check engine JEEP CHEROKEE 1994 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 1994, Model line: CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP CHEROKEE 1994Pages: 1784, PDF Size: 77.09 MB
Page 1011 of 1784

Excessive Oil Consumption: Although the PCM
monitors exhaust stream oxygen content through ox-
ygen sensor (closed loop), it cannot determine exces-
sive oil consumption.
Throttle Body Air Flow: The PCM cannot detect
a clogged or restricted air cleaner inlet or air filter
element.
Evaporative System: The PCM will not detect a
restricted, plugged or loaded EVAP canister.
Vacuum Assist: Leaks or restrictions in the vac-
uum circuits of vacuum assisted engine control sys-
tem devices are not monitored by the PCM. However,
a vacuum leak at the MAP sensor will be monitored
and a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) will be gener-
ated by the PCM.
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) System
Ground: The PCM cannot determine a poor system
ground. However, a DTC may be generated as a re-
sult of this condition.
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) Connector
Engagement: The PCM cannot determine spread or
damaged connector pins. However, a DTC may be
generated as a result of this condition.
HIGH AND LOW LIMITS
The powertrain control module (PCM) compares in-
put signal voltages from each input device. It will es-
tablish high and low limits that are programmed into
it for that device. If the input voltage is not within
specifications and other Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC) criteria are met, a DTC will be stored in mem-
ory. Other DTC criteria might include engine rpm
limits or input voltages from other sensors or
switches. The other inputs might have to be sensed
by the PCM when it senses a high or low input volt-
age from the control system device in question.
ACCESSING DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
A stored Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) can be dis-
played by cycling the ignition key On-Off-On-Off-On
within three seconds and observing the Malfunction
Indicator Lamp. This lamp was formerly referred to
as the Check Engine Lamp. The lamp is located on
the instrument panel.
They can also be displayed through the use of the
Diagnostic Readout Box (DRB) scan tool. The DRB
scan tool connects to the data link connector in the
engine compartment (Figs. 45 or 46). For operation of
the DRB, refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diag-
nostic Procedures service manual.
EXAMPLES:
²If the lamp flashes 4 times, pauses and flashes 1
more time, a flashing Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC)
number 41 is indicated.
²If the lamp flashes 4 times, pauses and flashes 6
more times, a flashing Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC) number 46 is indicated.After any stored DTC information has been ob-
served, the display will end with a flashing DTC
number 55. This will indicate the end of all stored
information.
Refer to the Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) charts
for DTC identification.
If the problem is repaired or ceases to exist, the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) cancels the DTC
after 51 engine starts.
Diagnostic Trouble Codes indicate the results of a
failure, but never identify the failed component di-
rectly.
The circuits of the data link connector are shown
in (Fig. 47).
ERASING TROUBLE CODES
After the problem has been repaired, use the DRB
scan tool to erase a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC).
Refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic Pro-
cedures service manual for operation of the DRB
scan tool.
Fig. 45 Data Link ConnectorÐYJ ModelsÐTypical
Fig. 46 Data Link ConnectorÐXJ ModelsÐTypical
14 - 50 FUEL SYSTEMJ
Page 1012 of 1784

DRB SCAN TOOL
For operation of the DRB scan tool, refer to the ap-
propriate Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures service
manual.
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC)
On the following pages, a list of diagnostic trouble
codes is provided for the 2.5L 4 cylinder and 4.0L 6
cylinder engines. A DTC indicates that the power-
train control module (PCM) has recognized an abnor-
mal signal in a circuit or the system. A DTC may
indicate the result of a failure, but never identify the
failed component directly.
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE DESCRIPTIONS
Diagnostic
Trouble
CodeDRB Scan Tool
DisplayDescription of Diagnostic Trouble Code
11* .......... NoCrank Reference
Signal at PCMNo crank reference signal detected during engine cranking.
12* ..........Battery Disconnect Direct battery input to PCM was disconnected within the last 50 Key-on
cycles.
13**.......... NoChange in MAP From
Start to RunNo difference recognized between the engine MAP reading and the
barometric (atmospheric) pressure reading at start-up.
14**.......... MAPSensor Voltage Too
LowMAP sensor input below minimum acceptable voltage.
or
MAP Sensor Voltage Too
HighMAP sensor input above maximum acceptable voltage.
