VIN JAGUAR XJ6 1997 2.G Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JAGUAR, Model Year: 1997, Model line: XJ6, Model: JAGUAR XJ6 1997 2.GPages: 227, PDF Size: 7.2 MB
Page 132 of 227
6Carefully check to make sure the
suspension and steering components do not
make contact with the hoses. Have an
assistant push on the vehicle and also turn the
steering wheel from lock-to-lock during
inspection.
7Bleed the brake system (see Section 9).
Metal brake line renewal
8When replacing brake lines, use the proper
parts only. Do not use copper line for any
brake system connections. Purchase steel
brake lines from a dealer or motor factors..
9Unless you’re using factory renewal brake
lines, you may need a tubing bender to bend
the lines to the proper shape.
10First, remove the line you intend to renew,
lay it on a clean workbench and measure it
carefully. Obtain a new line of the same length
and bend it to match the pattern of the old
line.
Warning: Do not crimp or
damage the line. No bend should
have a smaller radius than
9/16-inch. Make sure the
protective coating on the new line is
undamaged at the bends.
11When refitting the new line, make sure it’s
well supported by the brackets, the routing
matches the original and there’s plenty of
clearance between moving or hot
components.
12After refitting, check the master cylinder
fluid level and add fluid as necessary. Bleed
the brake system as outlined in Section 9 and
test the brakes carefully before driving the
vehicle. Be sure there are no leaks.
9 Brake hydraulic system-
bleeding
2
Warning: Wear eye protection
when bleeding the brake
system. If the fluid comes in
contact with your eyes,
immediately rinse them with water and
seek medical attention.Note:Bleeding the hydraulic system is
necessary to remove any air which has entered
the system during removal and refitting of a
hose, line, caliper or master cylinder.
1It will probably be necessary to bleed the
system at all four brakes if air has entered the
system due to low fluid level or if the brake
lines have been disconnected at the master
cylinder.
2If a brake line was disconnected at only one
wheel, then only that caliper or wheel cylinder
must be bled.
3If a brake line is disconnected at a fitting
located between the master cylinder and any
of the brakes, that part of the system served
by the disconnected line must be bled.
4Bleed the right rear, the left rear, the right
front and the left front caliper, in that order,
when the entire system is involved.
5Remove any residual vacuum from the
servo and pressure in the anti-lock braking
system (if equipped) by applying the brake
about 30 times with the engine off.
6Remove the master cylinder reservoir cover
and fill the reservoir with brake fluid. Refit the
cover. Note:Check the fluid level often during
the bleeding operation and add fluid as
necessary to prevent the fluid level from falling
low enough to allow air into the master
cylinder.
7Have an assistant on hand, as well as a
supply of new brake fluid, an empty clear
plastic container, a length of 3/16-inch clear
tubing to fit over the bleed screws and a
spanner to open and close the bleed screws.
8Beginning at the right rear wheel, loosen the
bleed screw slightly, then tighten it to a point
where it is snug but can still be loosened
quickly and easily.
9Place one end of the tubing over the bleed
valve and submerge the other end in brake
fluid in the container (see illustration).
10Have the assistant pump the brakes a few
times to build pressure in the system, then
hold the pedal firmly depressed.
11While the pedal is held depressed, open
the bleed screw just enough to allow fluid to
flow from the caliper. Watch for air bubbles toexit the submerged end of the tube. When the
fluid flow slows after a couple of seconds,
close the screw and have your assistant
release the pedal.
12Repeat Steps 10 and 11 until no more air
is seen leaving the tube, then tighten the
bleed screw and proceed to the left rear
wheel, the right front wheel and the left
front wheel, in that order, and perform the
same procedure. Be sure to check the fluid in
the master cylinder reservoir frequently.
13Never reuse old brake fluid. It contains
contaminates and moisture which could
damage the braking system.
14Refill the master cylinder with fluid at the
end of the operation.
15Check the operation of the brakes. The
pedal should feel solid when depressed, with
no sponginess. If necessary, repeat the entire
process.
Warning: Do not drive the car if
in doubt about the effectiveness
of the brake system.
10 Handbrake cable-
adjustment
1
1Slowly apply the handbrake and count the
number of clicks at the lever. It should be fully
applied within three to five clicks. If the lever is
still not fully applied by the fifth click, adjust
the handbrake cable as follows:
2Raise the vehicle and place it securely on
axle stands.
3Loosen the locknut (see illustration)and
tighten the cable adjuster until all slack has
been removed. Tighten the locknut. Make
sure the wheels turn freely with the handbrake
lever released
4Lower the vehicle and recheck the
handbrake lever. It should now be properly
adjusted. If it’s now fully applied within three
to five clicks, raise the vehicle again and
readjust the cable at the adjuster.
5Make sure the handbrake holds the vehicle
on an incline.
