wheel torque JEEP CJ 1953 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 1953, Model line: CJ, Model: JEEP CJ 1953Pages: 376, PDF Size: 19.96 MB
Page 302 of 376
N
REAR
AXLE a.
Place the transmission in neutral.
b.
Raise one wheel off the floor and place a block
in
front and at the
rear
of the
opposite
wheel.
c.
Apply a torque wrench to the axle shaft nut of
the elevated wheel.
d.
Turn
wheel with torque wrench. Disregard
breakaway
torque and observe torque required to
continuously
turn
wheel smoothly. Torque should
read
40 lb-ft [5,53 kg-m.] or more.
N-23. Powr-Lok
Differential Disassembly
/
and Reassembly
Refer
to
Figs.
N-38 and N-39.
The
procedure for overhauling disc type
Powr-Lok
differentials is as follows:
a.
Remove axle shafts following procedure de
scribed
in Par. N-2.
b.
Remove housing cover and gasket.
c.
Remove the
Powr-Lok
differential from the axle.
Do not remove the ring gear or bearing
cone
and
rollers
unless replacement is to be made.
Mark
the hearing cups so they may later be reassembled
with
the same bearing cones.
Mark
the differential
case halves for correct alignment at reassembly.
Each
pinion mate cross shaft should also be marked
so that each pin cam surface
will
match with the
same
V-ramp
in the case when reassembled.
d.
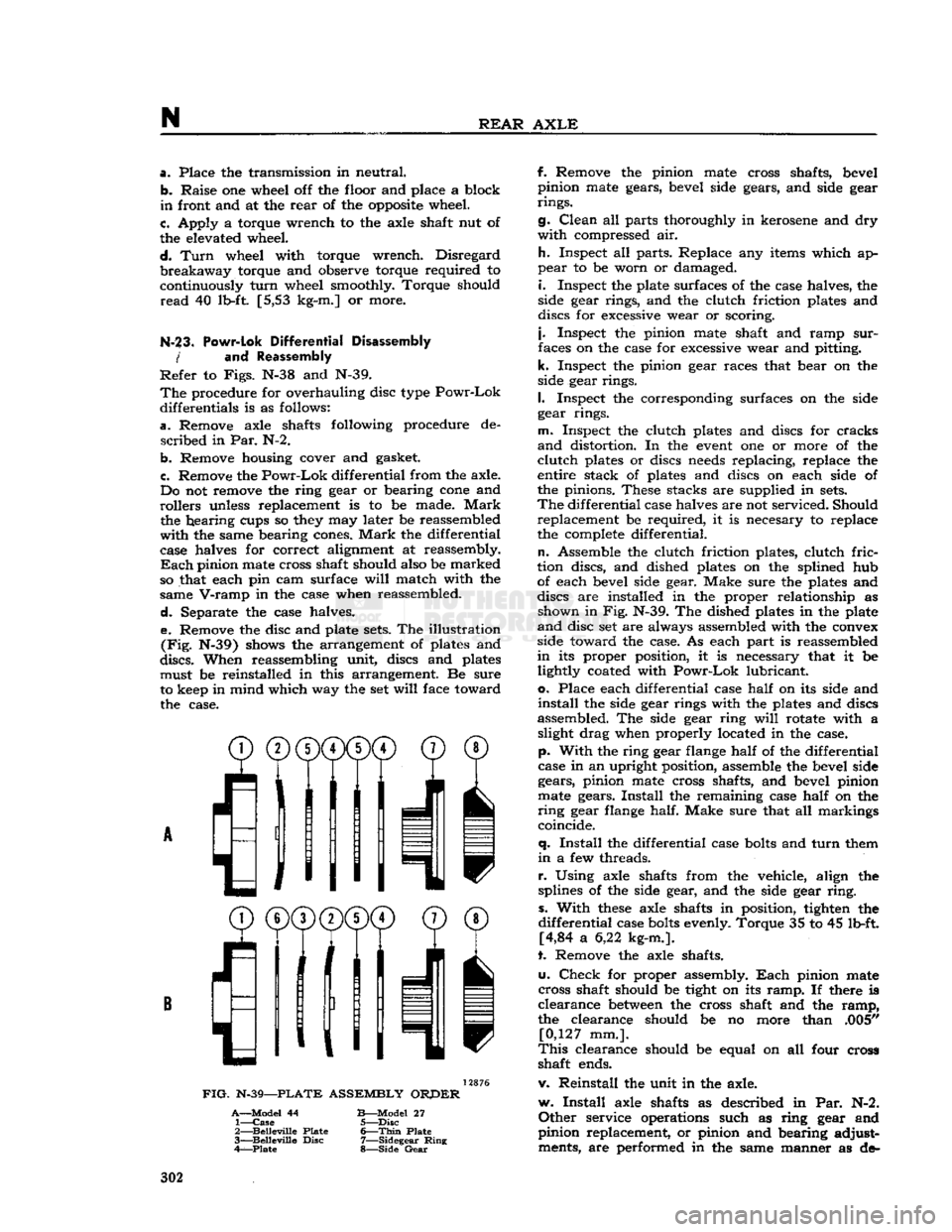
Separate the case halves. e. Remove the disc and plate
sets.
The illustration
(Fig.
N-39) shows the arrangement of plates and
discs.
When reassembling unit, discs and plates must be reinstalled in this arrangement. Be sure
to keep in mind which way the set
will
face toward the case.
^®(j)(j)CD©
® /'Ml
I
11
11 v
FIG.
N-39—PLATE
ASSEMBLY
ORPER
A—Model
44
B—Model
27 1—
Case
5—Disc
2—
Belleville
Plate
6—Thin
Plate
3—
Belleville
Disc
7—Sidegear
Ring
4—Plate
8—Side
Gear
f. Remove the pinion mate cross shafts, bevel
pinion mate gears, bevel side gears, and side gear
rings.
g.
Clean
all parts thoroughly in kerosene and dry
with
compressed air.
h.
Inspect all parts. Replace any items which ap
pear
to be worn or damaged.
i.
Inspect the plate surfaces of the case halves, the
side gear rings, and the clutch friction plates and
discs for excessive wear or scoring.
j.
Inspect the pinion mate shaft and ramp
sur
faces on the case for excessive wear and pitting,
k.
Inspect the pinion gear races that bear on the
side gear rings.
I.
Inspect the corresponding surfaces on the side
gear rings.
m.
Inspect the clutch plates and discs for cracks
and
distortion. In the
event
one or more of the
clutch
plates or discs
needs
replacing, replace the
entire stack of plates and discs on each side of
the pinions. These stacks are supplied in
sets.
The
differential case halves are not serviced. Should replacement be required, it is necesary to replace
the complete differential.
n.
Assemble the clutch friction plates, clutch
fric
tion discs, and dished plates on the splined hub of each bevel side gear. Make sure the plates and
discs are installed in the proper relationship as shown in Fig. N-39. The dished plates in the plate
and
disc set are always assembled with the convex
side toward the case. As each part is reassembled
in
its proper position, it is necessary that it be lightly coated with
Powr-Lok
lubricant,
o.
Place each differential case
half
on its side and
install
the side gear rings with the plates and discs
assembled. The side gear ring
will
rotate with a slight drag when properly located in the case,
p.
With
the ring gear flange
half
of the differential
case in an upright position, assemble the bevel side gears, pinion mate cross shafts, and bevel pinion
mate gears.
Install
the remaining case
half
on the
ring
gear flange half. Make sure that all markings
coincide.
q.
Install
the differential case
bolts
and
turn
them
in
a few threads.
r.
Using axle shafts from the vehicle, align the
splines of the side gear, and the side gear
ring,
s.
