engine JEEP CHEROKEE 1994 Service Owners Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 1994, Model line: CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP CHEROKEE 1994Pages: 1784, PDF Size: 77.09 MB
Page 159 of 1784

POWER BOOSTER VACUUM TEST
(1) Connect a vacuum gauge to the booster check
valve with a short length of hose and T-fitting (Fig.
3).
(2) Start and run engine at idle speed for one
minute.
(3) Clamp hose shut between vacuum source and
check valve (Fig. 3).
(4) Stop engine and observe vacuum gauge.
(5) If vacuum drops more than one inch HG (33
millibars) within 15 seconds, booster diaphragm or
check valve is faulty.
Fig. 3 Booster Vacuum Test Connections
5 - 12 BRAKESJ
Page 169 of 1784

POWER BRAKE BOOSTER
INDEX
page page
Power Brake Booster Installation............. 23
Power Brake Booster Operation............. 22Power Brake Booster Removal.............. 22
Service Information....................... 22
SERVICE INFORMATION
The power brake booster is not a serviceable com-
ponent. If a booster malfunction occurs, the booster
must be replaced as an assembly. The booster (Figs.
1 and 2), is attached to the dash panel and pedal sup-
port.
POWER BRAKE BOOSTER OPERATION
Booster Components
The booster assembly consists of a housing divided
into separate chambers by an internal diaphragm.The outer edge of the diaphragm is attached to the
booster housing. The diaphragm is in turn, connected
to the booster push rod.
Two push rods are used to operate the booster. One
push rod connects the booster to the brake pedal. The
second push rod (at the forward end of the housing),
strokes the master cylinder pistons. The rear push
rod is connected to the two diaphragms in the booster
housing.
The atmospheric inlet valve is opened and closed
by the push rod connected to the brake pedal. The
booster vacuum supply is through a hose attached to
a fitting on the intake manifold. The hose is con-
nected to a vacuum check valve in the booster hous-
ing. The check valve is a one-way device that
prevents vacuum leak back.
How Brake Boost Is Generated
Power assist is generated by utilizing the pressure
differential between normal atmospheric pressure
and a vacuum. The vacuum needed for booster oper-
ation is taken directly from the engine intake mani-
fold. The entry point for atmospheric pressure is
through an inlet valve at the rear of the housing.
The forward portion of the booster housing (area in
front of the two diaphragms), is exposed to manifold
vacuum. The rear portion (area behind the dia-
phragms), is exposed to normal atmospheric pressure
of 101.3 kilopascals (14.7 pounds/square in.).
Pressing the brake pedal causes the rear push rod
to open the inlet valve. This exposes the area behind
the diaphragm to atmospheric pressure. The result-
ing force applied to the diaphragm is what provides
the extra apply pressure for power assist.
POWER BRAKE BOOSTER REMOVAL
(1) Loosen but do not remove nuts attaching mas-
ter cylinder to booster (Fig. 3).
(2) Remove instrument panel lower trim cover.
(3) Remove retaining clip attaching booster push
rod to brake pedal (Fig. 4).
(4) Remove bolts/nuts attaching booster to dash
panel.
(5) In engine compartment, loosen vacuum hose
clamp and disconnect vacuum hose from booster
check valve (Fig. 5).
(6) Remove master cylinder attaching nuts and re-
move cylinder from mounting studs on booster.
Fig. 1 Power Brake Booster (XJ)
Fig. 2 Power Brake Booster (YJ)
5 - 22 BRAKESJ
Page 188 of 1784

4). The engine intake manifold serves as the vacuum
source for booster operation.
The booster is mounted on the engine compartment
side of the dash panel. The master cylinder is
mounted on attaching studs at the front of the
booster. The master cylinder central valves are di-
rectly actuated by the booster push rod.
The pedal travel sensor is mounted in the forward
face of the booster shell. The sensor plunger is actu-
ated by the booster diaphragm plate.
PEDAL TRAVEL SENSOR
The pedal travel sensor signals brake pedal posi-
tion to the antilock ECU. The sensor signal is based
on changes in electrical resistance. The resistance
changes occur in steps that are generated by changes
in brake pedal position. A resistance signal gener-
ated by changing brake pedal position, will cause the
ECU to run the antilock pump when necessary.
The sensor is a plunger-type, electrical switch
mounted in the forward housing of the power brake
booster (Fig. 5). The sensor plunger is actuated by
movement of the booster diaphragm plate.
The tip on the sensor plunger is color coded. The
tip must be matched to the color dot on the face of
the brake booster front shell (Fig. 5).
