jump cable JEEP DJ 1953 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 1953, Model line: DJ, Model: JEEP DJ 1953Pages: 376, PDF Size: 19.96 MB
Page 29 of 376
'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL
SERIES
SERVICE
MANUAL
C
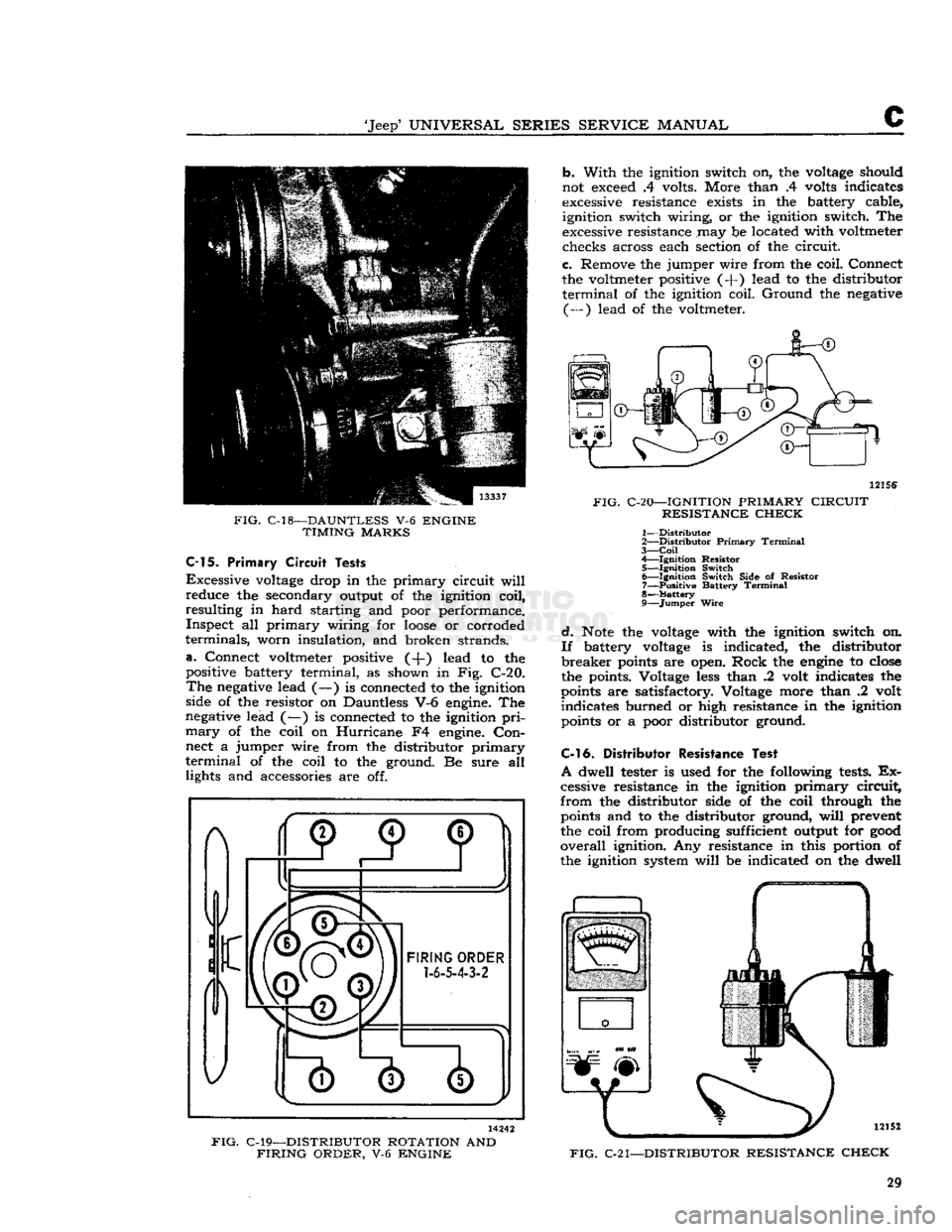
FIG.
C-18—DAUNTLESS
V-6
ENGINE
TIMING
MARKS
C-15.
Primary
Circuit
Tests
Excessive
voltage
drop in the primary circuit
will
reduce the secondary output of the ignition coil,
resulting in hard starting and poor performance. Inspect all primary wiring for
loose
or corroded
terminals, worn insulation, and broken strands,
a.
Connect voltmeter positive (-J-) lead to the
positive battery terminal, as shown in Fig. C-20.