15**.......... NoVehicle Speed Sensor
SignalNo vehicle distance (speed) sensor signal detected during road load
conditions.
17* ..........Engine is Cold Too Long Engine coolant temperature remains below normal operating temperatures
during vehicle travel (thermostat).
21**.......... O2SStays at Center Neither rich or lean condition detected from the oxygen sensor input.
or
O2S Shorted to Voltage Oxygen sensor input voltage maintained above the normal operating range.
22**.......... ECTSensor Voltage Too
HighEngine coolant temperature sensor input above maximum acceptable
voltage.
or
ECT Sensor Voltage Too
LowEngine coolant temperature sensor input below minimum acceptable voltage.
* Check Engine Lamp will not illuminate at all times if this Diagnostic Trouble Code was recorded. Cycle Ignition key as
described in manual and observe code flashed by Check Engine lamp.
** Check Engine Lamp will illuminate during engine operation if this Diagnostic Trouble Code was recorded.
Fig. 47 Data Link Connector Schematic
JFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 51
Page 1013 of 1784
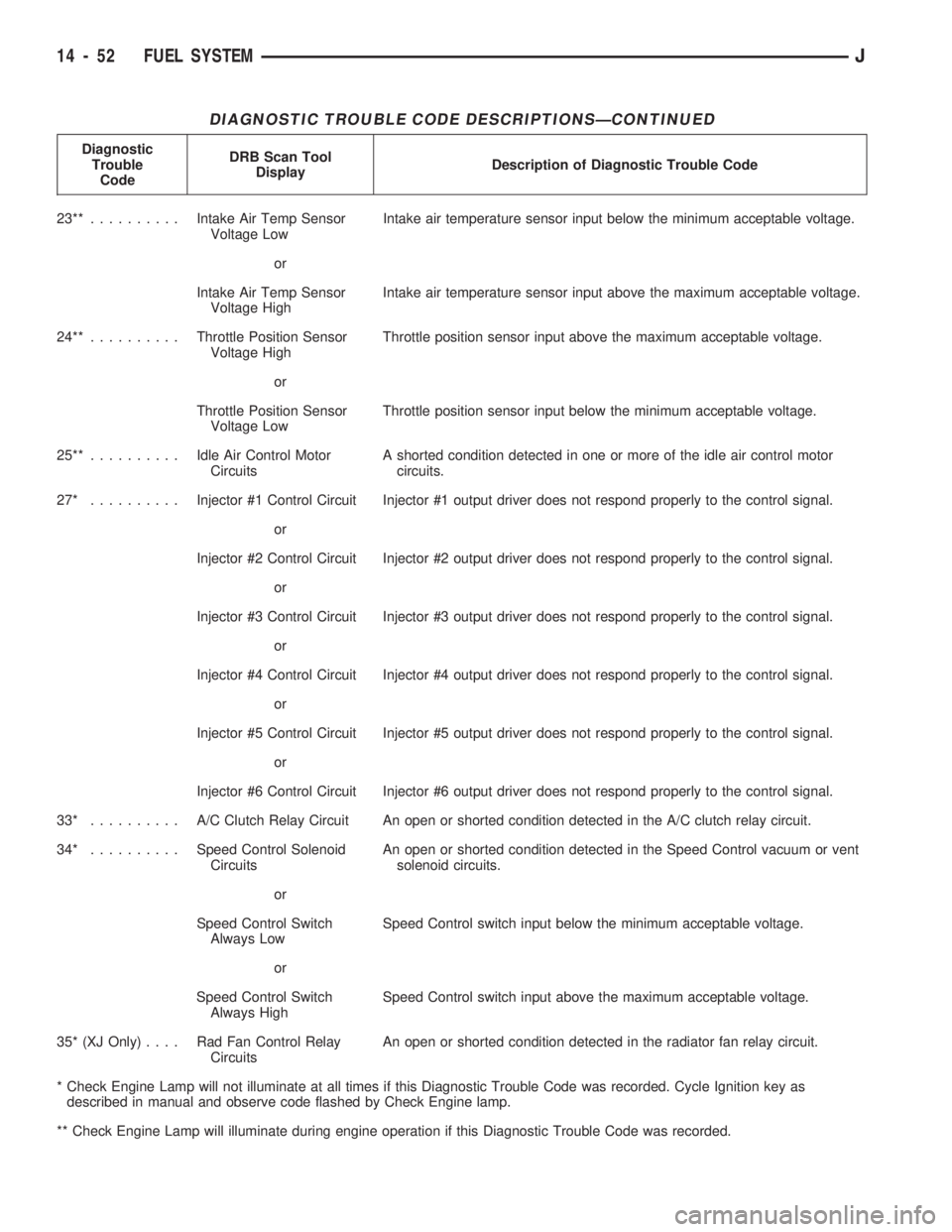
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE DESCRIPTIONSÐCONTINUED
Diagnostic
Trouble
CodeDRB Scan Tool
DisplayDescription of Diagnostic Trouble Code
23**..........Intake Air Temp Sensor
Voltage LowIntake air temperature sensor input below the minimum acceptable voltage.
