Engine JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 353 of 2199

OPERATION
The battery tray provides a secure mounting loca-
tion and supports the battery. On some vehicles, the
battery tray also provides the anchor point/s for the
battery holddown hardware. The battery tray and
the battery holddown hardware combine to secure
and stabilize the battery in the engine compartment,
which prevents battery movement during vehicle
operation. Unrestrained battery movement during
vehicle operation could result in damage to the vehi-
cle, the battery, or both.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the battery from the battery tray
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/BAT-
TERY - REMOVAL).
(2) Remove the Power Distribution Center (PDC)
from the stanchions on the outboard side of the bat-
tery tray and support unit. Refer toPower Distri-
bution Centerin the Power Distribution section of
this service manual for PDC removal procedure.
(3) Remove the one screw that secures the front of
the battery tray and support unit to the bracket on
the right side of the radiator support (Fig. 26).
(4) Remove the one screw that secures the out-
board side of the battery tray and support unit to the
right fender side cowl reinforcement.
(5) Remove the one nut that secures the rear of
the battery tray and support unit to the stud on the
right fender front wheelhouse inner panel.
(6) Remove the battery temperature sensor from
the battery tray. Refer toBattery Temperature
Sensorin the Charging section of this service man-
ual for battery temperature sensor removal proce-
dure.
(7) Remove the battery tray and support unit from
the right front corner of the engine compartment.
Fig. 25 Battery Tray and Support
1 - SCREW
2 - HOLD DOWN BRACKET
3 - BATTERY SUPPORT
4 - ACCUMULATOR
5 - NUT
6 - U-NUT
7 - STUD
8 - RADIATOR SUPPORT BRACKET
9 - U-NUT
10 - SCREW
11 - BATTERY TEMPERATURE SENSOR
12 - BATTERYFig. 26 Battery Tray and Support Remove/Install
1 - BATTERY TRAY AND SUPPORT
2 - NUT (1)
3 - STUD
4 - U-NUT (1)
5 - RADIATOR SUPPORT BRACKET
6 - SCREW (1)
7 - SCREW (1)
8F - 22 BATTERY SYSTEMWJ
BATTERY TRAY (Continued)
Page 354 of 2199

INSTALLATION
(1) Clean and inspect the battery tray and support
unit. Refer to the procedures in this section of the
service manual.
(2) Install the battery temperature sensor onto the
battery tray. Refer toBattery Temperature Sensor
in the Charging section of this service manual for
battery temperature sensor installation procedure.
(3) Position the battery tray and support unit into
the right front corner of the engine compartment. Be
certain that no hoses or wire harnesses are trapped
or pinched by the installation of the tray.
(4) Install and tighten the one nut that secures the
rear of the battery tray and support unit to the stud
on the right fender front wheelhouse inner panel.
Tighten the nut to 7.3 N´m (65 in. lbs.).(5) Install and tighten the one screw that secures
the outboard side of the battery tray and support
unit to the right fender side cowl reinforcement.
Tighten the screw to 8.1 N´m (72 in. lbs.).
(6) Install and tighten the one screw that secures
the front of the battery tray and support unit to the
bracket on the right side of the radiator support.
Tighten the screw to 8.1 N´m (72 in. lbs.).
(7) Install the Power Distribution Center (PDC)
onto the stanchions on the outboard side of the bat-
tery tray and support unit. Refer toPower Distri-
bution Centerin the Power Distribution section of
this service manual for PDC installation procedure.
(8) Install the battery onto the battery tray (Refer
to 8 - ELECTRICAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/BATTERY -
INSTALLATION).
