jump cable JEEP CHEROKEE 1994 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 1994, Model line: CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP CHEROKEE 1994Pages: 1784, PDF Size: 77.09 MB
Page 8 of 1784

JUMP STARTING, HOISTING AND TOWING
JUMP STARTING
WARNING: DO NOT ATTEMPT TO PUSH OR TOW A
VEHICLE TO START THE ENGINE. UNBURNED
FUEL COULD ENTER THE EXHAUST CATALYTIC
CONVERTER AND IGNITE AFTER THE ENGINE IS
STARTED. THIS COULD CAUSE THE CONVERTER
TO OVERHEAT AND RUPTURE.
BOOSTER BATTERY
WARNING: TO PREVENT PERSONAL INJURY OR
CLOTHING DAMAGE, DO NOT ALLOW BATTERY
(ACID) TO CONTACT EYES, SKIN OR CLOTHING.
DO NOT LEAN OVER A BATTERY WHEN CON-
NECTING JUMPER CABLES. DO NOT ALLOW THE
POSITIVE AND NEGATIVE CABLE CONNECTOR
CLAMPS TO CONTACT EACH OTHER. KEEP OPEN
FLAMES AND SPARKS AWAY FROM THE BATTERY
VENT HOLES. ALWAYS WEAR EYE PROTECTION
WHEN INVOLVED WITH BATTERIES.
If it is necessary to use a booster battery and
jumper cables to start an engine use the following
procedure.
(1) Engage the parking brake and shift the auto-
matic transmission to PARK, manual transmission
shift to NEUTRAL.
(2) Turn off all lights, the heater-A/C blower mo-
tor, and all other electrical loads.
WARNING: WHEN THE AIR TEMPERATURE IS BE-
LOW THE FREEZING POINT (0ÉC OR 32ÉF), THE
ACID IN A DISCHARGED VEHICLE BATTERY CAN
FREEZE. DO NOT ATTEMPT TO JUMP START AN
ENGINE BEFORE DETERMINING THE CONDITION
OF THE BATTERY.
(3) Inspect the general condition of the battery.
CAUTION: Do not permit metal surfaces on vehicles
to contact because this could establish ground con-
tinuity between vehicle bodies.
(4) Attach a red cable connector clamp to the pos-
itive (+) terminal on the booster battery. Connect
the other red cable connector clamp to the positive
(+) terminal on the discharged battery (Fig. 6).
CAUTION: Use care to avoid allowing the positive
(+) and negative (-) cable clamps to contact each
other. DO NOT lean over the battery when connect-
ing the cable clamps.WARNING: DO NOT CONNECT A JUMPER CABLE
CONNECTOR CLAMP TO THE NEGATIVE POST OF
THE DISCHARGED BATTERY.
(5) Connect a black jumper cable connector clamp
to the negative (-) terminal on the booster battery.
Connect the other black jumper cable connector
clamp to a good ground.
(6) Start the engine.
WARNING: THE USE OF ANY JUMPER CABLE DIS-
CONNECTION PROCEDURE OTHER THAN THAT
DESCRIBED BELOW COULD RESULT IN:
²PERSONAL INJURY CAUSED BY BATTERY
ELECTROLYTE SQUIRTING FROM THE BATTERY
VENTS.
²PERSONAL INJURY AND/OR PROPERTY DAM-
AGE CAUSED BY BATTERY EXPLOSION.
²DAMAGE TO THE BOOSTER VEHICLE OR THE
DISABLED VEHICLE CHARGING SYSTEM.
(7) After the engine is started, or if the engine
fails to start, the jumper cables must be disconnected
in the following order:
²Black (negative) cable connector clamp from the
engine ground contact.
²Black (negative) cable connector clamp from the
negative terminal (-) on the booster battery.
²Red (positive) cable connector clamps from the pos-
itive (+) terminals on both batteries.
Fig. 6 Jumper Cable Connections
JLUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE 0 - 7
Page 133 of 1784

87 and 30. Continuity should not be present between
terminals number 87A and 30.
(8) Disconnect jumper wires from relay and 12
Volt power source.
If continuity or resistance tests did not pass, re-
place relay. If tests passed, refer to Group 8W, Wir-
ing Diagrams for additional circuit information. Also
refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic Proce-
dures manual for operation of the DRB scan tool.
STARTER MOTOR RELAY TEST
Refer to Group 8A, Battery/Starting/Charging/Sys-
tem Diagnostics, for starter motor relay testing.
INJECTOR TEST
Disconnect the injector wire connector from the in-
jector. Place an ohmmeter on the injector terminals.
Resistance reading should be approximately 14.5
ohms61.2 ohms at 20ÉC (68ÉF). Proceed to following
Injector Diagnosis chart.
FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE TEST
Refer to the Fuel Delivery System section of this
group. See Fuel System Pressure Test.
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS (OBD)
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) has been
programmed to monitor many different circuits of the
fuel injection system. If a problem is sensed in a
monitored circuit often enough to indicate an actual
problem, a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) is stored.
The DTC will be stored in the PCM memory for
eventual display to the service technician. If the
problem is repaired or ceases to exist, the PCM can-
cels the DTC after 51 engine starts.
Certain criteria must be met for a diagnostic trou-
ble code (DTC) to be entered into PCM memory. The
criteria may be a specific range of engine rpm, en-
gine temperature and/or input voltage to the PCM.
It is possible that a DTC for a monitored circuit
may not be entered into memory even though a mal-
function has occurred. This may happen because one
of the DTC criteria for the circuit has not been met.
Example: assume that one of the criteria for the
MAP sensor circuit is that the engine must be oper-
ating between 750 and 2000 rpm to be monitored for
a DTC. If the MAP sensor output circuit shorts to
ground when the engine rpm is above 2400 rpm, a 0
volt input will be seen by the PCM. A DTC will not
be entered into memory because the condition does
not occur within the specified rpm range.
A DTC indicates that the powertrain control mod-
ule (PCM) has recognized an abnormal signal in a
circuit or the system. A DTC may indicate the result
of a failure, but never identify the failed component
directly.There are several operating conditions that the
PCM does not monitor and set a DTC for. Refer to
the following Monitored Circuits and Non-Monitored
Circuits in this section.
MONITORED CIRCUITS
The powertrain control module (PCM) can detect
certain problems in the fuel injection system.
Open or Shorted Circuit- The PCM can deter-
mine if sensor output (which is the input to PCM) is
within proper range. It also determines if the circuit
is open or shorted.
Output Device Current Flow- The PCM senses
whether the output devices are hooked up.
If there is a problem with the circuit, the PCM
senses whether the circuit is open, shorted to ground
(-), or shorted to (+) voltage.
Oxygen Sensor- The PCM can determine if the
oxygen sensor is switching between rich and lean.
This is, once the system has entered Closed Loop. Re-
fer to Open Loop/Closed Loop Modes Of Operation in
the Component Description/System Operation section
for an explanation of Closed (or Open) Loop opera-
tion.
NON-MONITORED CIRCUITS
The PCM does not monitor the following circuits,
systems or conditions that could have malfunctions
that result in driveability problems. A Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC) may not be displayed for these
conditions.