The
negative
lead (—) is connected to the ignition
side of the resistor on Dauntless V-6
engine.
The
negative
lead (—) is connected to the ignition
pri
mary
of the coil on Hurricane F4
engine.
Con
nect a jumper wire from the distributor primary
terminal
of the coil to the ground. Be sure all lights and accessories are off. b. With the ignition switch on, the
voltage
should
not
exceed
.4 volts. More than .4
volts
indicates
excessive
resistance
exists
in the battery cable, ignition switch wiring, or the ignition switch. The
excessive
resistance may be located with voltmeter checks across each section of the circuit.
c. Remove the jumper wire from the coil. Connect
the voltmeter positive (-f) lead to the distributor
terminal
of the ignition coil. Ground the
negative
(—) lead of the voltmeter.
12156
FIG.
C-20—IGNITION
PRIMARY
CIRCUIT
RESISTANCE
CHECK
1—
Distributor
2—
Distributor
Primary
Terminal
3—
Coil
4— Ignition Resistor 5— Ignition Switch 6— Ignition Switch Side of Resistor 7— Positive Battery
Terminal
8—
Battery
9—
Jumper
Wire
d.
Note
the
voltage
with the ignition switch on.
If
battery
voltage
is indicated, the distributor
breaker
points
are open. Rock the
engine
to
close
the points. Voltage
less
than .2 volt indicates the
points
are satisfactory. Voltage more than .2 volt indicates burned or high resistance in the ignition
points
or a poor distributor ground.
C-l
6. Distributor
Resistance
Test
A
dwell tester is used for the following
tests.
Ex
cessive resistance in the ignition primary circuit,
from the distributor side of the coil through the
points
and to the distributor ground,
will
prevent
the coil from producing sufficient output for
good
overall
ignition. Any resistance in this portion of
the ignition system
will
be indicated on the dwell
FIG.
C-21—DISTRIBUTOR
RESISTANCE
CHECK
14242
FIG.
C-19—DISTRIBUTOR
ROTATION
AND
FIRING
ORDER,
V-6
ENGINE
29
Page 30 of 376

c
TUNE-UP
meter during this
test
Connect the red lead
tc*
dis
tributor
primary
lead at the coil as shown in Fig.
C-21.
Connect black lead to the ground.
Turn
ignition switch on; with
engine
stopped, observe
dwell
meter. If the meter reads zero,
crank
the
engine
a fraction of a revolution to
close
the
breaker
points.
Distributor
resistance is normal, if dwell meter
pointer is within range of
black
bar. Distributor resistance is high, if
dwell
meter pointer is not
within
the black bar.
Remove test lead from
distri
butor terminal of coil and
connect
to
each
of the
following points to determine
where
the excessive resistance is:
Distributor
primary
terminal
Distributor
primary
terminal in the distributor
Breaker
point bracket
Ground
side of points
Distributor
housing
Where
a noticeable change occurs in the meter
reading
in
these
steps, make the necessary correc
tion and repeat the
test.
C-l 7. Distributor
Point
Dwell
Using
a dwell tester, connect red
lead
to the
distri
butor terminal at coil. Connect black lead to
ground.
Set selector switch to the number of
cylin
ders in the
engine
being tested. Operate
engine
speed at specified rpm. and
note
readings. Cam
dwell
angle must be 30° for the Dauntless V-6
Delco equipped engine, 29° ±: 3° Prestolite equipped
engine
and 42° for the
Hurricane
F4 engine. If the dwell reading is not to specifications,
trouble could be improper point spacing, point
rubbing,
defective block or breaker arm, or mis
aligned and worn distributor cam.
Adjust
dwell
as shown in Fig. C-14 for the Delco equipped
Dauntless V-6 engine. For cam dwell adjustment
of the Prestolite equipped V6 and
Hurricane
F4 engine, refer to Par. C-10,
step
a.
Dwell
variation is determined by noting any
dwell
change as the
engine
is operated at different
speeds.
Excessive
variation indicates a change in point opening that can result from shaft or bushing wear,
or
from the distributor plate shifting because of
wear
or
looseness.
Measure
dwell variation at idle speed, using same
test
hookup for checking dwell. Increase speed to 1750 rpm.;
note
dwell reading.
Then
slowly reduce
speed to idle while observing dwell meter. Dwell
variation
should not exceed 3°. If dwell variation
exceeds
3°
between
idle speed and 1750 rpm.,
probable wear in the distributor shaft, bushings, or
breaker
plate is indicated. Distributor should then be checked more thoroughly.
