brake JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JAGUAR, Model Year: 2010, Model line: XFR, Model: JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.GPages: 3039, PDF Size: 58.49 MB
Page 1295 of 3039
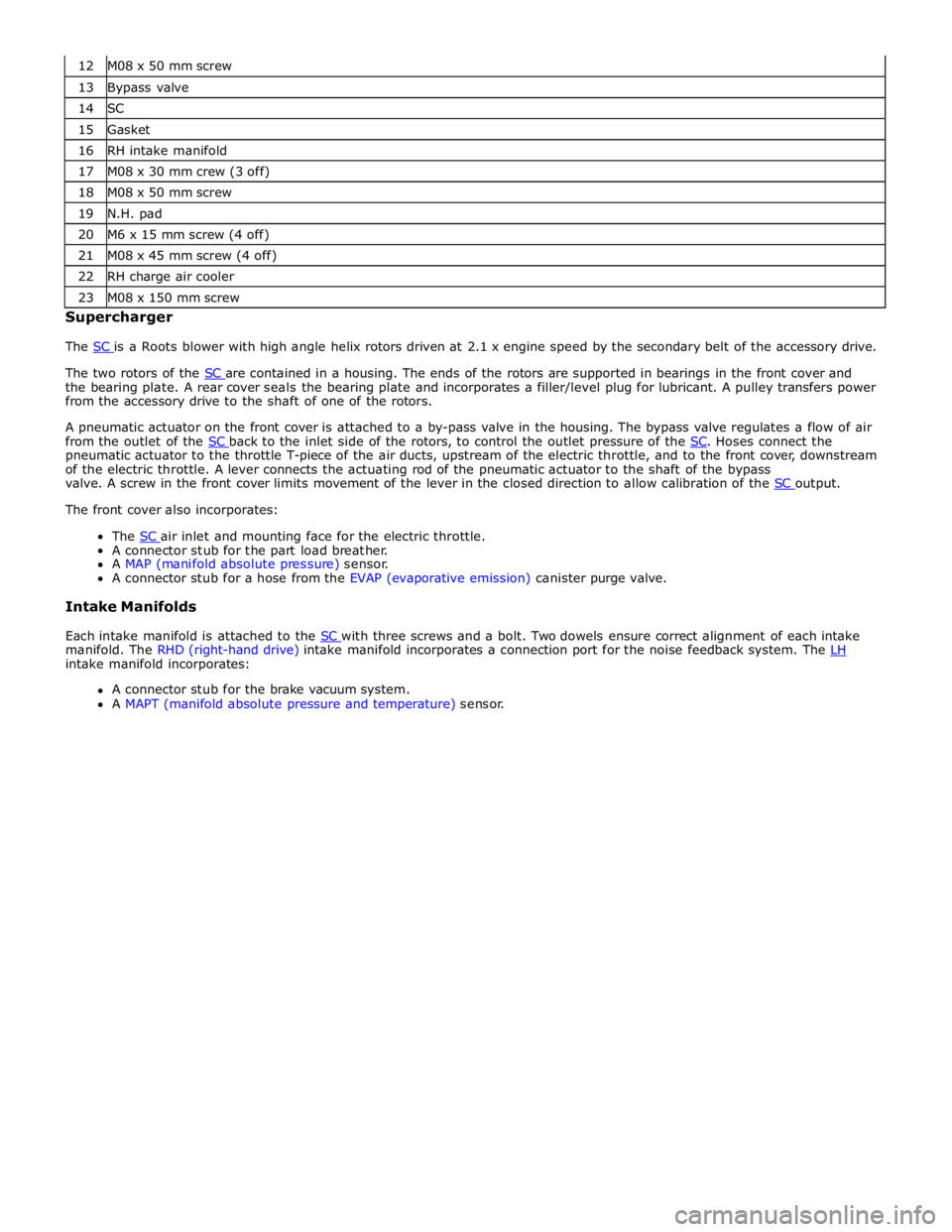
13 Bypass valve 14 SC 15 Gasket 16 RH intake manifold 17 M08 x 30 mm crew (3 off) 18 M08 x 50 mm screw 19 N.H. pad 20 M6 x 15 mm screw (4 off) 21 M08 x 45 mm screw (4 off) 22 RH charge air cooler 23 M08 x 150 mm screw Supercharger
The SC is a Roots blower with high angle helix rotors driven at 2.1 x engine speed by the secondary belt of the accessory drive.
