parking brake JEEP DJ 1953 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 1953, Model line: DJ, Model: JEEP DJ 1953Pages: 376, PDF Size: 19.96 MB
Page 17 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
B
Reinstall
the axle shafts, and
refill
the housings to
plug level using the universal joint lubricant
specified in
Lubrication
Specifications.
B-56.
Front
Axle Wheel Bearings
To
lubricate the wheel bearings, it is necessary
to remove, clean, repack, and adjust them. When
front wheel hubs and bearings are removed for
lubrication,
they should be thoroughly washed in a
suitable cleaning solvent. The bearings should be
carefully
dried and then given a thorough cleaning
and
inspection. Use a clean brush to remove all
particles
of old lubricant from bearings and hubs.
After
the bearings are cleaned, inspect them for
pitted races and rollers. Also, check the hub oil
seals.
Note:
Wheel bearing lithium base lubricants are
used at the factory for
initial
fill
of
these
bearings.
When
lithium base and sodium base lubricants are
mixed,
the result is a thinned-out mixture that
can
bleed through seals. It is therefore important
that lubricants with the correct base be used when
lubricating
the wheel bearings.
Should
leaks occur at wheel bearing seals, the leaks
may
be caused by a mixture of two
types
of
lubri
cants.
In such cases, the old lubricant should be
completely removed before new lubricant is added.
Wheel
bearings should be thoroughly cleaned,
lubricated
with lithium base and reinstalled.
Repack
the bearing
cones
and rollers with grease
and
reassemble hub in the reverse order of the
disassembly. Test the bearing adjustment as out
lined
in Section Q.
B-57.
Rear
Axle Wheel Bearings
The
Rear
wheel bearings an early models equipped
with
lubrication fittings with a vent opening
through the housings above each fitting should be
lubricated
sparingly, each
2,000
miles
[3.200
km.].
Use
a hand compressor and wheel bearing grease,
forcing
the grease through each lubrication fitting
until
it flows from the vent. Vent should be kept
clear
of obstruction or grease
will
back up into the
brakes.
Do not add grease after it flows from the
vent for it may be forced through the wheel key-
way
onto
the outside of the wheel and possibly
onto
the brake linings.
Rear
wheel bearings that do
not have lubrication fittings should be removed
each
12,000
miles
[19.200
km.] and the bearing
cleaned, inspected and repacked. Refer to proce
dure
in Par. B-56.
Note:
When servicing the Flanged Axle Unit
Bear
ing Assembly, refer to Section N, Par. N-5 for
proper
lubrication procedures.
B-58.
Propeller Shafts
and
Universal Joints
The
propeller shaft slip joints and universals should
be lubricated with a hand compressor grease gun so as to not damage the bearing seals. The units
should be lubricated with a
good
quality grease.
Refer
to the
Lubrication
Chart
for lubrication fre
quency and lubricant type and grade. B-59.
Lights
and
Controls
a.
Check
all interior and exterior lights and light
switches for proper operation, including: parking
lights, headlamps (high beam and low beam),
tail
lights, brake lights, directional lights, and in strument panel lights.
b.
Check
all instrument panel controls and
instru
ments for proper operation.
B-60.
Speedometer Cable
Remove the
speedometer
cable from its housing every
12,000
miles
[19.300
km.].
Clean
it thor
oughly and coat it with a
good
quality light graphite grease.
B-61.
Headlights
Refer
to Section H.
B-62.
Heater Controls
Apply
Lubriplate
130-A to all friction points and
pivot points on the heater controls panel unit as well as the pivot points at the dashpot. Apply
a
few drops of penetrating oil all along the Bowden
cable.
This
oil
will
penetrate into the center wire.
B-63.
Windshield Wiper and
Washer Controls
Lubricate
the friction points and the pivot points
on the windshield wiper transmission and linkage
arms
with a slight amount of
Lubriplate
130-A.
B-64.
Rotate Tires
Refer
to Section Q for the correct method of rotat ing the tires.
B-65.
Body Lube Points
•
Refer to Par. B-66 through B-68.
B-66.
Hood Hinge Pivot Points
Lubricate
the frictional points of the hood hinge
pivot points with a few drops of light-weight
engine
oil.
B-67.
Glove Compartment Door Latch
Sparingly
wipe
Lubriplate
130-A on the
glove
com
partment door latch.
B-68.
Tailgate Hinges
Lubricate
the friction points of the tailgate hinges
with
a few drops of light-weight
engine
oil.
B-69.
LUBRICATION
OF
OPTIONAL EQUIPMENT
B-70.
Pintle Hook
When
lubricating the vehicle, place a few drops of oil on the pintle hook and safety latch pivot pins.
B-7!.
Centrifugal Governor
Check
the oil level in the governor housing at each
vehicle lubrication. Use the same seasonal grade
oil
as is used in the
engine
and change oil at each
engine
oil change. Do not
fill
the housing above
the level indicating plug opening. Keep the vent
in
the filler plug open at all times. 17
Page 213 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL
SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
H
FIG.
H-52—MAIN
LIGHT SWITCH (LATE)
1—
Circuit
Breaker
2—
Light
Switch
3—
Rear
Lights
4—
Head
Lights
5—
Parking
Lights
The
light switch shown in
Fig.
H-51 was superseded
by the one shown in
Fig.
H-52.
H-127.
Headlight Dimmer Switch To
remove the headlight dimmer switch, first raise
the hood and disconnect the wires attached to the
switch.
Then
remove the two screws that hold the
dimmer
switch to the floor board. Remove the
switch.
Check
the operation of the dimmer switch
with
a
test
light. A
circuit
across two different pairs of contacts (one to headlights, the other to the
high-beam indicator light) should alternately light
the
test
lamp when the switch is operated.
H-128.
Stop Light Switch
The
stop
light switch is of the diaphragm type.
Should
the switch
become
inoperative, it is neces
sary
to install a new one.
Current
production vehicles are equipped with two
stop
light switches
that operate independently of each other. Both
switches are located along the
left
side of frame, in the front and
rear
brake lines.
Caution:
Do not apply the brakes while making
this exchange as air may enter the hydraulic line.
Bleed
the brakes after replacing the switch.
Fig.
H-54 shows the wiring of the
stop
light
circuit.
11500
FIG.
H-53—STOP
LIGHT SWITCH
FIG.
H-54—STOP
LIGHT CIRCUIT
1— Stop
Light
Switch
2—
Light
Switch
3—
Tail
Light
H-129. Head Lamp Service
H-130.
Head Lamp Replacement
Refer
to Fig. H-59.
Each
sealed beam head lamp can only be replaced as a
complete
unit.
A
sealed beam unit may be replaced by the fol lowing procedure:
a.
Remove door screw.
b.
Remove door.
c.
Remove retaining screws and retaining
ring.
d.
Remove sealed beam unit.