9•10 Braking system
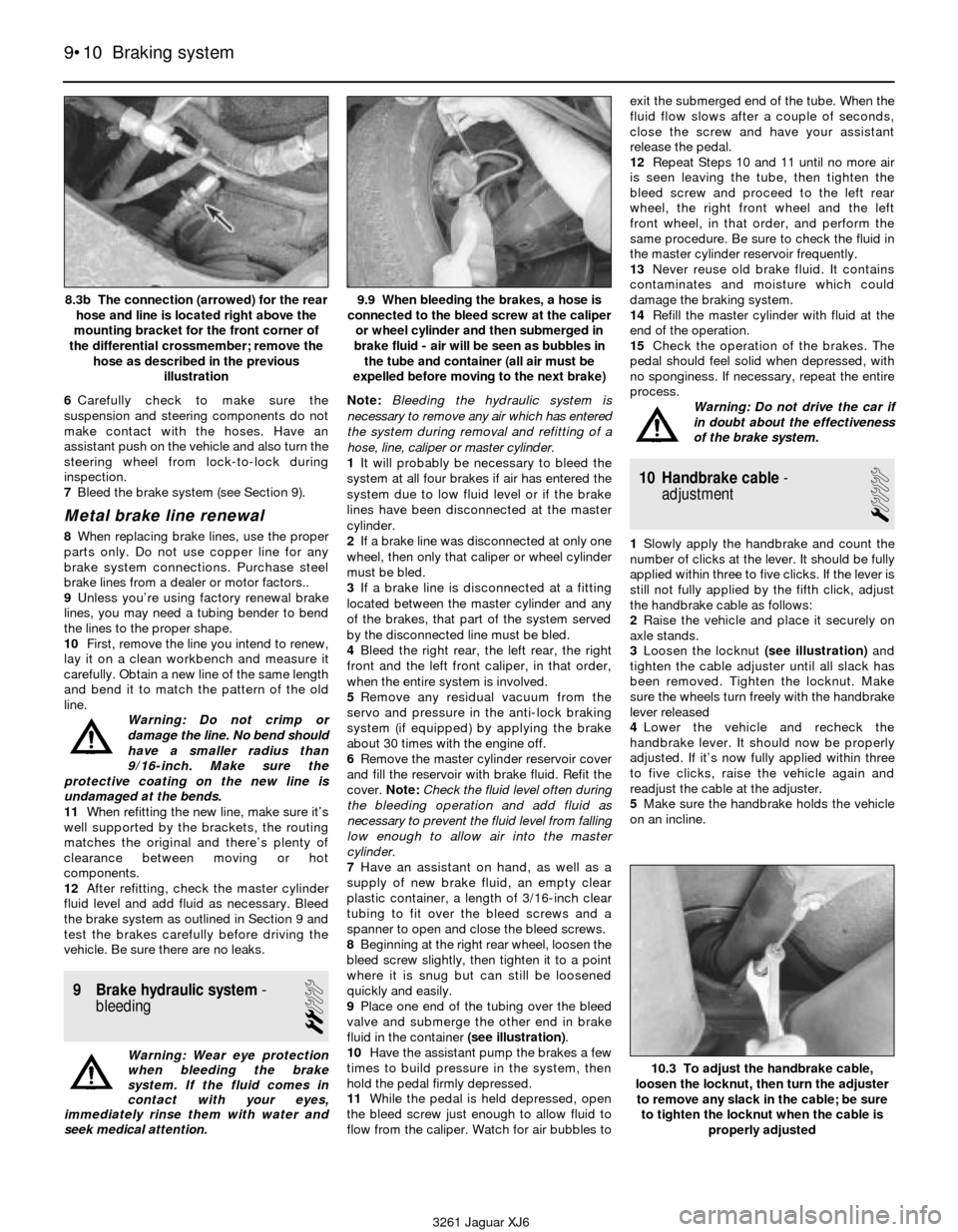
8.3b The connection (arrowed) for the rear
hose and line is located right above the
mounting bracket for the front corner of
the differential crossmember; remove the
hose as described in the previous
illustration9.9 When bleeding the brakes, a hose is
connected to the bleed screw at the caliper
or wheel cylinder and then submerged in
brake fluid - air will be seen as bubbles in
the tube and container (all air must be
expelled before moving to the next brake)
10.3 To adjust the handbrake cable,
loosen the locknut, then turn the adjuster
to remove any slack in the cable; be sure
to tighten the locknut when the cable is
properly adjusted
3261 Jaguar XJ6
Page 136 of 227

bulbs (open-circuit between the switch and
the bulbs), or the switch is defective.
5To remove the switch, reach up under the
dash and unplug the two electrical connectors
- one for the brake lights and one for the
cruise control system. Locate the two pairs of
leads coming down the pedal box and trace
them to their connectors on or near the
steering column.
6Remove the three switch-plate retaining
bolts and remove the switch assembly (see
illustrations). Inspect the switch-plate rubber
gasket for cracks or deterioration and renew it
if it’s damaged or worn.
7Place the switch assembly on a workbench
and connect an ohmmeter to the brake lightswitch terminals. With the switch plunger in its
normal, extended position (brake pedal not
applied), there should be no continuity (infinite
resistance) (see illustration); when the
plunger is depressed (brake pedal applied),
there should be continuity (zero resistance)
(see illustration). If the switch doesn’t
perform as described, renew it. If the switch
works in an opposite fashion, i.e. continuity
when the plunger is free, no continuity when
the plunger is depressed, you’ve tested the
cruise control switch! Switch the ohmmeter
leads to the other connector and recheck.
8To remove the switch from the plate,
remove the two small nuts on the back of the
plate (see illustration).9Refit the switch assembly and the switch
plate bolts but don’t tighten the bolts yet.
10Plug in the brake light and cruise control
connectors.
11The holes in the switch plate are slotted
for adjustment. While an assistant presses the
brake pedal, verify that the brake lights come
on; with the pedal released, make sure the
brake lights are off. If the lights don’t come on
when the pedal is depressed, or stay on when
the pedal is released, adjust the switch by
moving the plate until proper operation is
achieved. Tighten the switch-plate bolts.
12After tightening the switch-plate bolts,
check the switch again to make sure it
performs properly.
9•14 Braking system
13.6a To remove the brake light switch,
remove the three mounting plate screws
(arrowed) . . .13.6b . . . and carefully pry the switch plate
away from the pedal box - be careful not to
damage the gasket13.7a To check the brake light switch,
connect an ohmmeter to the switch
terminals; with the switch plunger
released, there should be no continuity
(infinite resistance)
13.7b With the switch plunger depressed,
there should be continuity
(zero resistance)13.8 If you’re replacing the switch, remove
these two nuts (arrowed) and transfer the
retaining plate to the new switch
3261 Jaguar XJ6
Page 139 of 227
1 General information
Warning: Whenever any of the
suspension or steering fasteners
are loosened or removed, they
must be inspected and if
necessary, replaced with new ones of the
same part number or of original equipment
quality and design. Torque wrench settings
must be followed for proper reassembly
and component retention. Never attempt
to heat, straighten or weld any suspension
or steering component. Instead, renew any
bent or damaged part.
