Front axle JEEP CHEROKEE 1994 Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 1994, Model line: CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP CHEROKEE 1994Pages: 1784, PDF Size: 77.09 MB
Page 30 of 1784
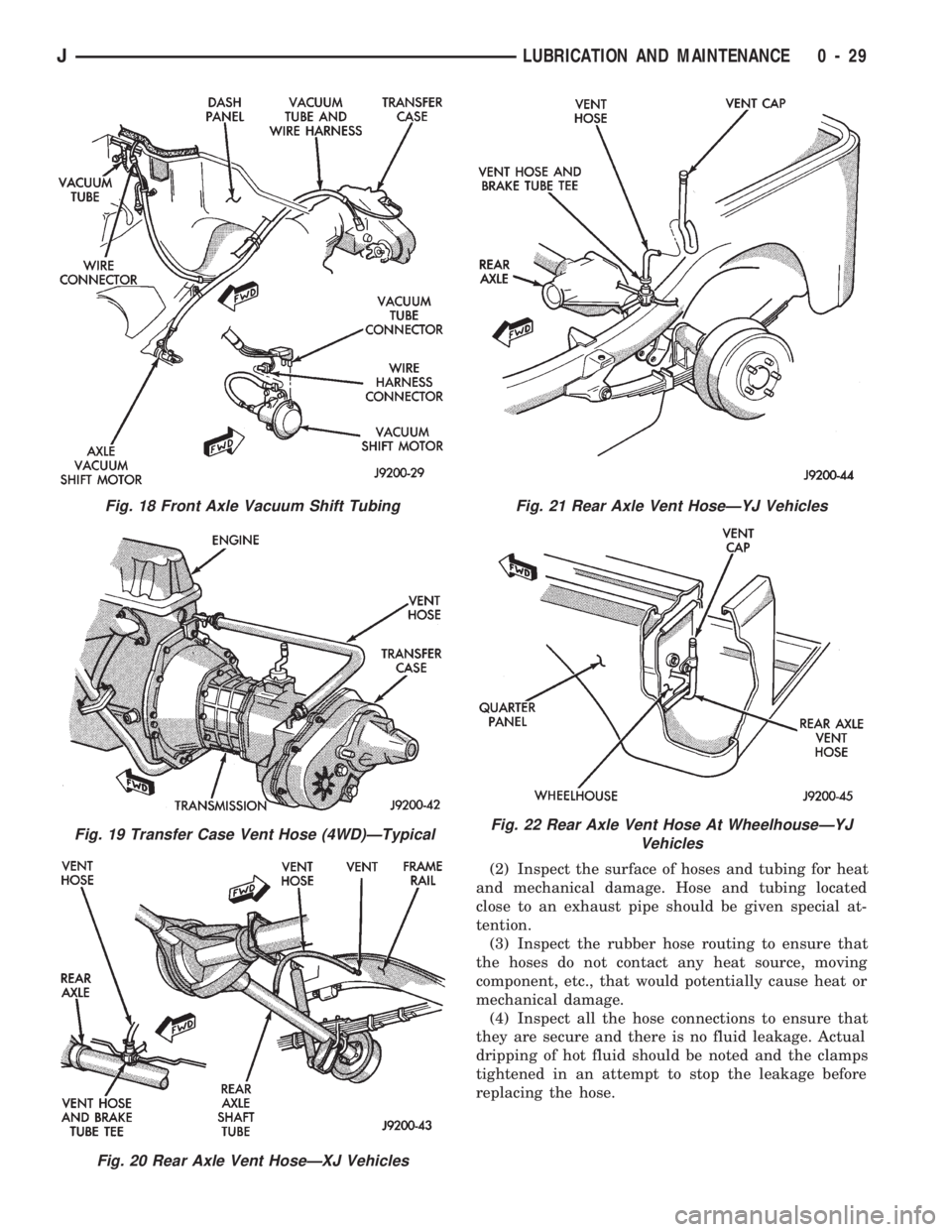
(2) Inspect the surface of hoses and tubing for heat
and mechanical damage. Hose and tubing located
close to an exhaust pipe should be given special at-
tention.
