fluid JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 1754 of 2199
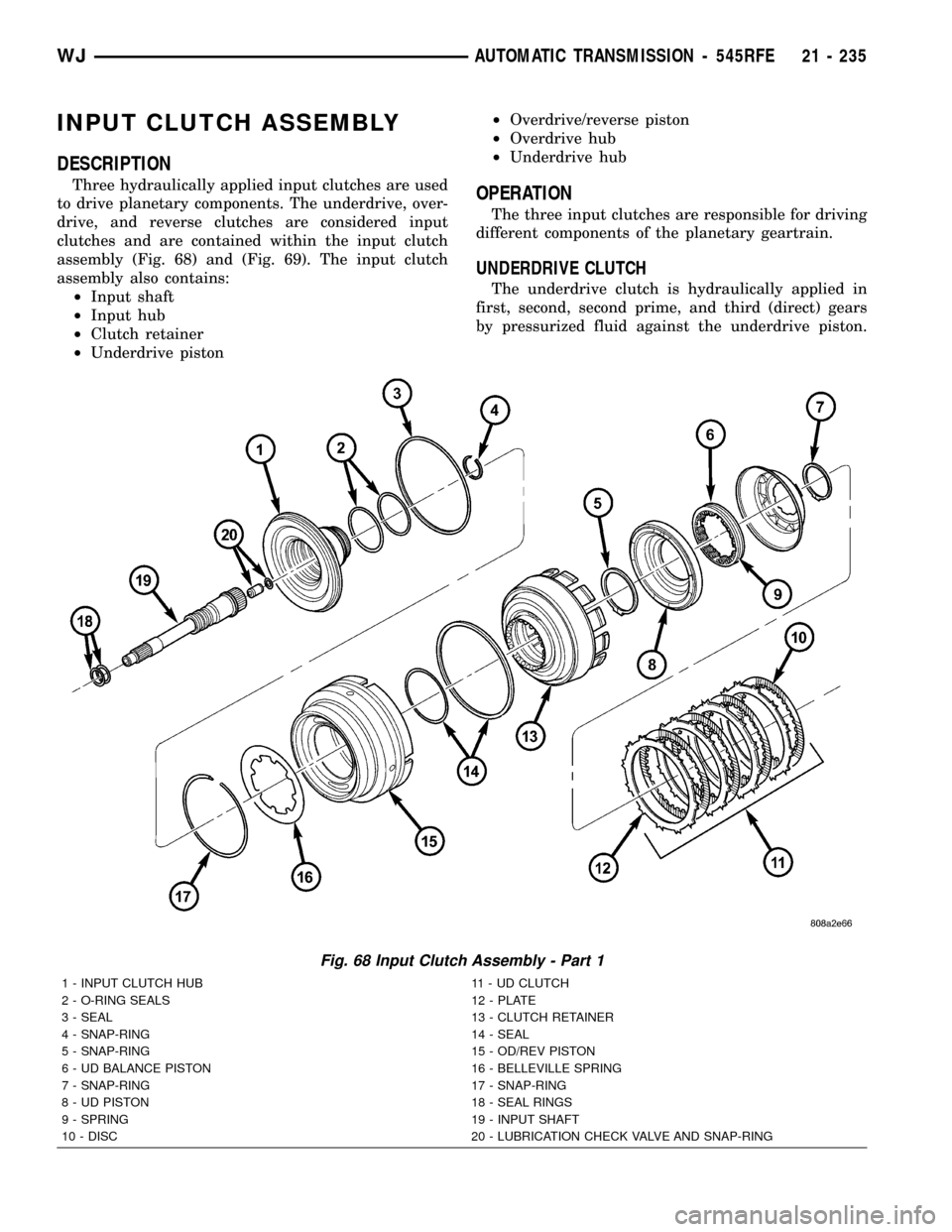
INPUT CLUTCH ASSEMBLY
DESCRIPTION
Three hydraulically applied input clutches are used
to drive planetary components. The underdrive, over-
drive, and reverse clutches are considered input
clutches and are contained within the input clutch
assembly (Fig. 68) and (Fig. 69). The input clutch
assembly also contains:
²Input shaft
²Input hub
²Clutch retainer
²Underdrive piston²Overdrive/reverse piston
²Overdrive hub
²Underdrive hubOPERATION
The three input clutches are responsible for driving
different components of the planetary geartrain.
