turn JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.G User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 53 of 2199

SINGLE CARDAN UNIVERSAL
JOINTS
DISASSEMBLY
NOTE: Individual components of cardan universal
joints are not serviceable. If worn or leaking, they
must be replaced as an assembly.
(1) Remove the propeller shaft.
(2) Tap the outside of the bearing cap assembly
with a drift to loosen snap ring.
(3) Remove snap rings from both sides of yoke
(Fig. 12).
(4) Set the yoke in an arbor press or vise with a
socket whose inside diameter is large enough to
receive the bearing cap positioned beneath the yoke.
(5) Position the yoke with the grease fitting, if
equipped, pointing up.
(6) Place a socket with an outside diameter
smaller than the upper bearing cap on the upper
bearing cap and press the cap through the yoke to
release the lower bearing cap (Fig. 13).
(7) If the bearing cap will not pull out of the yoke
by hand after pressing, tap the yoke ear near the
bearing cap to dislodge the cap.
(8) To remove the opposite bearing cap, turn the
yoke over and straighten the cross in the open hole.
Then, carefully press the end of the cross until the
remaining bearing cap can be removed (Fig. 14).
CAUTION: If the cross or bearing cap are not
straight during installation, the bearing cap willscore the walls of the yoke bore and damage can
occur.
Fig. 12 REMOVE SNAP RING
1 - SNAP RING
Fig. 13 PRESS OUT BEARING
1 - PRESS
2 - SOCKET
Fig. 14 PRESS OUT REMAINING BEARING
1 - CROSS
2 - BEARING CAP
3 - 8 PROPELLER SHAFTWJ
Page 60 of 2199

FRONT AXLE - 186FBI
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
FRONT AXLE - 186FBI
DESCRIPTION.........................15
OPERATION...........................15
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING................16
REMOVAL.............................20
INSTALLATION.........................21
ADJUSTMENTS........................21
SPECIFICATIONS.......................30
SPECIAL TOOLS.......................31
AXLE SHAFTS
REMOVAL.............................34
INSTALLATION.........................34
AXLE SHAFT SEALS
REMOVAL.............................35
INSTALLATION.........................35
AXLE - C/V JOINT
REMOVAL.............................35
INSTALLATION.........................35
AXLE - U-JOINT
REMOVAL.............................36INSTALLATION.........................37
PINION SEAL
REMOVAL.............................37
INSTALLATION.........................37
COLLAPSIBLE SPACER
REMOVAL.............................39
INSTALLATION.........................39
DIFFERENTIAL
REMOVAL.............................40
DISASSEMBLY.........................42
ASSEMBLY............................42
INSTALLATION.........................43
DIFFERENTIAL CASE BEARINGS
REMOVAL.............................44
INSTALLATION.........................44
PINION GEAR/RING GEAR
REMOVAL.............................45
INSTALLATION.........................46
FRONT AXLE - 186FBI
DESCRIPTION
The Front Beam-design Iron (FBI) axle consists of
a cast iron differential housing with axle shaft tubes
extending from either side. The tubes are pressed
into the differential housing and welded. The axles
are semi-floating axle shafts, meaning the loads are
supported by the hub bearings. The axle shafts are
retained by nuts at the hub bearings.
The differential case is a one-piece design. Differ-
ential bearing preload and ring gear backlash is
adjusted by the use of shims located between the dif-
ferential bearing cups and housing. Pinion bearing
preload is set and maintained by the use of a collaps-
ible spacer. A differential cover provides a means for
inspection and servicing.
An optional Vari-Loktdifferential has a one-piece
differential case which contains the gerotor pump
assembly and the clutch mechinism. This unit is ser-
viced as an assembly.
OPERATION
The axle receives power from the transfer case
through the front propeller shaft. The front propeller
shaft is connected to the pinion gear which rotatesthe differential through the gear mesh with the ring
gear bolted to the differential case. The engine power
is transmitted to the axle shafts through the pinion
mate and side gears. The side gears are splined to
the axle shafts.
STANDARD DIFFERENTIAL
During straight-ahead driving, the differential pinion
gears do not rotate on the pinion mate shaft. This
occurs because input torque applied to the gears is
divided and distributed equally between the two side
gears. As a result, the pinion gears revolve with the pin-
ion mate shaft but do not rotate around it (Fig. 1).
