Electronic Control JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 1530 of 2199

FOURTH GEAR POWERFLOW
Fourth gear overdrive range is electronically con-
trolled and hydraulically activated. Various sensor
inputs are supplied to the powertrain control module
to operate the overdrive solenoid on the valve body.
The solenoid contains a check ball that opens and
closes a vent port in the 3-4 shift valve feed passage.
The overdrive solenoid (and check ball) are not ener-
gized in first, second, third, or reverse gear. The vent
port remains open, diverting line pressure from the
2-3 shift valve away from the 3-4 shift valve. The
overdrive control switch must be in the ON position
to transmit overdrive status to the PCM. A 3-4
upshift occurs only when the overdrive solenoid is
energized by the PCM. The PCM energizes the over-
drive solenoid during the 3-4 upshift. This causes the
solenoid check ball to close the vent port allowing
line pressure from the 2-3 shift valve to act directly
on the 3-4 upshift valve. Line pressure on the 3-4
shift valve overcomes valve spring pressure moving
the valve to the upshift position. This action exposes
the feed passages to the 3-4 timing valve, 3-4 quick
fill valve, 3-4 accumulator, and ultimately to the
overdrive piston. Line pressure through the timing
valve moves the overdrive piston into contact with
the overdrive clutch. The direct clutch is disengaged
before the overdrive clutch is engaged. The boost
valve provides increased fluid apply pressure to the
overdrive clutch during 3-4 upshifts, and when accel-
erating in fourth gear. The 3-4 accumulator cushions
overdrive clutch engagement to smooth 3-4 upshifts.
The accumulator is charged at the same time as
apply pressure acts against the overdrive piston.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION
Automatic transmission problems can be a result of
poor engine performance, incorrect fluid level, incor-
rect linkage or cable adjustment, band or hydraulic
control pressure adjustments, hydraulic system mal-
functions or electrical/mechanical component mal-
functions. Begin diagnosis by checking the easily
accessible items such as: fluid level and condition,
linkage adjustments and electrical connections. A
road test will determine if further diagnosis is neces-
sary.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PRELIMINARY
Two basic procedures are required. One procedure
for vehicles that are drivable and an alternate proce-
dure for disabled vehicles (will not back up or move
forward).
VEHICLE IS DRIVEABLE
(1) Check for transmission fault codes using DRBt
scan tool.
(2) Check fluid level and condition.
(3) Adjust throttle and gearshift linkage if com-
plaint was based on delayed, erratic, or harsh shifts.
(4) Road test and note how transmission upshifts,
downshifts, and engages.
(5) Perform hydraulic pressure test if shift prob-
lems were noted during road test.
(6) Perform air-pressure test to check clutch-band
operation.
VEHICLE IS DISABLED
(1) Check fluid level and condition.
(2) Check for broken or disconnected gearshift or
throttle linkage.
(3) Check for cracked, leaking cooler lines, or loose
or missing pressure-port plugs.
(4) Raise and support vehicle on safety stands,
start engine, shift transmission into gear, and note
following:
(a) If propeller shaft turns but wheels do not,
problem is with differential or axle shafts.
(b) If propeller shaft does not turn and transmis-
sion is noisy, stop engine. Remove oil pan, and
check for debris. If pan is clear, remove transmis-
sion and check for damaged drive plate, converter,
oil pump, or input shaft.
(c) If propeller shaft does not turn and transmis-
sion is not noisy, perform hydraulic-pressure test to
determine if problem is hydraulic or mechanical.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ROAD TESTING
Before road testing, be sure the fluid level and con-
trol cable adjustments have been checked and
adjusted if necessary. Verify that diagnostic trouble
codes have been resolved.
Observe engine performance during the road test.
A poorly tuned engine will not allow accurate analy-
sis of transmission operation.
Operate the transmission in all gear ranges. Check
for shift variations and engine flare which indicates
slippage. Note if shifts are harsh, spongy, delayed,
early, or if part throttle downshifts are sensitive.
Slippage indicated by engine flare, usually means
clutch, band or overrunning clutch problems. If the
condition is advanced, an overhaul will be necessary
to restore normal operation.
A slipping clutch or band can often be determined
by comparing which internal units are applied in the
various gear ranges. The Clutch and Band Applica-
tion chart provides a basis for analyzing road test
results.
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 11
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE (Continued)
Page 1584 of 2199

(8) Engine starts must be possible with shifter
lever in PARK or NEUTRAL gate positions only.
Engine starts must not be possible in any other gate
positions other than PARK or NEUTRAL.
(9) With shifter lever handle push-button not
depressed and lever detent in:
²PARK position- apply forward force on center of
handle and remove pressure. Engine start must be
possible.
²PARK position- apply rearward force on center
of handle and remove pressure. Engine start must be
possible.
²NEUTRAL position- engine start must be possi-
ble.
²NEUTRAL position, engine running and brakes
applied- Apply forward force on center of shift han-
dle. Transmission should not be able to shift into
REVERSE detent.