Installation
of sealed beam unit is the reverse of
above procedure. When replacing head lamps,
check
lamp aim following procedures described in
Par.
H-132.
FIG.
H-55—PARKING
LIGHT (EARLY)
1—
Bezel
2—
Lens
3—
Bulb
4—
Gasket
5—
Housing
and Cable
6—
Screw
213
Page 224 of 376
H
ELECTRICAL
SYSTEM
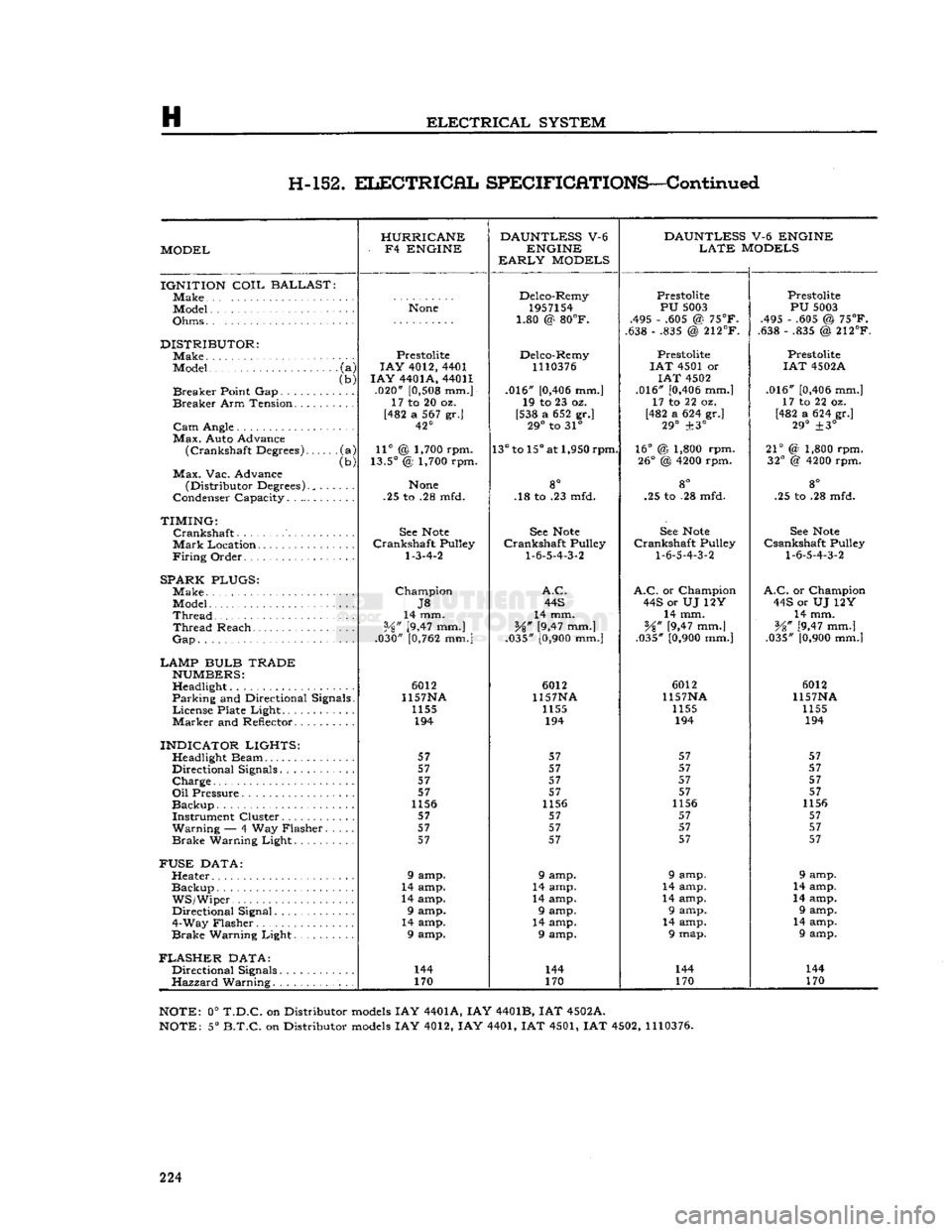
H-152.
ELECTRICAL
SPECIFICATIONS—Continued
HURRICANE DAUNTLESS
V-6
DAUNTLESS
V-6 ENGINE
MODEL -
F4
ENGINE
ENGINE
LATE
MODELS
EARLY
MODELS
IGNITION
COIL
BALLAST
]Make Delco-Remy
Prestolite Prestolite
Model
None
1957154
PU
5003
PU
5003
Ohms • • 1.80 @
80°F.
.495 - .605 @
75°F.
.495 - .605 @
75°F.
1.80 @
80°F.
.638 - .835 @
212°F.
.638 - .835 @
212°F.
DISTRIBUTOR:
Prestolite Delco-Remy Prestolite Prestolite
Model
•
(a)
LAY
4012, 4401
1110376
I
AT
4501 or
IAT
4502A
(b)
I
AY
4401A, 44011
IAT
4502
Breaker
Point Gap (b)
.020"
[0,508
mm.] .016"
[0,406
mm.] .016"
[0,406
mm.]
.016"
[0,406
mm.]
Breaker
Arm Tension. ..... 17 to 20 oz.
19 to 23 oz. 17 to 22 oz. 17 to 22 oz.
[482 a 567 gr.] [538 a 652 gr.] [482 a 624 gr.]
[482 a 624 gr.]
42° 29°
to 31°
29°
±3°
29°
±3°
Max.
Auto Advance
(Crankshaft
Degrees) •(a)
11°
@ 1,700 rpm.
13°
to
15°
at 1,950 rpm.
16°
@ 1,800 rpm.
21°
(2 1,800 rpm.
(Crankshaft
Degrees)
(b)
13.5°
@ 1,700 rpm.
26°
@
4200
rpm.
32°
@
4200
rpm.
Max.
Vac. Advance go
(Distributor Degrees)., . .
None
8° 8°
go
Condenser Capacity. . .25 to .28 mfd. .18 to .23 mfd. .25 to .28 mfd. .25 to .28 mfd.
TIMING:
Crankshaft
See
Note
See
Note
See
Note
See
Note
Mark
Location............
Crankshaft
Pulley
Crankshaft
Pulley
Crankshaft
Pulley
Csankshaft
Pulley
Firing
Order
1-3-4-2
1-6-5-4-3-2
1-6-5-4-3-2 1-6-5-4-3-2
SPARK PLUGS:
Make
Champion
A.C. A.C.
or Champion
A.C.
or Champion
J8
44S
44S or UJ 12Y 44S or UJ 12Y
Thread
14 mm.
14 mm. 14 mm. 14 mm.
Thread
Reach
Vz"
[9,47 mm.]
%"
[9,47 mm.]
¥%"
[9,47 mm.]
V8" [9,47 mm.]
Gap
.030"
[0,762
mm.]
