electrical circuit JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.G User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 299 of 2199

The two remote radio switch units share a common
steering wheel wire harness with the vehicle speed
control switches. The steering wheel wire harness is
connected to the instrument panel wire harness
through the clockspring. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
RESTRAINTS/CLOCKSPRING - DESCRIPTION) for
more information on this component.
For complete circuit diagrams, refer to the appro-
priate wiring information. The wiring information
includes wiring diagrams, proper wire and connector
repair procedures, details of wire harness routing
and retention, connector pin-out information and
location views for the various wire harness connec-
tors, splices and grounds.
OPERATION
The six switches in the two remote radio switch
units are normally open, resistor multiplexed
momentary switches that are hard wired to the Body
Control Module (BCM) through the clockspring. The
BCM sends a five volt reference signal to both switch
units on one circuit, and senses the status of all of
the switches by reading the voltage drop on a second
circuit.
When the BCM senses an input (voltage drop) from
any one of the remote radio switches, it sends the
proper switch status messages on the ProgrammableCommunication Interface (PCI) data bus network to
the radio receiver. The electronic circuitry within the
radio receiver is programmed to respond to these
remote radio switch status messages by adjusting the
radio settings as requested. For diagnosis of the
BCM or the PCI data bus, the use of a DRB scan tool
and the proper Diagnostic Procedures manual are
recommended.
For more information on the features and control
functions for each of the remote radio switches, see
the owner's manual in the vehicle glove box.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REMOTE
SWITCHES
Any diagnosis of the Audio system should
begin with the use of the DRB IIItdiagnostic
tool. For information on the use of the DRB
IIIt, refer to the appropriate Diagnostic Service
Manual.
For complete circuit diagrams, refer to the appro-
priate wiring information. The wiring information
includes wiring diagrams, proper wire and connector
repair procedures, details of wire harness routing
and retention, connector pin-out information and
location views for the various wire harness connec-
tors, splices and grounds.
WARNING: DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM
BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL,
STEERING COLUMN, SEAT BELT TENSIONER, SIDE
AIRBAG, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable. Remove the remote radio switch(es) (Fig. 16)
from the steering wheel.
(2) Use an ohmmeter to check the switch resis-
tances as shown in the Remote Radio Switch Test
chart. If the remote radio switch resistances check
OK, go to Step 3. If not OK, replace the faulty
switch.
Fig. 15 Remote Radio Switches
1 - PRESET ADVANCE
2 - SEEK
3 - MODE ADVANCE
4 - VOLUME
8A - 20 AUDIOWJ
REMOTE SWITCHES (Continued)
Page 300 of 2199

Remote Radio Switch Test
Switch Switch Position Resistance
Right
(White)Volume Up 1.210 Kilohms
Right
(White)Volume Down 3.010 Kilohms
Right
(White)Mode Advance 0.0511 Kilohms
Left
(Black)Seek Up 0.261 Kilohms
Left
(Black)Seek Down 0.681 Kilohms
Left
(Black)Pre-Set Station
Advance0.162 Kilohms
(3) Reconnect the battery negative cable. Turn the
ignition switch to the On position. Check for 5 volts
at the radio control mux circuit cavities of the steer-
ing wheel wire harness connectors for both remote
radio switches. If OK, go to Step 4. If not OK, repair
the open or shorted radio control mux circuit to the
Body Control Module (BCM) as required.
(4) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable. Disconnect the 22-way instrument panel wire
harness connector from the BCM. Check for continu-
ity between the remote radio switch ground circuit
cavities of the steering wheel wire harness connec-
tors for both remote radio switches and a good
ground. There should be no continuity. If OK, go to
Step 5. If not OK, repair the shorted remote radio
switch ground circuit to the BCM as required.(5) Check for continuity between the remote radio
switch ground circuit cavities of the steering wheel
wire harness connectors for both remote radio
switches and the 22-way instrument panel wire har-
ness connector for the BCM. There should be conti-
nuity. If OK, refer to the proper Diagnostic
Procedures manual to test the BCM and the PCI
data bus. If not OK, repair the open remote radio
switch ground circuit as required.