ELECTRONIC GOVERNOR
DESCRIPTION
Governor pressure is controlled electronically. Com-
ponents used for governor pressure control include:
²Governor body
²Valve body transfer plate
²Governor pressure solenoid valve
²Governor pressure sensor
²Fluid temperature thermistor
²Throttle position sensor (TPS)
²Transmission speed sensor
²Powertrain control module (PCM)
GOVERNOR PRESSURE SOLENOID VALVE
The solenoid valve is a duty-cycle solenoid which
regulates the governor pressure needed for upshifts
and downshifts. It is an electro-hydraulic device
located in the governor body on the valve body trans-
fer plate (Fig. 73).
GOVERNOR PRESSURE SENSOR
The governor pressure sensor measures output
pressure of the governor pressure solenoid valve (Fig.
74).
GOVERNOR BODY AND TRANSFER PLATE
The transfer plate is designed to supply transmis-
sion line pressure to the governor pressure solenoid
valve and to return governor pressure.
The governor pressure solenoid valve is mounted in
the governor body. The body is bolted to the lower
side of the transfer plate (Fig. 74).
GOVERNOR PRESSURE CURVES
There are four governor pressure curves pro-
grammed into the transmission control module. The
different curves allow the control module to adjust
governor pressure for varying conditions. One curve
is used for operation when fluid temperature is at, or
below, ±1ÉC (30ÉF). A second curve is used when fluid
temperature is at, or above, 10ÉC (50ÉF) during nor-
mal city or highway driving. A third curve is used
during wide-open throttle operation. The fourth curve
is used when driving with the transfer case in low
range.
OPERATION
Compensation is required for performance varia-
tions of two of the input devices. Though the slope of
the transfer functions is tightly controlled, offset may
vary due to various environmental factors or manu-
facturing tolerances.
The pressure transducer is affected by barometric
pressure as well as temperature. Calibration of the
zero pressure offset is required to compensate for
shifting output due to these factors.
Fig. 73 Governor Pressure Solenoid Valve
1 - SOLENOID FILTER
2 - GOVERNOR PRESSURE SOLENOID
Fig. 74 Governor Pressure Sensor
1 - GOVERNOR BODY
2 - GOVERNOR PRESSURE SENSOR/TRANSMISSION FLUID
TEMPERATURE THERMISTOR
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 65
BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK MECHANISM (Continued)
Page 1585 of 2199

Normal calibration will be performed when sump
temperature is above 50 degrees F, or in the absence
of sump temperature data, after the first 10 minutes
of vehicle operation. Calibration of the pressure
transducer offset occurs each time the output shaft
speed falls below 200 RPM. Calibration shall be
repeated each 3 seconds the output shaft speed is
below 200 RPM. A 0.5 second pulse of 95% duty cycle
is applied to the governor pressure solenoid valve
and the transducer output is read during this pulse.
Averaging of the transducer signal is necessary to
reject electrical noise.
Under cold conditions (below 50 degrees F sump),
the governor pressure solenoid valve response may
be too slow to guarantee 0 psi during the 0.5 second
calibration pulse. Calibration pulses are continued
during this period, however the transducer output
valves are discarded. Transducer offset must be read
at key-on, under conditions which promote a stable
reading. This value is retained and becomes the off-
set during the9cold9period of operation.
GOVERNOR PRESSURE SOLENOID VALVE
The inlet side of the solenoid valve is exposed to
normal transmission line pressure. The outlet side of
the valve leads to the valve body governor circuit.
The solenoid valve regulates line pressure to pro-
duce governor pressure. The average current sup-
plied to the solenoid controls governor pressure. One
amp current produces zero kPa/psi governor pres-
sure. Zero amps sets the maximum governor pres-
sure.
The powertrain control module (PCM) turns on the
trans control relay which supplies electrical power to
the solenoid valve. Operating voltage is 12 volts
(DC). The PCM controls the ground side of the sole-
noid using the governor pressure solenoid control cir-
cuit.
GOVERNOR PRESSURE SENSOR
The sensor output signal provides the necessary
feedback to the PCM. This feedback is needed to ade-
quately control governor pressure.
GOVERNOR BODY AND TRANSFER PLATE
The transfer plate channels line pressure to the
solenoid valve through the governor body. It also
channels governor pressure from the solenoid valve
to the governor circuit. It is the solenoid valve that
develops the necessary governor pressure.
GOVERNOR PRESSURE CURVES
LOW TRANSMISSION FLUID TEMPERATURE
When the transmission fluid is cold the conven-
tional governor can delay shifts, resulting in higherthan normal shift speeds and harsh shifts. The elec-
tronically controlled low temperature governor pres-
sure curve is higher than normal to make the
transmission shift at normal speeds and sooner. The
PCM uses a temperature sensor in the transmission
oil sump to determine when low temperature gover-
nor pressure is needed.
