oil level ISUZU TROOPER 1998 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ISUZU, Model Year: 1998, Model line: TROOPER, Model: ISUZU TROOPER 1998Pages: 3573, PDF Size: 60.36 MB
Page 16 of 3573

GENERAL REPAIR INSTRUCTIONS
1. Park the vehicle on level ground and chock the
front or rear wheels before lifting the vehicle.
2. Use covers on the vehicle body, seats, and
floor to prevent damage and/or
contaminations.
3. Disconnect the grounding cable from the
battery before performing service operations.
This will prevent cable damage or burning due
to shortcircuiting.
4. Raise the vehicle with a jack set against the
recommended lifting points (see ÒLifting
instructionsÓ in this section).
5. Support the vehicle on chassis stands.
6. Handle brake fluid and antifreeze solution with
great care.
Spilling these liquids on painted surfaces will
damage the paint.
7. The use of the proper tool(s) and special tool(s)
where specified is essential to efficient,
reliable, and safe service operations.
8. Always use genuine ISUZU replacement parts.
9. Discard used cotter pins, gasket, plastic clips,
O-rings, oil seals, lock washers, and self-
locking nuts at disassembly.
Normal function of these parts cannot be
guaranteed if they are reused.
10. Keep the disassembled parts neatly in groups.
This will facilitate smooth and correct
reassembly.11. Keep fixing nuts and bolts separate.
Fixing nuts and bolts vary in hardness and
design according to installation positions.
12. Clean all parts before inspection or
reassembly.
13. Clean the oil ports and other openings with
compressed air to make certain that they are
free of dirt and obstructions.
14. Lubricate the rotating and sliding faces of all
moving parts with oil or grease before
installation.
15. Use the recommended liquid gasket to prevent
leakage.
16. Carefully observe all nut and bolt torque
specifications.
17. When service operation is completed, make a
final check to be sure service has been done
properly and problem has been corrected.
18. When removing or replacing parts that require
refrigerant to be discharged from the air
conditioning system, be sure to use the
following tools to recover and recycle the
Refrigerant-134a (R-134a).
For 134a:
Use the R-134a Refrigerant Recovery/Recovery/
Recycling/Recharging/System (ACR
4) or its
equivalent to prevent the discharge of
refrigerant into the air.
0AÐ2 GENERAL INFORMATION
Page 26 of 3573

ABBREVIATIONS CHARTS
LIST OF AUTOMOTIVE ABBREVIATIONS WHICH MAY BE USED IN THIS MANUAL
A Ð Ampere(s)
ABS Ð Antilock Brake System
A/C Ð Air Conditioning
ACCEL Ð Accelerator
ACC Ð Accessary
Adj Ð Adjust
A/F Ð Air Fuel Ratio
AIR Ð Air Injection Reaction System
ALDL Ð Assembly Line Diagnostic Link
Alt Ð Altitude
AMP Ð Ampere(s)
ANT Ð Antenna
APS Ð Absolute Pressure Sensor
ASM Ð Assembly
A/T Ð Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
ATDC Ð After Top Dead Center
Auth Ð Authority
Auto Ð Automatic
BARO Ð Barometic
Bat Ð Battery
Bat+ Ð Battery Positive Terminal
Bbl Ð Barrel
BCM Ð Body Control Module
BHP Ð Brake Horsepower
BP Ð Back Pressure
BTDC Ð Before Top Dead Center
¡C ÐDegrees Celsius
Cat. Conv. Ð Catalytic Converter
cc Ð Cubic Centimeter
CCC Ð Computer Command Control
CCOT Ð Cycling Clutch Orifice Tube
CCP Ð Controlled Canister Purge
CID Ð Cubic Inch Displacement
CL Ð Closed Loop
CLCC Ð Closed Loop Carburetor Control
CO Ð Carbon Monoxide
Coax Ð Coaxial
Conn Ð Connector
Conv Ð Converter
CP Ð Canister Purge
CPS Ð Central Power Supply
Crank Ð Crankshaft
CTS Ð Coolant Temperature Sensor
Cu.In. Ð Cubic Inch
CV Ð Constant Velocity
Cyl Ð Cylinder(s)
C
3I Ð Computer Controlled Coil Ignition
DBM Ð Dual Bed Monolith
Diff Ð Differential
DIS Ð Direct Ignition System
Dist ÐDistributor
DOHC Ð Double Overhead Camshaft
DVM Ð Digital Voltmeter (10 meg.)