With
these
axle shafts in position, tighten the
differential
case
bolts
evenly. Torque 35 to 45 lb-ft. [4,84 a 6,22 kg-m.].
t. Remove the axle shafts.
u.
Check
for proper assembly.
Each
pinion mate
cross shaft should be tight on its
ramp.
If there is
clearance
between
the cross shaft and the
ramp,
the clearance should be no more than .005" [0,127 mm.].
This
clearance should be equal on all four cross
shaft ends.
v. Reinstall the unit in the axle.
w.
Install
axle shafts as described in Par. N-2.
Other
service operations such as ring gear and
pinion replacement, or pinion and bearing adjust ments, are performed in the same manner as de- 302
Page 303 of 376

'Jeep*
UNIVERSAL
SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
N
scribed
in
Pars.
N-ll through N-l9 for standard
axles, with the exception of the following torque
recommendations. Torque the differential case
bearing
cap screws 70 to 90 lb-ft. [9,7 a 12,4 kg-m.]
and
the cover screws 15 to 25 lb-ft. [2,1 a 3,4
kg-m.].
The ring gear screws on axles with Powr-
Lok
differentials should be torqued as follows:
Model
30 and 44 axles 35 to 55 lb-ft. [4,84 a 7,60 kg-m.].
N-24. TRAC-LOK DIFFERENTIAL
As
optional equipment
Trac-Lok
Model 44 differen
tial
is available on all Jeep Universal vehicles equipped with semi-float flanged axle shafts.
A
conventional differential transmits all of the
ring
gear torque through the differential gears to the axle shafts. Torque is at all
times
equal on the axle shafts, and if one wheel slips, the other wheel
can
only put out as much torque as the slipping
wheel.
The
Trac-Lok
differential is similar,
except
that
part
of the torque from the ring gear is trans mitted through clutch packs
between
the side gears
and
differential case. The multiple disc clutches
with
radial
grooves
on the plates and concentric
grooves
on the discs are
engaged
by a preload
from
Belleville springs, plus separating forces from
the side gears as torque is applied through the
ring
gear.
The
Trac-Lok
construction permits differential action when required for turning corners and transmits equal torque to both
wheels
when driving
straight
ahead. However, when one wheel tries to spin due to leaving the ground, a patch of ice,
etc., the clutch packs automatically provide more
torque to the wheel which is not trying to spin.
It
can be
seen
then that the
Trac-Lok
differential
resists wheel spin on bumpy roads and provides
more pulling power when one wheel tries to slip.
In
many cases of differences in traction, pulling
power
will
be automatically provided until both
wheels
start to slip.
In
diagnosis of vehicle operators' complaints, it
is important to recognize two things:
a.
If, with unequal traction, both
wheels
slip, the
Trac-Lok
has
done
all it can possibly do.
b.
In extreme cases of differences in traction, the
wheel with least traction may spin after the
Trac-
Lok
has transferred as much torque as possible
to the non-slipping wheel.
N-25.
Lubrication
The
Trac-Lok
differential requires a special
lubri
cant
and ordinary multipurpose gear lubricants
MUST
NOT be used. Use only 'Jeep* Differential
Oil,
Part
No. 94557.
Trac-Lok
differential may be cleaned only by disassembling the unit and wiping with clean rags. Do not flush the
Trac-Lok
unit.
Note:
The
Trac-Lok
differential is serviced at the
same time intervals as the standard differential.
N-26.
Trouble
Symptoms
If
noises
or roughness, such as chatter, are present
in
turning corners, the probable cause is incorrect
or
contaminated lubricant.
Before any differential is removed and disassem
bled for chatter complaints, the correctness of
lubri
cant
can and should be determined.
A
complete
lubricant
drain,
and
refill
with specified
Limited
Slip Differential lubricant
will
usually
correct
chatter.
The
following procedure is recommended to ensure
complete
removal of old lubricant.
a.
Warm
the lubricant by vehicle road operation,
or
5 minutes of operation in gear at 30 mph with
both
wheels
off the ground on a hoist.
Caution:
Never place the transmission in gear with
the
engine
running when only one wheel of a
Limited
Slip Differential equipped vehicle is raised.
The
vehicle might drive itself off the
jack
and produce damage or
injury.
b.
Drain
lubricant while
warm.
Remove
drain
plug
or
cover to
drain
completely. If cover is removed,
it
may be necessary to replace gasket at this time.
c.
Refill
axle with specified
Limited
Slip Differen
tial
lubricant.
d.
Operate the vehicle for approximately ten miles
[16,09
km.], making at least ten figure 8 turns
to flush the old lubricant out of the clutch packs.
e.
Repeat
steps
b, c, and d, making sure to replace
the cover gasket if required in
step
c.
f. It is possible that slight chatter, requiring ad
ditional
vehicle operation, may remain after
step
e. If chatter persists after 100 miles
[160,9
km.]
of vehicle operation, or remains severe after
step
e above, disassembly and repair
will
be necessary.
N-27.
Unit
Inoperative
Proper
performance and capabilities of
Limited
Slip
Differentials are
often
misunderstood. No
precise
methods
of measuring
Limited
Slip Dif
ferential
performance are generally available in the field. A functioning unit can be determined by
relatively
simple vehicle operational
tests,
as
follows:
a.
Place one wheel on
good
dry pavement, and the
other on ice, mud, grease, etc.
b.
Gradually
increase
engine
rpm to obtain maxi
mum
traction
prior
to "break-a-way." The ability
to
move
the vehicle
effectively
will
demonstrate
proper
performance.
c.
If extremely slick surfaces, such as ice or grease,
are
used
some
question may exist as to proper per
formance at
step
b. In
these
extreme cases a prop
erly
performing
Limited
Slip Differential
will
pro
vide greater "pulling" power by lightly applying
the parking brake.
N-23.
Trac-Lok
Differential Disassembly
and
Reassembly
It
is recommended that the
complete
axle assembly
be removed from the vehicle, when it
becomes
necessary to remove the
Trac-Lok
from the hous
ing.
Refer to Par. N-3 and N-12 for removal of axle shafts and differential case from axle housing. 303
Page 310 of 376

m
REAR AXLE
c. Attach the brake line
hose
at tee fitting on top
of housing.
d.
Attach parking brake cables at rear of brake
backing plate. DJ
models
only.
e. Connect the shock absorbers at the axle mount
ing pads.
f. Connect the propeller shaft at the rear universal
joint.
g. Adjust and bleed brakes. (See Section P).
h.
Install
wheels
and lower vehicle to floor.
i.
Check parking brake as described in Section P.
j.
Fill
the axle housing with the proper lubricant.
For
correct lubricant refer to the
Lubrication
Chart.
N-34.
TROUBLE
SHOOTING
The
following problems can be present with either the conventional differential,
Powr-Lok
or
Trac-
Lok
differential.
N-35. Backlash
Excessive
backlash in the vehicle drive line may be the results of
excessive
backlash in the trans
mission, propeller shaft spline, universal joint, ring gear and pinion, the axle shaft spline, or the dif
ferential.
Excessive
backlash in the differential may be meas
ured
as follows:
a.
Jack
up one rear wheel.
b. Put the transmission in gear.
c. Measure the travel of the jacked-up wheel on
a
10"
[25,40
cm.] radius from the wheel center.
This
total
movement
should not
exceed
IVi" [3,17 cm.] in a new unit. In order to restrict the
backlash
to the axles only, make sure that the
yoke of the propeller shaft
does
not
move
during
the check.
d.
If all causes of backlash mentioned
above
have
been
eliminated with the exception of the differen
tial
and that still
exceeds
the maximum allowable
movement, overhaul the differential.
N-36.
