tire pressure JEEP DJ 1953 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 1953, Model line: DJ, Model: JEEP DJ 1953Pages: 376, PDF Size: 19.96 MB
Page 172 of 376

H
ELECTRICAL
SYSTEM SUBJECT
PAR.
Directional
Signal
Lamps
H-138
Hazard
Warning
Lamps
H-139
Head
Lamp
Replacement H-130
Head
Lamp
Aiming Procedure H-131 Headlight Dimmer Switch H-127
License
Plate
Lamp
H-136
Main
Light
Switch. H-126
Marker
Lights .H-l40
Parking
and
Turn
Signal
Light
H-133
Stop
Light
Switch. H-l28
Tail,
Stop and
Turn
Signal
Lamp
.H-134
H-1. GENERAL
All
'Jeep' Universal vehicles are equipped with 12- volt electrical systems. Use caution around the higher
voltage
of the 12-volt system as accidental
short
circuits are more capable of damaging electri
cal
units. Also, arcs around the 12-volt battery are
more apt to ignite any gas that may be escaping
from
it. In the following paragraphs
will
be found
information about the battery, distributor, coil,
generator, alternator,
voltage
regulator and start ing motor. These units with the connecting wires,
make
up the
engine
electrical system. The wiring
diagram
will
show the different circuits of the en
gine
electrical system and the various units which
make
up
those
circuits.
With
plastic-covered wiring harnesses use only
rubber-insulated
wiring clips.
Caution:
All current production vehicles are 12- volt, negative ground. Whenever servicing a 12-
volt electrical system, use caution, as an accidental
short
circuit is capable of damaging electrical units. Disconnect battery ground cable before changing
electrical
components.
H-2.
Battery
The
battery is a storage reservoir for electrical
energy produced by the alternator or generator.
The
battery should store sufficient energy for
operation of the entire electrical system when the
alternator
or generator is not pr 1,scing output,
such
as when the ignition is first turned on. Of
particular
importance is maintaining the electrolyte
at the correct level, regularly checking with a
hydrometer, and maintaining clean, tight cable connections.
Battery
service information is given in this section.
Caution:
Do not allow flames or sparks to be
brought near the vent
openings
of the battery since
hydrogen gas may be present in the battery and might explode.
Note:
The liquid in the battery (electrolyte) is a
solution of sulphuric acid which, on contact, can
injure
skin or
eyes,
or damage clothes. If it is spilled
on the skin or spattered in the
eyes,
promptly flush
it
away with quantities of clear water only. If the
acid
is spilled on clothes, wet it thoroughly with a
weak
solution of ammonia, or with a solution of sodium bicarbonate or baking soda.
SUBJECT
PAR.
HORN
H-137
ELECTRICAL
COMPONENT
REPLACEMENT
H-150
WINDSHIPLD
WIPER SYSTEM
H-141
thru
149
SERVICE
DIAGNOSIS.
. .H-151
ELECTRICAL
SPECIFICATIONS
H-152
Caution:
When installing the battery, the nega
tive terminal must be grounded. Reverse polarity of the battery can cause severe damage to the charging system.
Battery
Inspection
a.
Check
the specific gravity of the electrolyte in
each cell of the battery. A hydrometer reading of 1.260 indicates that the battery is fully charged.
If
the reading is 1.225 or below, the battery
needs
recharging.
If one or more cells is 25 "points" (.025) or more lower than the other cells, this in
dicates that the cell is shorted, the cell is about to
fail,
or there is a
crack
in the battery partition in
the case. Unless the battery is repaired or replaced, battery trouble
will
soon
be experienced.
b.
Check
the electrolyte level in each cell, add
distilled
water to maintain the solution [9,5 mm.] above the plates. Avoid overfilling. Replace
the filler caps and tighten securely. It is important to keep the electrolyte level above the plates at all
times because plates that are
exposed
for any
length of time
will
be seriously damaged.
c.
Check
the wing nuts on the hold-down frame for tightness. Tighten them only with finger pres
sure,
never with pliers or a wrench. Excessive
pressure
could damage the battery case.
d.
Clean
the battery terminals and cable con nectors. Prepare a strong solution of baking soda
and
water and brush it around the terminals to
remove any corrosion that is present. The cell caps must be tight and their vents sealed to prevent
cleaning solution entering the cells. After cleaning,
connect cables to battery and coat the terminals
with
heavy grease.
e.
Inspect the battery cables and replace if badly
corroded
or frayed.
Check
tightness
of terminal
screws to ensure
good
electrical connections.
Check
the
tightness
of the negative ground cable connection at the frame to ensure a
good
ground
connection.
f.
Load
test
the battery. Connect a voltmeter across the battery. Run the starting motor for 15 seconds. If the
voltage
does
not drop below 10
volts the battery is satisfactory. If the
voltage
falls
below the figure given, yet the specific gravity is
above
1.225,
the condition of the battery is questionable.