WJBATTERY SYSTEM 8F - 23
BATTERY TRAY (Continued)
Page 355 of 2199

CHARGING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
CHARGING
DESCRIPTION.........................24
OPERATION...........................24
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CHARGING
SYSTEM............................24
SPECIFICATIONS
GENERATOR RATINGS - GAS POWERED . . 25
TORQUE - GAS POWERED.............25
SPECIAL TOOLS.......................26
BATTERY TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................26OPERATION...........................26
REMOVAL.............................26
INSTALLATION.........................26
GENERATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................27
OPERATION...........................27
REMOVAL.............................27
INSTALLATION.........................28
VOLTAGE REGULATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................28
OPERATION...........................28
CHARGING
DESCRIPTION
The charging system consists of:
²Generator
²Electronic Voltage Regulator (EVR) circuitry
within the Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
²Ignition switch
²Battery (refer to 8, Battery for information)
²Battery temperature sensor
²Generator Lamp (if equipped)
²Check Gauges Lamp (if equipped)
²Voltmeter (refer to 8, Instrument Cluster for
information)
²Wiring harness and connections (refer to 8, Wir-
ing for information)
OPERATION
The charging system is turned on and off with the
ignition switch. The system is on when the engine is
running and the ASD relay is energized. When the
ASD relay is on, voltage is supplied to the ASD relay
sense circuit at the PCM. This voltage is connected
through the PCM and supplied to one of the genera-
tor field terminals (Gen. Source +) at the back of the
generator.
The amount of DC current produced by the gener-
ator is controlled by the EVR (field control) circuitry
contained within the PCM. This circuitry is con-
nected in series with the second rotor field terminal
and ground.
A battery temperature sensor, located in the bat-
tery tray housing, is used to sense battery tempera-
ture. This temperature data, along with data from
monitored line voltage, is used by the PCM to vary
the battery charging rate. This is done by cycling theground path to control the strength of the rotor mag-
netic field. The PCM then compensates and regulates
generator current output accordingly.
All vehicles are equipped with On-Board Diagnos-
tics (OBD). All OBD-sensed systems, including EVR
(field control) circuitry, are monitored by the PCM.
Each monitored circuit is assigned a Diagnostic Trou-
ble Code (DTC). The PCM will store a DTC in elec-
tronic memory for certain failures it detects. Refer to
Diagnostic Trouble Codes in; Powertrain Control
Module; Electronic Control Modules for more DTC
information.
The Check Gauges Lamp (if equipped) monitors:
charging system voltage,engine coolant tempera-
ture and engine oil pressure. If an extreme condition
is indicated, the lamp will be illuminated. This is
done as reminder to check the three gauges. The sig-
nal to activate the lamp is sent via the CCD bus cir-
cuits. The lamp is located on the instrument panel.
Refer to 8, Instrument Cluster for additional infor-
mation.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CHARGING
SYSTEM
The following procedures may be used to diagnose
the charging system if:
²the check gauges lamp (if equipped) is illumi-
nated with the engine running
²the voltmeter (if equipped) does not register
properly
²an undercharged or overcharged battery condi-
tion occurs.
Remember that an undercharged battery is often
caused by:
²accessories being left on with the engine not
running
8F - 24 CHARGINGWJ
Page 356 of 2199

²a faulty or improperly adjusted switch that
allows a lamp to stay on. Refer to Ignition-Off Draw
Test in 8, Battery for more information.
INSPECTION
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) monitors
critical input and output circuits of the charging sys-
tem, making sure they are operational. A Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC) is assigned to each input and
output circuit monitored by the On-Board Diagnostic
(OBD) system. Some charging system circuits are
checked continuously, and some are checked only
under certain conditions.
Refer to Diagnostic Trouble Codes in; Powertrain
Control Module; Electronic Control Modules for more
DTC information. This will include a complete list of
DTC's including DTC's for the charging system.
To perform a complete test of the charging system,
refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic Proce-
dures service manual and the DRBtscan tool. Per-
form the following inspections before attaching the
scan tool.(1) Inspect the battery condition. Refer to 8, Bat-
tery for procedures.
(2) Inspect condition of battery cable terminals,
battery posts, connections at engine block, starter
solenoid and relay. They should be clean and tight.
Repair as required.
(3) Inspect all fuses in both the fuseblock and
Power Distribution Center (PDC) for tightness in
receptacles. They should be properly installed and
tight. Repair or replace as required.
(4) Inspect generator mounting bolts for tightness.
Replace or tighten bolts if required. Refer to the Gen-
erator Removal/Installation section of this group for
torque specifications.
(5) Inspect generator drive belt condition and ten-
sion. Tighten or replace belt as required. Refer to
Belt Tension Specifications in 7, Cooling System.
(6) Inspect automatic belt tensioner (if equipped).
Refer to 7, Cooling System for information.
(7) Inspect generator electrical connections at gen-
erator field, battery output, and ground terminal (if
equipped). Also check generator ground wire connec-
tion at engine (if equipped). They should all be clean
and tight. Repair as required.