The front suspension (see illustrations)
consists of unequal-length upper and lower
control arms, shock absorbers and coil
springs. The upper ends of the shocks are
attached to the body; the lower ends
are attached to the lower control arms. The
upper ends of the coil springs are seated
against the suspension crossmember; the
lower ends are seated against removable
plates which are bolted to the lower control
arms. The steering knuckles are attached to
balljoints in the upper and lower control arms.
An anti-roll bar is attached to the suspension
crossmember with a pair of bushing brackets
and to the lower control arms via a connecting
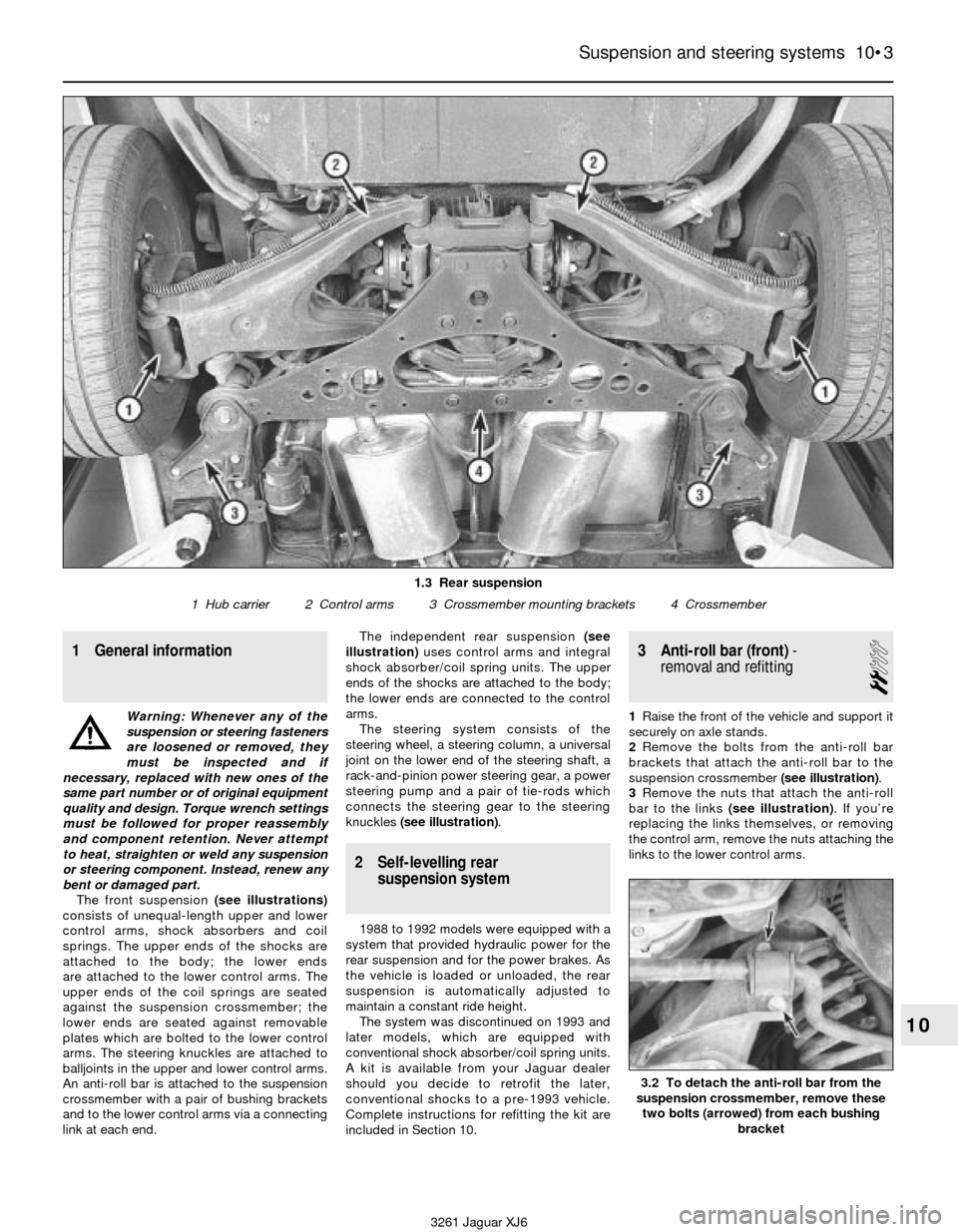
link at each end.The independent rear suspension (see
illustration)uses control arms and integral
shock absorber/coil spring units. The upper
ends of the shocks are attached to the body;
the lower ends are connected to the control
arms.
The steering system consists of the
steering wheel, a steering column, a universal
joint on the lower end of the steering shaft, a
rack-and-pinion power steering gear, a power
steering pump and a pair of tie-rods which
connects the steering gear to the steering
knuckles (see illustration).
2 Self-levelling rear
suspension system
1988 to 1992 models were equipped with a
system that provided hydraulic power for the
rear suspension and for the power brakes. As
the vehicle is loaded or unloaded, the rear
suspension is automatically adjusted to
maintain a constant ride height.
The system was discontinued on 1993 and
later models, which are equipped with
conventional shock absorber/coil spring units.
A kit is available from your Jaguar dealer
should you decide to retrofit the later,
conventional shocks to a pre-1993 vehicle.
Complete instructions for refitting the kit are
included in Section 10.
3 Anti-roll bar (front)-
removal and refitting
2
1Raise the front of the vehicle and support it
securely on axle stands.
2Remove the bolts from the anti-roll bar
brackets that attach the anti-roll bar to the
suspension crossmember (see illustration).
3Remove the nuts that attach the anti-roll
bar to the links (see illustration). If you’re
replacing the links themselves, or removing
the control arm, remove the nuts attaching the
links to the lower control arms.
