Pump JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JAGUAR, Model Year: 2010, Model line: XFR, Model: JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.GPages: 3039, PDF Size: 58.49 MB
Page 1345 of 3039

Component Description DIAGNOSTIC MODULE - TANK LEAKAGE PUMP (NAS ONLY)
The DMTL (diagnostic module - tank leakage) pump periodically checks the EVAP system and the fuel tank for leaks when the ignition is switched off. The DMTL system comprises the previously described components of the EVAP system with the following additional components; a DMTL pump and a DMTL filter.
The DMTL pump is connected to the atmospheric vent of the EVAP canister and incorporates an electric air pump, a PTC (positive temperature coefficient) heating element, a normally open change-over valve and a reference orifice. The DMTL pump
is only operated when the ignition is switched off and is controlled by the ECM. The ECM also monitors the electric air pump operation and the change-over valve for faults.
The DMTL filter protects the pump from dust being drawn into the system when the pump is being operated. The filter is
located on the fuel filler head and is connected to the DMTL pump by a vapor pipe.
The DMTL test is performed after the engine has stopped following a run of 10 minutes or more, providing that the vehicle fuel
tank is between 15 and 85% full, the ambient temperature is above 0 °C (32 °F) and less than 40 °C (104 °F) and the vehicle
was not started for at least 180 minutes prior to this run.
The DMTL pump is driven to pressurize the fuel tank and the current is measured with the change-over valve in different
states.
A comparison of the current draw in each state indicates the degree of any leak, and the ECM then sets the appropriate DTC (diagnostic trouble code).