SPECIFICATIONS
GENERATOR RATINGS - GAS POWERED
TYPE PART NUMBER RATED SAE AMPS ENGINES MINIMUM TEST AMPS
BOSCH 56041322 136 4.0L 6-Cylinder 100
DENSO 56041324 136 4.7L V-8 100
TORQUE - GAS POWERED
DESCRIPTION N-m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Generator Mounting Bolts-4.0L 55 41
Generator Vertical Mounting Bolt-4.7L 40 29
Generator (long) Horizontal Mounting
Bolt-4.7L55 41
Generator (short) Horizontal Mounting
Bolt-4.7L55 41
Generator B+ Terminal Nut 11 95
WJCHARGING 8F - 25
CHARGING (Continued)
Page 357 of 2199

SPECIAL TOOLS
BATTERY TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The Battery Temperature Sensor (BTS) is attached
to the battery tray located under the battery.
OPERATION
The BTS is used to determine the battery temper-
ature and control battery charging rate. This temper-
ature data, along with data from monitored line
voltage, is used by the PCM to vary the battery
charging rate. System voltage will be higher at colder
temperatures and is gradually reduced at warmer
temperatures.
The PCM sends 5 volts to the sensor and is
grounded through the sensor return line. As temper-
ature increases, resistance in the sensor decreases
and the detection voltage at the PCM increases.The BTS is also used for OBD II diagnostics. Cer-
tain faults and OBD II monitors are either enabled
or disabled, depending upon BTS input (for example,
disable purge and enable Leak Detection Pump
(LDP) and O2 sensor heater tests). Most OBD II
monitors are disabled below 20 degrees F.
REMOVAL
The battery temperature sensor is located under
the vehicle battery (Fig. 1) and is attached to a
mounting hole on the battery tray.
The battery temperature sensor is located under
the vehicle battery (Fig. 1) and is attached to a
mounting hole on the battery tray.
(1) Remove battery. Refer to Group 8A, Battery for
procedures.
(2) Remove battery tray.
(3) Pull sensor up from battery tray and discon-
nect engine wire harness.
(4) Remove sensor from battery tray.
INSTALLATION
The battery temperature sensor is located under
the vehicle battery (Fig. 1) and is attached to a
mounting hole on the battery tray.
(1) Position sensor into mounting hole and attach
wiring harness.
(2) Press sensor into top of battery tray.
(3) Install battery. Refer to Group 8A, Battery for
procedures.
GENERATOR DECOUPLER TOOL #8433
GENERATOR DECOUPLER TOOL #8823
Fig. 1 Battery Temperature Sensor Location
1 - BATTERY TEMPERATURE SENSOR
2 - ENGINE WIRE HARNESS
3 - BATTERY TRAY
8F - 26 CHARGINGWJ
CHARGING (Continued)
Page 358 of 2199

GENERATOR
DESCRIPTION
The generator is belt-driven by the engine using a
serpentine type drive belt. It is serviced only as a
complete assembly. If the generator fails for any rea-
son, the entire assembly must be replaced.
OPERATION
As the energized rotor begins to rotate within the
generator, the spinning magnetic field induces a cur-
rent into the windings of the stator coil. Once the
generator begins producing sufficient current, it also
provides the current needed to energize the rotor.
The Y type stator winding connections deliver the
induced AC current to 3 positive and 3 negative
diodes for rectification. From the diodes, rectified DC
current is delivered to the vehicle electrical system
through the generator battery terminal.
Although the generators appear the same exter-
nally, different generators with different output rat-
ings are used on this vehicle. Be certain that the
replacement generator has the same output rating
and part number as the original unit. Refer to Gen-
erator Ratings in the Specifications section at the
back of this group for amperage ratings and part
numbers.
Noise emitting from the generator may be caused
by: worn, loose or defective bearings; a loose or defec-
tive drive pulley; incorrect, worn, damaged or misad-
justed fan drive belt; loose mounting bolts; a
misaligned drive pulley or a defective stator or diode.
REMOVAL
WARNING: DISCONNECT NEGATIVE CABLE FROM
BATTERY BEFORE REMOVING BATTERY OUTPUT
WIRE (B+ WIRE) FROM GENERATOR. FAILURE TO
DO SO CAN RESULT IN INJURY OR DAMAGE TO
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM.