Fuel Pressure: Fuel pressure is controlled by the
vacuum assisted fuel pressure regulator. The PCM
cannot detect a clogged fuel pump inlet filter, clogged
in-line fuel filter, or a pinched fuel supply or return
line. However, these could result in a rich or lean
condition causing an oxygen sensor DTC to be stored
in the PCM.
Secondary Ignition Circuit: The PCM cannot
detect an inoperative ignition coil, fouled or worn
spark plugs, ignition cross firing, or open circuited
spark plug cables.
Engine Timing: The PCM cannot detect an incor-
rectly indexed timing chain, camshaft sprocket or
crankshaft sprocket. The PCM also cannot detect an
incorrectly indexed distributor. However, these could
result in a rich or lean condition causing an oxygen
sensor DTC to be stored in the PCM.
Cylinder Compression: The PCM cannot detect
uneven, low, or high engine cylinder compression.
Exhaust System: The PCM cannot detect a
plugged, restricted or leaking exhaust system.
Fuel Injector Malfunctions: The PCM cannot de-
termine if the fuel injector is clogged, or the wrong
injector is installed. However, these could result in a
rich or lean condition causing an oxygen sensor DTC
to be stored in the PCM.
14 - 48 FUEL SYSTEMJ
Page 289 of 1784

(5) Connect a 0-150 ampere scale D.C. ammeter in
series between generator battery terminal and dis-
connected generator output wire (Fig. 2). Connect
positive lead to generator battery terminal and neg-
ative lead to disconnected generator output wire.
(6) Connect positive lead of a test voltmeter (range
0-18 volts minimum) to disconnected generator out-
put wire. Connect negative lead of test voltmeter to
battery positive cable at positive post.
(7) Connect one end of a jumper wire to ground
and with other end probe green K20 lead wire at
back of generator (Fig. 2). This will generate a DTC.
CAUTION: Do not connect green/orange A142 lead
of wiring to ground. Refer to Group 8W - Wiring Di-
agrams for more information.
(8) Connect an engine tachometer and connect neg-
ative cable to battery.
(9) Connect a variable carbon pile rheostat be-
tween battery terminals. Be sure carbon pile is in
OPEN or OFF position before connecting leads. See
Load Testing in Battery Test Procedures for instruc-
tions.
TEST
(1) Start engine. Immediately after starting, re-
duce engine speed to idle.
(2) Adjust engine speed and carbon pile to main-
tain 20 amperes flowing in circuit. Observe voltmeter
reading. Voltmeter reading should not exceed 0.5
volts.
RESULTS
If a higher voltage drop is indicated, inspect, clean
and tighten all connections between generator bat-
tery terminal and battery positive post. A voltage
drop test may be performed at each connection to lo-
cate connection with excessive resistance. If resis-
tance tested satisfactorily, reduce engine speed, turn
OFF carbon pile and turn OFF ignition switch.
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove test ammeter, voltmeter, carbon pile,
and tachometer.
(3) Remove jumper wire.
(4) Connect generator output wire to generator
battery terminal. Tighten to 5 to 6 NIm (45 to 75 in.
lbs.).
(5) Connect negative cable to battery.
(6) Use DRB scan tool to erase DTC.
GENERATOR OUTPUT TEST
Generator output test determines whether genera-
tor can deliver its rated current output.PREPARATION
(1) Before starting any tests make sure vehicle has
a fully charged battery. Test and procedures on how
to check for a fully charged battery are shown in
Battery Test Procedures.
(2) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(3) Disconnect generator output wire at the gener-
ator battery terminal.
(4) Connect a 0-150 ampere scale D.C. ammeter in
series between generator battery terminal and dis-
connected generator output wire (Fig. 3). Connect
positive lead to generator battery terminal and neg-
ative lead to disconnected generator output wire.
(5) Connect positive lead of a test voltmeter (range
0-18 volts minimum) to generator battery terminal.
(6) Connect negative lead of test voltmeter to a
good ground.
(7) Connect an engine tachometer and connect bat-
tery negative cable.
(8) Connect a variable carbon pile rheostat be-
tween battery terminals. Be sure carbon pile is in
OPEN or OFF position before connecting leads. See
Load Testing in Battery Test Procedures.
(9) Connect one end of a jumper wire to ground
and with other end probe green K20 lead wire at
back of generator (Fig. 3). This will generate a DTC.
CAUTION: Do not connect green/orange A142 lead
of wiring to ground. Refer to Group 8W - Wiring Di-
agrams for more information.
TEST
(1) Start engine. Immediately after starting reduce
engine speed to idle.
(2) Adjust carbon pile and engine speed in incre-
ments until a speed of 1250 rpm and voltmeter read-
ing of 15 volts is obtained.
CAUTION: Do not allow voltage meter to read above
16 volts.
(3) The ammeter reading must be within limits
shown for that size of generator being tested. See
Generator Specifications in Battery/Starter/Genera-
tor Service.
RESULTS
(1) If reading is less than specified and generator
output wire resistance is not excessive, generator
should be replaced. Refer to Group 8B - Battery/
Starter/Generator Service.
(2) After current output test is completed reduce
engine speed, turn OFF carbon pile and turn OFF ig-
nition switch.
(3) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(4) Remove test ammeter, voltmeter, tachometer
and carbon pile.
8A - 16 BATTERY/STARTING/CHARGING SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICSJ
Page 290 of 1784
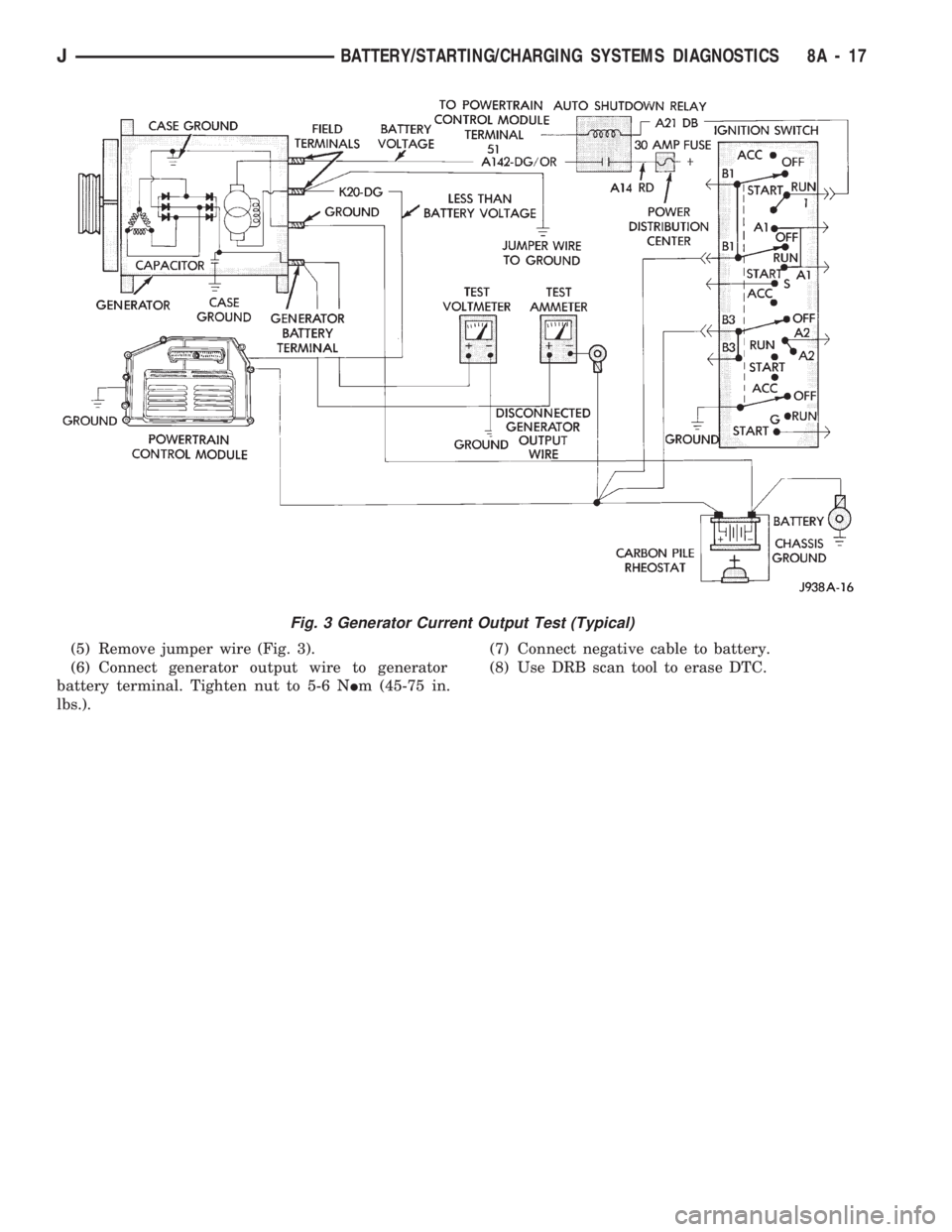
(5) Remove jumper wire (Fig. 3).