www.JagDocs.com
Page 1346 of 3039
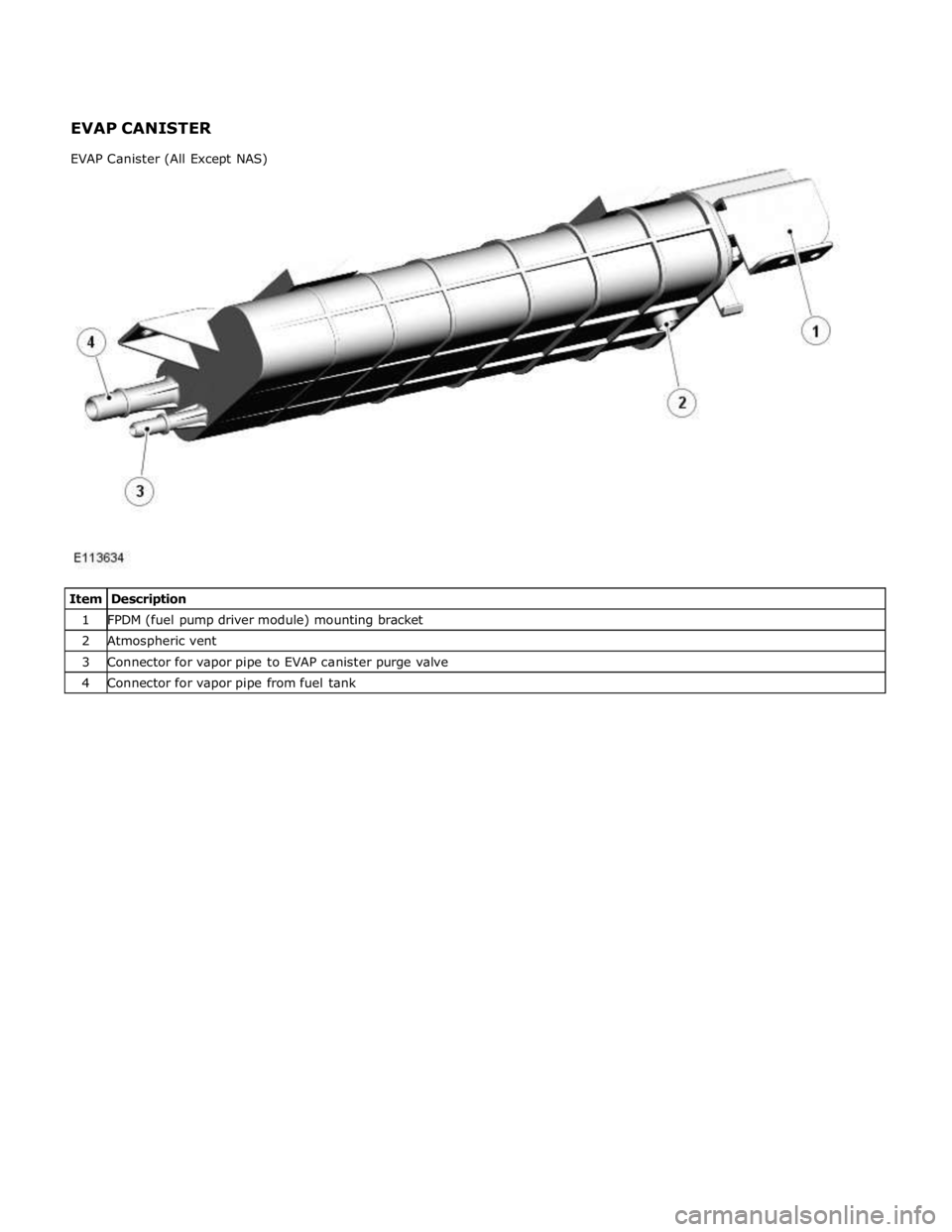
1 FPDM (fuel pump driver module) mounting bracket 2 Atmospheric vent 3 Connector for vapor pipe to EVAP canister purge valve 4 Connector for vapor pipe from fuel tank EVAP CANISTER
EVAP Canister (All Except NAS)
Page 1347 of 3039
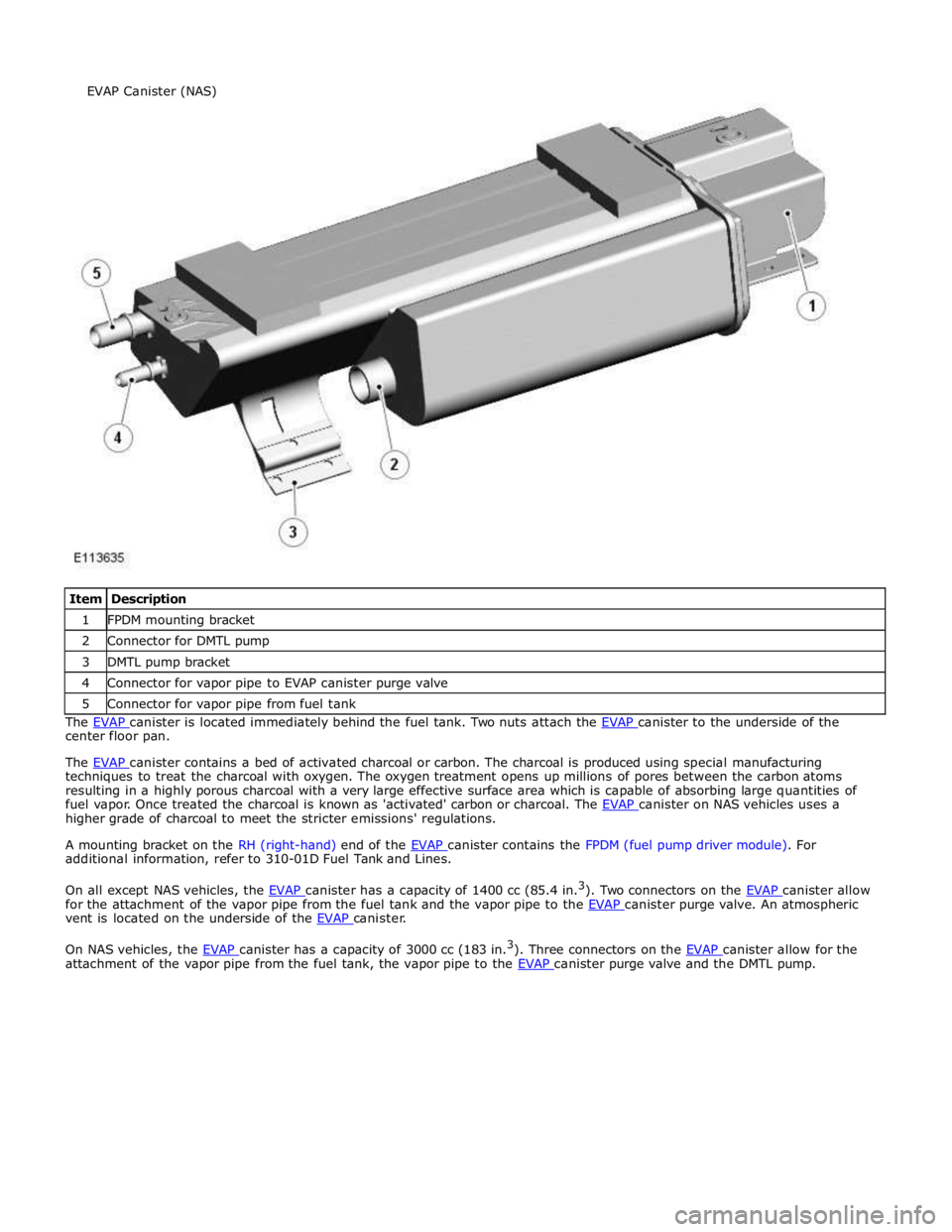
1 FPDM mounting bracket 2 Connector for DMTL pump 3 DMTL pump bracket 4 Connector for vapor pipe to EVAP canister purge valve 5 Connector for vapor pipe from fuel tank The EVAP canister is located immediately behind the fuel tank. Two nuts attach the EVAP canister to the underside of the center floor pan.
The EVAP canister contains a bed of activated charcoal or carbon. The charcoal is produced using special manufacturing techniques to treat the charcoal with oxygen. The oxygen treatment opens up millions of pores between the carbon atoms
resulting in a highly porous charcoal with a very large effective surface area which is capable of absorbing large quantities of
fuel vapor. Once treated the charcoal is known as 'activated' carbon or charcoal. The EVAP canister on NAS vehicles uses a higher grade of charcoal to meet the stricter emissions' regulations.
A mounting bracket on the RH (right-hand) end of the EVAP canister contains the FPDM (fuel pump driver module). For additional information, refer to 310-01D Fuel Tank and Lines.
On all except NAS vehicles, the EVAP canister has a capacity of 1400 cc (85.4 in.3
). Two connectors on the EVAP canister allow for the attachment of the vapor pipe from the fuel tank and the vapor pipe to the EVAP canister purge valve. An atmospheric vent is located on the underside of the EVAP canister.
On NAS vehicles, the EVAP canister has a capacity of 3000 cc (183 in.3
