Electronic Control JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 1050 of 2199
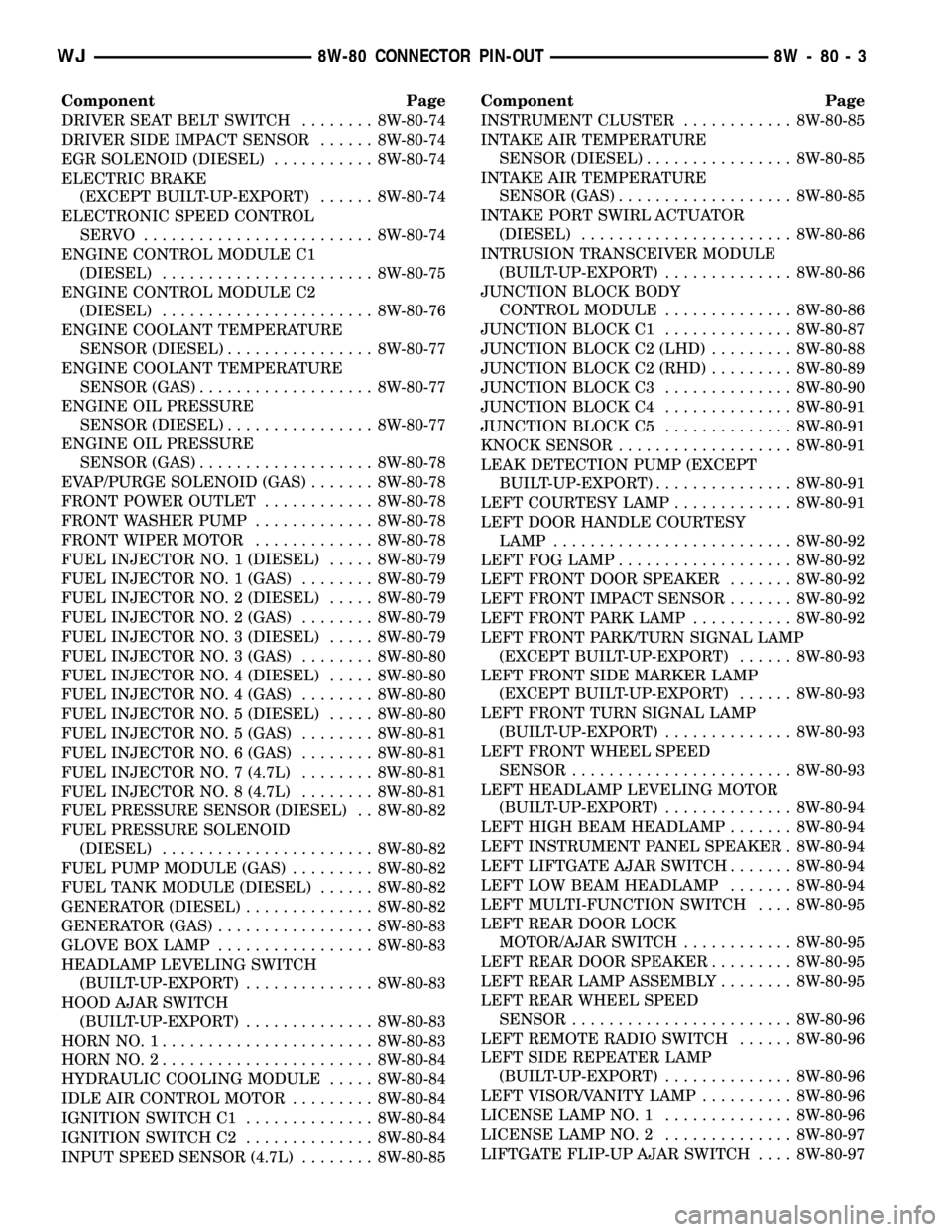
Component Page
DRIVER SEAT BELT SWITCH........ 8W-80-74
DRIVER SIDE IMPACT SENSOR...... 8W-80-74
EGR SOLENOID (DIESEL)........... 8W-80-74
ELECTRIC BRAKE
(EXCEPT BUILT-UP-EXPORT)...... 8W-80-74
ELECTRONIC SPEED CONTROL
SERVO ......................... 8W-80-74
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE C1
(DIESEL)....................... 8W-80-75
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE C2
(DIESEL)....................... 8W-80-76
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE
SENSOR (DIESEL)................ 8W-80-77
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE
SENSOR (GAS)................... 8W-80-77
ENGINE OIL PRESSURE
SENSOR (DIESEL)................ 8W-80-77
ENGINE OIL PRESSURE
SENSOR (GAS)................... 8W-80-78
EVAP/PURGE SOLENOID (GAS)....... 8W-80-78
FRONT POWER OUTLET............ 8W-80-78
FRONT WASHER PUMP............. 8W-80-78
FRONT WIPER MOTOR............. 8W-80-78
FUEL INJECTOR NO. 1 (DIESEL)..... 8W-80-79
FUEL INJECTOR NO. 1 (GAS)........ 8W-80-79
FUEL INJECTOR NO. 2 (DIESEL)..... 8W-80-79
FUEL INJECTOR NO. 2 (GAS)........ 8W-80-79
FUEL INJECTOR NO. 3 (DIESEL)..... 8W-80-79
FUEL INJECTOR NO. 3 (GAS)........ 8W-80-80
FUEL INJECTOR NO. 4 (DIESEL)..... 8W-80-80
FUEL INJECTOR NO. 4 (GAS)........ 8W-80-80
FUEL INJECTOR NO. 5 (DIESEL)..... 8W-80-80
FUEL INJECTOR NO. 5 (GAS)........ 8W-80-81
FUEL INJECTOR NO. 6 (GAS)........ 8W-80-81
FUEL INJECTOR NO. 7 (4.7L)........ 8W-80-81
FUEL INJECTOR NO. 8 (4.7L)........ 8W-80-81
FUEL PRESSURE SENSOR (DIESEL) . . 8W-80-82
FUEL PRESSURE SOLENOID
(DIESEL)....................... 8W-80-82
FUEL PUMP MODULE (GAS)......... 8W-80-82
FUEL TANK MODULE (DIESEL)...... 8W-80-82
GENERATOR (DIESEL).............. 8W-80-82
GENERATOR (GAS)................. 8W-80-83
GLOVE BOX LAMP................. 8W-80-83
HEADLAMP LEVELING SWITCH
