key battery JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.G Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JAGUAR, Model Year: 2010, Model line: XFR, Model: JAGUAR XFR 2010 1.GPages: 3039, PDF Size: 58.49 MB
Page 2085 of 3039
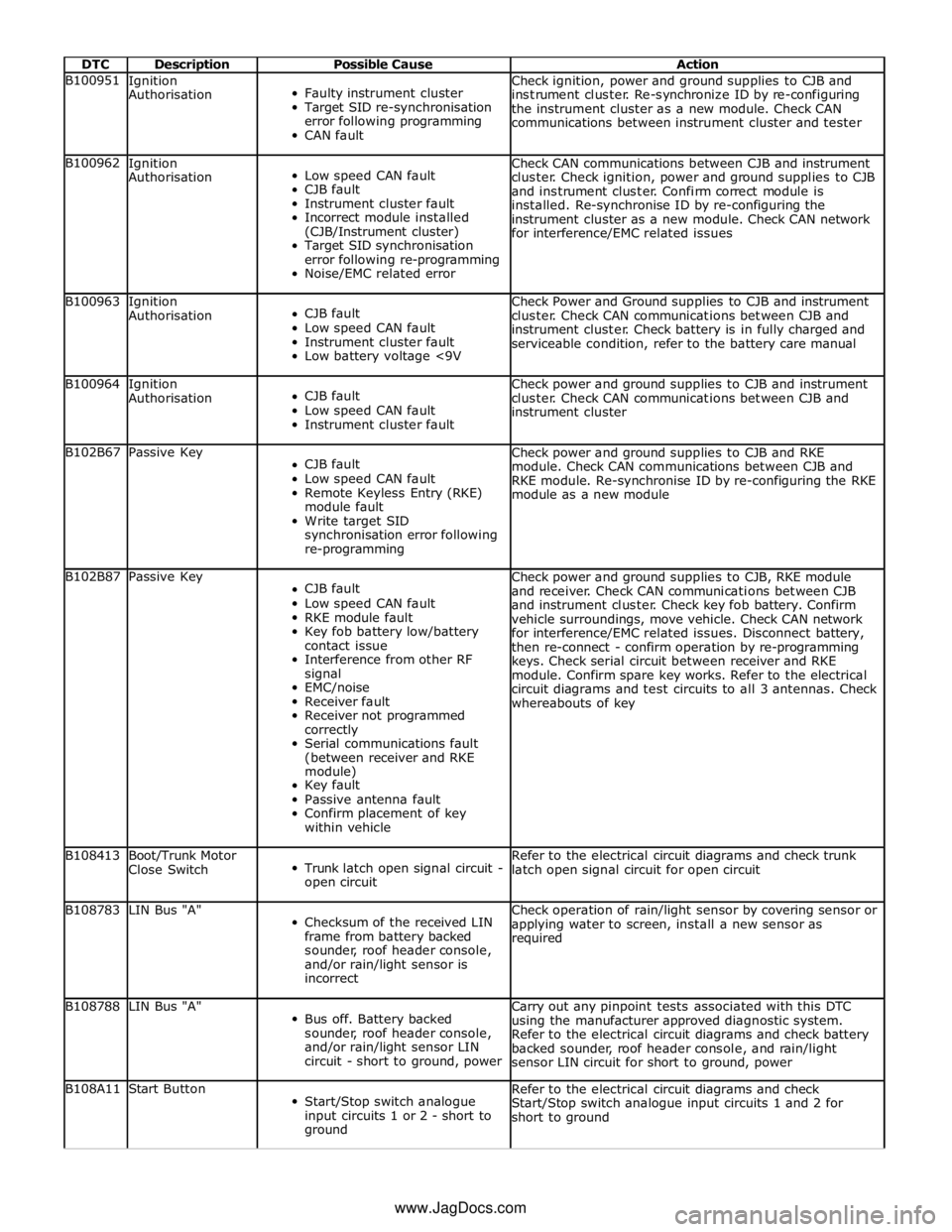
DTC Description Possible Cause Action B100951
Ignition
Authorisation
Faulty instrument cluster
Target SID re-synchronisation
error following programming
CAN fault Check ignition, power and ground supplies to CJB and
instrument cluster. Re-synchronize ID by re-configuring
the instrument cluster as a new module. Check CAN
communications between instrument cluster and tester B100962
Ignition
Authorisation
Low speed CAN fault
CJB fault
Instrument cluster fault
Incorrect module installed
(CJB/Instrument cluster)
Target SID synchronisation
error following re-programming
Noise/EMC related error Check CAN communications between CJB and instrument
cluster. Check ignition, power and ground supplies to CJB
and instrument cluster. Confirm correct module is
installed. Re-synchronise ID by re-configuring the
instrument cluster as a new module. Check CAN network
for interference/EMC related issues B100963
Ignition
Authorisation
CJB fault
Low speed CAN fault
Instrument cluster fault
Low battery voltage <9V Check Power and Ground supplies to CJB and instrument
cluster. Check CAN communications between CJB and
instrument cluster. Check battery is in fully charged and
serviceable condition, refer to the battery care manual B100964
Ignition
Authorisation
CJB fault
Low speed CAN fault
Instrument cluster fault Check power and ground supplies to CJB and instrument
cluster. Check CAN communications between CJB and
instrument cluster B102B67 Passive Key
CJB fault
Low speed CAN fault
Remote Keyless Entry (RKE)
module fault
Write target SID
synchronisation error following
re-programming Check power and ground supplies to CJB and RKE
module. Check CAN communications between CJB and
RKE module. Re-synchronise ID by re-configuring the RKE
module as a new module B102B87 Passive Key
CJB fault
Low speed CAN fault
RKE module fault
Key fob battery low/battery
contact issue
Interference from other RF
signal
EMC/noise
Receiver fault
Receiver not programmed
correctly
Serial communications fault
(between receiver and RKE
module)
Key fault
Passive antenna fault
Confirm placement of key
within vehicle Check power and ground supplies to CJB, RKE module
and receiver. Check CAN communications between CJB
and instrument cluster. Check key fob battery. Confirm
vehicle surroundings, move vehicle. Check CAN network
for interference/EMC related issues. Disconnect battery,
then re-connect - confirm operation by re-programming
keys. Check serial circuit between receiver and RKE
module. Confirm spare key works. Refer to the electrical
circuit diagrams and test circuits to all 3 antennas. Check
whereabouts of key B108413
Boot/Trunk Motor
Close Switch
Trunk latch open signal circuit -
open circuit Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check trunk
latch open signal circuit for open circuit B108783 LIN Bus "A"
Checksum of the received LIN
frame from battery backed
sounder, roof header console,
and/or rain/light sensor is
incorrect Check operation of rain/light sensor by covering sensor or
applying water to screen, install a new sensor as
required B108788 LIN Bus "A"
Bus off. Battery backed
sounder, roof header console,
and/or rain/light sensor LIN
circuit - short to ground, power Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC
using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system.