or
Intake Air Temp Sensor
Voltage HighIntake air temperature sensor input above the maximum acceptable voltage.
24**..........Throttle Position Sensor
Voltage HighThrottle position sensor input above the maximum acceptable voltage.
or
Throttle Position Sensor
Voltage LowThrottle position sensor input below the minimum acceptable voltage.
25**..........Idle Air Control Motor
CircuitsA shorted condition detected in one or more of the idle air control motor
circuits.
27* ..........Injector #1 Control Circuit Injector #1 output driver does not respond properly to the control signal.
or
Injector #2 Control Circuit Injector #2 output driver does not respond properly to the control signal.
or
Injector #3 Control Circuit Injector #3 output driver does not respond properly to the control signal.
or
Injector #4 Control Circuit Injector #4 output driver does not respond properly to the control signal.
or
Injector #5 Control Circuit Injector #5 output driver does not respond properly to the control signal.
or
Injector #6 Control Circuit Injector #6 output driver does not respond properly to the control signal.
33* .......... A/CClutch Relay Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the A/C clutch relay circuit.
34* ..........Speed Control Solenoid
CircuitsAn open or shorted condition detected in the Speed Control vacuum or vent
solenoid circuits.
or
Speed Control Switch
Always LowSpeed Control switch input below the minimum acceptable voltage.
or
Speed Control Switch
Always HighSpeed Control switch input above the maximum acceptable voltage.
35* (XJ Only).... RadFanControl Relay
CircuitsAn open or shorted condition detected in the radiator fan relay circuit.
* Check Engine Lamp will not illuminate at all times if this Diagnostic Trouble Code was recorded. Cycle Ignition key as
described in manual and observe code flashed by Check Engine lamp.
** Check Engine Lamp will illuminate during engine operation if this Diagnostic Trouble Code was recorded.
14 - 52 FUEL SYSTEMJ
Page 1014 of 1784

DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE DESCRIPTIONSÐCONTINUED
Diagnostic
Trouble
CodeDRB Scan Tool
DisplayDescription of Diagnostic Trouble Code
41**..........Generator Field Not
Switching ProperlyAn open or shorted condition detected in the generator field control circuit.
42* ..........Auto Shutdown Relay
Control CircuitAn open or shorted condition detected in the auto shutdown relay circuit.
44* ..........Battery Temp Sensor
Volts out of LimitAn open or shorted condition exists in the engine coolant temperature sensor
circuit or a problem exists in the PCM's battery temperature voltage circuit.
46**..........Charging System Voltage
Too HighBattery voltage sense input above target charging voltage during engine
operation.
47**..........Charging System Voltage
Too LowBattery voltage sense input below target charging during engine operation.
Also, no significant change detected in battery voltage during active test of
generator output.
51**.......... O2SSignal Stays Below
Center (Lean)Oxygen sensor signal input indicates lean air/fuel ratio condition during
engine operation.
52**.......... O2SSignal Stays Above
Center (Rich)Oxygen sensor signal input indicates rich air/fuel ratio condition during
engine operation.
53* ..........Internal PCM Failure PCM Internal fault condition detected.
or
PCM Failure SPI
CommunicationsPCM Internal fault condition detected.
54* .......... NoCamSync Signal at
PCMNo fuel sync (camshaft signal) detected during engine cranking.