g. Be sure the
engine
ground strap connection, 172
Page 214 of 376
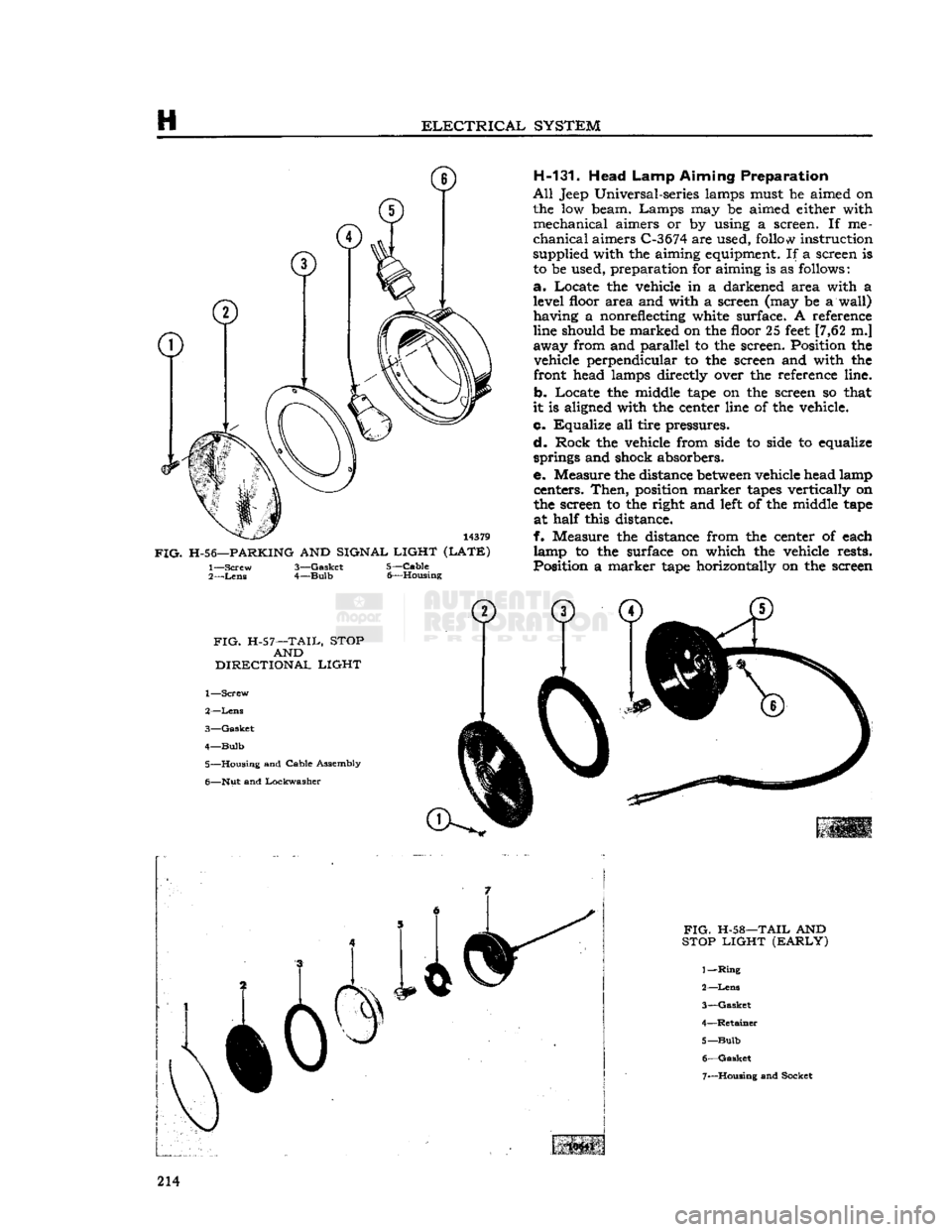
H
ELECTRICAL
SYSTEM
14379
FIG.
H-56—PARKING
AND SIGNAL LIGHT (LATE) 1—
Screw
2—
Lens
3—
Gasket
4—
Bulb
5—
Cable
6— Housing H-131. Head
Lamp
Aiming Preparation
All
Jeep Universal-series lamps must be aimed on
the low beam. Lamps may be aimed either with mechanical aimers or by using a screen. If me
chanical
aimers C-3674 are used,
follow
instruction
supplied with the aiming equipment. If a screen is to be used, preparation for aiming is as follows:
a.
Locate the vehicle in a darkened area with a level floor area and with a screen (may be a wall) having a nonreflecting white surface. A reference
line should be marked on the floor 25
feet
[7,62 m.]
away from and parallel to the screen. Position the vehicle perpendicular to the screen and with the
front head lamps directly over the reference line.
b. Locate the middle
tape
on the screen so that
it is aligned with the center line of the vehicle.
c. Equalize all tire pressures.
d.
Rock the vehicle from side to side to equalize springs and shock absorbers.
e. Measure the distance
between
vehicle head lamp centers.
Then,
position marker
tapes
vertically on
the screen to the right and
left
of the middle
tape
at half this distance.
f.
Measure the distance from the center of each
lamp to the surface on which the vehicle rests.
Position a marker
tape
horizontally on the screen
FIG.
H-57—TAIL, STOP AND
DIRECTIONAL
LIGHT
1—
Screw
2—
Lens
3—
Gasket
4—
Bulb
5— Housing and Cable Assembly
6— Nut and Lockwasher 10441
FIG.
H-58—TAIL AND
STOP LIGHT (EARLY)
1
—Ring
2—
Lens
3—
Gasket
4—
Retainer
5—
Bulb
6—
Gasket
7— Housing and Socket 214
Page 273 of 376
![JEEP DJ 1953 User Guide
Jeep*
UNIVERSAL
SERIES
SERVICE
MANUAL
K
ment, the shaft should have .004" to .008"
[0,102
a
0,203
mm.] end play. Adjustment is made by
selective
shim installation
between
the cap an JEEP DJ 1953 User Guide
Jeep*
UNIVERSAL
SERIES
SERVICE
MANUAL
K
ment, the shaft should have .004" to .008"
[0,102
a
0,203
mm.] end play. Adjustment is made by
selective
shim installation
between
the cap an](/img/16/57041/w960_57041-272.png)
'Jeep*
UNIVERSAL
SERIES
SERVICE
MANUAL
K
ment, the shaft should have .004" to .008"
[0,102
a
0,203
mm.] end play. Adjustment is made by
selective
shim installation
between
the cap and the
case. Shims .003", .010" and .031" [0,076,
0,254,
0,787
mm.] in thickness are available for this ad
justment. Do not install the rear cap oil seal until
the bearings are correctly adjusted. Both the front
and
rear oil seals may be installed with oil seal
driver
Tool W-143, shown in Fig. K-12.