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check battery
backed sounder, roof header console, and rain/light
sensor LIN circuit for short to ground, power B108A11 Start Button
Start/Stop switch analogue
input circuits 1 or 2 - short to
ground Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
Start/Stop switch analogue input circuits 1 and 2 for
short to ground www.JagDocs.com
Page 2122 of 3039
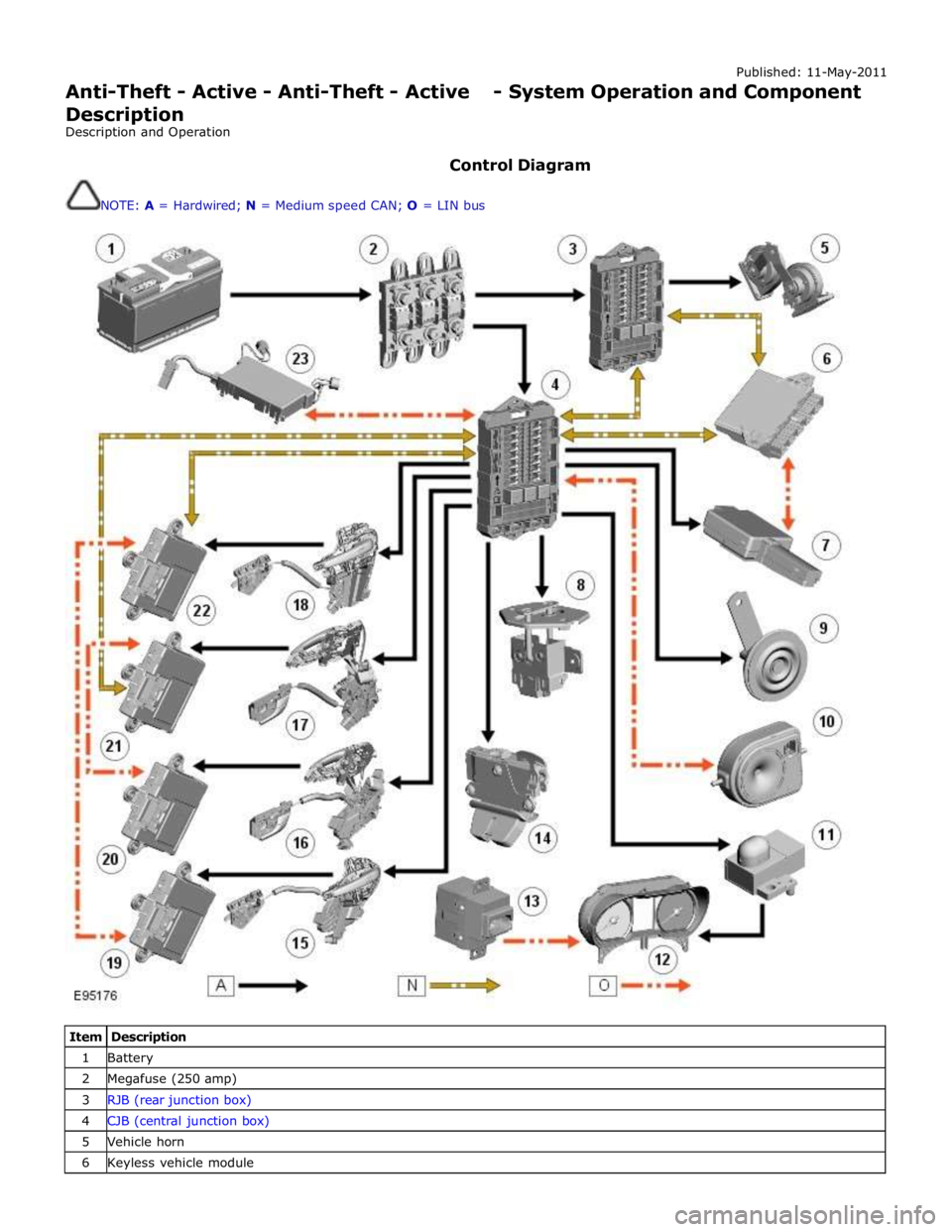
Published: 11-May-2011
Anti-Theft - Active - Anti-Theft - Active - System Operation and Component Description
Description and Operation
Control Diagram
NOTE: A = Hardwired; N = Medium speed CAN; O = LIN bus
Item Description 1 Battery 2 Megafuse (250 amp) 3 RJB (rear junction box) 4 CJB (central junction box) 5 Vehicle horn 6 Keyless vehicle module
Page 2123 of 3039

7 Central locking - Radio Frequency (RF) receiver 8 Engine compartment lid - latch mechanism 9 Passive sounder 10 Battery backed sounder 11 Alarm indicator 12 Instrument cluster 13 Start control unit 14 Luggage compartment lid - latch mechanism 15 Door latch mechanism - LH (left-hand) rear 16 Door latch mechanism - RH (right-hand) rear 17 Door latch mechanism - RH front 18 Door latch mechanism - LH front 19 Door module - LH rear 20 Door module - RH rear 21 Door module - RH front 22 Door module - LH front 23 Intrusion detection module
Anti-Theft - Active System Operation
The active anti-theft system is available with three different levels of vehicle protection depending on market specification:
Hinged panel sensing
Hinged panel and intrusion sensing
Hinged panel, intrusion and inclination sensing.
