ISUZU TROOPER 1998 Service Repair Manual
Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 1998, Model line: TROOPER, Model: ISUZU TROOPER 1998Pages: 3573, PDF Size: 60.36 MB
Page 881 of 3573

POWER ASSISTED BRAKE SYSTEM 5C – 3
BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
ROAD TESTING THE BRAKES
Brake Test
Brakes should be tested on a dry, clean, reasonably
smooth and level roadway. A true test of brake
performance cannot be made if the roadway is wet,
greasy or covered with loose dirt so that all tires do
not grip the road equally. Testing will also be
adversely affected if the roadway is crowned so as to
throw the weight of the vehicle toward wheels on one
side or if the roadway is so rough that wheels tend to
bounce. Test the brakes at different vehicle speeds
with both light and heavy pedal pressure; however,
avoid locking the wheels and sliding the tires. Locked
wheels and sliding tires do not indicate brake
efficiency, since heavily braked but turning wheels
will stop the vehicle in less distance than locked
wheels. More tire-to-road friction is present with a
heavily braked turning tire then with a sliding tire.
The standard brake system is designed and balanced
to avoid locking the wheels except at very high
deceleration levels.
It is designed this way because the shortest stopping
distance and best control is achieved without brake
lock-up.
Because of high deceleration capability, a firmer pedal
may be felt at higher deceleration levels.
External Conditions That Affect Brake
Performance
1. Tires: Tires having unequal contact and grip on the
road will cause unequal braking. Tires must be
equally inflated, identical in size, and the tread
pattern of right and left tires must be
approximately equal.
2. Vehicle loading: A heavily loaded vehicle requires
more braking effort.
3. Wheel Alignment: Misalignment of the wheels,
particularly in regard to excessive camber and
caster, will cause the brakes to pull to one side.
BRAKE FLUID LEAKS
With engine running at idle and the transmission in
“Neutral”, depress the brake pedal and hold a
constant foot pressure on the pedal. If pedal gradually
falls away with the constant pressure, the hydraulic
system may be leaking.
Check the master cylinder fluid level. While a slight
drop in reservoir level will result from normal lining
wear, an abnormally low level in resevoir indicates a
leak in the system. The hydraulic system may be
leaking internally as well as externally. Refer to
“Master Cylinder Inspection”. Also, the system may
appear to pass this test but still have slight leakage. If
fluid level is normal, check the vacuum booster push
Page 882 of 3573

5C – 4 POWER ASSISTED BRAKE SYSTEM
rod length. If an incorrect length push rod is found,
adjust or replace the push rod. Check the brake pedal
travel and the parking brake adjustment.
When checking the fluid level, the master cylinder
fluid level may be low from the “MAX” mark if the
front and rear linings are worn. This is not abnormal.
WARNING LIGHT OPERATION
When the ignition switch is in the START position, the
“BRAKE” warning light should glow and go OFF when
the ignition switch returns to the ON position.
The following conditions will activate the “BRAKE”
light:
1. Parking brake applied. The light should be ON
whenever the parking brake is applied and the
ignition switch is ON.
2. Low fluid level. A low fluid level in the master
cylinder will turn the “BRAKE” light ON.
3. During engine cranking the “BRAKE” light should
remain ON. This notifies the driver that the
warning circuit is operating properly.
4. Low vacuum warning light. The vacuum warning
device is equipped on the diesel engine equipped
vehicles. The “BRAKE” light comes on when the
reserved vacuum is lowered to a critical level or
power brake line is damaged.
NOTE:
Depressing the brake pedal repeatedly may cause the
brake warning light to come ON when the engine is
running at idling speed or at low speed. This is
because the amount of vacuum is used more than
that supplied by the vacuum pump, however, no
problem will occur actually.
If the lamp is still lighting even after 2 or 3 seconds at
idling speed, the vacuum line may be defective.
ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS)
Refer to Brake Control System for inspection and
diagnosis procedure of the hydraulic unit.