When
installing the end yokes on the output shafts,
inspect for the presence of
felt
seals in each oil
seal guard. (The oil seal guard is a part of each
yoke assembly.) Felt seals should be installed in the oil seal guards if
they
are not present. When
installing the shift
rail
oil seals in the front bear
ing cap, it is necessary to protect the seals against
damage when passing over the shift
rail
notches.
Protect them with the thimble, and install them with the driver, Tool W-130, shown in Fig. K-9.
K-7.
Transfer Case Installation
The
installation of the assembly in the vehicle is
the reverse of the removal operation covered in
Par.
K-2.
If
the transmission was removed from the vehicle,
lubricate the pilot bearing and also lubricate the
transmission and transfer case as outlined in the
"Lubrication
Section". Be sure that the clutch pedal has %"
[19,05
mm.] free travel as outlined
in
the
"Clutch
Section".
K-8.
Transfer Case Linkage Adjustment
Adjust
the link to provide
xh"
[12,7 mm.] clear
ance
between
the floor pan and the shift lever
bend when operating in four wheel drive low
position. Refer to Fig. K-4.
K-3.
TRENSFER
CESE
SERVICE
DIAGNOSIS
SYMPTOMS PROBABLE REMEDY
Slips
Out of
Gear (High-Low)
Shifting
Lock
Spring Weak Replace Spring
Bearing
Broken or Worn Replace
Shifting
Fork
Bent Replace
Slips
Out of
Front Wheel Drive
Shifting
Lock
Spring Weak. Replace
Bearing
Worn or Broken Replace
End
Play in Shaft. . . ..... Adjust Shifting
Fork
Bent.. Replace
Hard Shifting
Lack
of
Lubricant
Drain
and
Refill
Shift
Lever
Stuck on Shaft Remove, Clean and Lubricate
Shifting
Lock
Ball
Scored Replace
Ball
Shifting
Fork
Bent Replace
Fork
Low
Tire
Pressure Inflate
Grease Leak
at
Front
or
Rear Drive
Grease
Leak
at Covers. Install New Gaskets
Grease
Leak
between
Transmission and Transfer Cases Install New Gaskets
Grease
Leak
at Output Shaft Install New Oil Seal
K-10.
TRANSFER
CESE
SPECIFICATIONS
Transfer
Case:
All
Models
Spicer
18
On
Floor
Gear
Ratio: 1.00 to 1
2.46 to 1 273
Page 285 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL
SERIES
SERVICE
MANUAL
M
M-19.
SERVICE
DIAGNOSIS
SYMPTOMS
PROBABLE
REMEDY
Hard Steering
Lack
of
Lubrication
Lubricate
Tires
Soft.
. Inflate
Tight
Steering. Adjust. See "Steering" Section
Low Speed Shimmy
or
Wheel Fight
Spring
Clips and Shackles Loose
Front
Axle Shifted Insufficient Toe-In
Improper
Caster
Steering System Loose or Worn
Twisted Axle
High Speed Shimmy
or
Wheel Fight
Check
Conditions Under "Low Speed Shimmy"
Tire
Pressures Low or not
Equal
Wheel Out of Balance
Wheel Runout
Radial
Runout of Tires
Wheel Camber
Front
Springs
Settled
or Broken
Bent Steering Knuckle
Arm..................
Shock Absorbers not Effective
Steering
Gear
Loose on Frame
Front
Springs too Flexible
Tramp
Wheels Unbalanced
Wandering
Improper
Toe-in
Broken
Front Spring Main
Leaf
Axle Shifted Loose Spring Shackles or Clips
Improper
Caster
Tire
Pressure Uneven
Tightness in Steering System
Loose Wheel Bearings
Front
Spring
Settled
or Broken
Axle
Noisy
on
Pull
Pinion and Ring
Gear
Adjusted too Tight
Pinion Bearings Rough.
Axle Noisy
on
Coast
Excessive Back
Lash
at Ring and Pinion Gears.
End
Play in Pinion Shaft. . . Rough Bearing.
Axle Noisy
on
Coast
and
Pull
Ring
and Pinion Adjusted too Tight
Pinion Set too
Deep
in Ring
Gear
Pinion Bearing Loose or Worn
Back Lash
Axle Shaft Universal Joint Worn
Axle Shaft Improperly Adjusted
Worn
Differential Pinion Washers
Worn
Propeller Shaft Universal Joints.
Readjust
or Replace
Broken
Spring Center Bolt
Adjust
Reset
Adjust
or Overhaul Steering
Gear,
Front Axle or
Steering Parts
Straighten or Adjust
Inflate
Balance
Straighten Mount Properly
Same on Both Wheels
Repair
or Replace
Straighten or Replace
Replace or Repair Tighten
Over
Lubricated
Check
and Balance
Adjust—Check
for Bent Steering Knuckle Arm Replace
Spring
Center Bolt Broken
Adjust
or Replace
Reset Inflate
Adjust
Adjust
Repair
or Replace
Readjust
Replace
Readjust
Readjust
Replace
Readjust Readjust
Readjust
or Replace
Replace
Readjust
Replace
Repair
Emergency
Where difficulty is experienced with front axle differential making the vehicle inoperative,
remove
axle driving
flanges.
This will allow bringing vehicle in under its own power. Be sure the transfer
case
shift lever is in the neutral
(disengaged)
position.
285
Page 315 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL
SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
O Note:
If the steering-gear-to-frame
bolts
are not
properly
torqued, they
will
eventually
loosen
dur
ing operation of the vehicle. Loose
bolts
will
result
in
elongated
bolt
holes
making maintenance of bolt torque difficult, and may allow position of the
steering columns to be misaligned. Therefore,
proper
torquing is extremely important.