The system is controlled by software in the CJB and RJB and indicates a trigger condition: Visually, using the direction indicators, and
Audibly, using the vehicle horn and either a passive or active sounder to indicate a trigger condition.
The passive sounder takes the form of an anti-theft disc horn located at the rear of the engine compartment on the LH side. The active sounder takes the form of a battery backed sounder located in the same position.
Depending on market specification, the battery backed sounder may be fitted with an inclination sensor. Both types of battery
backed sounder are visually identical and can only be identified by their part number. Both are also intelligent units, and
communicate to the CJB over a LIN (local interconnect network) bus connection.
Monitoring of the hinged panels is carried out using switches located in each door latch assembly, the engine-compartment-lid
latch assembly, and the luggage-compartment-lid latch assembly. The condition of the switches is monitored by the CJB.
Monitoring of front door lock status is carried out using switches located in the door latch mechanisms. The condition of the
switches is monitored by the front door modules and transmitted to the CJB over the medium speed CAN (controller area
network) bus.
Monitoring of the cabin interior is carried out using an intrusion detection module mounted behind the roof console. The
intrusion detection module comprises an ultrasonic sound wave sensor to determine if there is movement within the cabin.
Information from the intrusion detection module is communicated to the CJB over a LIN bus connection.
CAUTIONS:
The intrusion detection module electrical connections, particularly those to the sensors mounted in the roof console, are
very delicate and must be handled with care.
The intrusion detection module is an electro-statically sensitive part and should only be handled in an electro-statically
controlled environment.
When armed, the active anti-theft system can be triggered in one of the following ways:
A door ajar switch indicates a door has been opened.
The engine compartment lid or luggage compartment lid ajar switches indicate that either has been opened.
Either front door latch mechanism indicates a door has been unlocked.
The emergency key blade is used to open either the LH front door or luggage compartment.
The CJB or RJB are disconnected (this may result in only a partial trigger).
An attempt is made to start the engine without a valid signal from the Smart Key.
Refer to: Anti-Theft - Passive (419-01B Anti-Theft - Passive, Description and Operation).
Page 2124 of 3039

The battery backed sounder is disconnected (partial trigger only).
The vehicle battery is disconnected on a vehicle fitted with a battery backed sounder (partial trigger only).
The inclination sensor detects a change in vehicle attitude.
The intrusion detection module detects movement within the cabin.
Door Modules Component Description
The door modules provide the interface between the door latch-motors, the door latch-switches and the CJB. The door modules
provide door switch status information and enable the door latch-motors on request from the CJB or the keyless vehicle
module.
Keyless Vehicle Module
The keyless vehicle module interfaces with the Central locking, Radio Frequency (RF) receiver and collects RF signal information
which is transmitted from the Smart Key. This information is translated into commands which are passed on the medium speed
CAN bus to the:
CJB,
RJB,
door modules, and
instrument cluster.
The keyless vehicle module also monitors:
2 interior antennae,
1 luggage compartment antenna,
a rear bumper antenna, and
4 door handle antennae if the passive entry system is fitted.
On vehicles with passive entry, the additional fast latch motors are controlled via the keyless vehicle module and the locking
status is passed to the CJB on the medium speed CAN bus.
Instrument Cluster
The instrument cluster controls the alarm indicator, and in conjunction with the ECM (engine control module), the engine
immobilization. The ECM controls the engine crank and fuel functions and the instrument cluster processes the valid
transponder information.
Alarm Indicator
The alarm indicator is a LED (light emitting diode) located in the body of the sunload/light sensor. When the ignition is off the
indicator gives a visual indication of the active anti-theft system to show if the alarm system is active or not active. Operation
of the alarm indicator is controlled by the instrument cluster which varies the flash rate of the LED to indicate the system
status of the alarm and the immobilization systems.
When the ignition is on, the indicator provides a visual indication of the status of the passive anti-theft (engine
immobilization) system. If the immobilization system is operating correctly, the LED will be illuminated for 3 seconds at
ignition on and then extinguish. If a fault exists in the immobilization system, the LED will be either permanently illuminated
or flashing for 60 seconds. This indicates that a fault exists and fault code has been recorded. After the 60 second period the
LED will flash at different frequencies which indicate the nature of the fault.
Refer to: Anti-Theft - Passive (419-01B Anti-Theft - Passive, Description and Operation).
Passive Anti-Theft Horn
The passive anti-theft horn is hardwired to the CJB which activates the horn when the alarm is triggered.
