dash JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 181 of 2199
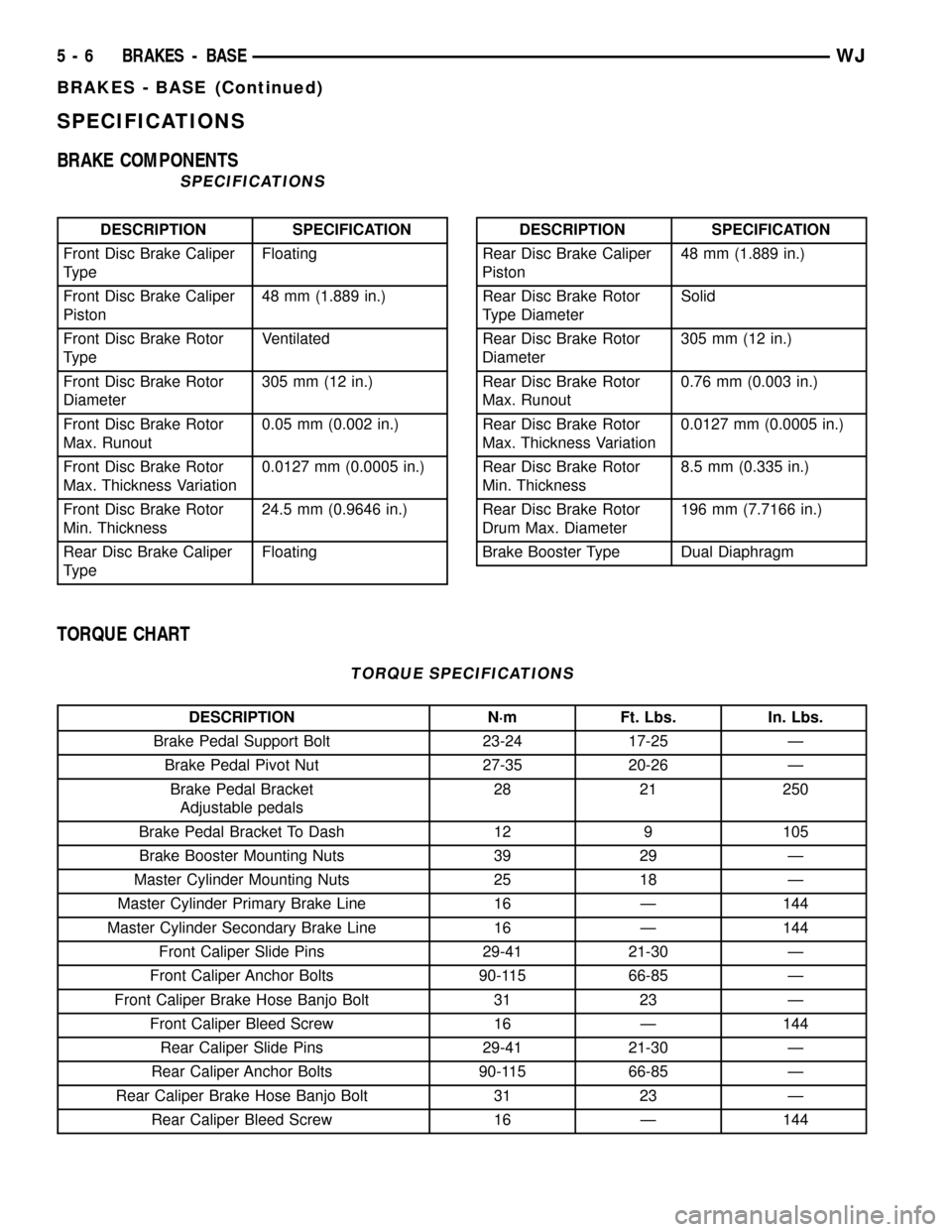
SPECIFICATIONS
BRAKE COMPONENTS
SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Front Disc Brake Caliper
TypeFloating
Front Disc Brake Caliper
Piston48 mm (1.889 in.)
Front Disc Brake Rotor
TypeVentilated
Front Disc Brake Rotor
Diameter305 mm (12 in.)
Front Disc Brake Rotor
Max. Runout0.05 mm (0.002 in.)