When turning corners, the outside wheel must
travel a greater distance than the inside wheel to
complete a turn. The difference must be compensated
for to prevent the tires from scuffing and skidding
through turns. To accomplish this, the differential
allows the axle shafts to turn at unequal speeds (Fig.
2). In this instance, the input torque applied to the
pinion gears is not divided equally. The pinion gears
now rotate around the pinion mate shaft in opposite
directions. This allows the side gear and axle shaft
attached to the outside wheel to rotate at a faster
speed.
WJFRONT AXLE - 186FBI 3 - 15
Page 61 of 2199

VARI-LOKTDIFFERENTIAL
In a standard differential if one wheel spins, the
opposite wheel will generate only as much torque as
the spinning wheel.
A gerotor pump and clutch pack are used to pro-
vide the torque transfer capability. One axle shaft is
splined to the gerotor pump and one of the differen-
tial side gears, which provides the input to the pump.
As a wheel begins to lose traction, the speed differ-
ential is transmitted from one side of the differential
to the other through the side gears. The motion of
one side gear relative to the other turns the inner
rotor of the pump. Since the outer rotor of the pump
is grounded to the differential case, the inner and
outer rotors are now moving relative to each other
and therefore creates pressure in the pump. The tun-ing of the front and rear axle orifices and valves
inside the gerotor pump is unique and each system
includes a torque-limiting pressure relief valve to
protect the clutch pack, which also facilitates vehicle
control under extreme side-to-side traction varia-
tions. The resulting pressure is applied to the clutch
pack and the transfer of torque is completed.
Under conditions in which opposite wheels are on
surfaces with widely different friction characteristics,
Vari-loktdelivers far more torque to the wheel on
the higher traction surface than do conventional
Trac-loktsystems. Because conventional Trac-lokt
differentials are initially pre-loaded to assure torque
transfer, normal driving (where inner and outer
wheel speeds differ during cornering, etc.) produces
torque transfer during even slight side-to-side speed
variations. Since these devices rely on friction from
this preload to transfer torque, normal use tends to
cause wear that reduces the ability of the differential
to transfer torque over time. By design, the Vari-lokt
system is less subject to wear, remaining more con-
sistent over time in its ability to transfer torque. The
coupling assembly is serviced as a unit. From a ser-
vice standpoint the coupling also benefits from using
the same lubricant supply as the ring and pinion
gears.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
GEAR NOISE
Axle gear noise can be caused by insufficient lubri-
cant, incorrect backlash, tooth contact, worn/damaged
gears or the carrier housing not having the proper
offset and squareness.
Gear noise usually happens at a specific speed
range. The noise can also occur during a specific type
of driving condition. These conditions are accelera-
tion, deceleration, coast or constant load.
When road testing, first warm-up the axle fluid by
driving the vehicle at least 5 miles and then acceler-
ate the vehicle to the speed range where the noise is
the greatest. Shift out-of-gear and coast through the
peak-noise range. If the noise stops or changes
greatly:
²Check for insufficient lubricant.
²Incorrect ring gear backlash.
²Gear damage.
Differential side gears and pinions can be checked
by turning the vehicle. They usually do not cause
noise during straight-ahead driving when the gears
are unloaded. The side gears are loaded during vehi-
cle turns. A worn pinion mate shaft can also cause a
snapping or a knocking noise.
Fig. 1 DIFFERENTIAL-STRAIGHT AHEAD DRIVING
1 - IN STRAIGHT AHEAD DRIVING EACH WHEEL ROTATES AT
100% OF CASE SPEED
2 - PINION GEAR
3 - SIDE GEAR
4 - PINION GEARS ROTATE WITH CASE
Fig. 2 DIFFERENTIAL-ON TURNS
1 - PINION GEARS ROTATE ON PINION SHAFT
3 - 16 FRONT AXLE - 186FBIWJ
FRONT AXLE - 186FBI (Continued)
Page 62 of 2199

BEARING NOISE
The axle shaft, differential and pinion bearings can
all produce noise when worn or damaged. Bearing
noise can be either a whining or a growling sound.
Pinion bearings have a constant-pitch noise. This
noise changes only with vehicle speed. Pinion bearing
noise will be higher pitched because it rotates at a
faster rate. Drive the vehicle and load the differen-
tial. If bearing noise occurs, the rear pinion bearing
is the source of the noise. If the bearing noise is
heard during a coast, the front pinion bearing is the
source.