UNDERDRIVE CLUTCH
The underdrive clutch is hydraulically applied in
first, second, second prime, and third (direct) gears
by pressurized fluid against the underdrive piston.
Fig. 68 Input Clutch Assembly - Part 1
1 - INPUT CLUTCH HUB 11 - UD CLUTCH
2 - O-RING SEALS 12 - PLATE
3 - SEAL 13 - CLUTCH RETAINER
4 - SNAP-RING 14 - SEAL
5 - SNAP-RING 15 - OD/REV PISTON
6 - UD BALANCE PISTON 16 - BELLEVILLE SPRING
7 - SNAP-RING 17 - SNAP-RING
8 - UD PISTON 18 - SEAL RINGS
9 - SPRING 19 - INPUT SHAFT
10 - DISC 20 - LUBRICATION CHECK VALVE AND SNAP-RING
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 235
Page 1755 of 2199
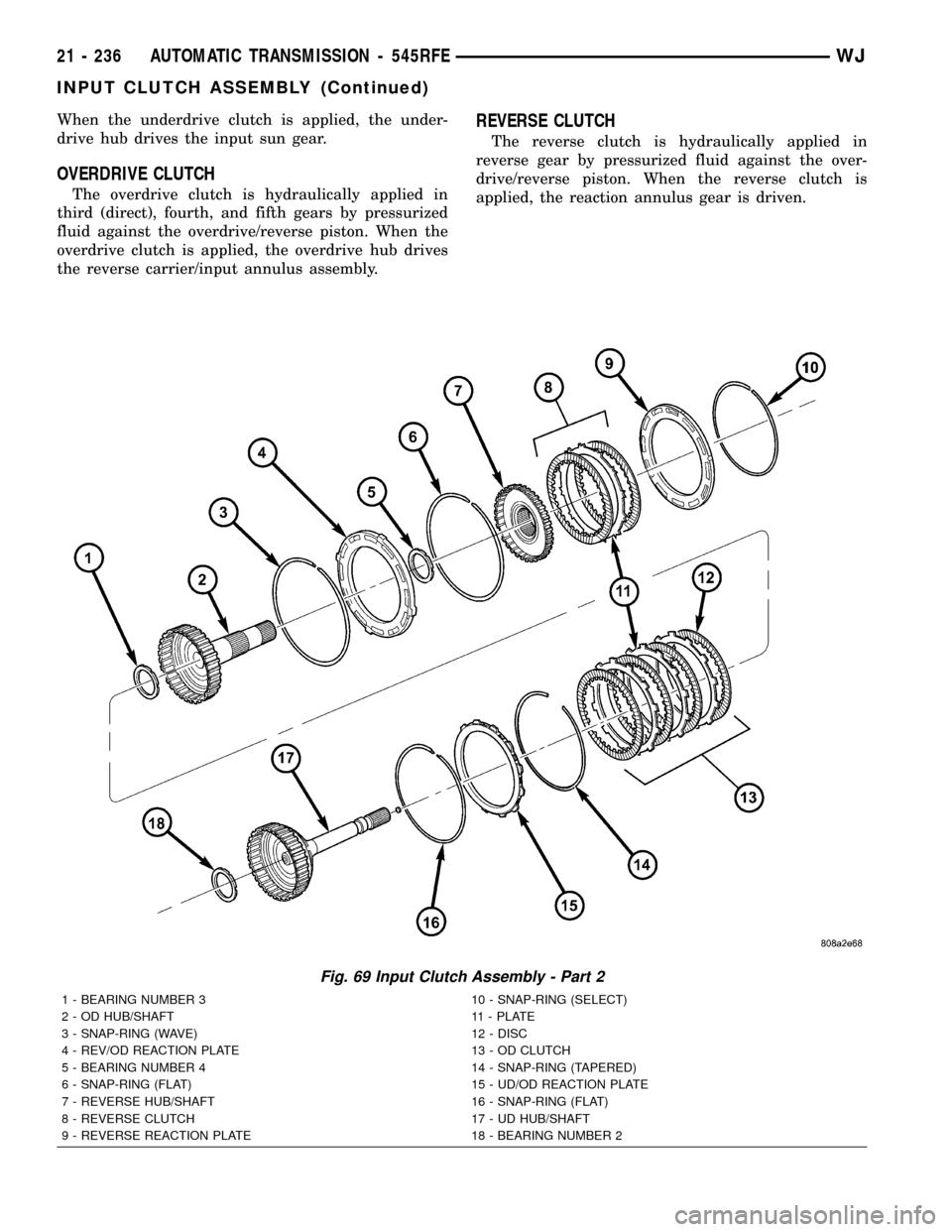
When the underdrive clutch is applied, the under-
drive hub drives the input sun gear.