.035"
[0,900
mm.] .035"
[0,900
mm.] .035"
[0,900
mm.|
LAMP BULB TRADE
NUMBERS:
Headlight 6012
6012 6012 6012
Parking
and Directional Signals. 1157NA
1157NA 1157NA 1157NA
License
Plate Light........ 1155
1155 1155 1155
Marker
and Reflector 194
194 194 194
INDICATOR LIGHTS:
57 57 57 57
Directional Signals........ 57
57 57 57
Charge
57
57 57 57
57 57 57 57
1156 1156 1156 1156
Instrument Cluster 57 57 57 57
Warning
— 4 Way Flasher. . 57
57 57 57
Brake
Warning Light 57
57 57 57
FUSE
DATA:
Heater 9 amp. 9 amp. 9 amp. 9 amp.
Backup
14 amp. 14 amp. 14 amp. 14 amp.
WS/Wiper.
14 amp. 14 amp. 14 amp. 14 amp.
Directional Signal 9 amp. 9 amp. 9 amp. 9 amp.
4-Way Flasher 14 amp. 14 amp. 14 amp. 14 amp.
Brake
Warning Light 9 amp. 9 amp. 9 map. 9 amp.
FLASHER
DATA:
Directional Signals. 144
144 144 144
Hazzard
Warning. 170
170 170 170
NOTE:
0°
T.D.C.
on Distributor
models
IAY 4401A, IAY 4401B, IAT 4502A.
NOTE:
5°
B.T.C.
on Distributor
models
IAY 4012, IAY 4401, IAT 4501, IAT 4502,
1110376.
224
Page 293 of 376
'Jeep*
UNIVERSAL
SERIES
SERVICE
MANUAL
N
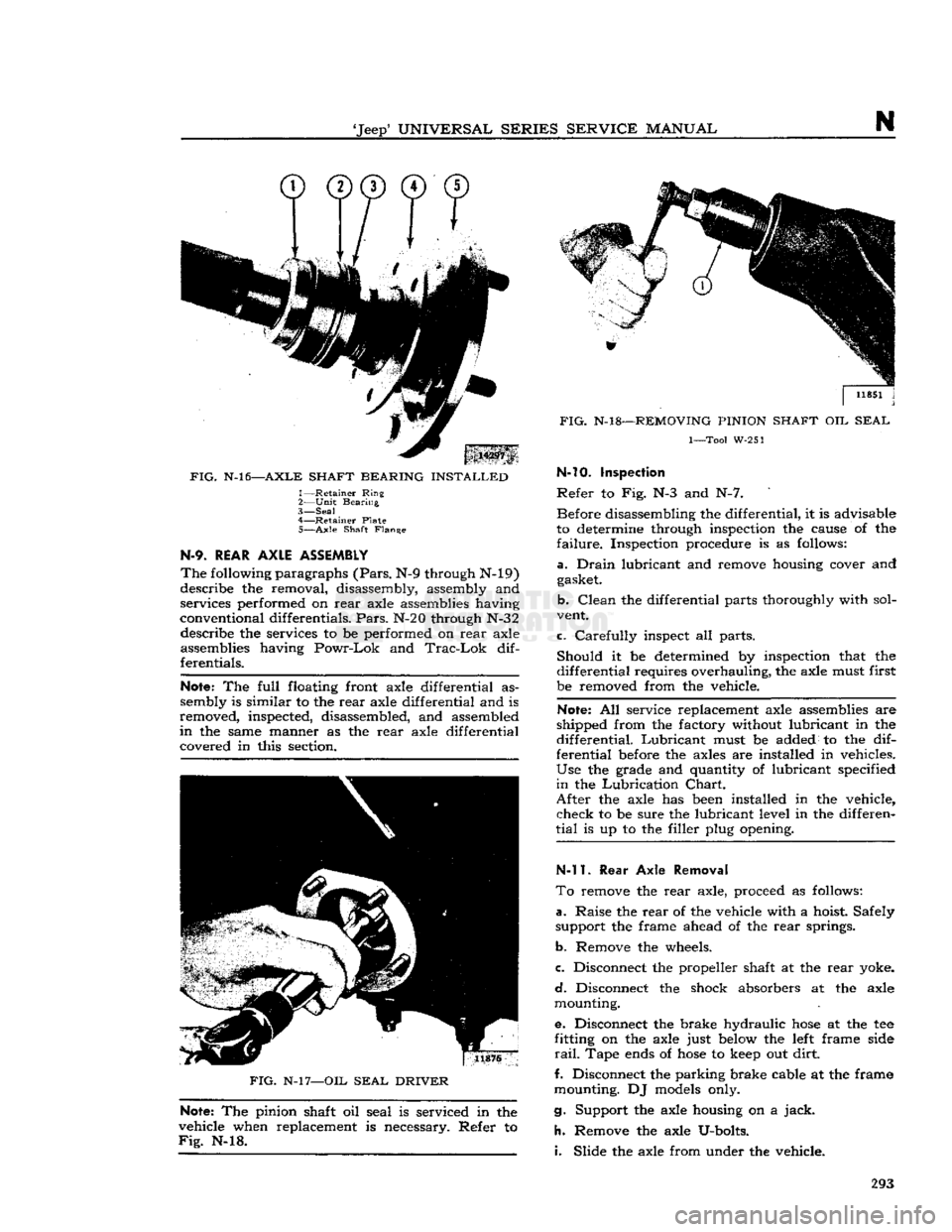
FIG.
N-l6—AXLE
SHAFT
BEARING
INSTALLED
1—
Retainer
Ring
2—
Unit
Bearing
3—
Seal
4—
Retainer
Plate
5—
Axle
Shaft
Flange
N-9.
REAR
AXLE
ASSEMBLY
The
following
paragraphs
(Pars.
N-9 through N-19)
describe the removal, disassembly, assembly and
services performed on
rear
axle assemblies having
conventional differentials.
Pars.
N-20 through N-32 describe the services to be performed on
rear
axle
assemblies having
Powr-Lok
and
Trac-Lok
dif
ferentials.
Note:
The
full
floating front axle differential as
sembly is similar to the
rear
axle differential and is
removed, inspected, disassembled, and assembled
in
the same manner as the
rear
axle differential
covered in this section.
FIG.
N-l
7—OIL
SEAL
DRIVER
Note:
The pinion shaft oil seal is serviced in the
vehicle when replacement is necessary. Refer to
Fig.
N-l8.
11851
j
J
FIG.
N-l8—REMOVING
PINION
SHAFT
OIL
SEAL
1—Tool
W-251 N-10. Inspection
Refer
to Fig. N-3 and N-7. Before disassembling the differential, it is advisable
to determine through inspection the cause of the
failure.
Inspection procedure is as follows:
a.
Drain
lubricant and remove housing cover and gasket.
b.
Clean
the differential parts thoroughly with sol
vent.
c.