Front Disc Brake Rotor
Max. Thickness Variation0.0127 mm (0.0005 in.)
Front Disc Brake Rotor
Min. Thickness24.5 mm (0.9646 in.)
Rear Disc Brake Caliper
TypeFloatingDESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Rear Disc Brake Caliper
Piston48 mm (1.889 in.)
Rear Disc Brake Rotor
Type DiameterSolid
Rear Disc Brake Rotor
Diameter305 mm (12 in.)
Rear Disc Brake Rotor
Max. Runout0.76 mm (0.003 in.)
Rear Disc Brake Rotor
Max. Thickness Variation0.0127 mm (0.0005 in.)
Rear Disc Brake Rotor
Min. Thickness8.5 mm (0.335 in.)
Rear Disc Brake Rotor
Drum Max. Diameter196 mm (7.7166 in.)
Brake Booster Type Dual Diaphragm
TORQUE CHART
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Brake Pedal Support Bolt 23-24 17-25 Ð
Brake Pedal Pivot Nut 27-35 20-26 Ð
Brake Pedal Bracket
Adjustable pedals28 21 250
Brake Pedal Bracket To Dash 12 9 105
Brake Booster Mounting Nuts 39 29 Ð
Master Cylinder Mounting Nuts 25 18 Ð
Master Cylinder Primary Brake Line 16 Ð 144
Master Cylinder Secondary Brake Line 16 Ð 144
Front Caliper Slide Pins 29-41 21-30 Ð
Front Caliper Anchor Bolts 90-115 66-85 Ð
Front Caliper Brake Hose Banjo Bolt 31 23 Ð
Front Caliper Bleed Screw 16 Ð 144
Rear Caliper Slide Pins 29-41 21-30 Ð
Rear Caliper Anchor Bolts 90-115 66-85 Ð
Rear Caliper Brake Hose Banjo Bolt 31 23 Ð
Rear Caliper Bleed Screw 16 Ð 144
5 - 6 BRAKES - BASEWJ
BRAKES - BASE (Continued)
Page 200 of 2199

STANDARD PROCEDURE - MASTER CYLINDER
BLEEDING PROCEDURE
A new master cylinder should be bled before instal-
lation on the vehicle. Required bleeding tools include
bleed tubes and a wood dowel to stroke the pistons.
Bleed tubes can be fabricated from brake line.
(1) Mount master cylinder in vise with brass jaws.
(2) Attach bleed tubes to cylinder outlet ports.
Then position each tube end into the bottom of the
reservoir (Fig. 50).
(3) Fill reservoir with fresh brake fluid.
(4) Press cylinder pistons inward with wood dowel.
Then release pistons and allow them to return under
spring pressure. Continue bleeding operations until
air bubbles are no longer visible in fluid.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the wire connector from the brake fluid
level sensor.
(2) Remove brake lines from master cylinder.
(3) Remove nuts that attach master cylinder to
booster studs (Fig. 51).
(4) Remove master cylinder from booster.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: Bleed new master cylinder on bench before
installation, refer to Service Procedures.
(1) Have an assistant depress the brake pedal
while guiding the master cylinder on the booster rod
and mounting studs.
CAUTION: Do not depress brake pedal too hard and
ensure the booster rod is in the master cylinder pis-
ton or booster/master cylinder damage will occur.(2) Install master cylinder mounting nuts and
tighten nuts to 25 N´m (18 lb. lbs.).
NOTE: Use original or factory replacement nuts only.
(3) Install brake lines and tighten to 16 N´m (144
in. lbs.).
(4) Install fluid level sensor connector.
(5) Fill and bleed brake system.
PEDAL
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - STANDARD PEDAL
A suspended-type brake pedal is used, the pedal
pivots on a shaft mounted in the pedal support
bracket. The bracket is attached to the dash panel.
The brake pedal assembly and pedal pad are the
only serviceable component.