Page 883 of 3573
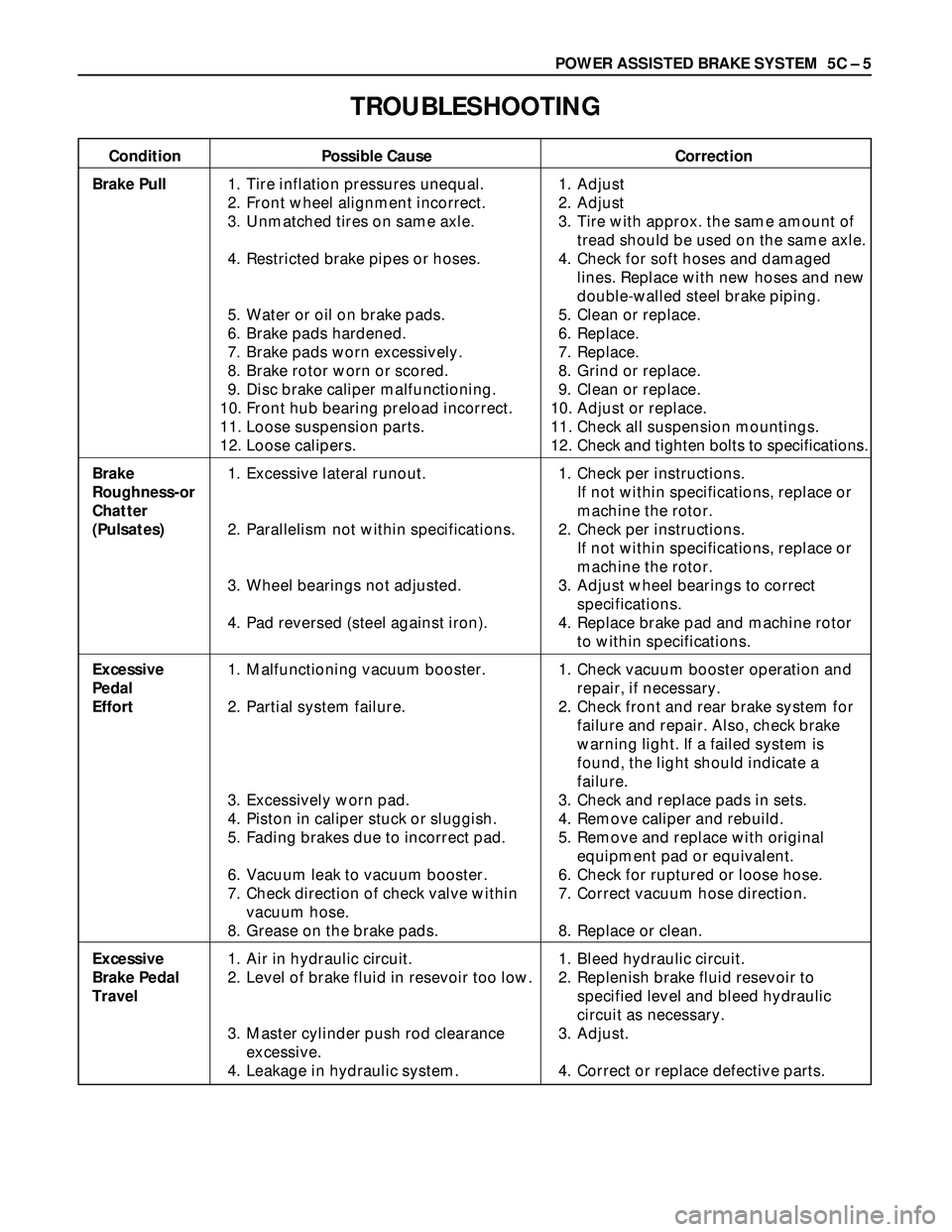
POWER ASSISTED BRAKE SYSTEM 5C – 5
TROUBLESHOOTING
Condition Possible Cause Correction
Brake Pull1. Tire inflation pressures unequal. 1. Adjust
2. Front wheel alignment incorrect. 2. Adjust
3. Unmatched tires on same axle. 3. Tire with approx. the same amount of
tread should be used on the same axle.
4. Restricted brake pipes or hoses. 4. Check for soft hoses and damaged
lines. Replace with new hoses and new
double-walled steel brake piping.
5. Water or oil on brake pads. 5. Clean or replace.
6. Brake pads hardened. 6. Replace.
7. Brake pads worn excessively. 7. Replace.
8. Brake rotor worn or scored. 8. Grind or replace.
9. Disc brake caliper malfunctioning. 9. Clean or replace.
10. Front hub bearing preload incorrect. 10. Adjust or replace.
11. Loose suspension parts. 11. Check all suspension mountings.
12. Loose calipers. 12. Check and tighten bolts to specifications.
Brake 1. Excessive lateral runout. 1. Check per instructions.
Roughness-orIf not within specifications, replace or
Chattermachine the rotor.
(Pulsates)2. Parallelism not within specifications. 2. Check per instructions.
If not within specifications, replace or
machine the rotor.