Rear
Wheel
Noise
Looseness of the rear axle shaft nut on semifloat- ing tapered rear axles may produce a clicking or
creaking
noise.
This
noise
can usually be
stopped
by torquing the wheel hub nut 150 to 175 lb-ft. [20,7 a 24,2 kg-m.]. If the condition has continued
for
some
time, slight wear may have resulted allow
ing the
noise
to persist. In this case, coat the hub,
key, and keyway on tapered axle shafts with white
lead and torque the nut as specified. If the
noise
persists after this treatment, replace the worn parts.
N-37.
SERVICE DIAGNOSIS
SYMPTOMS
Axle
Noisy on Pull and
Coast
Excessive
Back
Lash
Bevel
Gear
and Pinion. . . . . Adjust
End
Play Pinion Shaft Adjust
Worn
Pinion Shaft Bearing Adjust
Pinion
Set too Deep in Bevel
Gear
too Tight..... Adjust
Wrong
Lubricant
Being Used
(Powr-Lok
or
Trac-Lok
Differential) . Replace
Axle
Noisy on
Pull
Pinion
and Bevel
Gear
Improperly Adjusted Adjust
Pinion
Bearings Rough....................... Adjust
Pinion
Bearings Loose Adjust
Axle
Noisy on Coast
Excessive
Back
Lash
in Bevel
Gear
and Pinion. . . Adjust
End
Play in Pinion Shaft. . Adjust
Improper
Tooth Contact.
....................
Adjust
Rough Bearings Replace
Back
Lash
Worn
Differential Pinion
Gear
Washers Adjust
Excessive
Back
Lash
in Bevel
Gear
and Pinion. . . Adjust
Worn
Universal Joints Replace
PROBABLE REMEDY
310
Page 314 of 376
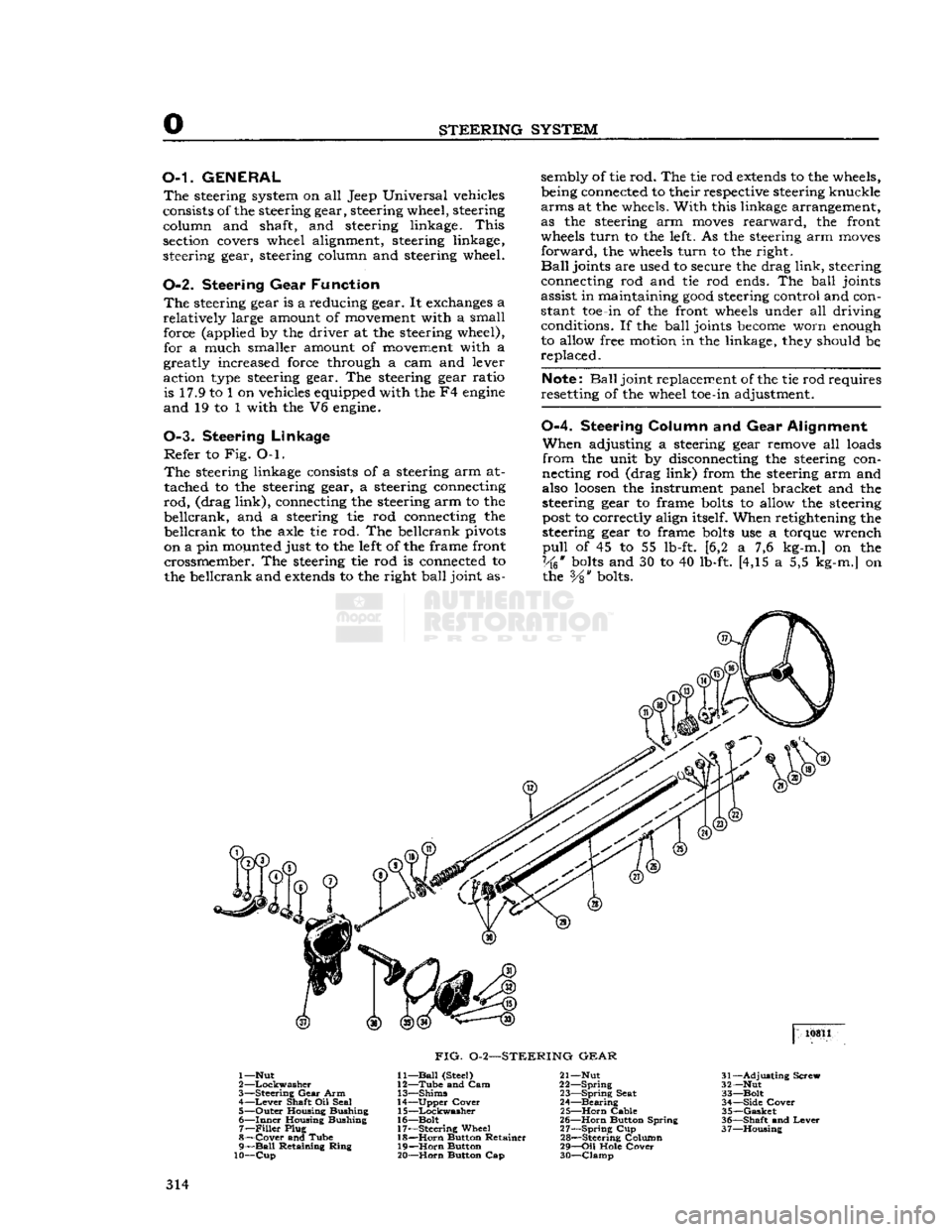
STEERING
SYSTEM
O-L
GENERAL
The
steering system on all Jeep Universal vehicles
consists of the steering gear, steering wheel, steering column and shaft, and steering linkage.
This
section covers wheel alignment, steering linkage,
steering gear, steering column and steering wheel.
0-2. Steering
Gear
Function
The
steering gear is a reducing gear. It exchanges a
relatively
large amount of movement with a small force (applied by the driver at the steering wheel), for a much smaller amount of movement with a
greatly increased force through a cam and lever
action type steering gear. The steering gear ratio is 17.9 to 1 on vehicles equipped with the F4
engine
and
19 to 1 with the V6 engine.
0-3. Steering
Linkage
Refer
to Fig. O-l.
The
steering linkage consists of a steering arm at
tached to the steering gear, a steering connecting
rod,
(drag
link),
connecting the steering arm to the
beilcrank,
and a steering tie rod connecting the
beilcrank
to the axle tie rod. The beilcrank pivots
on a pin mounted just to the left of the frame front crossmember. The steering tie rod is connected to
the beilcrank and
extends
to the right
ball
joint as sembly of tie rod. The tie rod
extends
to the wheels,
being connected to their respective steering knuckle
arms
at the wheels.
With
this linkage arrangement,
as the steering arm
moves
rearward,
the front
wheels
turn
to the left. As the steering arm
moves
forward,
the wheels
turn
to the right.
Ball
joints are used to secure the drag
link,
steering
connecting rod and tie rod ends. The
ball
joints
assist in maintaining
good
steering control and con
stant toe-in of the front wheels under all driving conditions. If the
ball
joints
become
worn enough
to allow free motion in the linkage, they should be,
replaced.
Note:
Ball
joint replacement of the tie rod requires
resetting of the wheel toe-in adjustment.
0-4.
Steering
Column
and Gear
Alignment
When
adjusting a steering gear remove all loads
from
the unit by disconnecting the steering con
necting rod (drag
link)
from the steering arm and
also
loosen
the instrument panel bracket and the
steering gear to frame
bolts
to allow the steering
post
to correctly align itself. When retightening the
steering gear to frame
bolts
use a torque wrench
pull
of 45 to 55 lb-ft. [6,2 a 7,6 kg-m.] on the
Vk*
bolts
and 30 to 40 lb-ft. [4,15 a 5,5 kg-m.] on the
Vs"
bolts. 10811
FIG.