The two rotors of the SC are contained in a housing. The ends of the rotors are supported in bearings in the front cover and the bearing plate. A rear cover seals the bearing plate and incorporates a filler/level plug for lubricant. A pulley transfers power
from the accessory drive to the shaft of one of the rotors.
A pneumatic actuator on the front cover is attached to a by-pass valve in the housing. The bypass valve regulates a flow of air
from the outlet of the SC back to the inlet side of the rotors, to control the outlet pressure of the SC. Hoses connect the pneumatic actuator to the throttle T-piece of the air ducts, upstream of the electric throttle, and to the front cover, downstream
of the electric throttle. A lever connects the actuating rod of the pneumatic actuator to the shaft of the bypass
valve. A screw in the front cover limits movement of the lever in the closed direction to allow calibration of the SC output. The front cover also incorporates:
The SC air inlet and mounting face for the electric throttle. A connector stub for the part load breather.
A MAP (manifold absolute pressure) sensor.
A connector stub for a hose from the EVAP (evaporative emission) canister purge valve.
Intake Manifolds
Each intake manifold is attached to the SC with three screws and a bolt. Two dowels ensure correct alignment of each intake manifold. The RHD (right-hand drive) intake manifold incorporates a connection port for the noise feedback system. The LH intake manifold incorporates:
A connector stub for the brake vacuum system.
A MAPT (manifold absolute pressure and temperature) sensor.
Page 1296 of 3039
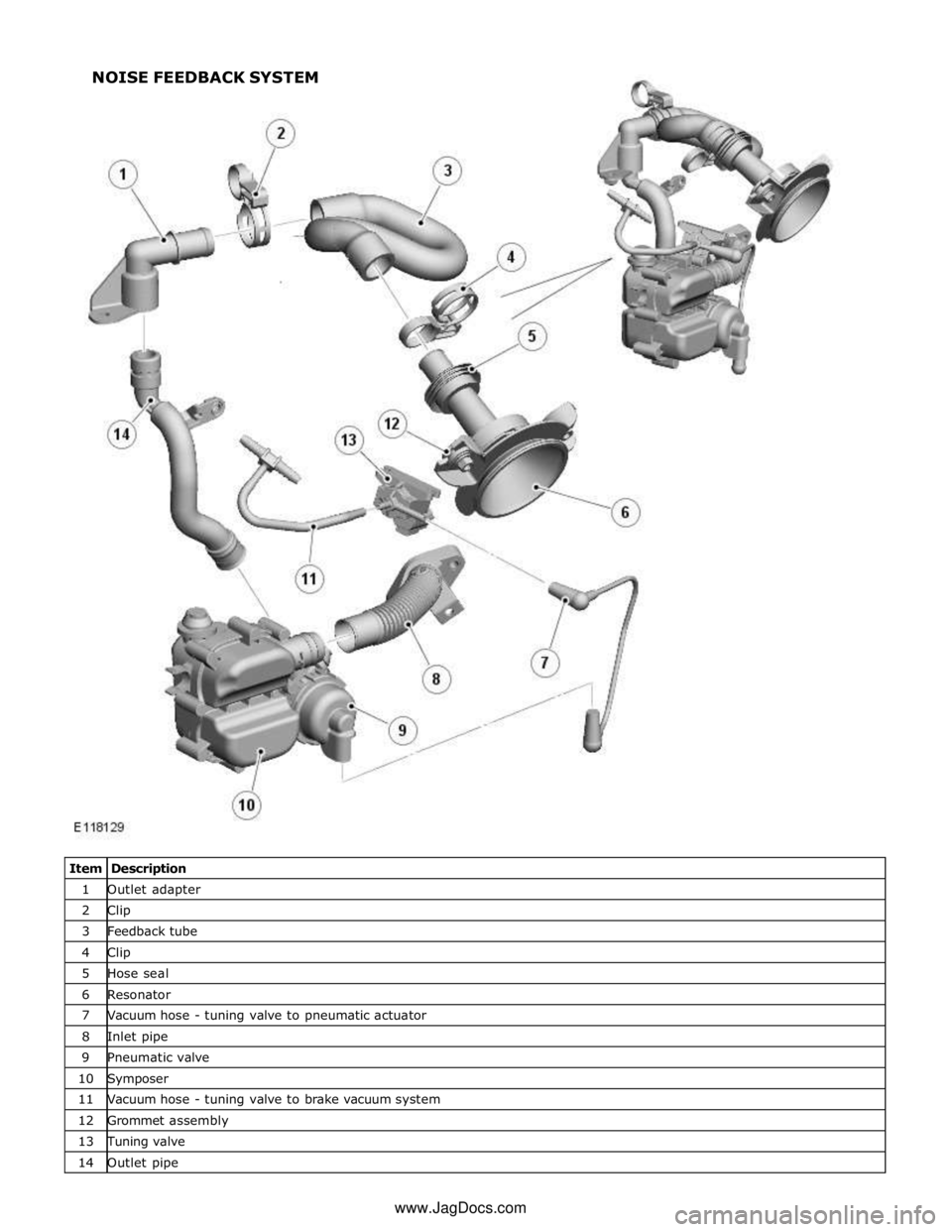
1 Outlet adapter 2 Clip 3 Feedback tube 4 Clip 5 Hose seal 6 Resonator 7 Vacuum hose - tuning valve to pneumatic actuator 8 Inlet pipe 9 Pneumatic valve 10 Symposer 11 Vacuum hose - tuning valve to brake vacuum system 12 Grommet assembly 13 Tuning valve 14 Outlet pipe NOISE FEEDBACK SYSTEM
www.JagDocs.com
Page 1298 of 3039

The tuning valve controls the application of vacuum pressure to the pneumatic valve. Two screws attach the tuning valve to the
same bracket as the symposer and pneumatic valve. The tuning valve is a normally-closed solenoid-operated valve installed in