55* .......... N/ACompletion of diagnostic trouble code display on the Malfunction Indicator
Lamp (Check Engine Lamp).
62* .......... PCMFailure SPI miles not
storedUnsuccessful attempt to update SPI miles in the PCM EEPROM.
63* .......... PCMFailure EEPROM
Write DeniedUnsuccessful attempt to write to an EEPROM location by the PCM.
* Check Engine Lamp will not illuminate at all times if this Diagnostic Trouble Code was recorded. Cycle Ignition key as
described in manual and observe code flashed by Check Engine lamp.
** Check Engine Lamp will illuminate during engine operation if this Diagnostic Trouble Code was recorded.
JFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 53
Page 1017 of 1784

INSTALLATION
(1) Install the fuel injector(s) into the fuel rail as-
sembly and install retaining clip(s).
(2) Install fuel rail. Refer to Fuel Rail Installation
in this section.
(3) Start engine and check for fuel leaks.
FUEL PUMP MODULE
Refer to the Fuel Delivery System section of this
group for removal/installation procedures.
FUEL PUMP RELAY
The Fuel Pump relay is located in the Power Dis-
tribution Center (PDC) (Figs. 1 or 2). For location of
this relay within the PDC, refer to label on PDC
cover.
FUEL RAIL ASSEMBLY
REMOVAL
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER CON-
STANT FUEL PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE
OFF) OF APPROXIMATELY 131-269 KPA (19-39
PSI). THIS PRESSURE MUST BE RELEASED BE-
FORE SERVICING THE FUEL RAIL.
(1) Remove fuel tank filler tube cap.
(2) Disconnect the negative battery cable from bat-
tery.
(3) Perform the Fuel System Pressure Release Pro-
cedure as described in the Fuel Delivery System sec-
tion of this Group.
(4) Remove and numerically attach a tag (if fuel
injector is not already tagged), the injector harness
connectors. Do this at each injector (Fig. 7).
(5) Disconnect vacuum line from fuel pressure reg-
ulator (Fig. 7).
(6) Disconnect fuel supply line from fuel rail and
the fuel return line from fuel pressure regulator (Fig.7). Refer to Fuel Tubes/Lines/Hoses and Clamps, or
Quick-Connect Fittings. These can both be found in
the Fuel Delivery section of this group.
(7) Remove fuel rail mounting bolts.
On models with automatic transmissions, it may be
necessary to remove automatic transmission throttle
line pressure cable (and bracket). This will aid in fuel
rail assembly removal.
(8) Remove fuel rail by gently rocking until all the
fuel injectors are out of the intake manifold.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position tips of all fuel injectors into the corre-
sponding injector bore in the intake manifold. Seat
injectors into manifold.
(2) Tighten fuel rail mounting bolts to 27 Nzm (20
ft. lbs.) torque.
(3) Connect injector harness connectors to appro-
priate (tagged) injector.
(4) Connect both fuel lines to fuel rail.
(5) Connect vacuum supply line to fuel pressure
regulator.
(6) Install protective cap to pressure test port fit-
ting.
(7) Install fuel tank cap.
(8) Connect negative battery cable to battery.
(9) Start engine and check for fuel leaks.
FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE RELEASE PROCEDURE
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE OFF)
OF APPROXIMATELY 100 KPA (14.5 PSI). BEFORE
SERVICING THE FUEL PUMP, FUEL LINES, FUEL
FILTER OR FUEL INJECTOR, THE FUEL SYSTEM
PRESSURE MUST BE RELEASED.
Refer to the Fuel Delivery System section of this
group. See Fuel Pressure Release procedure.
FUEL TANKS
Refer to the Fuel Tank section of this group for re-
moval/installation procedures.
FUEL TANK PRESSURE RELIEF/ROLLOVER VALVE
Refer to the Fuel Tank section of this group for re-
moval/installation procedures.
FUEL TUBES/LINES/HOSES AND CLAMPS
Refer to the Fuel Delivery System section of this
group for removal/installation procedures. Also refer
to Quick-Connect Fittings in the Fuel Delivery sec-
tion of this group.
IDLE AIR CONTROL (IAC) MOTOR
The IAC motor is mounted to the throttle body ad-
jacent to the throttle position sensor (Fig. 8).