C-l8. Check Ignition Wires
and
Connections
Examine
and clean the insulation on all ignition
wires
and check all connections. Wires should be
firm,
flexible, and free from roughness and minute
cracks.
Bend wires to check for brittle,
cracked,
or
loose
insulation. Since defective insulation
will
per
mit
crossfiring or missing of the engine, defective
wires
should be replaced.
C-l9. Test Ignition
Cables
To
remove cables from
spark
plugs, use
Spark
Plug
Cable
Remover
Tool
W-274.
Twist
the
boot
slightly to break the seal and, grasping the rubber
protector
boot,
lift straight up with a steady even
pull.
Do not grasp the cable and
jerk
the cable off; this
will
damage the cables. Do not use a probe
on
these
wires; puncturing them may cause a
separation in the conductor. To remove ignition cables from the distributor cap or coil tower,
loosen
the nipple first, then grasp the upper part of the nipple and the cable and gently
pull
straight up.
Test
the cable with an ohmmeter. Resistance value
per
foot
is
3000-7000
ohms. The ignition cables
can
be checked for
circuit
continuity by removing
the cable from the
spark
plug and holding the cable
end Vi" [6,35 mm.] from the engine. A strong
spark
indicates
good
conductor continuity.
When
connecting the cable to the
spark
plug, be
certain
a
good
connection is made and that the
protector
boot
fits tight on the
spark
plug. A
partially
seated cable creates an additional gap in
the
circuit
and the resulting
spark
jump
will
cause
terminal
corrosion and cable damage.
C-20. Coil
When
an ignition coil is suspected of being defec tive, it should be checked on the car. A coil may
break
down after it has reached operating tempera
ture.
It is important that the coil be at operating
temperature when
tests
are made.
Note:
The ignition coil and ballast resistor for the
V-6
engine
must be of the same manufacturer.
Ballast
resistors and ignition coils of one manufac
turer
are interchangeable with both units of the
other.
C-21.
Service Air
Cleaner
Refer
to Par.
B-2 2
for the correct service of the
air
cleaner.
C-22.
Check Fuel Lines and
Screens
Check
all fuel line connections to guard against
leakage.
Check
fuel pump filter F4
engine
and
fuel
line filter V-6 engine. Replace fuel filter if
necessary.
C-23. Check Fuel Pump a.
Fuel
pump pressure is important, for low pres
sure
will
seriously affect
engine
operation and high
pressure
will
cause excessive fuel consumption and
possibly flood the carburetor. Should there be any doubt of normal operation, check the pressure with
a
gauge
as shown in Fig.
C-2 2.
The minimum and
maximum
allowable pressures are 2% to 3% lbs. [0,176 a
0,264
kg-cm2], for the
Hurricane
F4 en
gine.
Fuel
pump pressure at carburetor (inlet) on
the Dauntless V6-225
engine
should be 3% lbs.
[0,264
kg-cm2] minimum at specified
R.P.M.
idle
with
the vapor
return
hose
squeezed off.
With
the
vapor
return
hose
open pump pressure should be
2
V2
lbs. [0,176 kg-cm2] minimum.
b.
Test for volume, as a pump may build up suffi
cient pressure but
fail
to produce sufficient volume.
Turn
down the carburetor fuel line fitting on the
pump and with the tank line connected, pump out
30
Page 173 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL
SERIES
SERVICE
MANUAL
H
FIG.
H-l—ENGINE
GROUND
STRAP—F4
ENGINE
Fig.
H-l, is tight at both connections. If
these
connections are
loose
-
or
dirty,
hard
starting or
failure
to start may result.
H-3.
Ignition System
The
ignition system consists of the battery, ignition
switch,
ignition coil ballast resistor (V-6 engine
only),
ignition coil, ignition distributor,
spark
plugs,
and
the low and high tension wiring.
Electrical
energy is obtained from the battery while cranking
and
from the alternator after the engine is running.
These
supply circuits must be considered part of
the ignition system.
The
ignition system furnishes the
spark
-for the
spark
plugs. The
spark
must occur in each cylinder
at exactly the proper time. To accomplish this, the following units are required.
a.
The battery, supplying the electrical energy.
Note: 'Jeep* vehicles equipped with Dauntless
V-6
engines have a ballast resistor connected be tween the ignition switch and the positive (+)
terminal
of the coil. The ballast resistor limits to
a
safe maximum the
primary
current flow through
the coil and the distributor contact points.
b.