DESCRIPTION - ADJUSTABLE PEDALS
The Adjustable Pedals System (APS) is designed to
enable the fore and aft repositioning of the brake and
accelerator pedals. This results in improved ergonom-
ics in relation to the steering wheel for taller and
shorter drivers. Being able to adjust the pedal posi-
Fig. 50 Master Cylinder Bleeding
1 - BLEEDING TUBES
2 - RESERVOIR
Fig. 51 Master Cylinder Mounting
1 - MOUNTING NUT
2 - SENSOR CONNECTOR
3 - MOUNTING NUT
4 - BRAKE LINES
WJBRAKES - BASE 5 - 25
MASTER CYLINDER (Continued)
Page 206 of 2199

REMOVAL
(1) Remove the master cylinder.
(2) Disconnect vacuum hose at booster check valve.
(3) Remove retainer clip (Fig. 60) that holds
booster push rod on pedal pin. Then slide push rod
off pin.
(4) Remove four nuts (Fig. 61) that attach booster
to dash panel.
(5) In engine compartment, slide booster forward,
tilt it upward slightly, and remove it from engine
compartment.
INSTALLATION
(1) Check condition of grommet that secures check
valve in booster. Replace grommet if cut, torn, or
loose.
(2) Install new booster dash seal.
(3) Align and position booster on engine compart-
ment side of dash panel.
(4) Inside passenger compartment:
(a) Lubricate pedal pin Mopar multi-mileage
grease.
(b) Install booster attaching nuts on studs.
Tighten attaching nuts to 39 N´m (29 ft. lbs.).
(c) Slide booster push rod on pedal pin. Then
secure rod to pin with retainer clip.
(5) In engine compartment, attach vacuum hose to
booster check valve.(6) Install the master cylinder with new gasket
and nuts.
CAUTION: The master cylinder installation proce-
dure must be perform as written or damage to the
booster/master cylinder may occur.
(7) Fill and bleed brake system.
ROTORS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FRONT DISC
BRAKE ROTOR
ROTOR MINIMUM THICKNESS
Rotor minimum usable thickness is 24.5 mm (0.964
in.). Do not resurface a rotor if machining would
cause thickness to fall below this limit.
Measure rotor thickness at the center of the brake
shoe contact surface. Replace the rotor if worn below
minimum thickness, or if refinishing would reduce
thickness below the allowable minimum.
FRONT ROTOR THICKNESS VARIATION
Variations in rotor thickness will cause pedal pul-
sation, noise and shudder.
Fig. 60 Retainer Clip
1 - RETAINER CLIP
2 - PUSH ROD
3 - PEDAL PIN
Fig. 61 Power Brake Booster Mounting
1 - BOOSTER
2 - DASH PANEL
WJBRAKES - BASE 5 - 31
POWER BRAKE BOOSTER (Continued)
Page 209 of 2199

INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - FRONT DISC BRAKE ROTOR
NOTE: If a new rotor is installed it must be match
mounted to the hub/bearing.
(1) Install rotor on hub studs in its original loca-
tion.
(2) Install the caliper anchor assembly on the
knuckle. Install anchor bolts and tighten to 90-115
N´m (66-85 ft. lbs.).
(3) Install wheel and tire assembly.
(4) Remove support and lower the vehicle.
(5) Pump brake pedal to seat caliper pistons and
brake shoes. Do not move vehicle until firm brake
pedal is obtained.
INSTALLATION - REAR DISC BRAKE ROTOR
(1) Install rotor on axle studs.
(2) Install the caliper anchor assembly.
(3) Install anchor bolts and tighten to 90-115 N´m
(66-85 ft. lbs.).
(4) Install wheel and tire assembly.
(5) Remove support and lower the vehicle.
(6) Pump brake pedal until caliper pistons and
brake shoes are seated.
PARKING BRAKE
OPERATION
The parking brakes operated by a automatic ten-
sioner mechanism built into the hand lever and cable
system. The front cable is connected to the hand
lever and the equalizer. The rear cables attached to
the equalizer and the parking brake shoe actuator.
A set of drum type brake shoes are used for park-
ing brakes. The shoes are mounted to the rear disc
brake adaptor. The parking brake drum is integrated
into the rear disc brake rotor.
Parking brake cable adjustment is controlled by an
automatic tensioner mechanism. The only adjust-
ment if necessary is to the park brake shoes if the
linings are worn.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PARKING BRAKE
NOTE: Parking brake adjustment is controlled by an
automatic cable tensioner and does not require
adjustment. The only adjustment that may be nec-
essary would be to the park brake shoes if they are
worn.