WHEEL SPEED SENSORS
A sensor is used at each wheel. The sensors convert
wheel speed into an electrical signal. This signal is trans-
mitted to the antilock electronic control unit (ECU).
A gear-type tone ring serves as the trigger mecha-
nism for each sensor. The tone rings are mounted at
the outboard ends of the front and rear axle shafts.
Different sensors are used at the front and rear
wheels (Fig. 6). The front/rear sensors have the same
electrical values but are not interchangeable.
ELECTRONIC CONTROL UNIT (ECU)
A separate electronic control unit (ECU) monitors,
operates and controls the antilock system (Fig. 7).
The ECU contains dual microprocessors. The logic
block in each microprocessor receives identical sensor
signals. These signals are processed and compared si-
multaneously (Fig. 8).
The ECU is located under the instrument panel. It
is located at the right side of the steering column.
The power up voltage source for the ECU is through
the ignition switch in the On and Run positions.
The antilock ECU is separate from the other vehi-
cle electronic control units. It contains a self check
program that illuminates the amber warning light
when a system fault is detected. Faults are stored in
a diagnostic program memory and are accessible
with the DRB II scan tool.
ABS faults remain in memory until cleared, or until af-
ter the vehicle is started approximately 50 times. Stored
faults arenoterased if the battery is disconnected.
ACCELERATION SWITCH
An acceleration switch (Fig. 9), provides an addi-
tional vehicle deceleration reference during 4-wheel
drive operation. The switch is monitored by the anti-
lock ECU at all times.
The switch reference signal is utilized by the ECU
when all wheels are decelerating at the same speed.
Equal wheel speeds occur during braking in undiffer-
entiated 4-wheel ranges.
Fig. 5 Pedal Travel Sensor Location
Fig. 6 Wheel Speed Sensors
JBRAKES 5 - 41
Page 196 of 1784

Clean the reservoir and caps thoroughly before
checking level or adding fluid. Cap open lines and
hoses during service to prevent dirt entry.
Dirt or foreign material entering the ABS hydrau-
lic system through the reservoir opening will circu-
late within the system. The result will be poor brake
performance and possible component failure. Use
clean, fresh fluid only to top off, or refill the system.
WHEEL SENSOR AIR GAP ADJUSTMENT
Only rear sensor air gap is adjustable. The front
sensors are fixed and cannot be adjusted.
A rear sensor air gap adjustment is only
needed when reinstalling an original sensor. Re-
placement sensors have an air gap spacer at-
tached to the sensor pickup face. The spacer
establishes correct air gap when pressed against
the tone ring during installation. As the tone
ring rotates, it peels the spacer off the sensor to
create the required air gap.
Preferred rear sensor air gap is 1.1 mm (0.043 in.).
Acceptable air gap range is 0.92 to 1.275 mm (0.036
to 0.050 in.).
Front sensor air gap is not adjustable. The front
sensors are fixed in position and cannot be adjusted.
Front sensor air gap can only be checked. Air gap
should be 0.040 to 1.3 mm (0.0157 to 0.051 in.). If
front sensor air gap is incorrect, the sensor is either
loose, or damaged.
FRONT WHEEL SENSOR REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle and turn wheel outward for eas-
ier access to sensor.
(2) Remove sensor wire from mounting brackets.
(3) Clean sensor and surrounding area before removal.
(4) Remove bolt attaching sensor to steering
knuckle and remove sensor.
(5) Unseat grommet retaining sensor wire in wheel
house panel.
(6) In engine compartment, disconnect sensor wire con-
nector at harness plug. Then remove sensor and wire.
FRONT WHEEL SENSOR INSTALLATION
(1) Apply Mopar Lock N' Seal or Loctite 242 to
bolt that attaches sensor to steering knuckle. Use
new sensor bolt if original bolt is worn or damaged.
(2) Position sensor on steering knuckle. Seat sen-
sor locating tab in hole in knuckle and install sensor
attaching bolt finger tight.
(3) Tighten sensor bolt to 14 NIm (11 ft. lbs.) torque.
(4) Attach sensor wire to steering knuckle bracket
with grommets on sensor wire.
(5) Route sensor wire forward and behind shock
absorber. Then attach sensor wire to spring seat
bracket with grommets on sensor wire.
(6) Route sensor wire to outer sill bracket. Remove
all twists or kinks from wire.(7) Attach sensor wire to sill bracket with grom-
met. Be sure wire is free of twists and kinks.