NORMAL OPERATION
Normal operation is refined through the increased
computing power of the PCM and through access to
data on engine operating conditions provided by the
PCM that were not available with the previous
stand-alone electronic module. This facilitated the
development of a load adaptive shift strategy - the
ability to alter the shift schedule in response to vehi-
cle load condition. One manifestation of this capabil-
ity is grade9hunting9prevention - the ability of the
transmission logic to delay an upshift on a grade if
the engine does not have sufficient power to main-
tain speed in the higher gear. The 3-2 downshift and
the potential for hunting between gears occurs with a
heavily loaded vehicle or on steep grades. When
hunting occurs, it is very objectionable because shifts
are frequent and accompanied by large changes in
noise and acceleration.
WIDE OPEN THROTTLE OPERATION
In wide-open throttle (WOT) mode, adaptive mem-
ory in the PCM assures that up-shifts occur at the
preprogrammed optimum speed. WOT operation is
determined from the throttle position sensor, which
is also a part of the emission control system. The ini-
tial setting for the WOT upshift is below the opti-
mum engine speed. As WOT shifts are repeated, the
PCM learns the time required to complete the shifts
by comparing the engine speed when the shifts occur
to the optimum speed. After each shift, the PCM
adjusts the shift point until the optimum speed is
reached. The PCM also considers vehicle loading,
grade and engine performance changes due to high
altitude in determining when to make WOT shifts. It
does this by measuring vehicle and engine accelera-
tion and then factoring in the shift time.
TRANSFER CASE LOW RANGE OPERATION
On four-wheel drive vehicles operating in low
range, the engine can accelerate to its peak more
rapidly than in Normal range, resulting in delayed
shifts and undesirable engine9flare.9The low range
governor pressure curve is also higher than normal
to initiate upshifts sooner. The PCM compares elec-
tronic vehicle speed signal used by the speedometer
to the transmission output shaft speed signal to
determine when the transfer case is in low range.
21 - 66 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42REWJ
ELECTRONIC GOVERNOR (Continued)
Page 1697 of 2199
INSTALLATION........................253
OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................254
OPERATION..........................254
REMOVAL............................254
INSTALLATION........................254
OVERDRIVE SWITCH
DESCRIPTION........................254
OPERATION..........................254
PARK LOCK CABLE
REMOVAL............................255
INSTALLATION........................255
PISTONS
DESCRIPTION........................256
OPERATION..........................256
PLANETARY GEARTRAIN
DESCRIPTION........................258
OPERATION..........................260
DISASSEMBLY........................260
CLEANING...........................260
INSPECTION.........................260
ASSEMBLY...........................261
SHIFT MECHANISM
DESCRIPTION........................261
OPERATION..........................261
REMOVAL............................261
INSTALLATION........................263
SOLENOID SWITCH VALVE
DESCRIPTION........................263
OPERATION..........................263
SOLENOIDS
DESCRIPTION........................263OPERATION..........................264
TORQUE CONVERTER
DESCRIPTION........................264
OPERATION..........................268
REMOVAL............................269
INSTALLATION........................269
TRANSMISSION CONTROL RELAY
DESCRIPTION........................270
OPERATION..........................270
TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................270
OPERATION..........................270
TRANSMISSION SOLENOID/TRS ASSEMBLY
DESCRIPTION........................271
OPERATION..........................271
REMOVAL............................272
INSTALLATION........................272
TRANSMISSION TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................272
OPERATION..........................272
VALVE BODY
DESCRIPTION........................273
OPERATION..........................273
REMOVAL............................274
DISASSEMBLY........................275
CLEANING...........................277
INSPECTION.........................277
ASSEMBLY...........................278
INSTALLATION........................279
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION -
545RFE
DESCRIPTION
The 545RFE automatic transmission is a sophisti-
cated, multi-range, electronically controlled transmis-
sion which combines optimized gear ratios for
responsive performance, state of the art efficiency
features and low NVH. Other features include driver
adaptive shifting and three planetary gear sets to
provide wide ratio capability with precise ratio steps
for optimum driveability. The three planetary gear
sets also make available a unique alternate second
gear ratio. The primary 2nd gear ratio fits between
1st and 3rd gears for normal through-gear accelera-
tions. The alternate second gear ratio (2prime) allows
smoother 4-2 kickdowns at high speeds to provide
2nd gear passing performance over a wider highway
cruising range. An additional overdrive ratio (0.67:1)
is also provided for greater fuel economy and less
NVH at highway speeds.The hydraulic portion of the transmission consists
of the transmission fluid, fluid passages, hydraulic
valves, and various line pressure control components.
The primary mechanical components of the trans-
mission consist of the following:
²Three multiple disc input clutches
²Three multiple disc holding clutches
²Five hydraulic accumulators
²Three planetary gear sets
²Dual Stage Hydraulic oil pump
²Valve body
²Solenoid pack
The TCM is the ªheartº or ªbrainº of the electronic
control system and relies on information from vari-
ous direct and indirect inputs (sensors, switches, etc.)
to determine driver demand and vehicle operating
conditions. With this information, the TCM can cal-
culate and perform timely and quality shifts through
various output or control devices (solenoid pack,
transmission control relay, etc.).