0-2—STEERING
GEAR
1—Nut
2
—Lockwasher
3—
Steering
Gear
Arm 4—
Lever
Shaft Oil Seal
5—
Outer
Housing Bushing
6—
Inner
Housing Bushing 7—
Filler
Plug
8—
Cover
and Tube
9—
Ball
Retaining
Ring
10—Cup
11—
Ball
(Steel)
12—
Tube
and Cam
13—
Shims
14—
Upper
Cover
15—
Lockwasher
16—
Bolt
17—
Steering
Wheel 18—
Horn
Button Retainer
19—
Horn
Button
20—
Horn
Button Cap 21— Nut
22—
Spring
23—
Spring
Seat
24—
Bearing
25—
Horn
Cable
26—
Horn
Button Spring
27—
Spring
Cup
28—
Steering Column
29—
Oil
Hole
Cover
30—
Clamp
31—
Adjusting
Screw
32— Nut
33—
Bolt
34—
Side
Cover
35—
Gasket
36—
Shaft
and
Lever
37—
Housing
314
Page 315 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL
SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
O Note:
If the steering-gear-to-frame
bolts
are not
properly
torqued, they
will
eventually
loosen
dur
ing operation of the vehicle. Loose
bolts
will
result
in
elongated
bolt
holes
making maintenance of bolt torque difficult, and may allow position of the
steering columns to be misaligned. Therefore,
proper
torquing is extremely important.
Do not tighten the steering gear to dampen out
steering trouble. Adjust the steering gear only to
remove lost motion or play within the unit.
0-5. Steering
Gear
Adjustment
The
cam and lever steering gear is illustrated in
Fig.
0-2. It consists of a
spiral
cam, and a cross shaft and lever assembly with two lever studs.
When
the steering wheel is turned, the cam
moves
the studs, causing rotary movement of the cross
shaft, which in
turn
causes angular movement of
the*steering arm.
Two
adjustments of the steering gear are necessary:
up and down play of the steering shaft, and adjustment of the lever studs (tapered pins) in the
cam
groove.
Adjustment
of the
ball
thrust bearings to eliminate up and down play of the steering shaft is ac
complished by removing shims which are installed
between
the steering gear housing and the upper
cover. Before making this adjustment
loosen
the
housing side cover adjusting screw to free the pins
in
the cam groove. Loosen the housing cover to
cut and remove a shim or more as required.
Install
the screws and tighten. Adjustment should be
made to have a slight drag but allow the steering
wheel to
turn
freely with thumb and forefinger
lightly gripping the rim.
Shims
installed for adjustment are .002*, .003", and .010"
[.0508,
.0762
and .254 mm.] in thickness.
Adjustment
of the tapered pins in the cam
groove
is accomplished by adjusting screw. Unlock the
adjusting
screw and
turn
it in until a very slight
drag
is felt through the mid-position when turning
the steering wheel slowly from one extreme position
to the other.
Backlash
of the pins in the
groove
shows up as
end play of lever shaft, also as backlash of steer ing arm.
The
cam
groove
is purposely cut shallow in the
straight
ahead driving position for each pin.
This
feature permits a
close
adjustment for normal
straight
ahead driving and provides precision steer ing and permits take up of backlash at this point
after the wear occurs without causing a bind else
where.
Always
adjust within the high range through
the mid-position of pin travel. Do not adjust off
"straight
ahead" position.
Backlash
in turned posi
tions is not objectionable.
0-6.
Front
Wheel Alignment Adjustments
To
ensure correct alignment, a definite procedure
for inspection of the steering system is recom mended. It is
suggested
that the following sequence
be used:
a.
Equalize
tire pressures and level vehicle.
b.
Check
steering gear to steering column align
ment.
c.
Inspect steering knuckle pivots, spindle, and
wheel bearing
looseness.
d.
Check
wheel runout.
e.
Test wheel balance and bearing adjustment.
f.
Check
for spring sag.
g.
Inspect brakes and shock absorbers.
h.
Check
steering gear assembly adjustment and
steering connecting rod.
i.
Check
caster,
j.
Check
toe-in.
k.
Check
toe-out
on turns.
I.
Check
camber.
m.
Check
tracking of front and
rear
wheels,
n.
Check
frame alignment.
The
factors of alignment, caster, camber, and toe-
in,
are all interrelated and if one adjustment is
made, another adjustment may be affected.
There
fore, after an alignment job is completed, make a
complete recheck of all the adjustments to be sure
the
settings
are within the limit. Be sure all front
suspension and steering system nuts and
bolts
are
all
properly torqued before taking wheel alignment readings.
Proper
alignment of front wheels must be main
tained in order to ensure
ease
of steering and satisfactory tire life.
The
most important factors of front wheel alignment are wheel camber, axle caster and wheel
toe-in.
Wheel
toe-in is the distance the wheels are closer
together
at the front than at the
rear.
Wheel
camber is the amount the wheels incline out
ward
at the top from a vertical position.
Front
axle caster is the amount in
degrees
that the
steering pivot pins are tilted towards the front or
rear
of the vehicle. Positive caster is inclination of
the top of the pivot pin towards the
rear
of the ve
hicle.
Zero caster is the vertical position of the
pivot pin. Negative or reverse caster is the in
clination
of the top of the pin towards the front
of the vehicle.
These
points should be checked at regular inter
vals,
particularly when the front axle has been
subjected to a heavy impact. When checking wheel alignment, it is important that wheel bearings and
knuckle
bearings be in proper adjustment. Loose bearings
will
affect instrument readings when
checking
the camber, pivot pin inclination and
toe-in.
To
accurately check camber and caster, use a wheel
aligning fixture.
Camber
and caster of the front
wheels are both preset.
Camber
cannot be altered
but caster can be adjusted by installing caster shims
between
the axle pad and the springs. Wheel toe-in
may
be adjusted. To measure wheel toe-in, use a
wheel aligning fixture or follow the procedure given
in Par.
0-8.
0-7.
Front Wheel Toe-in
Toe-in
as illustrated in
Fig.