(6) Connect generator output wire to generator
battery terminal. Tighten nut to 5-6 NIm (45-75 in.
lbs.).(7) Connect negative cable to battery.
(8) Use DRB scan tool to erase DTC.
Fig. 3 Generator Current Output Test (Typical)
JBATTERY/STARTING/CHARGING SYSTEMS DIAGNOSTICS 8A - 17
Page 326 of 1784

(4) Using insulated pliers, hold the cable terminal
approximately 12 mm (1/2 in.) from the engine cylin-
der head or block while rotating the engine with the
starter motor. Observe the spark plug cable terminal
for an arc. If steady arcing occurs, it can be expected
that the ignition secondary system is operating cor-
rectly. If steady arcing occurs at the spark plug ca-
bles, but the engine will not start, connect the DRB
scan tool. Refer to the Powertrain Diagnostic Proce-
dures service manual for DRB operation.
FAILURE TO START TEST
To prevent unnecessary diagnostic time and wrong
test results, the previous Checking For Spark test
should be performed prior to this test.
WARNING: SET PARKING BRAKE OR BLOCK THE
DRIVE WHEELS BEFORE PROCEEDING WITH THIS
TEST.
(1) Unplug the ignition coil harness connector at
the coil (Fig. 14).
(2) Connect a set of small jumper wires (18 gauge
or smaller) between the ignition coil and coil electri-
cal connector (Fig. 15).
(3) Determine that sufficient battery voltage (12.4
volts) is present for the starting and ignition sys-
tems.
(4) Crank the engine for 5 seconds while monitor-
ing the voltage at the coil positive terminal:
²If the voltage remains near zero during the entire
period of cranking, refer to On-Board Diagnostics in
Group 14, Fuel Systems. Check the powertrain con-
trol module (PCM) and auto shut down relay.
²If voltage is at near battery voltage and drops to
zero after 1-2 seconds of cranking, check the cam-
shaft position sensor-to-PCM circuit. Refer to On-
Board Diagnostics in Group 14, Fuel Systems.
²If voltage remains at near battery voltage during
the entire 5 seconds, turn the key off. Remove the60-way connector (Fig. 16) from the PCM. Check 60-
way connector for any spread terminals.
(5) Remove test lead from the coil positive termi-
nal. Connect an 18 gauge jumper wire between the
battery positive terminal and the coil positive termi-
nal.
(6) Make the special jumper shown in Figure 17.
Using the jumper,momentarilyground terminal-19
of the 60-way connector. A spark should be generated
at the coil cable when the ground is removed.
(7) If spark is generated, replace the powertrain
control module (PCM).
(8) If spark is not seen, use the special jumper to
ground the coil negative terminal directly.
(9) If spark is produced, repair wiring harness for
an open condition.
Fig. 14 Coil Harness ConnectorÐTypical
Fig. 15 Coil TerminalsÐTypical
Fig. 16 PCM 60-Way Connector
Fig. 17 Special Jumper Ground-to-Coil Negative
Terminal
JIGNITION SYSTEMS 8D - 13
Page 331 of 1784

Check the high-tension cable connections for good
contact at the ignition coil, distributor cap towers
and spark plugs. Terminals should be fully seated.
The terminals and spark plug covers should be in
good condition. Terminals should fit tightly to the ig-
nition coil, distributor cap and spark plugs. The
spark plug cover (boot) of the cable should fit tight
around the spark plug insulator. Loose cable connec-
tions can cause corrosion and increase resistance, re-
sulting in shorter cable service life.
Clean the high tension cables with a cloth moist-
ened with a nonflammable solvent and wipe dry.
Check for brittle or cracked insulation.
When testing secondary cables for damage with an
oscilloscope, follow the instructions of the equipment
manufacturer.
If an oscilloscope is not available, spark plug cables
may be tested as follows:
CAUTION: Do not leave any one spark plug cable
disconnected for longer than necessary during test-
ing. This may cause possible heat damage to the
catalytic converter. Total test time must not exceed
ten minutes.
With the engine not running, connect one end of a
test probe to a good ground. Start the engine and run
the other end of the test probe along the entire
length of all spark plug cables. If cables are cracked
or punctured, there will be a noticeable spark jump
from the damaged area to the test probe. The cable
running from the ignition coil to the distributor cap
can be checked in the same manner. Cracked, dam-
aged or faulty cables should be replaced with resis-
tance type cable. This can be identified by the words
ELECTRONIC SUPPRESSION printed on the cable
jacket.
Use an ohmmeter to test for open circuits, exces-
sive resistance or loose terminals. Remove the dis-
tributor cap from the distributor.Do not remove
cables from cap.Remove cable from spark plug.
Connect ohmmeter to spark plug terminal end of ca-
ble and to corresponding electrode in distributor cap.
Resistance should be 250 to 1000 Ohms per inch of
cable. If not, remove cable from distributor cap tower
and connect ohmmeter to the terminal ends of cable.
If resistance is not within specifications as found in
the Spark Plug Cable Resistance chart, replace the
cable. Test all spark plug cables in this manner.To test ignition coil-to-distributor cap cable, do not
remove the cable from the cap. Connect ohmmeter to
rotor button (center contact) of distributor cap and
terminal at ignition coil end of cable. If resistance is
not within specifications as found in the Spark Plug
Cable Resistance chart, remove the cable from the
distributor cap. Connect the ohmmeter to the termi-
nal ends of the cable. If resistance is not within spec-
ifications as found in the Spark Plug Cable
Resistance chart, replace the cable. Inspect the igni-
tion coil tower for cracks, burns or corrosion.