21 - 178 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFEWJ
Page 1698 of 2199
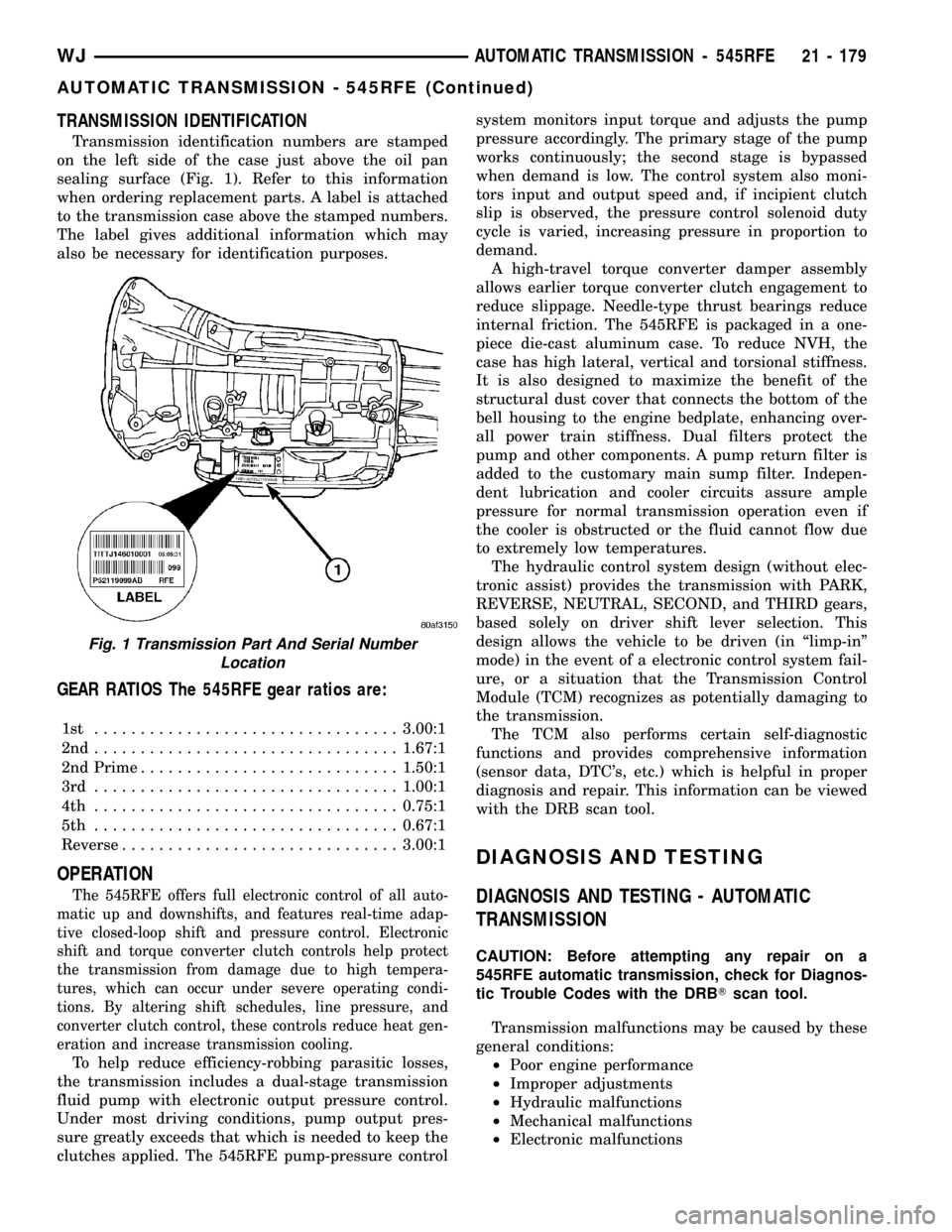
TRANSMISSION IDENTIFICATION
Transmission identification numbers are stamped
on the left side of the case just above the oil pan
sealing surface (Fig. 1). Refer to this information
when ordering replacement parts. A label is attached
to the transmission case above the stamped numbers.
The label gives additional information which may
also be necessary for identification purposes.
GEAR RATIOS The 545RFE gear ratios are:
1st .................................3.00:1
2nd.................................1.67:1
2nd Prime............................1.50:1
3rd .................................1.00:1
4th .................................0.75:1
5th .................................0.67:1
Reverse..............................3.00:1
OPERATION
The 545RFE offers full electronic control of all auto-
matic up and downshifts, and features real-time adap-
tive closed-loop shift and pressure control. Electronic
shift and torque converter clutch controls help protect
the transmission from damage due to high tempera-
tures, which can occur under severe operating condi-
tions. By altering shift schedules, line pressure, and
converter clutch control, these controls reduce heat gen-
eration and increase transmission cooling.
To help reduce efficiency-robbing parasitic losses,
the transmission includes a dual-stage transmission
fluid pump with electronic output pressure control.