0-3, is necessary to
off
set the
effect
of camber as shown in Fig. Q-4. 315
Page 320 of 376
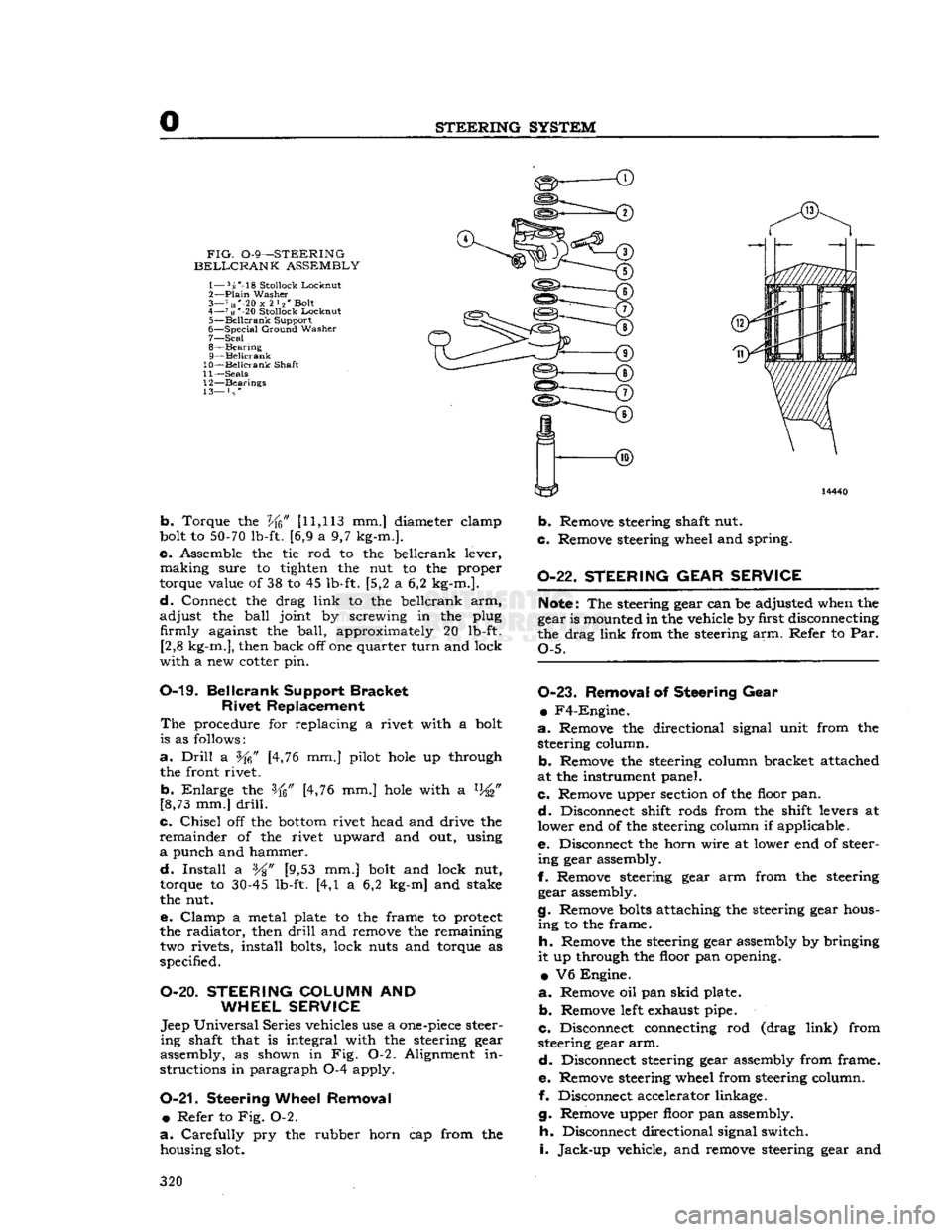
STEERING
SYSTEM
FIG.
0-9—STEERING
BELLCRANK
ASSEMBLY
1— 5s'-18
Stollock
Lockout
2—
Plain
Washer
3— 7 us"-20
x
2 l2' Bolt
4—
71«
*-20
Stollock
Locknut
5—
Beilcrank
Support
6—
Special
Ground
Washer
7— Seal
8—
Bearing
9— Beilcrank
10— Beilcrank
Shaft
11—
Seals
12—
Bearings
13— } s *
b.
Torque the
Vfc"
[11,113
mm.] diameter elamp
bolt to
50-70
lb-ft. [6,9 a 9,7 kg-m.].
c.
Assemble the tie rod to the beilcrank lever,
making
sure to tighten the nut to the proper
torque value of 38 to 45 lb-ft. [5,2 a 6,2 kg-m.].
d.
Connect the drag
link
to the beilcrank arm,
adjust
the
ball
joint by screwing in the plug firmly against the
ball,
approximately 20 lb-ft. [2,8 kg-m.], then back off one quarter
turn
and lock
with
a new cotter pin.
0-19.
Beilcrank
Support
Bracket
Rivet
Replacement
The
procedure for replacing a rivet with a bolt
is as follows:
a.
Drill
a [4,76 mm.] pilot
hole
up through
the front rivet.
b.
Enlarge
the [4,76 mm.]
hole
with a %"
[8,73 mm.]
drill.
c.
Chisel
off the
bottom
rivet head and drive the
remainder
of the rivet upward and out, using
a
punch and hammer.
d.
Install
a %" [9,53 mm.] bolt and lock nut,
torque to
30-45
lb-ft. [4,1 a 6,2 kg-m] and stake
the nut.
e.
Clamp
a metal plate to the frame to protect
the radiator, then
drill
and remove the remaining two rivets, install bolts, lock nuts and torque as
specified.
O-20.
STEERING
COLUMN
AND
WHEEL SERVICE
Jeep
Universal
Series vehicles use a
one-piece
steer
ing
shaft that is integral with the steering gear
assembly, as shown in Fig. 0-2. Alignment in
structions in paragraph 0-4 apply.
0-21.
Steering
Wheel Removal •
Refer to Fig. 0-2.
a.
Carefully
pry the rubber horn cap from the housing slot.
b.
Remove steering shaft nut.
c.
Remove steering wheel and spring.
0-22.
STEERING GEAR SERVICE
Note:
The steering gear can be adjusted when the
gear is mounted in the vehicle by first disconnecting
the drag
link
from the steering arm. Refer to Par.
Q-5.
0-23.
Removal
of
Steering Gear
•
F4-Engine.
a.
Remove the directional signal unit from the steering column.
b.
Remove the steering column bracket attached
at the instrument panel.
c.
Remove upper section of the floor pan.
d.
Disconnect shift rods from the shift levers at
lower end of the steering column if applicable.
e.
Disconnect the horn wire at lower end of steer
ing
gear assembly.
f.
Remove steering gear arm from the steering gear assembly.
g.
Remove
bolts
attaching the steering gear hous
ing
to the frame.
h.
Remove the steering gear assembly by bringing
it
up through the floor pan opening.
•
V6 Engine.
a.
Remove oil pan
skid
plate.
b.
Remove
left
exhaust pipe.
c.
Disconnect connecting rod (drag
link)
from
steering gear arm.
d.
Disconnect steering gear assembly from frame.
e.
Remove steering wheel from steering column.
f. Disconnect accelerator linkage.
g.
Remove upper floor pan assembly.
h.
Disconnect directional signal switch.
i.
Jack-up
vehicle, and remove steering gear and
320
Page 321 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL
SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
O
column assembly down through the floor pan open
ing and out from under vehicle.
0-24.
Disassembly
of
Steering
Gear
Refer
to Fig. 0-2.
When
the steering gear arm is installed on early
production vehicles, the line across the face of the
arm
and the end of the shaft should be in align ment. On later production vehicles, blind splines
on the lever shaft and in the steering gear arm en
sure
correct positioning of the arm.
a.
Remove the steering gear arm with a puller
C-3646.
Caution:
Do not use a hammer or
wedge
to re
move
the steering arm from the shaft and lever.
This
can cause damage to the shaft assembly.
b.
Loosen the lock nut and unscrew the adjusting
screw
two turns.
c.
Remove the side cover screws and washers. Re
move
the side cover and gasket.
d.
Remove lever shaft.
e.
Remove upper cover plate screws. Remove cam,
wheel tube, and bearing assembly from the housing.
f.
Clean
all parts with suitable cleaning solvent and wipe dry.
g.
After dismantling as outlined above is com
pleted, inspect cam
grooves
for wear, chipping and
scoring,
also the
ball
races on the cam ends and the
separate
ball
cups. Existence of any of
these
condi tions indicates the necessity for parts replacement.
h.
Inspect the tapered stud mounted on the lever
shaft for flat
spots
and chipping. In the case of
either, replacement is usually advisable. Inspect the
lever shaft for wear and
test
the fit of the shaft in
the bushings.
i.
Inspect condition of the oil seal at outer end of
lever shaft and the bearing at top end of steering
column.
0-25.
Reassembly
of
Steering
Gear
e Refer to Fig. 0-2.
Reassemble all parts to wheel tube in reverse order
of dismantling. Assemble cam, wheel tube and
bearing
assembly in housing, seating the lower
bearing
ball
cup in the housing.