OVERDRIVE CLUTCH
The overdrive clutch is hydraulically applied in
third (direct), fourth, and fifth gears by pressurized
fluid against the overdrive/reverse piston. When the
overdrive clutch is applied, the overdrive hub drives
the reverse carrier/input annulus assembly.
REVERSE CLUTCH
The reverse clutch is hydraulically applied in
reverse gear by pressurized fluid against the over-
drive/reverse piston. When the reverse clutch is
applied, the reaction annulus gear is driven.
Fig. 69 Input Clutch Assembly - Part 2
1 - BEARING NUMBER 3 10 - SNAP-RING (SELECT)
2 - OD HUB/SHAFT 11 - PLATE
3 - SNAP-RING (WAVE) 12 - DISC
4 - REV/OD REACTION PLATE 13 - OD CLUTCH
5 - BEARING NUMBER 4 14 - SNAP-RING (TAPERED)
6 - SNAP-RING (FLAT) 15 - UD/OD REACTION PLATE
7 - REVERSE HUB/SHAFT 16 - SNAP-RING (FLAT)
8 - REVERSE CLUTCH 17 - UD HUB/SHAFT
9 - REVERSE REACTION PLATE 18 - BEARING NUMBER 2
21 - 236 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFEWJ
INPUT CLUTCH ASSEMBLY (Continued)
Page 1763 of 2199

(23) Install the reverse clutch pack into the input
clutch retainer (Fig. 77).
(24) Install the reverse reaction plate into the
input clutch retainer.
(25) Install the reverse reaction plate selective
snap-ring into the input clutch retainer.
(26) Mount a dial indicator to the assembly, push
down on the clutch discs, pull up on the reaction
plate to ensure the plate is properly seated and zero
the indicator against the reverse clutch discs (Fig.
81). Apply 20 psi of air pressure to the reverse clutch
and record the dial indicator reading. Measure and
record Reverse clutch pack measurement in four (4)
places, 90É apart. Take average of four measurements
and compare with Reverse clutch pack clearance
specification. The correct clutch clearance is 0.58-1.47
mm (0.023-0.058 in.). Adjust as necessary. Install the
chosen snap-ring and re-measure to verify selection.
(27) Remove the reverse clutch pack from the
input clutch retainer.
(28) Install the number 2 bearing onto the under-
drive hub with outer race against the hub with petro-
leum jelly.
(29) Install the underdrive hub into the input
clutch retainer.
(30) Install the number 3 bearing into the over-
drive hub with the outer race against the hub with
petroleum jelly.
(31) Install the overdrive hub into the input clutch
retainer.
(32) Install the number 4 bearing into the reverse
hub with outer race against the hub with petroleum
jelly.(33) Install the reverse hub into the input clutch
retainer.
(34) Install the complete reverse clutch pack.
(35) Install the reverse reaction plate and snap-
ring.
(36) Push up on reaction plate to allow reverse
clutch to move freely.