For removal and installation of spark plug cables,
refer to Spark Plug Secondary Cables in the Compo-
nent Removal/Installation section.
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR TEST
To perform a complete test of this sensor and its
circuitry, refer to the DRB scan tool. Also refer to the
appropriate Powertrain Diagnostics Procedures man-
ual. To test the sensor only, refer to the following:
The throttle position sensor can be tested with a
digital voltmeter. The center terminal of the sensor
connector is the output terminal (Figs. 30 or 31).
SPARK PLUG CABLE RESISTANCE
Fig. 30 SensorÐ2.5L Engine
Fig. 31 SensorÐ4.0L Engine
8D - 18 IGNITION SYSTEMSJ
Page 394 of 1784

TEST PROCEDURES
INDEX
page page
Checking for Diagnostic Trouble Code......... 5
Electrical Tests at Powertrain Control Module.... 6
Electrical Tests at Servo.................... 5
Inoperative System........................ 5
Operational Check (Road Test)............... 7
Road Test............................... 5Speed Control Switch (Turn Signal Lever) Test . . . 7
Stop Lamp Speed Control Switch Test......... 7
Vacuum Supply Test....................... 7
Vehicle Speed Control System Electrical Tests . . . 5
Vehicle Speed Sensor Test.................. 5
ROAD TEST
Refer to Operational Check (Road Test) section to
verify reports of speed control system malfunction.
INOPERATIVE SYSTEM
Road test vehicle to verify reports of speed control
system malfunction. An inspection should be made
for loose electrical and vacuum connections at the
servo.
Check for correct installation of the vacuum check
valve in the hose from servo to vacuum source. The
word VAC on the valve must point toward the vac-
uum source.
Corrosion should be removed from electrical termi-
nals and a light coating of Mopar MultiPurpose
Grease, or equivalent, applied.
Inspection also should be made to verify that both
ends of the speed control cable are securely attached.
CHECKING FOR DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE
(1) When trying to verify a speed control system
electronic malfunction use a DRB scan tool to find
the cause (refer to Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures
manual).
If DRB is not available, the Diagnostic Trouble
Code (DTC) may be determined with the following
method:
(a) With key inserted in ignition switch, cycle
switch to ON position 3 times. On third cycle, leave
switch in ON position.
(b) After switch has been cycled 3 times, observe
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (CHECK ENGINE)
on instrument cluster. If a DTC is present, the code
will be displayed in a series of flashes representing
digits. Three flashes in rapid succession, a slight
pause, then 4 flashes in rapid succession would in-
dicate DTC 34.
(2) If a DTC 34 is observed, perform tests in the
sections Electrical Tests at Servo and Electrical Tests
at Powertrain Control Module.
If a DTC 15 is observed, perform test for a faulty
vehicle speed sensor.
(3) Correct any problems found when performing
these tests and recheck for DTC if changes were
made.
VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR TEST
For testing of the vehicle speed sensor and related
components, refer to Powertrain Diagnostic Proce-
dures manual.
VEHICLE SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM ELECTRICAL
TESTS
Vehicle speed control systems may be tested using
two different methods. One involves use of a DRB
scan tool. If this test method is desired, refer to Pow-
ertrain Diagnostic Procedures manual.
The other test method uses a voltmeter. The volt-
meter method is described in the following tests.
If any information is needed concerning wiring, re-
fer to Section 8W - Wiring Diagrams.
CAUTION: When test probing for voltage or conti-
nuity at electrical connectors, care must be taken
not to damage connector, terminals, or seals. If
these components are damaged, intermittent or
complete system failure may occur.
ELECTRICAL TESTS AT SERVO
(1) Turn ignition switch to the ON position. With
speed control switch in the ON position, setup a volt-
meter to read battery voltage and connect negative
lead to a good chassis ground.
(2) Disconnect 4-way connector going to servo
(Figs. 2 and 3). Blue wire with red tracer of main
harness 4-way connector should read approximately
battery voltage. If not, check for loose connections,
brake switch adjustment or, repair main harness as
necessary.
(3) Connect a jumper wire between male and fe-
male terminals of blue wire with red tracer. The
other 3 male terminals from servo should show bat-
tery voltage. If not, replace servo.
(4) Using an ohmmeter, connect one lead to a good
body ground. Touch other lead to black wire terminal
in 4-way connector of main harness. Meter should
show continuity. If not, repair ground circuit as nec-
essary.
JVEHICLE SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM 8H - 5
Page 1009 of 1784

87 and 30. Continuity should not be present between
terminals number 87A and 30.
(8) Disconnect jumper wires from relay and 12
Volt power source.
If continuity or resistance tests did not pass, re-
place relay. If tests passed, refer to Group 8W, Wir-
ing Diagrams for additional circuit information. Also
refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic Proce-
dures manual for operation of the DRB scan tool.
STARTER MOTOR RELAY TEST
Refer to Group 8A, Battery/Starting/Charging/Sys-
tem Diagnostics, for starter motor relay testing.
INJECTOR TEST
Disconnect the injector wire connector from the in-
jector. Place an ohmmeter on the injector terminals.
Resistance reading should be approximately 14.5
ohms61.2 ohms at 20ÉC (68ÉF). Proceed to following
Injector Diagnosis chart.
FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE TEST
Refer to the Fuel Delivery System section of this
group. See Fuel System Pressure Test.
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS (OBD)
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) has been
programmed to monitor many different circuits of the
fuel injection system. If a problem is sensed in a
monitored circuit often enough to indicate an actual
problem, a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) is stored.
The DTC will be stored in the PCM memory for
eventual display to the service technician. If the
problem is repaired or ceases to exist, the PCM can-
cels the DTC after 51 engine starts.
Certain criteria must be met for a diagnostic trou-
ble code (DTC) to be entered into PCM memory. The
criteria may be a specific range of engine rpm, en-
gine temperature and/or input voltage to the PCM.
It is possible that a DTC for a monitored circuit
may not be entered into memory even though a mal-
function has occurred. This may happen because one
of the DTC criteria for the circuit has not been met.
Example: assume that one of the criteria for the
MAP sensor circuit is that the engine must be oper-
ating between 750 and 2000 rpm to be monitored for
a DTC. If the MAP sensor output circuit shorts to
ground when the engine rpm is above 2400 rpm, a 0
volt input will be seen by the PCM. A DTC will not
be entered into memory because the condition does
not occur within the specified rpm range.
A DTC indicates that the powertrain control mod-
ule (PCM) has recognized an abnormal signal in a
circuit or the system. A DTC may indicate the result
of a failure, but never identify the failed component
directly.There are several operating conditions that the
PCM does not monitor and set a DTC for. Refer to
the following Monitored Circuits and Non-Monitored
Circuits in this section.
MONITORED CIRCUITS
The powertrain control module (PCM) can detect
certain problems in the fuel injection system.
Open or Shorted Circuit- The PCM can deter-
mine if sensor output (which is the input to PCM) is
within proper range. It also determines if the circuit
is open or shorted.
Output Device Current Flow- The PCM senses
whether the output devices are hooked up.
If there is a problem with the circuit, the PCM
senses whether the circuit is open, shorted to ground
(-), or shorted to (+) voltage.