3. Wheel bearings not adjusted. 3. Adjust wheel bearings to correct
specifications.
4. Pad reversed (steel against iron). 4. Replace brake pad and machine rotor
to within specifications.
Excessive 1. Malfunctioning vacuum booster. 1. Check vacuum booster operation and
Pedal repair, if necessary.
Effort2. Partial system failure. 2. Check front and rear brake system for
failure and repair. Also, check brake
warning light. If a failed system is
found, the light should indicate a
failure.
3. Excessively worn pad. 3. Check and replace pads in sets.
4. Piston in caliper stuck or sluggish. 4. Remove caliper and rebuild.
5. Fading brakes due to incorrect pad. 5. Remove and replace with original
equipment pad or equivalent.
6. Vacuum leak to vacuum booster. 6. Check for ruptured or loose hose.
7. Check direction of check valve within 7. Correct vacuum hose direction.
vacuum hose.
8. Grease on the brake pads. 8. Replace or clean.
Excessive 1. Air in hydraulic circuit. 1. Bleed hydraulic circuit.
Brake Pedal 2. Level of brake fluid in resevoir too low. 2. Replenish brake fluid resevoir to
Travelspecified level and bleed hydraulic
circuit as necessary.
3. Master cylinder push rod clearance 3. Adjust.
excessive.
4. Leakage in hydraulic system. 4. Correct or replace defective parts.
Page 884 of 3573
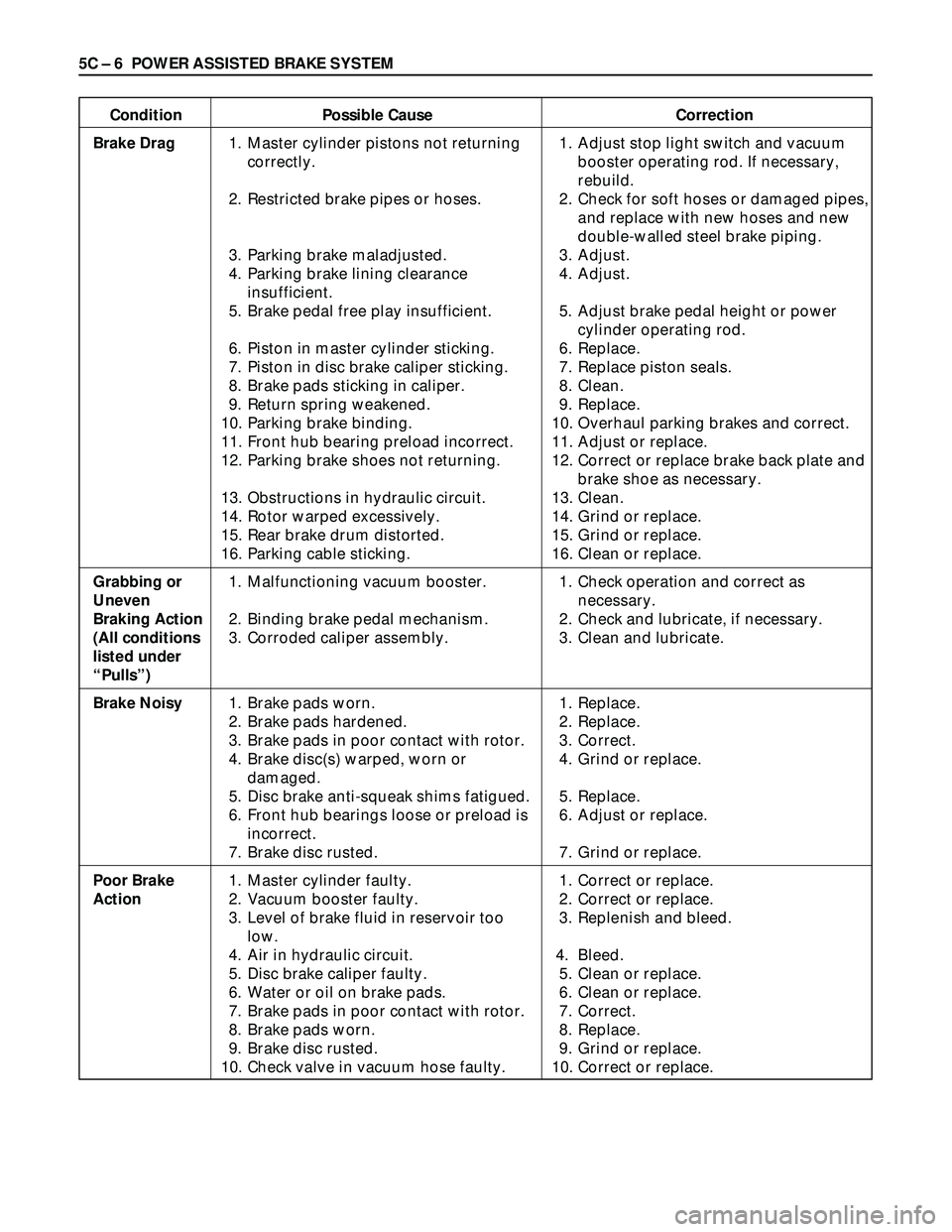
5C – 6 POWER ASSISTED BRAKE SYSTEM
Condition Possible Cause Correction
Brake Drag1. Master cylinder pistons not returning 1. Adjust stop light switch and vacuum
correctly. booster operating rod. If necessary,
rebuild.