Under most driving conditions, pump output pres-
sure greatly exceeds that which is needed to keep the
clutches applied. The 545RFE pump-pressure controlsystem monitors input torque and adjusts the pump
pressure accordingly. The primary stage of the pump
works continuously; the second stage is bypassed
when demand is low. The control system also moni-
tors input and output speed and, if incipient clutch
slip is observed, the pressure control solenoid duty
cycle is varied, increasing pressure in proportion to
demand.
A high-travel torque converter damper assembly
allows earlier torque converter clutch engagement to
reduce slippage. Needle-type thrust bearings reduce
internal friction. The 545RFE is packaged in a one-
piece die-cast aluminum case. To reduce NVH, the
case has high lateral, vertical and torsional stiffness.
It is also designed to maximize the benefit of the
structural dust cover that connects the bottom of the
bell housing to the engine bedplate, enhancing over-
all power train stiffness. Dual filters protect the
pump and other components. A pump return filter is
added to the customary main sump filter. Indepen-
dent lubrication and cooler circuits assure ample
pressure for normal transmission operation even if
the cooler is obstructed or the fluid cannot flow due
to extremely low temperatures.
The hydraulic control system design (without elec-
tronic assist) provides the transmission with PARK,
REVERSE, NEUTRAL, SECOND, and THIRD gears,
based solely on driver shift lever selection. This
design allows the vehicle to be driven (in ªlimp-inº
mode) in the event of a electronic control system fail-
ure, or a situation that the Transmission Control
Module (TCM) recognizes as potentially damaging to
the transmission.
The TCM also performs certain self-diagnostic
functions and provides comprehensive information
(sensor data, DTC's, etc.) which is helpful in proper
diagnosis and repair. This information can be viewed
with the DRB scan tool.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION
CAUTION: Before attempting any repair on a
545RFE automatic transmission, check for Diagnos-
tic Trouble Codes with the DRBTscan tool.
Transmission malfunctions may be caused by these
general conditions:
²Poor engine performance
²Improper adjustments
²Hydraulic malfunctions
²Mechanical malfunctions
²Electronic malfunctions
Fig. 1 Transmission Part And Serial Number
Location
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 179
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE (Continued)
Page 1780 of 2199

Replace the driving shell if worn, cracked or dam-
aged.
Replace planetary gear sets if gears, pinion pins, or
carrier are damaged in any way. Replace the annulus
gears and supports if either component is worn or
damaged.
Replace the output shaft if the machined surfaces
are scored, pitted, or damaged in any way. Also
replace the shaft if the splines are damaged, or
exhibits cracks at any location.
ASSEMBLY
(1) Clean and inspect all components. Replace any
components which show evidence of excessive wear
or scoring.
(2) Install the number 11 bearing into the input
planetary carrier so that the inner race will be
toward the front of the transmission (Fig. 104).
(3) Install the input sun gear into the input carrier
(Fig. 104).
(4) Install the number 10 bearing onto the rear of
the reverse planetary carrier with the inner race
toward the carrier (Fig. 104).
(5) Install the number 9 bearing onto the front of
the reverse planetary carrier with the outer race
toward the carrier and the inner race facing upward
(Fig. 104).
(6) Install the reverse planetary gear carrier into
the input carrier (Fig. 104).
(7) Install the input annulus gear into the input
carrier (Fig. 104).
(8) Install the snap-ring to hold the input annulus
gear into the input carrier (Fig. 104).
SHIFT MECHANISM
DESCRIPTION
The gear shift mechanism provides six shift posi-
tions which are:
²Park (P)
²Reverse (R)
²Neutral (N)
²Drive (D)
²Manual second (2)
²Manual low (1)
OPERATION
MANUAL LOW (1) range provides FIRST gear
only. Overrun braking is also provided in this range.
MANUAL SECOND (2) range provides FIRST and
SECOND gear only.
DRIVE range provides FIRST, SECOND, THIRD
and OVERDRIVE FOURTH and FIFTH gear ranges.
The shift into OVERDRIVE FOURTH and FIFTH
gear range occurs only after the transmission hascompleted the shift into D THIRD gear range. No
further movement of the shift mechanism is required
to complete the 3-4 or 4-5 shifts.
The FOURTH and FIFTH gear upshifts occurs
automatically when the overdrive selector switch is
in the ON position. An upshift to FOURTH and
FIFTH gears may not occur or may be delayed in
some of the possible shift schedules. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL MOD-
ULES/TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE -
OPERATION)
REMOVAL
(1) Remove any necessary console parts for access
to shift lever assembly and shifter cables. (Refer to
23 - BODY/INTERIOR/FLOOR CONSOLE -
REMOVAL)
(2) Shift transmission into PARK.
(3) Disconnect the transmission shift cable at shift
lever and shifter assembly bracket (Fig. 105).
(4) Disconnect the park lock cable from the shifter
BTSI lever and the shifter assembly bracket. (Fig.
106)
(5) Disconnect the transfer case shift cable from
the transfer case shift lever pin (Fig. 107), if
equipped.
(6) Remove the clip holding the transfer case shift
cable to the shifter assembly bracket, if equipped.
(7) Remove the transfer case shift cable from the
shifter assembly bracket, if equipped.