Battery Backed Sounder
Operation of the battery backed sounder is controlled by the CJB on the LIN bus. The sounder is also connected with a
permanent battery supply via the CJB. An integral, rechargeable battery powers the sounder if the battery power supply from
the CJB is interrupted.
Dependant on vehicle, a incitation sensor is incorporated into the battery backed sounder, to monitor vehicle attitude, see
Inclination Sensor.
Inclination Sensor
The CJB monitors the inclination sensor and will activate the alarm system if the vehicle is being raised.
Intrusion Detection Module
The intrusion detection module comprises an ultrasonic sound wave sensor which monitors the vehicle's interior.
The intrusion detection module is activated with volumetric mode which in turn is enabled when the vehicle is double locked.
The vehicle can be locked and alarmed with the module de-activated if a pet is to be left in the vehicle for example by single-
Page 2126 of 3039

Anti-Theft - Active - Anti-Theft - Active
Diagnosis and Testing
Principles of Operation Published: 26-Feb-2014
For a detailed description of the anti-theft - active system, refer to the relevant Description and Operation sections in the
workshop manual. REFER to: (419-01A Anti-Theft - Active)
Anti-Theft - Active (Description and Operation), Anti-Theft - Active (Description and Operation), Anti-Theft - Active (Description and Operation).
Inspection and Verification
CAUTION: Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not
guarantee confirmation of a fault, and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being tested and/or the donor vehicle.
1. Verify the customer concern.
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of damage and system integrity.
Visual Inspection
Mechanical Electrical
Door latch micro switches
Hood ajar switch
Passive anti-theft alarm horn (if installed)
Battery backed sounder (if installed) or battery backed sounder with tilt sensor (if
installed)
Vehicle horns
Fuse(s)
Electrical
connector(s)
Wiring Harness
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible) before proceeding to
the next step.
4. If the cause is not visually evident, check for Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and refer to the relevant DTC Index. For
additional diagnosis and testing information, refer to the relevant Diagnosis and Testing section in the workshop
manual
REFER to: Remote Keyless Entry (RKE) Module (419-10 Multifunction Electronic Modules, Diagnosis and Testing).
DTC Index
CAUTION: Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not
guarantee confirmation of a fault, and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being tested and/or the donor vehicle
NOTES:
If the control module or a component is suspect and the vehicle remains under manufacturer warranty, refer to the
Warranty Policy and Procedures manual (section B1.2), or determine if any prior approval programme is in operation, prior to
the installation of a new module/component.
Generic scan tools may not read the codes listed, or may read only five digit codes. Match the five digits from the scan
tool to the first five digits of the seven digit code listed to identify the fault (the last two digits give additional information
read by the manufacturer approved diagnostic system).
When performing electrical voltage or resistance tests, always use a digital multimeter (DMM) accurate to three decimal
places, and with an up-to-date calibration certificate. When testing resistance, always take the resistance of the DMM leads
into account.
Check and rectify basic faults before beginning diagnostic routines involving pinpoint tests.
Inspect connectors for signs of water ingress, and pins for damage and/or corrosion.
If DTCs are recorded and, after performing the pinpoint tests, a fault is not present, an intermittent concern may be the
cause. Always check for loose connections and corroded terminals.
Page 2128 of 3039

DTC Description Possible Causes Action B10EE-11
Rear Door Passenger
Side Double Locking
Motor - Circuit short to
ground
Rear door passenger side double
locking motor control circuit -
short to ground
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