(8) Verify sensor wire routing. Wire should loop
forward and above sill bracket. Loose end of wire
should be below sill bracket and towards brake hose.
(9) Seat sensor wire grommet in body panel and
clip wire to brake line at grommet location.
(10) Connect sensor wire to harness in engine com-
partment.
REAR WHEEL SENSOR REMOVAL
(1) On XJ models, if separate connectors are not
used to attach sensor harness to each sensor wire,
proceed as follows:
(a) Raise and fold rear seat forward for access to
rear sensor connectors (Figs. 4 and 5).
(b) Disconnect sensors at rear harness connectors.
(c) Push sensor grommets and sensor wires
through floorpan.
Fig. 4 Acceleration Switch And Rear Sensor
Connections (XJ)
Fig. 5 Rear Sensor Connections (XJ)
JABS COMPONENT SERVICE 5 - 49
Page 200 of 1784

ECU REPLACEMENTÐXJ
ECU Removal
(1) Turn ignition key to Off position.
(2) Remove screws attaching ECU to mounting
bracket (Fig. 12).
(3) Disconnect ECU wiring harness.
(4) Remove ECU.
ECU Installation
(1) If new ECU is being installed, transfer mount-
ing bracket to new ECU.
(2) Tighten ECU-to-mounting bracket screws to
8-13 Nzm (75-115 in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Connect wire harness to ECU.
(4) Position and install ECU.
(5) Tighten ECU attaching nuts to 10-14 Nzm (85-
125 in. lbs.) torque.
ECU REPLACEMENTÐYJ
The antilock electronic control unit (ECU) is attached
to the dash panel inside the passenger compartment. It
is positioned just above the heater/air conditioning ple-
num housing, in line with the glove box (Fig. 13).
The ECU is attached to the dash panel by bolts
and nuts that are accessible from the engine com-
partment. The fasteners are located just to the right
of the battery.
On models with air conditioning, it will be neces-
sary to remove the air conditioning fascia panel and
ducts for access to the ECU and harness connecter.
HCU REMOVALÐXJ
(1) Remove air cleaner.
(2) Remove clamp that secures air cleaner hose
and pipe to fender apron (Fig. 14).(3) Position suitable size fluid drain container un-
der master cylinder reservoir hoses. Disconnect reser-
voir hoses from HCU and drain fluid into container.