DVOM Ð Digital Volt Ohmmeter
DVDV Ð Differential Vacuum Delay Valve
EAC ÐElectric Air Control
EAS Ð Electric Air Switching
EBCM Ð Electronic Brake Control Module
ECC Ð Electronic Climate Control
ECM Ð Electronic Control Module
ECU Ð Electronic Control Unit
Ð Engine Calibration Unit (PROM)
EECS Ð Evaporative Emission Control System
EFE Ð Early Fuel Evaporation
EFI Ð Electronic Fuel Injection
EGR Ð Exhaust Gas Recirculation
EGR/TVS Ð Exhaust Gas Recirculation/Thermostatic
Vacuum Switch
ELC Ð Electronic Level Control
ESC Ð Electronic Spark Control
EST Ð Electronic Spark Control
ETR Ð Electronically Tuned Receiver
EVRV Ð Electronic Vacuum Regulator Valve (EGR)
Exh Ð Exhaust
¡F Ð Degrees Fahrenheit
FF Ð Front Drive Front Engine
FL Ð Fusible Link
FLW Ð Fusible Link Wire
FRT ÐFront
FWD Ð Front Wheel Drive
4WD Ð Four Wheel Drive
4x4 Ð Four Wheel Drive
4 A/T Ð Four Speed Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
Gal Ð Gallon
Gen Ð Generator
Gov Ð Governor
g Ð Gram
Harn Ð Harness
HC Ð Hydrocarbons
HD ÐHeavy Duty
HEI Ð High Energy Ignition
Hg Ð Mercury
HiAlt Ð High Altitude
HVAC Ð Heater-Vent-Air Conditioning
IAC Ð Idle Air Control
IC Ð Integrated Circuit
ID Ð Identification
Ð Inside Diameter
IDI Ð Integrated Direct Ignition
IGN Ð Ignition
ILC Ð Idle Load Compensator
INJ ÐInjection
IP Ð Instrument Panel
IPC Ð Instrument Panel Cluster
INT Ð Intake
J/B Ð Junction Block
km Ð Kilometers
km/h Ð Kilometer per Hour
kPa Ð KiloPascals
KV Ð Kilovolts (thousands of volts)
KW Ð Kilowatts
0AÐ12 GENERAL INFORMATION
Page 260 of 3573
1D Ð 4 COMPRESSOR OVERHAUL
COMPRESSOR OIL
OIL SPECIFICATION
·The HFC-134a system requires a synthetic
(PAG) compressor oil.
·Compressor (PAG) oil varies according to
compressor model. Be sure to use oil specified
for the model of compressor.
DKV-14D : ZXL-200PG
(ISUZU PART NO.
8-97101-336-0)
DKS-15CH : ZXL-100PG
(ISUZU PART NO.
8-97101-338-0)
HANDLING OF OIL
·The oil should be free from moisture, dust,
metal powder, etc.
·Do not mix with other oil
·The water content in the oil increases when
exposed to the air. After use, seal oil from air
immediately.
·The compressor oil must be stored in steel
containers, not in plastic containers.
COMPRESSOR OIL CHECK
The oil used to lubricate the compressor is
circulating with the refrigerant.
Whenever replacing any component of the system
or a large amount of gas leakage occurs, add oil to
maintain the original amount of oil.
Oil Capacity
Capacity total in system 150cc (4.2 Imp fl oz)
Compressor (Service
150cc (4.2 Imp fl oz)
parts) charging amount
Checking and Adjusting for Used Compressor
1) Perform Oil return operation.
(Refer to ÒOil Return OperationÓ in this section.)
2) Discharge refrigerant and remove the
compressor.
3) Drain the compressor oil and measure the
extracted oil with a measuring cylinder.