(3) Inspect the rubber hose routing to ensure that
the hoses do not contact any heat source, moving
component, etc., that would potentially cause heat or
mechanical damage.
(4) Inspect all the hose connections to ensure that
they are secure and there is no fluid leakage. Actual
dripping of hot fluid should be noted and the clamps
tightened in an attempt to stop the leakage before
replacing the hose.
Fig. 18 Front Axle Vacuum Shift Tubing
Fig. 19 Transfer Case Vent Hose (4WD)ÐTypical
Fig. 20 Rear Axle Vent HoseÐXJ Vehicles
Fig. 21 Rear Axle Vent HoseÐYJ Vehicles
Fig. 22 Rear Axle Vent Hose At WheelhouseÐYJ
Vehicles
JLUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE 0 - 29
Page 32 of 1784

FRONT WHEEL BEARINGS
Only 2WD XJ vehicles are equipped with front
wheel bearings. XJ vehicles have semi-floating axle
shafts and axle shaft bearings that are lubricated via
differential lube oil.
RECOMMENDED MAINTENANCEÐ2WD XJ
VEHICLES
The front wheel bearings should be lubricated (re-
packed) at the same time as front brake pad/caliper
service is conducted.
LUBRICANT SPECIFICATION
Wheel bearings should be lubricated with a lubri-
cant that is identified as NLGI GC-LB lubricant.
INSPECTION/LUBRICATION
(1) Remove the wheel/tire and the disc brake cali-
per.Do not disconnect the caliper brake fluid
hose unless the caliper must also be removed for
maintenance. Support the caliper with a hanger
to prevent brake fluid hose damage.
(2) Remove the dust cap, the cotter pin, the nut re-
tainer, the adjustment nut, and the thrust washer
from the spindle (Fig. 3). Discard the cotter pin.
(3) Remove the wheel outer bearing from the hub.
(4) Remove the wheel hub/disc brake rotor from
the spindle.
(5) Remove the seal and the inner wheel bearing
from the hub cavity.
(6) After removal, inspect both front wheel bearing
races for indications of pitting, brinelling and exces-
sive heat.
(7) Wipe the spindle clean and apply a small
amount of chassis/wheel bearing lubricant (NLGI
GC-LB lubricant) to prevent rust. Wipe the wheel
hub cavity clean.
CAUTION: Do not over-fill the wheel hub cavity with
lubricant. Excessive lubricant can cause overheat-ing and bearing damage. Also, excessive lubricant
can be forced out of the wheel hub cavity and con-
taminate the brake rotor/pads.
(8) Partially fill the wheel hub cavity with chassis/
wheel bearing lubricant (NLGI GC-LB lubricant).
(9) Pack the wheel bearings with chassis/wheel
bearing lubricant (NLGI GC-LB lubricant). Ensure
that sufficient lubricant is forced between the bear-
ing rollers.
(10) Install the wheel inner bearing in the wheel
hub and install a replacement seal.
(11) Clean the disc brake rotor contact surfaces, if
necessary.
(12) Install the wheel hub/disc brake rotor on the
spindle.
(13) Install the wheel outer bearing, the thrust
washer, and the spindle nut.
(14) Tighten the spindle nut with 28 NIm (21 ft.
lbs.) torque while rotating the disc brake rotor to
seat the bearings.
(15) Loosen the spindle nut 1/2 turn. While rotat-
ing the disc brake rotor, tighten the spindle nut with
2NIm (19 in. lbs.) torque.
(16) Install the nut retainer and a replacement cot-
ter pin.
(17) Clean the dust cap and apply wheel bearing
lubricant to the inside surface.Do not fill the dust
cap with lubricant.