The parking brake switch is in circuit with the red
warning lamp in the dash. The switch will cause the
lamp to illuminate only when the parking brakes are
applied. If the lamp remains on after parking brake
release, the switch or wires are faulty.
If the red lamp comes on a fault has occurred in
the front or rear brake hydraulic system.
If the red warning lamp and yellow warning lamp
come on, the electronic brake distribution may be at
fault.
In most cases, the actual cause of an improperly
functioning parking brake (too loose/too tight/won't
hold), can be traced to a parking brake component.
NOTE: The leading cause of improper parking brake
operation, is excessive clearance between the park-
ing brake shoes and the shoe braking surface.
Excessive clearance is a result of lining and/or
drum wear, drum surface machined oversize.
Excessive parking brake lever travel (sometimes
described as a loose lever or too loose condition), is
the result of worn brake shoes, improper brake shoe
adjustment, or improperly assembled brake parts.
A too loose condition can also be caused by inoper-
ative or improperly assembled parking brake shoe
parts.
A condition where the parking brakes do not hold,
will most probably be due to a wheel brake compo-
nent.
Items to look for when diagnosing a parking brake
problem, are:
²Brake shoe wear
²Drum surface (in rear rotor) machined oversize
²Front cable not secured to lever
²Rear cable not attached to actuator
²Rear cable seized
²Parking brake lever not seated
²Parking brake lever bind
5 - 34 BRAKES - BASEWJ
ROTORS (Continued)
Page 281 of 2199

AUDIO
DESCRIPTION
An audio system is standard factory-installed
equipment on this model. The standard equipment
audio system includes an AM/FM/cassette (RBB sales
code) radio receiver, and speakers in six locations.
Several combinations of radio receivers and speaker
systems are offered as optional equipment on this
model. The audio system uses an ignition switched
control of battery current so that the system will only
operate when the ignition switch is in the On or
Accessory positions.
A Compact Disc (CD) changer with a ten disc mag-
azine, remote radio switches with six functions
mounted to the backs of the steering wheel spokes,
and a memory system that automatically stores and
recalls up to twenty radio station presets (ten AM
and ten FM) and the last station listened to for two
drivers are optional factory-installed equipment on
this model. Refer to Electrical, Power Seats for more
information on the memory system.
The audio system includes the following compo-
nents:
²Antenna
²Compact disc changer (available with RBP sales
code radio receivers only)
²Power amplifier (with premium speaker system
only)
²Radio noise suppression components
²Radio receiver
²Remote radio switches
²Speakers
Certain functions and features of the audio system
rely upon resources shared with other electronic
modules in the vehicle over the Programmable Com-
munications Interface (PCI) data bus network. The
PCI data bus network allows the sharing of sensor
information. This helps to reduce wire harness com-
plexity, internal controller hardware, and component
sensor current loads. At the same time, this system
provides increased reliability, enhanced diagnostics,
and allows the addition of many new feature capabil-
ities. For diagnosis of these electronic modules or of
the PCI data bus network, the use of a DRB scan
tool and the proper Diagnostic Procedures manual
are recommended.
The other electronic modules that may affect audio
system operation are as follows:
²Body Control Module (BCM)- (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL MOD-
ULES/BODY CONTROL/CENTRAL TIMER MODUL
- DESCRIPTION) for more information.
²Driver Door Module (DDM)(Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL MOD-ULES/DRIVER DOOR MODULE - DESCRIPTION)
for more information.
²Passenger Door Module (PDM)(Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL MOD-
ULES/DRIVER DOOR MODULE - DESCRIPTION)
for more information.
The audio system includes the following major
components, which are described in further detail
elsewhere in this service information:
²Amplifier- On models equipped with the
optional premium speaker system, an audio power
amplifier is located on the rear floor panel under-
neath the right end of the rear seat cushion in the
passenger compartment.
²Antenna Body and Cable- The most visible
component of the antenna body and cable are the
antenna adapter and the antenna cap nut, which are
located on the top of the right front fender panel of
the vehicle, near the right end of the cowl plenum.