INPUT SPEED SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The Input and Output Speed Sensors are two-wire
magnetic pickup devices that generate AC signals as
rotation occurs. They are mounted in the left side of
the transmission case and are considered primary
inputs to the Transmission Control Module (TCM).
OPERATION
The Input Speed Sensor provides information on
how fast the input shaft is rotating. As the teeth of
the input clutch hub pass by the sensor coil, an AC
voltage is generated and sent to the TCM. The TCM
interprets this information as input shaft rpm.
The Output Speed Sensor generates an AC signal
in a similar fashion, though its coil is excited by rota-
tion of the rear planetary carrier lugs. The TCM
interprets this information as output shaft rpm.
The TCM compares the input and output speed
signals to determine the following:
²Transmission gear ratio
²Speed ratio error detection
²CVI calculation
The TCM also compares the input speed signal and
the engine speed signal to determine the following:
²Torque converter clutch slippage
²Torque converter element speed ratio
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle.
(2) Place a suitable fluid catch pan under the
transmission.
(3) Remove the wiring connector from the input
speed sensor (Fig. 82).
(4) Remove the bolt holding the input speed sensor
to the transmission case.
(5) Remove the input speed sensor from the trans-
mission case.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the input speed sensor into the trans-
mission case.
(2) Install the bolt to hold the input speed sensor
into the transmission case. Tighten the bolt to 11.9
N´m (105 in.lbs.).
Fig. 81 Measuring Reverse Clutch Clearance
1 - TOOL C-3339
2 - REVERSE CLUTCH PACK
21 - 244 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFEWJ
INPUT CLUTCH ASSEMBLY (Continued)
Page 1764 of 2199

(3) Install the wiring connector onto the input
speed sensor
(4) Verify the transmission fluid level. Add fluid as
necessary.
(5) Lower vehicle.
LINE PRESSURE (LP) SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The TCM utilizes a closed-loop system to control
transmission line pressure. The system contains a
variable force style solenoid, the Pressure Control
Solenoid, mounted on the side of the solenoid and
pressure switch assembly. The solenoid is duty cycle
controlled by the TCM to vent the unnecessary line
pressure supplied by the oil pump back to the sump.
The system also contains a variable pressure style
sensor, the Line Pressure Sensor, which is a direct
input to the TCM. The line pressure solenoid moni-
tors the transmission line pressure and completes the
feedback loop to the TCM. The TCM uses this infor-
mation to adjust its control of the pressure control
solenoid to achieve the desired line pressure.
OPERATION
The TCM calculates the desired line pressure
based upon inputs from the transmission and engine.
The TCM calculates the torque input to the trans-
mission and uses that information as the primary
input to the calculation. The line pressure is set to a
predetermined value during shifts and when the
transmission is in the PARK and NEUTRAL posi-tions. This is done to ensure consistent shift quality.
During all other operation, the actual line pressure is
compared to the desired line pressure and adjust-
ments are made to the pressure control solenoid duty
cycle.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle.
(2) Place a suitable fluid catch pan under the
transmission.
(3) Remove the wiring connector from the line
pressure sensor (Fig. 83).
(4) Remove the bolt holding the line pressure sen-
sor to the transmission case.
(5) Remove the line pressure sensor from the
transmission case.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the line pressure sensor into the trans-
mission case.
(2) Install the bolt to hold the line pressure sensor
into the transmission case. Tighten the bolt to 11.9
N´m (105 in.lbs.).
(3) Install the wiring connector onto the line pres-
sure sensor
(4) Verify the transmission fluid level. Add fluid as
necessary.
(5) Lower vehicle.
Fig. 82 Input Speed Sensor
1 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
2 - LINE PRESSURE SENSOR
3 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR
Fig. 83 Line Pressure Sensor
1 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
2 - LINE PRESSURE SENSOR
3 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 245
INPUT SPEED SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1767 of 2199

OIL PUMP
DESCRIPTION
The oil pump (Fig. 87) is located at the front of the
transmission inside the bell housing and behind the
transmission front cover. The oil pump consists of
two independent pumps (Fig. 88), a number of valves
(Fig. 89), a front seal (Fig. 90), and a bolt on reaction
shaft. The converter clutch switch and regulator
valves, pressure regulator valve, and converter pres-
sure limit valve are all located in the oil pump valve
body.