4) If the amount of oil drained is much less than
90cc (2.5 Imp fl oz), some refrigerant may have
leaked out. Conduct leak tests on connections
of each system, and if necessary, repair or
replace faulty parts.5) Check the compressor oil for contamination.
(Refer to ÒContamination of Compressor OilÓ in
this section.)
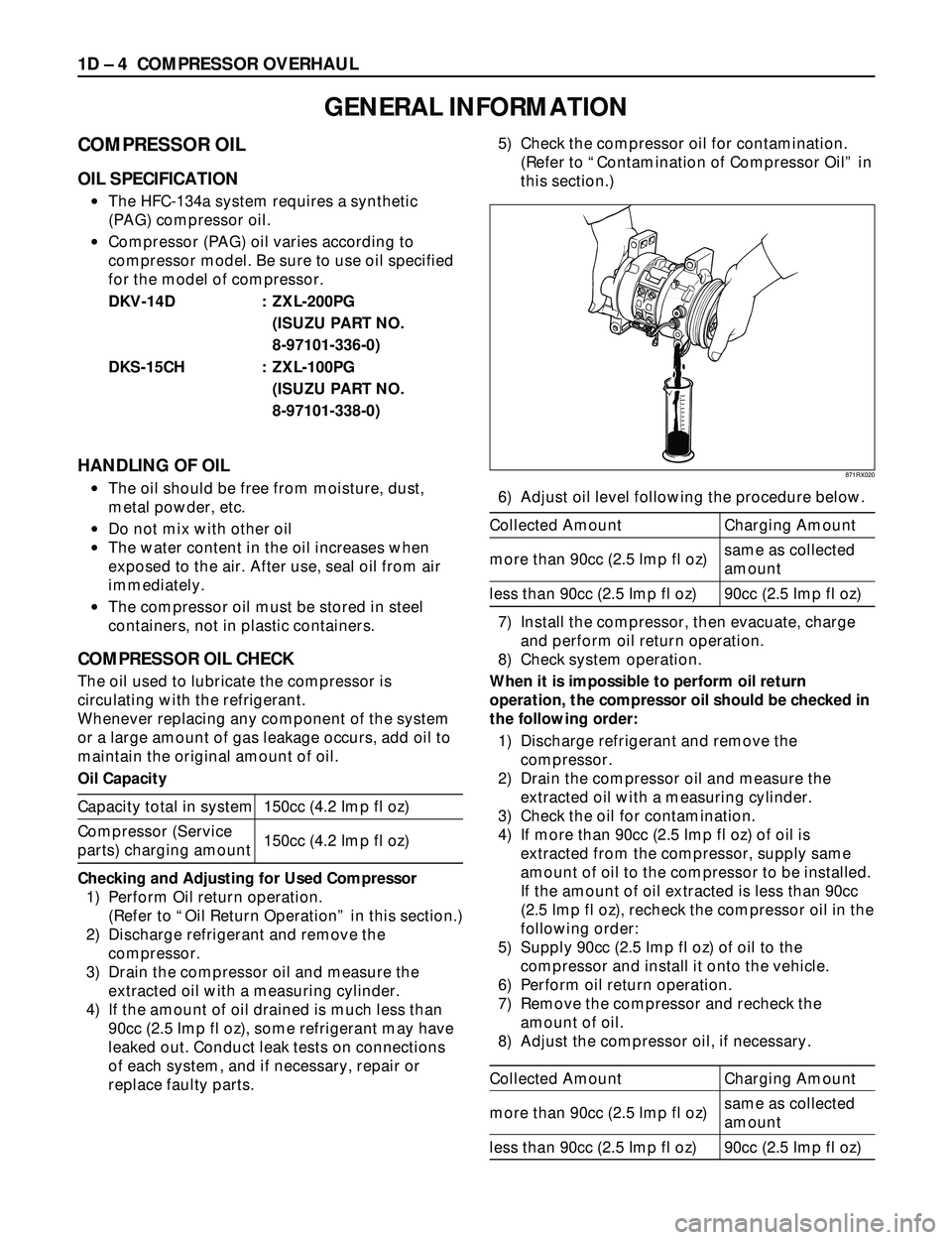
6) Adjust oil level following the procedure below.
Collected Amount Charging Amount
same as collected
more than 90cc (2.5 Imp fl oz)
amount
less than 90cc (2.5 Imp fl oz) 90cc (2.5 Imp fl oz)
7) Install the compressor, then evacuate, charge
and perform oil return operation.
8) Check system operation.
When it is impossible to perform oil return
operation, the compressor oil should be checked in
the following order:
1) Discharge refrigerant and remove the
compressor.
2) Drain the compressor oil and measure the
extracted oil with a measuring cylinder.
3) Check the oil for contamination.
4) If more than 90cc (2.5 Imp fl oz) of oil is
extracted from the compressor, supply same
amount of oil to the compressor to be installed.
If the amount of oil extracted is less than 90cc
(2.5 Imp fl oz), recheck the compressor oil in the
following order:
5) Supply 90cc (2.5 Imp fl oz) of oil to the
compressor and install it onto the vehicle.
6) Perform oil return operation.
7) Remove the compressor and recheck the
amount of oil.
8) Adjust the compressor oil, if necessary.
Collected Amount Charging Amount
same as collected
more than 90cc (2.5 Imp fl oz)
amount
less than 90cc (2.5 Imp fl oz) 90cc (2.5 Imp fl oz)
GENERAL INFORMATION
871RX020
Page 261 of 3573

COMPRESSOR OVERHAUL 1D Ð 5
Checking and Adjusting for Compressor
Replacement
150cc (4.2 Imp fl oz) of oil is charged in compressor
(service parts). So it is necessary to drain the proper
amount of oil from the new compressor.
1) Perform oil return operation.
2) Discharge refrigerant and remove the
compressor.
3) Drain the compressor oil and measure the
extracted oil.
4) Check the compressor oil for contamination.
5) Adjust oil level as required.
Amount of oil drained Draining amount of oil
from used compressor from new compressor
less than Same as drained
90cc (2.5 Imp fl oz) amount
more than
90cc (2.5 Imp fl oz)
90cc (2.5 Imp fl oz)
6) Evacuate, charge and perform oil return
operation.
7) Check system operation.
CONTAMINATION OF COMPRESSOR OIL
Unlike engine oil, no cleaning agent is added to the
compressor oil. Even if the compressor runs for a
long period of time (approximately 1 season), the
oil never becomes contaminated as long as there is
nothing wrong with the compressor or its method
of use.
Inspect the extracted oil for any of the following
conditions:
·The capacity of the oil has increased.
·The oil has changed color to red.
·Foreign substances, metal powder, etc., are
present in the oil.