²Antenna Mast- The antenna mast is a metal
rod that extends upward from the antenna body and
cable on the top of the right front fender panel of the
vehicle, near the right end of the cowl plenum.
²Radio- The radio for this model is located in
the instrument panel center stack area, inboard of
the instrument cluster and above the heater and air
conditioner controls.
²Radio Noise Suppression Ground Strap-A
radio noise suppression ground strap is installed
between the rear of the engine cylinder head(s) and
the dash panel sheet metal in the engine compart-
ment.
²Speaker- The standard speaker system
includes six speakers in six locations, while the pre-
mium speaker system includes an amplifier for the
six speakers in six locations.
Hard wired circuitry connects the audio system
components to each other through the electrical sys-
tem of the vehicle. These hard wired circuits are
integral to several wire harnesses, which are routed
throughout the vehicle and retained by many differ-
ent methods. These circuits may be connected to each
other, to the vehicle electrical system and to the
audio system components through the use of a com-
bination of soldered splices, splice block connectors
and many different types of wire harness terminal
connectors and insulators. Refer to the appropriate
wiring information in this service manual for com-
plete standard and premium audio system circuit
diagrams. The wiring information includes proper
wire and connector repair procedures, further details
on wire harness routing and retention, as well as
pin-out and location views for the various wire har-
ness connectors, splices, and grounds.
8A - 2 AUDIOWJ
Page 314 of 2199

inputs to or receive outputs from the BCM must also
be checked. The most reliable, efficient, and accurate
means to diagnose the BCM, the PCI data bus net-
work, and the electronic modules that provide inputs
to or receive outputs from the BCM requires the use
of a DRBIIItscan tool and the appropriate diagnostic
information. The DRBIIItscan tool can provide con-
firmation that the PCI data bus network is func-
tional, that all of the modules are sending and
receiving the proper messages over the PCI data bus,
and that the BCM is receiving the proper hard wired
inputs and responding with the proper hard wired
outputs needed to perform its many functions.
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
REMOVAL
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the instrument panel fuse cover.(Refer
to 8 - ELECTRICAL/POWER DISTRIBUTION/FUSE
COVER - REMOVAL).
(3) Access and disconnect the instrument panel
wire harness connectors from the BCM (Fig. 3).
(4) Remove the mounting screws (Torx T-20) that
secure the BCM to the JB.(5) Pull the BCM straight out towards the dash
panel far enough to disconnect the integral BCM to
JB connector.
(6) Remove the BCM.INSTALLATION
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
(1) Position the Body Control Module (BCM) to its
mounting location (Fig. 3).
(2) Align the terminal pins of the BCM connector
with the connector on the JB.
(3) Engage the BCM integral connector into the
JB.
(4) Install the four screws. Tighten the screws to
2.2 N´m (20 in. lbs.).
Fig. 3 Body Control Module Remove/Install
1 - JUNCTION BLOCK
2 - SCREWS (4)
3 - BODY CONTROL MODULE
4 - FUSE COVER LOCATOR CHANNELS
5 - FUSE COVER MOUNTING SLOTS
6 - INSTRUMENT PANEL WIRE HARNESS CONNECTORS
WJELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES 8E - 5
BODY CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 351 of 2199

(4) Loosen the battery positive cable terminal
clamp pinch-bolt hex nut.
(5) Disconnect the battery positive cable terminal
clamp from the battery positive terminal post. If nec-
essary, use a battery terminal puller to remove the
terminal clamp from the battery post.
(6) Unlatch and open the cover on the Power Dis-
tribution Center (PDC).
(7) Remove the two nuts that secure the battery
positive cable and generator output cable eyelet ter-
minal to the B(+) terminal studs in the PDC.
(8) Remove the battery positive cable and genera-
tor output cable eyelet terminal from the B(+) termi-
nal studs in the PDC.
(9) Disconnect the battery wire harness connector
from the right headlamp and dash wire harness con-
nector located near the front of the battery.
(10) Remove the screw that secures the battery
negative cable eyelet terminal to the inner fender
shield near the front of the battery.
(11) On models with the 4.7L engine, remove the
nut that secures the battery harness clip to the stud
on the right side of the intake manifold and remove
the clip from the stud.