REMOVAL
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, REFER TO ELECTRICAL, RESTRAINTS
BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL,
STEERING COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL
COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. FAILURE
TO TAKE THE PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD
RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT
AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL INJURY.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the driver side airbag from the steer-
ing wheel. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RESTRAINTS/
DRIVER AIRBAG - REMOVAL) for the procedures.
(3) Remove the speed control switch located on the
same side of the steering wheel as the remote radio
switch that is being serviced. Refer to Electrical,
Speed Control for the procedures.
(4) Disconnect the steering wheel wire harness
connector from the connector receptacle of the remote
radio switch (Fig. 17).
(5) From the inside of the steering wheel rear trim
cover, press firmly and evenly outward on the back of
the switch.
(6) From the outside of the steering wheel rear
trim cover, remove the remote radio switch from the
trim cover mounting hole.
INSTALLATION
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, REFER TO ELECTRICAL, RESTRAINTS
BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL,
STEERING COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL
COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. FAILURE
TO TAKE THE PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD
RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT
AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL INJURY.
(1) Position the remote radio switch to the mount-
ing hole on the outside of the steering wheel rear
trim cover. Be certain that the connector receptacle is
oriented toward the bottom of the switch and pointed
toward the center of the steering wheel.
Fig. 16 Remote Radio Switches
1 - BLACK (LEFT) SWITCH
2 - WHITE (RIGHT) SWITCH
WJAUDIO 8A - 21
REMOTE SWITCHES (Continued)
Page 301 of 2199

(2) Press firmly and evenly on the remote radio
switch until each of the switch snap features is fully
engaged in the mounting hole of the steering wheel
rear trim cover.
(3) Reconnect the steering wheel wire harness con-
nector to the connector receptacle of the remote radio
switch.
(4) Install the speed control switch onto the steer-
ing wheel. Refer to Electrical, Speed Control for the
procedures.
(5) Install the driver side airbag onto the steering
wheel. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RESTRAINTS/
DRIVER AIRBAG - INSTALLATION) for the proce-
dures.
(6) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
SPEAKER
DESCRIPTION
STANDARD
The standard equipment speaker system includes
speakers in six locations. One 6.4 centimeter (2.50
inch) diameter tweeter is installed on each end of the
instrument panel top pad. One 15.2 by 22.9 centime-
ter (6 by 9 inch) full-range speaker is located in each
front door. There is also one full-range 16.5 centime-
ter (6.5 inch) diameter full-range speaker located in
each rear door.
PREMIUM
The optional premium speaker system features six
Infinity model speakers in six locations. Each of the
standard speakers is replaced with Infinity model
speakers. One 6.4 centimeter (2.50 inch) diameter
Infinity tweeter is installed on each end of the
instrument panel top pad. One 15.2 by 22.9 centime-
ter (6 by 9 inch) Infinity woofer is located in each
front door. There is also one full-range 16.5 centime-
ter (6.5 inch) diameter Infinity full-range speaker
located in each rear door. The premium speaker sys-
tem also includes an additional Infinity power ampli-
fier. The total available power of the premium
speaker system is about 180 watts.
OPERATION
STANDARD
Each of the two tweeters and four full-range speak-
ers used in the standard speaker system is driven by
the amplifier that is integral to the factory-installed
radio receiver. For complete circuit diagrams, refer to
the appropriate wiring information. The wiring infor-
mation includes wiring diagrams, proper wire and
connector repair procedures, details of wire harness
routing and retention, connector pin-out information
and location views for the various wire harness con-
nectors, splices and grounds.
PREMIUM
The six Infinity speakers used in the premium
speaker system are all driven by the radio receiver
through an Infinity power amplifier. For complete cir-
cuit diagrams, refer to the appropriate wiring infor-
mation. The wiring information includes wiring
diagrams, proper wire and connector repair proce-
dures, details of wire harness routing and retention,
connector pin-out information and location views for
the various wire harness connectors, splices and
grounds.