2. Restricted brake pipes or hoses. 2. Check for soft hoses or damaged pipes,
and replace with new hoses and new
double-walled steel brake piping.
3. Parking brake maladjusted. 3. Adjust.
4. Parking brake lining clearance 4. Adjust.
insufficient.
5. Brake pedal free play insufficient. 5. Adjust brake pedal height or power
cylinder operating rod.
6. Piston in master cylinder sticking. 6. Replace.
7. Piston in disc brake caliper sticking. 7. Replace piston seals.
8. Brake pads sticking in caliper. 8. Clean.
9. Return spring weakened. 9. Replace.
10. Parking brake binding. 10. Overhaul parking brakes and correct.
11. Front hub bearing preload incorrect. 11. Adjust or replace.
12. Parking brake shoes not returning. 12. Correct or replace brake back plate and
brake shoe as necessary.
13. Obstructions in hydraulic circuit. 13. Clean.
14. Rotor warped excessively. 14. Grind or replace.
15. Rear brake drum distorted. 15. Grind or replace.
16. Parking cable sticking. 16. Clean or replace.
Grabbing or1. Malfunctioning vacuum booster. 1. Check operation and correct as
Uneven necessary.
Braking Action 2. Binding brake pedal mechanism. 2. Check and lubricate, if necessary.
(All conditions3. Corroded caliper assembly. 3. Clean and lubricate.
listed under
“Pulls”)
Brake Noisy1. Brake pads worn. 1. Replace.
2. Brake pads hardened. 2. Replace.
3. Brake pads in poor contact with rotor. 3. Correct.
4. Brake disc(s) warped, worn or 4. Grind or replace.
damaged.
5. Disc brake anti-squeak shims fatigued. 5. Replace.
6. Front hub bearings loose or preload is 6. Adjust or replace.
incorrect.
7. Brake disc rusted. 7. Grind or replace.
Poor Brake1. Master cylinder faulty. 1. Correct or replace.
Action2. Vacuum booster faulty. 2. Correct or replace.
3. Level of brake fluid in reservoir too 3. Replenish and bleed.
low.