(8) Disengage all wiring connectors from the
shifter assembly.
(9) Remove all nuts holding the shifter assembly to
the floor pan (Fig. 108).
Fig. 105 Transmission Shift Cable
1 - SHIFT LEVER PIN
2 - ADJUSTMENT SCREW
3 - SHIFT CABLE
4 - SHIFTER ASSEMBLY BRACKET
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 261
PLANETARY GEARTRAIN (Continued)
Page 1783 of 2199

A solenoid can also be described by the method by
which it is controlled. Some of the possibilities
include variable force, pulse-width modulated, con-
stant ON, or duty cycle. The variable force and pulse-
width modulated versions utilize similar methods to
control the current flow through the solenoid to posi-
tion the solenoid plunger at a desired position some-
where between full ON and full OFF. The constant
ON and duty cycled versions control the voltage
across the solenoid to allow either full flow or no flow
through the solenoid's valve.
OPERATION
When an electrical current is applied to the sole-
noid coil, a magnetic field is created which produces
an attraction to the plunger, causing the plunger to
move and work against the spring pressure and the
load applied by the fluid the valve is controlling. The
plunger is normally directly attached to the valve
which it is to operate. When the current is removed
from the coil, the attraction is removed and the
plunger will return to its original position due to
spring pressure.
The plunger is made of a conductive material and
accomplishes this movement by providing a path for
the magnetic field to flow. By keeping the air gap
between the plunger and the coil to the minimum
necessary to allow free movement of the plunger, the
magnetic field is maximized.
TORQUE CONVERTER
DESCRIPTION
The torque converter (Fig. 109) is a hydraulic
device that couples the engine crankshaft to the
transmission. The torque converter consists of an
outer shell with an internal turbine, a stator, an
overrunning clutch, an impeller and an electronically
applied converter clutch. The converter clutch pro-vides reduced engine speed and greater fuel economy
when engaged. Clutch engagement also provides
reduced transmission fluid temperatures. The con-
verter clutch engages in third gear. The torque con-
verter hub drives the transmission oil (fluid) pump
and contains an o-ring seal to better control oil flow.
The torque converter is a sealed, welded unit that
is not repairable and is serviced as an assembly.
CAUTION: The torque converter must be replaced if
a transmission failure resulted in large amounts of
metal or fiber contamination in the fluid. If the fluid
is contaminated, flush the fluid cooler and lines.
Fig. 109 Torque Converter Assembly
1 - TURBINE ASSEMBLY
2-STATOR
3 - CONVERTER HUB
4 - O-RING
5 - IMPELLER ASSEMBLY
6 - CONVERTER CLUTCH PISTON
7 - TURBINE HUB
21 - 264 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFEWJ
SOLENOIDS (Continued)
Page 1830 of 2199
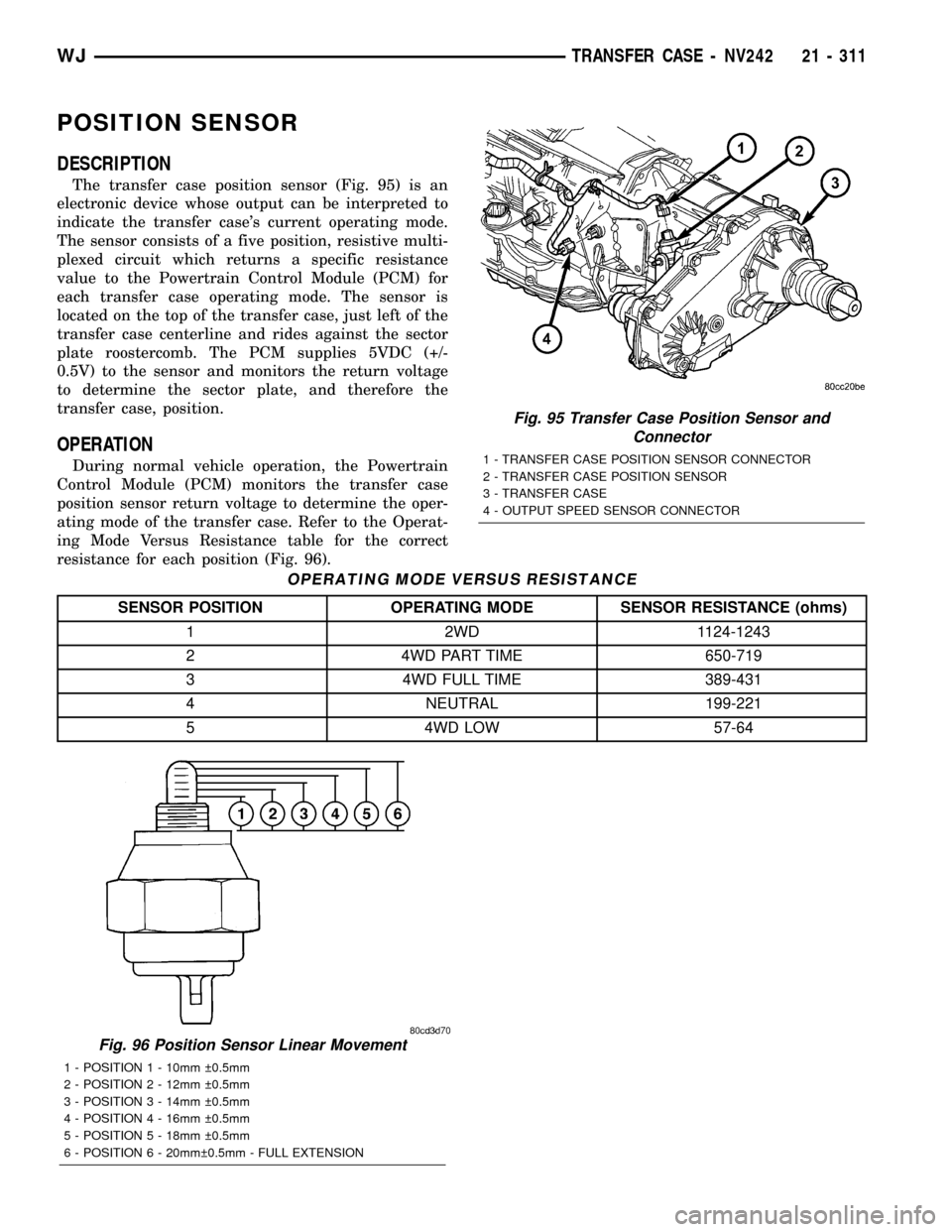
POSITION SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The transfer case position sensor (Fig. 95) is an
electronic device whose output can be interpreted to
indicate the transfer case's current operating mode.
The sensor consists of a five position, resistive multi-