Fig. 17 Remote Radio Switches Remove/Install
1 - STEERING WHEEL
2 - SPEED CONTROL SWITCH
3 - SCREW
4 - DRIVER SIDE AIRBAG MODULE
5 - REMOTE RADIO SWITCH
6 - REAR TRIM COVER
8A - 22 AUDIOWJ
REMOTE SWITCHES (Continued)
Page 306 of 2199

CHIME/BUZZER
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
CHIME WARNING SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION..........................1
OPERATION............................1DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CHIME
WARNING SYSTEM.....................3
CHIME WARNING SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION
The chime warning system uses a single chime
tone generator that is integral to the Body Control
Module (BCM) to provide an audible indication of
vehicle conditions that may require the attention of
the vehicle operator (Fig. 1). The chime warning sys-
tem includes the following major components:
²Body Control Module
²Door Ajar Switch
²Headlamp Switch
²Ignition Switch
²Seat Belt SwitchHard wired circuitry connects many of the chime
warning system components to each other through
the electrical system of the vehicle.
If the BCM or the chime tone generator are dam-
aged or faulty, the BCM unit must be replaced.
OPERATION
The chime warning system components operate on
battery voltage received through the Ignition-Off
Draw (IOD) fuse in the Power Distribution Center
(PDC) on a non-switched B(+) circuit so that the sys-
tem may operate regardless of the ignition switch
position.
Fig. 1 Chime Warning System
1 - IGNITION SWITCH
2 - SEAT BELT SWITCH
3 - DOOR AJAR SWITCH4 - HEADLAMP SWITCH
5 - BODY CONTROL MODULE
WJCHIME/BUZZER 8B - 1
Page 312 of 2199

INSTALLATION
(1) Install the module on the mounting pins in the
vehicle.
(2) Reconnect the electrical connector.
(3) Install the two mounting clips for the module
(Fig. 1).
(4) Install the adjustable pedal motor. (Refer to 5 -
BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/PEDAL -
INSTALLATION).
(5) Install the steering column opening cover
(Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/STEER-
ING COLUMN OPENING COVER - INSTALLA-
TION).
(6) Install the cluster bezel (Refer to 23 - BODY/
INSTRUMENT PANEL/CLUSTER BEZEL -
INSTALLATION).
(7) Reconnect the negative battery cable.
BODY CONTROL MODULE
DESCRIPTION
A Body Control Module (BCM) is concealed below
the driver side end of the instrument panel (Fig. 2).
The BCM utilizes integrated circuitry and informa-
tion carried on the Programmable Communications
Interface (PCI) data bus network along with many
hard wired inputs to monitor many sensor and
switch inputs throughout the vehicle. In response to
those inputs, the internal circuitry and programming
of the BCM allow it to control and integrate many
electronic functions and features of the vehiclethrough both hard wired outputs and the transmis-
sion of electronic message outputs to other electronic
modules in the vehicle over the PCI data bus. The
electronic functions and features that the BCM sup-
ports or controls include the following:
The BCM for this model is serviced only as a com-
plete unit. Many of the electronic features in the
vehicle controlled or supported by the BCM are pro-
grammable using either the Electronic Vehicle Infor-
mation Center (EVIC) user interface, or the DRBIIIt
scan tool. In addition, the BCM software is Flash
compatible, which means it can be reprogrammed
using Flash reprogramming procedures. A BCM can
only be repaired by or replaced through an autho-
rized electronic warranty repair station. Refer to the
latest version of the Warranty Policies and Proce-
dures manual for a current listing of authorized elec-
tronic repair stations.OPERATION
The Body Control Module (BCM) is designed to
control and integrate many of the electronic features
and functions of the vehicle. The microprocessor-
based BCM hardware and software monitors many
hard wired switch and sensor inputs as well as those
resources it shares with other electronic modules in
the vehicle through its communication over the PCI
data bus network. The internal programming of the
BCM microprocessor allows the BCM to determine
the tasks it needs to perform and their priorities. The
Fig. 1 ADJUSTABLE PEDALS MODULE
1 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
2 - MODULE MOUNTING BRACKET
3 - BRAKE BOOSTER
4 - ADJUSTABLE PEDALS MOUNTING BRACKET
5 - ADJUSTABLE PEDALS CONTROL MODULE
6 - HOLD DOWN CLIPS
Fig. 2 Body Control Module
1 - JUNCTION BLOCK
2 - SCREWS (4)
3 - BODY CONTROL MODULE
4 - FUSE COVER LOCATOR CHANNELS
5 - FUSE COVER MOUNTING SLOTS
6 - INSTRUMENT PANEL WIRE HARNESS CONNECTORS
WJELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES 8E - 3
ADJUSTABLE PEDALS MODULE (Continued)
Page 315 of 2199

(5) Connect the two instrument panel wire harness
connectors to the BCM.