The ignition coil, transforming the battery low
tension current to high tension current that jumps
the
spark
plug gap in the cylinders under com
pression.
c.
The distributor, delivering the
spark
to the
proper
cylinders and incorporates the mechanical
breaker,
that
opens
and closes the
primary
circuit at the exact time.
d.
The
spark
plugs, providing the gap in the engine
cylinders.
e. The wiring, connecting the various ignition
units.
f. The ignition switch controling the battery
current
when it is desired to start or
stop
the engine.
g. The firing order for the
Hurricane
F4 engine is
1-3-4-2.
Cylinder
No. 1 is the cylinder closest to the
radiator.
h.
The firing order for the Dauntless V-6 engine
is
1-6-5-4-3-2.
Cylinders
1-3-5 are on the left bank
and
cylinders 2-4-6 are on the right bank. H-4.
PRIMARY
CIRCUIT
Before testing the
primary
circuit,
make certain
that the battery is satisfactory or install a fully
charged
battery for the
primary
circuit
tests. Also,
check
the starter motor for excessive voltage drop
and
check the starter motor itself for excessive
draw.
a.
Measure the voltage at the coil
primary
termi
nals
while cranking the engine with the starter
motor. If the voltage is less than 9 volts the trouble
will
be found in the
primary
circuit.
If there is no voltage at all, check for a break in the
primary
circuit,
possibly in the coil
primary
winding.
b.
To check the
primary
circuit,
turn
the ignition
on,
turn
the engine until the points are closed, and
then measure the voltage drop across each portion
of the circuit with a voltmeter.
Note: Most voltage drops
will
be found at the con
nections of wires to terminals as
dirt,
oxidation etc. can cause excessive resistance at
these
points.
Measure
voltage drops in wires to take this into
account.
c.
Connect the voltmeter from the battery cable
terminal
on the starter solenoid to the battery
terminal
of the coil
primary.
If the voltmeter reads more than 0.2 volt, perform the checks given in
steps, d, e, and f following.
d.
Connect the voltmeter from the solenoid termi
nal
to the battery terminal of the ignition switch.
If
the voltmeter reads more than .05 volt, check
and
clean the connections at solenoid, light switch,
and
ignition switch.
e. If the voltmeter reading in
step
d is less than .05 volt, connect the voltmeter from the battery
terminal
to the ignition terminal on the ignition
switch.
If the voltage drop is more than 0.1 volt,
repair
or replace the ignition switch.
f. If the voltage drop in
step
e is not more than 0.1 volt, connect the voltmeter from the ignition
terminal
of the ignition switch to the battery termi
nal
of the coil
primary.
If the voltmeter reads more
than
.05 volt, clean and tighten the connections
and
check again. If the voltmeter again reads more
than
.05 volt, replace the wire.
g. Connect the voltmeter from the distributor
primary
terminal on the coil to the coil terminal on
the distributor. Voltage drop should not exceed .05 volt.
Clean
and tighten connections if necessary.
h.
Connect the voltmeter from the coil terminal
on the distributor to a clean,
paint-
free spot on the
distributor
body. The reading should not exceed .05
volt. If more, it indicates excessive resistance
through the points or in the distributor internal connections.
Clean
and align the points and make
sure
the breaker arm connection to the
primary
terminal
as well as the stationary contact point mounting in the body is clean and tight.
i.
Open the points and check the voltmeter. It
should read close to peak voltage. Low voltage in dicates that a circuit through the distributor (a
short)
exists while the points are open.
j.
Disconnect the condenser lead and open the points. A jump to
full
voltage indicates a short in 173
Page 174 of 376

H
ELECTRICAL
SYSTEM
the condenser. Replace the condenser. If there is
no jump to full voltage, overhaul or replace the
distributor.
k.
With the points closed, connect the voltmeter
from
a clean, paint-free
post
on the distributor
body to the negative
post
of the battery. The volt
age drop should be practically zero, a hardly
readable deflection on the voltmeter. If the volt meter registers a
voltage
drop, perform the checks
in
steps
1
and m following.
I.
Check
for
voltage
drop in the battery ground
cable.
Clean
the battery
post,
cable terminals, and contact surface on the bellhousing, or on body if
a
noticeable deflection of the voltmeter occurs,
m.
Check
for any
voltage
drop
between
the dis
tributor
body and a clean, paint-free
spot
on the
cylinder
block. If there is any
voltage
drop, remove
the distributor and clean the mounting surfaces of
distributor
body and cylinder block.