4. Air in hydraulic circuit. 4. Bleed.
5. Disc brake caliper faulty. 5. Clean or replace.
6. Water or oil on brake pads. 6. Clean or replace.
7. Brake pads in poor contact with rotor. 7. Correct.
8. Brake pads worn. 8. Replace.
9. Brake disc rusted. 9. Grind or replace.
10. Check valve in vacuum hose faulty. 10. Correct or replace.
Page 885 of 3573
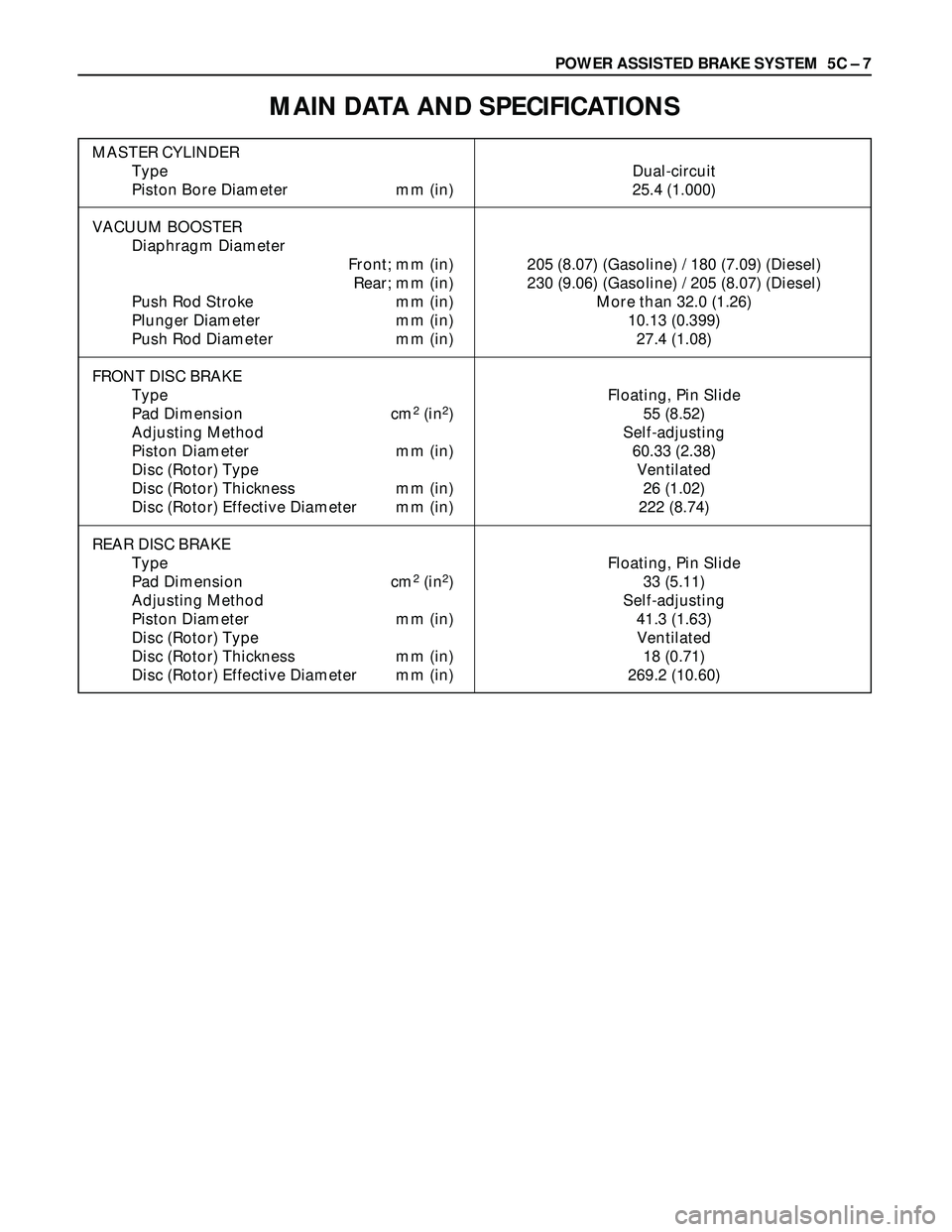
POWER ASSISTED BRAKE SYSTEM 5C – 7
MAIN DATA AND SPECIFICATIONS
MASTER CYLINDER
Type Dual-circuit
Piston Bore Diameter mm (in) 25.4 (1.000)
VACUUM BOOSTER
Diaphragm Diameter
Front; mm (in) 205 (8.07) (Gasoline) / 180 (7.09) (Diesel)
Rear; mm (in) 230 (9.06) (Gasoline) / 205 (8.07) (Diesel)
Push Rod Stroke mm (in) More than 32.0 (1.26)
Plunger Diameter mm (in) 10.13 (0.399)
Push Rod Diameter mm (in) 27.4 (1.08)
FRONT DISC BRAKE
Type Floating, Pin Slide
Pad Dimension cm
2(in2) 55 (8.52)
Adjusting Method Self-adjusting
Piston Diameter mm (in) 60.33 (2.38)
Disc (Rotor) Type Ventilated
Disc (Rotor) Thickness mm (in) 26 (1.02)
Disc (Rotor) Effective Diameter mm (in) 222 (8.74)
REAR DISC BRAKE
Type Floating, Pin Slide
Pad Dimension cm
2(in2) 33 (5.11)
Adjusting Method Self-adjusting
Piston Diameter mm (in) 41.3 (1.63)
Disc (Rotor) Type Ventilated
Disc (Rotor) Thickness mm (in) 18 (0.71)
Disc (Rotor) Effective Diameter mm (in) 269.2 (10.60)
Page 886 of 3573
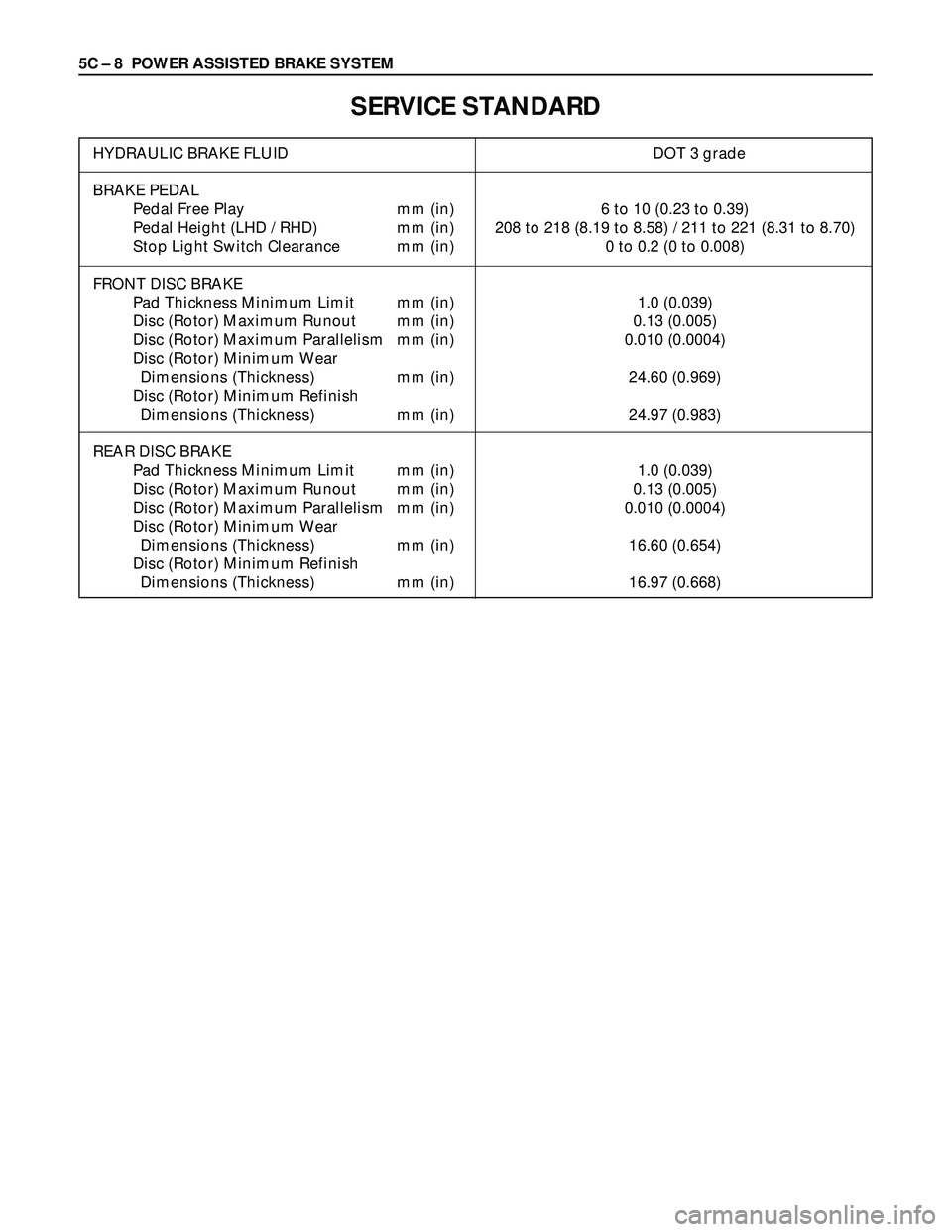
5C – 8 POWER ASSISTED BRAKE SYSTEM