). Three connectors on the EVAP canister allow for the attachment of the vapor pipe from the fuel tank, the vapor pipe to the EVAP canister purge valve and the DMTL pump. EVAP Canister (NAS)
Page 1361 of 3039

DIAGNOSTICS
The ECM stores each fault as a DTC (diagnostic trouble code). The DTC and associated environmental and freeze frame data can be read using Jaguar approved diagnostic equipment, which can also read real time data from each sensor, the adaption
values currently being employed and the current fueling, ignition and idle speed settings.
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE Component Description
The ECM is installed in the front passenger side of the engine compartment, on a bracket attached to the engine bulkhead. The ECM has the capability of adapting its fuel and ignition control outputs in response to several sensor inputs. The ECM receives inputs from the following:
CKP sensor. CMP (camshaft position) sensors (4 off).
ECT (engine coolant temperature) sensor.
Knock sensors (4 off).
MAP (manifold absolute pressure) sensor.
MAFT sensors (2 off). MAPT (manifold absolute pressure and temperature) sensor.
Throttle position sensor.
Heated oxygen sensors (4 off).
APP sensor. Ambient air temperature sensor.
FRP (fuel rail pressure) sensor. For additional information, refer to 303-04G Fuel Charging and Controls.
Engine cooling fan. For additional information, refer to 303-03D Engine Cooling.
Stoplamp switch. For additional information, refer to 206-09 Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist.
Speed control cancel/suspend switch. For additional information, refer to 310-03D Speed Control.
Oil level and temperature sensor. For additional information, refer to 303-01F Engine.