Oxygen Sensor- The PCM can determine if the
oxygen sensor is switching between rich and lean.
This is, once the system has entered Closed Loop. Re-
fer to Open Loop/Closed Loop Modes Of Operation in
the Component Description/System Operation section
for an explanation of Closed (or Open) Loop opera-
tion.
NON-MONITORED CIRCUITS
The PCM does not monitor the following circuits,
systems or conditions that could have malfunctions
that result in driveability problems. A Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC) may not be displayed for these
conditions.
Fuel Pressure: Fuel pressure is controlled by the
vacuum assisted fuel pressure regulator. The PCM
cannot detect a clogged fuel pump inlet filter, clogged
in-line fuel filter, or a pinched fuel supply or return
line. However, these could result in a rich or lean
condition causing an oxygen sensor DTC to be stored
in the PCM.
Secondary Ignition Circuit: The PCM cannot
detect an inoperative ignition coil, fouled or worn
spark plugs, ignition cross firing, or open circuited
spark plug cables.
Engine Timing: The PCM cannot detect an incor-
rectly indexed timing chain, camshaft sprocket or
crankshaft sprocket. The PCM also cannot detect an
incorrectly indexed distributor. However, these could
result in a rich or lean condition causing an oxygen
sensor DTC to be stored in the PCM.
Cylinder Compression: The PCM cannot detect
uneven, low, or high engine cylinder compression.
Exhaust System: The PCM cannot detect a
plugged, restricted or leaking exhaust system.
Fuel Injector Malfunctions: The PCM cannot de-
termine if the fuel injector is clogged, or the wrong
injector is installed. However, these could result in a
rich or lean condition causing an oxygen sensor DTC
to be stored in the PCM.
14 - 48 FUEL SYSTEMJ
Page 1755 of 1784

GRILLE OPENING PANEL (GOP), GRILLE.....23-3
GRILLEÐXJ VEHICLES, AIR EXHAUST.....23-30
GROUND, POWER.....................14-22
GROUP INDEX; ELECTRICAL..............8A-1
GUARD, BRUSH........................23-3
GUARD/EDGE PROTECTOR STRIP, DOOR
EDGE..............................23-61
GUIDES AND CHARTS, DIAGNOSIS........21-76
HALF METAL DOOR MIRROR (EXTERNAL) . . 23-158
HALF-METAL DOOR LATCH STRIKER......23-175
HALF-METAL SOFT TOP DOOR..........23-173
HAND DRIVE, BATTERY CLASSIFICATIONS
AND RATINGSÐLEFT.................8B-10
HAND DRIVE, BATTERY CLASSIFICATIONS
AND RATINGSÐRIGHT................8B-10
HAND DRIVE, BATTERY REPLACEMENTÐ
LEFT...............................8B-1
HAND DRIVE, BATTERY REPLACEMENTÐ
RIGHT..............................8B-2
HAND DRIVE, BELT SERVICEÐEXCEPT
RIGHT..............................7-34
HAND DRIVE, BELT SERVICEÐWITH
RIGHT..............................7-35
HAND DRIVE, DRIVERS DOOR POWER
LOCK SWITCHÐ2-DOOR LEFT...........8P-2
HAND DRIVE, DRIVERS DOOR POWER
LOCK SWITCHÐ2-DOOR RIGHT..........8P-3
HAND DRIVE, DRIVERS DOOR POWER
WINDOW SWITCHÐ2-DOOR LEFT........8S-6
HAND DRIVE, DRIVERS DOOR POWER
WINDOW SWITCHÐ2-DOOR RIGHT......8S-7
HAND DRIVE, GENERATOR
REPLACEMENTÐLEFT.................8B-7
HAND DRIVE, GENERATOR
REPLACEMENTÐRIGHT................8B-9
HAND DRIVE (RHD), BELT TENSIONÐ
EXCEPT RIGHT.......................7-33
HAND DRIVE (RHD), BELT TENSIONÐ
RIGHT..............................7-34
HAND DRIVE VEHICLES, RIGHT............23-1
HAND DRIVE, WASHER PUMP
REPLACEMENTÐLEFT.................8K-2
HAND DRIVE, WASHER PUMP
REPLACEMENTÐRIGHT................8K-3
HANDLE, DOOR EXTERNAL..............23-55
HANDLE, FULL-METAL DOOR ASSIST.....23-175
HANDLE, FULL-METAL DOOR LATCH
EXTERNAL RELEASE.................23-178
HANDLE, FULL-METAL DOOR LATCH
INSIDE RELEASE AND LOCK...........23-175
HANDLE, FULL-METAL DOOR WINDOW
GLASS REGULATOR.................23-175
HANDLE, TAILGATE LATCH AND
RELEASE..........................23-160
HANDLEÐXJ VEHICLES, ASSIST.........23-118
HANGER BRACKET, MUFFLER/TAILPIPE.....13-16
HARD TOP DOME/CARGO LAMP BULB
REPLACEMENTÐYJ VEHICLES..........8L-20
HARD TOP LIFTGATE GLASS............23-162
HARD TOP QUARTER WINDOW GLASS....23-188
HARD TOP REPAIR....................23-165
HARD TOP ROOF VENT................23-165
HARD TOP SERVICE...................23-164
HARD TOP SERVICE INFORMATION.......23-164
HAZARD LAMPSÐXJ....................8J-1
HAZARD LAMPSÐYJ....................8J-2
HCU DIAGNOSIS........................5-4
HCU INSTALLATIONÐXJ.................5-54
HCU INSTALLATIONÐYJ.................5-54
HCU PUMP AND PEDAL TRAVEL
SENSOR OPERATION...................5-44
HCU REMOVALÐXJ.....................5-53
HCU REMOVALÐYJ.....................5-54
HCU SOLENOID VALVE OPERATION.........5-43
HEAD COVER, ENGINE CYLINDER......9-18,9-59
HEAD, ENGINE CYLINDER............9-19,9-60
HEAD GASKET FAILURE DIAGNOSIS,
ENGINE CYLINDER.....................9-5
HEADLAMP BEAM ADJUSTMENT...........8L-3
HEADLAMP BULB REPLACEMENT
..........8L-3
HEADLAMP DELAY FUNCTION TROUBLE
DIAGNOSISÐXJ VEHICLES
.............8L-16
HEADLAMP DELAY MODULE
REPLACEMENTÐXJ VEHICLES
..........8L-16
HEADLAMP DELAY MODULEÐXJ
VEHICLES, SENTINEL
.................8L-15HEADLAMP DIMMER SWITCH
REPLACEMENT.......................8L-6
HEADLAMP SWITCH REPLACEMENT........8L-4
HEADLAMP SWITCH/ILLUMINATION
RHEOSTAT..........................8E-21
HEADLAMP TROUBLE DIAGNOSISÐ
XJ VEHICLES.........................8L-1
HEADLAMP TROUBLE DIAGNOSISÐYJ
VEHICLES...........................8L-2
HEADLAMPS...........................0-35