If any of these conditions exists, compressor oil is
contaminated. Whenever contaminated
compressor oil is discovered, the receiver/drier
must be replaced.
OIL RETURN OPERATION
There is close affinity between the oil and the
refrigerant. During normal operation, part of the oil
recirculates with the refrigerant in the system.
When checking the amount of oil in the system, or
replacing any component of the system, the
compressor must be run in advance for oil return
operation. The procedure is as follows:
1) Open the all doors and engine hood.
2) Start the engine and A/C switch is ÒONÓ and
Set the fan control knob at its highest position.
3) Run the compressor for more than 20 minutes
between 800 and 1,000 rpm in order to operate
the system.
4) Stop the engine.
REPLACEMENT OF COMPONENT PARTS
When replacing system component parts, supply
the following amount of oil to the component parts
to be installed.
Component parts to be installed Amount of oil
Evaporator 50cc (1.4 Imp fl oz)
Condenser 30cc (0.8 Imp fl oz)
Receiver/drier 30cc (0.8 Imp fl oz)
871RX013
Page 280 of 3573

1D Ð 24 COMPRESSOR OVERHAUL
6. Remove any excess oil resulting from installing the
new seal parts from the shaft and inside the
compressor neck.
7. Install the clutch plate and hub assembly as
described previously.8. Reinstall compressor belt and tighten bracket.
9. Evacuate and charge the refrigerant system.
COMPRESSOR PRESSURE RELIEF VALVE
Removal
1. Recover the refrigerant using Refrigerant Recovery
System.
2. Remove old pressure relief valve.
Installation
1. Clean valve seat area on rear head.2. Lubricate O-ring of new pressure relief valve and
O-ring assembly with new 525 viscosity refrigerant
oil. Install new valve and torque in place, 9.0 Nám
(6.1 ft lbs)
3. Evacuate and recharge the system.
4. Leak test system.
COMPRESSOR OIL
Compressor Oil Check
The oil used to lubricate the compressor is circulating
with the refrigerant.
Whenever replacing any component of the system or a
large amount of gas leakage occurs, add oil to maintain
the original amount of oil.
Checking and Adjusting Oil Quantity for
Used Compressor
1. Perform oil return operation. Refer to Oil Return
Operation in this section.
2. Discharge and recover refrigerant and remove the
compressor.
3. Drain the compressor oil and measure the extracted
oil with a measuring cylinder.
4. If the amount of oil drained is much less than 90 cc
(3.0 fl. oz.), some refrigerant may have leaked out.
Conduct a leak tests on the connections of each
system, and if necessary, repair or replace faulty
parts.
5. Check the compressor oil contamination. (Refer to
Contamination of Compressor Oil in this section.)
6. Adjust the oil level following the next procedure
below.7. Install the compressor, then evacuate, charge and
perform the oil return operation.
8. Check system operation.
When it is impossible to preform oil return
operation, the compressor oil should be checked in
the following order:
1. Discharge and recover refrigerant and remove the
compressor.
2. Drain the compressor oil and measure the extracted
oil with a measuring cylinder.
3. Check the oil for contamination.
4. If more than 90 cc (3.0 fl. oz.) of oil is extracted from
the compressor, supply the same amount of oil to
the compressor to be installed. If the amount of oil
extracted is less than 90 cc (3.0 fl. oz.), recheck the
compressor oil in the following order:
5. Supply 90 cc (3.0 fl. oz.) of oil to the compressor
and install it onto the vehicle.
6. Evacuate and recharge with the proper amount of
refrigerant.
7. Perform the oil return operation.
8. Remove the compressor and recheck the amount of
oil.
9. Adjust the compressor oil, if necessary.
Checking and Adjusting for Compressor
Replacement
The oil is not charged in compressor (service parts). So
it is necessary to charge the proper amount of oil to the
new compressor. (Oil Capacity)
Capacity total in system 150 cc (5.0 fl.oz)
Compressor (Service 150 cc (5.0 fl.oz)
parts) charging amount
(Collected Amount) (Charging Amount)
more than 90 cc same as collected
(3.0 fl.oz) amount
less than 90 cc (3.0 fl.oz) 90 cc (3.0 fl.oz)
(Collected Amount) (Charging Amount)
more than 90 cc same as collected
(3.0 fl.oz) amount
less than 90 cc (3.0 fl.oz) 90 cc (3.0 fl.oz)
Page 281 of 3573

COMPRESSOR OVERHAUL 1D Ð 25
1. Perform oil return operation.
2. Discharge and recover the refrigerant and remove
the compressor.
3. Drain the compressor oil and measure the extracted
oil.
4. Check the compressor oil for contamination.
5. Adjust the oil level as required.
6. Evacuate, charge and perform the oil return
operation.
7. Check the system operation.
Contamination of Compressor Oil
Unlike engine oil, no cleaning agent is added to the
compressor oil. Even if the compressor runs for a long
period of time (approximately one season), the oil never
becomes contaminated as long as there is nothing
wrong with the compressor or its method of use.