Fuel LP (low pressure) sensor. For additional information, refer to 310-01D Fuel Tank and Lines.
Fuel pump driver module. For additional information, refer to 310-01D Fuel Tank and Lines.
The ECM provides outputs to the following: Electronic throttle.
Main relay.
Heater elements of the heated oxygen sensors (4 off).
Fuel injectors (8 off). For additional information, refer to 303-04G Fuel Charging and Controls. www.JagDocs.com
Page 1369 of 3039
Published: 16-Sep-2013
Electronic Engine Controls - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Electronic Engine Controls
Diagnosis and Testing
Principle of Operation
For a detailed description of electronic engine controls, refer to the relevant Description and Operation section of the workshop
manual. REFER to: (303-14D Electronic Engine Controls - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol)
Electronic Engine Controls (Description and Operation), Electronic Engine Controls (Description and Operation), Electronic Engine Controls (Description and Operation).
Inspection and Verification
1. Verify the customer concern.
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of damage and system integrity.
Visual Inspection
Mechanical Electrical
Engine oil level and condition
Cooling system coolant level
Fuel level
Fuel contamination/grade/quality
Throttle body
Front End Accessory Drive (FEAD) belt
Air cleaner condition
Fuses
Wiring harness
Electrical connector(s)
Sensor(s)
Engine Control Module
Transmission Control Module
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible) before proceeding to
the next step.
4. If the cause is not visually evident, verify the customer concern and refer to the Symptom Chart below, alternatively,
check for Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and refer to the DTC Index.
Symptom Chart
Symptom Possible Cause Action Engine non-start Engine does not crank
Security system /Immobilizer
engaged
Engine in shut-down mode
ECM relay
Battery
Starting system
Engine seized
Check that the security system is disarmed
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for ECM relay tests
Ensure the battery is in fully charged and
serviceable condition
For starting system tests refer to the
relevant section of the workshop manual
For engine system tests refer to the relevant
section of the workshop manual Engine cranks, but does not fire
Engine breather system
disconnected/restricted
Ignition system
Fuel system
Electronic engine controls
Ensure the engine breather system is free
from restriction and is correctly installed
For ignition system tests refer to the
relevant section of the workshop manual
For fuel system tests refer to the relevant
section of the workshop manual
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for electronic engine control tests Engine cranks and fires, but will not
start
Evaporative emissions purge
valve
Fuel pump
Spark plugs
Ignition coil failure(s)
For purge valve tests refer to the relevant
section of the workshop manual
For fuel system tests refer to the relevant
section of the workshop manual
For ignition system tests refer to the
relevant section of the workshop manual Difficult to start Difficult cold start
Check engine coolant
level/anti-freeze content
Battery
Electronic engine controls
Exhaust gas recirculation
Check the engine coolant level and
condition. Refer to the relevant sections of
the workshop manual
Ensure the battery is in a fully charged and
serviceable condition. Refer to the battery
Page 1370 of 3039
Symptom Possible Cause Action (EGR) valve stuck open
Fuel pump
Evaporative emissions purge
valve care manual and the relevant sections of the
workshop manual.
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for electronic engine control tests
Refer to the relevant section of the
workshop manual and check the Exhaust Gas
Recirculation (EGR) valve and associated
hoses and connections.
For fuel system tests refer to the relevant
section of the workshop manual
Refer to the relevant section of the
workshop manual and check the purge valve
and associated hoses and connections. Difficult hot start
Injector leak
Electronic engine controls
Evaporative emissions purge
valve
Fuel pump
Ignition system
EGR valve stuck open
Refer to the relevant section of the
workshop manual, carry out injector leak
tests, install new injectors as necessary.
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for electronic engine control tests
Refer to the relevant section of the
workshop manual and check the purge valve
and associated hoses and connections.
For fuel system tests refer to the relevant
section of the workshop manual
For ignition system tests refer to the
relevant section of the workshop manual
Refer to the relevant section of the
workshop manual and check the Exhaust Gas
Recirculation (EGR) valve and associated
hoses and connections. Difficult to start after hot soak
(vehicle standing, engine off, after
engine has reached operating
temperature)
Injector leak
Electronic engine controls
Evaporative emissions purge
valve
Fuel pump
Ignition system
EGR valve stuck open
Refer to the relevant section of the
workshop manual, carry out injector leak
tests, install new injectors as necessary.