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable at battery.
(2) Remove generator drive belt. Refer to Cooling
System for procedure.
(3) Unsnap cable protector cover from B+ mount-
ing stud (Fig. 2) .
(4) Disconnect (unsnap) 2±wire field connector at
rear of generator (Fig. 2) .
(5) Remove generator mounting bolts (Fig. 3) or
(Fig. 4).
(6) Remove generator from vehicle.
Fig. 2 Generator B+ Cable and Field Wire
Connections (TypicalÐ4.0L Engine Shown)
1 - FIELD WIRE CONNECTOR
2 - B+ CABLE
3 - GENERATOR
4 - B+ CABLE MOUNTING NUT
5 - CABLE PROTECTOR
Fig. 3 Remove/Install GeneratorÐ4.7L V-8 Engine
1 - LOWER BOLTS
2 - REAR BOLT
3 - GENERATOR
WJCHARGING 8F - 27
Page 359 of 2199

INSTALLATION
(1) Position generator to engine and install mount-
ing bolts.
(2) Tighten generator mounting bolts as follows:
²Vertical mounting bolt 4.7L engineÐ40 N´m (29
ft. lbs.)
²Long horizontal mounting bolt 4.7L engineÐ55
N´m (41 ft. lbs.)
²Short horizontal mounting bolt 4.7L engineÐ55
N´m (41 ft. lbs.)
²Generator mounting bolts 4.0L engineÐ55 N´m
(41 ft. lbs.)
²B+ terminal nutÐ11 N´m (95 in. lbs.)
(3) Snap 2±wire field connector into rear of gener-
ator.
(4) Snap cable protector cover to B+ mounting
stud.
CAUTION: Never force a belt over a pulley rim
using a screwdriver. The synthetic fiber of the belt
can be damaged.
CAUTION: When installing a serpentine accessory
drive belt, the belt MUST be routed correctly. The
water pump will be rotating in the wrong direction if
the belt is installed incorrectly, causing the engine
to overheat. Refer to belt routing label in engine
compartment, or refer to Belt Schematics in 7, Cool-
ing System.(5) Install generator drive belt. Refer to 7, Cooling
System for procedure.
(6) Install negative battery cable to battery.
VOLTAGE REGULATOR
DESCRIPTION
The Electronic Voltage Regulator (EVR) is not a
separate component. It is actually a voltage regulat-
ing circuit located within the Powertrain Control
Module (PCM). The EVR is not serviced separately. If
replacement is necessary, the PCM must be replaced.
OPERATION
The amount of DC current produced by the gener-
ator is controlled by EVR circuitry contained within
the PCM. This circuitry is connected in series with
the generators second rotor field terminal and its
ground.
Voltage is regulated by cycling the ground path to
control the strength of the rotor magnetic field. The
EVR circuitry monitors system line voltage (B+) and
battery temperature (refer to Battery Temperature
Sensor for more information). It then determines a
target charging voltage. If sensed battery voltage is
0.5 volts or lower than the target voltage, the PCM
grounds the field winding until sensed battery volt-
age is 0.5 volts above target voltage. A circuit in the
PCM cycles the ground side of the generator field up
to 100 times per second (100Hz), but has the capabil-
ity to ground the field control wire 100% of the time
(full field) to achieve the target voltage. If the charg-
ing rate cannot be monitored (limp-in), a duty cycle
of 25% is used by the PCM in order to have some
generator output. Also refer to Charging System
Operation for additional information.
Fig. 4 Remove/Install GeneratorÐ4.0L 6±Cylinder
Engine
1 - GENERATOR
2 - UPPER BOLT
3 - LOWER BOLT
8F - 28 CHARGINGWJ
GENERATOR (Continued)
Page 360 of 2199

STARTING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
STARTING
DESCRIPTION.........................29
OPERATION...........................30
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - STARTING
SYSTEM............................30
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE - STARTER...................35
STARTER MOTOR - GAS POWERED......35
STARTER MOTOR
DESCRIPTION.........................35
OPERATION...........................36DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - STARTER
MOTOR .............................36
REMOVAL.............................37
INSTALLATION.........................38
STARTER MOTOR RELAY
DESCRIPTION.........................38
OPERATION...........................38
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - STARTER RELAY . 38
REMOVAL.............................39
INSTALLATION.........................40
STARTING
DESCRIPTION
An electrically operated engine starting system is
standard factory-installed equipment on this model.