(18) Install the dust cap.
(19) Install the disc brake caliper.
POWER STEERING SYSTEM
RECOMMENDED MAINTENANCE
The condition of power steering system should be
inspected and the fluid level checked. Add fluid as
necessary.
FLUID SPECIFICATION
Jeeptpower steering systems require MOPAR
Power Steering Fluid, or an equivalent product.
The original power steering fluid installed in
Jeeptvehicles includes black-light leak detec-
tion dye.
INSPECTION
Inspect the power steering system (Figs. 4 and 5)
for the sources of fluid leaks, steering gear housing
cracks and ensure that the steering gear is securely
attached to the vehicle frame rail. Inspect the steer-
ing damper for leaks and loose connections.
FLUID LEVEL
The fluid level dipstick is attached to the reservoir
cap (Fig. 6). The fluid level in the reservoir can be
determined with the fluid either hot or cold.
(1) Remove the cap from the reservoir.
Fig. 3 2WD Front Wheel BearingsÐXJ Vehicles
JLUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE 0 - 31
Page 34 of 1784

(5) Inspect the reservoir rubber diaphragm seal for
cracks, cuts and distortion.
(6) Inspect the brake fluid tubing fittings and the
master cylinder housing for indications of fluid leak-
age. Repair as necessary.
(7) Install the brake fluid reservoir cover.
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEMÐXJ VEHICLES
The anti-lock brake system fluid reservoir for XJ
Vehicles is located in the engine compartment at the
left side of the dash panel.
(1) Turn the ignition switch ON and allow the
pump motor to operate until it automatically de-en-
ergizes.
(2) Clean the cover before removing it.
CAUTION: Over-filling could cause fluid overflow
and possible reservoir damage when the pump mo-
tor energizes.
(3) The brake fluid level should be no lower than
the MIN arrow indicator on the side of the reservoir
(Fig. 8). If not, add brake fluid as necessary. Raise
the fluid level to the MAX arrow indicator only. Do
not over-fill the reservoir.
(4) Turn the ignition switch OFF.
BRAKE SYSTEM INSPECTION
BRAKE FLUID HOSES/TUBING
(1) Inspect all brake fluid rubber hoses (Fig. 9) for
cracks, swelling, kinks, a distorted condition and
fluid leakage.
(2) Inspect the brake fluid hoses and tubing that
are routed along the frame rail.
PADS/LININGS, ADJUSTER, WHEEL CYLINDERS AND
CALIPER
The front disk brake pads can be visually inspected
via the brake caliper inspection ports.(1) Inspect the brake pads and linings for excessive
wear, cracks, charred surfaces and broken rivets.
(2) Inspect the brake pads and linings for contam-
ination with brake fluid, axle lubricant and/or an-
other fluid.
(3) Replace the brake pads and/or linings if they
are worn to within 0.78 mm (1/32 in) of the rivet
head.
(4) Operate the rear brake self-adjuster lever and
pivot. Test the operation of the self-adjuster screw for
ease of movement.
(5) Inspect the self-adjuster components for bent
areas, frayed cables, loose or overheated springs, and
a binding condition.
Fig. 7 Reservoir Fluid LevelÐTypicalFig. 8 Reservoir Fluid LevelÐAnti-Lock Brake
System
Fig. 9 Rubber Brake Fluid HoseÐTypical
JLUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE 0 - 33
Page 38 of 1784

FRONT SUSPENSION AND AXLE
CONTENTS
page page
AXLE NOISE/VIBRATION DIAGNOSIS....... 16
FRONT WHEEL ALIGNMENT............... 5
GENERAL INFORMATION.................. 1
MODEL 30 AXLE AND TUBE AXLE (2WD) . . 20TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS................ 47
XJ FRONT SUSPENSION................. 10
YJ FRONT SUSPENSION................. 13
GENERAL INFORMATION
FRONT SUSPENSION
XJ VEHICLES
The Cherokee front suspension is a link/coil design
comprised of (Fig. 1);
²Drive axle (4WD), tube axle (2WD)
²Track bar
²Stabilizer bar
²Upper and lower suspension arms
²Coil springs
²Dual-action shock absorbers²Jounce bumpers (used to limit the travel of the
suspension)
The link/coil suspension allows each wheel to adapt
to different road surfaces without greatly affecting
the opposite wheel. Wheels are attached to a hub/
bearings which bolts to the knuckles. The hub/bear-
ing is not serviceable and is replaced as a unit.