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for electronic engine control tests
Refer to the relevant section of the
workshop manual and check the purge valve
and associated hoses and connections.
For fuel system tests refer to the relevant
section of the workshop manual
For ignition system tests refer to the
relevant section of the workshop manual
Refer to the relevant section of the
workshop manual and check the Exhaust Gas
Recirculation (EGR) valve and associated
hoses and connections. Engine cranks too fast/slow
Compressions high/low
Battery
Starting system
Refer to the relevant section of the
workshop manual, carry out compression
tests.
Ensure the battery is in a fully charged and
serviceable condition. Refer to the battery
care manual and the relevant sections of the
workshop manual.
For starting system tests refer to the
relevant section of the workshop manual Engine stalls Engine stalls soon after start
Breather system
disconnected/restricted
ECM relay
Electronic engine controls
Ignition system
Air intake system restricted
Air leakage
Fuel lines
Ensure the engine breather system is free
from restriction and is correctly installed
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for ECM relay tests
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for electronic engine control tests
For ignition system tests refer to the
relevant section of the workshop manual
Check for blockage in air cleaner element
and air intake system
Check for leakage in air intake system
For fuel system tests refer to the relevant
section of the workshop manual
Page 1371 of 3039
Symptom Possible Cause Action Engine stalls on overrun
ECM relay
Throttle position (TP)
sensors
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for ECM relay and TP sensor tests Engine stalls at steady speed
ECM relay
crankshaft position sensor
TP sensors
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for ECM relay, crankshaft position
sensor, and TP sensor tests Engine stalls with speed control
enabled
ECM relay
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for ECM relay tests Engine stalls when manoeuvring
ECM relay
TP sensors
Additional engine loads
(PAS, air conditioning, etc)
Transmission malfunction
CAN malfunction
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for ECM relay, and TP sensor tests
Check for excessive loads being placed on
the engine from PAS, air conditioning
systems etc.
Refer to the workshop manual or
transmission troubleshooting guide for
transmission system tests.
Refer to the relevant section of the
workshop manual and the electrical wiring
diagrams to perform CAN network tests. Poor driveability Engine hesitates/poor acceleration
Fuel pressure, fuel pump,
fuel lines
Injector leak
Air leakage
Electronic engine controls
Ignition system
EGR valve stuck
Transmission malfunction
Restricted pedal travel
(carpet, etc)
For fuel system tests refer to the relevant
section of the workshop manual
Carry out fuel injector leak tests, install new
injectors as necessary.
Check for leakage from air intake system
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for electronic engine control tests
For ignition system tests refer to the
relevant section of the workshop manual
Refer to the relevant section of the
workshop manual and check the Exhaust Gas
Recirculation (EGR) valve and associated
hoses and connections.
Refer to the workshop manual or
transmission troubleshooting guide for
transmission system tests.
Ensure accelerator pedal is free from
restriction Engine backfires
Fuel pump, fuel lines
Air leakage
Electronic engine controls
Ignition system
Sticking variable camshaft
timing (VCT) hub
For fuel system tests refer to the relevant
section of the workshop manual
Check for leakage from air intake system
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for electronic engine control tests
For ignition system tests refer to the
relevant section of the workshop manual
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for VCT system tests Engine surges
Fuel pump, fuel lines
Electronic engine controls
Ignition system
For fuel system tests refer to the relevant
section of the workshop manual
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for electronic engine control tests
For ignition system tests refer to the
relevant section of the workshop manual Engine detonates/knocks
Electronic engine controls
Fuel pump, fuel lines, fuel
quality
Air leakage
Sticking VCT hub
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for electronic engine control tests
For fuel system tests refer to the relevant
section of the workshop manual
Check for leakage from air intake system
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for VCT system tests www.JagDocs.com
Page 1423 of 3039

The TCM can be reprogrammed using a Jaguar approved diagnostic system using a flash code. The TCM processor has a 440 kb internal flash memory. Of this capacity, approximately 370 kb are used by the basic transmission program. The remainder,
approximately 70 kb is used to store vehicle-specific application data.