Fig. 7 Fuel Injector HarnessÐTypical
14 - 56 FUEL SYSTEMJ
Page 1019 of 1784

(3) Lower the vehicle.
PARK NEUTRAL SWITCH
Refer to Group 21, Transmissions for park neutral
switch service.
POWER STEERING PRESSURE SWITCHÐ2.5L
ENGINE ONLY
The power steering pressure switch is installed in
the power steering high pressure hose (Figs. 11 or
12).
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the electrical connector from the
power steering pressure switch.
(2) Place a small container or shop towel beneath
the switch to collect any excess fluid.
(3) Remove the switch.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the power steering switch.
(2) Connect the electrical connector to the switch.(3) Check power steering fluid and add as neces-
sary.
(4) Start the engine and again check power steer-
ing fluid. Add fluid if necessary.
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (PCM)
On XJ models, the PCM is located in the engine
compartment next to the air cleaner (Fig. 13). On YJ
models, the PCM is located in the engine compart-
ment behind the windshield washer fluid reservoir
(Fig. 14).
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the negative battery cable at the
battery.
(2) YJ Models Only: Remove the windshield
washer fluid tank.
(3) Loosen the 60-Way connector mounting bolt
(Figs. 13 or 14).
(4) Remove the electrical connector by pulling
straight back.
(5) Remove the three PCM mounting bolts.
(6) Remove PCM.
Fig. 11 Power Steering Pressure SwitchÐYJ Models
Fig. 12 Power Steering Pressure SwitchÐXJ Models
Fig. 13 PCM LocationÐXJ Models
Fig. 14 PCM LocationÐYJ Models
14 - 58 FUEL SYSTEMJ
Page 1021 of 1784
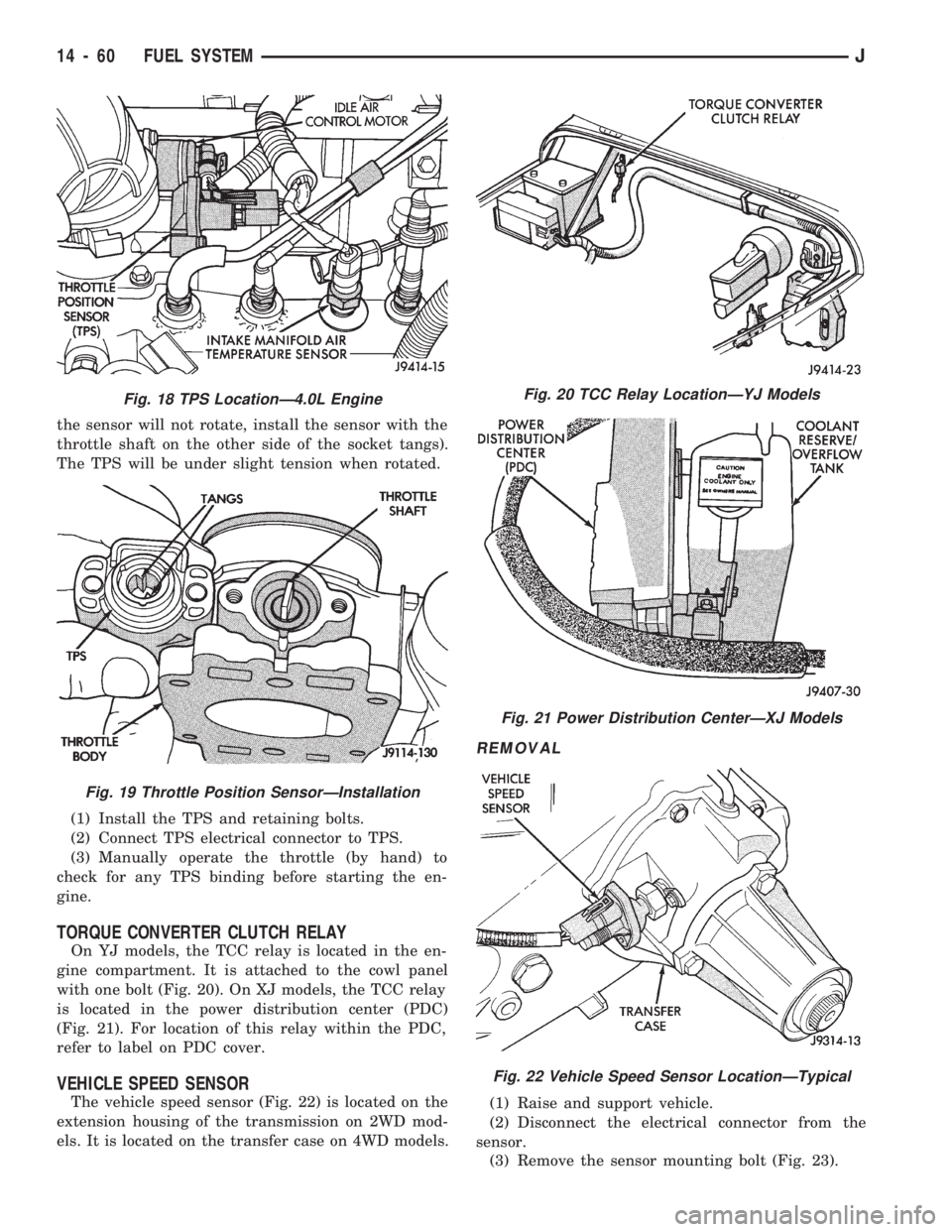
the sensor will not rotate, install the sensor with the
throttle shaft on the other side of the socket tangs).
The TPS will be under slight tension when rotated.
(1) Install the TPS and retaining bolts.
(2) Connect TPS electrical connector to TPS.
(3) Manually operate the throttle (by hand) to
check for any TPS binding before starting the en-
gine.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH RELAY
On YJ models, the TCC relay is located in the en-
gine compartment. It is attached to the cowl panel
with one bolt (Fig. 20). On XJ models, the TCC relay
is located in the power distribution center (PDC)
(Fig. 21). For location of this relay within the PDC,