the vacuum line between a T-connection in the brake vacuum system and the pneumatic valve. A vent cap on the tuning valve
allows atmospheric pressure into the vacuum line to the pneumatic valve when the tuning valve is closed.
The outlet pipe carries sound from the pneumatic valve to the feedback tube via the outlet adapter. The outlet pipe is a push
fit on the pneumatic valve and in the outlet adapter. A screw attaches the outlet adapter to an engine harness bracket
installed between the two intake manifolds.
Feedback Tube
The feedback tube transfers the sound from the symposer system to the resonator. Clips secure the feedback tube to the
outlet adapter of the symposer system and to the resonator.
Resonator
The resonator directs the sound from the feedback tube into the passenger compartment. The resonator is installed in the
passenger compartment side of the engine bulkhead, on two mounting grommets each consisting of an isolator and a
compression limiter. A hose seal isolates the resonator where it passes through the secondary bulkhead.
Page 1372 of 3039

Symptom Possible Cause Action No throttle response
Electronic engine controls
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for electronic engine control tests Speed control inhibited or disabled
Default mode enabled
Speed control, brake switch
Electronic engine controls
CAN fault
Check message center for default message,
read DTCs and refer to DTC Index
Refer to the relevant section of the
workshop manual for speed control, and
brake switch tests.
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for electronic engine control tests
Refer to the relevant section of the
workshop manual and the electrical wiring
diagrams to perform CAN network tests. Poor throttle response
Breather system
disconnected/restricted
Electronic engine controls
Transmission malfunction
Traction control event
Air leakage
Ensure engine breather system is free from
restriction and is correctly installed
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for electronic engine control tests
Refer to the workshop manual or
transmission troubleshooting guide for
transmission system tests.