(BUILT-UP-EXPORT).............. 8W-80-83
HOOD AJAR SWITCH
(BUILT-UP-EXPORT).............. 8W-80-83
HORN NO. 1....................... 8W-80-83
HORN NO. 2....................... 8W-80-84
HYDRAULIC COOLING MODULE..... 8W-80-84
IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR......... 8W-80-84
IGNITION SWITCH C1.............. 8W-80-84
IGNITION SWITCH C2.............. 8W-80-84
INPUT SPEED SENSOR (4.7L)........ 8W-80-85Component Page
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER............ 8W-80-85
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE
SENSOR (DIESEL)................ 8W-80-85
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE
SENSOR (GAS)................... 8W-80-85
INTAKE PORT SWIRL ACTUATOR
(DIESEL)....................... 8W-80-86
INTRUSION TRANSCEIVER MODULE
(BUILT-UP-EXPORT).............. 8W-80-86
JUNCTION BLOCK BODY
CONTROL MODULE.............. 8W-80-86
JUNCTION BLOCK C1.............. 8W-80-87
JUNCTION BLOCK C2 (LHD)......... 8W-80-88
JUNCTION BLOCK C2 (RHD)......... 8W-80-89
JUNCTION BLOCK C3.............. 8W-80-90
JUNCTION BLOCK C4.............. 8W-80-91
JUNCTION BLOCK C5.............. 8W-80-91
KNOCK SENSOR................... 8W-80-91
LEAK DETECTION PUMP (EXCEPT
BUILT-UP-EXPORT)............... 8W-80-91
LEFT COURTESY LAMP............. 8W-80-91
LEFT DOOR HANDLE COURTESY
LAMP.......................... 8W-80-92
LEFT FOG LAMP................... 8W-80-92
LEFT FRONT DOOR SPEAKER....... 8W-80-92
LEFT FRONT IMPACT SENSOR....... 8W-80-92
LEFT FRONT PARK LAMP........... 8W-80-92
LEFT FRONT PARK/TURN SIGNAL LAMP
(EXCEPT BUILT-UP-EXPORT)...... 8W-80-93
LEFT FRONT SIDE MARKER LAMP
(EXCEPT BUILT-UP-EXPORT)...... 8W-80-93
LEFT FRONT TURN SIGNAL LAMP
(BUILT-UP-EXPORT).............. 8W-80-93
LEFT FRONT WHEEL SPEED
SENSOR........................ 8W-80-93
LEFT HEADLAMP LEVELING MOTOR
(BUILT-UP-EXPORT).............. 8W-80-94
LEFT HIGH BEAM HEADLAMP....... 8W-80-94
LEFT INSTRUMENT PANEL SPEAKER . 8W-80-94