Steering knuckles pivot on replaceable ball studs at-
tached to the axle tube yokes.
The upper and lower suspension arms are different
lengths, with bushings at both ends. They bolt the
Fig. 1 XJ Front Suspension
JFRONT SUSPENSION AND AXLE 2 - 1
Page 39 of 1784

axle assembly to the frame. The lower arms uses
shims at the frame mount to allow for adjustment of
caster and pinion angle. The suspension arm travel
(jounce or rebound) is limited through the use of rub-
ber bumpers.
Suspension components which use rubber bushings
should be tightened at vehicle ride height. This will
prevent premature failure of the bushing and main-
tain ride comfort. Bushings must never be lubricated.
The coil springs control ride quality and maintain
proper ride height. The coil springs mount up in the
fender shield which is part of the unitized body
bracket. A rubber isolator is located between the top
of the spring and the frame. The bottom of the spring
seats on a axle pad and is retained with a clip.
The shock absorbers dampen jounce and rebound of
the vehicle over various road conditions. The top of
the shock absorbers are bolted to the frame. The bot-
tom of the shocks are bolted to the axle spring
bracket.
The stabilizer bar is used to minimize vehicle front
sway during turns. The spring steel bar helps to con-
trol the vehicle body in relationship to the suspen-
sion. The bar extends across the front underside of
the chassis and connects to the frame rails. Links are
connected from the bar to the axle brackets. Stabi-
lizer bar mounts are isolated by rubber bushings.
The track bar is used to minimize front axle side-
to-side movement. The bar is attached to a frame rail
bracket with a ball stud and isolated with a bushing
at the axle bracket.
TUBE AXLE (2WD VEHICLES)
The front axle used on two-wheel drive vehicles is
a one-piece, tubular axle (Fig. 2). The tubular axle
mounts in the same bracketry as does the four-wheel
drive front axle. The steering knuckles and hub bear-
ing assemblies are the same as used on the Model 30
drive axle.
YJ VEHICLES
The Wrangler (YJ) front suspension is leaf spring
design comprised of (Fig. 3);
²Drive axle
²Track bar
²Stabilizer bar
²Leaf springs
²Dual-action shock absorbers
²Jounce bumpers (used to limit the travel of the
suspension)
The front suspension uses semi-elliptic multi-leaf
springs mounted on the drive axle. The rearward end
of the springs are mounted to the frame rail hangers
through rubber bushings. The bushings isolate road
noise as the springs move. The forward end of the
springs are attached to the frame with shackles. The
spring and shackles use rubber bushings to isolate
road noise. The shackles allow the springs to changetheir length as the vehicle moves over various road
conditions. The spring and axle travel (jounce or re-
bound) is limited through use of rubber bumpers
mounted on the frame.
Suspension components which use rubber bushings
should be tightened at vehicle ride height. This will
prevent premature failure of the bushing and main-
tain ride comfort. The bushings should never be lu-
bricated.
Fig. 2 Front AxleÐ 2WD Vehicles
Fig. 3 YJ Front Suspension
2 - 2 FRONT SUSPENSION AND AXLEJ
Page 40 of 1784

The shocks absorbers dampen jounce and rebound
of the vehicle over various road conditions. The top of
the shock absorbers are bolted to the frame. The bot-
tom of the shocks are bolted to the axle bracket.