Note:
New plastic retainer type cam bearings are
now available for the Ross steering gears. The new
bearings replace, and are interchangeable with,
the lock ring type cam bearings on gears equipped
with
early type cams.
With
adjusting shims in place, assemble upper
cover and adjust the cam bearings.
Assemble lever shaft in housing and with gasket
in
place assemble the side cover and set adjusting
screw
for a minimum backlash of the studs in the
cam
groove, with the steering gear at the center
point of travel.
When
assembling upper bearing spring and spring
seat in jacket tube make sure that the spring seat
is positioned correctly. It must be installed with
the lengthwise flange down against the bearing and
not up inside of spring coil.
0-26.
Installation
of
Steering
Gear
a.
After the gear has been properly adjusted, as
outlined in Par. 0-5, install steering gear assembly
in
chassis in the reverse order in which it was re
moved.
b.
After installing the assembly in the vehicle,
jack
up front of vehicle and place the front wheels
in
the straight ahead position.
c.
Temporarily install the steering wheel to locate
the mid-position of the steering gear. To locate the mid-position,
turn
the steering wheel as far to the
right
as possible and then
turn
in the
opposite
di
rection
as far as possible, noting the total number
of turns.
Turn
the wheel back just ^ of the total movement to place the gear in mid-position.
d.
With
the steering gear in mid-position and the
wheels in the straight ahead position install steer ing gear arm on lever shaft with the
ball
end down.
When
installed the line across the face of the arm
and
end of shaft should be in alignment.
0-27.
Steering
Wheel
Installation
•
Refer to Fig. 0-2.
a.
Install
steering wheel and spring on shaft.
Align
scribe marks on shaft and hub of wheel.
b.
Install
steering shaft nut and torque 20 to 25
lb-ft. [2,8 a 3,4 kg-m.].
c.
Install
horn cap. Test horn.
321
Page 338 of 376
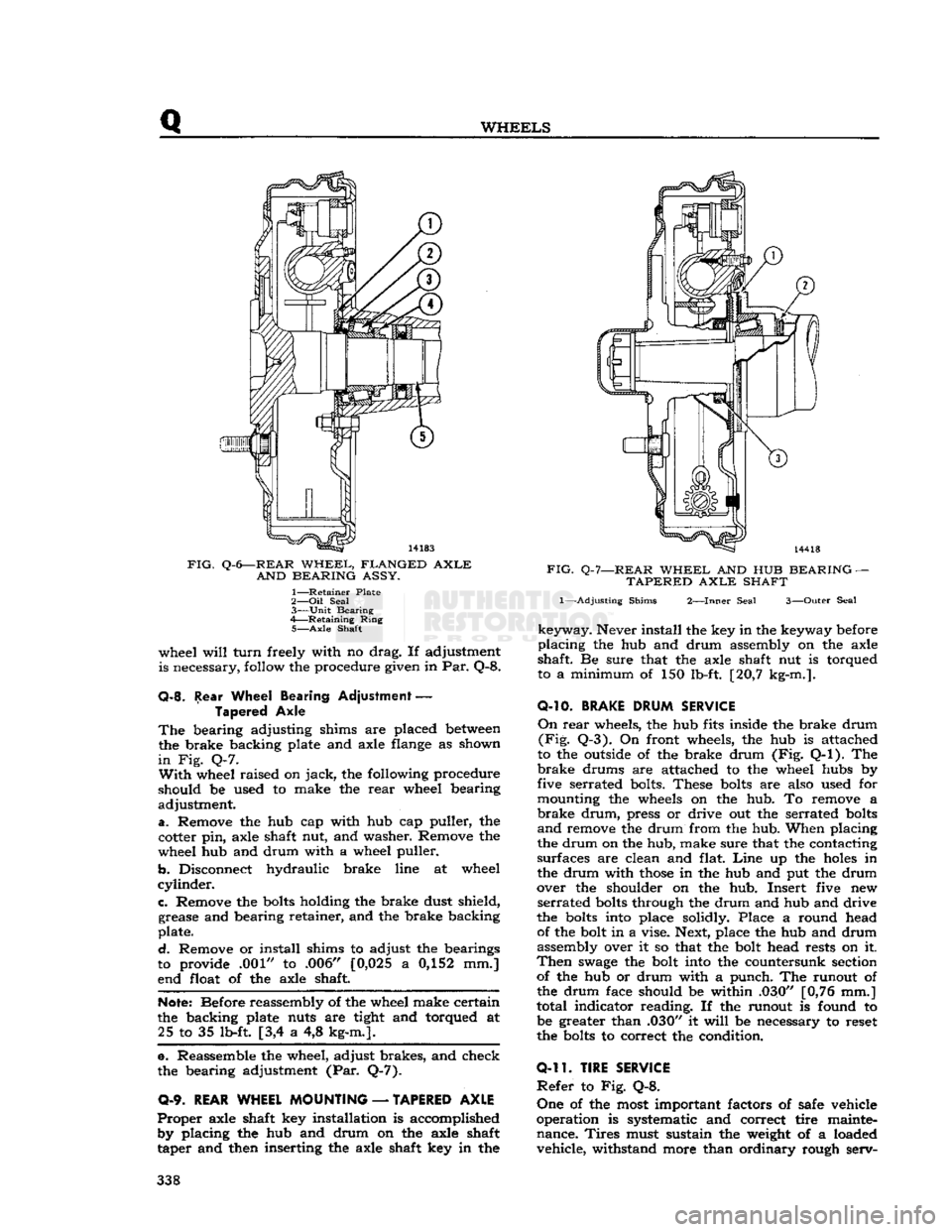
Q
WHEELS
FIG.
Q-6—REAR
WHEEL,
FLANGED
AXLE
AND
BEARING
ASSY.
1—
Retainer
Plate
2— Oil
Seal
3—
Unit
Bearing
4—
Retaining
Ring
5—
Axle
Shaft
wheel
will
turn
freely with no drag. If adjustment
is necessary, follow the procedure given in Par. Q-8.
Q-8.
Rear Wheel Bearing Adjustment
—
Tapered Axle
The
bearing adjusting shims are placed
between
the brake backing plate and axle flange as shown
in
Fig. Q-7.
With
wheel raised on
jack,
the following procedure
should be used to make the
rear
wheel bearing
adjustment.
a.
Remove the hub cap with hub cap puller, the
cotter pin, axle shaft nut, and washer. Remove the
wheel hub and drum with a wheel puller.
b.
Disconnect hydraulic brake line at wheel
cylinder.
c.
Remove the
bolts
holding the brake dust shield, grease and bearing retainer, and the brake backing
plate.
d.
Remove or install shims to adjust the bearings
to provide .001" to .006" [0,025 a 0,152 mm.]
end float of the axle shaft.
Note:
Before reassembly of the wheel make certain
the backing plate nuts are tight and torqued at 25 to 35 lb-ft [3,4 a 4,8 kg-m.].
e. Reassemble the wheel, adjust brakes, and check
the bearing adjustment (Par. Q-7).
0-9.
REAR WHEEL MOUNTING
—
TAPERED AXLE
Proper
axle shaft key installation is accomplished by placing the hub and drum on the axle shaft
taper and then inserting the axle shaft key in the
FIG.
Q-7—REAR
WHEEL
AND HUB
BEARING
—
TAPERED
AXLE
SHAFT
1—-Adjusting
Shims
2—Inner
Seal
3—Outer
Seal
keyway.
Never install the key in the keyway before
placing
the hub and drum assembly on the axle
shaft. Be sure that the axle shaft nut is torqued
to a minimum of 150 lb-ft. [20,7 kg-m.].
O-10.