Discard old fluid and remove reservoir.
(4) Disconnect pump motor and solenoid harness
wires at HCU (Fig. 15).
Fig. 12 Antilock ECU Mounting (XJ)
Fig. 13 ECU Location (YJ)
Fig. 14 Air Cleaner And Harness Connector Location (XJ)
Fig. 15 HCU Wire Harness Connections
JABS COMPONENT SERVICE 5 - 53
Page 201 of 1784
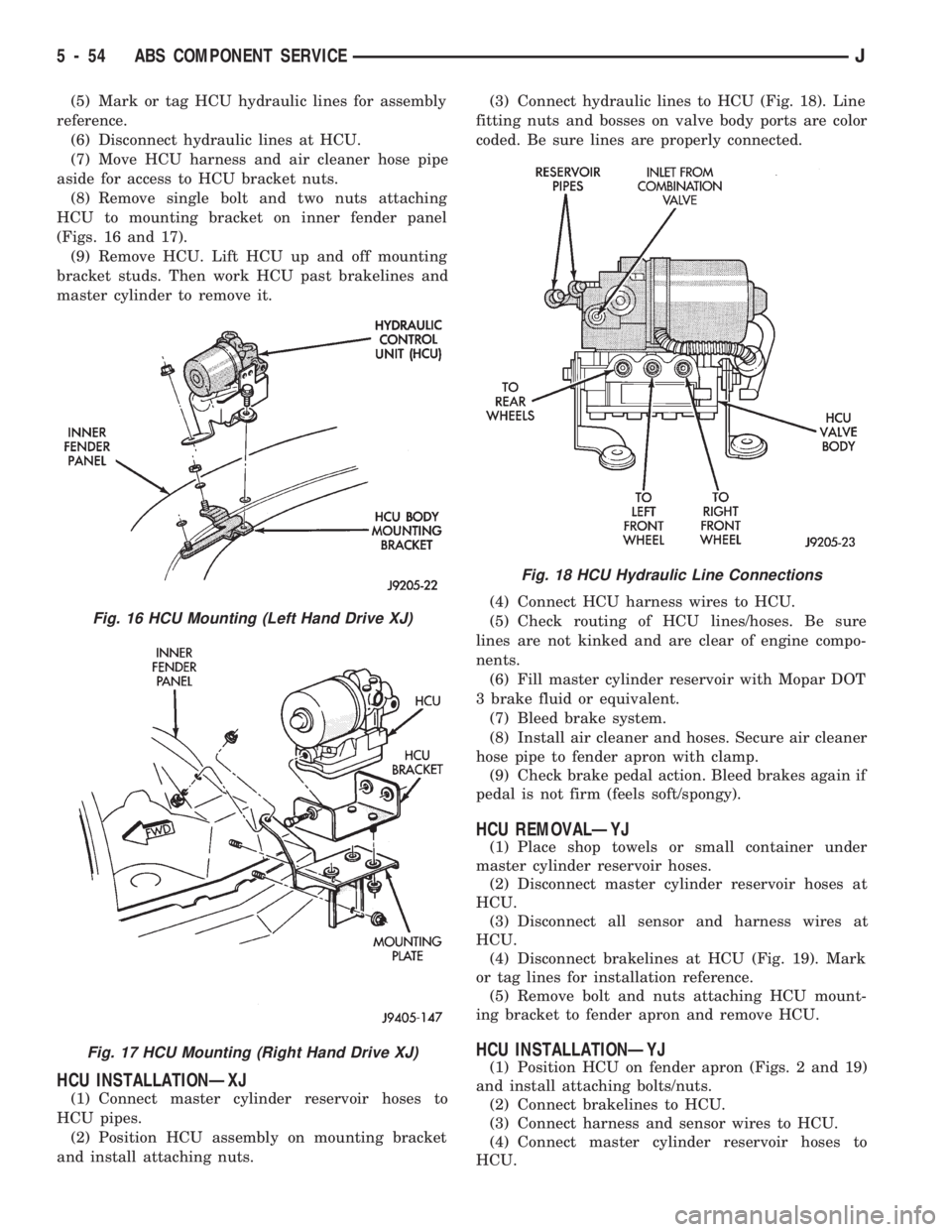
(5) Mark or tag HCU hydraulic lines for assembly
reference.
(6) Disconnect hydraulic lines at HCU.
(7) Move HCU harness and air cleaner hose pipe
aside for access to HCU bracket nuts.
(8) Remove single bolt and two nuts attaching
HCU to mounting bracket on inner fender panel
(Figs. 16 and 17).
(9) Remove HCU. Lift HCU up and off mounting
bracket studs. Then work HCU past brakelines and
master cylinder to remove it.
HCU INSTALLATIONÐXJ
(1) Connect master cylinder reservoir hoses to
HCU pipes.
(2) Position HCU assembly on mounting bracket
and install attaching nuts.(3) Connect hydraulic lines to HCU (Fig. 18). Line
fitting nuts and bosses on valve body ports are color
coded. Be sure lines are properly connected.
(4) Connect HCU harness wires to HCU.
(5) Check routing of HCU lines/hoses. Be sure
lines are not kinked and are clear of engine compo-
nents.
(6) Fill master cylinder reservoir with Mopar DOT
3 brake fluid or equivalent.
(7) Bleed brake system.
(8) Install air cleaner and hoses. Secure air cleaner
hose pipe to fender apron with clamp.
(9) Check brake pedal action. Bleed brakes again if
pedal is not firm (feels soft/spongy).
HCU REMOVALÐYJ
(1) Place shop towels or small container under
master cylinder reservoir hoses.
(2) Disconnect master cylinder reservoir hoses at
HCU.
(3) Disconnect all sensor and harness wires at
HCU.
(4) Disconnect brakelines at HCU (Fig. 19). Mark
or tag lines for installation reference.
(5) Remove bolt and nuts attaching HCU mount-
ing bracket to fender apron and remove HCU.
HCU INSTALLATIONÐYJ
(1) Position HCU on fender apron (Figs. 2 and 19)
and install attaching bolts/nuts.
(2) Connect brakelines to HCU.
(3) Connect harness and sensor wires to HCU.
(4) Connect master cylinder reservoir hoses to
HCU.