refer to label on PDC cover.
VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR
The vehicle speed sensor (Fig. 22) is located on the
extension housing of the transmission on 2WD mod-
els. It is located on the transfer case on 4WD models.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Disconnect the electrical connector from the
sensor.
(3) Remove the sensor mounting bolt (Fig. 23).
Fig. 18 TPS LocationÐ4.0L Engine
Fig. 19 Throttle Position SensorÐInstallation
Fig. 20 TCC Relay LocationÐYJ Models
Fig. 21 Power Distribution CenterÐXJ Models
Fig. 22 Vehicle Speed Sensor LocationÐTypical
14 - 60 FUEL SYSTEMJ
Page 1026 of 1784

SERVICE DIAGNOSIS/PROCEDURES
INDEX
page page
Runout................................. 4
Unbalance............................... 3Universal Joint Angle Measurement............ 4
Vibration................................ 3
VIBRATION
Tires that are out-of-round or wheels that are un-
balanced will cause a low frequency vibration. Refer
to Group 22, Wheels and Tires for additional infor-
mation.
Brake drums that are unbalanced will cause a
harsh, low frequency vibration. Refer to Group 5,
Brakes for additional information.
Driveline vibration can also result from loose or
damaged engine mounts. Refer to Group 21, Trans-
missions for additional information.
Propeller shaft vibration will increase as the vehi-
cle speed is increased. A vibration that occurs within
a specific speed range is not caused by propeller
shaft unbalance. Defective universal joints or an in-
correct propeller shaft angle are usually the cause.
UNBALANCE
If propeller shaft unbalance is suspected, it can be
verified with the following procedure.
Removing and re-indexing the propeller shaft
180É may eliminate some vibrations.
²Clean all the foreign material from the propeller
shaft and the universal joints.²Inspect the propeller shaft for missing balance
weights, broken welds, and bent areas.If the pro-
peller shaft is bent, it must be replaced.
²Ensure the universal joints are not worn, are prop-
erly installed, and are correctly aligned with the
shaft.
²Check the universal joint clamp screws torque
(1) Raise the vehicle.
(2) Remove the wheel and tires assembly. Install
the wheel lug nuts to retain the brake drums.
(3) Mark and number the shaft six inches from the
yoke end at four positions 90É apart.