Engine Stall
If the vehicle stalls it will coast down in gear, with the transmission providing drive to the engine. A restart can be attempted
at this point and the engine may start and the driver can continue.
If the coast down speed reduces such that the speed of the engine is less than 600 rev/min, the transmission will go to
neutral, D illumination will flash in the instrument cluster. The driver needs to select neutral or park and then press the brake
pedal to restart the engine.
If the start/stop button is pressed when driving, the message ENGINE STOP BUTTON PRESSED is displayed in the message
center but there will be no change to the ignition state. If the driver requires to switch off the engine, the start/stop button
must be pressed for a second time. The engine will be stopped and will be back driven by the transmission as the vehicle
coasts down. When the engine speed is less than 600 rev/min the transmission engages neutral (flashing D illumination in the
instrument cluster). When vehicle speed is less than 2 km/h (1.2 mph) Park is engaged. The JaguarDrive selector automatically
rotates back to its lowered P position and the vehicle ignition is switched off.
The park engagement is prevented in a stall case as the ignition power is on and D was the last selected gear. The park
engagement speed at ignition off is from the least value of the wheel speeds (CAN signal) and transmission output speed (internal signal).
TRANSMISSION Component Description
The transmission comprises the main casing which houses all of the transmission components. The main casing also
incorporates an integral bell housing.
A fluid pan is attached to the lower face of the main casing and is secured with bolts. The fluid pan is sealed to the main
casing with a gasket. Removal of the fluid pan allows access to the Mechatronic valve block. The fluid pan has a magnet
located around the drain plug which collects any metallic particles present in the transmission fluid.