SERVICE STANDARD
HYDRAULIC BRAKE FLUID DOT 3 grade
BRAKE PEDAL
Pedal Free Play mm (in) 6 to 10 (0.23 to 0.39)
Pedal Height (LHD / RHD) mm (in) 208 to 218 (8.19 to 8.58) / 211 to 221 (8.31 to 8.70)
Stop Light Switch Clearance mm (in) 0 to 0.2 (0 to 0.008)
FRONT DISC BRAKE
Pad Thickness Minimum Limit mm (in) 1.0 (0.039)
Disc (Rotor) Maximum Runout mm (in) 0.13 (0.005)
Disc (Rotor) Maximum Parallelism mm (in) 0.010 (0.0004)
Disc (Rotor) Minimum Wear
Dimensions (Thickness) mm (in) 24.60 (0.969)
Disc (Rotor) Minimum Refinish
Dimensions (Thickness) mm (in) 24.97 (0.983)
REAR DISC BRAKE
Pad Thickness Minimum Limit mm (in) 1.0 (0.039)
Disc (Rotor) Maximum Runout mm (in) 0.13 (0.005)
Disc (Rotor) Maximum Parallelism mm (in) 0.010 (0.0004)
Disc (Rotor) Minimum Wear
Dimensions (Thickness) mm (in) 16.60 (0.654)
Disc (Rotor) Minimum Refinish
Dimensions (Thickness) mm (in) 16.97 (0.668)
Page 887 of 3573

POWER ASSISTED BRAKE SYSTEM 5C – 9
SERVICING
FILLING MASTER CYLINDER RESERVOIR
CAUTION:
1) Use only specified brake fluid. Do not use any
fluid which contains a petroleum base. Do not
use a container which has been used for
petroleum based fluids or a container which is
wet with water. Petroleum based fluids will
cause swelling and distortion of rubber parts in
the hydraulic brake system. Water mixed with
brake fluid lowers the fluid boiling point. Keep all
fluid containers capped to prevent
contamination.