Carefully
inspect all parts.
Should
it be determined by inspection that the
differential
requires overhauling, the axle must first
be removed from the vehicle.
Note:
All service replacement axle assemblies are
shipped from the factory without lubricant in the
differential.
Lubricant
must be added to the dif
ferential
before
the axles are installed in vehicles.
Use
the grade and quantity of lubricant specified
in
the
Lubrication
Chart.
After
the axle has
been
installed in the vehicle,
check
to be sure the lubricant level in the differen
tial
is up to the filler plug opening.
N-l
1.
Rear
Axle Removal
To
remove the
rear
axle, proceed as follows:
a.
Raise the
rear
of the vehicle with a hoist. Safely
support the frame ahead of the
rear
springs.
b.
Remove the wheels.
c.
Disconnect the propeller shaft at the
rear
yoke.
d.
Disconnect the shock absorbers at the axle
mounting.
e. Disconnect the brake hydraulic
hose
at the tee
fitting on the axle just
below
the
left
frame side
rail.
Tape
ends
of
hose
to
keep
out
dirt.
f. Disconnect the parking brake cable at the frame
mounting. DJ
models
only.
g. Support the axle housing on a
jack.
h.
Remove the axle U-bolts.
i.
Slide the axle from under the vehicle. 293
Page 303 of 376

'Jeep*
UNIVERSAL
SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
N
scribed
in
Pars.
N-ll through N-l9 for standard
axles, with the exception of the following torque
recommendations. Torque the differential case
bearing
cap screws 70 to 90 lb-ft. [9,7 a 12,4 kg-m.]
and
the cover screws 15 to 25 lb-ft. [2,1 a 3,4
kg-m.].
The ring gear screws on axles with Powr-
Lok
differentials should be torqued as follows:
Model
30 and 44 axles 35 to 55 lb-ft. [4,84 a 7,60 kg-m.].
N-24. TRAC-LOK DIFFERENTIAL
As
optional equipment
Trac-Lok
Model 44 differen
tial
is available on all Jeep Universal vehicles equipped with semi-float flanged axle shafts.
A
conventional differential transmits all of the
ring
gear torque through the differential gears to the axle shafts. Torque is at all
times
equal on the axle shafts, and if one wheel slips, the other wheel
can
only put out as much torque as the slipping
wheel.
The
Trac-Lok
differential is similar,
except
that
part
of the torque from the ring gear is trans mitted through clutch packs
between
the side gears
and
differential case. The multiple disc clutches
with
radial
grooves
on the plates and concentric
grooves
on the discs are
engaged
by a preload
from
Belleville springs, plus separating forces from
the side gears as torque is applied through the
ring
gear.
The
Trac-Lok
construction permits differential action when required for turning corners and transmits equal torque to both
wheels
when driving
straight
ahead. However, when one wheel tries to spin due to leaving the ground, a patch of ice,
etc., the clutch packs automatically provide more
torque to the wheel which is not trying to spin.
It
can be
seen
then that the
Trac-Lok
differential
resists wheel spin on bumpy roads and provides
more pulling power when one wheel tries to slip.
In
many cases of differences in traction, pulling
power
will
be automatically provided until both
wheels
start to slip.
In
diagnosis of vehicle operators' complaints, it
is important to recognize two things:
a.
If, with unequal traction, both
wheels
slip, the
Trac-Lok
has
done
all it can possibly do.
b.
In extreme cases of differences in traction, the
wheel with least traction may spin after the
Trac-
Lok
has transferred as much torque as possible
to the non-slipping wheel.
N-25.
Lubrication
The
Trac-Lok
differential requires a special
lubri
cant
and ordinary multipurpose gear lubricants
MUST
NOT be used. Use only 'Jeep* Differential
Oil,
Part
No. 94557.
Trac-Lok
differential may be cleaned only by disassembling the unit and wiping with clean rags. Do not flush the
Trac-Lok
unit.
Note:
The
Trac-Lok
differential is serviced at the
same time intervals as the standard differential.
N-26.
Trouble
Symptoms
If
noises
or roughness, such as chatter, are present
in
turning corners, the probable cause is incorrect
or
contaminated lubricant.
Before any differential is removed and disassem
bled for chatter complaints, the correctness of
lubri
cant
can and should be determined.
A
complete
lubricant
drain,
and
refill
with specified
Limited
Slip Differential lubricant
will
usually
correct
chatter.
The
following procedure is recommended to ensure
complete
removal of old lubricant.
a.
Warm
the lubricant by vehicle road operation,
or
5 minutes of operation in gear at 30 mph with
both
wheels
off the ground on a hoist.
Caution:
Never place the transmission in gear with
the
engine
running when only one wheel of a
Limited
Slip Differential equipped vehicle is raised.
The
vehicle might drive itself off the
jack
and produce damage or
injury.
b.
Drain
lubricant while
warm.
Remove
drain
plug
or
cover to
drain
completely. If cover is removed,
it
may be necessary to replace gasket at this time.
c.
Refill
axle with specified
Limited
Slip Differen
tial
lubricant.
d.
Operate the vehicle for approximately ten miles
[16,09
km.], making at least ten figure 8 turns
to flush the old lubricant out of the clutch packs.
e.
Repeat
steps
b, c, and d, making sure to replace
the cover gasket if required in
step
c.
f. It is possible that slight chatter, requiring ad
ditional
vehicle operation, may remain after
step
e. If chatter persists after 100 miles
[160,9
km.]
of vehicle operation, or remains severe after
step
e above, disassembly and repair
will
be necessary.
N-27.
Unit
Inoperative
Proper
performance and capabilities of
Limited
Slip
Differentials are
often
misunderstood. No
precise
methods
of measuring
Limited
Slip Dif
ferential
performance are generally available in the field. A functioning unit can be determined by
relatively
simple vehicle operational
tests,
as
follows:
a.
Place one wheel on
good
dry pavement, and the
other on ice, mud, grease, etc.
b.
Gradually
increase
engine
rpm to obtain maxi
mum
traction
prior
to "break-a-way." The ability
to
move
the vehicle
effectively
will
demonstrate
proper
performance.
c.
If extremely slick surfaces, such as ice or grease,
are
used
some
question may exist as to proper per
formance at
step
b. In
these
extreme cases a prop
erly
performing
Limited
Slip Differential
will
pro
vide greater "pulling" power by lightly applying
the parking brake.
N-23.
Trac-Lok
Differential Disassembly
and
Reassembly
It
is recommended that the
complete
axle assembly
be removed from the vehicle, when it
becomes
necessary to remove the
Trac-Lok
from the hous
ing.
Refer to Par. N-3 and N-12 for removal of axle shafts and differential case from axle housing. 303
Page 310 of 376

m
REAR AXLE
c. Attach the brake line
hose
at tee fitting on top
of housing.
d.