Suspension and steering systems 10•3
10
1.3 Rear suspension
1 Hub carrier 2 Control arms 3 Crossmember mounting brackets 4 Crossmember
3.2 To detach the anti-roll bar from the
suspension crossmember, remove these
two bolts (arrowed) from each bushing
bracket
3261 Jaguar XJ6
Page 141 of 227

12Remove the four balljoint retaining bolts
(see illustration).
13If the dust boot is damaged, pry it out
(see illustration).
14Remove the balljoint.
15Refitting is the reverse of removal. Tighten
the balljoint bolts and the ball stud nut to the
torque listed in this Chapter’s Specifications.
16Remove the jack from under the control
arm, refit the front wheel. Lower the vehicle
and tighten the wheel nuts to the torque listed
in the Chapter 1 Specifications.
6 Steering knuckle-
removal and refitting
3
1Loosen the wheel nuts, raise the front of the
vehicle and place it securely on axle stands.
Remove the wheel.
2Remove the front brake caliper and
mounting bracket (see Chapter 9). Do not
disconnect the brake hose. Hang the caliper
out of the way with a piece of wire.
3Remove the brake disc (see Chapter 9).
4Remove the ABS sensor (see illustration).
5Remove the brake shield (see illustration).
6Disconnect the tie-rod end from the
steering knuckle (see Section 15).
7Disconnect the upper and lower balljoints
from the steering knuckle (see Section 5).
8Remove the steering knuckle.
9Refitting is the reverse of removal. Tighten
the balljoint nuts and the tie-rod end nuts to the
specified torque. Tighten the brake fasteners to
the torque values listed in the Chapter 9
Specifications.
7 Upper control arm-
removal and refitting
3
1Loosen the wheel nuts, raise the vehicle
and support it securely on axle stands.
Remove the wheel.
2Support the lower control arm with a trolley
jack (see illustration 4.2).
3Disconnect the upper balljoint from the
steering knuckle (see Section 5).4If you’re removing the right upper control
arm on a vehicle equipped with the power
hydraulic system, remove the three Torx
screws which attach the accumulator (see
illustration)and push the assembly aside just
far enough to clear the pivot bolt.
5Remove the upper control arm pivot bolt
and nut (see illustration). When removing the
nut, note the number of washers used and the
order in which they’re installed. Put these
parts in a plastic bag.
6Remove the upper control arm. Inspect the
bushings at either end of the arm and renew
them if they’re damaged or worn.
7Refitting is the reverse of removal. Be sure
to refit the washers in the same order in which
they were removed. Raise the suspensionwith the trolley jack to simulate normal ride
height, then tighten the upper control arm
pivot bolt and nut to the torque listed in this
Chapter’s Specifications.
8 Coil spring (front)-
removal and refitting
3
Warning: The coil springs cannot
be removed without a special
spring compressor tool (Jaguar
tool JD115). Do not try to remove
a coil spring without this special tool. If you
do, you could be seriously injured.
1Loosen the wheel nuts, raise the vehicle
Suspension and steering systems 10•5
10
5.11 Strike the steering knuckle in this
area to pop the lower ball stud loose from
the steering knuckle5.12 To detach the lower balljoint from the
lower control arm, remove these four bolts
(arrowed)5.13 To detach the dust boot from the
steering knuckle, pry the lower lip of the
boot out of its groove in the knuckle
6.5 To detach the brake shield from the
steering knuckle, remove these three
screws (arrowed)6.4 To detach the ABS sensor from the
steering knuckle, remove this bolt
7.4 Remove these three Torx screws