OPERATION
As the torque converter rotates, the converter hub
rotates the oil pump drive gear. As the drive gear
rotates both driven gears, a vacuum is created when
the gear teeth come out of mesh. This suction draws
fluid through the pump inlet from the oil pan. As the
gear teeth come back into mesh, pressurized fluid is
forced into the pump outlet and to the oil pump
valves.
At low speeds, both sides of the pump supply fluid
to the transmission. As the speed of the torque con-
verter increases, the flow from both sides increases
until the flow from the primary side alone is suffi-
cient to meet system demands. At this point, the
check valve located between the two pumps closes.
The secondary side is shut down and the primary
side supplies all the fluid to the transmission.
CONVERTER CLUTCH SWITCH VALVE
The converter clutch switch valve is used to control
the hydraulic pressure supplied to the front (OFF)
side of the torque converter clutch.
CONVERTER CLUTCH REGULATOR VALVE
The converter clutch regulator valve is used to con-
trol the hydraulic pressure supplied to the back (ON)
side of the torque converter clutch.
TORQUE CONVERTER LIMIT VALVE
The torque converter limit valve serves to limit the
available line pressure to the torque converter clutch
to approximately 120 psi.
Fig. 87 Oil Pump
1 - OIL PUMP TO CASE BOLT (6)
2 - OIL PUMP
Fig. 88 Oil Pump Gears
1 - PUMP HOUSING
2 - DRIVE GEAR
3 - DRIVEN GEARS
Fig. 89 Oil Pump Valves
1 - TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH ACCUMULATOR VALVE
2 - TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH CONTROL VALVE
3 - TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH SWITCH VALVE
4 - PUMP VALVE BODY
5 - PRESSURE REGULATOR VALVE
6 - TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH LIMIT VALVE
21 - 248 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFEWJ
Page 1768 of 2199

STANDARD PROCEDURE - OIL PUMP VOLUME
CHECK
Measuring the oil pump output volume will deter-
mine if sufficient oil flow to the transmission oil
cooler exists, and whether or not an internal trans-
mission failure is present.
Verify that the transmission fluid is at the proper
level. Refer to the Fluid Level Check procedure in
this section. If necessary, fill the transmission to the
proper level with MopartATF +4, type 9602, Auto-
matic Transmission Fluid.
(1) Disconnect theTo coolerline at the cooler
inlet and place a collecting container under the dis-
connected line.CAUTION: With the fluid set at the proper level,
fluid collection should not exceed (1) quart or inter-
nal damage to the transmission may occur.
(2) Run the engineat 1800 rpm, with the shift
selector in neutral. Verify that the transmission fluid
temperature is below 104.5É C (220É F) for this test.
(3) If one quart of transmission fluid is collected in
the container in 30 seconds or less, oil pump flow vol-
ume is within acceptable limits. If fluid flow is inter-
mittent, or it takes more than 30 seconds to collect
one quart of fluid, refer to the Hydraulic Pressure
tests in this section for further diagnosis.
(4) Re-connect theTo coolerline to the transmis-
sion cooler inlet.
Fig. 90 Oil Pump Reaction Shaft
1 - PUMP HOUSING 4 - SEAL RING (5)
2 - SEAL 5 - REACTION SHAFT SUPPORT
3 - OIL FILTER SEAL 6 - PUMP VALVE BODY
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 249
OIL PUMP (Continued)
Page 1773 of 2199

OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The Input and Output Speed Sensors are two-wire
magnetic pickup devices that generate AC signals as
rotation occurs. They are mounted in the left side of
the transmission case and are considered primary
inputs to the Transmission Control Module (TCM).
OPERATION
The Input Speed Sensor provides information on
how fast the input shaft is rotating. As the teeth of
the input clutch hub pass by the sensor coil, an AC
voltage is generated and sent to the TCM. The TCM
interprets this information as input shaft rpm.