The stabilizer bar is used to minimize vehicle front
sway during turns. The spring steel bar helps to con-
trol the vehicle body in relationship to the suspen-
sion. The bar extends across the front underside of
the chassis and connects to the frame rails. Links are
connected from the bar to the axle brackets. Stabi-
lizer bar mounts are isolated by rubber bushings.
The track bar is used to minimize front axle side-
to-side movement. The track bar is attached to a
frame rail bracket and the axle bracket.
The bar uses bushings at both ends.
FRONT DRIVE AXLE
It is not necessary to remove the complete axle
from the vehicle for routine differential service. If
the differential housing or axle shaft tubes are dam-
aged, the complete axle assembly can be removed
and serviced.
For complete drive axle assembly removal and in-
stallation refer to Drive Axle Assembly Replacement
in this Group.
The removable cover provides for servicing without
removing axle from vehicle.
The integral type housing, hypoid gear design has
the centerline of the pinion set above the centerline
of the ring gear.
The Model 30 axle has the assembly part number
and gear ratio listed on a tag. The tag is attached to
the housing cover (Fig. 4). Build date identification
codes are stamped on the axle shaft tube cover side.XJ and YJ axles are equipped with an optional
A.B.S. brake system. The A.B.S. tone rings are
pressed onto the axle shaft near the hub and
knuckle. For additional information on the A.B.S.
system refer to Group 5, Brakes.
²XJ vehicles use a non-disconnect axle.
²YJ vehicles use a vacuum disconnect axle (Fig. 5).
STANDARD DIFFERENTIAL OPERATION
The differential gear system divides the torque be-
tween the axle shafts. It allows the axle shafts to ro-
tate at different speeds when turning corners.
Each differential side gear is splined to an axle
shaft. The pinion gears are mounted on a pinion
mate shaft and are free to rotate on the shaft. The
pinion gear is fitted in a bore in the differential case
and is positioned at a right angle to the axle shafts.
In operation, power flow occurs as follows:
²Pinion gear rotates the ring gear
²Ring gear (bolted to the differential case) rotates
the case
²Differential pinion gears (mounted on the pinion
mate shaft in the case) rotate the side gears
²Side gears (splined to the axle shafts) rotate the
shafts
During straight-ahead driving, the differential pin-
ion gears do not rotate on the pinion mate shaft. This
occurs because input torque applied to gears is di-
vided and distributed equally between the two side
gears. As a result, the pinion gears revolve with the
pinion mate shaft but do not rotate around it (Fig. 6).
When turning corners, the outside wheel must travel
a greater distance than the inside wheel. This difference
must be compensated for in order to prevent the wheels
from scuffing and skidding through the turn. To accom-
plish this, the differential allows the axle shafts to turn
at unequal speeds (Fig. 7). In this instance, the input
torque applied to the pinion gears is not divided
equally. The pinion gears now rotate around the pinion
mate shaft in opposite directions. This allows the side
gear and axle shaft attached to the outside wheel to ro-
tate at a faster speed.