Do not tighten the steering gear to dampen out
steering trouble. Adjust the steering gear only to
remove lost motion or play within the unit.
0-5. Steering
Gear
Adjustment
The
cam and lever steering gear is illustrated in
Fig.
0-2. It consists of a
spiral
cam, and a cross shaft and lever assembly with two lever studs.
When
the steering wheel is turned, the cam
moves
the studs, causing rotary movement of the cross
shaft, which in
turn
causes angular movement of
the*steering arm.
Two
adjustments of the steering gear are necessary:
up and down play of the steering shaft, and adjustment of the lever studs (tapered pins) in the
cam
groove.
Adjustment
of the
ball
thrust bearings to eliminate up and down play of the steering shaft is ac
complished by removing shims which are installed
between
the steering gear housing and the upper
cover. Before making this adjustment
loosen
the
housing side cover adjusting screw to free the pins
in
the cam groove. Loosen the housing cover to
cut and remove a shim or more as required.
Install
the screws and tighten. Adjustment should be
made to have a slight drag but allow the steering
wheel to
turn
freely with thumb and forefinger
lightly gripping the rim.
Shims
installed for adjustment are .002*, .003", and .010"
[.0508,
.0762
and .254 mm.] in thickness.
Adjustment
of the tapered pins in the cam
groove
is accomplished by adjusting screw. Unlock the
adjusting
screw and
turn
it in until a very slight
drag
is felt through the mid-position when turning
the steering wheel slowly from one extreme position
to the other.
Backlash
of the pins in the
groove
shows up as
end play of lever shaft, also as backlash of steer ing arm.
The
cam
groove
is purposely cut shallow in the
straight
ahead driving position for each pin.
This
feature permits a
close
adjustment for normal
straight
ahead driving and provides precision steer ing and permits take up of backlash at this point
after the wear occurs without causing a bind else
where.
Always
adjust within the high range through
the mid-position of pin travel. Do not adjust off
"straight
ahead" position.
Backlash
in turned posi
tions is not objectionable.
0-6.
Front
Wheel Alignment Adjustments
To
ensure correct alignment, a definite procedure
for inspection of the steering system is recom mended. It is
suggested
that the following sequence
be used:
a.
Equalize
tire pressures and level vehicle.
b.
Check
steering gear to steering column align
ment.
c.
Inspect steering knuckle pivots, spindle, and
wheel bearing
looseness.
d.
Check
wheel runout.
e.
Test wheel balance and bearing adjustment.
f.
Check
for spring sag.
g.
Inspect brakes and shock absorbers.
h.
Check
steering gear assembly adjustment and
steering connecting rod.
i.
Check
caster,
j.
Check
toe-in.
k.
Check
toe-out
on turns.
I.
Check
camber.
m.
Check
tracking of front and
rear
wheels,
n.
Check
frame alignment.
The
factors of alignment, caster, camber, and toe-
in,
are all interrelated and if one adjustment is
made, another adjustment may be affected.
There
fore, after an alignment job is completed, make a
complete recheck of all the adjustments to be sure
the
settings
are within the limit. Be sure all front
suspension and steering system nuts and
bolts
are
all
properly torqued before taking wheel alignment readings.
Proper
alignment of front wheels must be main
tained in order to ensure
ease
of steering and satisfactory tire life.
The
most important factors of front wheel alignment are wheel camber, axle caster and wheel
toe-in.
Wheel
toe-in is the distance the wheels are closer
together
at the front than at the
rear.
Wheel
camber is the amount the wheels incline out
ward
at the top from a vertical position.
Front
axle caster is the amount in
degrees
that the
steering pivot pins are tilted towards the front or
rear
of the vehicle. Positive caster is inclination of
the top of the pivot pin towards the
rear
of the ve
hicle.
Zero caster is the vertical position of the
pivot pin. Negative or reverse caster is the in
clination
of the top of the pin towards the front
of the vehicle.
These
points should be checked at regular inter
vals,
particularly when the front axle has been
subjected to a heavy impact. When checking wheel alignment, it is important that wheel bearings and
knuckle
bearings be in proper adjustment. Loose bearings
will
affect instrument readings when
checking
the camber, pivot pin inclination and
toe-in.
To
accurately check camber and caster, use a wheel
aligning fixture.
Camber
and caster of the front
wheels are both preset.
Camber
cannot be altered
but caster can be adjusted by installing caster shims
between
the axle pad and the springs. Wheel toe-in
may
be adjusted. To measure wheel toe-in, use a
wheel aligning fixture or follow the procedure given
in Par.
0-8.
0-7.
Front Wheel Toe-in
Toe-in
as illustrated in
Fig.
0-3, is necessary to
off
set the
effect
of camber as shown in Fig. Q-4. 315
Page 317 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
The
purpose of caster Fig. O-S, is to provide steer
ing stability which
will
keep the front wheels in the
straight
ahead position and also assist in straighten
ing up the wheels when coming out of a
turn.
Caster
of the front wheels is preset. If the angle of
caster,
when accurately measured, is found to be
incorrect,
correct it to the specification given at
the end of this section by either installing new
parts
or installing caster shims
between
the axle
pad
and the springs.
If
the camber and toe-in are correct and it is known
the the axle is not twisted, a satisfactory check
may
be made by testing the vehicle on the road.
Before road testing, make sure all tires are properly
inflated,
being particularly careful that both front
tires are inflated to exactly the same pressure.
If
vehicle turns easily to either side but is
hard
to
straighten out, insufficient caster for easy handling of vehicle is indicated. If correction is necessary, it
can
usually be accomplished by installing shims
between
the springs and axle pads to secure the
desired
result.