The Output Speed Sensor generates an AC signal
in a similar fashion, though its coil is excited by rota-
tion of the rear planetary carrier lugs. The TCM
interprets this information as output shaft rpm.
The TCM compares the input and output speed
signals to determine the following:
²Transmission gear ratio
²Speed ratio error detection
²CVI calculation
The TCM also compares the input speed signal and
the engine speed signal to determine the following:
²Torque converter clutch slippage
²Torque converter element speed ratio
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle.
(2) Place a suitable fluid catch pan under the
transmission.
(3) Remove the wiring connector from the output
speed sensor (Fig. 96).
(4) Remove the bolt holding the output speed sen-
sor to the transmission case.
(5) Remove the output speed sensor from the
transmission case.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the output speed sensor into the trans-
mission case.
(2) Install the bolt to hold the output speed sensor
into the transmission case. Tighten the bolt to 11.9
N´m (105 in.lbs.).
(3) Install the wiring connector onto the output
speed sensor
(4) Verify the transmission fluid level. Add fluid as
necessary.
(5) Lower vehicle.
OVERDRIVE SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The overdrive OFF (control) switch is located in
the shifter handle. The switch is a momentary con-
tact device that signals the PCM to toggle current
status of the overdrive function.
OPERATION
At key-on, fourth and fifth gear operation is
allowed. Pressing the switch once causes the over-
drive OFF mode to be entered and the overdrive OFF
switch lamp to be illuminated. Pressing the switch a
second time causes normal overdrive operation to be
restored and the overdrive lamp to be turned off. The
overdrive OFF mode defaults to ON after the ignition
switch is cycled OFF and ON. The normal position
for the control switch is the ON position. The switch
must be in this position to energize the solenoids and
allow upshifts to fourth and fifth gears. The control
switch indicator light illuminates only when the over-
drive switch is turned to the OFF position, or when
illuminated by the transmission control module.
Fig. 96 Output Speed Sensor
1 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
2 - LINE PRESSURE SENSOR
3 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR
21 - 254 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFEWJ
Page 1775 of 2199
PISTONS
DESCRIPTION