Attach parking brake cables at rear of brake
backing plate. DJ
models
only.
e. Connect the shock absorbers at the axle mount
ing pads.
f. Connect the propeller shaft at the rear universal
joint.
g. Adjust and bleed brakes. (See Section P).
h.
Install
wheels
and lower vehicle to floor.
i.
Check parking brake as described in Section P.
j.
Fill
the axle housing with the proper lubricant.
For
correct lubricant refer to the
Lubrication
Chart.
N-34.
TROUBLE
SHOOTING
The
following problems can be present with either the conventional differential,
Powr-Lok
or
Trac-
Lok
differential.
N-35. Backlash
Excessive
backlash in the vehicle drive line may be the results of
excessive
backlash in the trans
mission, propeller shaft spline, universal joint, ring gear and pinion, the axle shaft spline, or the dif
ferential.
Excessive
backlash in the differential may be meas
ured
as follows:
a.
Jack
up one rear wheel.
b. Put the transmission in gear.
c. Measure the travel of the jacked-up wheel on
a
10"
[25,40
cm.] radius from the wheel center.
This
total
movement
should not
exceed
IVi" [3,17 cm.] in a new unit. In order to restrict the
backlash
to the axles only, make sure that the
yoke of the propeller shaft
does
not
move
during
the check.
d.
If all causes of backlash mentioned
above
have
been
eliminated with the exception of the differen
tial
and that still
exceeds
the maximum allowable
movement, overhaul the differential.
N-36.
Rear
Wheel
Noise
Looseness of the rear axle shaft nut on semifloat- ing tapered rear axles may produce a clicking or
creaking
noise.
This
noise
can usually be
stopped
by torquing the wheel hub nut 150 to 175 lb-ft. [20,7 a 24,2 kg-m.]. If the condition has continued
for
some
time, slight wear may have resulted allow
ing the
noise
to persist. In this case, coat the hub,
key, and keyway on tapered axle shafts with white
lead and torque the nut as specified. If the
noise
persists after this treatment, replace the worn parts.
N-37.
SERVICE DIAGNOSIS
SYMPTOMS
Axle
Noisy on Pull and
Coast
Excessive
Back
Lash
Bevel
Gear
and Pinion. . . . . Adjust
End
Play Pinion Shaft Adjust
Worn
Pinion Shaft Bearing Adjust
Pinion
Set too Deep in Bevel
Gear
too Tight..... Adjust
Wrong
Lubricant
Being Used
(Powr-Lok
or
Trac-Lok
Differential) . Replace
Axle
Noisy on
Pull
Pinion
and Bevel
Gear
Improperly Adjusted Adjust
Pinion
Bearings Rough....................... Adjust
Pinion
Bearings Loose Adjust
Axle
Noisy on Coast
Excessive
Back
Lash
in Bevel
Gear
and Pinion. . . Adjust
End
Play in Pinion Shaft. . Adjust
Improper
Tooth Contact.
....................
Adjust
Rough Bearings Replace
Back
Lash
Worn
Differential Pinion
Gear
Washers Adjust
Excessive
Back
Lash
in Bevel
Gear
and Pinion. . . Adjust
Worn
Universal Joints Replace
PROBABLE REMEDY
310
Page 323 of 376
'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL
SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
P
BRAKES
SUBJECT
PAR
GENERAL.
. P-l
Brake
Maintenance P-5
Master
Cylinder.
P-2
Parking
Brake
P-3
Transmission
Brake
P-4
BRAKE SERVICE
.P-6 Bleeding Brakes P-7
Brake
Adjustments P-14
Brake
Hoses P-8
Brake
Shoe
Initial
Adjustment P-l9
Brake
Shoe Installation P-l8
Brake
Pedal Adjustment P-9
Hand
Brake.
P-10 Inspection P-17
SUBJECT
PAR
Brake
Shoe Removal P-l6
Master
Cylinder Reconditioned. . P-20
Parking
Brake
Adjustment
.P-l 1
Relining
Transmission
Brake
P-13
Relining
Wheel
Brake
P-l5
Transmission
Brake
Adjustment .P-12
Wheel
Brake
Units P-14
Wheel
Cylinder Reconditioning P-21
TROUBLESHOOTING
P-2 2 Squeaky Brakes P-23
Rattles in Brakes P-24
SERVICE
DIAGNOSIS.
P-25
SPECIFICATIONS
P-2 6
P-1. GENERAL
A
double-safety
hydraulic brake system in con
junction with self-adjusting wheel brake units are
standard
equipment on all current production
'Jeep* vehicles. The
double-safety
brake system
Is
equipped with dual
stop
light switches that op
erate independently of each other, thus eliminating
possible
stop
light failure. Service information for
self adjusting brakes starts with Par. P-14.
All
four-wheel-drive vehicles are equipped with a transmission brake that operates in the drive line
and
is mounted to the rear of the transfer case. Two-wheel-drive vehicles
(DJ-5,
DJ-6)
are equipped
with a hand-operated parking brake that operates at the rear wheels.
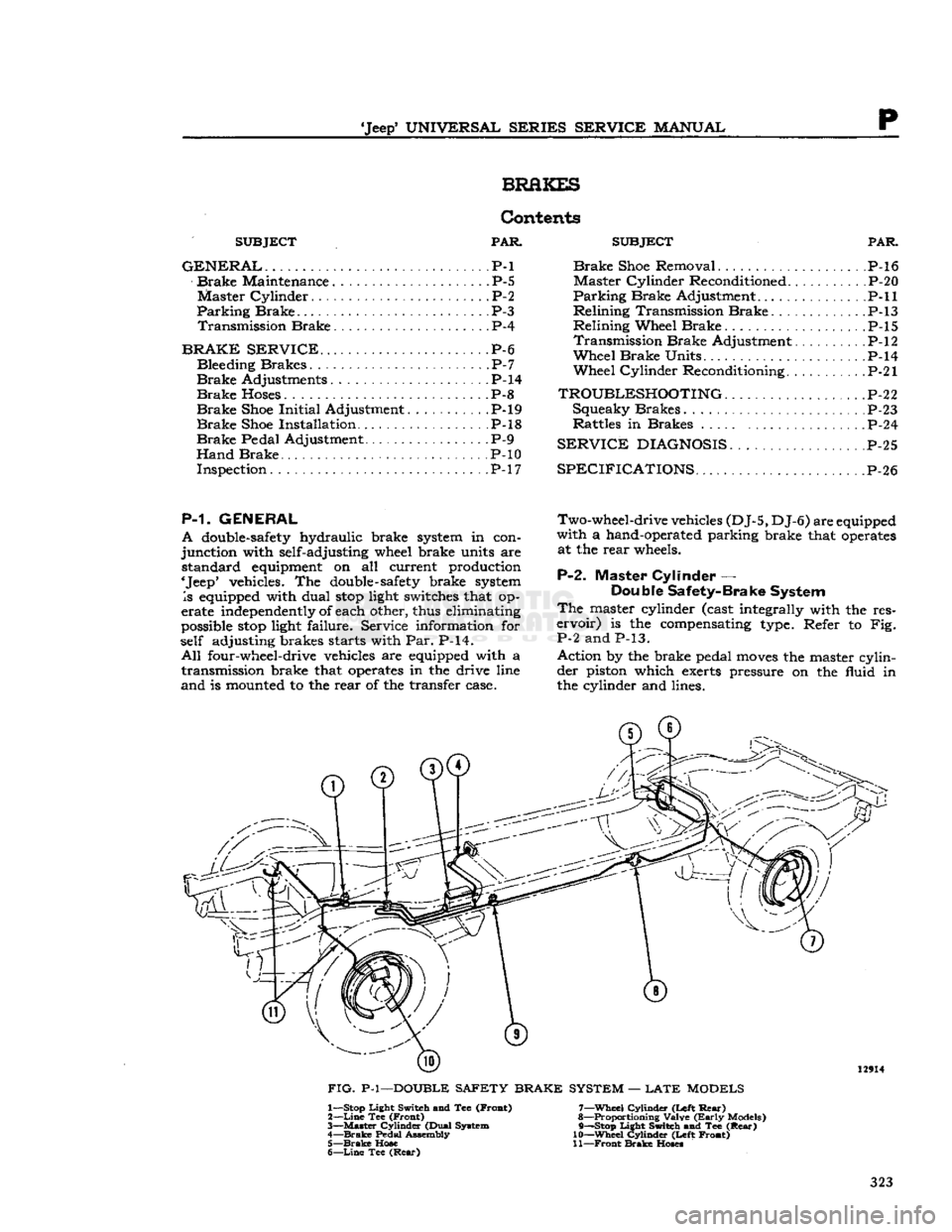
P-2.