(6) Reinstall the instrument panel fuse cover to
the bottom of the BCM and JB unit. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/POWER DISTRIBUTION/FUSE
COVER - INSTALLATION).
(7) Connect the battery negative cable.
COMMUNICATION
DESCRIPTION
The Programmable Communication Interface (PCI)
data bus system is a single wire multiplex system
used for vehicle communications. Multiplexing is a
system that enables the transmission of several mes-
sages over a single channel or circuit.
Many of the control modules in a vehicle require
information from the same sensing device. Multiplex-
ing reduces wire harness complexity, sensor current
loads and controller hardware because each sensing
device is connected to only one controller, which
reads and distributes the sensor information to the
other controllers over the data bus. Also, because
each controller on the data bus can access the con-
troller sensor inputs to every other controller on the
data bus, more function and feature capabilities are
possible.
A multiplex system allows the information flowing
between controllers to be monitored using a diagnos-
tic scan tool. This system allows a control module to
broadcast message data out onto the bus where all
other control modules can read the messages that are
being sent. When a module reads a message on the
data bus that it requires, it relays that message to
its microprocessor. Each module ignores the mes-
sages on the data bus that it dosen't recognize.
OPERATION
Data exchange between modules is achieved by
serial transmission of encoded data over a single wire
broadcast network. The PCI data bus messages are
carried over the bus in the form of Variable Pulse
Width Modulated (VPWM) signals. The PCI data bus
speed is an average 10.4 Kilo-bits per second (Kbps).
The voltage network used to transmit messages
requires biasing and termination. Each module on
the PCI data bus system provides its own biasing
and termination. Each module (also referred to as a
node) terminates the bus through a terminating
resistor and a terminating capacitor. The Powertrain
Control Module (PCM) is the only dominant node for
the PCI data bus system.
The PCI bus uses low and high voltage levels to
generate signals. The voltage on the buss varies
between zero and seven and one-half volts. The lowand high voltage levels are generated by means of
variable-pulse width modulation to form signals of
varying length.
When a module is transmitting on the bus, it is
reading the bus at the same time to ensure message
integrity.
Each module is capable of transmitting and receiv-
ing data simultaneously.
The PCI data bus can be monitored using the
DRBIIItscan tool. It is possible for the bus to pass
all DRBIIIttests and still be faulty if the voltage
parameters are all within the specified range and
false messages are being sent.
CONTROLLER ANTILOCK
BRAKE
DESCRIPTION
The Controler Antilock Brake (CAB) is mounted to
the Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) and operates the
ABS system (Fig. 4).
OPERATION
The CAB voltage is supplied by the ignition switch
in the RUN position. The CAB contains dual micro-
processors. A logic block in each microprocessor
receives identical sensor signals. These signals are
processed and compared simultaneously. The CAB
contains a self check program that illuminates the
ABS warning light when a system fault is detected.