The starting system is designed to provide the vehi-
cle operator with a convenient, efficient and reliable
means of cranking and starting the internal combus-
tion engine used to power the vehicle and all of its
accessory systems from within the safe and secure
confines of the passenger compartment. See the own-
er's manual in the vehicle glove box for more infor-
mation and instructions on the recommended use
and operation of the factory-installed starting sys-
tem.
The starting system consists of the following com-
ponents:
²Battery
²Starter relay
²Starter motor (including an integral starter sole-
noid)
²Ignition switch
²Park/neutral position switch
²Wire harnesses and connections (including the
battery cables).
This group provides complete service information
for the starter motor and the starter relay. Complete
service information for the other starting system
components can be located as follows:
²Refer toBatteryin the proper section of Group
8A - Battery for complete service information for the
battery.
²Refer toIgnition Switch and Key Lock Cyl-
inderin the proper section of Group 8D - Ignition
System for complete service information for the igni-
tion switch.²Refer toPark/Neutral Position Switchin the
proper section of Group 21 - Transmission for com-
plete service information for the park/neutral posi-
tion switch.
²Refer to the proper section ofGroup 8W - Wir-
ing Diagramsfor complete service information and
circuit diagrams for the starting system wiring com-
ponents.
Group 8A covers the Battery, Group 8B covers the
Starting Systems, and Group 8C covers the Charging
System. We have separated these systems to make it
easier to locate the information you are seeking
within this Service Manual. However, when attempt-
ing to diagnose any of these systems, it is important
that you keep their interdependency in mind.
The battery, starting, and charging systems in the
vehicle operate with one another, and must be tested
as a complete system. In order for the vehicle to start
and charge properly, all of the components that are
used in these systems must perform within specifica-
tions.
The diagnostic procedures used in each of these
groups include the most basic conventional diagnostic
methods, to the more sophisticated On-Board Diag-
nostics (OBD) built into the Powertrain Control Mod-
ule (PCM). Use of an induction-type milliampere
ammeter, volt/ohmmeter, battery charger, carbon pile
rheostat (load tester), and 12-volt test lamp may be
required.
All OBD-sensed systems are monitored by the
PCM. Each monitored circuit is assigned a Diagnos-
tic Trouble Code (DTC). The PCM will store a DTC in
electronic memory for any failure it detects. Refer to
On-Board Diagnostic Test For Charging System
in the Diagnosis and Testing section of Group 8C -
Charging System for more information.
WJSTARTING 8F - 29
Page 361 of 2199

OPERATION
The starting system components form two separate
circuits. A high-amperage feed circuit that feeds the
starter motor between 150 and 350 amperes, and a
low-amperage control circuit that operates on less
than 20 amperes. The high-amperage feed circuit
components include the battery, the battery cables,
the contact disc portion of the starter solenoid, and
the starter motor. The low-amperage control circuit
components include the ignition switch, the park/
neutral position switch, the starter relay, the electro-
magnetic windings of the starter solenoid, and the
connecting wire harness components.
Battery voltage is supplied through the low-amper-
age control circuit to the coil battery terminal of the
starter relay when the ignition switch is turned to
the momentary Start position. The park/neutral posi-
tion switch is installed in series between the starter
relay coil ground terminal and ground. This normally
open switch prevents the starter relay from being
energized and the starter motor from operating
unless the automatic transmission gear selector is in
the Neutral or Park positions.
When the starter relay coil is energized, the nor-
mally open relay contacts close. The relay contacts
connect the relay common feed terminal to the relay
normally open terminal. The closed relay contacts
energize the starter solenoid coil windings.
The energized solenoid pull-in coil pulls in the sole-
noid plunger. The solenoid plunger pulls the shift
lever in the starter motor. This engages the starter
overrunning clutch and pinion gear with the starter
ring gear on the automatic transmission torque con-
verter drive plate.
As the solenoid plunger reaches the end of its
travel, the solenoid contact disc completes the high-
amperage starter feed circuit and energizes the sole-
noid plunger hold-in coil. Current now flows between
the solenoid battery terminal and the starter motor,
energizing the starter.Once the engine starts, the overrunning clutch pro-
tects the starter motor from damage by allowing the
starter pinion gear to spin faster than the pinion
shaft. When the driver releases the ignition switch to
the On position, the starter relay coil is de-energized.