HEADLINER.........................23-121
HEAT SHIELDS........................14-12
HEAT SHIELDS, EXHAUST................11-1
HEAT SHIELDS, MUFFLER AND TAILPIPE . . . 13-17
HEATER AND A/C CONTROL PANEL
REPLACEMENT......................24-26
HEATER CONTROL CABLE REPLACEMENT . . . 24-30
HEATER CONTROL PANEL REPLACEMENT . . . 24-39
HEATER CORE........................24-28
HEATER CORE AND HOUSING............24-40
HEATER CORE HOUSING REPLACEMENT . . . 24-29
HEATER, ENGINE BLOCK.................7-37
HEATER/DEFROSTER OPERATION.........24-37
HEATER/DEFROSTER/INSTRUMENT
PANEL OUTLET DOOR VACUUM MOTOR
REPLACEMENT......................24-30
HEATING ELEMENT TEST, OXYGEN
SENSOR (O2S)......................14-45
HEATING SCHEMATIC...................24-24
HEATING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS............24-11
HEATING SYSTEMÐYJ VEHICLES.........24-14
HIGH LINE CLUSTER...................8E-12
HIGH MOUNTED STOP LAMP (CHMSL)Ð
XJ, CENTER.........................8L-10
HIGH MOUNTED STOP LAMP (CHMSL)Ð
YJ, CENTER.........................8L-11
HINGE, LIFTGATE......................23-67
HINGE REPLACEMENT, HOOD.............23-9
HINGE, TAILGATE.....................23-159
HINGE/HINGE PIN REPLACEMENT, DOOR . . . 23-58
HINGES, FULL-METAL DOOR............23-179
HITCHES, TRAILER.....................23-88
HOISTING AND TOWING, JUMP
STARTING,............................0-7
HOLDDOWN AND FLOOR BRACKETSÐ
XJ VEHICLES, SPARE TIRE/WHEEL......23-128
HONING CYLINDER BORES................9-2
HOOD..........................23-6,23-137
HOOD ADJUSTMENT....................23-9
HOOD ALIGNMENT....................23-138
HOOD HINGE REPLACEMENT..............23-9
HOOD INSULATOR PANEL..............23-138
HOOD LATCH REPLACEMENT............23-10
HOOD LATCH STRIKER REPLACEMENT.....23-10
HOOD SAFETY LATCH.................23-139
HOOKÐXJ VEHICLES, REAR TOW.........23-87
HOOKS, FRONT TOW....................13-5
HOOKS, TOW.........................13-14
HORN PAD REPLACEMENT, HORN SWITCH . . . 8G-3
HORN SWITCH (HORN PAD)
REPLACEMENT.......................8G-3
HOSE REPLACEMENT, PRESSURE AND
RETURN............................19-9
HOSE ROUTING SCHEMATICS,
VACUUM............................25-1
HOSE SPLASH SHIELDÐXJ VEHICLES,
FUEL FILLER........................23-86
HOSES, BRAKE BLEEDINGÐBRAKE FLUID
AND LEVELÐBRAKELINES..............5-13
HOSES, BRAKELINES....................5-15
HOSES, COOLING SYSTEM...............7-26
HOSES/TUBING, RUBBER AND PLASTIC.....0-28
HOUSING, AIR CLEANER; EMISSION
CONTROL SYSTEMS...................25-8
HOUSING, AIR CLEANER; FUEL SYSTEM....14-54
HOUSING AND PARK LOCK COMPONENT
OVERHAUL, ADAPTER................21-120
HOUSING END PLUG...................19-26
HOUSING, EVAPORATOR................24-42
HOUSING, EVAPORATOR/BLOWER.........24-33
HOUSING, HEATER CORE................24-40
HOUSING LEAK DIAGNOSIS, CONVERTER
. . . 21-73
HOUSING, LIFTGATE LICENSE PLATE
LAMP
..............................23-72
HOUSING REPLACEMENT, CLUTCH
.........6-11
HOUSING REPLACEMENT, HEATER CORE
. . . 24-29HOUSING SEAL REPLACEMENT,
ADAPTER..........................21-182
HOUSINGS, INSTRUMENT CLUSTER
AND GAUGE........................23-190
HUB BEARING AND AXLE SHAFT...........2-24
HYDRAULIC CLUTCH....................0-22
HYDRAULIC COMPONENTS................5-1
HYDRAULIC CONTROL UNIT (HCU).........5-39
HYDRAULIC FLOW DURING FULL
THROTTLE 3-2 DOWNSHIFT............21-92
HYDRAULIC FLOW DURING PART
THROTTLE 3-2 DOWNSHIFT............21-91
HYDRAULIC FLOW IN D RANGE FIRST
GEAR..............................21-87
HYDRAULIC FLOW IN D RANGE SECOND
GEAR..............................21-88
HYDRAULIC FLOW IN D RANGE THIRD
GEAR..............................21-89
HYDRAULIC FLOW IN MANUAL FIRST
GEAR (1) POSITION..................21-94
HYDRAULIC FLOW IN MANUAL SECOND
(2) RANGE..........................21-93
HYDRAULIC FLOW IN PARK AND NEUTRAL . . . 21-86
HYDRAULIC FLOW IN REVERSE..........21-95
HYDRAULIC FLOW IN THIRD GEAR
(CONVERTER CLUTCH ENGAGED)........21-90
HYDRAULIC LINKAGE INSTALLATION,
CLUTCH.............................6-12
HYDRAULIC LINKAGE REMOVAL,
CLUTCH.............................6-11
HYDRAULIC PRESSURE TEST......21-71,21-168
HYDRAULIC SYSTEM..................21-160
HYDRAULIC TAPPETS...............9-24,9-65
HYDROMETER TEST....................8A-3
IDENTIFICATION, AW-4 VALVE AND
SPRING...........................21-330
IDENTIFICATION, CIRCUIT................8W-2
IDENTIFICATION, COMPONENT............8W-2
IDENTIFICATION, ENGINE AND
TRANSMISSION/TRANSFER CASE.....INTRO.-3
IDENTIFICATION, MAJOR COMPONENT . . INTRO.-3
IDENTIFICATION NUMBER (VIN)
DECODING, VEHICLE...............INTRO.-2
IDENTIFICATION NUMBER (VIN) PLATE,
VEHICLE.........................INTRO.-1
IDENTIFICATION, TRANSFER CASE
. 21-273,21-293
IDENTIFICATION, TRANSMISSION
.....21-1,21-32,
21-66,21-157
IDENTIFICATION, WIRE CODE
.............8W-2
IDENTIFICATION, WIRING AND
COMPONENT
.......................8W-13
IDLE AIR CONTROL (IAC) MOTOR
.........14-56
IDLE AIR CONTROL (IAC) MOTORÐPCM
OUTPUT
............................14-25
IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR TEST
.........14-46
IDLE SWITCHÐPCM INPUT, EXTENDED
....14-21
IDLE SWITCH TEST, EXTENDED
...........14-45
IGNITION CABLES, DISTRIBUTOR CAP
AND ROTOR
.........................0-18
IGNITION CIRCUIT SENSEÐPCM INPUT
....14-21
IGNITION COIL; FUEL SYSTEM
...........14-57
IGNITION COIL; IGNITION SYSTEMS
. . 8D-4,8D-11,