LEFT LIFTGATE AJAR SWITCH....... 8W-80-94
LEFT LOW BEAM HEADLAMP....... 8W-80-94
LEFT MULTI-FUNCTION SWITCH.... 8W-80-95
LEFT REAR DOOR LOCK
MOTOR/AJAR SWITCH............ 8W-80-95
LEFT REAR DOOR SPEAKER......... 8W-80-95
LEFT REAR LAMP ASSEMBLY........ 8W-80-95
LEFT REAR WHEEL SPEED
SENSOR........................ 8W-80-96
LEFT REMOTE RADIO SWITCH...... 8W-80-96
LEFT SIDE REPEATER LAMP
(BUILT-UP-EXPORT).............. 8W-80-96
LEFT VISOR/VANITY LAMP.......... 8W-80-96
LICENSE LAMP NO. 1.............. 8W-80-96
LICENSE LAMP NO. 2.............. 8W-80-97
LIFTGATE FLIP-UP AJAR SWITCH.... 8W-80-97
WJ8W-80 CONNECTOR PIN-OUT 8W - 80 - 3
Page 1121 of 2199

DRIVER SEAT BELT SWITCH-2WAY
CAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
1 R57 20DG DRIVER SEAT BELT SWITCH SENSE
2 R59 20LB DRIVER SEAT BELT SWITCH GROUND
DRIVER SIDE IMPACT SENSOR - BLACK 4 WAY
CAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
1- -
2- -
3 R133 20LB/DG DRIVER SIDE IMPACT SENSOR GROUND
4 R131 20LG/YL DRIVER SIDE IMPACT SENSOR SIGNAL
EGR SOLENOID (DIESEL) - BLACK 2 WAY
CAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
1 F15 18RD/DG FUSED AUTO SHUT DOWN RELAY OUTPUT
2 K35 20GY/YL EGR SOLENOID CONTROL
ELECTRIC BRAKE (EXCEPT BUILT-UP-EXPORT) - BLUE 4 WAY
CAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
1 Z151 14BK GROUND
2 L50 18WT/TN PRIMARY BRAKE SWITCH SIGNAL
3 B40 12LB TRAILER TOW BRAKE B(+)
4 F9 14RD/BK FUSED B(+)
ELECTRONIC SPEED CONTROL SERVO - BLACK 4 WAY
CAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
1 V36 20TN/RD (RHD/GAS) SPEED CONTROL VACUUM SOLENOID CONTROL
1 V36 18TN/RD (LHD GAS) SPEED CONTROL VACUUM SOLENOID CONTROL
2 V35 20LG/RD (RHD/GAS) SPEED CONTROL VENT SOLENOID CONTROL
2 V35 18LG/RD (LHD GAS) SPEED CONTROL VENT SOLENOID CONTROL
3 V30 20DB/RD SPEED CONTROL BRAKE SWITCH OUTPUT
4 Z307 20BK GROUND
8W - 80 - 74 8W-80 CONNECTOR PIN-OUTWJ
Page 1180 of 2199
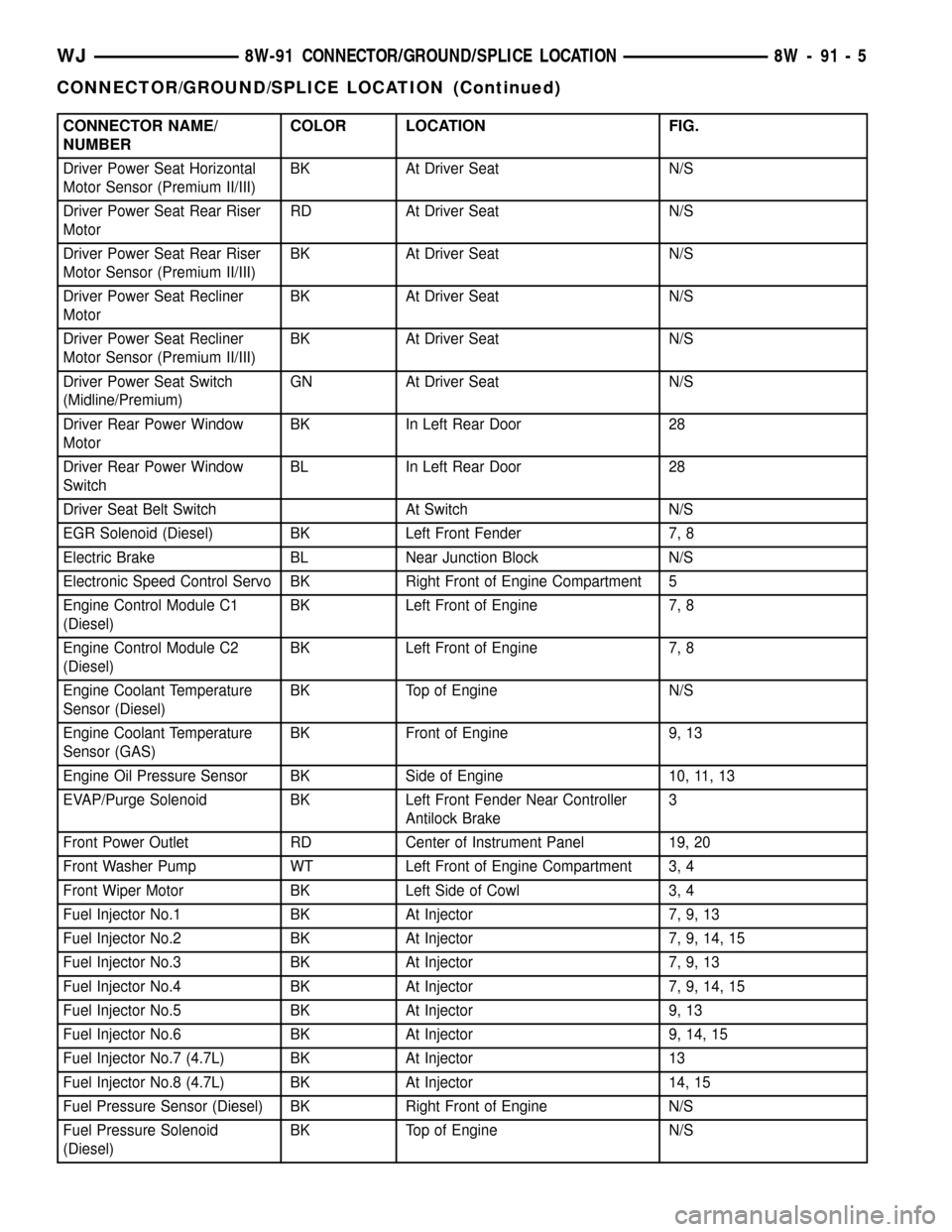
CONNECTOR NAME/
NUMBERCOLOR LOCATION FIG.