This causes the relay contacts to open. When the
relay contacts open, the starter solenoid plunger
hold-in coil is de-energized.
When the solenoid plunger hold-in coil is de-ener-
gized, the solenoid plunger return spring returns the
plunger to its relaxed position. This causes the con-
tact disc to open the starter feed circuit, and the shift
lever to disengage the overrunning clutch and pinion
gear from the starter ring gear.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - STARTING
SYSTEM
The battery, starting, and charging systems oper-
ate with one another, and must be tested as a com-
plete system. In order for the vehicle to start and
charge properly, all of the components involved in
these systems must perform within specifications.
Group 8A covers the Battery, Group 8B covers the
Starting Systems, and Group 8C covers the Charging
System. We have separated these systems to make it
easier to locate the information you are seeking
within this Service Manual. However, when attempt-
ing to diagnose any of these systems, it is important
that you keep their interdependency in mind.
The diagnostic procedures used in these groups
include the most basic conventional diagnostic meth-
ods, to the more sophisticated On-Board Diagnostics
(OBD) built into the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM). Use of an induction-type milliampere amme-
ter, volt/ohmmeter, battery charger, carbon pile rheo-
stat (load tester), and 12-volt test lamp may be
required.
All OBD-sensed systems are monitored by the
PCM. Each monitored circuit is assigned a Diagnos-
tic Trouble Code (DTC). The PCM will store a DTC in
electronic memory for any failure it detects. Refer to
On-Board Diagnostic Test For Charging System
in the Diagnosis and Testing section of Group 8C -
Charging System for more information.
8F - 30 STARTINGWJ
STARTING (Continued)
Page 362 of 2199
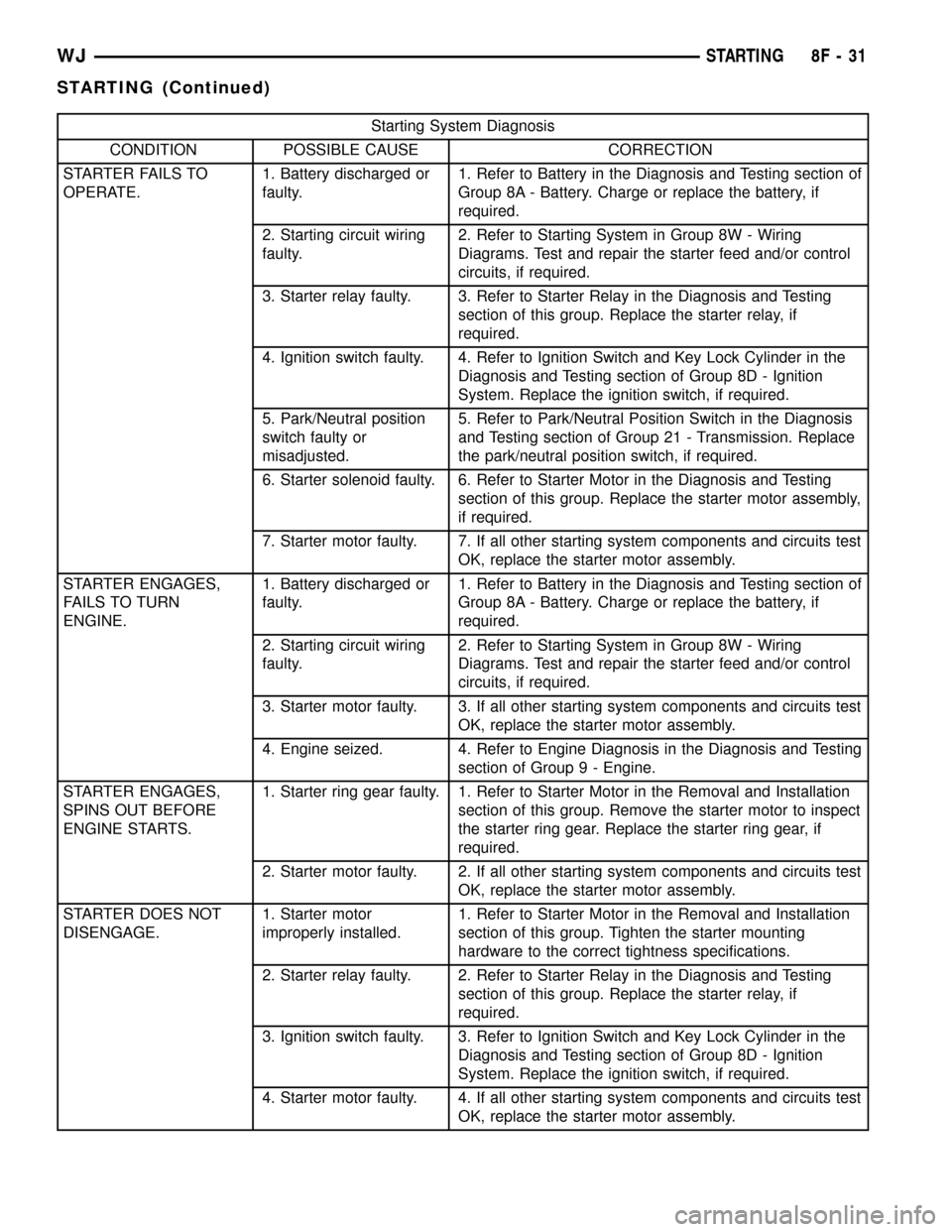
Starting System Diagnosis
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
STARTER FAILS TO
OPERATE.1. Battery discharged or
faulty.1. Refer to Battery in the Diagnosis and Testing section of
Group 8A - Battery. Charge or replace the battery, if
required.
2. Starting circuit wiring
faulty.2. Refer to Starting System in Group 8W - Wiring
Diagrams. Test and repair the starter feed and/or control
circuits, if required.
3. Starter relay faulty. 3. Refer to Starter Relay in the Diagnosis and Testing