Fig. 4 Model 30 Differential Cover
Fig. 5 Disconnect Feature
JFRONT SUSPENSION AND AXLE 2 - 3
Page 41 of 1784
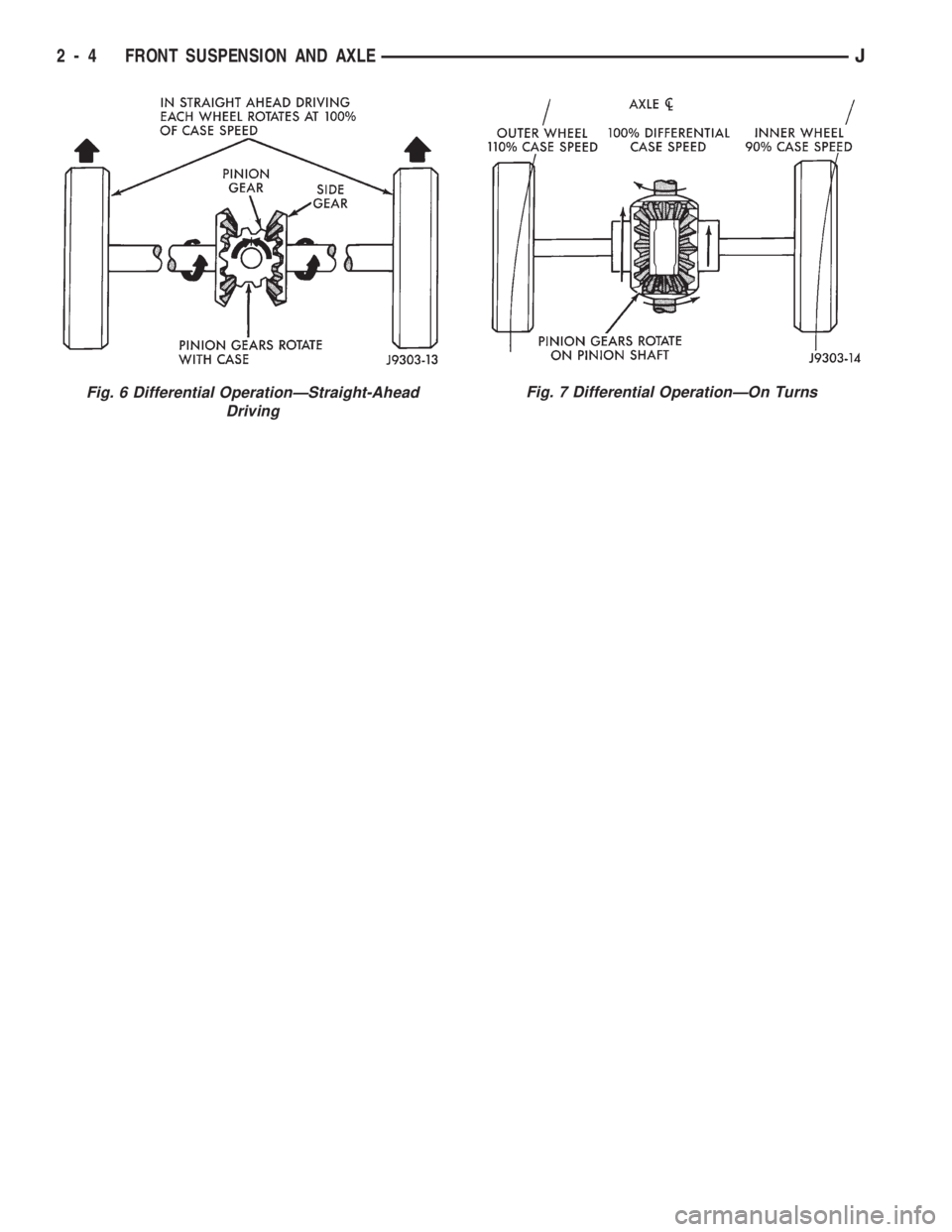
Fig. 6 Differential OperationÐStraight-Ahead
DrivingFig. 7 Differential OperationÐOn Turns
2 - 4 FRONT SUSPENSION AND AXLEJ
Page 42 of 1784

FRONT WHEEL ALIGNMENT
INDEX
page page
Alignment Measurements and Adjustments...... 6
General Information........................ 5Pre-Alignment Inspection.................... 6
GENERAL INFORMATION
Front wheel alignment involves the correct posi-
tioning of the wheels in relation to the vehicle. The
positioning is accomplished through suspension and
steering linkage adjustments. An alignment is con-
sidered essential for efficient steering, good direc-
tional stability and to maximize tire wear. The most
important measurements of front end alignment are
caster, camber and toe position.