(12) Unlatch and remove the cover from the gener-
ator output terminal stud housing on the back of the
generator.
(13) Remove the nut that secures the generator
output cable eyelet terminal to the generator output
terminal stud.
(14) Remove the generator output cable eyelet ter-
minal from the generator output terminal stud.
(15) Disconnect the battery wire harness connector
from the generator field terminal connector recepta-
cle on the back of the generator.(16) Remove the screw that secures the battery
negative cable ground eyelet terminal to the right
side of the engine block.
(17) Remove the nut that secures the battery pos-
itive cable eyelet terminal to the B(+) terminal stud
on the starter solenoid.
(18) Remove the battery positive cable eyelet ter-
minal from the B(+) terminal stud on the starter
solenoid.
(19) Disconnect the battery wire harness connector
from the connector receptacle on the starter solenoid.
(20) Remove the battery wire harness from the
engine compartment.
INSTALLATION
Both the battery negative cable and the battery
positive cable are serviced in the battery wire har-
ness. If either battery cable is damaged or faulty, the
battery wire harness unit must be replaced.
(1) Clean and inspect the battery cable terminal
clamps and the battery terminal posts.
(2) Position the battery wire harness into the
engine compartment (Fig. 23) or (Fig. 24).
(3) Reconnect the battery wire harness connector
to the connector receptacle on the starter solenoid.
(4) Install the battery positive cable eyelet termi-
nal onto the B(+) terminal stud on the starter sole-
noid.Fig. 22 TEST GROUND CIRCUIT RESISTANCE -
TYPICAL
1 - VOLTMETER
2 - BATTERY
3 - ENGINE GROUND
Fig. 23 Battery Cables - 4.0L Engine
1 - BATTERY POSITIVE CABLE
2 - BATTERY NEGATIVE CABLE
3 - CLIPS
8F - 20 BATTERY SYSTEMWJ
BATTERY CABLE (Continued)
Page 352 of 2199

(5) Install and tighten the nut that secures the
battery positive cable eyelet terminal to the B(+) ter-
minal stud on the starter solenoid. Tighten the nut to
11.3 N´m (100 in. lbs.).
(6) Install and tighten the screw that secures the
battery negative cable ground eyelet terminal to the
right side of the engine block. Tighten the screw to
10.2 N´m (90 in. lbs.) for 4.0L engines, or 13.0 N´m
(115 in. lbs.) for 4.7L engines.
(7) Reconnect the battery wire harness connector
to the generator field terminal connector receptacle
on the back of the generator.
(8) Install the generator output cable eyelet termi-
nal onto the generator output terminal stud.
(9) Install and tighten the nut that secures the
generator output cable eyelet terminal to the genera-
tor output terminal stud. Tighten the nut to 10.7
N´m (95 in. lbs.).
(10) Position the cover for the generator output
terminal stud housing onto the back of the generator
and snap it into place.
(11) On models with the 4.7L engine, install the
battery harness clip onto the stud on the right side of
the intake manifold, then install and tighten the nut
that secures the clip to the stud. Tighten the nut to
11.3 N´m (100 in. lbs.).
(12) Install and tighten the screw that secures the
battery negative cable eyelet terminal to the inner
fender shield near the front of the battery. Tighten
the screw to 28.2 N´m (250 in. lbs.).(13) Reconnect the battery wire harness connector
to the right headlamp and dash wire harness connec-
tor located near the front of the battery.
(14) Install the battery positive cable and genera-
tor output cable eyelet terminal onto the PDC B(+)
terminal studs.
(15) Install and tighten the two nuts that secure
the battery positive cable and generator output cable
eyelet terminal to the PDC B(+) terminal studs.
Tighten the nuts to 11.3 N´m (100 in. lbs.).
(16) Close and latch the PDC cover.
(17) Reconnect the battery positive cable terminal
clamp to the battery positive terminal post. Tighten
the terminal clamp pinch-bolt hex nut to 6.8 N´m (60
in. lbs.).
(18) Reconnect the battery negative cable terminal
clamp to the battery negative terminal post. Tighten
the terminal clamp pinch-bolt hex nut to 6.8 N´m (60
in. lbs.).