section of this group. Replace the starter relay, if
required.
4. Ignition switch faulty. 4. Refer to Ignition Switch and Key Lock Cylinder in the
Diagnosis and Testing section of Group 8D - Ignition
System. Replace the ignition switch, if required.
5. Park/Neutral position
switch faulty or
misadjusted.5. Refer to Park/Neutral Position Switch in the Diagnosis
and Testing section of Group 21 - Transmission. Replace
the park/neutral position switch, if required.
6. Starter solenoid faulty. 6. Refer to Starter Motor in the Diagnosis and Testing
section of this group. Replace the starter motor assembly,
if required.
7. Starter motor faulty. 7. If all other starting system components and circuits test
OK, replace the starter motor assembly.
STARTER ENGAGES,
FAILS TO TURN
ENGINE.1. Battery discharged or
faulty.1. Refer to Battery in the Diagnosis and Testing section of
Group 8A - Battery. Charge or replace the battery, if
required.
2. Starting circuit wiring
faulty.2. Refer to Starting System in Group 8W - Wiring
Diagrams. Test and repair the starter feed and/or control
circuits, if required.
3. Starter motor faulty. 3. If all other starting system components and circuits test
OK, replace the starter motor assembly.
4. Engine seized. 4. Refer to Engine Diagnosis in the Diagnosis and Testing
section of Group 9 - Engine.
STARTER ENGAGES,
SPINS OUT BEFORE
ENGINE STARTS.1. Starter ring gear faulty. 1. Refer to Starter Motor in the Removal and Installation
section of this group. Remove the starter motor to inspect
the starter ring gear. Replace the starter ring gear, if
required.
2. Starter motor faulty. 2. If all other starting system components and circuits test
OK, replace the starter motor assembly.
STARTER DOES NOT
DISENGAGE.1. Starter motor
improperly installed.1. Refer to Starter Motor in the Removal and Installation
section of this group. Tighten the starter mounting
hardware to the correct tightness specifications.
2. Starter relay faulty. 2. Refer to Starter Relay in the Diagnosis and Testing
section of this group. Replace the starter relay, if
required.
3. Ignition switch faulty. 3. Refer to Ignition Switch and Key Lock Cylinder in the
Diagnosis and Testing section of Group 8D - Ignition
System. Replace the ignition switch, if required.
4. Starter motor faulty. 4. If all other starting system components and circuits test
OK, replace the starter motor assembly.
WJSTARTING 8F - 31
STARTING (Continued)