Driver Power Seat Horizontal
Motor Sensor (Premium II/III)BK At Driver Seat N/S
Driver Power Seat Rear Riser
MotorRD At Driver Seat N/S
Driver Power Seat Rear Riser
Motor Sensor (Premium II/III)BK At Driver Seat N/S
Driver Power Seat Recliner
MotorBK At Driver Seat N/S
Driver Power Seat Recliner
Motor Sensor (Premium II/III)BK At Driver Seat N/S
Driver Power Seat Switch
(Midline/Premium)GN At Driver Seat N/S
Driver Rear Power Window
MotorBK In Left Rear Door 28
Driver Rear Power Window
SwitchBL In Left Rear Door 28
Driver Seat Belt Switch At Switch N/S
EGR Solenoid (Diesel) BK Left Front Fender 7, 8
Electric Brake BL Near Junction Block N/S
Electronic Speed Control Servo BK Right Front of Engine Compartment 5
Engine Control Module C1
(Diesel)BK Left Front of Engine 7, 8
Engine Control Module C2
(Diesel)BK Left Front of Engine 7, 8
Engine Coolant Temperature
Sensor (Diesel)BK Top of Engine N/S
Engine Coolant Temperature
Sensor (GAS)BK Front of Engine 9, 13
Engine Oil Pressure Sensor BK Side of Engine 10, 11, 13
EVAP/Purge Solenoid BK Left Front Fender Near Controller
Antilock Brake3
Front Power Outlet RD Center of Instrument Panel 19, 20
Front Washer Pump WT Left Front of Engine Compartment 3, 4
Front Wiper Motor BK Left Side of Cowl 3, 4
Fuel Injector No.1 BK At Injector 7, 9, 13
Fuel Injector No.2 BK At Injector 7, 9, 14, 15
Fuel Injector No.3 BK At Injector 7, 9, 13
Fuel Injector No.4 BK At Injector 7, 9, 14, 15
Fuel Injector No.5 BK At Injector 9, 13
Fuel Injector No.6 BK At Injector 9, 14, 15
Fuel Injector No.7 (4.7L) BK At Injector 13
Fuel Injector No.8 (4.7L) BK At Injector 14, 15
Fuel Pressure Sensor (Diesel) BK Right Front of Engine N/S
Fuel Pressure Solenoid
(Diesel)BK Top of Engine N/S
WJ8W-91 CONNECTOR/GROUND/SPLICE LOCATION 8W - 91 - 5
CONNECTOR/GROUND/SPLICE LOCATION (Continued)
Page 1226 of 2199

8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTION
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
POWER DISTRIBUTION
DESCRIPTION..........................1
OPERATION............................1
SPECIAL TOOLS
POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS.........2
CIGAR LIGHTER OUTLET
DESCRIPTION..........................2
OPERATION............................2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CIGAR LIGHTER
OUTLET.............................2
CIGAR LIGHTER OUTLET DOOR SPRING
REMOVAL.............................3
INSTALLATION..........................3
IOD FUSE
DESCRIPTION..........................3
OPERATION............................4
REMOVAL.............................4
INSTALLATION..........................4
JUNCTION BLOCK
DESCRIPTION..........................5
OPERATION............................5
REMOVAL.............................5
INSTALLATION..........................6
POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER
DESCRIPTION..........................7
OPERATION............................8
REMOVAL.............................8
DISASSEMBLY
POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER
DISASSEMBLY........................9ASSEMBLY
POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER
ASSEMBLY..........................11
INSTALLATION.........................12
POWER OUTLET
DESCRIPTION - FRONT POWER OUTLET....12
OPERATION - FRONT POWER OUTLET......12
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER OUTLET . 12
REMOVAL.............................13
INSTALLATION.........................13
POWER OUTLET RELAY
DESCRIPTION.........................13
OPERATION...........................14
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER OUTLET
RELAY..............................14
REMOVAL.............................15
INSTALLATION.........................15
IOD WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR
DESCRIPTION.........................15
OPERATION...........................15
FUSE COVER
REMOVAL.............................16
INSTALLATION.........................16
REAR POWER OUTLET
DESCRIPTION - REAR POWER OUTLET.....16
OPERATION - REAR POWER OUTLET.......17
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REAR POWER
OUTLET............................17
REMOVAL.............................17
INSTALLATION.........................18
POWER DISTRIBUTION
DESCRIPTION
This group covers the various standard and
optional power distribution components used on this
model. The power distribution system for this vehicle
consists of the following components:
²Power Distribution Center (PDC)
²Junction Block (JB)
²Power Outlets
The power distribution system also incorporates
various types of circuit control and protection fea-
tures, including:
²Automatic resetting circuit breakers
²Blade-type fuses
²Bus bars
²Cartridge fuses²Circuit splice blocks
²Flashers
²Fusible links
²Standard and Micro-Relays
Following are general descriptions of the major
components in the power distribution system. See the
owner's manual in the vehicle glove box for more
information on the features and use of all of the
power distribution system components. Refer to Wir-
ing Diagrams for complete circuit diagrams.