Routine inspection of the front suspension
and steering components is a good preventative
maintenance practice. Inspection also helps to
ensure safe operation of the vehicle.
²CASTER is the forward or rearward tilt of the
steering knuckle from vertical. Tilting the top of the
knuckle rearward provides positive caster. Tilting the
top of the knuckle forward provides negative caster.
Caster is a directional stability angle whichenables the front wheels to return to a straight
ahead position after turns (Fig. 1).
²CAMBER is the inward or outward tilt of the
wheel relative to the center of the vehicle. Tilting the
top of the wheel inward provides negative camber.
Tilting the top of the wheel outward provides positive
camber. Incorrect camber will cause wear on the in-
side or outside edge of the tire (Fig. 1).
²WHEEL TOE POSITION is the difference between
the leading inside edges and trailing inside edges of
the front tires (Fig. 1). Incorrect wheel toe position is
the most common cause of unstable steering and un-
even tire wear. The wheel toe position is thefinal
front wheel alignment adjustment.
²STEERING AXIS INCLINATION ANGLE is mea-
sured in degrees and is the angle that the steering
knuckles are tilted (Fig. 1). The inclination angle has
a fixed relationship with the camber angle. It will
Fig. 1 Wheel Alignment Measurements
JFRONT SUSPENSION AND AXLE 2 - 5
Page 43 of 1784

not change except when a spindle or ball stud is
damaged or bent. The angle is not adjustable and the
damaged component(s) must be replaced to correct
mis-alignment.
CAUTION:Do not attempt to modify any suspension
or steering component by heating and bending.
PRE-ALIGNMENT INSPECTION
Before starting a front wheel alignment, the follow-
ing inspection and necessary corrections must be
completed.
(1) Tires with the same recommended air pressure,
size, and thread wear. Refer to Group 22, Tires And
Wheels for diagnosis information.
(2) Front wheel bearings for wear.
(3) Ball studs, steering linkage pivot points and
steering gear for looseness, roughness, binding or
wear. Refer to Group 19, Steering for additional in-
formation.
(4) Front wheels for excessive radial or lateral
runout and unbalance. Refer to Group 22, Tires And
Wheels for diagnosis information.
(5) Suspension components for wear and noise.
Check components for correct torque. Refer to Groups
2 and 3, Suspension and Axle for additional informa-
tion.
ALIGNMENT MEASUREMENTS AND ADJUSTMENTS
Before each alignment reading, the vehicle should
be jounced (rear first, then front). Grasp each bumper
at the center and jounce the vehicle up and down
several times. Always release the bumper in the
down position.Set the front end alignment to
specifications with the vehicle at its NOR-
MALLY RIDE HEIGHT.
CAMBER
The wheel camber angle (Fig. 1) is preset at ZERO
DEGREES (0É). The angle is not adjustable and can-
not be altered.
CASTER
The caster angle (Fig. 1) is set at:
²XJ manual transmission, POSITIVE 6.5 DE-
GREES (+6.5É).
²XJ automatic transmission, POSITIVE 8.0 DE-
GREES (+8.0É).
²YJ all transmissions, POSITIVE 6.0 DEGREES
(+6.0É).
Before checking the caster of the front axle for cor-
rect angle. Be sure the axle is not bent or twisted.
Road test the vehicle, and make left and right
turns. If the steering wheel returns to the center po-
sition unassisted, the caster angle is correct. How-ever, if steering wheel does not return toward the
center position unassisted, an incorrect caster angle
is probable.
Caster can be adjusted by installing the appropri-
ate size shims (Fig. 2, 3).Changing caster angle
will also change the front propeller shaft angle.
The propeller shaft angle has priority over
caster. Refer to Group 16, Propeller Shafts for
additional information.