Master Cylinder —
Double Safety-Brake System
The
master cylinder (cast integrally with the res
ervoir)
is the compensating type. Refer to Fig.
P-2 and P-13.
Action by the brake pedal
moves
the master cylinder piston which exerts pressure on the fluid in
the cylinder and lines. 12914
FIG.
P-l—DOUBLE SAFETY BRAKE SYSTEM —
LATE
MODELS 1— Stop Light Switch and Tee (Froat)
2—
Line
Tee (Front)
3—
Master
Cylinder (Dual System
4—
Brake
Pedal Assembly 5—
Brake
Hose
6—
Line
Tee
(Rear)
7—
Wheel
Cylinder (Left
Rear)
8— Proportioning Valve
(Early
Models)
9— —Stop Light Switch and Tee
(Rear)
10—
Wheel
Cylinder (Left Front)
11—
Front
Brake
Hoses
323
Page 324 of 376
p
BRAKES
13264
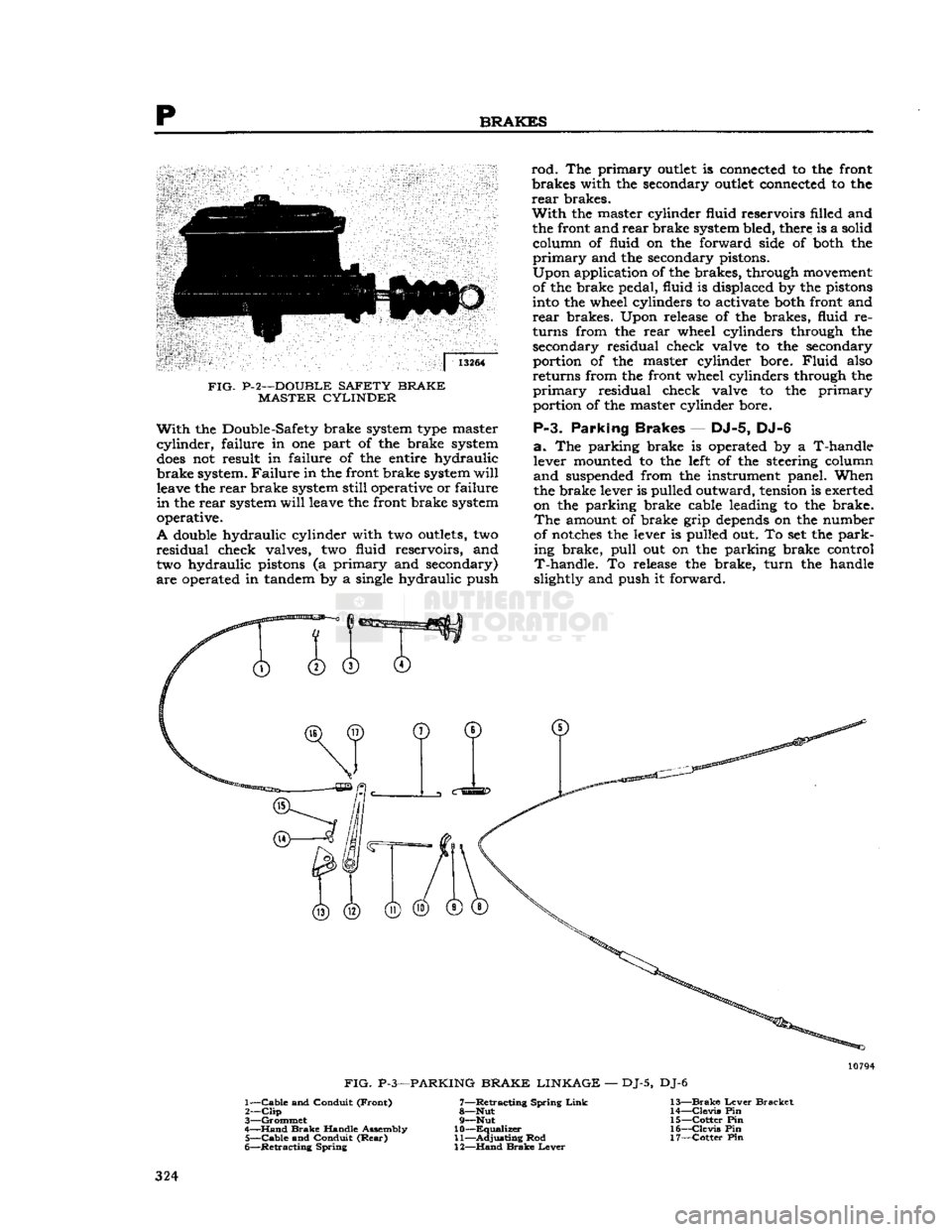
FIG- P-2—DOUBLE
SAFETY BRAKE
MASTER
CYLINDER
With
the Double-Safety brake system type master
cylinder,
failure
in one part of the brake system
does
not result in
failure
of the entire hydraulic
brake system. Failure in the
front
brake system
will
leave the rear brake system
still
operative or
failure
in
the rear system
will
leave the
front
brake system
operative.