OPERATION
The power distribution system for this vehicle is
designed to provide safe, reliable, and centralized dis-
tribution points for the electrical current required to
operate all of the standard and optional factory-in-
stalled electrical and electronic powertrain, chassis,
safety, security, comfort and convenience systems. At
WJ8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTION 8W - 97 - 1
Page 1230 of 2199

JUNCTION BLOCK
DESCRIPTION
An electrical Junction Block (JB) is concealed
beneath the driver side of the instrument panel in
the passenger compartment of the vehicle (Fig. 3).
The JB combines the functions previously provided
by a separate fuseblock module and relay center. The
JB serves to simplify and centralize numerous elec-
trical components, as well as to distribute electrical
current to many of the accessory systems in the vehi-
cle. It also eliminates the need for numerous splice
connections. The JB houses up to thirty-three blade-
type mini fuses, up to two blade-type automatic
resetting circuit breakers, the electronic combination
flasher, the Daytime Running Lamp (DRL) module
(Canada only) and up to twelve International Stan-
dards Organization (ISO) relays (three standard-type
and nine micro-type). The JB also incorporates an
integral connector and mounting for the Body Con-
trol Module (BCM). The BCM is secured with four
screws directly to the dash panel side of the JB.
Refer toBody Control Modulein Electronic Con-
trol Modules for additional information covering the
BCM.
The molded plastic JB housing has integral mounts
that are secured with two screws and two snap
retainers to the instrument panel steering column
support bracket behind the instrument panel steer-ing column opening cover. The JB is concealed above
the molded plastic instrument panel fuse cover. Inte-
gral latches molded into the fuse cover secure it the
JB, the BCM and the 16-way data link connector tab
of the instrument panel steering column support
bracket. The fuse cover can be pulled downward to
disengage the latches and provide service access to
all of the fuses, relays and wire harness connectors of
the JB. The fuse cover has a fuse puller and spare
fuses secured to its upper surface. Refer toInstru-
ment Panel Fuse Coverin Body for additional ser-
vice information.
The JB unit cannot be repaired and is only ser-
viced as an assembly. If any internal circuit or the JB
housing is faulty or damaged, the entire JB unit
must be replaced. The BCM is available for separate
service replacement.
OPERATION
All of the circuits entering and leaving the Junc-
tion Block (JB) do so through up to five wire harness
connectors, which are connected to the JB through
integral connector receptacles molded into the JB
housing. Internal connection of all of the JB circuits
is accomplished by a printed circuit board. There are
also two separate wire harness connections to con-
nector receptacles that are integral to the BCM.
Refer toJunction Blockin Wiring Diagrams for
additional information and the location of complete
JB circuit diagrams.
REMOVAL
WARNING: DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM
BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL,
STEERING COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL
COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCON-
NECT AND ISOLATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE
(GROUND) CABLE, THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR
THE AIRBAG SYSTEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE
BEFORE PERFORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR
SERVICE. THIS IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DIS-
ABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE
THE PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN
ACCIDENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSI-
BLE PERSONAL INJURY.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the fuse cover from the bottom of the
Junction Block (JB).
(3) Remove the steering column opening cover
from the instrument panel. Refer toSteering Col-
umn Opening Coverin Body for the location of
steering column opening cover removal procedures.
Fig. 3 Junction Block Location
1 - REAR LATCHES
2 - JUNCTION BLOCK AND BODY CONTROL MODULE UNIT
3 - INSTRUMENT PANEL FUSE COVER
4 - SIDE LATCH
5 - FRONT LATCHES
WJ8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTION 8W - 97 - 5
Page 1231 of 2199

(4) Reach behind the JB to disconnect the two
instrument panel wire harness connectors from the
Body Control Module (BCM) connector receptacles
located near the bottom of the JB (Fig. 4).