Inspect the extracted oil for any of the following
conditions:
·The capacity of the oil has increased.
·The oil has changed to red.
·Foreign substances, metal powder, etc., are present
in the oil.
If any of these conditions exists, the compressor
oil is contaminated. Whenever contaminated
compressor oil is discovered, the receiver/drier
must be replaced.
Oil Return Operation
There is close affinity between the oil and the
refrigerant. During normal operation, part of the oil
recirculates with the refrigerant in the system. When
checking the amount of oil in the system, or replacing
any component of the system, the compressor must be
run in advance for oil return operation. The procedure
is as follows:
1. Open all the doors and the engine hood.
2. Start the engine and air conditioning switch to "ON"
and set the fan control knob at its highest position.
3. Run the compressor for more than 20 minutes
between 800 and 1,000 rpm in order to operate the
system.
4. Stop the engine.
Replacement of Component Parts
When replacing the system component parts, supply
the following amount of oil to the component parts to be
installed.
Compressor Leak Testing (External and
Internal)
Bench-Check Procedure
1. Install test plate J-39893 on rear head of compressor.
2. Using Refrigerant Recovery System, attach center
hose of manifold gage set on charging station to a
refrigerant drum standing in an upright drum.
3. Connect charging station high and low pressure
lines to corresponding fittings on test plate J-39893.
Suction port (low-side) of compressor has large
internal opening. Discharge port (high-side) has
smaller internal opening into compressor and
deeper recess.
4. Open low pressure control, high pressure control
and refrigerant control on charging station to allow
refrigerant vapor to flow into compressor.
5. Using a leak detector, check for leaks at pressure
relief valve, rear head switch location, compressor
front and rear head seals, center cylinder seal,
through bolt head gaskets and compressor shaft
seal. After checking, shut off low pressure control
and high-pressure control on charging station.
6. If an external leak is present, perform the necessary
corrective measures and recheck for leaks to make
certain the leak has been connected.
7. Recover the refrigerant.
8. Disconnect both hoses from the test plate J-39893.
9. Add 90 ml (3 oz.) new PAG lubricant to the
compressor assembly. Rotate the complete
compressor assembly (not the crankshaft or drive
plate hub) slowly several turns to distribute oil to all
cylinder and piston areas.
10. Install a M9 ´1.25 threaded nut on the compressor
crankshaft if the drive plate and clutch assembly are
not installed.
11. Using a box-end wrench or socket and handle,
rotate the compressor crankshaft or clutch drive
plate on the crankshaft several turns to insure
piston assembly to cylinder wall lubrication.
12. Using Refrigerant Recovery System, connect the
charging station high-pressure line to the test plate
J-39893 high-side connector.
13. Using Refrigerant Recovery System, connect the
charging station low-pressure line to the low
pressure port of the test plate J-39893. Oil will drain
out of the compressor suction port if the compressor
is positioned with the suction port downward. (Component parts to be (Amount of Oil)
installed)
Evaporator 50 cc (1.7 fl. oz.)
Condenser 30 cc (1.0 fl. oz.)
Receiver/dryer 30 cc (1.0 fl. oz.)
Refrigerant line (one 10 cc (0.3 fl. oz.)
piece)
(Amount of oil drained (Charging amount of oil
from used compressor) to new compressor)
more than 90 cc same as drained amount
(3.0 fl.oz)
less than 90 cc (3.0 fl.oz) 90 cc (3.0 fl.oz)
Page 295 of 3573

SERVICE INFORMATION 00 – 13
STEERING
INSPECTION
Visual check
Check the following parts:
• Oil leakage.
• Steering system for looseness or damage.
• Steering function
• Joint ball for oil leakage or damage.
• Joint ball rubber boot for damage.
MAINTENANCE
The hydraulic system should be kept clean and fluid level
in the reservoir should be checked at regular intervals and
fluid added when required. Refer to "MAINTENANCE AND
LUBRICATION" in section 0B of the manual for type of
fluid to be used and intervals for filling.
If the system contains some dirt, flush it as detailed later
in this section. If it is exceptionally dirty, both the pump
and the gear must be completely disassembled before
further usage.
All tubes, hoses, and fittings should be inspected for
leakage at regular intervals. Fittings must be tight. Make
sure the clips, clamps and supporting tubes and hoses are
in place and properly secured.
Power steering hoses and lines must not be twisted,
kinked or tightly bent. Air in the system will cause spongy
action and noisy operation. When a hose is disconnected
or when fluid is lost, for any reason, the system must be
bled after refilling. Refer to "Bleeding the Power Steering
System" in this section.
FLUID LEVEL
1. Run the engine until the power steering fluid reaches
normal operating temperature, about 55°C (130°F),
then shut the engine off.
2. Check the level of fluid in the reservoir.
3. If the fluid level is low, add power steering fluid as
specified in "MAINTENANCE AND LUBRICATION" in
section 0B to the proper level and install the receiver
cap.
4. When checking the fluid level after the steering
system has been serviced, air must be bled from the
system. Refer to "Bleeding the Power Steering
System" in this section.