A fluid filter is located inside the fluid pan. If the transmission fluid becomes contaminated or after any service work, the fluid
pan with integral filter must be replaced.
The integral bell housing provides protection for the torque converter assembly and also provides the attachment for the
gearbox to the engine cylinder block. The torque converter is a non-serviceable assembly which also contains the lock-up clutch
mechanism. The torque converter drives a crescent type pump via drive tangs. The fluid pump is located in the main casing,
behind the torque converter.
The main casing contains the following major components:
Input shaft
Output shaft
Mechatronic valve block which contains the solenoids, speed sensors and the TCM Three rotating multiplate drive clutches
Two fixed multiplate brake clutches
A single planetary gear train and a double planetary gear train.
Page 1424 of 3039
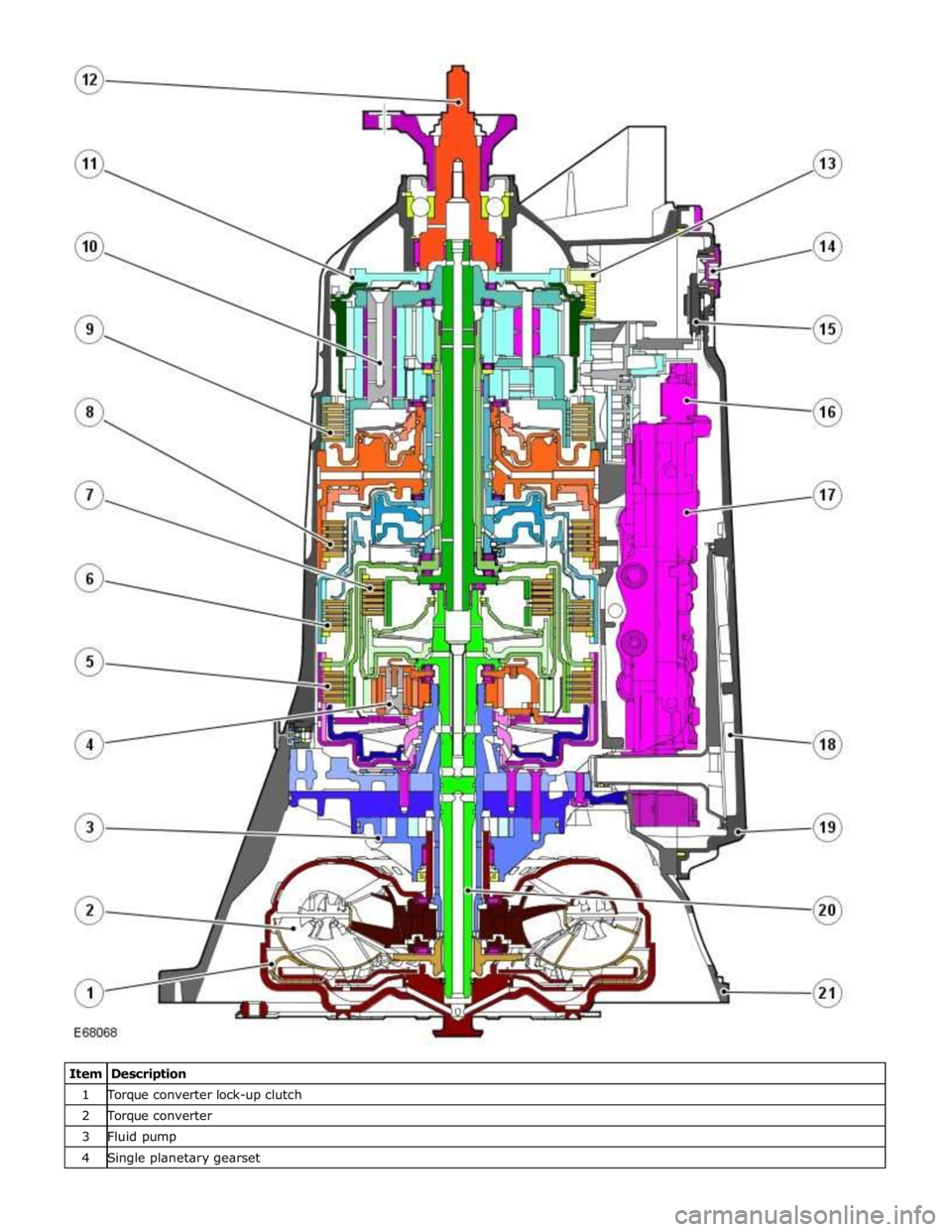
1 Torque converter lock-up clutch 2 Torque converter 3 Fluid pump 4 Single planetary gearset
Page 1426 of 3039
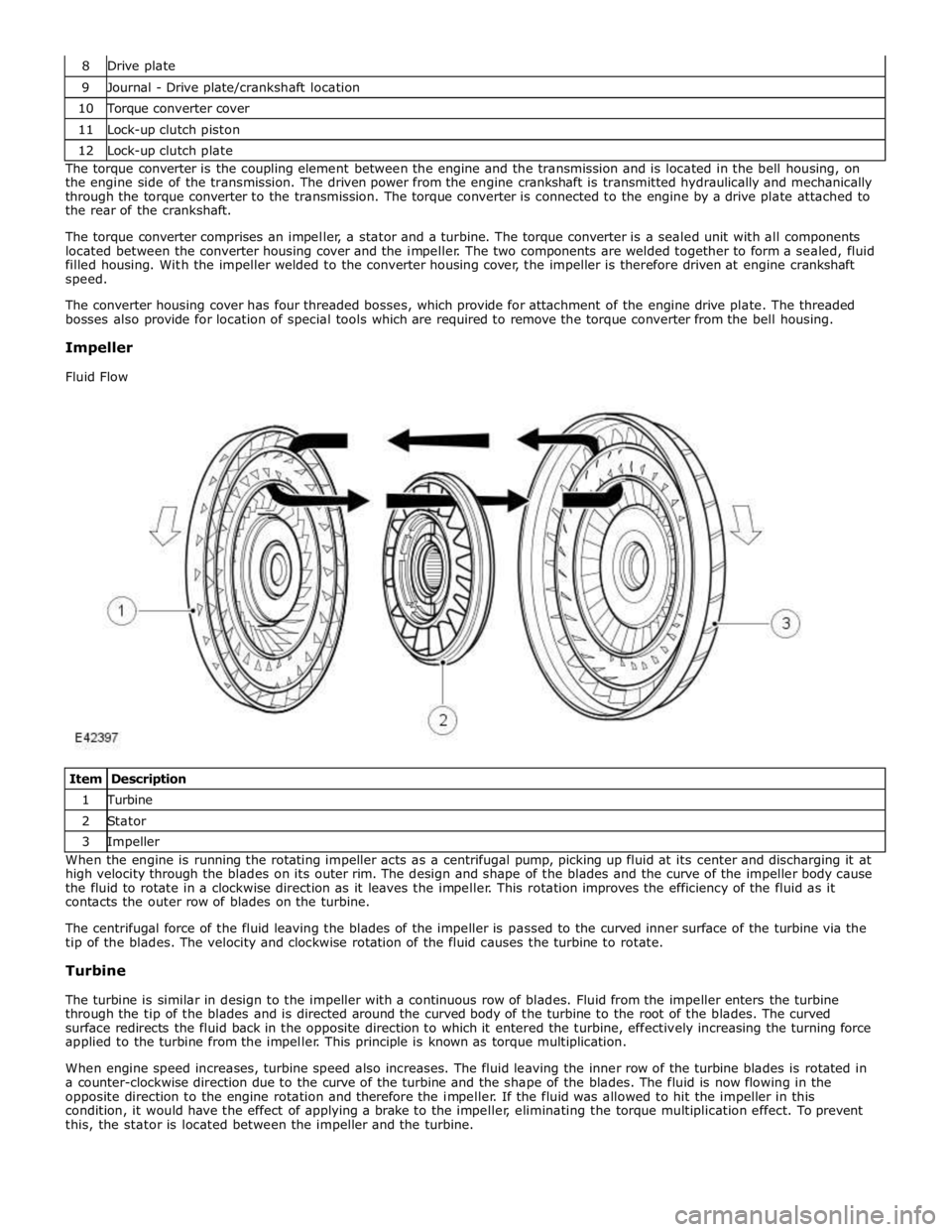
9 Journal - Drive plate/crankshaft location 10 Torque converter cover 11 Lock-up clutch piston 12 Lock-up clutch plate The torque converter is the coupling element between the engine and the transmission and is located in the bell housing, on
the engine side of the transmission. The driven power from the engine crankshaft is transmitted hydraulically and mechanically
through the torque converter to the transmission. The torque converter is connected to the engine by a drive plate attached to
the rear of the crankshaft.
The torque converter comprises an impeller, a stator and a turbine. The torque converter is a sealed unit with all components
located between the converter housing cover and the impeller. The two components are welded together to form a sealed, fluid
filled housing. With the impeller welded to the converter housing cover, the impeller is therefore driven at engine crankshaft
speed.