(arrowed) and move the accumulator
assembly to the side a little to provide
clearance for pulling out the pivot bolt7.5 To detach the upper control arm from
the crossmember, remove the nut (at the
rear) and pull the bolt out from the front;
note the fitted order of the spacer washers
3261 Jaguar XJ6
Page 142 of 227
and support it securely on axle stands.
Remove the wheel.
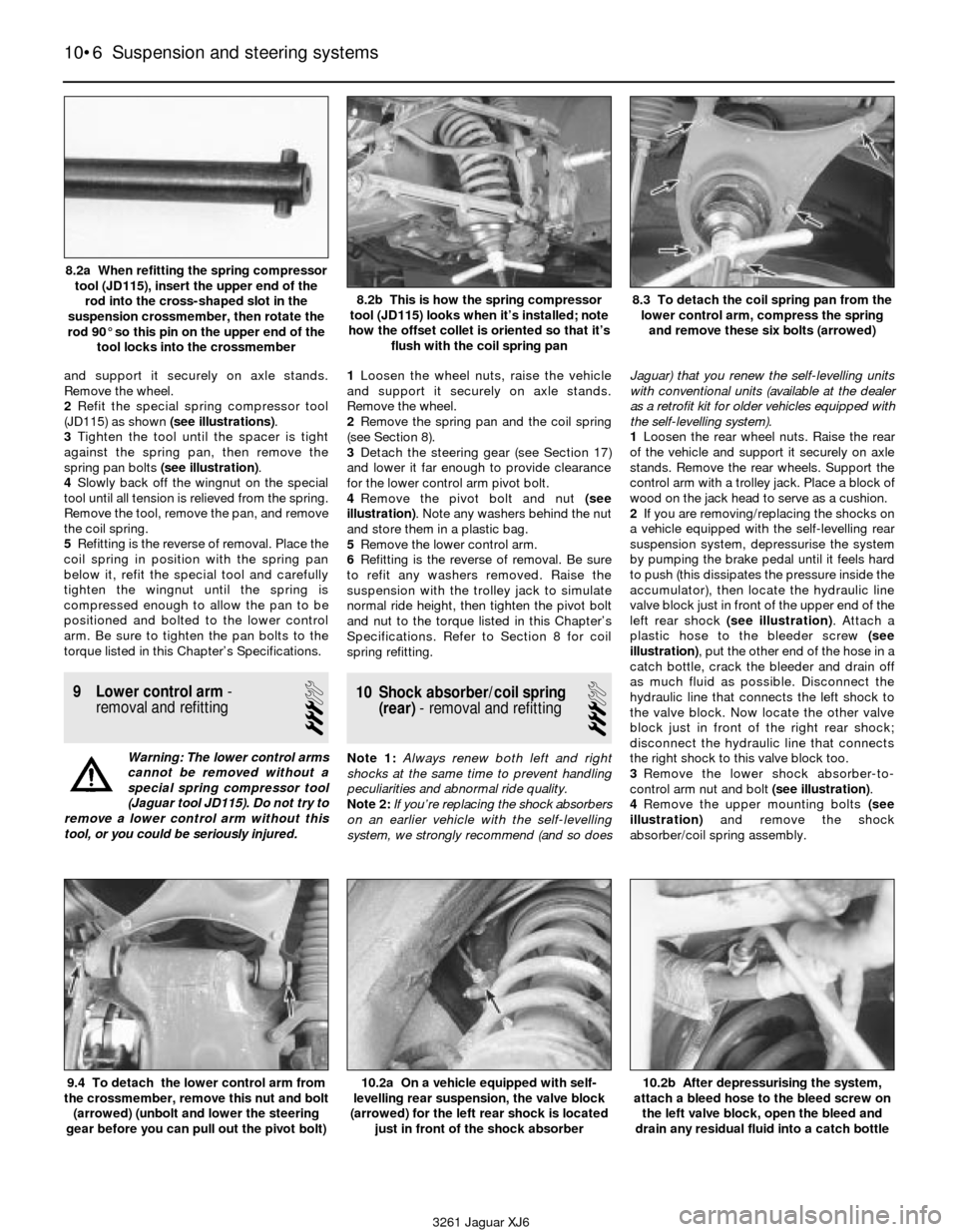
2Refit the special spring compressor tool
(JD115) as shown (see illustrations).
3Tighten the tool until the spacer is tight
against the spring pan, then remove the
spring pan bolts (see illustration).
4Slowly back off the wingnut on the special
tool until all tension is relieved from the spring.
Remove the tool, remove the pan, and remove
the coil spring.
5Refitting is the reverse of removal. Place the
coil spring in position with the spring pan
below it, refit the special tool and carefully
tighten the wingnut until the spring is
compressed enough to allow the pan to be
positioned and bolted to the lower control
arm. Be sure to tighten the pan bolts to the
torque listed in this Chapter’s Specifications.
9 Lower control arm-
removal and refitting
3
Warning: The lower control arms
cannot be removed without a
special spring compressor tool
(Jaguar tool JD115). Do not try to
remove a lower control arm without this
tool, or you could be seriously injured.1Loosen the wheel nuts, raise the vehicle
and support it securely on axle stands.
Remove the wheel.
2Remove the spring pan and the coil spring
(see Section 8).
3Detach the steering gear (see Section 17)
and lower it far enough to provide clearance
for the lower control arm pivot bolt.
4Remove the pivot bolt and nut (see
illustration). Note any washers behind the nut
and store them in a plastic bag.
5Remove the lower control arm.
6Refitting is the reverse of removal. Be sure
to refit any washers removed. Raise the
suspension with the trolley jack to simulate
normal ride height, then tighten the pivot bolt
and nut to the torque listed in this Chapter’s
Specifications. Refer to Section 8 for coil
spring refitting.
10 Shock absorber/coil spring
(rear)- removal and refitting
3
Note 1: Always renew both left and right
shocks at the same time to prevent handling
peculiarities and abnormal ride quality.
Note 2:If you’re replacing the shock absorbers
on an earlier vehicle with the self-levelling
system, we strongly recommend (and so doesJaguar) that you renew the self-levelling units
with conventional units (available at the dealer
as a retrofit kit for older vehicles equipped with
the self-levelling system).
1Loosen the rear wheel nuts. Raise the rear
of the vehicle and support it securely on axle
stands. Remove the rear wheels. Support the
control arm with a trolley jack. Place a block of
wood on the jack head to serve as a cushion.
2If you are removing/replacing the shocks on
a vehicle equipped with the self-levelling rear
suspension system, depressurise the system
by pumping the brake pedal until it feels hard
to push (this dissipates the pressure inside the
accumulator), then locate the hydraulic line
valve block just in front of the upper end of the
left rear shock (see illustration). Attach a
plastic hose to the bleeder screw (see
illustration), put the other end of the hose in a
catch bottle, crack the bleeder and drain off
as much fluid as possible. Disconnect the
hydraulic line that connects the left shock to
the valve block. Now locate the other valve
block just in front of the right rear shock;
disconnect the hydraulic line that connects
the right shock to this valve block too.