A
double hydraulic
cylinder
with
two outlets, two
residual
check valves, two
fluid
reservoirs, and
two
hydraulic pistons (a
primary
and secondary)
are operated in tandem by a single hydraulic push
rod.
The
primary
outlet is connected to the
front
brakes
with
the secondary outlet connected to the rear brakes.
With
the master
cylinder
fluid
reservoirs
filled
and the
front
and rear brake system
bled,
there is a
solid
column
of
fluid
on the
forward
side of both the
primary
and the secondary pistons.
Upon
application
of the brakes, through movement
of
the brake pedal,
fluid
is displaced by the pistons
into
the wheel cylinders to activate both
front
and
rear brakes.
Upon
release
of the brakes,
fluid
re
turns
from
the rear wheel cylinders through the secondary residual check valve to the secondary
portion
of the master
cylinder
bore.
Fluid
also
returns
from
the
front
wheel cylinders through the
primary
residual check valve to the
primary
portion
of the master
cylinder
bore.
P-3.
Parking
Brakes
— DJ-5, DJ-6
a.
The parking brake is operated by a T-handle
lever
mounted to the
left
of the steering
column
and
suspended
from
the instrument panel. When
the brake lever is
pulled
outward, tension is exerted
on
the parking brake cable leading to the brake.
The
amount of brake
grip
depends
on the number
of
notches the lever is
pulled
out. To set the park
ing
brake,
pull
out on the parking brake
control
T-handle.
To
release
the brake,
turn
the handle
slightly
and push it
forward.
0
FIG.
P-3—PARKING
BRAKE LINKAGE
—
DJ-5,
DJ-6
1—
Cable
and
Conduit
(Front)
7—Retracting
Spring
Link
13—Brake
Lever
Bracket
2—
Clip
8—Nut
14—Clevis
Pin
3—
Grommet
9—Nut
15—Cotter
Pin
4—
Hand
Brake
Handle
Assembly
10—Equalizer
16—Clevis
Pin
5—
Cable
and
Conduit
(Rear)
11—Adjusting
Rod
17—Cotter
Pin
6—
Retracting
Spring
12—Hand
Brake
Lever
324
Page 325 of 376
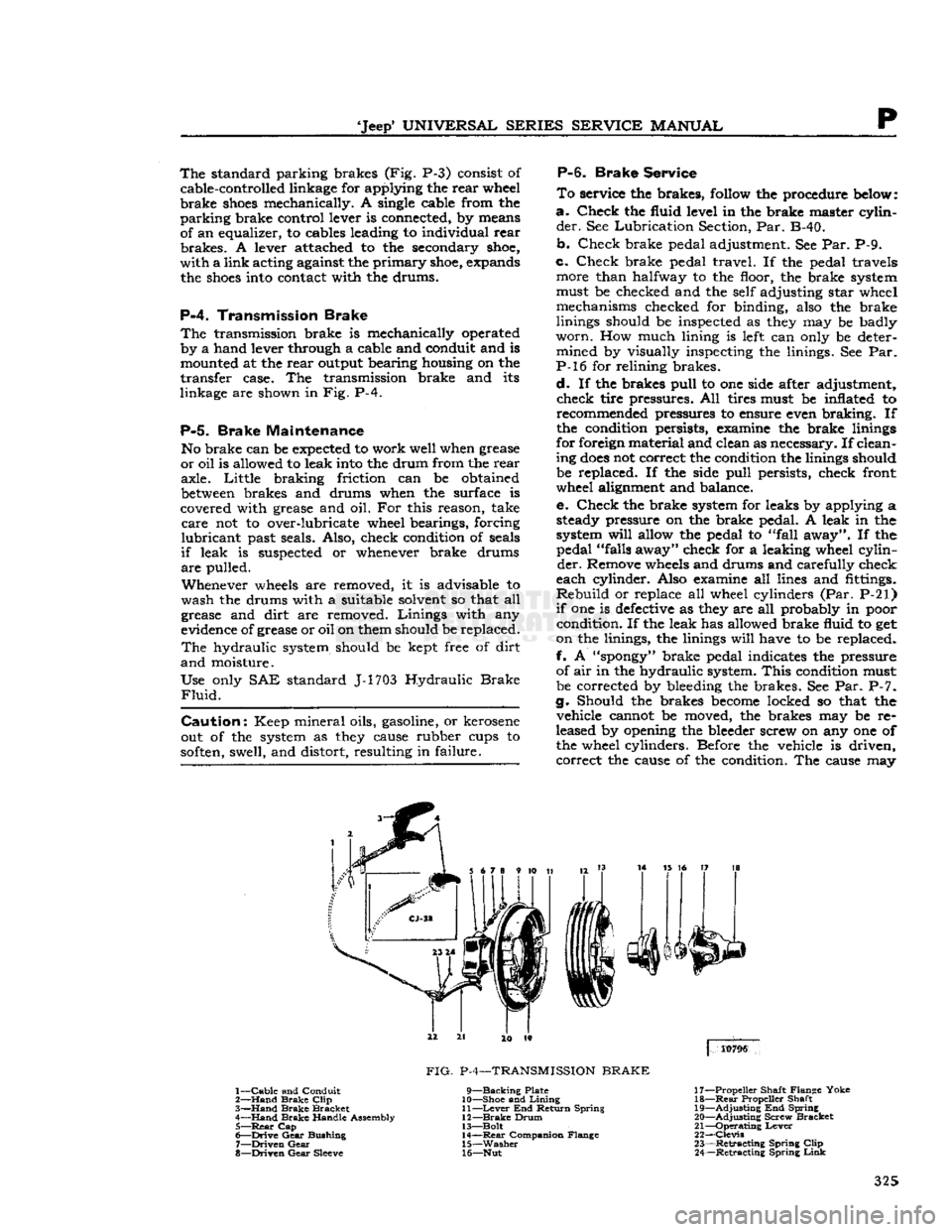
'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL
SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
P The
standard parking brakes (Fig. P-3) consist of
cable-controlled linkage for applying the rear wheel
brake
shoes
mechanically. A single cable from the
parking
brake control lever is connected, by means of an equalizer, to cables leading to individual rear
brakes.
A lever attached to the secondary
shoe,
with a link acting against the
primary
shoe,
expands the
shoes
into
contact with the drums.
P-4.
Transmission Brake
The
transmission brake is mechanically operated
by a hand lever through a cable and conduit and is mounted at the rear output bearing housing on the
transfer case. The transmission brake and its
linkage are shown in Fig. P-4.
P-5.
Brake Maintenance
No brake can be
expected
to work well when grease
or oil is allowed to leak
into
the drum from the rear axle. Little braking friction can be obtained
between
brakes and drums when the surface is
covered with grease and oil. For this reason, take
care
not to over-lubricate wheel bearings, forcing
lubricant
past seals. Also, check condition of seals
if
leak is suspected or whenever brake drums
are
pulled.