BRAKE
DRUM
SERVICE
On
rear
wheels, the hub fits inside the brake drum
(Fig.
Q-3). On front wheels, the hub is attached
to the outside of the brake drum (Fig. Q-l). The
brake
drums are attached to the wheel hubs by
five serrated bolts. These
bolts
are also used for
mounting the wheels on the hub. To remove a
brake
drum,
press or drive out the serrated
bolts
and
remove the drum from the hub. When placing
the drum on the hub, make sure that the contacting
surfaces are clean and flat.
Line
up the
holes
in
the drum with
those
in the hub and put the drum
over the shoulder on the hub. Insert five new
serrated
bolts
through the drum and hub and drive
the
bolts
into place solidly. Place a round head of the bolt in a vise. Next, place the hub and drum
assembly over it so that the bolt head rests on it.
Then
swage
the bolt into the countersunk section of the hub or drum with a punch. The runout of
the drum face should be within .030" [0,76 mm.]
total indicator reading. If the runout is found to be greater than .030" it
will
be necessary to reset
the
bolts
to correct the condition.
0-11.
TIRE SERVICE
Refer
to Fig. Q-8.
One
of the most important factors of safe vehicle
operation is systematic and correct tire mainte nance.
Tires
must sustain the weight of a loaded vehicle, withstand more than ordinary rough serv- 338
Page 340 of 376
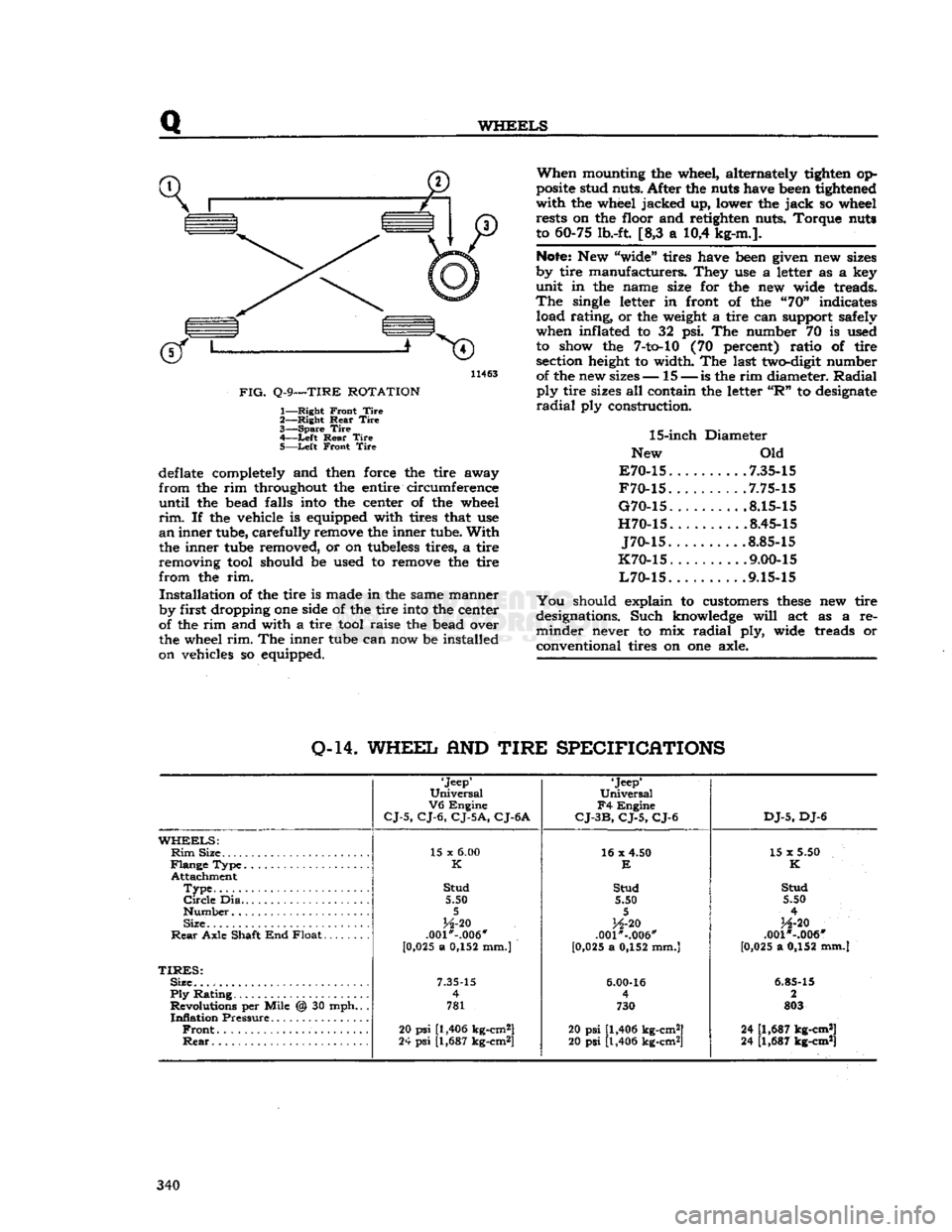
Q
WHEELS
11463
FIG.
Q-9—TIRE
ROTATION
1—
Right
Front
Tire
2—
Right
Rear
Tire
3—
Spare
Tire
4—
-Left
Rear
Tire
5—
Left
Front
Tire
deflate completely and then force the tire away
from
the rim throughout the entire circumference
until
the bead falls into the center of the wheel
rim.
If the vehicle is equipped with tires that use
an
inner tube, carefully remove the inner tube.
With
the inner tube removed, or on tubeless tires, a tire
removing tool should be used to remove the tire
from
the rim.
Installation
of the tire is made in the same manner
by first dropping one side of the tire into the center
of the rim and with a tire tool raise the bead over
the wheel
rim.
The inner tube can now be installed
on vehicles so equipped.
When
mounting the wheel, alternately tighten op
posite stud nuts. After the nuts have been tightened
with
the wheel jacked up, lower the
jack
so wheel rests on the floor and retighten nuts. Torque nuts
to 60-75 lb.-ft. [8,3 a 10,4 kg-m.].
Note:
New "wide" tires have been given new sizes
by tire manufacturers. They use a letter as a key
unit
in the name size for the new wide treads.
The
single letter in front of the "70" indicates load rating, or the weight a tire can support safely
when inflated to 32 psi. The number 70 is used to show the
7-to-10
(70 percent) ratio of tire section height to width. The last two-digit number of the new sizes— 15 —
is
the rim diameter.
Radial
ply
tire sizes all contain the letter
"R"
to designate
radial
ply construction.
15-inch
Diameter
New Old
E70-15
7.35-15
F70-15
.7.75-15
G70-15
8.15-15
H70-15
8.45-15
J70-15
.8.85-15
K70-15
. .... .9.00-15
L70-15
9.15-15
You
should explain to customers
these
new tire
designations. Such knowledge
will
act as a re
minder
never to mix
radial
ply, wide treads or
conventional tires on one axle.
0-14.
WHEEL
AND
TIRE
SPECIFICATIONS
'Jeep'
Universal
V6
Engine
CJ-5,
CJ-6,
CJ-5A,
CJ-6A
'Jeep*
Universal
F4
Engine
CJ-3B,
CJ-5,
CJ-6
DJ-5,
DJ-6
WHEELS:
Rim
Size 15 x
6.00
16 x 4.50
15 x 5.50
K
E
K
Attachment
Type
Stud
Stud Stud
Circle
Dia 5.50 5.50 5.50
5 5
4
Size
H-20
H-20
H-20
Rear
Axle Shaft End Float .001*-.006"
.001"-.006" .001 *-.006"
[0 ,025 a 0,152 mm.)