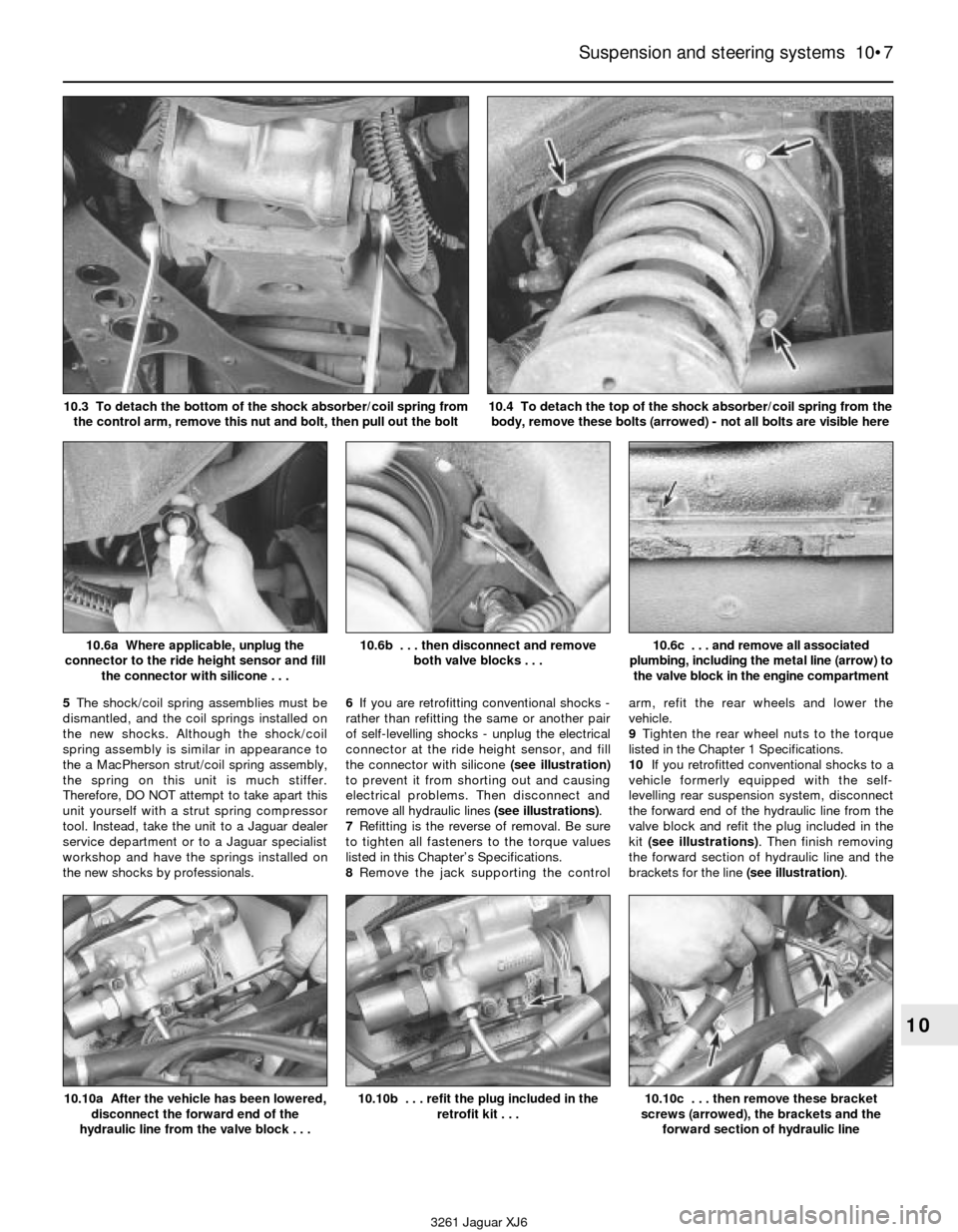
3Remove the lower shock absorber-to-
control arm nut and bolt (see illustration).
4Remove the upper mounting bolts (see
illustration)and remove the shock
absorber/coil spring assembly.
10•6 Suspension and steering systems
9.4 To detach the lower control arm from
the crossmember, remove this nut and bolt
(arrowed) (unbolt and lower the steering
gear before you can pull out the pivot bolt)10.2a On a vehicle equipped with self-
levelling rear suspension, the valve block
(arrowed) for the left rear shock is located
just in front of the shock absorber10.2b After depressurising the system,
attach a bleed hose to the bleed screw on
the left valve block, open the bleed and
drain any residual fluid into a catch bottle
3261 Jaguar XJ6 8.2a When refitting the spring compressor
tool (JD115), insert the upper end of the
rod into the cross-shaped slot in the
suspension crossmember, then rotate the
rod 90° so this pin on the upper end of the
tool locks into the crossmember
8.2b This is how the spring compressor
tool (JD115) looks when it’s installed; note
how the offset collet is oriented so that it’s
flush with the coil spring pan8.3 To detach the coil spring pan from the
lower control arm, compress the spring
and remove these six bolts (arrowed)
Page 143 of 227
5The shock/coil spring assemblies must be
dismantled, and the coil springs installed on
the new shocks. Although the shock/coil
spring assembly is similar in appearance to
the a MacPherson strut/coil spring assembly,
the spring on this unit is much stiffer.
Therefore, DO NOT attempt to take apart this
unit yourself with a strut spring compressor
tool. Instead, take the unit to a Jaguar dealer
service department or to a Jaguar specialist
workshop and have the springs installed on
the new shocks by professionals.6If you are retrofitting conventional shocks -
rather than refitting the same or another pair
of self-levelling shocks - unplug the electrical
connector at the ride height sensor, and fill
the connector with silicone (see illustration)
to prevent it from shorting out and causing
electrical problems. Then disconnect and
remove all hydraulic lines (see illustrations).
7Refitting is the reverse of removal. Be sure
to tighten all fasteners to the torque values
listed in this Chapter’s Specifications.
8Remove the jack supporting the controlarm, refit the rear wheels and lower the
vehicle.
9Tighten the rear wheel nuts to the torque
listed in the Chapter 1 Specifications.
10If you retrofitted conventional shocks to a
vehicle formerly equipped with the self-
levelling rear suspension system, disconnect
the forward end of the hydraulic line from the
valve block and refit the plug included in the
kit (see illustrations). Then finish removing
the forward section of hydraulic line and the
brackets for the line (see illustration).
Suspension and steering systems 10•7
10
10.6a Where applicable, unplug the
connector to the ride height sensor and fill
the connector with silicone . . .10.6b . . . then disconnect and remove
both valve blocks . . .10.6c . . . and remove all associated
plumbing, including the metal line (arrow) to
the valve block in the engine compartment
3261 Jaguar XJ6 10.3 To detach the bottom of the shock absorber/coil spring from
the control arm, remove this nut and bolt, then pull out the bolt
10.4 To detach the top of the shock absorber/coil spring from the
body, remove these bolts (arrowed) - not all bolts are visible here
10.10a After the vehicle has been lowered,
disconnect the forward end of the
hydraulic line from the valve block . . .10.10b . . . refit the plug included in the
retrofit kit . . .10.10c . . . then remove these bracket
screws (arrowed), the brackets and the
forward section of hydraulic line
Page 145 of 227

sure you have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery.