(5) Reach behind the JB to remove the screw that
secures the instrument panel wire harness bulkhead
connector to the connector receptacle located near the
top of the JB and disconnect the connector.
(6) Disconnect the fused B(+) and the IOD wire
harness connectors from the connector receptacles
located near the bottom of the JB (Fig. 5).
(7) Remove the screws that secure the right and
left body wire harness bulkhead connectors to the
connector receptacles located near the center of the
JB and disconnect the connectors.
(8) Remove the two screws that secure the JB to
the instrument panel steering column support
bracket (Fig. 6).
(9) To disengage the two snap clips that secure the
top of the JB to the instrument panel steering col-
umn support bracket, grasp the bottom of the junc-
tion block firmly with both hands and pull it
downward sharply.
(10) Remove the JB from the instrument panel
steering column support bracket.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: If the Junction Block (JB) is being replaced
with a new unit, be certain to transfer each of the
optional fuses, circuit breakers and relays from thefaulty JB to the proper cavities of the replacement
JB. Refer to Junction Block in Wiring Diagrams for
the location of complete circuit diagrams and cavity
assignments for the JB. The Body Control Module
(BCM) must also be transferred to the new JB.
Refer to Body Control Module in Electronic Control
Modules for the location of the BCM removal and
installation procedures.
(1)
Position the JB into its mounting location on the
instrument panel steering column support bracket.
(2) Align the snap clips at the top of the JB with
the mounting holes in the instrument panel steering
column support bracket.
(3) Grasp the bottom of the JB firmly with both
hands and push it upward sharply to engage the two
snap clips that secure the top of the JB to the instru-
ment panel steering column support bracket.
(4)
Install and tighten the two screws that secure the
JB to the instrument panel steering column support
bracket. Tighten the screws to 2.2 N´m (20 in. lbs.).
Fig. 4 Junction Block Connections
1 - SCREW
2 - JUNCTION BLOCK
3 - BULKHEAD CONNECTOR
4 - BODY CONTROL MODULE
5 - INSTRUMENT PANEL WIRE HARNESS CONNECTORS
Fig. 5 Junction Block Connections
1 - SNAP CLIPS
2 - SCREW
3 - CONNECTOR
4 - LEFT BODY WIRE HARNESS
5 - IOD CONNECTOR
6 - FUSED B+ CONNECTOR
7 - RIGHT BODY WIRE HARNESS
8 - SCREW
9 - CONNECTOR
10 - JUNCTION BLOCK
8W - 97 - 6 8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTIONWJ
JUNCTION BLOCK (Continued)
Page 1240 of 2199

ground at all times. If not OK, repair the open
ground circuit to ground as required.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the steering column opening cover
from the instrument panel. Refer toSteering Col-
umn Opening Coverin Body for the procedure.
(3) The power outlet / cigar lighter relay is located
on the left side of the combination flasher in the
junction block.
(4) Remove the power outlet / cigar lighter relay
from the junction block.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the power outlet / cigar lighter relay in
the proper receptacle in the junction block.
(2) Align the power outlet / cigar lighter relay ter-
minals with the terminal cavities in the junction
block receptacle.
(3) Push in firmly on the power outlet / cigar
lighter relay until the terminals are fully seated in
the terminal cavities in the junction block receptacle.
(4) Install the steering column opening cover onto
the instrument panel. Refer toSteering Column
Opening Coverin Body for the procedure.
(5) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
IOD WIRE HARNESS
CONNECTOR
DESCRIPTION
All vehicles are equipped with an Ignition-Off
Draw (IOD) connector that is located in a molded
connector receptacle on the lower rear surface of the
Junction Block (JB) housing (Fig. 17). The JB is con-
cealed above the molded plastic instrument panel
fuse cover. Integral latches molded into the fuse
cover secure it the JB, the Body Control Module
(BCM) and the 16-way data link connector tab of the
instrument panel steering column support bracket.
The fuse cover can be pulled downward to disengage
the latches and provide service access to all of the
fuses, relays and wire harness connectors of the JB.
Refer toInstrument Panel Fuse Coverin the
index of this service manual for the location of addi-
tional service information covering the fuse cover.
OPERATION
The term ignition-off draw identifies a normal con-
dition where power is being drained from the battery
with the ignition switch in the Off position. The IOD
connector feeds the memory and sleep mode func-
tions for some of the electronic modules in the vehicleas well as various other accessories that require bat-
tery current when the ignition switch is in the Off
position, including the clock.
The IOD connector can be used by the vehicle
owner as a convenient means of reducing battery
depletion when a vehicle is to be stored for periods
not to exceed about twenty days (short-term storage).