8D-26
IGNITION COILÐPCM OUTPUT
...........14-26
IGNITION COIL RESISTANCE
.............8D-11
IGNITION KEY WARNING SWITCH
REPLACEMENT
.......................8U-4
IGNITION OFF DRAW (IOD) DIAGNOSIS
.....8A-8
IGNITION SECONDARY CIRCUIT
DIAGNOSIS
.........................8D-12
IGNITION SWITCH; BRAKES
...............5-42
IGNITION SWITCH CONTINUITY TESTS
.....8D-31
IGNITION SWITCH; IGNITION SYSTEMS
....8D-30
IGNITION SWITCH INSTALLATION/
ADJUSTMENT
.......................8D-31
IGNITION SWITCH REMOVAL
............8D-30
IGNITION SWITCH TESTING
.............8D-30
IGNITION TIMING
......................8D-14
IGNITION WIRING, SECONDARY
...........8W-1
ILLUMINATED ENTRY SYSTEM SERVICE
INFORMATION
.......................8L-20
ILLUMINATED ENTRY SYSTEM TROUBLE
DIAGNOSIS
....................8L-21,8L-22
JINDEX11
Description Group-Page Description Group-Page Description Group-Page
Page 1757 of 1784

INSTRUMENT PANEL ILLUMINATION
LAMPS............................8E-16
INSTRUMENT PANEL LAMPS..............8E-4
INSTRUMENT PANEL REPLACEMENT.......8E-8
INSTRUMENT PANEL SERVICE..........23-192
INSULATION PANEL, DASH PANEL........23-95
INSULATOR PANEL, DASH PANEL.........23-11
INSULATOR PANEL, HOOD..............23-138
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR......14-54
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSORÐ
PCM INPUT.........................14-20
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR TEST . . . 14-43
INTAKE DUCT, FRESH AIR...............24-41
INTAKE MANIFOLD.....................14-57
INTAKE MANIFOLDÐ2.5L ENGINE..........11-8
INTAKE MANIFOLDÐ4.0L ENGINE..........11-9
INTAKE MANIFOLD AIR TEMPERATURE
SENSOR.......................8D-5,8D-27
INTAKE MANIFOLD AIR TEMPERATURE
SENSOR TEST.......................8D-14
INTAKE MANIFOLD LEAKAGE DIAGNOSIS.....9-5
INTERCHANGEABILITY, PARTS............21-66
INTERIOR COMPONENTS..........23-91,23-190
INTERIOR LAMPS......................8L-19
INTERIOR LAMPS, XJ..................8L-23
INTERIOR LAMPS, YJ..................8L-23
INTERIOR PAINT CODES, XJ............23-205
INTERIOR PAINT CODES, YJ............23-206
INTERIOR REARVIEW MIRROR...........23-74
INTERIOR REARVIEW MIRROR
SUPPORT BRACKET REPLACEMENT......23-75
INTERIOR TRIM PANELS AND SCUFF
PLATESÐXJ VEHICLES...............23-112
INTERLOCK CABLE ADJUSTMENT (XJ),
PARK........................21-97,21-186
INTERMEDIATE (COUPLING) SHAFT . . 19-21,19-43
INTERMITTENT WINDSHIELD WASHER,
DIAGNOSING........................8K-12
INTERMITTENT WIPER MODULE...........8K-5
INTERMITTENT WIPER WASHER..........8K-20
INTERNATIONAL VEHICLE CONTROL
AND DISPLAY SYMBOLS............INTRO.-3
IN-VEHICLE SERVICE, 30RH/32RH.........21-96
IN-VEHICLE SERVICE, AW-4.............21-173
ISOLATION, COMPRESSOR..............24-17
JACK STORAGEÐXJ VEHICLES..........23-127
JOINT ANGLE MEASUREMENT,
UNIVERSAL..........................16-4
JOINT REPLACEMENT, UNIVERSAL.........16-9
JOINTS, UNIVERSAL....................16-2
JOUNCE BUMPER, REAR................13-18
JUMP STARTING........................0-7
JUMP STARTING, HOISTING AND TOWING.....0-7
KEY LOCK CYLINDER, DOOR.............23-54
KEY LOCK CYLINDER, FULL-METAL
DOOR............................23-178
KEY LOCK CYLINDERS.............23-2,23-132
KEY WARNING SWITCH REPLACEMENT,
IGNITION............................8U-4
KEYLESS ENTRY.......................8P-8
KNOCK, LOW SPEED; FRONT
SUSPENSION AND AXLE................2-17
KNOCK, LOW SPEED; REAR SUSPENSION
AND AXLES...........................3-8
KNUCKLE AND BALL STUDS, STEERING.....2-30
LABEL, TIRE INFLATION PRESSURE.....INTRO.-3
LABEL, VEHICLE EMISSION CONTROL
INFORMATION (VECI)
..................25-1
LABEL, VEHICLE SAFETY CERTIFICATION
. INTRO.-1
LABELS/DECALS/PLATES
...........23-1,23-132
LABELS/PLATES, CODES AND
DIMENSIONS, DESIGNATIONS,
.......INTRO.-1
LAG TEST, TIME
......................21-169
LAMP, 4WD INDICATOR
..................8E-2
LAMP, ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS)
INDICATOR
..........................8E-2
LAMP BEAM ADJUSTMENT, FOG
..........8L-12
LAMP, BRAKE INDICATOR; INSTRUMENT
PANEL AND GAUGESÐXJ
...............8E-2
LAMP, BRAKE INDICATOR; INSTRUMENT
PANEL AND GAUGESÐYJ
..............8E-16
LAMP BULB REPLACEMENT, BACK-UP/
REAR TURN SIGNAL/TAIL
...............8L-9
LAMP BULB REPLACEMENT, FRONT PARK/
TURN SIGNAL
........................8L-8LAMP BULB REPLACEMENT, SIDE
MARKER............................8L-7
LAMP BULB REPLACEMENT,
UNDERHOOD........................8L-18
LAMP BULB REPLACEMENTÐYJ
VEHICLES, HARDTOP DOME/CARGO.....8L-20
LAMP BULB/ELEMENT REPLACEMENT,
FOG ...............................8L-13
LAMP (CHECK ENGINE), MALFUNCTION
INDICATOR; INSTRUMENT PANEL
AND GAUGESÐXJ................8E-2,8E-4
LAMP (CHECK ENGINE), MALFUNCTION
INDICATOR; INSTRUMENT PANEL
AND GAUGESÐYJ...................8E-16
LAMP (CHMSL)ÐXJ, CENTER HIGH
MOUNTED STOP.....................8L-10
LAMP (CHMSL)ÐYJ, CENTER HIGH
MOUNTED STOP.....................8L-11
LAMP, COOLANT TEMPERATURE
INDICATOR..........................8E-1
LAMP FOR DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES,
INDICATOR (CHECK ENGINE)...........8A-19
LAMP HOUSING, LIFTGATE LICENSE
PLATE .............................23-72
LAMP, I/P ASH RECEIVER TRAY..........23-92
LAMP, LICENSE PLATE..................8L-10
LAMP, LOW FUEL WARNING..............8E-2
LAMPÐPCM OUTPUT, EMR..............14-24
LAMPÐPCM OUTPUT, GENERATOR.......14-25