plexed circuit which returns a specific resistance
value to the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) for
each transfer case operating mode. The sensor is
located on the top of the transfer case, just left of the
transfer case centerline and rides against the sector
plate roostercomb. The PCM supplies 5VDC (+/-
0.5V) to the sensor and monitors the return voltage
to determine the sector plate, and therefore the
transfer case, position.
OPERATION
During normal vehicle operation, the Powertrain
Control Module (PCM) monitors the transfer case
position sensor return voltage to determine the oper-
ating mode of the transfer case. Refer to the Operat-
ing Mode Versus Resistance table for the correct
resistance for each position (Fig. 96).
OPERATING MODE VERSUS RESISTANCE
SENSOR POSITION OPERATING MODE SENSOR RESISTANCE (ohms)
1 2WD 1124-1243
2 4WD PART TIME 650-719
3 4WD FULL TIME 389-431
4 NEUTRAL 199-221
5 4WD LOW 57-64
Fig. 96 Position Sensor Linear Movement
1 - POSITION 1 - 10mm 0.5mm
2 - POSITION 2 - 12mm 0.5mm
3 - POSITION 3 - 14mm 0.5mm
4 - POSITION 4 - 16mm 0.5mm
5 - POSITION 5 - 18mm 0.5mm
6 - POSITION 6 - 20mm 0.5mm - FULL EXTENSION
Fig. 95 Transfer Case Position Sensor and
Connector
1 - TRANSFER CASE POSITION SENSOR CONNECTOR
2 - TRANSFER CASE POSITION SENSOR
3 - TRANSFER CASE
4 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
WJTRANSFER CASE - NV242 21 - 311
Page 2078 of 2199

HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - COOLING SYSTEM
REQUIREMENTS.......................1
DESCRIPTION - HEATER AND AIR
CONDITIONER........................1
DESCRIPTION - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM
SERVICE PORT........................1
OPERATION
OPERATION - HEATER AND AIR
CONDITIONER........................2
OPERATION - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM
SERVICE PORT........................2DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C
PERFORMANCE.......................2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEATER
PERFORMANCE.......................6
STANDARD PROCEDURE - DIODE
REPLACEMENT.......................6
SPECIFICATIONS
A/C APPLICATION TABLE................7
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS..............8
CONTROLS.............................9
DISTRIBUTION..........................36
PLUMBING.............................51
HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - COOLING SYSTEM
REQUIREMENTS
To maintain the performance level of the heating-
air conditioning system, the engine cooling system
must be properly maintained. The use of a bug
screen is not recommended. Any obstructions in front
of the radiator or condenser will reduce the perfor-
mance of the air conditioning and engine cooling sys-
tems.
The engine cooling system includes the heater core
and the heater hoses. Refer to Cooling for more infor-
mation before opening, or attempting any service to
the engine cooling system.
DESCRIPTION - HEATER AND AIR
CONDITIONER
A manual temperature control type heating-air
conditioning system is standard factory-installed
equipment on this model. An electronically controlled
Automatic Zone Control (AZC) type heating-air con-
ditioning system is an available factory-installed
option.