Simply disconnect the IOD connector from the JB
receptacle. However, it must be remembered that dis-
connecting the IOD connector will not eliminate IOD,
but only reduce this normal condition. When a vehi-
cle will not be used for more than twenty days, but
less than thirty days, remove the IOD fuse from the
Power Distribution Center (PDC). If a vehicle will be
stored for more than about thirty days, the battery
negative cable should be disconnected to eliminate
normal IOD; and, the battery should be tested and
recharged at regular intervals during the vehicle
storage period to prevent the battery from becoming
discharged or damaged. Refer toIgnition-Off Draw
Fig. 17 Ignition-Off Draw Connector
1 - SNAP CLIPS
2 - SCREW
3 - CONNECTOR
4 - LEFT BODY WIRE HARNESS
5 - IOD CONNECTOR
6 - FUSED B+ CONNECTOR
7 - RIGHT BODY WIRE HARNESS
8 - SCREW
9 - CONNECTOR
10 - JUNCTION BLOCK
WJ8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTION 8W - 97 - 15
POWER OUTLET RELAY (Continued)
Page 1467 of 2199

MAP SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION
On the 4.0L six-cylinder engine the MAP sensor is
mounted to the engine throttle body. On the 4.7L V-8
engine the MAP sensor is mounted to front of the
intake manifold.
DESCRIPTION - 4.7L
The MAP sensor is located on the front of the
intake manifold. An o-ring seals the sensor to the
intake manifold.
OPERATION
The MAP sensor is used as an input to the Power-
train Control Module (PCM). It contains a silicon
based sensing unit to provide data on the manifold
vacuum that draws the air/fuel mixture into the com-
bustion chamber. The PCM requires this information
to determine injector pulse width and spark advance.
When manifold absolute pressure (MAP) equals
Barometric pressure, the pulse width will be at max-
imum.
A 5 volt reference is supplied from the PCM and
returns a voltage signal to the PCM that reflects
manifold pressure. The zero pressure reading is 0.5V
and full scale is 4.5V. For a pressure swing of 0±15
psi, the voltage changes 4.0V. To operate the sensor,
it is supplied a regulated 4.8 to 5.1 volts. Ground is
provided through the low-noise, sensor return circuit
at the PCM.
The MAP sensor input is the number one contrib-
utor to fuel injector pulse width. The most important
function of the MAP sensor is to determine baromet-
ric pressure. The PCM needs to know if the vehicle is
at sea level or at a higher altitude, because the air
density changes with altitude. It will also help to cor-
rect for varying barometric pressure. Barometric
pressure and altitude have a direct inverse correla-
tion; as altitude goes up, barometric goes down. At
key-on, the PCM powers up and looks at MAP volt-
age, and based upon the voltage it sees, it knows the
current barometric pressure (relative to altitude).
Once the engine starts, the PCM looks at the voltage
again, continuously every 12 milliseconds, and com-
pares the current voltage to what it was at key-on.
The difference between current voltage and what it
was at key-on, is manifold vacuum.
During key-on (engine not running) the sensor
reads (updates) barometric pressure. A normal range
can be obtained by monitoring a known good sensor.
As the altitude increases, the air becomes thinner
(less oxygen). If a vehicle is started and driven to avery different altitude than where it was at key-on,
the barometric pressure needs to be updated. Any
time the PCM sees Wide Open Throttle (WOT), based
upon Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) angle and RPM,
it will update barometric pressure in the MAP mem-
ory cell. With periodic updates, the PCM can make
its calculations more effectively.
The PCM uses the MAP sensor input to aid in cal-
culating the following:
²Manifold pressure
²Barometric pressure
²Engine load
²Injector pulse-width
²Spark-advance programs
²Shift-point strategies (certain automatic trans-
missions only)
²Idle speed
²Decel fuel shutoff
The MAP sensor signal is provided from a single
piezoresistive element located in the center of a dia-
phragm. The element and diaphragm are both made
of silicone. As manifold pressure changes, the dia-
phragm moves causing the element to deflect, which
stresses the silicone. When silicone is exposed to
stress, its resistance changes. As manifold vacuum
increases, the MAP sensor input voltage decreases
proportionally. The sensor also contains electronics
that condition the signal and provide temperature
compensation.
The PCM recognizes a decrease in manifold pres-
sure by monitoring a decrease in voltage from the
reading stored in the barometric pressure memory
cell. The MAP sensor is a linear sensor; meaning as
pressure changes, voltage changes proportionately.
The range of voltage output from the sensor is usu-
ally between 4.6 volts at sea level to as low as 0.3
volts at 26 in. of Hg. Barometric pressure is the pres-
sure exerted by the atmosphere upon an object. At
sea level on a standard day, no storm, barometric
pressure is approximately 29.92 in Hg. For every 100
feet of altitude, barometric pressure drops .10 in. Hg.
If a storm goes through it can change barometric
pressure from what should be present for that alti-
tude. You should know what the average pressure
and corresponding barometric pressure is for your
area.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 4.0L
The MAP sensor is mounted to the side of the
throttle body (Fig. 40). An L-shaped rubber fitting is
used to connect the MAP sensor to throttle body (Fig.
31).
(1) Remove air cleaner duct and air resonator box
at throttle body.