(19) Apply a thin coating of petroleum jelly or
chassis grease to the exposed surfaces of the battery
cable terminal clamps and the battery terminal
posts.BATTERY TRAY
DESCRIPTION
The battery is mounted in a molded plastic battery
tray and support unit (Fig. 25) located in the right
front corner of the engine compartment. The battery
tray and support unit is secured at the rear with a
nut to a stud on the front wheelhouse inner panel, at
the outboard side with a screw to the side cowl rein-
forcement panel, and at the front with a screw
through a U-nut on a bracket of the radiator support.
The battery tray and support unit also includes
three upright stanchions that are molded into the
outboard side of the unit. These stanchions support
the Power Distribution Center (PDC). Refer to
Power Distribution Centerin the Power Distribu-
tion section of this service manual for more informa-
tion on the PDC.
A hole in the bottom of the battery tray is fitted
with a battery temperature sensor. Refer toBattery
Temperature Sensorin the Charging section of
this service manual for more information on the bat-
tery temperature sensor. Refer toBattery Hold
Downin this section of the service manual for more
information on the battery hold down hardware.
Fig. 24 Battery Cables - 4.7L Engine
1 - BATTERY POSITIVE CABLE
2 - BATTERY NEGATIVE CABLE
3 - CLIPS
WJBATTERY SYSTEM 8F - 21
BATTERY CABLE (Continued)
Page 392 of 2199

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
HORN SOUNDS
CONTINUOUSLY1. Faulty horn relay. 1. Refer to Horn Relay for the proper horn relay
diagnosis and testing procedures. Replace the
horn relay or repair the shorted horn relay control
circuit, if required.
2. Faulty horn switch. 2. Refer to Horn Switch for the proper horn switch
diagnosis and testing procedures. Replace the
horn switch or repair the shorted horn switch
circuit, if required.
HORN
DESCRIPTION
The dual electromagnetic diaphragm-type horns
are standard equipment on this model. Both horns
are secured to a mounting bracket. The mounting
bracket is secured with a screw to the back side of
the right extension of the radiator closure assembly,
just ahead of the right front wheel house and below
the front wheel house extension. The two horns are
connected in parallel. Each horn is grounded through
its wire harness connector and circuit to an eyelet
secured to the right inner fender shield near the bat-
tery, and receives battery feed through the closed
contacts of the horn relay.
The horns cannot be repaired or adjusted and, if
faulty or damaged, they must be individually
replaced.
OPERATION
Within the two halves of the molded plastic horn
housing are a flexible diaphragm, a plunger, an elec-
tromagnetic coil and a set of contact points. The dia-
phragm is secured in suspension around its
perimeter by the mating surfaces of the horn hous-
ing. The plunger is secured to the center of the dia-
phragm and extends into the center of the
electromagnet. The contact points control the current
flow through the electromagnet.
When the horn is energized, electrical current
flows through the closed contact points to the electro-
magnet. The resulting electromagnetic field draws
the plunger and diaphragm toward it until that
movement mechanically opens the contact points.
When the contact points open, the electromagnetic
field collapses allowing the plunger and diaphragm to
return to their relaxed positions and closing the con-
tact points again. This cycle continues repeating at a
very rapid rate producing the vibration and move-
ment of air that creates the sound that is directed
through the horn outlet.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HORN
Refer to the appropriate wiring information. The
wiring information includes wiring diagrams, proper
wire and connector repair procedures, details of wire
harness routing and retention, connector pin-out
information and location views for the various wire
harness connectors, splices and grounds.
(1) Disconnect the wire harness connector(s) from
the horn connector receptacle(s). Measure the resis-
tance between the ground circuit cavity of the horn(s)
wire harness connector(s) and a good ground. There
should be no measurable resistance. If OK, go to Step
2. If not OK, repair the open ground circuit to ground
as required.
(2) Check for battery voltage at the horn relay out-
put circuit cavity of the horn(s) wire harness connec-
tor(s). There should be zero volts. If OK, go to Step 3.
If not OK, repair the shorted horn relay output cir-
cuit or replace the faulty horn relay as required.