Fig. 16 HCU Mounting (Left Hand Drive XJ)
Fig. 17 HCU Mounting (Right Hand Drive XJ)
Fig. 18 HCU Hydraulic Line Connections
5 - 54 ABS COMPONENT SERVICEJ
Page 208 of 1784
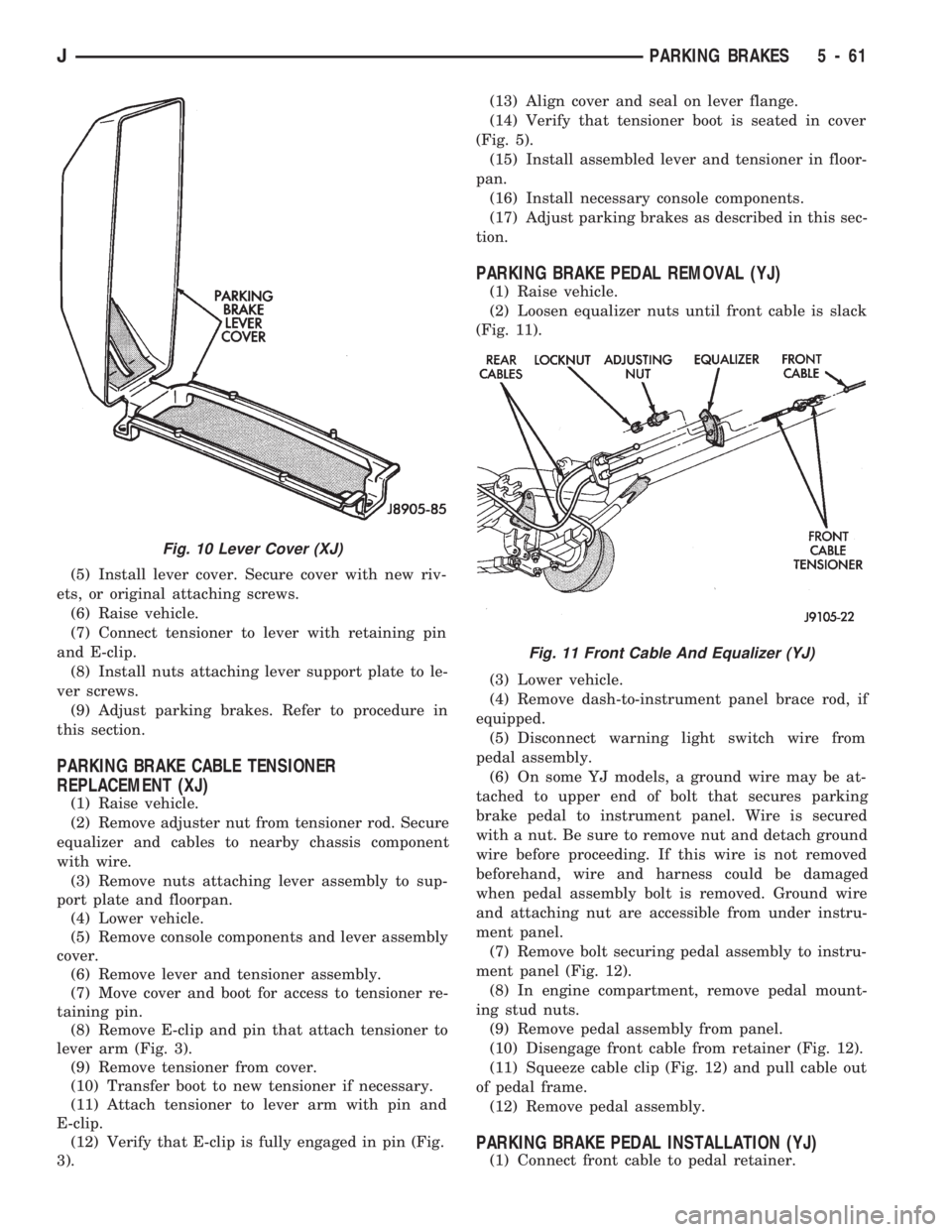
(5) Install lever cover. Secure cover with new riv-
ets, or original attaching screws.
(6) Raise vehicle.
(7) Connect tensioner to lever with retaining pin
and E-clip.
(8) Install nuts attaching lever support plate to le-
ver screws.
(9) Adjust parking brakes. Refer to procedure in
this section.
PARKING BRAKE CABLE TENSIONER
REPLACEMENT (XJ)
(1) Raise vehicle.
(2) Remove adjuster nut from tensioner rod. Secure
equalizer and cables to nearby chassis component
with wire.
(3) Remove nuts attaching lever assembly to sup-
port plate and floorpan.
(4) Lower vehicle.
(5) Remove console components and lever assembly
cover.
(6) Remove lever and tensioner assembly.
(7) Move cover and boot for access to tensioner re-
taining pin.
(8) Remove E-clip and pin that attach tensioner to
lever arm (Fig. 3).
(9) Remove tensioner from cover.
(10) Transfer boot to new tensioner if necessary.
(11) Attach tensioner to lever arm with pin and
E-clip.