Faults are stored in a diagnostic program memory
and are accessible with the DRBIIItscan tool. ABS
faults remain in memory until cleared, or until after
the vehicle is started approximately 50 times. Stored
Fig. 4 Controller Antilock Brakes
1 - HCU
2 - MOTOR
3 - CAB
8E - 6 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESWJ
BODY CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 332 of 2199
ENGINE SYSTEMS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
BATTERY SYSTEM......................... 1
CHARGING.............................. 24STARTING............................... 29
BATTERY SYSTEM
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
BATTERY SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION..........................2
OPERATION............................2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BATTERY
SYSTEM.............................2
CLEANING.............................5
INSPECTION...........................6
SPECIFICATIONS........................6
SPECIAL TOOLS........................7
BATTERY
DESCRIPTION..........................7
OPERATION............................8
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BATTERY.......8
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - BATTERY
CHARGING...........................9
STANDARD PROCEDURE - USING MICRO
420 ELECTRICAL TESTER..............10
STANDARD PROCEDURE - BUILT-IN
INDICATOR TEST.....................11
STANDARD PROCEDURE - OPEN-CIRCUIT
VOLTAGE TEST.......................12
STANDARD PROCEDURE - IGNITION-OFF
DRAW TEST.........................13STANDARD PROCEDURE - CHECKING
BATTERY ELECTROLYTE LEVEL.........14
REMOVAL.............................15
INSTALLATION.........................15
BATTERY HOLDDOWN
DESCRIPTION.........................16
OPERATION...........................16
REMOVAL.............................16
INSTALLATION.........................16
BATTERY CABLE
DESCRIPTION.........................17
OPERATION...........................18
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BATTERY
CABLES............................18
REMOVAL.............................19
INSTALLATION.........................20
BATTERY TRAY
DESCRIPTION.........................21
OPERATION...........................22
REMOVAL.............................22
INSTALLATION.........................23
WJENGINE SYSTEMS 8F - 1
Page 333 of 2199

BATTERY SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION
A single 12-volt battery system is standard factory-
installed equipment on this model. All of the compo-
nents of the battery system are located within the
engine compartment of the vehicle. The service infor-
mation for the battery system in this vehicle covers
the following related components, which are covered
in further detail elsewhere in this service manual:
²Battery- The storage battery provides a reli-
able means of storing a renewable source of electrical
energy within the vehicle.
²Battery Cables- The battery cables connect
the battery terminal posts to the vehicle electrical
system.
²Battery Holddown- The battery holddown
hardware secures the battery in the battery tray in
the engine compartment.
²Battery Tray- The battery tray provides a
secure mounting location in the vehicle for the bat-
tery and an anchor point for the battery holddown
hardware.
For battery system maintenance schedules and jump
starting procedures, see the owner's manual in the vehi-
cle glove box. Optionally, refer to Lubrication and Main-
tenance for the recommended battery maintenance
schedules and for the proper battery jump starting pro-
cedures. While battery charging can be considered a
maintenance procedure, the battery charging procedures
and related information are located in the standard pro-
cedures section of this service manual. This was done
because the battery must be fully-charged before any
battery system diagnosis or testing procedures can be
performed. Refer to Standard procedures for the proper
battery charging procedures.
OPERATION
The battery system is designed to provide a safe,
efficient, reliable and mobile means of delivering and
storing electrical energy. This electrical energy is
required to operate the engine starting system, as
well as to operate many of the other vehicle acces-
sory systems for limited durations while the engine
and/or the charging system are not operating. The
battery system is also designed to provide a reserve
of electrical energy to supplement the charging sys-
tem for short durations while the engine is running
and the electrical current demands of the vehicle
exceed the output of the charging system. In addition
to delivering, and storing electrical energy for the
vehicle, the battery system serves as a capacitor and
voltage stabilizer for the vehicle electrical system. It
absorbs most abnormal or transient voltages caused
by the switching of any of the electrical components
or circuits in the vehicle.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BATTERY SYSTEM
The battery, starting, and charging systems in the
vehicle operate with one another and must be tested
as a complete system. In order for the engine to start
and the battery to maintain its charge properly, all of
the components that are used in these systems must
perform within specifications. It is important that
the battery, starting, and charging systems be thor-
oughly tested and inspected any time a battery needs
to be charged or replaced. The cause of abnormal bat-
tery discharge, overcharging or early battery failure
must be diagnosed and corrected before a battery is
replaced and before a vehicle is returned to service.