Whenever
wheels
are removed, it is advisable to
wash the drums with a suitable solvent so that all
grease and dirt are removed. Linings with any
evidence of grease or oil on them should be replaced.
The
hydraulic system should be kept free of dirt
and
moisture.
Use only SAE standard J-1703 Hydraulic
Brake
Fluid.
Caution:
Keep mineral oils, gasoline, or kerosene
out of the system as
they
cause rubber cups to
soften,
swell, and distort, resulting in failure.
P-6.
Brake
Service
To
service the brakes,
follow
the procedure
below:
a.
Check the fluid level in the brake master cylin
der.
See Lubrication Section, Par. B-40.
b. Check brake pedal adjustment. See Par. P-9.
c. Check brake pedal travel. If the pedal travels more than halfway to the floor, the brake system
must be checked and the self adjusting star wheel mechanisms checked for binding, also the brake
linings should be inspected as
they
may be badly
worn.
How much lining is
left
can only be deter mined by visually inspecting the linings. See Par.
P-l6 for relining brakes.
d.
If the brakes pull to one side after adjustment, check tire pressures. All tires must be inflated to recommended pressures to ensure even braking. If
the condition persists, examine the brake linings
for foreign material and clean as necessary. If clean
ing
does
not correct the condition the linings should be replaced. If the side pull persists, check front
wheel alignment and balance.
e. Check the brake system for leaks by applying a steady pressure on the brake pedal. A leak in the
system
will
allow the pedal to "fall away". If the pedal "falls away" check for a leaking wheel cylin
der.
Remove
wheels
and drums and carefully check
each cylinder. Also examine all lines and fittings.
Rebuild
or replace all wheel cylinders (Par. P-21)
if
one is
defective
as
they
are all probably in poor condition. If the leak has allowed brake fluid to get
on the linings, the linings
will
have to be replaced.
f. A
"spongy"
brake pedal indicates the pressure of air in the hydraulic system.
This
condition must
be corrected by bleeding the brakes. See Par. P-7.
g. Should the brakes
become
locked so that the vehicle cannot be moved, the brakes may be re
leased by opening the bleeder screw on any one of the wheel cylinders. Before the vehicle is driven, correct the cause of the condition. The cause may
3
14 15 16 17 18
4
10796
1—
Cable
and Conduit
2—
Hand
Brake
Clip
3—
Hand
Brake
Bracket
4—
Hand
Brake
Handle Assembly 5—
Rear
Cap
6—
Drive
Gear
Bushing
7—
Driven
Gear
8—
Driven
Gear
Sleeve
FIG.
P-4—TRANSMISSION
BRAKE
9—Backing
Plate
10— Shoe and
Lining
11—
Lever
End Return Spring
12—
Brake
Drum
13— Bolt 14—
Rear
Companion Flange
15—
Washer
16— Nut 17— Propeller Shaft Flange Yoke
18—
Rear
Propeller Shaft
19—
Adjusting
End Spring
20—
Adjusting
Screw Bracket
21—
Operating
Lever
22—
Clevis
23—
Retracting
Spring
Clip
24—
Retracting
Spring
Link
325
Page 327 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL
SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
P
lengthening of the brake master cylinder eye bolt.
This
is
done
so the primary cup
will
clear the by
pass port when the piston is in the off position,
otherwise the compensating action of the master
cylinder
for expansion and contraction of the fluid
in
the system, due to temperature changes,
will
be destroyed and cause the brakes to drag.
Note:
Some older 'Jeep' vehicles may
develop
side
movement
of the clutch and brake pedals resulting
from wear of the pedals, shafts, and bushings. One
way to
compensate
for this wear is to install a pedal
slack
adjuster kit,
Part
No.
921936.
FIG.
P-6—HAND
BRAKE
ADJUSTMENT
P-10.
Hand Brake
On
Model DJ-5 and DJ-6 vehicles the rear brake
shoes
are operated through cables and conduits to
form the hand or parking brake. A brake cable
equalizer and adjusting rod, Fig. P-6, is located directly back of the frame center cross member.
P-11.
Parking Brake Adjustment
•
Model DJ-5, DJ-6.
The
foot
brakes must be satisfactorily adjusted be
fore attempting adjustment of the hand brake.
To
adjust the hand brake raise both rear
wheels
free of the floor.
Pull
up three
notches
on the hand
brake
lever and tighten the adjustment until the
rear
brakes drag slightly. Release the hand brake
lever and check the rear
wheels
for drag. The
wheels
must turn freely with the lever released.
P-12.
Transmission Brake Adjustment
The
transmission brake is located on the propeller
shaft at the rear of the transfer case, see Fig. P-4.
The
brake is operated by a cable connection from
the brake handle mounted on the instrument panel.
To
adjust the transmission brake, the following
sequence
should be followed:
Make
sure that the brake handle on the instrument
panel is fully released. Give due attention to the
cable and operating linkage to see that
they
do
not bind. If necessary free up the cable and
lubri
cate it. Rotate the brake drum until one pair of the
three
sets
of
holes
are over the
shoe
adjusting screw
wheels
in the brake. Use the
edge
of the
holes
in
the brake drum as a fulcrum for suitable adjusting
tool
or a screwdriver, rotate each notched adjusting
screw by moving the handle of the
tool
away from
the center of the drive shaft until the
shoes
are
snug in the drum.
Back
off seven
notches
on the
adjusting screw
wheels
to secure proper running clearance
between
the
shoes
and the drum. Refer
to Fig. P-8.
P-13.
Relining Transmission Brake
Note:
The condition of the brake lining on the
transmission brake can be visually checked through
the adjusting
holes
in the brake drum.
FIG.
P-7—REMOVING
TRANSMISSION
BRAKE
DRUM
1— Tool W-172
2—
Adapter
3—
Brake
Drum
a.
To reline the brake
shoes
and make a major ad
justment, first remove the four universal joint at taching nuts and lower the propeller shaft. Remove
the retracting spring clevis pin and the spring clip.
Remove the hug lock nut, the nut and washer from
the transfer case output shaft. Both the universal
joint companion
flange
and the brake drum may be readily removed by using puller Tool No. W-172
which
is illustrated in Fig. P-7. Remove the two
brake
shoe
retracting springs and the
shoes.
b. Clean all parts with a suitable cleaning solution
and
examine them for damage or wear.
Brake
shoes
may be distorted by improper lining
installation and the lining should be ground true
after installation on the
shoes.
For this reason it
is recommended that new or replacement
shoe
and
lining assemblies be installed.
c. To reassemble, first turn both adjusting screw
wheels
away from the center to "all off" position.
Place a light film of grease on the brake actuating
cam
and install the
shoes.
Install the black
shoe
re
turn
spring next to the cam and the yellow spring next to the notch adjusting wheel screw. Place the
brake
drum and universal joint
flange
in position
and
install the transfer case output shaft washer,
nut and hug lock nut. 327