14 - 48 FUEL INJECTIONWJ
Page 1491 of 2199

KEY-IN IGNITION SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The key-in ignition switch is concealed within and
integral to the ignition switch, which is mounted on
the steering column. The key-in ignition switch is
actuated by the ignition lock cylinder mechanism,
and is hard wired between a body ground and the
Body Control Module (BCM) through the instrument
panel wire harness.
The key-in ignition switch cannot be adjusted or
repaired and, if faulty or damaged, the entire igni-
tion switch unit must be replaced,(Refer to 19 -
STEERING/COLUMN/LOCK CYLINDER HOUSING
- REMOVAL). For complete circuit diagrams, refer to
Body Control Modulein the Contents of Wiring
Diagrams.
OPERATION
The key-in ignition switch closes a path to ground
for the BCM when the ignition key is inserted in the
ignition lock cylinder, and opens the ground path
when the key is removed from the ignition lock cyl-
inder. The BCM monitors the key-in ignition switch
status through an internal pull-up, then sends the
proper switch status messages to other electronic
modules over the Programmable Communications
Interface (PCI) data bus network. The key-in ignition
switch status is also used by the BCM as an input
for chime warning system operation.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
KEY-IN IGNITION SWITCH
For complete circuit diagrams, refer toBody Con-
trol Modulein the Contents of Wiring Diagrams.
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, REFER TO GROUP 8M - PASSIVE
RESTRAINT SYSTEMS BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY
STEERING WHEEL, STEERING COLUMN, OR
INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS OR
SERVICE. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable. Disconnect the instrument panel wire harness
connector from the key-in ignition switch connector
receptacle on the ignition switch. Check for continu-
ity between the key-in ignition switch sense and
ground terminals of the key-in ignition switch con-
nector receptacle. There should be continuity with
the key inserted in the ignition lock cylinder, and no
continuity with the key removed from the ignition
lock cylinder. If OK, go to Step 2. If not OK, replace
the faulty ignition switch unit.
(2) Check for continuity between the ground cir-
cuit cavity of the instrument panel wire harness con-
nector for the key-in ignition switch and a good
ground. There should be continuity. If OK, go to Step
3. If not OK, repair the open ground circuit to ground
as required.
(3) Disconnect the gray 26-way instrument panel
wire harness connector from the Body Control Mod-
ule (BCM) connector receptacle. Check for continuity
between the key-in ignition switch sense circuit cav-
ity of the instrument panel wire harness connector
for the key-in ignition switch and a good ground.
There should be no continuity. If OK, go to Step 4. If
not OK, repair the shorted key-in ignition switch
sense circuit as required.
(4) Check for continuity between the key-in igni-
tion switch sense circuit cavities of the instrument
panel wire harness connector for the key-in ignition
switch and the gray 26-way instrument panel wire
harness connector for the BCM. There should be con-
tinuity. If OK, use a DRB scan tool and the proper
Diagnostic Procedures manual to test the BCM. If
not OK, repair the open key-in ignition switch sense
circuit as required.
LOCK CYLINDER
REMOVAL
The ignition key must be in the key cylinder for
cylinder removal. The key cylinder must be removed
first before removing ignition switch.
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable at battery.
(2) If equipped with an automatic transmission,
place shifter in PARK position.
(3) Rotate key to ON position.
19 - 14 COLUMNWJ
Page 1522 of 2199

STANDARD PROCEDURE - TORQUE
CONVERTER DRAINBACK VALVE........134
TRANSMISSION TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................134
OPERATION..........................134
VALVE BODY
DESCRIPTION........................135
OPERATION..........................139REMOVAL............................154
DISASSEMBLY........................155
CLEANING...........................165
INSPECTION.........................166
ASSEMBLY...........................167
INSTALLATION........................175
ADJUSTMENTS - VALVE BODY...........175
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION -
42RE
DESCRIPTION
The 42RE is a four speed fully automatic transmis-
sion (Fig. 1) with an electronic governor. The 42RE is
equipped with a lock-up clutch in the torque con-
verter. First through third gear ranges are provided
by the clutches, bands, overrunning clutch, and plan-
etary gear sets in the transmission. Fourth gear
range is provided by the overdrive unit that contains
an overdrive clutch, direct clutch, planetary gear set,
and overrunning clutch.The transmission contains a front, rear, and direct
clutch which function as the input driving compo-
nents. It also contains the kickdown (front) and the
low/reverse (rear) bands which, along with the over-
running clutch and overdrive clutch, serve as the
holding components. The driving and holding compo-
nents combine to select the necessary planetary gear
components, in the front, rear, or overdrive planetary
gear set, transfer the engine power from the input
shaft through to the output shaft.
The valve body is mounted to the lower side of the
transmission and contains the valves to control pres-
sure regulation, fluid flow control, and clutch/band
application. The oil pump is mounted at the front of
the transmission and is driven by the torque con-
verter hub. The pump supplies the oil pressure nec-
essary for clutch/band actuation and transmission
lubrication.
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 42RE 21 - 3