The service information for these systems has been
separated within this service manual to make it eas-
ier to locate the specific information you are seeking.
However, when attempting to diagnose any of these
systems, it is important that you keep their interde-
pendency in mind.
The diagnostic procedures used for the battery,
starting, and charging systems include the most
basic conventional diagnostic methods, to the more
sophisticated On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) built into
the Powertrain Control Module (PCM). Use of an
induction-type milliampere ammeter, a volt/ohmme-
ter, a battery charger, a carbon pile rheostat (load
tester) and a 12-volt test lamp may be required. All
OBD-sensed systems are monitored by the PCM.
Each monitored circuit is assigned a Diagnostic Trou-
ble Code (DTC). The PCM will store a DTC in elec-
tronic memory for any failure it detects. Refer to
Charging System for the proper charging system on-
board diagnostic test procedures.
MICRO 420 ELECTRICAL SYSTEM TESTER
The Micro 420 automotive battery tester is
designed to help the dealership technicians diagnose
a defective battery. Follow the instruction manual
supplied with the tester to properly diagnose a vehi-
cle. If the instruction manual is not available refer to
the standard procedure in this section, which
includes the directions for using the Micro 420 elec-
trical system tester.
8F - 2 BATTERY SYSTEMWJ
Page 335 of 2199
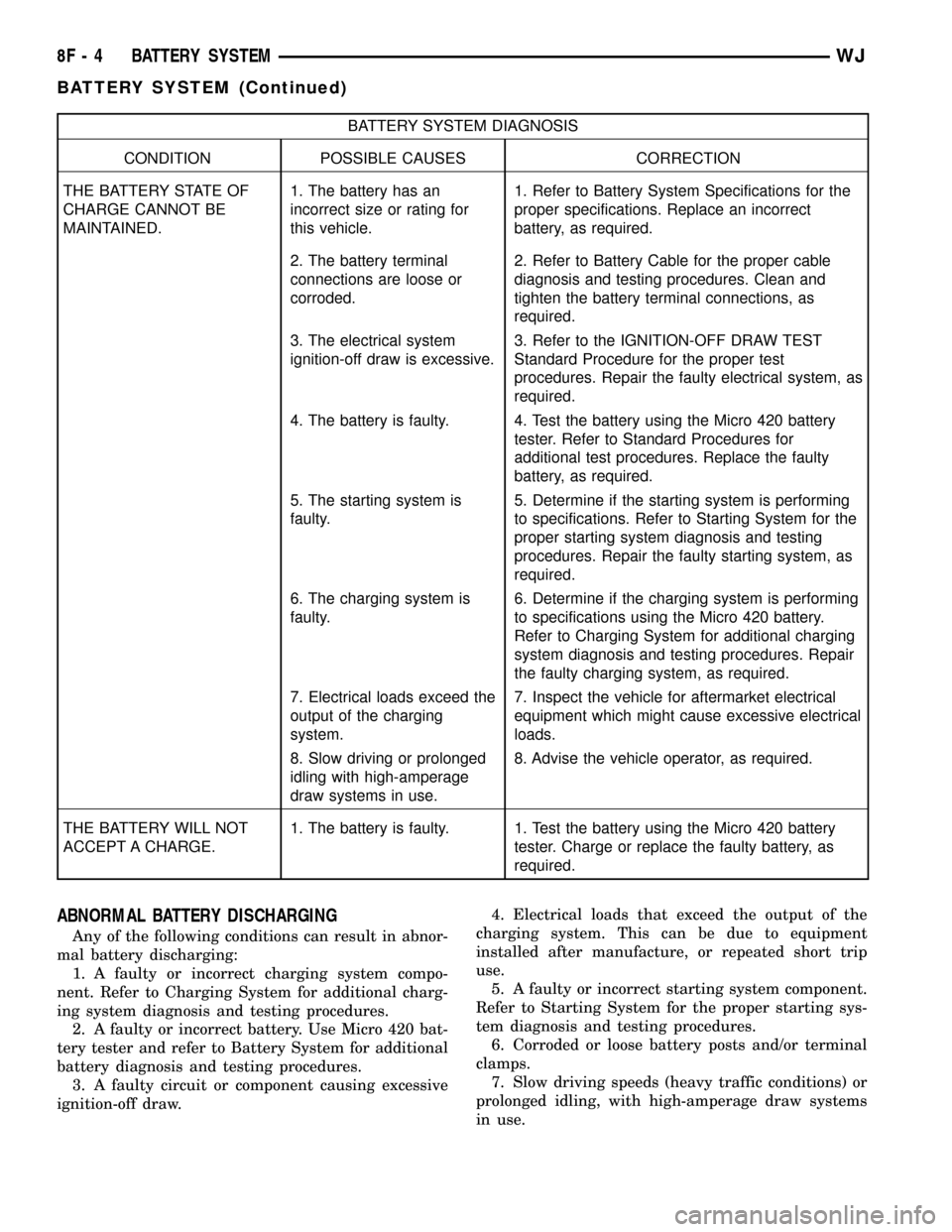
BATTERY SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
THE BATTERY STATE OF
CHARGE CANNOT BE
MAINTAINED.1. The battery has an
incorrect size or rating for
this vehicle.1. Refer to Battery System Specifications for the
proper specifications. Replace an incorrect
battery, as required.
2. The battery terminal
connections are loose or
corroded.2. Refer to Battery Cable for the proper cable
diagnosis and testing procedures. Clean and
tighten the battery terminal connections, as
required.
3. The electrical system
ignition-off draw is excessive.3. Refer to the IGNITION-OFF DRAW TEST
Standard Procedure for the proper test
procedures. Repair the faulty electrical system, as
required.
4. The battery is faulty. 4. Test the battery using the Micro 420 battery
tester. Refer to Standard Procedures for
additional test procedures. Replace the faulty
battery, as required.
5. The starting system is
faulty.5. Determine if the starting system is performing