Check for leakage in air intake system Engine defaults, warning light and
messages. Refer to the owner
handbook
Electronic engine controls
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for electronic engine control tests DTC Index
WARNING: Fuel injector voltage will reach 65Volts during operation and have a high current requirement.
CAUTION: When probing connectors to take measurements in the course of the pinpoint tests, use the adaptor kit, part
number 3548-1358-00.
NOTES:
If the module/component is suspect and the vehicle remains under the Manufacturers warranty, refer to the Warranty
Policy and Procedure manual (section B1.2), or determine if any prior approval programme is in operation, prior to the
installation of a new module/component.
Generic scan tools may not read the codes listed, or may read only five digit codes. Match the five digits from the scan
tool to the first five digits of the seven digit code listed to identify the fault (the last two digits give additional information
read by the manufacturer-approved diagnostic system).
When performing electrical voltage or resistance tests, always use a digital multimeter (DMM) accurate to three decimal
places, and with an up-to-date calibration certificate. When testing resistance, always take the resistance of the DMM leads
into account.
Check and rectify basic faults before beginning diagnostic routines involving pinpoint tests.
If DTCs are recorded and, after performing the pinpoint tests, a fault is not present, an intermittent concern may be the
cause. Always check for loose connections and corroded terminals.
DTC Description Possible Causes Action B10A2-31 Crash Input - No signal
Loss of communication between
Restraints Control Module (RCM)
and Engine Control Module
(ECM) Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check Restraints Control Module (RCM) Pulse
Width Modulated (PWM) SRS signal line circuit,
hard wired connection between Engine Control
Module (ECM) and Restraints Control Module
(RCM) for short to ground, short to power, open
circuit. Repair circuit as required, clear DTC and
retest system to confirm repair.
Page 1374 of 3039

Published: 11-May-2011
Electronic Engine Controls - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Powertrain Control Module
(PCM) Long Drive Cycle Self-Test
General Procedures
WARNING: Where possible, all road tests should be on well surfaced and dry roads. Always comply with speed limits and
local traffic regulations.
NOTES:
This procedure is an overcheck only. If fault codes are found, interrogation of the relevant system must be carried out and
claimed against.
The vehicle must exceed 50mph (80 km/h) during the road test.
1. Connect the diagnostic equipment to the vehicle.
2. Follow on screen prompts and check for engine management fault codes.
3. Clear the fault codes following the on screen procedure.
4. Disconnect the diagnostic equipment from the vehicle.
5. NOTE: Make sure cruise control is not engaged. Make sure
the engine temperature is above 60 ºC (140 ºF).
Carry out a road test and perform the following operations.
1. Accelerate to 55 mph (88 km/h) in 5th gear and cruise for 2
minutes with the engine speed at or above 1800rpm.
2. Lift off the throttle and allow the vehicle to decelerate until the
engine speed is less than 1000 rpm.
3. Stop the vehicle.
4. Release brake, allow the vehicle to move with no throttle for 1
minute.
5. Road test is now complete.
6. Connect the diagnostic equipment to the vehicle.
7. NOTE: If fault codes are found, interrogation of the relevant
system must be carried out and claimed against.
Follow on screen prompts and check for engine management fault codes.
8. Disconnect the diagnostic equipment from the vehicle.
Page 1412 of 3039

TCM (transmission control module) 6 Diagnostic socket 7 Instrument cluster 8 JaguarDrive selector 9 Clockspring 10 Steering wheel audio switches 11 Downshift paddle switch 12 Upshift paddle switch 13 ECM (engine control module)
POWER FLOWS System Operation
Operation of the transmission is controlled by the TCM (transmission control module), which electrically activates various
solenoids to control the transmission gear selection. The sequence of solenoid activation is based on programmed information
in the TCM memory and physical transmission operating conditions such as vehicle speed, throttle position, engine load and JaguarDrive selector position.