All vehicles are equipped with a common HVAC
housing assembly (Fig. 1). The system combines air
conditioning, heating, and ventilating capabilities in
a single unit housing mounted under the instrument
panel.DESCRIPTION - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM
SERVICE PORT
The two refrigerant system service ports are used
to charge, recover/recycle, evacuate, and test the air
conditioning refrigerant system. Unique service port
coupler sizes are used on the R-134a system to
ensure that the refrigerant system is not accidentally
contaminated by the use of the wrong refrigerant
(R-12), or refrigerant system service equipment.
Fig. 1 Blend-Air HVAC System - (typical)
1 - Blend Door
2 - Expansion Valve
3 - Evaporator Core
4 - Blower Assembly
5 - Recirculation Door
6 - Evaporator Probe
7 - Heater Core
8 - Heat/Defrost Door
9 - Panel/Defrost Door
WJHEATING & AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 1
Page 2079 of 2199

OPERATION
OPERATION - HEATER AND AIR CONDITIONER
Outside fresh air enters the vehicle through the
cowl top opening at the base of the windshield, and
passes through a plenum chamber to the HVAC sys-
tem blower housing. Air flow velocity can then be
adjusted with the blower motor speed selector switch
on the a/c heater control panel. The air intake open-
ings must be kept free of snow, ice, leaves, and other
obstructions for the HVAC system to receive a suffi-
cient volume of outside air.
It is also important to keep the air intake openings
clear of debris because leaf particles and other debris
that is small enough to pass through the cowl ple-
num screen can accumulate within the HVAC hous-
ing. The closed, warm, damp and dark environment
created within the HVAC housing is ideal for the
growth of certain molds, mildews and other fungi.
Any accumulation of decaying plant matter provides
an additional food source for fungal spores, which
enter the housing with the fresh air. Excess debris,
as well as objectionable odors created by decaying
plant matter and growing fungi can be discharged
into the passenger compartment during HVAC sys-
tem operation.
Both the manual and AZC heater and air condi-
tioner are blend-air type systems. In a blend-air sys-
tem, a blend door controls the amount of
unconditioned air (or cooled air from the evaporator)
that is allowed to flow through, or around, the heater
core. A temperature control knob on the a/c heater
control panel determines the discharge air tempera-
ture by energizing the blend door actuator, which
operates the blend door. This allows an almost imme-
diate control of the output air temperature of the sys-
tem. The AZC system will have separate blend doors
and temperature controls for each front seat occu-
pant.
The mode control knob on the a/c heater control
panel is used to direct the conditioned air to the
selected system outlets. On manual temperature con-
trol systems, the mode control knob switches engine
vacuum to control the mode doors, which are oper-
ated by vacuum actuators. On AZC systems, the
mode control knob switches electrical current to con-
trol the mode doors, which are operated by electronic
actuators.
The outside air intake can be shut off on manual
temperature control systems by selecting the Recircu-
lation Mode with the mode control knob. The outside
air intake can be shut off on Automatic Zone Control
(AZC) type system by pushing the Recirculation
Mode button. This will operate the recirculation door
that closes off the outside fresh air intake and recir-
culates the air that is already inside the vehicle.The air conditioner for all models is designed for
the use of non-CFC, R-134a refrigerant. The air con-
ditioning system has an evaporator to cool and dehu-
midify the incoming air prior to blending it with the
heated air. This air conditioning system uses a ther-
mal expansion valve to meter refrigerant flow to the
evaporator coil. To maintain minimum evaporator
temperature and prevent evaporator freezing, the
system utilizes an evaporator thermister probe with
the appropriate operating logic located in the body
control module (BCM).
OPERATION - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM SERVICE
PORT
The high pressure service port is located on the liq-
uid line near the receiver/drier. The low pressure ser-
vice port is located on the suction line near the
evaporator at the rear of the engine compartment.
Each of the service ports has a threaded plastic
protective cap installed over it from the factory. After
servicing the refrigerant system, always reinstall
both of the service port caps.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C
PERFORMANCE
The air conditioning system is designed to provide
the passenger compartment with low temperature
and low specific humidity air. The evaporator, located
in the HVAC housing on the dash panel below the
instrument panel, is cooled to temperatures near the
freezing point. As warm damp air passes through the
cooled evaporator, the air transfers its heat to the
refrigerant in the evaporator and the moisture in the
air condenses on the evaporator fins. During periods
of high heat and humidity, an air conditioning sys-
tem will be more effective in the Recirculation Mode.
With the system in the Recirculation Mode, only air
from the passenger compartment passes through the
evaporator. As the passenger compartment air dehu-
midifies, the air conditioning system performance
levels improve.
Humidity has an important bearing on the tempera-
ture of the air delivered to the interior of the vehicle. It
is important to understand the effect that humidity has
on the performance of the air conditioning system.
When humidity is high, the evaporator has to perform a
double duty. It must lower the air temperature, and it
must lower the temperature of the moisture in the air
that condenses on the evaporator fins. Condensing the
moisture in the air transfers heat energy into the evap-
orator fins and tubing. This reduces the amount of heat
the evaporator can absorb from the air. High humidity
greatly reduces the ability of the evaporator to lower
the temperature of the air.
24 - 2 HEATING & AIR CONDITIONINGWJ
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)