0-11-
Front
Wheel
Turning
Angle
When
the front wheels are turned, the inside wheel
on the
turn
travels in a smaller circle than the outside wheel, therefore, it is necessary for the wheels
to toe out to prevent the tire on the inside wheel
frOm
being scuffed sideways.
This
angle for toe out
on turns is designed to permit both front wheels to
turn
on a common center by having the ends of the
steering
knuckle
arms closer
together
than the king
pins.
To
avoid possible damage to the universal joints
on the front axles of 4-wheel drive vehicles, it is advisable to check the turning angle.
Wearing
away
of the upset
edge
on the spindle housing bolt which
10607
FIG.
0-6—TURNING
ANGLE
STOP
SCREW
1—Stop
Screw
contacts the
stop
screw
will
increase the turning
angle to the point where the universal joints may
be damaged.
The
Jeep Universal Series vehicles should have a
turning
angle of not more than 27^° both left and
right.
To adjust the
stop
screw, it is necessary to
loosen
the locknut holding the
stop
screw. When
the adjustment has been made, tighten the locknut
on the screw to prevent any movement. Refer to
Fig.
O 6.
The
left steering knuckle arm controls the relation
ship of the front wheels on a left
turn
and the right
arm
controls the relation on a right
turn.
0-12. Steering
Knuckle
Arm
Should
a steering knuckle arm
become
bent, the
knuckle
housing must be replaced. It is not safe to
straighten the knuckle arm.
0-13.
Front
Wheel
Shimmy
Wheel
shimmy may be caused by various condi
tions in the wheels, axle or steering system, or a
combination of
these
conditions. Outlined below
will
be found the usual corrections of this fault:
a.
Equalize
tire pressures and see that they are
according
to specifications.
b.
Check
the wheel bearings for
looseness.
Be sure
that the inner wheel bearing race is not too
loose
on the spindle.
c.
Remove both steering knuckles and carefully inspect the upper and lower king pin bearings.
Inspect
the bearing cups for evidence of brinelling,
pitting, or fretting. Any bearings that show the slightest imperfection must be
replaced.
Reassemble
and
lubricate the front axle and steering linkage,
installing
new steering knuckle oil seals if present
seals show any wear.
d.
With
full
weight on the front wheels and one
man
working the steering play with the steering
wheel, a second man should closely observe the steering bell
crank
for any rocking motion and the
double tie rod socket for any rocking motion or
looseness
at both points. Replace the complete bell
crank
assembly if it has even the slightest rocking motion. The same applies to the double tie rod
socket.
e.
Check
wheel run-out.
This
check should include
radial
run-out and wheel
looseness
on the hub.
f- Test wheel balance—check for blowout patches,
uniform
tire tread, vulcanized tires, mud on inside
of wheels, and tires creeping on the
rims.
g.
Try
switching front wheels and tires to the
rear,
criss-crossing
them in this operation.
h.
Check
for front
spring
sag. Also check for broken
spring
leaves, broken center
spring
bolt,
loose
spring
clips
(or tight clips), over-lubrication of spring leaves, spring shackle bracket
loose
on frame, and
loose
rear
spring shackle. Be sure that the shock
absorbers
are operating properly to eliminate bobbing of the front end.
i.
Check
brakes to make sure that one
does
not
drag.
j.
Check
the steering assembly and steering con necting rod.
This
includes the up-and-down-play
of the steering worm shaft, end play of the cross 317
Page 325 of 376
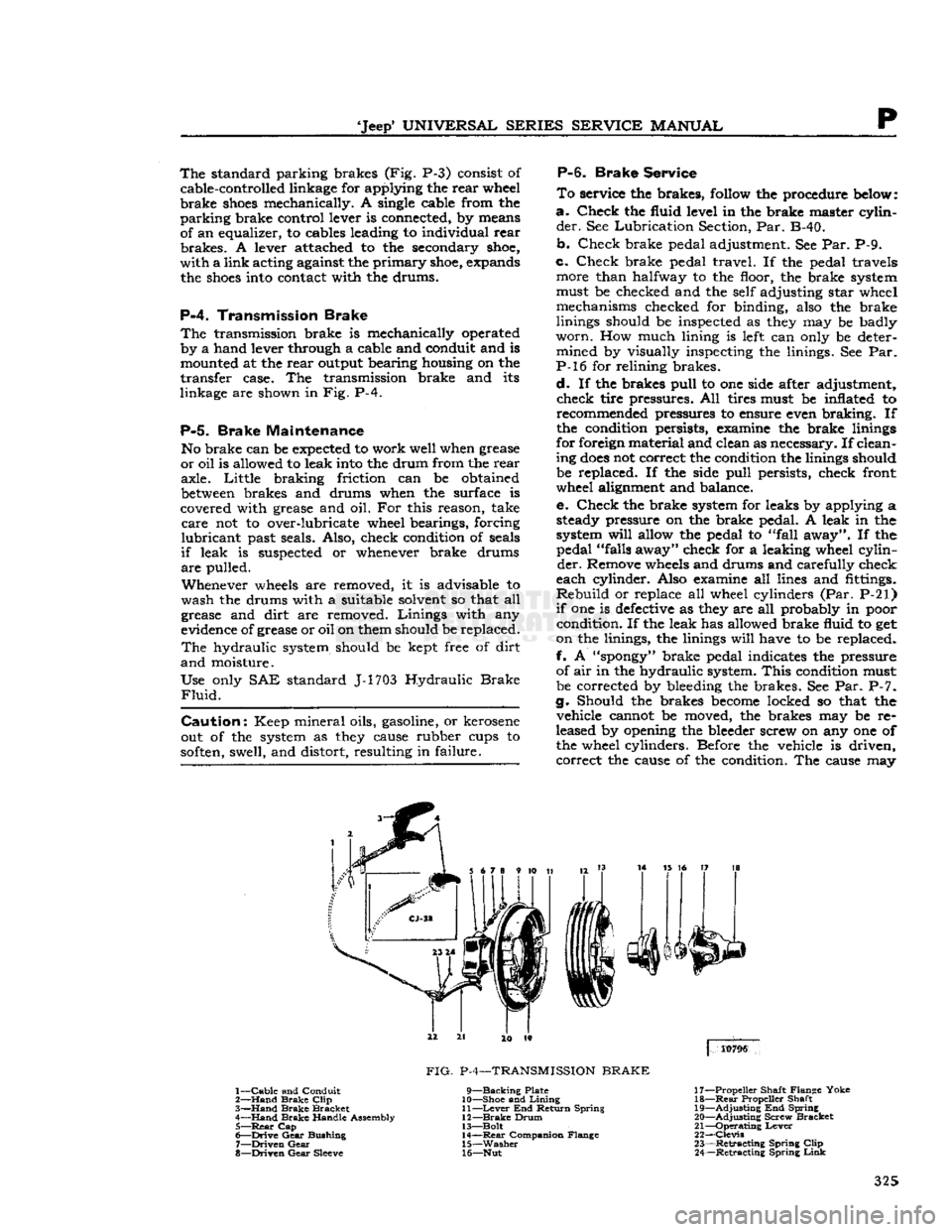
'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL
SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
P The
standard parking brakes (Fig. P-3) consist of
cable-controlled linkage for applying the rear wheel
brake
shoes
mechanically. A single cable from the
parking
brake control lever is connected, by means of an equalizer, to cables leading to individual rear