2) Always fill the master cylinder reservoid when
the engine is cold.
3) Never allow the brake fluid to come in contact
with the painted surfaced.
The master cylinder reservoir must be kept properly
filled to ensure adequate reserve and to prevent air
and moisture from entering the hydraulic system.
However, because of expansion due to heat absorbed
from the brakes and the engine, the reservoir must not
be overfilled. The brake fluid reservoir is on the
master cylinder, which is located under the hood on
the driver side of the cowl. Thoroughly clean reservoir
cap before removal to avoid getting dirt into reservoir.
Remove cap and diaphragm. Add fluid as required to
bring level to the “MAX” mark on the reservoir tank.
Use “DOT 3“ Hydraulic Brake Fluid. If the fluid cap
diaphragm is stretched, return it to the original
position before installing.
DETERIORATION OF BRAKE FLUID
Using any other brake fluid than speficied or brake
fluid with mineral oil or water mixed in will drop the
boiling point of brake fluid. It may, in turn, reuslt in
vapor lock or deteriorated rubber parts of the
hydraulic system. Be sure to change brake fluid at
specified intervals.
If rubber parts are deteriorated, remover all the
system parts and clean them with alcohol. Prior to
reassembly, dry the cleaned parts with air to remove
the alcohol. Replace all hoses and rubber parts of the
system.
LEAKAGE OF BRAKE FLUID
With engine idling, set shift lever in the neutral
position and continue to depress brake pedal at a
constant pedal application force.
Should the pedal stroke become deeper gradually,
leak from the hydraulic pressure system is possible.
Make sure by visual check that there is no leak.
Page 888 of 3573

5C – 10 POWER ASSISTED BRAKE SYSTEM
BLEEDING BRAKE HYDRAULIC SYSTEM
A bleeding operation is necessary to remove air from
the hydraulic brake system whenever air is introduced
into the hydraulic system. It may be necessary to
bleed the hydraulic system at all four brakes if air has
been introduced through a low fluid level or by
disconnecting brake pipes at the master cylinder. If a
brake pipe is disconneted at one wheel, only that
wheel cylinder/caliper needs to be bled. If pipes are
disconnected at any fitting located between master
cylinder and brakes, then the brake system served by
the disconnected pipe must be bled.
1. For 4-wheel Antilock Brake System (ABS)
equipped vehicle, be sure to remove the ABS main
fuse 40A located at the relay and fuse box before
bleeding air. If you attempt to bleed air without
removing the main fuse, air cannot be let out
thoroughly, and this may cause damage to the
hydraulic unit. After bleeding air, be sure to
replace the ABS main fuse back to its original
position.
2. Set the parking brake completely, then start the
engine.
NOTE:
The vacuum booster will be damaged if the bleeding
operation is performed with the engine off.
3. Remove the master cylinder reservoir cap.
4. Fill the master cylinder reservoir with brake fluid.
Keep the reservoir at least half full during the air
bleeding operation.
5. Always use new brake fluid for replenishment.
6. In replenishing brake fluid, take care that air
bubbles do not enter the brake fluid.
•When the master cylinder is replaced or
overhauled, first bleed the air from the master
cylinder, then from each wheel cylinder and
caliper following the procedures described
below.
Bleeding the Master Cylinder
7. Disconnect the rear wheel brake pipe 1from the
master cylinder. Check the fluid level and
replenish as necessary. If replenished, leave the
system for at least one minute.