SERVICING
Page 312 of 3573
2A – 10 POWER STEERING
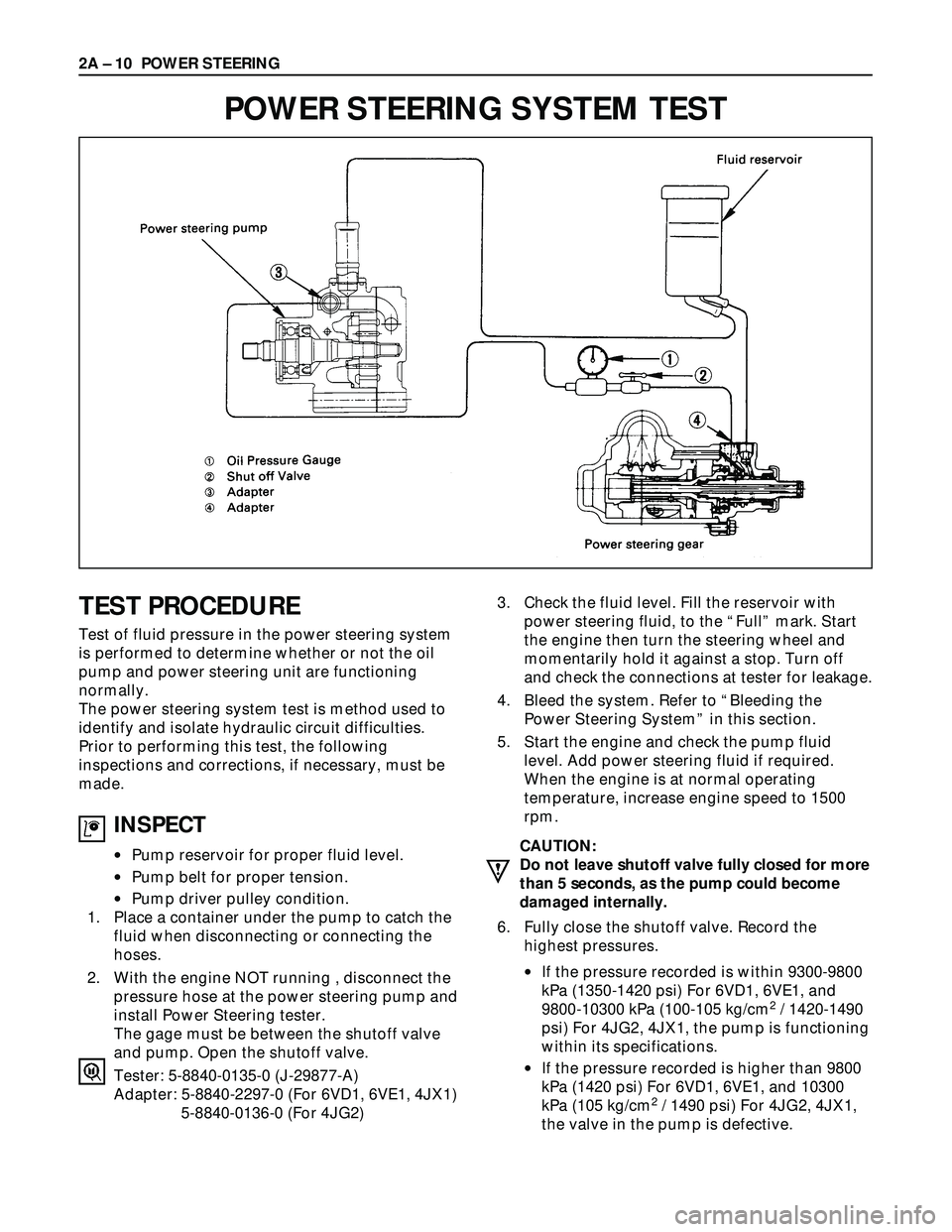
POWER STEERING SYSTEM TEST
TEST PROCEDURE
Test of fluid pressure in the power steering system
is performed to determine whether or not the oil
pump and power steering unit are functioning
normally.
The power steering system test is method used to
identify and isolate hydraulic circuit difficulties.
Prior to performing this test, the following
inspections and corrections, if necessary, must be
made.
INSPECT
•Pump reservoir for proper fluid level.
•Pump belt for proper tension.
•Pump driver pulley condition.
1. Place a container under the pump to catch the
fluid when disconnecting or connecting the
hoses.
2. With the engine NOT running , disconnect the
pressure hose at the power steering pump and
install Power Steering tester.
The gage must be between the shutoff valve
and pump. Open the shutoff valve.
Tester: 5-8840-0135-0 (J-29877-A)
Adapter: 5-8840-2297-0 (For 6VD1, 6VE1, 4JX1)
5-8840-0136-0 (For 4JG2)3. Check the fluid level. Fill the reservoir with
power steering fluid, to the “Full” mark. Start
the engine then turn the steering wheel and
momentarily hold it against a stop. Turn off
and check the connections at tester for leakage.