brakes.
A lever attached to the secondary
shoe,
with a link acting against the
primary
shoe,
expands the
shoes
into
contact with the drums.
P-4.
Transmission Brake
The
transmission brake is mechanically operated
by a hand lever through a cable and conduit and is mounted at the rear output bearing housing on the
transfer case. The transmission brake and its
linkage are shown in Fig. P-4.
P-5.
Brake Maintenance
No brake can be
expected
to work well when grease
or oil is allowed to leak
into
the drum from the rear axle. Little braking friction can be obtained
between
brakes and drums when the surface is
covered with grease and oil. For this reason, take
care
not to over-lubricate wheel bearings, forcing
lubricant
past seals. Also, check condition of seals
if
leak is suspected or whenever brake drums
are
pulled.
Whenever
wheels
are removed, it is advisable to
wash the drums with a suitable solvent so that all
grease and dirt are removed. Linings with any
evidence of grease or oil on them should be replaced.
The
hydraulic system should be kept free of dirt
and
moisture.
Use only SAE standard J-1703 Hydraulic
Brake
Fluid.
Caution:
Keep mineral oils, gasoline, or kerosene
out of the system as
they
cause rubber cups to
soften,
swell, and distort, resulting in failure.
P-6.
Brake
Service
To
service the brakes,
follow
the procedure
below:
a.
Check the fluid level in the brake master cylin
der.
See Lubrication Section, Par. B-40.
b. Check brake pedal adjustment. See Par. P-9.
c. Check brake pedal travel. If the pedal travels more than halfway to the floor, the brake system
must be checked and the self adjusting star wheel mechanisms checked for binding, also the brake
linings should be inspected as
they
may be badly
worn.
How much lining is
left
can only be deter mined by visually inspecting the linings. See Par.
P-l6 for relining brakes.
d.
If the brakes pull to one side after adjustment, check tire pressures. All tires must be inflated to recommended pressures to ensure even braking. If
the condition persists, examine the brake linings
for foreign material and clean as necessary. If clean
ing
does
not correct the condition the linings should be replaced. If the side pull persists, check front
wheel alignment and balance.
e. Check the brake system for leaks by applying a steady pressure on the brake pedal. A leak in the
system
will
allow the pedal to "fall away". If the pedal "falls away" check for a leaking wheel cylin
der.
Remove
wheels
and drums and carefully check
each cylinder. Also examine all lines and fittings.
Rebuild
or replace all wheel cylinders (Par. P-21)
if
one is
defective
as
they
are all probably in poor condition. If the leak has allowed brake fluid to get
on the linings, the linings
will
have to be replaced.
f. A
"spongy"
brake pedal indicates the pressure of air in the hydraulic system.
This
condition must
be corrected by bleeding the brakes. See Par. P-7.
g. Should the brakes
become
locked so that the vehicle cannot be moved, the brakes may be re
leased by opening the bleeder screw on any one of the wheel cylinders. Before the vehicle is driven, correct the cause of the condition. The cause may
3
14 15 16 17 18
4
10796
1—
Cable
and Conduit
2—
Hand
Brake
Clip
3—
Hand
Brake
Bracket
4—
Hand
Brake
Handle Assembly 5—
Rear
Cap
6—
Drive
Gear
Bushing
7—
Driven
Gear
8—
Driven
Gear
Sleeve
FIG.
P-4—TRANSMISSION
BRAKE
9—Backing
Plate
10— Shoe and
Lining
11—
Lever
End Return Spring
12—
Brake
Drum
13— Bolt 14—
Rear
Companion Flange
15—
Washer
16— Nut 17— Propeller Shaft Flange Yoke
18—
Rear
Propeller Shaft
19—
Adjusting
End Spring
20—
Adjusting
Screw Bracket
21—
Operating
Lever
22—
Clevis
23—
Retracting
Spring
Clip
24—
Retracting
Spring
Link
325
Page 326 of 376

p
BRAKES
be either a defective master cylinder or the use of
low grade brake fluid which has expanded because
of heat. Use standard duty brake fluid conforming to
SAE-J1703
specification.