The converter housing cover has four threaded bosses, which provide for attachment of the engine drive plate. The threaded
bosses also provide for location of special tools which are required to remove the torque converter from the bell housing.
Impeller
Fluid Flow
Item Description 1 Turbine 2 Stator 3 Impeller When the engine is running the rotating impeller acts as a centrifugal pump, picking up fluid at its center and discharging it at
high velocity through the blades on its outer rim. The design and shape of the blades and the curve of the impeller body cause
the fluid to rotate in a clockwise direction as it leaves the impeller. This rotation improves the efficiency of the fluid as it
contacts the outer row of blades on the turbine.
The centrifugal force of the fluid leaving the blades of the impeller is passed to the curved inner surface of the turbine via the
tip of the blades. The velocity and clockwise rotation of the fluid causes the turbine to rotate.
Turbine
The turbine is similar in design to the impeller with a continuous row of blades. Fluid from the impeller enters the turbine
through the tip of the blades and is directed around the curved body of the turbine to the root of the blades. The curved
surface redirects the fluid back in the opposite direction to which it entered the turbine, effectively increasing the turning force
applied to the turbine from the impeller. This principle is known as torque multiplication.
When engine speed increases, turbine speed also increases. The fluid leaving the inner row of the turbine blades is rotated in
a counter-clockwise direction due to the curve of the turbine and the shape of the blades. The fluid is now flowing in the
opposite direction to the engine rotation and therefore the impeller. If the fluid was allowed to hit the impeller in this
condition, it would have the effect of applying a brake to the impeller, eliminating the torque multiplication effect. To prevent
this, the stator is located between the impeller and the turbine.