(12) Verify that E-clip is fully engaged in pin (Fig.
3).(13) Align cover and seal on lever flange.
(14) Verify that tensioner boot is seated in cover
(Fig. 5).
(15) Install assembled lever and tensioner in floor-
pan.
(16) Install necessary console components.
(17) Adjust parking brakes as described in this sec-
tion.
PARKING BRAKE PEDAL REMOVAL (YJ)
(1) Raise vehicle.
(2) Loosen equalizer nuts until front cable is slack
(Fig. 11).
(3) Lower vehicle.
(4) Remove dash-to-instrument panel brace rod, if
equipped.
(5) Disconnect warning light switch wire from
pedal assembly.
(6) On some YJ models, a ground wire may be at-
tached to upper end of bolt that secures parking
brake pedal to instrument panel. Wire is secured
with a nut. Be sure to remove nut and detach ground
wire before proceeding. If this wire is not removed
beforehand, wire and harness could be damaged
when pedal assembly bolt is removed. Ground wire
and attaching nut are accessible from under instru-
ment panel.
(7) Remove bolt securing pedal assembly to instru-
ment panel (Fig. 12).
(8) In engine compartment, remove pedal mount-
ing stud nuts.
(9) Remove pedal assembly from panel.
(10) Disengage front cable from retainer (Fig. 12).
(11) Squeeze cable clip (Fig. 12) and pull cable out
of pedal frame.
(12) Remove pedal assembly.
PARKING BRAKE PEDAL INSTALLATION (YJ)
(1) Connect front cable to pedal retainer.
Fig. 10 Lever Cover (XJ)
Fig. 11 Front Cable And Equalizer (YJ)
JPARKING BRAKES 5 - 61
Page 219 of 1784

when handling the cover and disc. Impact can distort
the cover, diaphragm spring, release fingers and the
hub of the clutch disc.
Use an alignment tool when positioning the disc on
the flywheel. The tool prevents accidental misalign-
ment which could result in cover distortion and disc
damage.
A frequent cause of clutch cover distortion (and
consequent misalignment) is improper bolt tighten-
ing. To avoid warping the cover, the bolts must tight-
ened alternately (diagonal pattern) and evenly (2-3
threads at a time) to specified torque.
Clutch Housing Misalignment
Clutch housing alignment is important to proper
clutch operation. The housing maintains alignment
between the crankshaft and transmission input shaft.
Misalignment can cause clutch noise, hard shifting,
incomplete release and chatter. It can also result in
premature wear of the pilot bearing, cover release
fingers and clutch disc. In severe cases, misalign-
ment can also cause premature wear of the transmis-
sion input shaft and shaft bearing.
Housing misalignment is generally caused by in-
correct seating on the engine or transmission, loose
housing bolts, missing alignment dowels or housing
damage. Infrequently, misalignment may also be
caused by housing mounting surfaces that are not
completely parallel. Misalignment can be corrected
with shims.INSTALLATION METHODS AND PARTS
USAGE
Distortion of clutch components during installation
and the use of non-standard components are addi-
tional causes of clutch malfunction.
Improper clutch cover bolt tightening can distort
the cover. The usual result is clutch grab, chatter
and rapid wear. Tighten the cover bolts as described
in Clutch Service section.
An improperly seated flywheel and/or clutch hous-
ing are additional causes of clutch failure. Improper
seating will produce misalignment and additional
clutch problems.
The use of non-standard or low quality parts will
also lead to problems and wear. Use recommended
factory quality parts to avoid comebacks.
INSPECTION AND DIAGNOSIS CHARTS
The clutch inspection chart (Fig. 1) outlines items
to be checked before and during clutch installation.
Use the chart as a check list to help avoid overlook-
ing potential problem sources during service opera-
tions.
The diagnosis charts describe common clutch prob-
lems, causes and correction. Fault conditions are
listed at the top of each chart. Conditions, causes and
corrective action are outlined in the indicated col-
umns.
The charts are provided as a convenient reference
when diagnosing faulty clutch operation.
