rapid after glow (Delay timer) time
: After glow time
ti
td
ta
(For broken lines,
water temperature
is 70¡C or above)
Page 1722 of 3573
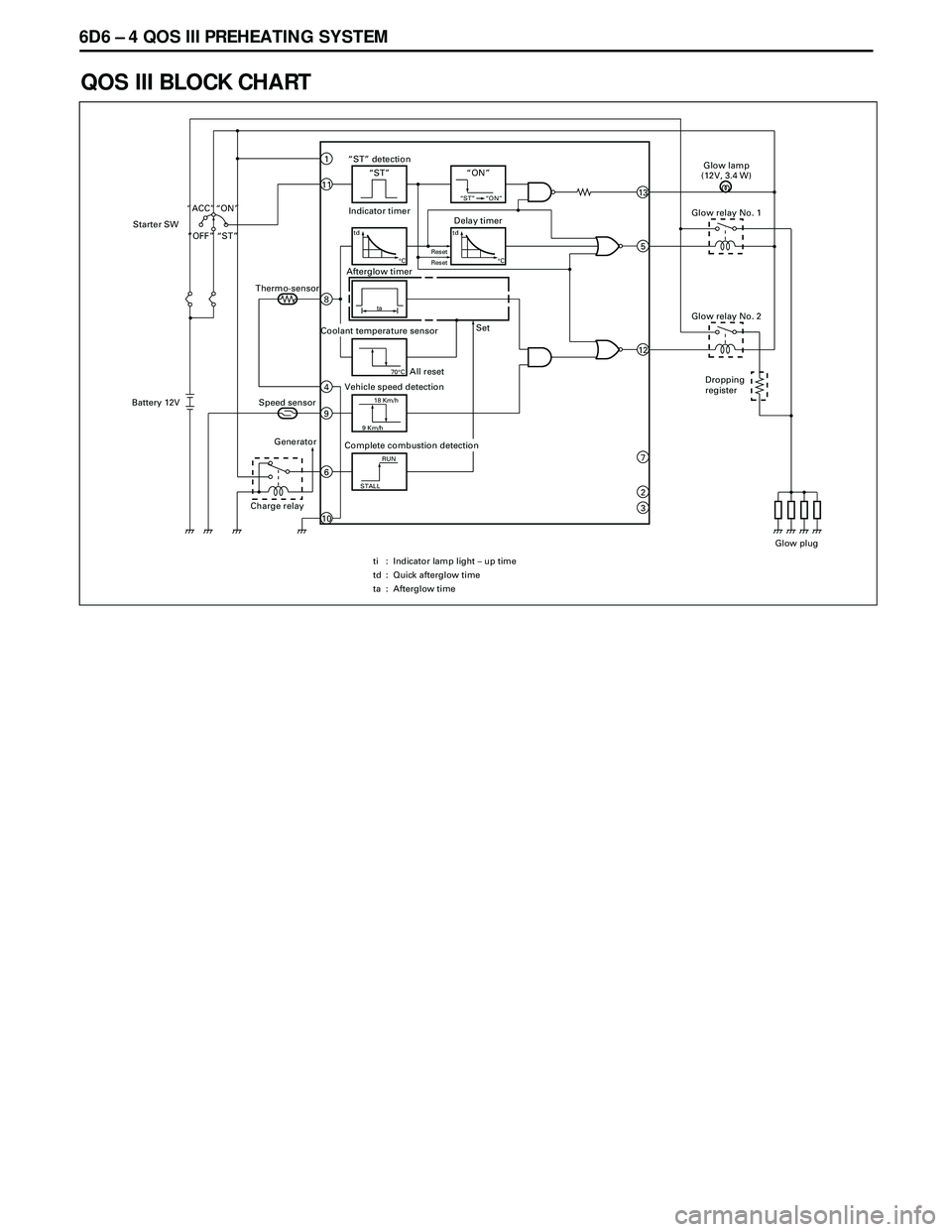
6D6 Ð 4 QOS III PREHEATING SYSTEM
QOS III BLOCK CHART
“ST” detection“ST”
Indicator timer
11
1“ON”
“ST” “ON”13
tdDelay timer
¡C
td
¡CResetReset5
ta
Afterglow timer
Coolant temperature sensor
70¡CAll reset
12
Vehicle speed detection
9 Km/h18 Km/h
Complete combustion detection
STALLRUN
Set 8
4
9
6
10
Thermo-sensor
Speed sensor
Generator
Charge relay
Glow relay No. 1
Glow lamp
(12V, 3.4 W)
Glow relay No. 2
Glow plug
Battery 12VStarter SW
“OFF” “ST” “ACC” “ON”
: Indicator lamp light – up time
: Quick afterglow time
: Afterglow time ti
td
ta7
2
3
Dropping
register
Page 1723 of 3573
QOS III PREHEATING SYSTEM 6D6 Ð 5
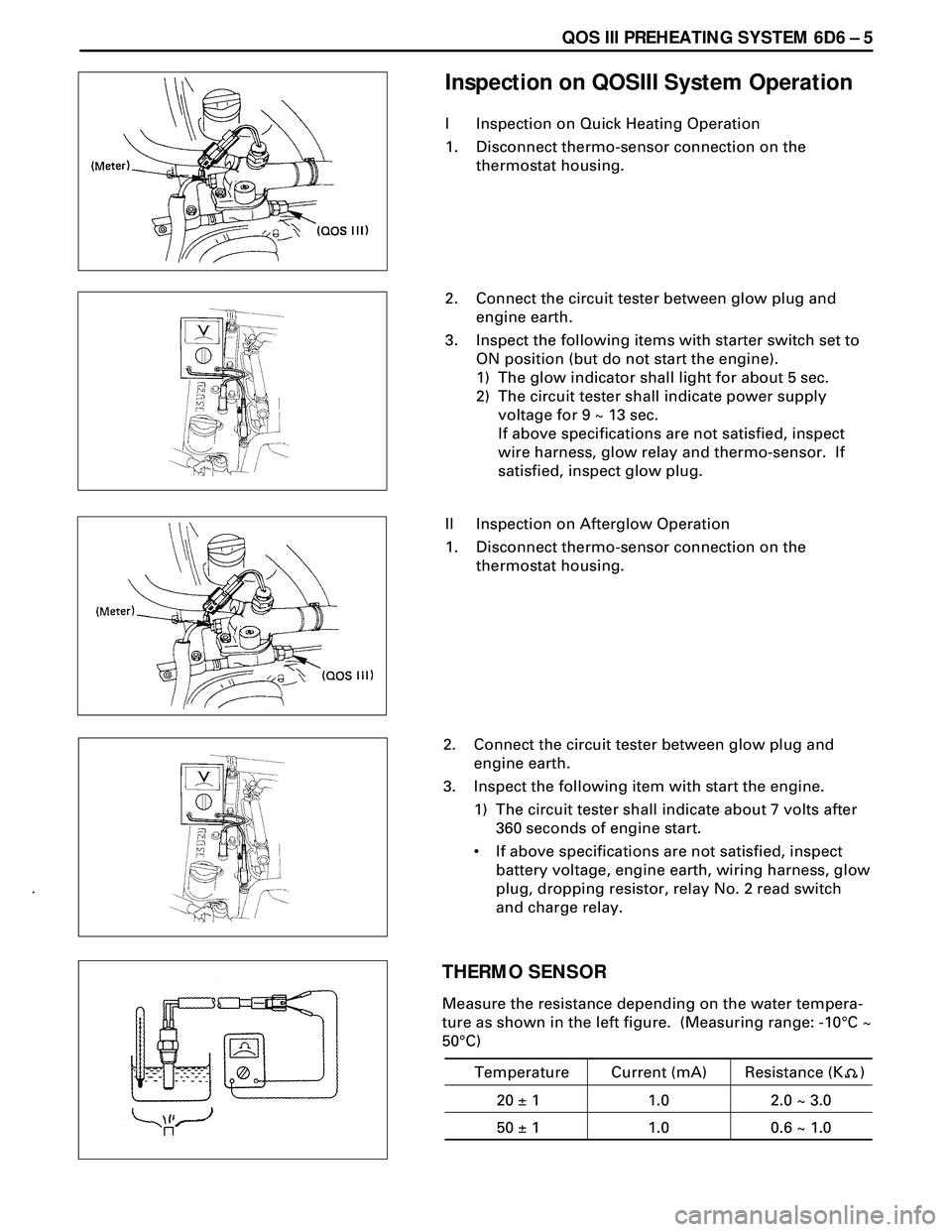
Inspection on QOSIII System Operation
I Inspection on Quick Heating Operation
1. Disconnect thermo-sensor connection on the
thermostat housing.
2. Connect the circuit tester between glow plug and
engine earth.
3. Inspect the following items with starter switch set to
ON position (but do not start the engine).
1) The glow indicator shall light for about 5 sec.
2) The circuit tester shall indicate power supply
voltage for 9 ~ 13 sec.
If above specifications are not satisfied, inspect
wire harness, glow relay and thermo-sensor. If
satisfied, inspect glow plug.
II Inspection on Afterglow Operation
1. Disconnect thermo-sensor connection on the
thermostat housing.
2. Connect the circuit tester between glow plug and
engine earth.
3. Inspect the following item with start the engine.
1) The circuit tester shall indicate about 7 volts after
360 seconds of engine start.
¥ If above specifications are not satisfied, inspect
battery voltage, engine earth, wiring harness, glow
plug, dropping resistor, relay No. 2 read switch
and charge relay.
THERMO SENSOR
Measure the resistance depending on the water tempera-
ture as shown in the left figure. (Measuring range: -10¡C ~
50¡C)
Current (mA)
20 ± 1 1.0
50 ± 1Resistance (K )
1.0
2.0 ~ 3.0
0.6 ~ 1.0 Temperature