4. Bleed the system. Refer to “Bleeding the
Power Steering System” in this section.
5. Start the engine and check the pump fluid
level. Add power steering fluid if required.
When the engine is at normal operating
temperature, increase engine speed to 1500
rpm.
CAUTION:
Do not leave shutoff valve fully closed for more
than 5 seconds, as the pump could become
damaged internally.
6. Fully close the shutoff valve. Record the
highest pressures.
•If the pressure recorded is within 9300-9800
kPa (1350-1420 psi) For 6VD1, 6VE1, and
9800-10300 kPa (100-105 kg/cm
2/ 1420-1490
psi) For 4JG2, 4JX1, the pump is functioning
within its specifications.
•If the pressure recorded is higher than 9800
kPa (1420 psi) For 6VD1, 6VE1, and 10300
kPa (105 kg/cm
2/ 1490 psi) For 4JG2, 4JX1,
the valve in the pump is defective.
Page 314 of 3573

BLEEDING THE POWER
STEERING SYSTEM
When a power steering pump or gear has been
installed, or an oil line has been disconnected, the
air that has entered the system must be bled out
before the vehicle is operated. If air is allowed to
remain in the power steering fluid system, noisy
and unsatisfactory operation of the system may
result.
BLEEDING PROCEDURE
When bleeding the system, and any time fluid is
added to the power steering system, be sure to use
only power steering fluid as specified in
“MAINTENANCE AND LUBRICATION” in section
0B.
1. Fill the pump fluid reservoir to the proper
level and let the fluid settle for at least two
minutes.
2. Start the engine and let it run for a few
seconds.
Do not turn the steering wheel. Then turn the
engine off.
3. Add fluid if necessary.
4. Repeat the above procedure until the fluid
level remains constant after running the
engine.
5. Raise the front end of the vehicle so that the
wheels are off the ground.
6. Start the engine. Slowly turn the steering
wheel right and left, lightly contacting the
wheel stops.
7. Add power steering fluid if necessary.
8. Bring down the vehicle, set the steering wheel
at the straight forward position after turning it
to its full steer positions 2 or 3 times, and stop
the engine.
9. Stop the engine. Check the fluid level and
refill as required.
10. If the fluid is extremely foamy, allow the
vehicle to stand a few minutes and repeat the
above procedure.
INSPECT
•Belt for tightness.
•Pulley for looseness or damage. The pulley
should not wobble with the engine running.
•Make sure that hose and pipes are properly
fitted.
•Fluid level and fill to the proper level.
FLUSHING THE POWER
STEERING SYSTEM
1. Raise the front end of the vehicle off the
ground until the wheels are free to turn.
2. Remove the fluid return line at the reservoir
inlet connector and plug the connector.
Position the line toward a large container to
catch the draining fluid.
3. While running the engine at idle, fill the
reservoir with new power steering fluid. Turn
the steering wheel in both directions. Do not
contact wheel stops or hold the wheel in a
corner, or fluid will stop and the pump will be