test rear door passenger side double locking
motor control circuit for short ground B10EE-15
Rear Door Passenger
Side Double Locking
Motor - Circuit short to
battery or open
Rear door passenger side double
locking motor control circuit -
short to power, open circuit
Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with
this DTC using the manufacturer approved
diagnostic system. Refer to the electrical
circuit diagrams and test rear door
passenger side double locking motor control
circuit for short power, open circuit B10F1-11
Key In Switch - Circuit
short to ground
Keyless vehicle module, key IN
status circuit - short to ground
Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with
this DTC using the manufacturer approved
diagnostic system. Refer to the electrical
circuit diagrams and check keyless vehicle
module, key IN status circuit for short to
ground B10F1-12
Key In Switch - Circuit
short to battery
Keyless vehicle module, key IN
status circuit - short to power
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check keyless vehicle module, key IN status
circuit for short to power B10F1-13
Key In Switch - Circuit
open
Keyless vehicle module, key IN
status circuit - open circuit
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check keyless vehicle module, key IN status
circuit for open circuit B1108-11
Driver Door Central
Locking Motor - Circuit
short to ground
Driver door central locking motor
control circuit - short to ground
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
test driver door central locking motor control
circuit for short ground B1108-15
Driver Door Central
Locking Motor - Circuit
short to battery or open
Driver door central locking motor
control circuit - short to power,
open circuit
Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with
this DTC using the manufacturer approved
diagnostic system. Refer to the electrical
circuit diagrams and test driver door central
locking motor control circuit for short to
power, open circuit B1109-11
Passenger Door Central
Locking Motor - Circuit
short to ground
Short to ground
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
test passenger door central locking motor
circuit for short to ground B1109-15
Passenger Door Central
Locking Motor - Circuit
short to battery or open
Short to power or open circuit
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
test passenger door central locking motor
circuit for short to power or open circuit B110A-11
Rear Door Driver Side
Central Locking Motor -
Circuit short to ground
Rear driver door central locking
motor control circuit - short to
ground
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
test rear driver door central locking motor
control circuit for short ground B110A-15
Rear Door Driver Side
Central Locking Motor -
Circuit short to battery
or open
Rear driver door central locking
motor control circuit - short to
power, open circuit
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
test rear driver door central locking motor
control circuit for short to power, open circuit B110B-11
Rear Door Passenger
Side Central Locking
Motor - Circuit short to
ground
Rear passenger door central
locking motor circuit short circuit
to ground
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check the circuit B110B-15
Rear Door Passenger
Side Central Locking
Motor - Circuit short to
battery or open
Rear passenger door central
locking motor circuit short circuit
to power or open circuit
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check the circuit B1163-11
Left Mirror Heater
Output Short To Ground
- Circuit short to ground
Short to ground
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
test left mirror heater output circuit for short
to ground
Page 2133 of 3039
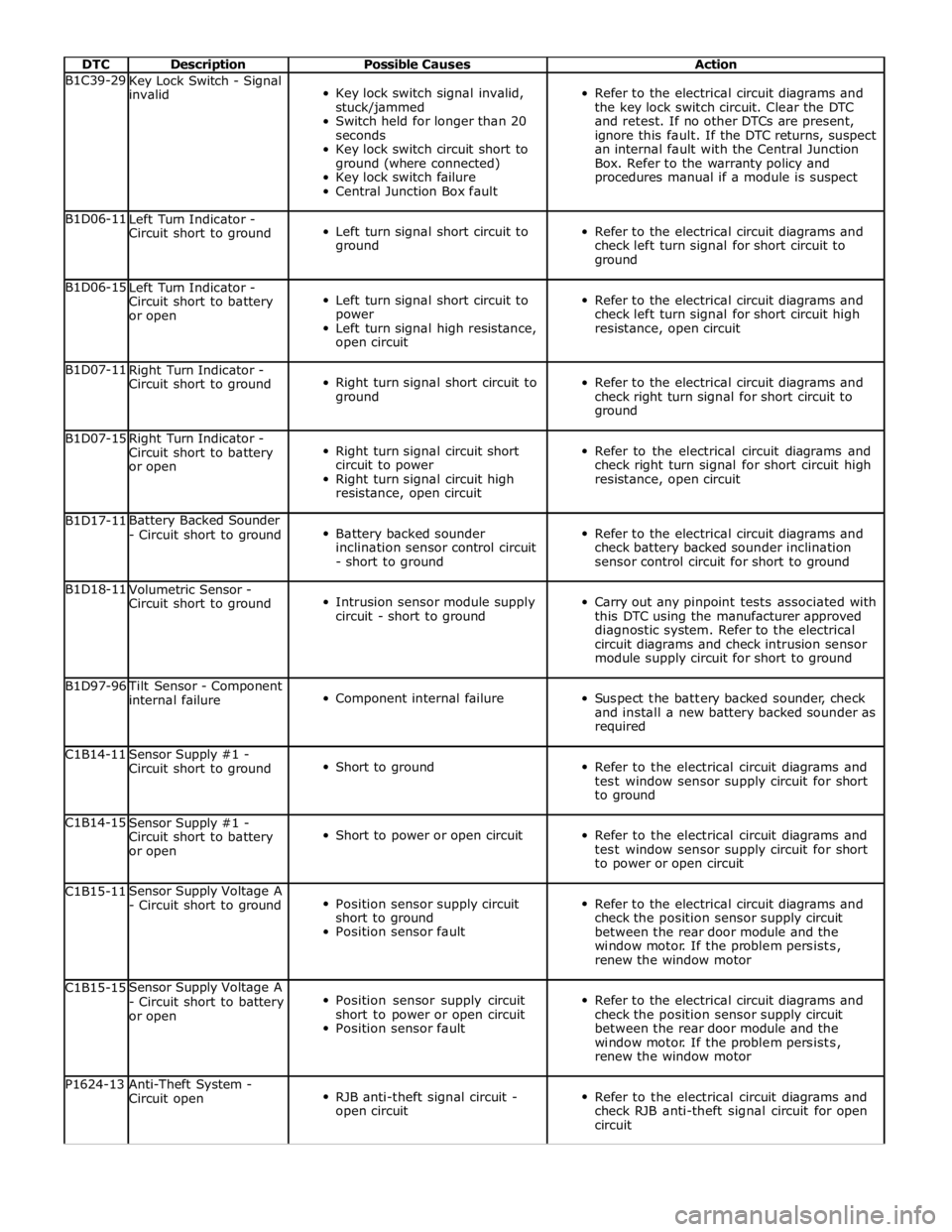
DTC Description Possible Causes Action B1C39-29
Key Lock Switch - Signal
invalid
Key lock switch signal invalid,
stuck/jammed
Switch held for longer than 20
seconds
Key lock switch circuit short to
ground (where connected)
Key lock switch failure
Central Junction Box fault
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