P-7.
Bleeding
Brakes
The
hydraulic
brake system must be bled whenever
a
fluid line has been disconnected or air
gets
into the system. A leak in the system may sometimes
be indicated by the presence of a spongy brake
pedal.
Air trapped in the system is compressible
and
does
not permit the pressure, applied to the
brake
pedal, to be transmitted solidly through to
the brakes. The system must be absolutely free
from
air at all times. When bleeding brakes, bleed
at that wheel with the
longest
line from the master
FIG.
P-5—BLEEDING
BRAKES
1—Bleeder
Screw
cylinder
first, the next
longest
second, etc. During
the bleeding operation the master cylinder must
be kept at least %
full
of hydraulic brake fluid.
To
bleed the brakes, first carefully clean all
dirt
from
around the master cylinder filler plug. If
bleeder tank is used follow the manufacturers in
structions.
Remove the filler plug and
fill
the master
cylinder
to the lower
edge
of filler neck.
Clean
off
all
bleeder connections at all four wheel cylinders.
Attach
bleeder
hose
and fixture to right
rear
wheel
cylinder
bleeder screw and place end of tube in a
glass jar, and submerged in brake fluid. Open the bleeder valve one-half to three-quarters of a
turn.
See
Fig.
P-5.
Depress the
foot
pedal, allowing it to return very
slowly. Continue this pumping action to force the
fluid
through the line and out of the bleeder
hose
which
carries with it any air in the system. When bubbles cease to appear at the end of the bleeder
hose, close the bleeder valve and remove the hose.
After
the bleeding operation at each wheel cylinder
has been completed,
fill
the master cylinder reser
voir
and replace the filler plug.
Do not re-use the liquid which has been removed
from
the lines through the bleeding process because
of air bubbles and
dirt.
P-8.
Brake Hoses
a.
Hydraulic
lines (tubing and hose) are the means
of transmitting fluid under pressure between the master cylinder and the wheel cylinders.
Note:
On
some
vehicles a proportioning valve is
located in the
rear
brake line along the inside left
frame
side
rail.
The valve is not serviceable and
must be replaced as an assembly.
Should
replacement be necessary make certain the valve is properly positioned with the centerline of
the hex plug (in the bottom of the valve) in the
vertical
position. Refer to Fig. P-l.
The
hoses
are the flexible links between the wheels
or
axles and the frame or body. The
hoses
must
withstand
the fluid pressures without expansion
and
must be free to flex during spring deflection
and
wheel turns without causing damage to the
hose.
b.
Hydraulic
lines are subject to damage and
deterioration. Hoses should be inspected for cuts,
chafing,
cracks,
twists and
loose
frame supports.
Hydraulic
tubing should be inspected for signs of
leakage (due to faulty flares or
loose
connections);
restrictions
(due to dents or corrosion); and wear (due to friction against other metal parts). Always
use correct type and size of wrench on fittings.
Avoid
damage to female fittings by supporting fit
ting with tube nut during removal of assembly.
c.
On fittings where gaskets are used, always use
a
new gasket. Copper gaskets take a set and may
not form a
good
seal if reused.
d.
When replacing hydraulic brake hose, attach
hose
to wheel cylinder and securely tighten hose,
then attach
opposite
end to frame fitting or tubing.
Avoid
twists in
hose
when assembling to frame fitting
or
tubing. Hold
hose
end securely with
wrench
while attaching tubing to hose. If
hose
end
clip
is used, make certain clip is assembled properly.
Check
for interference during spring deflection or
rebound and during front wheel turns.
e.
Check
for any possible contact between front
brake
hose
and inner sidewall of tire when the front
wheels are in maximum
turn
position.
Check
for sufficient but not excessive length of
hose
between
the clamp and the wheels by turning the wheels
from
one extreme
turn
position to the otherl
f.
Check
that there is no possibility of any contact between the
tail
pipe and
rear
brake
hose
under
all
operating conditions.
P-9.
Brake Pedal Adjustment
There
should always be at least W [12,7 mm.]
free pedal travel before the push rod
engages
the master cylinder piston.
This
adjustment is accomplished by shortening or 326
Page 331 of 376

'Jeep*
UNIVERSAL SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
P
f. On vehicles without a transmission brake hold
the brake
shoes
in their relative position and
engage
the parking brake cable
into
the parking
brake
lever.
g. On vehicles without a transmission brake in
stall
the parking brake strut and spring
between
the parking brake lever and the primary
shoe.
h.
Place the brake
shoes
on the backing plate and
install
the retainer pins, springs and retainers.
i.
Install the anchor pin plate.
j.
Install the lever and
sleeve
on the primary
shoe
then install the secondary return spring, then the
primary
return spring.
Important:
A
"L"
or "R" is located on the hex
agon
side of the lever crank for identification. The
lever crank marked "R" applies to the primary
shoe
on the
left
rear brake assembly. The lever
crank
marked
"L"
applies to the primary
shoe
on
the right rear brake assembly.
k. Place the upper linkage rod in the
groove
of the
anchor pin and
engage
the hook of the link rod
into
the adjusting lever.
I.
Install the brake drum. Install the wheel and
tire
assembly.
m. Adjust the brakes as described
below.
P-19.
Brake
Shoe
Initial
Adjustment —
a.
Should wheel brake units have
been
disassem bled for any reason, an initial adjustment
MUST
be made
before
drum installation.
b.
When the brake parts have
been
installed in
their correct position, initially adjust the adjusting
screw assemblies to a point where approximately Y% [9,53 mm.] of threads are
exposed
between
the
star
wheel and star wheel nut.
Note:
Following the initial adjustment and final
assembly, check brake pedal height to ensure
brake
operation. Then drive the car in reverse and
FIG.