Worn or damaged differential bearings usually pro-
duce a low pitch noise. Differential bearing noise is
similar to pinion bearing noise. The pitch of differen-
tial bearing noise is also constant and varies only
with vehicle speed.
Axle shaft bearings produce noise and vibration
when worn or damaged. The noise generally changes
when the bearings are loaded. Road test the vehicle.
Turn the vehicle sharply to the left and to the right.
This will load the bearings and change the noise
level. Where axle bearing damage is slight, the noise
is usually not noticeable at speeds above 30 mph.
LOW SPEED KNOCK
Low speed knock is generally caused by a worn
U-joint or by worn side-gear thrust washers. A worn
pinion shaft bore will also cause low speed knock.
VIBRATION
Vibration at the rear of the vehicle is usually
caused by a:
²Damaged drive shaft.
²Missing drive shaft balance weight(s).²Worn or out-of-balance wheels.
²Loose wheel lug nuts.
²Worn U-joint(s).
²Loose/broken springs.
²Damaged axle shaft bearing(s).
²Loose pinion gear nut.
²Excessive pinion yoke run out.
²Bent axle shaft(s).
Check for loose or damaged front±end components
or engine/transmission mounts. These components
can contribute to what appears to be a rear-end
vibration. Do not overlook engine accessories, brack-
ets and drive belts.
All driveline components should be examined
before starting any repair.
(Refer to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING)
DRIVELINE SNAP
A snap or clunk noise when the vehicle is shifted
into gear (or the clutch engaged), can be caused by:
²High engine idle speed.
²Transmission shift operation.
²Loose engine/transmission/transfer case mounts.
²Worn U-joints.
²Loose spring mounts.
²Loose pinion gear nut and yoke.
²Excessive ring gear backlash.
²Excessive side gear to case clearance.
The source of a snap or a clunk noise can be deter-
mined with the assistance of a helper. Raise the vehi-
cle on a hoist with the wheels free to rotate. Instruct
the helper to shift the transmission into gear. Listen
for the noise, a mechanics stethoscope is helpful in
isolating the source of a noise.
WJFRONT AXLE - 186FBI 3 - 17
FRONT AXLE - 186FBI (Continued)
Page 73 of 2199
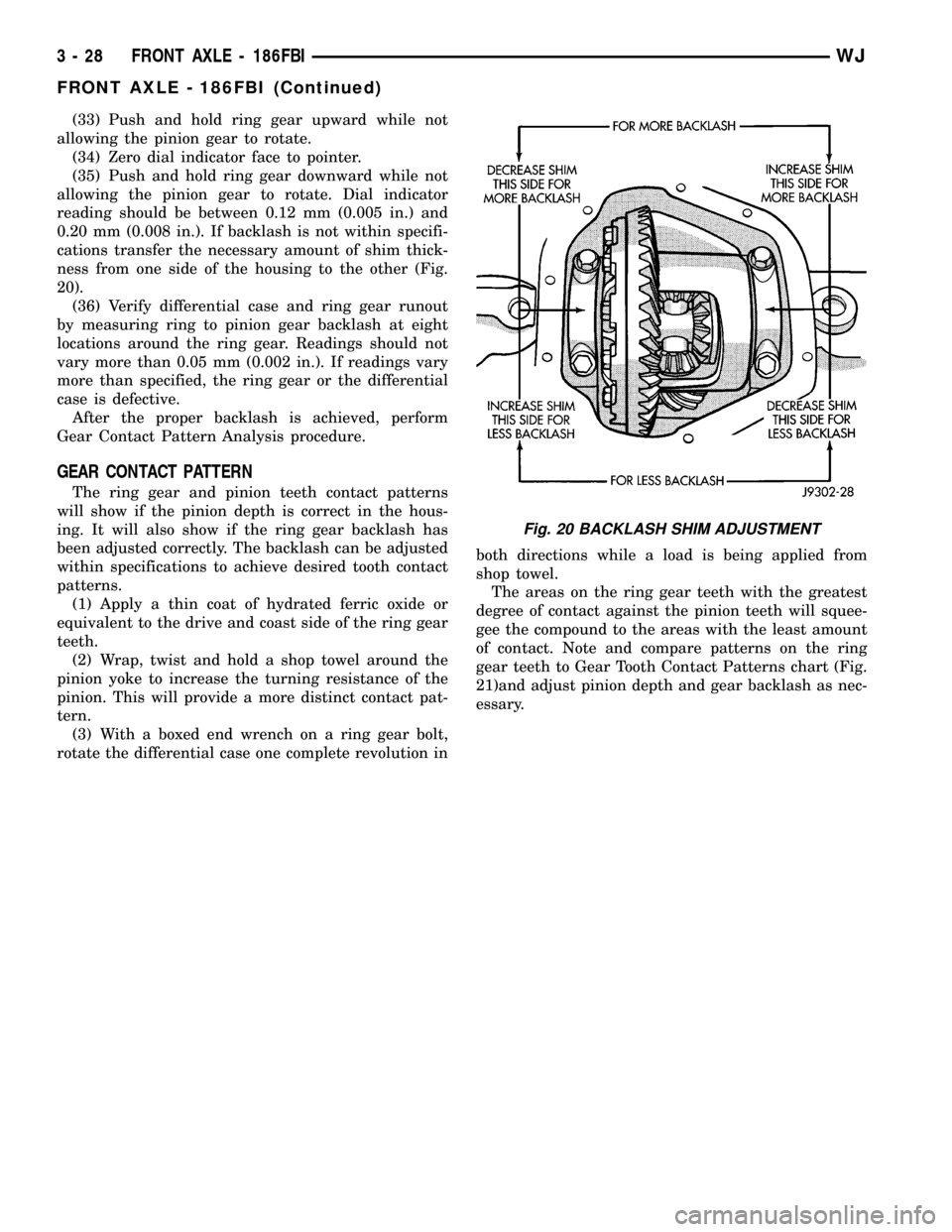
(33) Push and hold ring gear upward while not
allowing the pinion gear to rotate.
(34) Zero dial indicator face to pointer.