6 - 4 CLUTCH DIAGNOSISJ
Page 225 of 1784

CLUTCH SERVICE
INDEX
page page
Clutch Cover and Disc Installation............ 10
Clutch Cover and Disc Removal............. 10
Clutch Fluid Level........................ 14
Clutch Housing Replacement................ 11
Clutch Hydraulic Linkage Installation.......... 12
Clutch Hydraulic Linkage Removal........... 11Clutch Pedal Installation................... 15
Clutch Pedal Removal..................... 15
Clutch Safety Precautions.................. 10
Flywheel Service......................... 15
Pilot Bearing Replacement................. 11
Release Bearing Replacement............... 11
CLUTCH SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
WARNING: EXERCISE CARE WHEN SERVICING
CLUTCH COMPONENTS. DUST AND DIRT ON
CLUTCH PARTS USE MAY CONTAIN ASBESTOS FI-
BERS. BREATHING EXCESSIVE CONCENTRATIONS
OF THESE FIBERS CAN CAUSE SERIOUS BODILY
HARM. WEAR A RESPIRATOR DURING SERVICE
AND NEVER CLEAN CLUTCH COMPONENTS WITH
COMPRESSED AIR OR WITH A DRY BRUSH. EI-
THER CLEAN THE COMPONENTS WITH A WATER
DAMPENED RAGS OR USE A VACUUM CLEANER
SPECIFICALLY DESIGNED FOR REMOVING ASBES-
TOS FIBERS AND DUST. DO NOT CREATE DUST
BY SANDING A CLUTCH DISC. REPLACE THE DISC
IF THE FRICTION MATERIAL IS DAMAGED OR
CONTAMINATED. DISPOSE OF ALL DUST AND
DIRT CONTAINING ASBESTOS FIBERS IN SEALED
BAGS OR CONTAINERS. THIS WILL HELP MINIMIZE
EXPOSURE TO YOURSELF AND TO OTHERS. FOL-
LOW ALL RECOMMENDED SAFETY PRACTICES
PRESCRIBED BY THE OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY
AND HEALTH ADMINISTRATION (OSHA) AND THE
ENVIRONMENTAL SAFETY AGENCY (EPA), FOR
THE HANDLING AND DISPOSAL OF PRODUCTS
CONTAINING ASBESTOS.
CLUTCH COVER AND DISC REMOVAL
(1) Remove transmission. Refer to procedures in
Group 21.
(2) If original clutch cover will be reinstalled,
mark position of cover on flywheel for assembly ref-
erence. Use paint or a scriber for this purpose.
(3) If clutch cover is to be replaced, cover bolts can
be removed in any sequence. However, if original
cover will be reinstalled, loosen cover bolts evenly
and in rotation to relieve spring tension equally.
This is necessary avoid warping cover.
(4) Remove cover bolts and remove cover and disc
(Fig. 2).
CLUTCH COVER AND DISC INSTALLATION
(1) Lightly scuff sand flywheel face with 180 grit
emery cloth. Then clean surface with a wax and
grease remover.
(2) Lubricate pilot bearing with Mopar high tem-
perature bearing grease.
(3) Check runout and free operation of new clutch
disc as follows:
(a) Slide disc onto transmission input shaft
splines. Disc should slide freely on splines.
(b) Leave disc on shaft and check face runout
with dial indicator. Check runout at disc hub and
about 6 mm (1/4 in.) from outer edge of facing.
(c) Face runout should not exceed 0.5 mm (0.020
in.). Obtain another clutch disc if runout exceeds
this limit.
(4) Position clutch disc on flywheel. Be sure side of
disc marked flywheel side is positioned against fly-
wheel (Fig. 2). If disc is not marked, be sure flat side
of disc hub is toward flywheel.
(5) Insert clutch alignment tool in clutch disc (Fig.
3).
(6) Insert alignment tool in pilot bearing and posi-
tion disc on flywheel. Be sure disc hub is positioned
correctly. Side of hub marked Flywheel Side should
face flywheel (Fig. 2). If disc is not marked, place flat
side of disc against flywheel.
(7) Position clutch cover over disc and on flywheel
(Fig. 3).
(8) Install clutch cover bolts finger tight.
(9) Tighten cover bolts evenly and in rotation a
few threads at a time.Cover bolts must be tight-
ened evenly and to specified torque to avoid dis-
torting cover. Tightening torques are 31 Nzm (23
ft. lbs.) on 2.5L engines and 54 Nzm (40 ft. lbs.) on
4.0L engines.
(10) Apply light coat of Mopar high temperature
bearing grease to pilot bearing hub and splines of
transmission input shaft.Do not overlubricate
shaft splines. This will result in grease contami-
nation of disc.
(11) Install transmission (Fig. 4). Refer to proce-
dures in Group 21.