the key lock switch circuit. Clear the DTC
and retest. If no other DTCs are present,
ignore this fault. If the DTC returns, suspect
an internal fault with the Central Junction
Box. Refer to the warranty policy and
procedures manual if a module is suspect B1D06-11
Left Turn Indicator -
Circuit short to ground
Left turn signal short circuit to
ground
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check left turn signal for short circuit to
ground B1D06-15
Left Turn Indicator -
Circuit short to battery
or open
Left turn signal short circuit to
power
Left turn signal high resistance,
open circuit
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check left turn signal for short circuit high
resistance, open circuit B1D07-11
Right Turn Indicator -
Circuit short to ground
Right turn signal short circuit to
ground
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check right turn signal for short circuit to
ground B1D07-15
Right Turn Indicator -
Circuit short to battery
or open
Right turn signal circuit short
circuit to power
Right turn signal circuit high
resistance, open circuit
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check right turn signal for short circuit high
resistance, open circuit B1D17-11 Battery Backed Sounder
- Circuit short to ground
Battery backed sounder
inclination sensor control circuit
- short to ground
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check battery backed sounder inclination
sensor control circuit for short to ground B1D18-11
Volumetric Sensor -
Circuit short to ground
Intrusion sensor module supply
circuit - short to ground
Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with
this DTC using the manufacturer approved
diagnostic system. Refer to the electrical
circuit diagrams and check intrusion sensor
module supply circuit for short to ground B1D97-96 Tilt Sensor - Component
internal failure
Component internal failure
Suspect the battery backed sounder, check
and install a new battery backed sounder as
required C1B14-11
Sensor Supply #1 -
Circuit short to ground
Short to ground
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
test window sensor supply circuit for short
to ground C1B14-15
Sensor Supply #1 -
Circuit short to battery
or open
Short to power or open circuit
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
test window sensor supply circuit for short
to power or open circuit C1B15-11 Sensor Supply Voltage A
- Circuit short to ground
Position sensor supply circuit
short to ground
Position sensor fault
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check the position sensor supply circuit
between the rear door module and the
window motor. If the problem persists,
renew the window motor C1B15-15 Sensor Supply Voltage A
- Circuit short to battery
or open
Position sensor supply circuit
short to power or open circuit
Position sensor fault
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check the position sensor supply circuit
between the rear door module and the
window motor. If the problem persists,
renew the window motor P1624-13
Anti-Theft System -
Circuit open
RJB anti-theft signal circuit -
open circuit
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check RJB anti-theft signal circuit for open
circuit
Page 2142 of 3039
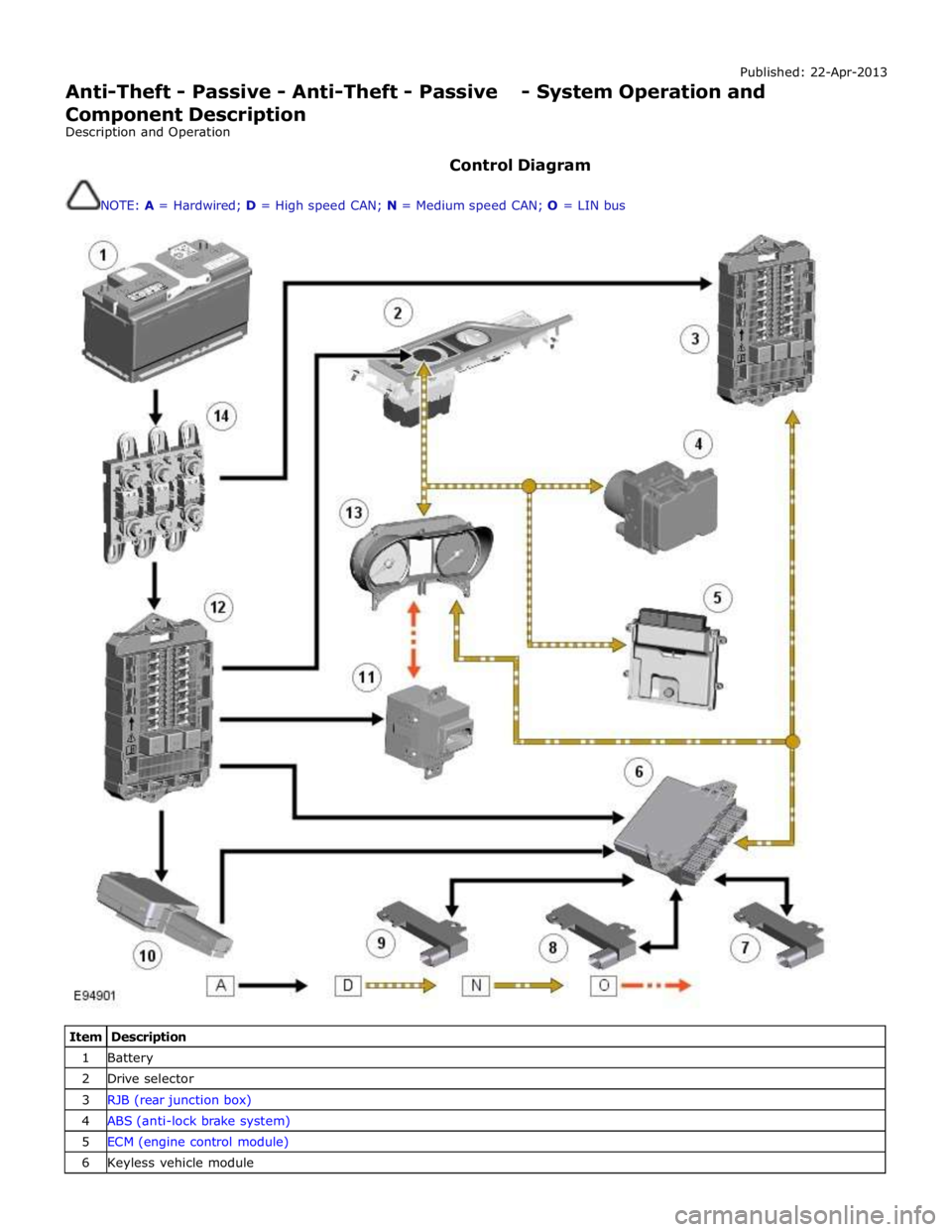
Published: 22-Apr-2013
Anti-Theft - Passive - Anti-Theft - Passive - System Operation and
Component Description
Description and Operation
Control Diagram
NOTE: A = Hardwired; D = High speed CAN; N = Medium speed CAN; O = LIN bus
Item Description 1 Battery 2 Drive selector 3 RJB (rear junction box) 4 ABS (anti-lock brake system) 5 ECM (engine control module) 6 Keyless vehicle module
Page 2143 of 3039

7 Low frequency antenna - front 8 Low frequency antenna - center 9 Low frequency antenna - rear 10 Radio frequency receiver 11 Start control module 12 CJB (central junction box) 13 Instrument cluster 14 Megafuse (250 amp)
System Operation
The passive start function prevents the vehicle from being started by unauthorized persons. It does this by immobilizing the
ignition, fuel and engine crank functions. The system is automatic and requires no input from the driver.