(35) Push and hold ring gear downward while not
allowing the pinion gear to rotate. Dial indicator
reading should be between 0.12 mm (0.005 in.) and
0.20 mm (0.008 in.). If backlash is not within specifi-
cations transfer the necessary amount of shim thick-
ness from one side of the housing to the other (Fig.
20).
(36) Verify differential case and ring gear runout
by measuring ring to pinion gear backlash at eight
locations around the ring gear. Readings should not
vary more than 0.05 mm (0.002 in.). If readings vary
more than specified, the ring gear or the differential
case is defective.
After the proper backlash is achieved, perform
Gear Contact Pattern Analysis procedure.
GEAR CONTACT PATTERN
The ring gear and pinion teeth contact patterns
will show if the pinion depth is correct in the hous-
ing. It will also show if the ring gear backlash has
been adjusted correctly. The backlash can be adjusted
within specifications to achieve desired tooth contact
patterns.
(1) Apply a thin coat of hydrated ferric oxide or
equivalent to the drive and coast side of the ring gear
teeth.
(2) Wrap, twist and hold a shop towel around the
pinion yoke to increase the turning resistance of the
pinion. This will provide a more distinct contact pat-
tern.
(3) With a boxed end wrench on a ring gear bolt,
rotate the differential case one complete revolution inboth directions while a load is being applied from
shop towel.
The areas on the ring gear teeth with the greatest
degree of contact against the pinion teeth will squee-
gee the compound to the areas with the least amount
of contact. Note and compare patterns on the ring
gear teeth to Gear Tooth Contact Patterns chart (Fig.
21)and adjust pinion depth and gear backlash as nec-
essary.
Fig. 20 BACKLASH SHIM ADJUSTMENT
3 - 28 FRONT AXLE - 186FBIWJ
FRONT AXLE - 186FBI (Continued)
Page 77 of 2199
INSTALLER W-162-D
CUP 8109
SEAL INSTALLER 8110
TURNBUCKLE 6797
PINION DEPTH SET 6774
DUMMY SHIMS 8107
PINION BLOCK 8804
SEAL REMOVER 7794-A
CLAMP INSTALLER C-4975-A
SPANNER WRENCH 6958
3 - 32 FRONT AXLE - 186FBIWJ
FRONT AXLE - 186FBI (Continued)
Page 80 of 2199

AXLE SHAFT SEALS
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Remove axle shafts.
(3) Remove differential assembly.
(4) Remove inner axle shaft seals with a pry bay.
INSTALLATION
(1) Remove any sealer remaining from original
seals.