P-12—BRAKE SHOE ADJUSTMENT
1—
Star
Wheel
2—
Lever
3—
Screwdriver
4—
Brake
Adjusting Tool
forward,
making 10 to 15 brake applications prior
to road testing.
This
action balances the adjust
ment of the four brake units and raises the brake
pedal.
c. Adjustment may be made manually by removing the access
slot
cover and using a brake adjust
ing
tool
or screw driver to rotate the star wheel
until
the wheel is in the locked position. To tighten, rotate the star wheel in the clockwise direction.
Then
back off the star wheel at least 15 to 20
notches
(clicks).
d.
To back off the star wheel on the brake, insert
ice pick or thin blade screw driver in adjusting screw
slot
to hold lever away from adjusting screw.
Back
off on adjusting screw until wheel and drum
turn
freely. Replace adjusting
hole
cover.
Caution:
DO NOT attempt to back off on ad
justing screw without holding adjuster lever away from screw as adjuster
will
be damaged.
P-20. Master Cylinder Reconditioning —
Dual
System
Refer
to Fig. P-13.
DISASSEMBLY
a.
Remove the filler cap and empty all fluid.
b.
Remove the snap ring, push rod assembly, and
the primary and secondary piston assemblies. Air pressure applied in the piston
stop
hole
will
help
facilitate the removal of the secondary piston as
sembly.
c. The residual check valves are located under
the front and rear fluid
outlet
tube
seats.
d.
The
tube
seats
must be removed with the
self-
tapping screws supplied in the repair kit to permit removal of the check valves. Screw the self-tapping
screws
into
the
tube
seats
and place two screw
driver
tips under the screw head and force the
screw upward as shown in Fig. P-14.
e. Remove the expander in the rear secondary cup, secondary cups, return spring, cup protector,
pri
mary
cup, and washer from the secondary piston.
f. The primary piston, with the rubber cups in stalled, is supplied in the repair kit.
CLEANING
a.
After disassembly, immersion of all metal parts
in
clean brake fluid or a brake system cleaner is
recommended. Use air
hose
to blow out dirt and cleaning solvent from recesses and internal pas
sages.
When overhauling a hydraulic brake unit,
use all parts furnished in the repair kit. Discard
all
old rubber parts.
b.
After cleaning, place
all"
hydraulic
system parts
on clean paper or in a clean pan.
INSPECTION
Inspect all other parts for damage or
excessive
wear.
Replace any damaged, worn, or chipped
parts.
Inspect hydraulic cylinder bore for
signs
of
scoring, rust, pitting, or etching. Any of
these
will
require
replacement of the hydraulic cylinder. 331
Page 334 of 376

p
BRAKES
P-25.
SERVICE
SYMPTOMS
Brakes Drag
Brake
Shoes
Improperly Adjusted
Piston Cups Enlarged . . •.
«•
Mineral
Oil or Improper Brake
Fluid
in System. . .
Improper
Pedal Adjustment
Clogged Master Cylinder By-Pass Port...
One
Brake Drags
Brake
Shoe
Adjustment Incorrect
v Brake
Hose
Clogged.
Return
Spring Broken
Wheel Cylinder Piston
01
Cups
Defective.........
Loose or Damaged Wheel Bearings
Brake Grabs
—
Vehicle Pulls
to One
Side
Grease
or Brake
Fluid
on
Lining................
Dirt
Between
Lining
and Drum
Drum
Scored or Rough
Loose Wheel Bearings. .
Axle Spring Clips Loose
Brake
Backing Plate Loose
Brake
Lining
..
Brake
Shoe
Reversed
Tires
Under-Inflated -
Tires
Worn Unequally
Glazed
or Worn
Lining
Restricted Brake
Line
Excessive Pedal Travel
Normal
Lining
Wear
Lining
Worn Out ... .
Leak
in Brake
Line.
Scored Brake Drums
Incorrect
Brake
Lining.
Air
in Hydraulic System
Spongy Brake Pedal
Air
in
Lines.
Brake
Shoe
Adjustment Incorrect
Insufficient Brake
Fluid
Excessive Pedal Pressure
Grease
or Brake
Fluid
in
Lining
Shoes
Improperly Adjusted
Warped
Brake
Shoes
Distorted Brake Drums
Glazed
or Worn
Lining
Restricted Brake
Line
Faulty
Brake Cylinder Insufficient Brake
Fluid.
Squeaky Brakes
Shoes
Warped or Drums Distorted
Lining
Loose.....
Dirt
Imbedded in
Lining
Improper
Adjustment.
Oil
or Grease on
Lining
Glazed
or Worn
Lining.
Drum
Scored
DIAGNOSIS
PROBABLE
REMEDY
Adjust
Flush
all
lines
with Alcohol. Install new cups in wheel and Master Cylinders
Adjust
Master Cylinder Eye Bolt
Clean
Master Cylinder
Adjust
Replace Replace
Replace
Adjust
or Replace
Replace
Lining
Clean
with Wire Brush
Turn
Drum and Replace
Lining
Adjust
Tighten Tighten
Different Kinds on Opposite Wheels
Forward
and
Rear
Shoes
misinstalled
Inflate
Replace or Rotate Replace Linings
Locate
and Repair
Adjust
Replace
Locate
and Repair Replace or Regrind Replace
Fill
Master
Cylinder
— Bleed Lines
Bleed Lines
Adjust
Fill
Master Cylinder
Replace
Lining
Major
Adjustment
Replace
Replace or Regrind Replace Linings * .
Locate
and Repair
Repair
or Replace
Fill
Master Cylinder Replace
Replace
Wire
Brush or Replace
Adjust
Replace Linings Replace Linings
Turn
Drum and Replace Linings 334