to specifications. Refer to Starting System for the
proper starting system diagnosis and testing
procedures. Repair the faulty starting system, as
required.
6. The charging system is
faulty.6. Determine if the charging system is performing
to specifications using the Micro 420 battery.
Refer to Charging System for additional charging
system diagnosis and testing procedures. Repair
the faulty charging system, as required.
7. Electrical loads exceed the
output of the charging
system.7. Inspect the vehicle for aftermarket electrical
equipment which might cause excessive electrical
loads.
8. Slow driving or prolonged
idling with high-amperage
draw systems in use.8. Advise the vehicle operator, as required.
THE BATTERY WILL NOT
ACCEPT A CHARGE.1. The battery is faulty. 1. Test the battery using the Micro 420 battery
tester. Charge or replace the faulty battery, as
required.
ABNORMAL BATTERY DISCHARGING
Any of the following conditions can result in abnor-
mal battery discharging:
1. A faulty or incorrect charging system compo-
nent. Refer to Charging System for additional charg-
ing system diagnosis and testing procedures.
2. A faulty or incorrect battery. Use Micro 420 bat-
tery tester and refer to Battery System for additional
battery diagnosis and testing procedures.
3. A faulty circuit or component causing excessive
ignition-off draw.4. Electrical loads that exceed the output of the
charging system. This can be due to equipment
installed after manufacture, or repeated short trip
use.
5. A faulty or incorrect starting system component.
Refer to Starting System for the proper starting sys-
tem diagnosis and testing procedures.
6. Corroded or loose battery posts and/or terminal
clamps.
7. Slow driving speeds (heavy traffic conditions) or
prolonged idling, with high-amperage draw systems
in use.
8F - 4 BATTERY SYSTEMWJ
BATTERY SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 340 of 2199

to determine its cranking capacity. A battery that is
fully-charged, but does not pass the load test, is
faulty and must be replaced.
NOTE: Completely discharged batteries may take
several hours to accept a charge. Refer to Standard
Procedures for the proper battery charging proce-
dures.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - BATTERY
CHARGING
Battery charging is the means by which the bat-
tery can be restored to its full voltage potential. A
battery is fully-charged when:
²Micro 420 electrical system tester indicates bat-
tery is OK.