in pressure relief mode. A sudden overflow
from the reservoir may develop if the wheel is
held at a stop.
4. While refilling the reservoir, check the
draining fluid for contamination. If foreign
material is still evident, replace all lines,
disassemble and clean or replace the power
steering system components. Do not re-use
any drained power steering fluid.
5. Install all the lines and hoses. Fill the system
with new power steering fluid and bleed the
system as described in “Bleeding The Power
Steering System”. Operate the engine for
about 15 minutes. 2A – 12 POWER STEERING
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
Page 439 of 3573
DIFFERENTIAL (FRONT) 4A1±2
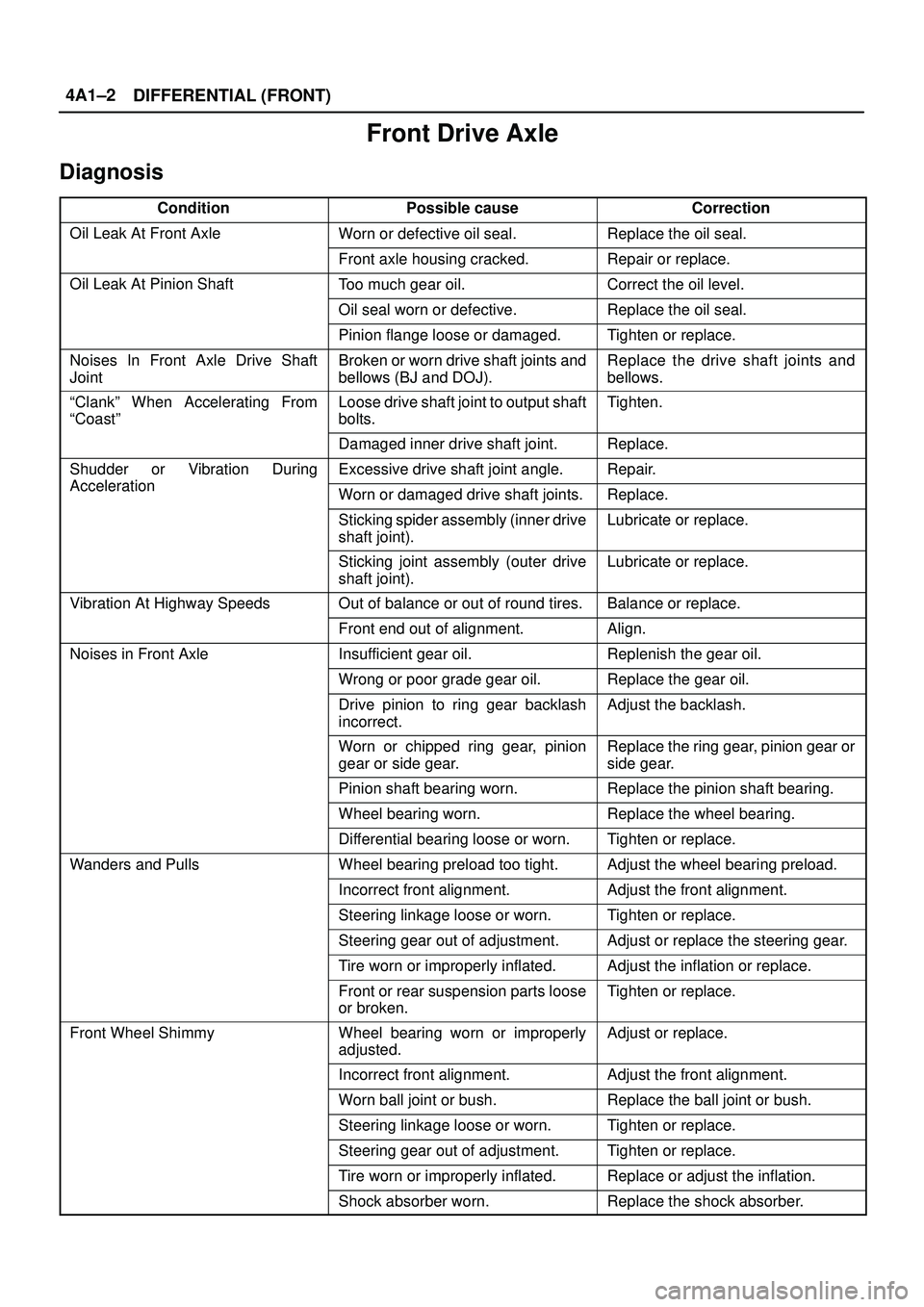
Front Drive Axle
Diagnosis
ConditionPossible causeCorrection
Oil Leak At Front AxleWorn or defective oil seal.Replace the oil seal.
Front axle housing cracked.Repair or replace.
Oil Leak At Pinion ShaftToo much gear oil.Correct the oil level.
Oil seal worn or defective.Replace the oil seal.
Pinion flange loose or damaged.Tighten or replace.
Noises In Front Axle Drive Shaft
JointBroken or worn drive shaft joints and
bellows (BJ and DOJ).Replace the drive shaft joints and
bellows.
ªClankº When Accelerating From
ªCoastºLoose drive shaft joint to output shaft
bolts.Tighten.
Damaged inner drive shaft joint.Replace.
Shudder or Vibration During
Acceleration
Excessive drive shaft joint angle.Repair.
AccelerationWorn or damaged drive shaft joints.Replace.
Sticking spider assembly (inner drive
shaft joint).Lubricate or replace.
Sticking joint assembly (outer drive
shaft joint).Lubricate or replace.
Vibration At Highway SpeedsOut of balance or out of round tires.Balance or replace.
Front end out of alignment.Align.
Noises in Front AxleInsufficient gear oil.Replenish the gear oil.
Wrong or poor grade gear oil.Replace the gear oil.
Drive pinion to ring gear backlash
incorrect.Adjust the backlash.
Worn or chipped ring gear, pinion
gear or side gear.Replace the ring gear, pinion gear or
side gear.
Pinion shaft bearing worn.Replace the pinion shaft bearing.
Wheel bearing worn.Replace the wheel bearing.
Differential bearing loose or worn.Tighten or replace.
Wanders and PullsWheel bearing preload too tight.Adjust the wheel bearing preload.
Incorrect front alignment.Adjust the front alignment.
Steering linkage loose or worn.Tighten or replace.
Steering gear out of adjustment.Adjust or replace the steering gear.
Tire worn or improperly inflated.Adjust the inflation or replace.
Front or rear suspension parts loose
or broken.Tighten or replace.
Front Wheel ShimmyWheel bearing worn or improperly
adjusted.Adjust or replace.
Incorrect front alignment.Adjust the front alignment.
Worn ball joint or bush.Replace the ball joint or bush.
Steering linkage loose or worn.Tighten or replace.
Steering gear out of adjustment.Tighten or replace.
Tire worn or improperly inflated.Replace or adjust the inflation.
Shock absorber worn.Replace the shock absorber.