LAMPÐPCM OUTPUT, MALFUNCTION
INDICATOR.........................14-26
LAMP REPLACEMENT, DOME.............8L-20
LAMP REPLACEMENT, FOG..............8L-15
LAMP REPLACEMENT, UNDERHOOD.......8L-18
LAMP, SEAT BELT REMINDER............8E-16
LAMP SERVICE INFORMATION, DOME/
COURTESY.........................8L-19
LAMP SERVICE INFORMATION, FOG.......8L-12
LAMP SERVICE INFORMATION,
UNDERHOOD........................8L-17
LAMP, SERVICE REMINDER INDICATOR
(SRI)...............................25-1
LAMP SPEED CONTROL SWITCH TEST,
STOP...............................8H-7
LAMP SUPPORT BRACKET, I/P TWEETER
SPEAKER/COURTESY.................23-95
LAMP SWITCH REPLACEMENT, FOG.......8L-14
LAMP TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS, DOME/
COURTESY.........................8L-19
LAMP TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS, FOG.........8L-12
LAMP, UPSHIFT INDICATOR;
INSTRUMENT PANELAND GAUGESÐXJ....8E-2
LAMP, UPSHIFT INDICATOR;
INSTRUMENT PANELAND GAUGESÐYJ . . . 8E-16
LAMPÐYJ RENEGADE VEHICLES, FOG....23-150
LAMP/REAR WIPER SWITCHES, REAR
DEFOGGER/FOG......................8E-21
LAMPS, EXTERIOR......................8L-1
LAMPS, INDICATOR....................8E-14
LAMPS INOPERATIVE, DIAGNOSISÐ
HAZARD.........................8J-1,8J-2
LAMPS, INSTRUMENT PANEL.............8E-4
LAMPS, INSTRUMENT PANEL
ILLUMINATION......................8E-16
LAMPS, INTERIOR.....................8L-19
LAMPS OUT, DIAGNOSINGÐALL..........8E-16
LAMPS, XJ EXTERIOR..................8L-23
LAMPSÐXJ, HAZARD...................8J-1
LAMPS, XJ INTERIOR..................8L-23
LAMPS, YJ EXTERIOR..................8L-23
LAMPSÐYJ, HAZARD...................8J-2
LAMPS, YJ INTERIOR..................8L-23
LATCH ADJUSTMENT, DOOR.............23-55
LATCH AND RELEASE HANDLE,
TAILGATE..........................23-160
LATCH ASSEMBLY REPLACEMENT,
SOLENOID...........................8P-6
LATCH, DOOR.........................23-56
LATCH EXTERNAL RELEASE HANDLE,
FULL-METAL DOOR..................23-178
LATCH, FULL-METAL DOOR
.............23-179
LATCH, HOOD SAFETY
.................23-139
LATCH INSIDE RELEASE AND LOCK
HANDLE, FULL-METAL DOOR
..........23-175
LATCH RELEASE AND LOCK RODS,
DOOR INSIDE
.......................23-57LATCH RELEASE CABLE REPLACEMENT....23-10
LATCH REPLACEMENT, HOOD............23-10
LATCH STRIKER AND BUMPERÐXJ
VEHICLES, REAR SEATBACK...........23-111
LATCH STRIKER, HALF-METAL DOOR.....23-175
LATCH STRIKER REPLACEMENT, HOOD....23-10
LATCH STRIKER REPLACEMENT, SAFETY . . . 23-10
LATCH STRIKER, TAILGATE.............23-161
LATCH/KEY LOCK CYLINDER/STRIKER,
LIFTGATE...........................23-68
LEAD CORRECTION CHART...............22-5
LEAF SPRING; FRONT SUSPENSION AND
AXLE...............................2-14
LEAF SPRING; REAR SUSPENSION AND
AXLES............................3-3,3-6
LEAF SPRING EYE BUSHING
REPLACEMENT; FRONT SUSPENSION
AND AXLE...........................2-15
LEAF SPRING EYE BUSHING
REPLACEMENT; REAR SUSPENSION
AND AXLES........................3-4,3-6
LEAK DETECTION AND REPAIR, FIXED
GLASS WATER................23-83,23-189
LEAK DIAGNOSIS, CONVERTER HOUSING . . . 21-73
LEAK DOWN TEST, FUEL PRESSURE........14-7
LEAK TEST, REFRIGERANT................24-8
LEAKAGE DIAGNOSIS, GEAR
..............19-8
LEAKAGE DIAGNOSIS, INTAKE
MANIFOLD
............................9-5
LEAKAGE DIAGNOSIS, PUMP
..............19-8
LEAKAGE TEST, CYLINDER COMBUSTION
PRESSURE
...........................9-6
LEAKAGE TEST DIAGNOSIS, CYLINDER
COMBUSTION PRESSURE
................9-6
LEAKS, REPAIRING
.....................22-3
LEAKS, TESTING COOLING SYSTEM FOR
....7-18
LEFT HAND DRIVE, DRIVERS DOOR
POWER LOCK SWITCHÐ2-DOOR
.........8P-2
LEFT HAND DRIVE, DRIVERS DOOR
POWER WINDOW SWITCHÐ2-DOOR
......8S-6
LETTERS, JEEP BODY CODE
...............5-2
LEVEL AND CONDITION, CHECKING
FLUID
.......................21-96,21-173
LEVEL AND CONDITION, FLUID
...........21-69
LEVEL, BRAKE FLUID
....................5-13
LEVELÐBRAKELINES AND HOSES,
BRAKE BLEEDINGÐBRAKE FLUID
........5-13
LEVEL, CLUTCH FLUID
...................6-14
LEVEL, COMPRESSOR OIL
................24-6
LEVEL, CORRECT FLUID
.................5-48
LEVEL, TRANSFER CASE FILL
...........21-294
LEVELS, OPERATING SOUND
...............5-3
LEVER INSTALLATION (XJ WITH FULL
CONSOLE), PARKING BRAKE
............5-60
LEVER INSTALLATION (XJ WITH MINI
CONSOLE), PARKING BRAKE
............5-58
LEVER INSTALLATION (XJ WITHOUT
CONSOLE), PARKING BRAKE
............5-60
LEVER POSITIONS, TRANSMISSION
RANGES AND SHIFT
.................21-157
LEVER REMOVAL (XJ WITH FULL
CONSOLE), PARKING BRAKE
............5-59
LEVER REMOVAL (XJ WITH MINI
CONSOLE), PARKING BRAKE
............5-58
LEVER REMOVAL (XJ WITHOUT
CONSOLE), PARKING BRAKE
............5-60
LICENSE PLATE LAMP
..................8L-10
LICENSE PLATE LAMP HOUSING,
LIFTGATE
...........................23-72
LICENSE PLATE SCREW ANCHOR
AND BUMPER, LIFTGATE
..............23-72
LIFTGATE ADJUSTMENT
.................23-70
LIFTGATE GLASS, HARD TOP
............23-162
LIFTGATE GLASS WEATHERSTRIP SEAL
REPLACEMENT
.....................23-163
LIFTGATE HINGE
.......................23-67
LIFTGATE LATCH/KEY LOCK CYLINDER/
STRIKER
...........................23-68
LIFTGATE LICENSE PLATE LAMP
HOUSING
...........................23-72
LIFTGATE LICENSE PLATE SCREW
ANCHOR AND BUMPER
...............23-72
JINDEX13
Description Group-Page Description Group-Page Description Group-Page