²All of the battery cells are gassing freely during
battery charging.
²Three hydrometer tests, taken at one-hour inter-
vals, indicate no increase in the temperature-cor-
rected specific gravity of the battery electrolyte.
²Open-circuit voltage of the battery is 12.4 volts
or above.
WARNING: NEVER EXCEED TWENTY AMPERES
WHEN CHARGING A COLD (-1É C [30É F] OR
LOWER) BATTERY. THE BATTERY MAY ARC INTER-
NALLY AND EXPLODE. PERSONAL INJURY AND/OR
VEHICLE DAMAGE MAY RESULT.
WARNING: IF THE BATTERY SHOWS SIGNS OF
FREEZING, LEAKING, LOOSE POSTS, DO NOT
TEST, ASSIST-BOOST, OR CHARGE. THE BATTERY
MAY ARC INTERNALLY AND EXPLODE. PERSONAL
INJURY AND/OR VEHICLE DAMAGE MAY RESULT.
WARNING: EXPLOSIVE HYDROGEN GAS FORMS IN
AND AROUND THE BATTERY. DO NOT SMOKE,
USE FLAME, OR CREATE SPARKS NEAR THE BAT-
TERY. PERSONAL INJURY AND/OR VEHICLE DAM-
AGE MAY RESULT.
WARNING: THE BATTERY CONTAINS SULFURIC
ACID, WHICH IS POISONOUS AND CAUSTIC. AVOID
CONTACT WITH THE SKIN, EYES, OR CLOTHING.
IN THE EVENT OF CONTACT, FLUSH WITH WATER
AND CALL A PHYSICIAN IMMEDIATELY. KEEP OUT
OF THE REACH OF CHILDREN.WARNING: IF THE BATTERY IS EQUIPPED WITH
REMOVABLE CELL CAPS, BE CERTAIN THAT EACH
OF THE CELL CAPS IS IN PLACE AND TIGHT
BEFORE THE BATTERY IS RETURNED TO SER-
VICE. PERSONAL INJURY AND/OR VEHICLE DAM-
AGE MAY RESULT FROM LOOSE OR MISSING
CELL CAPS.
CAUTION: Always disconnect and isolate the bat-
tery negative cable before charging a battery. Do
not exceed sixteen volts while charging a battery.
Damage to the vehicle electrical system compo-
nents may result.
CAUTION: Battery electrolyte will bubble inside the
battery case during normal battery charging. Elec-
trolyte boiling or being discharged from the battery
vents indicates a battery overcharging condition.
Immediately reduce the charging rate or turn off the
charger to evaluate the battery condition. Damage
to the battery may result from overcharging.
CAUTION: The battery should not be hot to the
touch. If the battery feels hot to the touch, turn off
the charger and let the battery cool before continu-
ing the charging operation. Damage to the battery
may result.
After the battery has been charged to 12.4 volts or
greater, perform a load test to determine the battery
cranking capacity. Refer to Standard Procedures for
the proper battery load test procedures. If the battery
will endure a load test, return the battery to service.
If the battery will not endure a load test, it is faulty
and must be replaced.
Clean and inspect the battery hold downs, tray,
terminals, posts, and top before completing battery
service. Refer to Battery System Cleaning for the
proper battery system cleaning procedures, and Bat-
tery System Inspection for the proper battery system
inspection procedures.
CHARGING A COMPLETELY DISCHARGED
BATTERY
The following procedure should be used to recharge
a completely discharged battery. Unless this proce-
dure is properly followed, a good battery may be
needlessly replaced.
(1) Measure the voltage at the battery posts with a
voltmeter, accurate to 1/10 (0.10) volt (Fig. 5). If the
reading is below ten volts, the battery charging cur-
rent will be low. It could take some time before the
battery accepts a current greater than a few milliam-
peres. Such low current may not be detectable on the
ammeters built into many battery chargers.
WJBATTERY SYSTEM 8F - 9
BATTERY (Continued)