At the request of the CJB, the keyless vehicle module prompts each of the Low Frequency (LF) antennae to output a signal. When the Smart Key is in the vehicle cabin, it detects the LF signals and responds with a Radio Frequency (RF)
data-identification signal back to the keyless vehicle module via the RF receiver.
If the data received matches that stored in the keyless vehicle module it continues the passive start process by
communicating a 'Smart Key valid’ signal to the CJB via the medium speed CAN (controller area network) bus.
Once the CJB receives the authorization and confirms a response with an internal calculation, it passes the result to the
instrument cluster on the medium speed CAN bus.
Before the instrument cluster sends a mobilization signal to the ECMit will exchange encrypted data with: The electric steering lock mechanism to authorize unlocking the steering column.
The RJB to authorize fuel pump operation. Once the RJB receives the authorization and confirms the response with an internal calculation, it will enable the FPDM (fuel pump driver module).
The CJB to authorize the ignition status. If the drive selector is in the park position and the driver presses the brake
pedal and simultaneously presses the start/stop switch, the CJB interprets this as an engine crank request. Before the
engine crank request is allowed, the CJB compares a brake pressure signal received from the ABS module. The brake pressure signal is compared to an internally stored threshold value within the CJB. If the signal is greater than the
stored threshold value, a crank request signal is sent to the ECM on the high speed CAN bus.
Once these factors have been confirmed, and the vehicle is in 'Park', the engine can be started by pressing the brake pedal and
the Stop/Start button simultaneously.
NOTES:
If the keyless vehicle module fails to locate the Smart Key, the message 'SMART KEY NOT FOUND PLEASE INSERT IN
SLOT' will appear in the instrument cluster message center. When inserted the start control module will read the transponder
within the Smart Key. If the transponder identification is valid, authorization will be transmitted to the instrument cluster on
the LIN (local interconnect network) bus.
When the vehicle is delivered from the factory the passive start function is inhibited. In this condition the vehicle can
only be started by placing the Smart Key in the start control module. The system should be switched on during the Pre-Delivery
Inspection (PDI) using the Jaguar approved diagnostic system. For additional information, refer to the PDI Manual.
To ensure optimum long term reliability of the smart key the battery must be replaced with a brand new, unused battery. If a
used battery is installed the "SMART KEY BATTERY LOW" message may not be cleared. To avoid contamination of the contacts
the battery should be removed from its packaging and installed into the smart key while wearing gloves. To confirm that the
replacement battery is working correctly press the unlock button twice while holding the smart key outside the vehicle, then
enter the vehicle with the smart key, press the start button and confirm that the "SMART KEY BATTERY LOW" message is not
displayed.
Start Control Module Component Description
The start control module is used if the keyless vehicle module is unable to authorise the Smart Key.
If the keyless vehicle module is unable to identify the Smart Key, for example if the Smart Key battery voltage is low or there
is local RF interference, the transponder within the Smart Key can be read in the conventional manner. The driver will be
alerted to this by a chime and a message in the instrument cluster message center 'SMART KEY NOT FOUND PLEASE INSERT IN
SLOT'.
Once inserted the start control module will read the transponder within the Smart Key. If the transponder identification is
valid, authorization will be transmitted to the instrument cluster on the LIN bus.
NOTE: Inserting the Smart Key into the start control module will not charge the Smart Key battery. The battery is
non-chargeable and must be replaced if defective.