2Pry off the centre pad (see illustration).
3Remove the steering wheel nut and mark
the relationship of the steering wheel hub to
the shaft (see illustration).
4Slide the steering wheel off the steering
shaft (see illustration).
5Refitting is the reverse of removal. Make
sure you align the match marks you made on
the steering wheel and the shaft. Tighten the
steering wheel nut to the torque listed in this
Chapter’s Specifications.
15 Tie-rod ends-
removal and refitting
2
1Loosen the wheel nuts, raise the front of the
vehicle and support it securely on axle stands.
Remove the front wheel.
2Back off the locknut that locks the tie-rod
end to the tie-rod, then paint an alignment
mark on the threads to ensure the new tie-rod
end is installed in the same position (see
illustration).
3Loosen the nut on the tie-rod ball stud, then
fit a small puller and pop the ball stud loose
(see illustration). Remove the nut and
separate the ball stud from the steering
knuckle. Unscrew the tie-rod end from the tie-
rod.
4Refitting is the reverse of removal. Make
sure you thread the tie-rod end all the way up
to the mark on the threads, but no further.
Tighten the ball stud nut to the torque listed in
this Chapter’s Specifications. Tighten the
locknut securely.
5Have the toe-in checked and, if necessary,
adjusted at a dealer service department or
alignment workshop.
16 Steering gear boots- renewal
2
1Remove the tie-rod ends (see Section 15).
2Cut the boot clamps at both ends of the old
boots (see illustration)and slide off the
boots.3While the boots are removed, inspect the
seals in the end of the steering gear. If they’re
leaking, have them replaced by a dealer
service department or other qualified repair
workshop, or replace the steering gear with a
new or rebuilt unit (see Section 17).
4Slide the new boots into place and refit new
boot clamps.
5Refit the tie-rod ends (see Section 15).
Suspension and steering systems 10•9
10
14.4 To remove the steering wheel,
simply pull it straight off15.2 Back off this locknut and mark the
threads to ensure that the new tie-rod end
is installed properly
15.3 Loosen the ball stud nut, fit a small
puller and pop the ball stud loose from the
steering knuckle
3261 Jaguar XJ6 14.2 To remove the centre pad from the steering wheel,
simply pry it off
14.3 After removing the steering wheel nut, make a pair of
alignment marks on the steering wheel and steering shaft to
ensure proper reassembly
16.2 Cut off the boot clamps (arrowed)
and slide the boot off the steering gear
Page 148 of 227

None of these three angles are adjustable on
the rear wheels. Even the non-adjustable
angles should be checked to determine if any
of the suspension components are bent.
Getting the proper wheel alignment is a
very exacting process, one in which
complicated and expensive machines are
necessary to perform the job properly.
Because of this, you should have a technician
with the proper equipment perform these
tasks. We will, however, use this space to give
you a basic idea of what is involved with a
wheel alignment so you can better understand
the process and deal intelligently with the
workshop that does the work.Toe-in is the turning in of the wheels. The
purpose of a toe specification is to ensure
parallel rolling of the wheels. In a vehicle with
zero toe-in, the distance between the front
edges of the wheels will be the same as the
distance between the rear edges of the
wheels. The actual amount of toe-in is
normally only a fraction of an inch. Toe-in is
controlled by the tie-rod end position on the
tie-rod. Incorrect toe-in will cause the tyres to
wear improperly by making them scrub
against the road surface.
Camber is the tilting of the wheels from
vertical when viewed from one end of the
vehicle. When the wheels tilt out at the top, the camber is said to be positive (+). When
the wheels tilt in at the top the camber is
negative (-). The amount of tilt is measured in
degrees from vertical and this measurement is
called the camber angle. This angle affects the
amount of tyre tread which contacts the road
and compensates for changes in the suspension
geometry when the vehicle is cornering or
travelling over an undulating surface.
Caster is the tilting of the front steering axis
from the vertical. A tilt toward the rear is
positive caster and a tilt toward the front is
negative caster. Caster is adjusted by moving
shims from one side of the upper control arm
balljoint to the other.
10•12 Suspension and steering systems
3261 Jaguar XJ6
Page 149 of 227
3261 Jaguar XJ6
11
Chapter 11
Bodywork and fittings
Body - maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Body repair - major damage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Body repair - minor damage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Bonnet - removal, refitting and adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Bonnet and boot lid support struts - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . 9
Bonnet release latch and cable - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Boot lid - removal, refitting and adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Boot lid latch and lock cylinder - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Bumpers - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Centre console - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Cowl cover - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Dashboard trim panels - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Door - removal, refitting and adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Door latch, lock cylinder and handles - removal and refitting . . . . . . 20
Door trim panel - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18Door window glass - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Door window glass regulator - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Front spoiler - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Front wing - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
General information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Hinges and locks - maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Instrument cluster housing - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Outside mirrors - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Radiator grille - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Seats - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Steering column cover - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Upholstery and carpets - maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Vinyl trim - maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Windscreen and fixed glass - replacement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
11•1
Contents
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanic
Difficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert DIY
or professional
Degrees of difficulty
54321
1 General information
These models feature a “unibody”
construction, using a floor pan with front and
rear frame side rails which support the body
components, front and rear suspension
systems and other mechanical components.
Certain components are particularly vulnerable
to accident damage and can be unbolted and
repaired or replaced. Among these parts are
the body mouldings, bumpers, front wings,
bonnet and boot lids and all glass.
Only general body maintenance practices
and body panel repair procedures within the
scope of the do-it-yourselfer are included in
this Chapter.