Fig. 2 AdjustmentÐYJ Vehicles
Fig. 3 AdjustmentÐXJ Vehicles
2 - 6 FRONT SUSPENSION AND AXLEJ
Page 44 of 1784
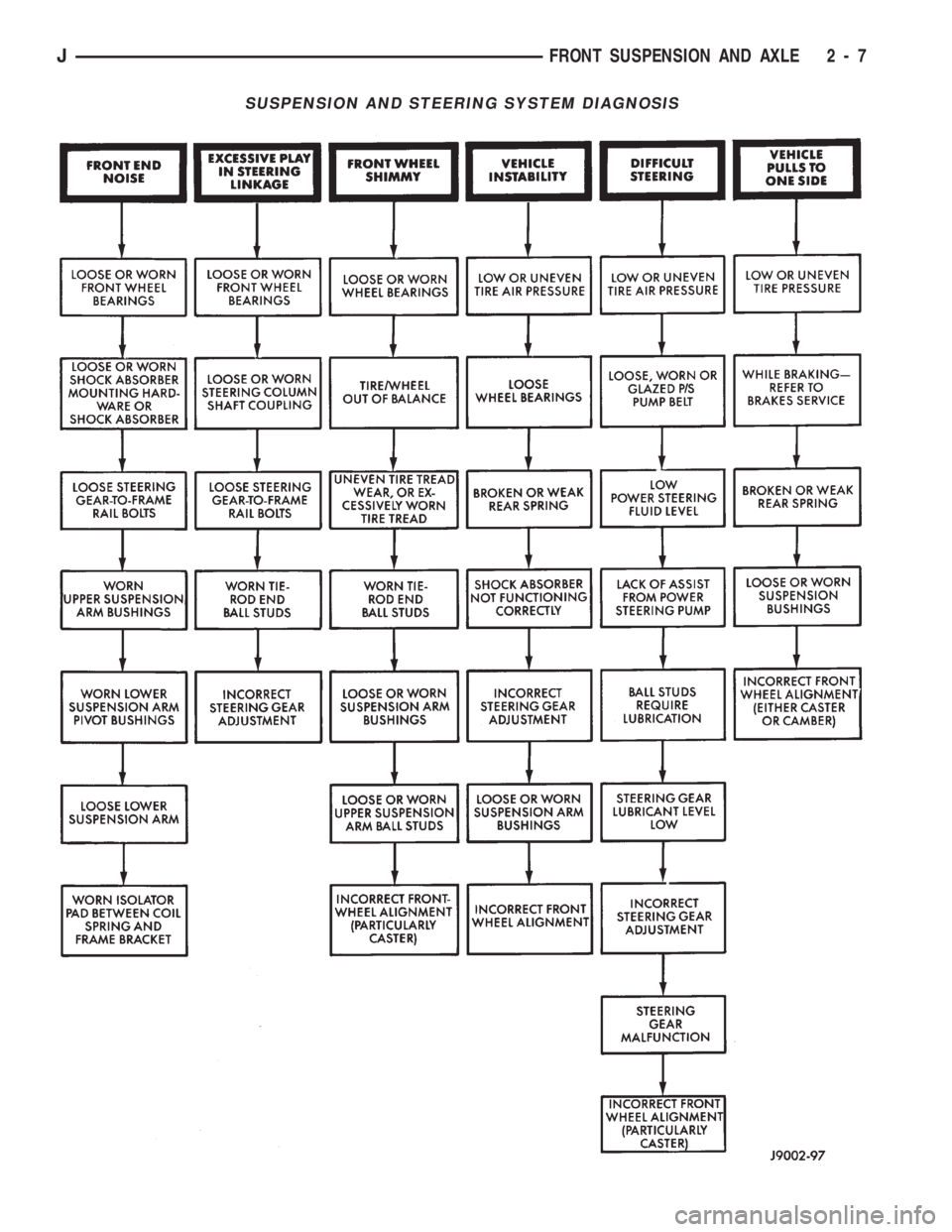
SUSPENSION AND STEERING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
JFRONT SUSPENSION AND AXLE 2 - 7