(3) Depress the horn switch. There should now be
battery voltage at the horn relay output circuit cavity
of the horn(s) wire harness connector(s). If OK,
replace the faulty horns. If not OK, repair the open
horn relay output circuit to the horn relay as
required.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Raise and support the vehicle.
(3) Remove the lower front half of the inner liner
from the right front fender wheel house. (Refer to 23
- BODY/EXTERIOR/FRONT FENDER - REMOVAL).
(4) Reach through the front of the right front
fender wheel house opening to access and disconnect
the two right headlamp and dash wire harness con-
nectors from the horn connector receptacles (Fig. 1).
Be certain to disengage the connector lock tabs
before disconnecting them from the horn connector
receptacles.
(5) Remove the screw that secures the horn
mounting bracket to the right extension of the radi-
ator closure assembly.
WJHORN 8H - 3
HORN SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 393 of 2199

(6) Remove both horns and the mounting bracket
from the right extension of the radiator closure
assembly as a unit.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position both horns and the mounting bracket
onto the right extension of the radiator closure
assembly as a unit.
(2) Install and tighten the screw that secures the
horn mounting bracket to the right extension of the
radiator closure assembly. Tighten the screw to 11.3
N´m (100 in. lbs.).
(3) Reconnect the two right headlamp and dash
wire harness connectors to the horn connector recep-
tacles. Be certain to engage the connector lock tabs
after reconnecting them to the horn connector recep-
tacles.
(4) Install the lower front half of the inner liner to
the right front fender wheel house. (Refer to 23 -
BODY/EXTERIOR/FRONT FENDER - INSTALLA-
TION) for the procedure.
(5) Lower the vehicle.
(6) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
HORN RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The horn relay is a electromechanical device that
switches battery current to the horn when the horn
switch grounds the relay coil. The horn relay is
located in the Power Distribution Center (PDC) inthe engine compartment. If a problem is encountered
with a continuously sounding horn, it can usually be
quickly resolved by removing the horn relay from the
PDC until further diagnosis is completed. See the
fuse and relay layout label affixed to the inside sur-
face of the PDC cover for horn relay identification
and location.
The horn relay is a International Standards Orga-
nization (ISO) micro-relay. Relays conforming to the
ISO specifications have common physical dimensions,
current capacities, terminal patterns, and terminal
functions. The ISO micro-relay terminal functions
are the same as a conventional ISO relay. However,
the ISO micro-relay terminal pattern (or footprint) is
different, the current capacity is lower, and the phys-
ical dimensions are smaller than those of the conven-
tional ISO relay.
The horn relay cannot be repaired or adjusted and,
if faulty or damaged, it must be replaced.
OPERATION
The ISO relay consists of an electromagnetic coil, a
resistor or diode, and three (two fixed and one mov-
able) electrical contacts. The movable (common feed)
relay contact is held against one of the fixed contacts
(normally closed) by spring pressure. When the elec-
tromagnetic coil is energized, it draws the movable
contact away from the normally closed fixed contact,
and holds it against the other (normally open) fixed
contact.
When the electromagnetic coil is de-energized,
spring pressure returns the movable contact to the
normally closed position. The resistor or diode is con-
nected in parallel with the electromagnetic coil in the
relay, and helps to dissipate voltage spikes that are
produced when the coil is de-energized.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HORN RELAY
The horn relay (Fig. 2) is located in the Power Dis-
tribution Center (PDC) between the battery and the
right inner fender shield on the passenger side of the
engine compartment. If a problem is encountered
with a continuously sounding horn, it can usually be
quickly resolved by removing the horn relay from the
PDC until further diagnosis is completed. See the
fuse and relay layout label affixed to the inside sur-
face of the PDC cover for horn relay identification
and location. For complete circuit diagrams, refer to
the appropriate wiring information. The wiring infor-
mation includes wiring diagrams, proper wire and
connector repair procedures, details of wire harness
routing and retention, connector pin-out information
and location views for the various wire harness con-
nectors, splices and grounds.
Fig. 1 Horns Remove/Install
1 - RADIATOR CLOSURE ASSEMBLY
2 - HORNS AND MOUNTING BRACKET
3 - RIGHT HEADLAMP AND DASH WIRE HARNESS
CONNECTORS
8H - 4 HORNWJ
HORN (Continued)