Page 2172 of 3039
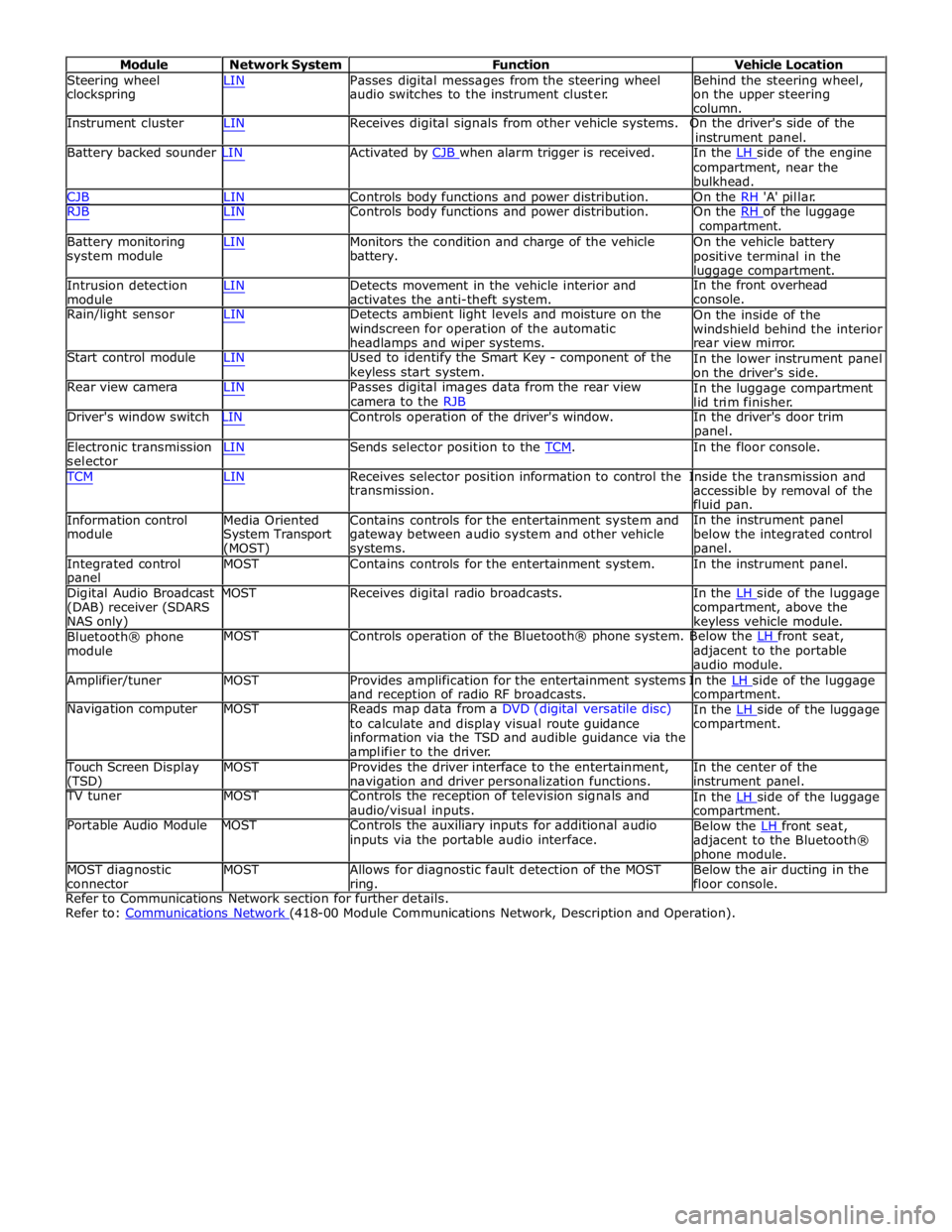
Module Network System Function Vehicle Location
Steering wheel
clockspring LIN Passes digital messages from the steering wheel
audio switches to the instrument cluster. Behind the steering wheel,
on the upper steering
column.
Instrument cluster LIN Receives digital signals from other vehicle systems. On the driver's side of the
instrument panel.
Battery backed sounder LIN Activated by CJB when alarm trigger is received. In the LH side of the engine compartment, near the
bulkhead.
CJB LIN Controls body functions and power distribution. On the RH 'A' pillar.
RJB LIN Controls body functions and power distribution. On the RH of the luggage compartment.
Battery monitoring
system module
Intrusion detection
module LIN Monitors the condition and charge of the vehicle
battery.
LIN Detects movement in the vehicle interior and
activates the anti-theft system. On the vehicle battery
positive terminal in the
luggage compartment.
In the front overhead
console.
Rain/light sensor LIN Detects ambient light levels and moisture on the
windscreen for operation of the automatic
headlamps and wiper systems.
Start control module LIN Used to identify the Smart Key - component of the
keyless start system.
Rear view camera LIN Passes digital images data from the rear view
camera to the RJB On the inside of the
windshield behind the interior
rear view mirror.
In the lower instrument panel
on the driver's side.
In the luggage compartment
lid trim finisher.
Driver's window switch LIN Controls operation of the driver's window. In the driver's door trim
panel.
Electronic transmission
selector LIN Sends selector position to the TCM. In the floor console. TCM LIN Receives selector position information to control the Inside the transmission and
Information control
module
Media Oriented
System Transport
(MOST) transmission.
Contains controls for the entertainment system and
gateway between audio system and other vehicle
systems. accessible by removal of the
fluid pan.
In the instrument panel
below the integrated control
panel.
Integrated control
panel MOST Contains controls for the entertainment system. In the instrument panel.
Digital Audio Broadcast MOST Receives digital radio broadcasts. In the LH side of the luggage (DAB) receiver (SDARS
NAS only)
Bluetooth® phone
module compartment, above the
keyless vehicle module.
MOST Controls operation of the Bluetooth® phone system. Below the LH front seat, adjacent to the portable
audio module.
Amplifier/tuner MOST Provides amplification for the entertainment systems In the LH side of the luggage and reception of radio RF broadcasts.
Navigation computer MOST Reads map data from a DVD (digital versatile disc)
to calculate and display visual route guidance
information via the TSD and audible guidance via the
amplifier to the driver. compartment.
In the LH side of the luggage compartment.
Touch Screen Display
(TSD) MOST Provides the driver interface to the entertainment,
navigation and driver personalization functions. In the center of the
instrument panel.
TV tuner MOST Controls the reception of television signals and
audio/visual inputs.
Portable Audio Module MOST Controls the auxiliary inputs for additional audio
inputs via the portable audio interface. In the LH side of the luggage compartment.
Below the LH front seat, adjacent to the Bluetooth®
phone module.
MOST diagnostic
connector MOST Allows for diagnostic fault detection of the MOST
ring. Below the air ducting in the
floor console.
Refer to Communications Network section for further details.
Refer to: Communications Network (418-00 Module Communications Network, Description and Operation).