6 - 10 CLUTCH SERVICEJ
Page 227 of 1784
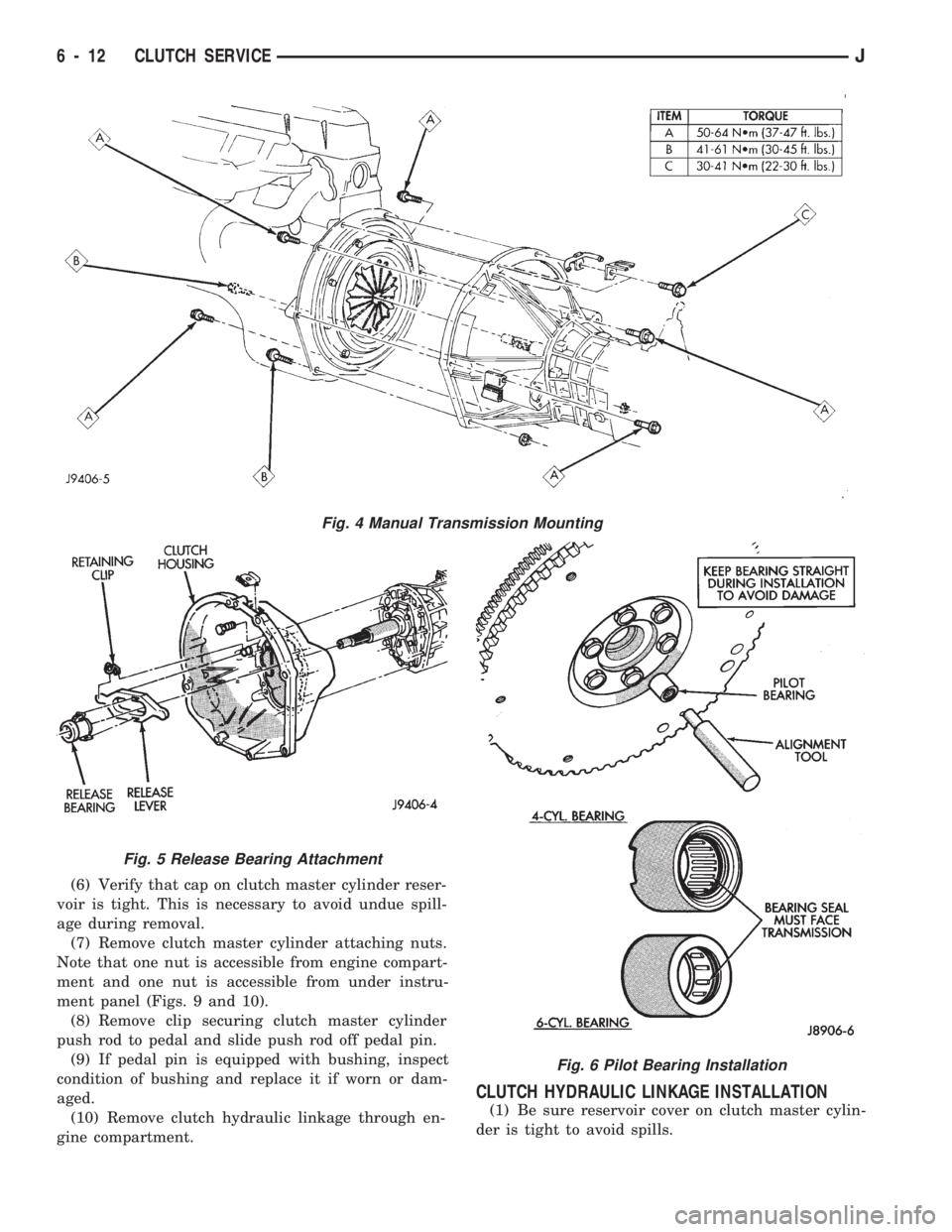
(6) Verify that cap on clutch master cylinder reser-
voir is tight. This is necessary to avoid undue spill-
age during removal.
(7) Remove clutch master cylinder attaching nuts.
Note that one nut is accessible from engine compart-
ment and one nut is accessible from under instru-
ment panel (Figs. 9 and 10).
(8) Remove clip securing clutch master cylinder
push rod to pedal and slide push rod off pedal pin.
(9) If pedal pin is equipped with bushing, inspect
condition of bushing and replace it if worn or dam-
aged.
(10) Remove clutch hydraulic linkage through en-
gine compartment.
CLUTCH HYDRAULIC LINKAGE INSTALLATION
(1) Be sure reservoir cover on clutch master cylin-
der is tight to avoid spills.
Fig. 4 Manual Transmission Mounting
Fig. 5 Release Bearing Attachment
Fig. 6 Pilot Bearing Installation
6 - 12 CLUTCH SERVICEJ