weight JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.G Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JAGUAR, Model Year: 2010, Model line: XFR, Model: JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.GPages: 3039, PDF Size: 58.49 MB
Page 2170 of 3039
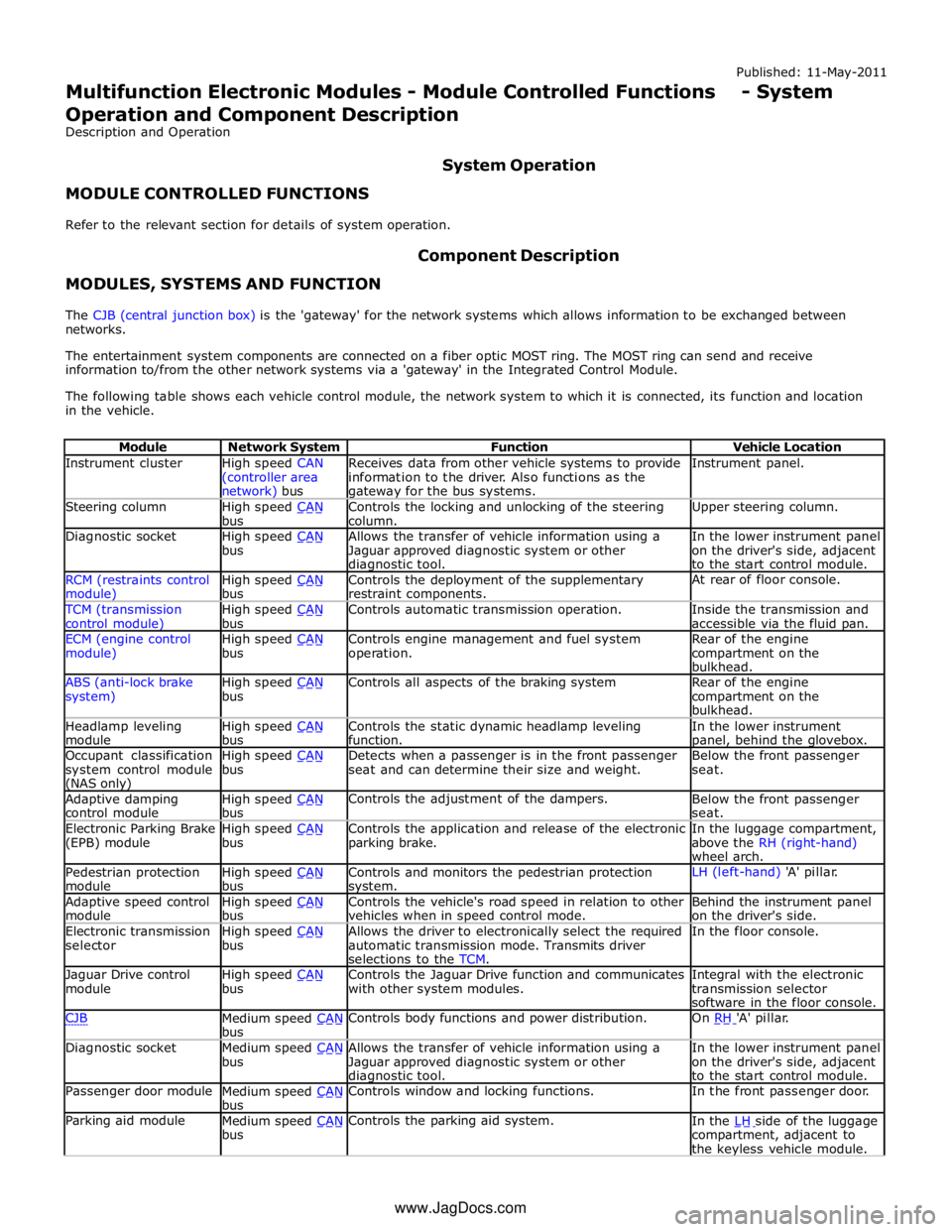
Instrument cluster
High speed CAN
(controller area network) bus Receives data from other vehicle systems to provide
information to the driver. Also functions as the gateway for the bus systems. Instrument panel. Steering column
High speed CAN bus Controls the locking and unlocking of the steering
column. Upper steering column. Diagnostic socket
High speed CAN bus Allows the transfer of vehicle information using a
Jaguar approved diagnostic system or other diagnostic tool. In the lower instrument panel
on the driver's side, adjacent
to the start control module. RCM (restraints control module) High speed CAN bus Controls the deployment of the supplementary
restraint components. At rear of floor console. TCM (transmission
control module) High speed CAN bus Controls automatic transmission operation.
Inside the transmission and
accessible via the fluid pan. ECM (engine control
module) High speed CAN bus Controls engine management and fuel system
operation. Rear of the engine
compartment on the
bulkhead. ABS (anti-lock brake
system) High speed CAN bus Controls all aspects of the braking system
Rear of the engine
compartment on the
bulkhead. Headlamp leveling
module High speed CAN bus Controls the static dynamic headlamp leveling
function. In the lower instrument panel, behind the glovebox. Occupant classification
system control module (NAS only) High speed CAN bus Detects when a passenger is in the front passenger
seat and can determine their size and weight. Below the front passenger
seat. Adaptive damping
control module High speed CAN bus Controls the adjustment of the dampers.