H-5.
SECONDARY
CIRCUIT
If
satisfactory ignition is not obtainable with cor
rect
point gap and tension; satisfactory condenser;
sufficient primary voltage; and correctly cleaned, gapped, and installed spark plugs; the secondary
circiut
should be investigated.
a.
Test the coil.
Bring
the coil up to operating
temperature using the coil heat feature of a coil tester, if available. Refer to the coil tester manu
facturer's
instructions for specific hook-ups for
performing the checks given in
steps
b, c, and d following.
b. Connect the positive lead of the tester to the
battery terminal of the coil primary winding.
Con
nect the tester ground lead to the coil tower. Mea
sure
the resistance of the secondary winding. If the
resistance is more than
20,000
ohms, a fault in the
secondary winding is indicated.
c.
Check
for a grounded secondary by touching the tester ground lead to the coil cover. If resistance
is not over
100,000
ohms, the secondary is grounded
to the cover.
d.
If the secondary winding is satisfactory, mea
sure
the primary current draw in accordance with
the instructions of the
test
equipment manu
facturer.
e.
Check
the secondary circuit for leakage. With the coil primary in the circuit with the breaker unit of the tester, connect a long, high-tension
test
lead
to the coil tower.
Check
the secondary circuit for
leakage by performing the checks given in
steps
f. g, h, and i following.
Note:
In the following
tests,
a slight sparking and
meter deflection
will
usually be
seen
just as contact
is made.
This
is caused by capacitance and
does
not
indicate defective insulation.
f.
Check
distributor cap. Remove the coil lead from the cap and touch the
test
lead to the center contact
inside the cap. If the meter reading drops when the contact is touched or if sparking is seen, a leakage
path is present
between
the center contact and one
of the plug towers.
This
leakage path
will
be in the
form
of a
crack
or carbon track in the cap. Discon nect the spark plug wires from the cap one at a
time and
test
each plug contact with the high-
voltage
lead and with all other plug wires con
nected. Any sparking or meter drop indicates that
a
leakage path exists
between
that particular con
tact and an adjacent one. Testing the adjacent contacts
will
determine which pair is at fault,
g-
Check
distributor rotor. Touch the
test
lead to
the spring contact in the center of the distributor
rotor.
Any leakage in the rotor insulation
between
the contact and the shaft
will
cause a drop in the meter reading and usually sparking
will
be seen.
h.
Check
spark plug wires. Disconnect the spark
plug wires from the plugs and
test
the plug terminal of each. The meter reading should not drop below
the open secondary value (value before making contact). If it
does
or if a large spark occurs when
the
test
lead and the plug wire are separated, there
is a break in the insulation on that wire.
i.
Check
the coil tower insulation. Remove the
high-tension
test
lead from the coil tower and touch
the ground lead of the coil tester to several points
around
the base of the tower. Any sparking or deflection of the meter indicates a leakage path in
the tower insulation.
H-6.
Alternator Charging System
All
Jeep
Universal
Series vehicles have, as standard
equipment a 35-amp., 12-volt, negative ground
alternator and a transistorized
voltage
regulator.
For
repairing the alternator, many of its major components are furnished as complete assemblies
including:
complete brush assembly which requires no soldering or unsoldering of leads; two complete
rectifying
diode
assemblies which eliminate the need for removing and replacing individual diodes;
a
complete isolation
diode
assembly; and a rotor assembly complete with shaft,
pole
pieces, field coil,
and
slip rings.
The
transistorized
voltage
regulator is an electronic
switching device. It
senses
the
voltage
appearing at the auxiliary terminal of the alternator and
supplies the necessary field current for maintaining the system
voltage
at the output
terminal.
The out
put current is determined by the battery electrical
load;
such as headlights, heater, etc.
The
transistorized
voltage
regulator is a sealed unit,
has no adjustments, and must be replaced as a
complete unit.
H-7.
Starting System
The
operation of the starter motor is controlled by
the ignition switch. The starter is made up of a
frame,
field coil, armature, and brushes.
The
starter solenoid electrically
closes
the circuit
between
the battery and the starter motor. When the ignition key is turned to its extreme right, the
solenoid is energized and
closes
the battery-to- starter-motor circuit.
Note:
All Jeep Universal Series vehicles have the
starter
solenoid switch secured to the starter motor
assembly. The Hurricane F4 and Dauntless V-6
engine
Prestolite starter drive is of the inertia type
(rexr
continued on
page
176) 174