(2) Install oil seals with Discs 8110 and Turn-
buckle 6797 (Fig. 24). Tighten tool until disc bottoms
in housing.
(3) Install differential and axle shafts.
(4) Fill differential with lubricant.
(5) Remove support and lower vehicle.
AXLE - C/V JOINT
REMOVAL
NOTE: The only service procedure to be performed
on the axle C/V joint, is the replacement of the joint
seal boot. If any failure of internal axle shaft com-
ponents is diagnosed during a vehicle road test, the
axle shaft must be replaced as an assembly.
(1) Remove axle shaft.
(2) Remove large and small C/V boot clamps (Fig.
25) and discard.
(3) Slid boot off the C/V joint housing and slide it
down the axle shaft.
(4) Remove C/V joint from axle then slid boot off
the axle.
(5) Thoroughly clean and inspect axle C/V joint
assembly and axle shaft for any signs of excessive
wear.
INSTALLATION
(1) Slidenewboot over axle shaft.
(2) Install C/V joint onto the axle shaft.
(3) Distribute 1/2 the amount of grease provided in
seal boot service package(DO NOT USE ANY
OTHER TYPE OF GREASE)into axle C/V joint
assembly housing. Put the remaining amount into
the sealing boot.
(4) Position boot on the axle locating grove and on
the C/V joint.
Fig. 24 AXLE SEAL TOOLS
1 - TURNBUCKLE
2 - DISCS
Fig. 25 OUTER C/V BOOT CLAMPS
1 - C/V JOINT HOUSING
2 - LARGE CLAMP
3 - AXLE SHAFT
4 - SMALL CLAMP
5 - SEALING BOOT
WJFRONT AXLE - 186FBI 3 - 35
Page 85 of 2199

²New Bearings: 1.7 to 3.4 N´m (15 to 30 in. lbs.).
(9) Install propeller shaft with reference marks
aligned.
(10) Install brake rotors and calipers.
(11) Add gear lubricant if necessary.
(12) Install wheel and tire assemblies.
(13) Lower vehicle.
DIFFERENTIAL
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove lubricant fill hole plug from the differ-
ential housing cover.
(3) Remove differential cover and drain lubricant.
(4) Clean the housing cavity with a flushing oil,
light engine oil or lint free cloth.Never use water,
steam, kerosene or gasoline for cleaning.
(5) Remove hub bearings and axle shafts.
(6) Note installation reference letters stamped on
the bearing caps and housing machined sealing sur-
face (Fig. 38).
(7) Loosen the differential bearing cap bolts.
(8) Position Spreader W-129-B with Adapter Kit
6987B on differential locating holes (Fig. 39). Install
hold down clamps and tighten the tool turnbuckle
finger-tight.
Fig. 37 PINION COMPANION FLANGE
1 - COMPANION FLNAGE
2 - DIFFERENTIAL HOUSING
3 - SPANNER WRENCH
Fig. 38 BEARING CAP IDENTIFICATION
1 - REFERENCE LETTERS
2 - REFERENCE LETTERS
Fig. 39 DIFFERENTIAL SPREADER LOCATION
1 - DIFFERENTIAL HOUSING
2 - ADAPTER
3 - HOLD DOWN CLAMPS
4 - SPREADER
5 - TURNBUCKLE
3 - 40 FRONT AXLE - 186FBIWJ
COLLAPSIBLE SPACER (Continued)
Page 88 of 2199

INSTALLATION
NOTE: If replacement differential bearings or differ-
ential case are being installed, differential side
bearing shim requirements may change. Refer to
Adjustments (Differential Bearing Preload and Gear
Backlash) to determine the proper shim selection.
(1) Position Spreader W-129-B with Adapter Kit
6987B on differential locating holes. Install hold
down clamps and tighten the tool turnbuckle finger-
tight.
(2) Install a Pilot Stud C-3288-B at the left side of
the differential housing. Attach Dial Indicator C-3339
to pilot stud. Load the indicator plunger against the
opposite side of the housing and zero the indicator.
(3) Spread the housing enough to install the case
in the housing. Measure the distance with the dial
indicator.
CAUTION: Never spread the housing over 0.50 mm
(0.020 in). If housing is over-spread, it could dis-
torted and damaged the housing.
(4) Remove the dial indicator.
(5) Install differential case in the housing (Fig.