Below the front passenger
seat. Electronic Parking Brake
(EPB) module High speed CAN bus Controls the application and release of the electronic
parking brake. In the luggage compartment,
above the RH (right-hand)
wheel arch. Pedestrian protection
module High speed CAN bus Controls and monitors the pedestrian protection system. LH (left-hand) 'A' pillar. Adaptive speed control
module High speed CAN bus Controls the vehicle's road speed in relation to other
vehicles when in speed control mode. Behind the instrument panel
on the driver's side. Electronic transmission
selector High speed CAN bus Allows the driver to electronically select the required
automatic transmission mode. Transmits driver
selections to the TCM. In the floor console. Jaguar Drive control
module High speed CAN bus Controls the Jaguar Drive function and communicates
with other system modules. Integral with the electronic
transmission selector
software in the floor console. CJB
Medium speed CAN bus Controls body functions and power distribution. On RH 'A' pillar. Diagnostic socket
Medium speed CAN bus Allows the transfer of vehicle information using a
Jaguar approved diagnostic system or other diagnostic tool. In the lower instrument panel
on the driver's side, adjacent
to the start control module. Passenger door module
Medium speed CAN bus Controls window and locking functions. In the front passenger door. Parking aid module
Medium speed CAN bus Controls the parking aid system.
In the LH side of the luggage compartment, adjacent to
the keyless vehicle module. www.JagDocs.com
Page 2611 of 3039

Published: 30-May-2012
Supplemental Restraint System - Air Bag and Safety Belt Pretensioner
Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) - Overview
Description and Operation
OVERVIEW
WARNING: All pyrotechnic devices are dangerous. Before performing any procedures on any pyrotechnic device, read all
information contained within the Standard Workshop Practices section of this manual.
Refer to: Standard Workshop Practices (100-00 General Information, Description and Operation).
The SRS (supplemental restraint system) provides additional protection for the vehicle occupants in certain impact conditions.
The system is controlled by the RCM (restraints control module), which is mounted beneath the floor console. The system
includes twin stage drivers and front passenger airbags.
The RCM receives inputs from various sensors around the vehicle and determines which, if any, airbags should be deployed.
The SRS features an occupant detection system. The occupant detection system comprises a mat fitted inside the front passenger seat. By monitoring the condition of the mat, the RCM can determine if the front passenger seat is occupied. It uses this information to determine which airbags to deploy in the event of an impact. This information is also used to illuminate the
safety belt instrument cluster warning lamp if the front passenger seat is occupied and the safety belt is not engaged.
North American Specification (NAS) vehicles also feature an occupant classification system. The occupant classification system
comprises a control module, pressure pad and safety belt tension sensor. The system can determine the size and weight of the
front seat passenger. This information is transmitted to the RCM over the high speed CAN (controller area network) bus. The RCM uses this information to help determine which airbags to deploy in the event of an impact.
Page 2694 of 3039

Part N-umber
Body Repairs - General Information - Body Repairs
Description and Operation
General Information
Introduction Published: 11-May-2011
The body plays a significant role in the increasing trend of ever more rapidly changing model variants. The different customer
groups are strongly influenced by the design and shape of the body. At the same time the stability of the body plays the most
important part in ensuring passenger and driver safety. Lightweight construction, alternative materials, composite materials,
plastics and appropriate joining processes are all design features that characterise modern Jaguar vehicle bodies.
In terms of manufacturing technology, modern safety cell bodies can be produced almost without any problems. Jaguar
guarantee high quality standards by ensuring that mechanical strength properties are tried and tested in numerous computer
simulations, crash tests, by testing materials and by employing sophisticated manufacturing technologies. In the event of
repairs it is vital that the production quality standards are upheld. This requires a well-equipped workshop, and places
particular emphasis on the qualifications of the workshop technicians. Up-to-date knowledge of current manufacturing
technologies and continuous training on new repair methods and techniques are vital for high-quality body repairs. The model-
specific repair manuals and the general repair techniques provide valuable support when undertaking body repairs.
Always follow the repair instructions published in this manual. Failure to observe this instruction can result in serious
impairment of vehicle safety. All specified safety requirements must be met after the work has been carried out.
Vehicle design
The body
The XF adopts the latest generation steels, especially in the upper body – including high carbon steels, dual-phase,
hot-formed boron steels, and bake-hardened steels to form a vertical safety ‘ring’ around the occupant cell. As well as
combining strength with lightness, these steels improve corrosion resistance, by making best use of zinc and improving e-coat
paint flow – and new thinking means that in spite of their strength, the XF’s A and B-pillars are impressively slim, to the
benefit of both visibility and accessibility. Similarly, the lower sills are the first component on any Jaguar to use incredibly
strong, dual-phase DP600 steel.
The safety of the driver and the passengers is paramount for every body design. There are two key safety aspects in the body:
Safety passenger cell
Crumple zones
Safety passenger cell
Stable pillars, rocker panel and door profiles.
Side impact protection in the doors.
Doors are designed to open even in the event of extreme deformation.
Crumple zone
Dynamic absorption of deforming forces.
Protection of the passenger cell. www.JagDocs.com