(4) Run and accelerate the vehicle until vibration
occurs. Note the intensity and speed the vibration oc-
curred. Stop the engine.
(5) Install a screw clamp at position 1 (Fig. 1).
(6) Start the engine and re-check for vibration. If
there is little or no change in vibration, move the
clamp to one of the other three positions. Repeat the
vibration test.
(7) If there is no difference in vibration at the
other positions, the vibration may not be propshaft
unbalance.
DRIVELINE VIBRATION
JPROPELLER SHAFTS 16 - 3
Page 1028 of 1784
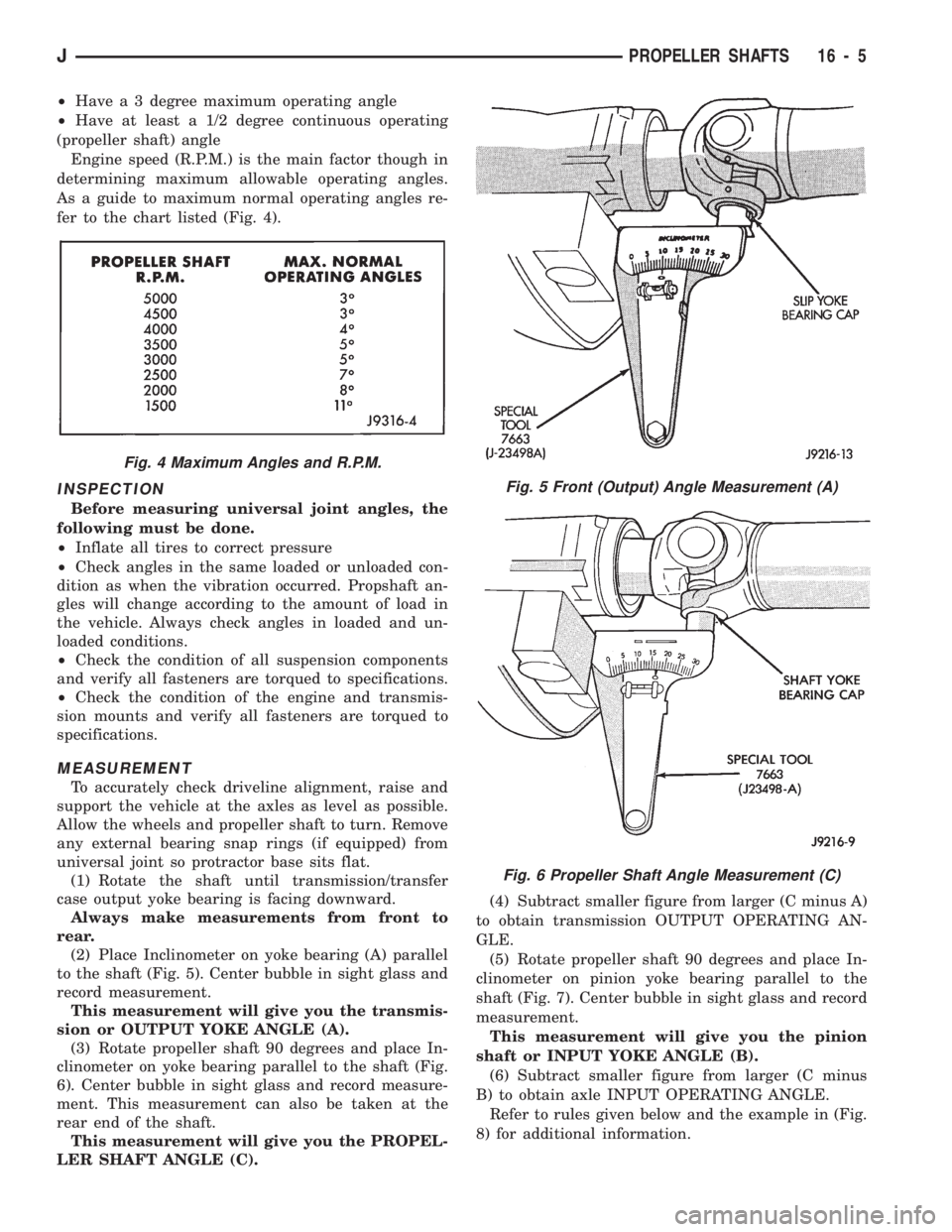
²Have a 3 degree maximum operating angle
²Have at least a 1/2 degree continuous operating
(propeller shaft) angle
Engine speed (R.P.M.) is the main factor though in
determining maximum allowable operating angles.