2 Body- maintenance
1
1The condition of your vehicle’s body is very
important, because the resale value depends
a great deal on it. It’s much more difficult to
repair a neglected or damaged body than it is
to repair mechanical components. The hidden
areas of the body, such as the wheel wells,
the frame and the engine compartment, areequally important, although they don’t require
as frequent attention as the rest of the body.
2Once a year, or every 12,000 miles, it’s a
good idea to have the underside of the body
steam cleaned. All traces of dirt and oil will be
removed and the area can then be inspected
carefully for rust, damaged brake lines, frayed
electrical wires, damaged cables and other
problems. The front suspension components
should be greased after completion of this job.
3At the same time, clean the engine and the
engine compartment with a steam cleaner or
water soluble degreaser.
4The wheel wells should be given close
attention, since undercoating can peel away
and stones and dirt thrown up by the tyres
can cause the paint to chip and flake, allowing
rust to set in. If rust is found, clean down to
the bare metal and apply an anti-rust paint.
5The body should be washed about once a
week. Wet the vehicle thoroughly to soften the
dirt, then wash it down with a soft sponge and
plenty of clean soapy water. If the surplus dirt
is not washed off very carefully, it can wear
down the paint.
6Spots of tar or asphalt thrown up from the
road should be removed with a cloth soaked
in solvent.
7Once every six months, wax the body and
chrome trim. If a chrome cleaner is used to
remove rust from any of the vehicle’s plated
parts, remember that the cleaner also removes
part of the chrome, so use it sparingly.
3 Vinyl trim- maintenance
1
Don’t clean vinyl trim with detergents,
caustic soap or petroleum-based cleaners.
Plain soap and water works just fine, with a
soft brush to clean dirt that may be ingrained.
Wash the vinyl as frequently as the rest of the
vehicle.
After cleaning, application of a high quality
rubber and vinyl protectant will help prevent
oxidation and cracks. The protectant can also
be applied to weather-stripping, vacuum lines
and rubber hoses (which often fail as a result
of chemical degradation) and to the tyres.
4 Upholstery and carpets-
maintenance
1
1Every three months remove the carpets or
mats and clean the interior of the vehicle
(more frequently if necessary). Vacuum the
upholstery and carpets to remove loose dirt
and dust.
2Leather upholstery requires special care.
Stains should be removed with warm water
and a very mild soap solution. Use a clean,
damp cloth to remove the soap, then wipe
Page 151 of 227

spray painting technique is mastered. Cover
the repair area with a thick coat of primer. The
thickness should be built up using several thin
layers of primer rather than one thick one.
Using 600-grit wet-or-dry sandpaper, rub
down the surface of the primer until it is very
smooth. While doing this, the work area
should be thoroughly rinsed with water and
the wet-or-dry sandpaper periodically rinsed
as well. Allow the primer to dry before
spraying additional coats.
21Spray on the top coat, again building up
the thickness by using several thin layers of
paint. Begin spraying at the top of the repair
area and then, using a side-to-side motion,
work down until the whole repair area and
about two inches of the surrounding original
paint is covered. Remove all masking material
10 to 15 minutes after spraying on the final
coat of paint. Allow the new paint at least two
weeks to harden, then use a very fine rubbing
compound to blend the edges of the new
paint into the existing paint. Finally, apply a
coat of wax.
6 Body repair- major damage
5
1Major damage must be repaired by an auto
body workshop specifically equipped to
perform unibody repairs. These workshops
have the specialised equipment required to
do the job properly.
2If the damage is extensive, the body must
be checked for proper alignment or the
vehicle’s handling characteristics may be
adversely affected and other components
may wear at an accelerated rate.
3Due to the fact that most of the major body
components (bonnet, front wings, etc.) are
separate and replaceable units, any seriously
damaged components should be replaced
rather than repaired. Sometimes thecomponents can be found in a scrapyard that
specialises in used vehicle components, often
at considerable savings over the cost of new
parts.
7 Hinges and locks-
maintenance
1
Once every 3000 miles, or every three
months, the hinges and latch assemblies on
the doors, bonnet and boot should be given a
few drops of light oil or lock lubricant. The
door latch strikers should also be lubricated
with a thin coat of grease to reduce wear and
ensure free movement. Lubricate the door
and boot locks with spray-on graphite
lubricant.
8 Windscreen and fixed glass-
replacement
5
Replacement of the windscreen and fixed
glass requires the use of special fast-setting
adhesive/caulk materials and some
specialised tools. It is recommended that
these operations be left to a dealer or a
workshop specialising in glass work.
9 Bonnet and boot lid support
struts- removal and refitting
1
1Open the bonnet or boot lid and support it
securely.
2Using a small screwdriver, detach the
retaining clips at both ends of the support
strut. Then pry or pull sharply to detach it from
the vehicle(see illustrations).
3Refitting is the reverse of removal.
10 Bonnet- removal,
refitting and adjustment
2
Note:The bonnet is heavy and somewhat
awkward to remove and refit - at least two
people should perform this procedure.
Removal and refitting
1Use blankets or pads to cover the wings
and the area in front of the bonnet. This will
protect the body and paint as the bonnet is
lifted off.
2Make marks or scribe a line around the
bonnet hinge to ensure proper alignment
during refitting.
3Disconnect any cables or wires that will
interfere with removal.
4Have an assistant support the bonnet.
Remove the hinge-to-bonnet screws or bolts
(see illustration).
5Lift off the bonnet.
6Refitting is the reverse of removal.
Adjustment
7Before the bonnet can be adjusted
properly, both bonnet striker assemblies
Bodywork and fittings 11•3
1110.4 With the help of an assistant to hold
the bonnet, remove the retaining bolts
(arrowed) from each hinge plate, then lift
off the bonnet
3261 Jaguar XJ69.2b The boot lid support strut requires prising out a locking pin
to detach it from the locating stud
9.2a Use a small screwdriver to prise the clip out of its locking
groove, then detach the end of the strut from the mounting stud