Item Description 1 Torque input from engine 2 Torque converter lock-up clutch 3 Single web planetary gear carrier 4 Single web planetary gears 5 Single web sunwheel 1 6 Double web sunwheel 2 7 Double web planetary gears - long 8 Double web planetary gear carrier 9 Double web planetary gears - short 10 Double web sunwheel 3 11 Torque output from transmission A Multiplate clutch B Multiplate clutch C Multiplate brake D Multiplate brake E Multiplate clutch Engine torque is transferred, via operation of single or combinations of clutches to the 2 planetary gear trains. Both gear trains
are controlled by reactionary inputs from brake clutches to produce the 6 forward gears and 1 reverse gear. The ratios are as
follows: www.JagDocs.com
Page 1413 of 3039

Ration 4.171 2.340 1.521 1.143 0.867 0.691 3.403 Shift Elements
Item Description 1 Turbine shaft 2 Stator shaft 3 Single web planetary gear train 4 Ring gear 1 5 Clutch A 6 Clutch B 7 Clutch E 8 Brake clutch C 9 Fixed connection to transmission housing 10 Shaft key 11 Brake clutch D 12 Double web planetary gear train 13 Planetary gears - long 14 Ring gear 2 15 Sunwheel 2 16 Sunwheel 3 17 Double web planetary gear carrier 18 Planetary gears - short 19 Single web planetary gear carrier 20 Sunwheel 1 The shift elements are three rotating multiplate clutches (A, B and E) and two fixed multiplate brakes (C and D). All shifts
from 1st to 6th gears are power-on overlapping shifts. Overlapping shifts can be described as one of the clutches continuing to
transmit drive at a lower main pressure until the next required clutch is able to accept the input torque.
The shift elements, clutches and brakes are actuated hydraulically. Fluid pressure is applied to the required clutch and/or brake,
pressing the plates together and allowing drive to be transmitted through the plates. The purpose of the shift elements
is to perform power-on shifts with no interruption to traction and smooth transition between gear ratios.
Page 1414 of 3039

The JaguarDrive selector and the selector valve spool are in the 'D' position. Engine torque is transmitted from the torque
converter turbine shaft to the ring gear 1 of the single web planetary gear train and the outer plate carrier of clutch 'E'.
Ring gear 1 drives the planetary gears which rotate around sunwheel 1. This drives the planetary gear carrier 1 and also the
outer plate carrier of clutch 'A' and the inner plate carrier of clutch 'B'.
When clutch 'A' is engaged, sunwheel 3 in the double web planetary gear train is driven and meshes with the short planetary
gears.
The double web planetary gear train is locked against the transmission housing by brake 'D'. This allows ring gear 2 (output
shaft) to be driven in the same direction as the engine via the long planetary gears.
NOTE: Refer to 'Shift Elements' illustration for key
Power Flow 1st Gear
Page 1415 of 3039

Power Flow 2nd Gear
The JaguarDrive selector and the selector spool valve are in the 'D' position. Engine torque is transmitted from the torque
converter turbine shaft to the ring gear 1 of the single web planetary gear train and the outer plate carrier of clutch 'E'.
Ring gear 1 drives the planetary gears which rotate around sunwheel 1. This drives the planetary gear carrier 1 and also the
outer plate carrier of clutch 'A' and the inner plate carrier of clutch 'B'.
When clutch 'A' is engaged, sunwheel 3 in the double web planetary gear train is driven and meshes with the short planetary
gears.
Sunwheel 2 is locked to the transmission housing by brake clutch 'C'. The long planetary gears, which are also meshed with the
short planetary gears, roll around the fixed sunwheel 2 and transmit drive to the double web planetary gear train carrier and
ring gear 2 in the direction of engine rotation.