[0,025 a 0,152 mm.] [0,025 a 0,152 mm.]
TIRES:
Size.
7.35-15
6.00-16
6.85-15
Ply
Rating 4
4 2
Revolutions per Mile @ 30 mph.. . 781 730 803
Inflation
Pressure
Front
20
psi
[1,406 kg-cm2]
20 psi [1,406 kg-cm2] 24 [1,687 kg-cm*]
Rear
24
psi
[1,687 kg-cm*]
20 psi [1,406 kg-cm2] 24 [1,687 kg-cm*] 340
Page 346 of 376
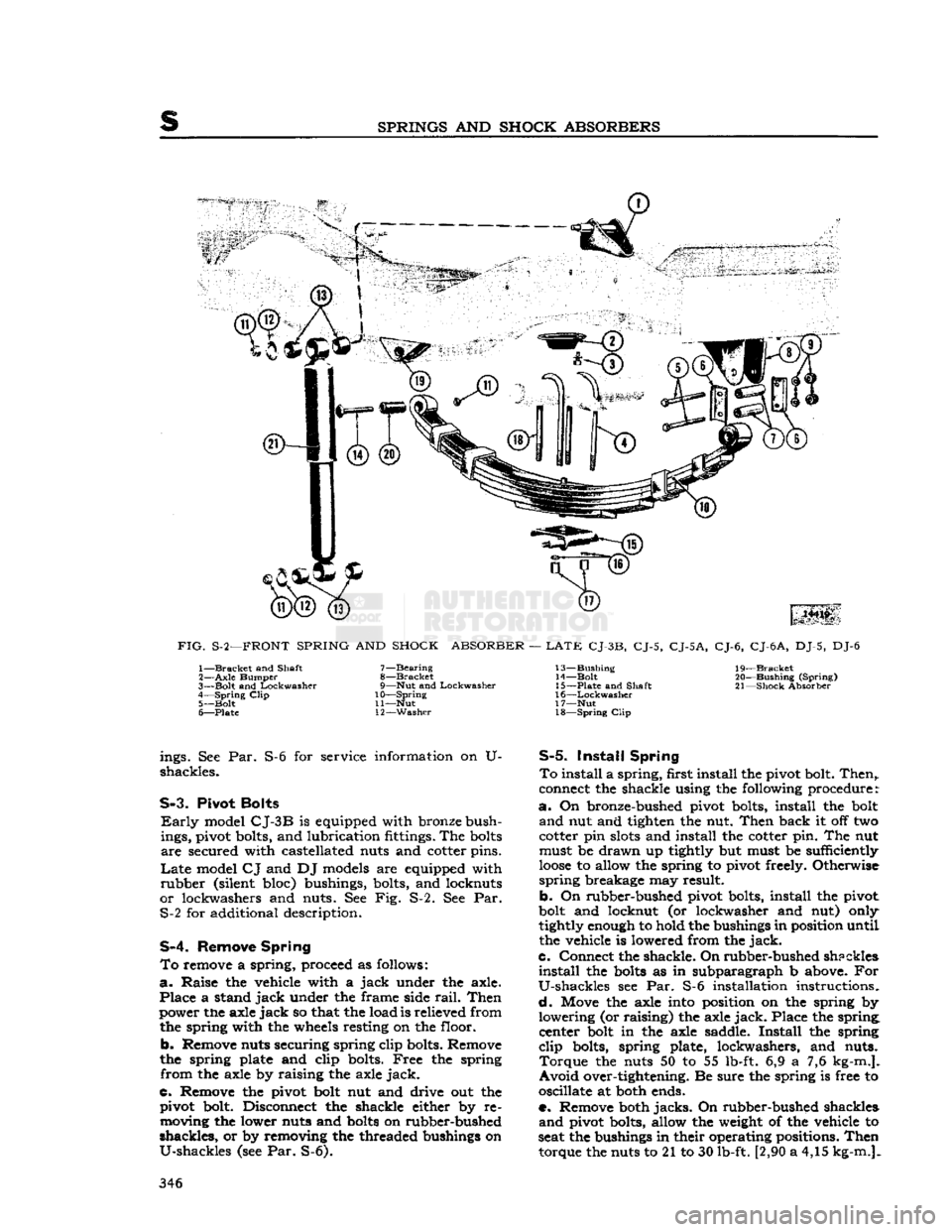
SPRINGS
AND
SHOCK
ABSORBERS
FIG.
S-2—FRONT
SPRING
AND
SHOCK
ABSORBER
—
LATE
CJ-3B,
CJ-5,
CJ-5A,
CJ-6,
CJ-6
A,
DJ-5, DJ-6 1—
Bracket
and Shaft
2—
Axle
Bumper
3—
Bolt
and
Lockwasher
4—
Spring
Clip
5—
Bolt
6—
Plate
7—
Bearing
8—
Bracket
9—
Nut
and
Lockwasher
10—
Spring
11—
Nut
12—
Washer
13—
Bushing
14—
Bolt
15—
Plate
and Shaft
16—
Lockwasher
17—
Nut
18—
Spring
Clip
19—
Bracket
20—
Bushing
(Spring)
21—
Shock
Absorber ings. See Par.
shackles.
S-6 for service information on U-
S-3.
Pivot
Bolts
Early
model
CJ-3B
is equipped with bronze bush
ings, pivot bolts, and lubrication fittings. The
bolts
are
secured with castellated nuts and cotter pins.
Late
model
CJ
and DJ models are equipped with
rubber
(silent bloc) bushings, bolts, and locknuts
or
lockwashers and nuts. See Fig. S-2. See Par. S-2 for additional description.
S-4.
Remove
Spring
To
remove a spring, proceed as follows:
a.
Raise
the vehicle with a
jack
under the axle.
Place
a stand
jack
under the frame side
rail.
Then
power the axle
jack
so that the load is relieved from the spring with the wheels resting on the floor.
b.
Remove nuts securing spring clip bolts. Remove
the spring plate and clip bolts.
Free
the spring
from
the axle by raising the axle
jack.
C.
Remove the pivot bolt nut and drive out the pivot bolt. Disconnect the shackle either by removing the lower nuts and
bolts
on rubber-bushed
shackles,
or by removing the threaded bushings on
U-shackles
(see Par. S-6).
S-5.
Install
Spring
To
install a
spring,
first install the pivot bolt.
Then,,
connect the shackle using the following procedure:
a.
On bronze-bushed pivot bolts, install the bolt
and
nut and tighten the nut.
Then
back it off two
cotter pin
slots
and install the cotter pin. The nut must be
drawn
up tightly but must be sufficiently
loose
to allow the spring to pivot freely. Otherwise
spring
breakage may result.
b.
On rubber-bushed pivot bolts, install the pivot
bolt and locknut (or lockwasher and nut) only
tightly enough to hold the bushings in position until
the vehicle is lowered from the
jack.
c.
Connect the shackle. On
rubber-bushed
shpckles
install
the
bolts
as in subparagraph b above. For
U-shackles
see Par. S-6 installation instructions.
d.
Move the axle into position on the spring by
lowering
(or raising) the axle
jack.
Place the spring, center bolt in the axle saddle.
Install
the spring
clip
bolts, spring plate, lockwashers, and nuts.
Torque
the nuts 50 to 55 lb-ft. 6,9 a 7,6 kg-m.].
Avoid
over-tightening. Be sure the spring is free to
oscillate at both ends.
e. Remove both
jacks.
On rubber-bushed shackles
and
pivot bolts, allow the weight of the vehicle to
seat the bushings in their operating positions.
Then
torque the nuts to 21 to 30 lb-ft. [2,90 a 4,15 kg-m.]. 346