8. Depress the brake pedal slowly once and hold it
depressed.
9. Completely seal the delivery port of the master
cylinder where the pipe was disconnected with
your finger, then release the brake pedal slowly.
10. Release your finger from the delivery port when
the brake pedal returns completely.
11. Repeat steps 7 through 9 until the brake fluid
comes out of the delivery port during step 7.
NOTE:
Do not allow the fluid level in the reservoir to go
below the half-way mark.
21
Page 889 of 3573

POWER ASSISTED BRAKE SYSTEM 5C – 11
12. Reconnect the brake pipe 1to the master cylinder
and tighten the pipe.
13. Depress the brake pedal slowly once and hold it
depressed.
14. Loosen the rear wheel brake pipe 1at the master
cylinder.
15. Retighten the brake pipe, then release the brake
pedal slowly.
16. Repeat steps 13 through 15 until no air comes out
from the port when the brake pipe is loosened.
NOTE:
Be very careful not to allow the brake fluid to come in
contact with painted surfaces.
17. Bleed the air from the front wheel brake pipe
connection 2by repeating steps 7 through 16.
Bleeding the Caliper
18. Bleed the air from each wheel in the order listed
below.
LHD models:
1) Right rear caliper
2) Left rear caliper
3) Load sensing proportioning valve (only for
Europe and South Africa)
4) Right front caliper
5) Left front caliper
RHD models:
1) Left rear caliper
2) Right rear caliper
3) Load sensing proportioning valve (only for
Europe and South Africa)
4) Left front caliper
5) Right front caliper
Conduct air bleeding from the wheels in the above
order. If no brake fluid comes out, it suggests that air
is mixed in the master cylinder. In this case, bleed air
from the master cylinder in accordance with Steps 7
through 17, and then bleed air from the caliper.
19. Place the proper size box end wrench over the
bleeder screw.
20. Cover the bleeder screw with a transparent tube,
and submerge the free end of the transparent tube
in a transparent container containing brake fluid.
21. Pump the brake pedal slowly three (3) times
(once/sec), then hold it depressed.
22. Loose the bleeder screw until fluid flows through
the tube.
23. Retighten the bleeder screw.
24. Release the brake pedal slowly.
25. Repeat step 21 through 24 until the air is
compeletely removed. It may be necessary to
repeat the bleeding procedure 10 or more times
for front wheels and 15 or more times for rear
wheels.
26. Go to the next wheel in the sequence after each
wheels is bled. Be sure to monitor reservoir fluid
level.
Page 890 of 3573

5C – 12 POWER ASSISTED BRAKE SYSTEM
27. Depress the brake pedal to check if you feel
“sponginess” after the air has been removed from
all wheel cylinders and calipers. If the pedal feels
“spongy”, the entire bleeding procedure must be
repeated.
28. After the bleeding operation is completed on each
individual wheel, check the level of brake fluid in
the reservoir and replenish up to the “MAX” level if
necessary.
29. Attach the reservoir cap.
•If the diaphragm inside the cap is deformed,
reform it and install.
30. Stop the engine.
FLUSHING BRAKE HYDRAULIC SYSTEM
It is recommended that the entire hydraulic system be
thoroughly flushed with clean brake fluid whenever
new parts are installed in the hydraluic system.
Approximately one quart of fluid is required to flush
the hydraulic system.
The system must be flushed if there is any doubt as to
the grade of fluid in the system or if fluid has been
used which contains the slightest trace of mineral oil.
All rubber parts that have been subjected to a
contaminated fluid must be replaced.
BRAKE PIPES AND HOSES
The hydraulic brake system components are
interconnected by special steel piping and flexible
hoses. Flexible hoses are used between the frame and
the front calipers, the frame and rear axle case and the
rear axle and the rear calipers.
When the hydraulic pipes have been disconnected for
any reason, the brake system must be bled after
reconnecting the pipe; refer to “Bleeding Brake
Hydraulic System” in this section.
BRAKE HOSE INSPECTION
The brake hoses should be inspected at least twice a
year. The brake hose assembly should be checked for
road hazard, cracks and chafing of the outer cover,
and for leaks and blisters. Inspect for proper routing
and mounting of the hose. A brake hose that rubs on
suspension components will wear and eventually fail.
A light and mirror may be needed for an adequate
inspection. If any of the above conditions are
observed on the brake hose, adjust or replace the
hose as necessary.
CAUTION:
Never allow brake components such as calipers to
hang from the brake hoses, as damage to the hoses
may occur.