NOTE: Refer to 'Shift Elements' illustration for key
Page 1420 of 3039
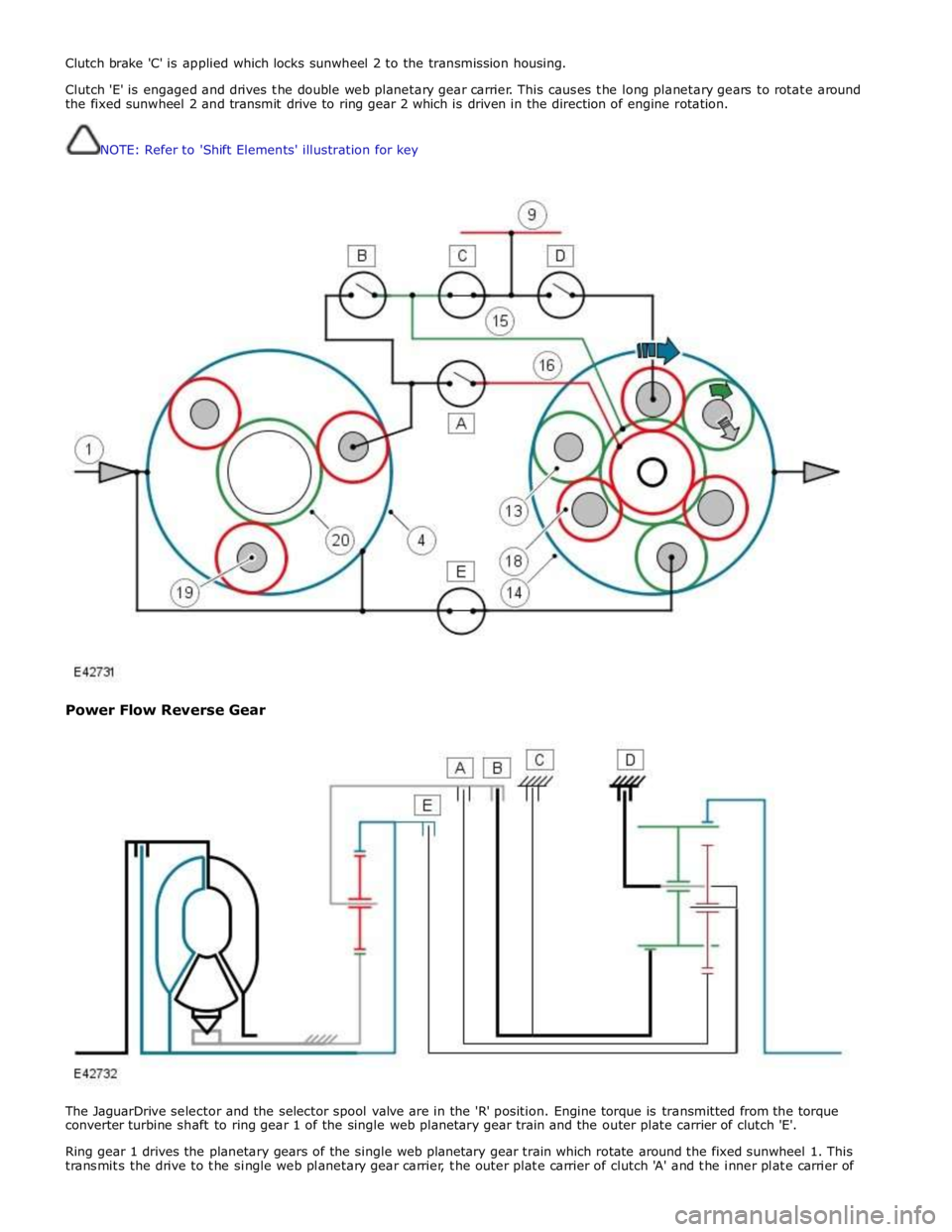
Clutch brake 'C' is applied which locks sunwheel 2 to the transmission housing.
Clutch 'E' is engaged and drives the double web planetary gear carrier. This causes the long planetary gears to rotate around
the fixed sunwheel 2 and transmit drive to ring gear 2 which is driven in the direction of engine rotation.
NOTE: Refer to 'Shift Elements' illustration for key
Power Flow Reverse Gear
The JaguarDrive selector and the selector spool valve are in the 'R' position. Engine torque is transmitted from the torque
converter turbine shaft to ring gear 1 of the single web planetary gear train and the outer plate carrier of clutch 'E'.
Ring gear 1 drives the planetary gears of the single web planetary gear train which rotate around the fixed sunwheel 1. This
transmits the drive to the single web planetary gear carrier, the outer plate carrier of clutch 'A' and the inner plate carrier of