46). Make sure the differential bearing cups remain
on the bearings and the preload shims remain
between the face of the bearing cup and housing. Tap
the differential case to ensure the bearings cups and
shims are fully seated in the housing.
CAUTION: On a Vari-lokTdifferential the oil feed
tube must be pointed at the bottom of the housing.
If differential is installed with the oil feed tube
pointed at the top, the anti-rotation tabs will be
damaged.
(6) Install the bearing caps at their original loca-
tions (Fig. 47).
(7) Loosely install differential bearing cap bolts.
(8) Remove axle housing spreader.
(9) Tighten the bearing cap bolts to 61 N´m (45 ft.
lbs.).
(10) Install the hub bearings and axle shafts.
Fig. 46 DIFFERENTIAL CASE REMOVAL
1 - DIFFERENTIAL HOUSING
2 - DIFFERENTIAL CASE
3 - BEARING CUPS
Fig. 47 Bearing Cap Reference
1 - REFERENCE LETTERS
2 - REFERENCE LETTERS
WJFRONT AXLE - 186FBI 3 - 43
DIFFERENTIAL (Continued)
Page 95 of 2199

REAR AXLE - 198RBI
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
REAR AXLE - 198RBI
DESCRIPTION.........................50
OPERATION...........................50
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING................51
REMOVAL.............................55
INSTALLATION.........................56
ADJUSTMENTS........................56
SPECIFICATIONS.......................65
SPECIAL TOOLS.......................66
AXLE SHAFTS
REMOVAL.............................69
INSTALLATION.........................69
AXLE BEARINGS/SEALS
REMOVAL.............................69
INSTALLATION.........................70
PINION SEAL
REMOVAL.............................71
INSTALLATION.........................71
COLLAPSIBLE SPACER
REMOVAL.............................73INSTALLATION.........................73
DIFFERENTIAL
REMOVAL.............................75
DISASSEMBLY.........................77
ASSEMBLY............................77
INSTALLATION.........................77
DIFFERENTIAL-TRAC-LOC
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING................79
DISASSEMBLY.........................79
CLEANING............................82
INSPECTION..........................82
ASSEMBLY............................82
DIFFERENTIAL CASE BEARINGS
REMOVAL.............................83
INSTALLATION.........................84
PINION GEAR/RING GEAR
REMOVAL.............................84
INSTALLATION.........................86
REAR AXLE - 198RBI
DESCRIPTION
The Rear Beam-design Iron (RBI) axle housing has
an iron center casting with axle shaft tubes extend-
ing from either side. The tubes are pressed into and
welded to the differential housing to form a one-piece
axle housing. The axles has semi-floating axle shafts,
meaning that loads are supported by the axle shaft
and bearings. The axle shafts are retained by bearing
retainer plates on the axles which are bolted to
flanges at the outboard end of the axle tubes.
The differential case is a one-piece design. Differ-
ential bearing preload and ring gear backlash is
adjusted by the use of selective spacer shims. Pinion
bearing preload is set and maintained by the use of a
collapsible spacer. A differential cover provides a
means for inspection and service.
Axles with optional Trac-Loktdifferential have a
one-piece differential case, and the same internal
components as a standard differential, plus two
clutch disc packs.
OPERATION
The axle receives power from the transmission/
transfer case through the rear propeller shaft. Therear propeller shaft is connected to the pinion gear
which rotates the differential through the gear mesh
with the ring gear bolted to the differential case. The
engine power is transmitted to the axle shafts
through the pinion mate and side gears. The side
gears are splined to the axle shafts.
STANDARD DIFFERENTIAL
During straight-ahead driving, the differential pin-
ion gears do not rotate on the pinion mate shaft. This
occurs because input torque applied to the gears is
divided and distributed equally between the two side
gears. As a result, the pinion gears revolve with the
pinion mate shaft but do not rotate around it (Fig. 1).
When turning corners, the outside wheel must
travel a greater distance than the inside wheel to
complete a turn. The difference must be compensated
for to prevent the tires from scuffing and skidding
through turns. To accomplish this, the differential
allows the axle shafts to turn at unequal speeds (Fig.
2). In this instance, the input torque applied to the
pinion gears is not divided equally. The pinion gears
now rotate around the pinion mate shaft in opposite
directions. This allows the side gear and axle shaft
attached to the outside wheel to rotate at a faster
speed.
3 - 50 REAR AXLE - 198RBIWJ