As a guide to maximum normal operating angles re-
fer to the chart listed (Fig. 4).
INSPECTION
Before measuring universal joint angles, the
following must be done.
²Inflate all tires to correct pressure
²Check angles in the same loaded or unloaded con-
dition as when the vibration occurred. Propshaft an-
gles will change according to the amount of load in
the vehicle. Always check angles in loaded and un-
loaded conditions.
²Check the condition of all suspension components
and verify all fasteners are torqued to specifications.
²Check the condition of the engine and transmis-
sion mounts and verify all fasteners are torqued to
specifications.
MEASUREMENT
To accurately check driveline alignment, raise and
support the vehicle at the axles as level as possible.
Allow the wheels and propeller shaft to turn. Remove
any external bearing snap rings (if equipped) from
universal joint so protractor base sits flat.
(1) Rotate the shaft until transmission/transfer
case output yoke bearing is facing downward.
Always make measurements from front to
rear.
(2) Place Inclinometer on yoke bearing (A) parallel
to the shaft (Fig. 5). Center bubble in sight glass and
record measurement.
This measurement will give you the transmis-
sion or OUTPUT YOKE ANGLE (A).
(3) Rotate propeller shaft 90 degrees and place In-
clinometer on yoke bearing parallel to the shaft (Fig.
6). Center bubble in sight glass and record measure-
ment. This measurement can also be taken at the
rear end of the shaft.
This measurement will give you the PROPEL-
LER SHAFT ANGLE (C).(4) Subtract smaller figure from larger (C minus A)
to obtain transmission OUTPUT OPERATING AN-
GLE.
(5) Rotate propeller shaft 90 degrees and place In-
clinometer on pinion yoke bearing parallel to the
shaft (Fig. 7). Center bubble in sight glass and record
measurement.
This measurement will give you the pinion
shaft or INPUT YOKE ANGLE (B).
(6) Subtract smaller figure from larger (C minus
B) to obtain axle INPUT OPERATING ANGLE.
Refer to rules given below and the example in (Fig.
8) for additional information.
Fig. 4 Maximum Angles and R.P.M.
Fig. 5 Front (Output) Angle Measurement (A)
Fig. 6 Propeller Shaft Angle Measurement (C)
JPROPELLER SHAFTS 16 - 5
Page 1040 of 1784

POWER STEERING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
PUMP PRESSURE TEST
(1) Check belt tension and adjust as necessary.
(2) Disconnect high pressure hose at gear or pump.
Use a container for dripping fluid.
(3) Connect Gauge 7617 (J21567) to both hoses us-
ing adapter fitting (Fig. 1). Connect spare pressure
hose to gear or pump.
(4) Open the test valve completely.
(5) Start engine and let idle.
(6) Check fluid level, add fluid as necessary.
(7) Gauge should read below 862 kPa (125 psi), if
above, inspect the hoses for restrictions and repair as
necessary. The initial pressure should be in the
range of 345-552 kPa (50-80 psi).CAUTION: The following test procedure involves
testing maximum pump pressure output and flow
control valve operation. Do not leave valve closed
for more than 5 seconds as the pump could be
damaged.
(8) Close valve fully three times and record highest
pressure indicated each time.All three readings
must be above specifications and within 345
kPa (50 psi) of each other.
²Pressures above specifications but not within 345
kPa (50 psi) of each other, replace pump.
²Pressures within 345 kPa (50 psi) of each other
but below specifications, replace pump.
CAUTION: Do not force the pump to operate against
the stops for more than 2 to 4 seconds at a time.
Pump damage will result.
(9) Open the test valve, turn steering wheel ex-
treme left and right positions against the stops.
Record the highest indicated pressure at each posi-
tion. Compare readings to specifications. If highest
output pressures are not the same against either
stop, the gear is leaking internally and must be re-
paired.
Fig. 1 Pressure Test Gauge
PUMP OPERATING SPECIFICATIONS
JSTEERING 19 - 3