There are several sizes and types of pistons used in
an automatic transmission. Some pistons are used to
apply clutches. They all have in common the fact
that they are round or circular in shape, located
within a smooth walled cylinder, which is closed at
one end and converts fluid pressure into mechanical
movement. The fluid pressure exerted on the piston
is contained within the system through the use of
piston rings or seals.
OPERATION
The principal which makes this operation possible
is known as Pascal's Law. Pascal's Law can be stated
as: ªPressure on a confined fluid is transmitted
equally in all directions and acts with equal force on
equal areas.º
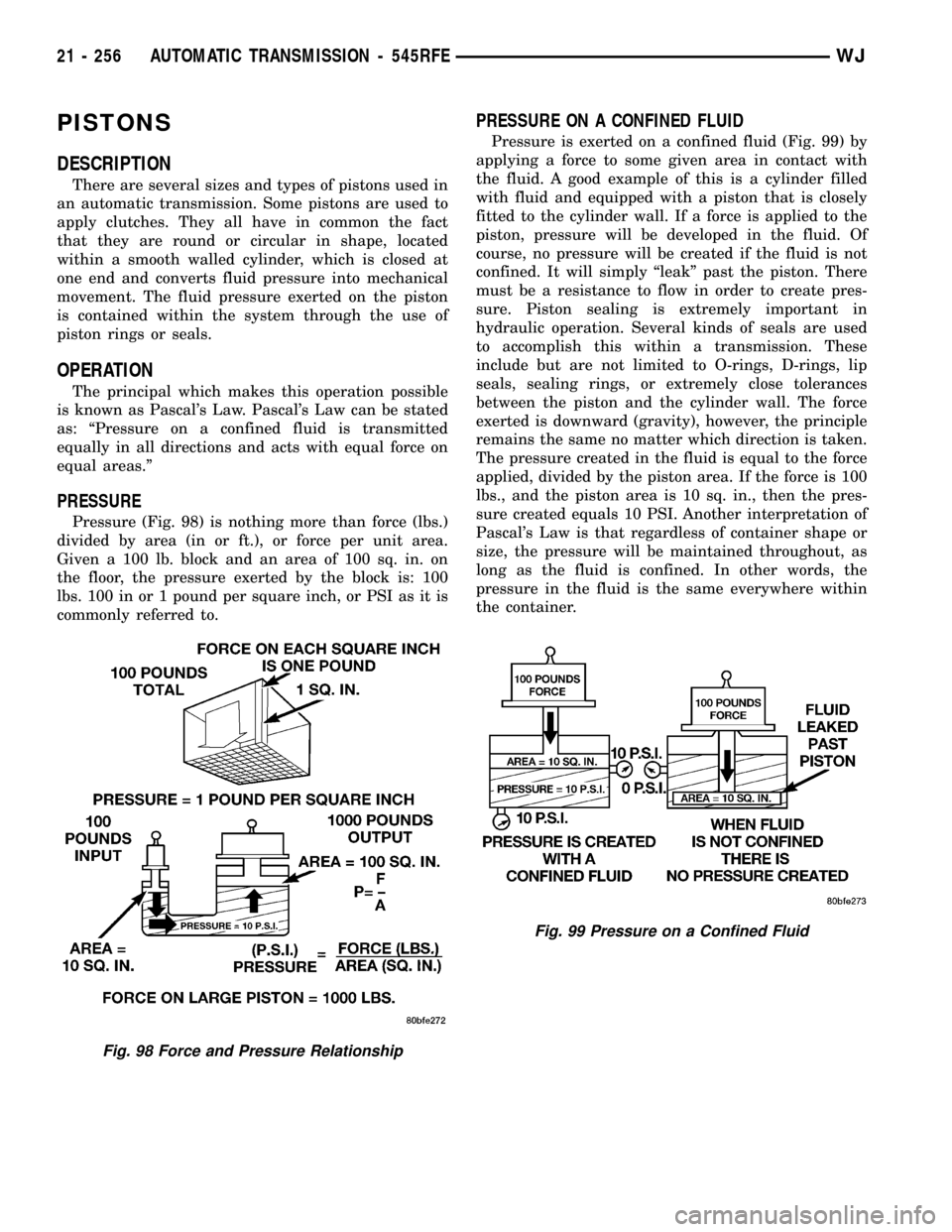
PRESSURE
Pressure (Fig. 98) is nothing more than force (lbs.)
divided by area (in or ft.), or force per unit area.
Given a 100 lb. block and an area of 100 sq. in. on
the floor, the pressure exerted by the block is: 100
lbs. 100 in or 1 pound per square inch, or PSI as it is
commonly referred to.
PRESSURE ON A CONFINED FLUID
Pressure is exerted on a confined fluid (Fig. 99) by
applying a force to some given area in contact with
the fluid. A good example of this is a cylinder filled
with fluid and equipped with a piston that is closely
fitted to the cylinder wall. If a force is applied to the
piston, pressure will be developed in the fluid. Of
course, no pressure will be created if the fluid is not
confined. It will simply ªleakº past the piston. There
must be a resistance to flow in order to create pres-
sure. Piston sealing is extremely important in
hydraulic operation. Several kinds of seals are used
to accomplish this within a transmission. These
include but are not limited to O-rings, D-rings, lip
seals, sealing rings, or extremely close tolerances
between the piston and the cylinder wall. The force
exerted is downward (gravity), however, the principle
remains the same no matter which direction is taken.
The pressure created in the fluid is equal to the force
applied, divided by the piston area. If the force is 100
lbs., and the piston area is 10 sq. in., then the pres-
sure created equals 10 PSI. Another interpretation of
Pascal's Law is that regardless of container shape or
size, the pressure will be maintained throughout, as
long as the fluid is confined. In other words, the
pressure in the fluid is the same everywhere within
the container.
Fig. 98 Force and Pressure Relationship
Fig. 99 Pressure on a Confined Fluid
21 - 256 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFEWJ
Page 1776 of 2199
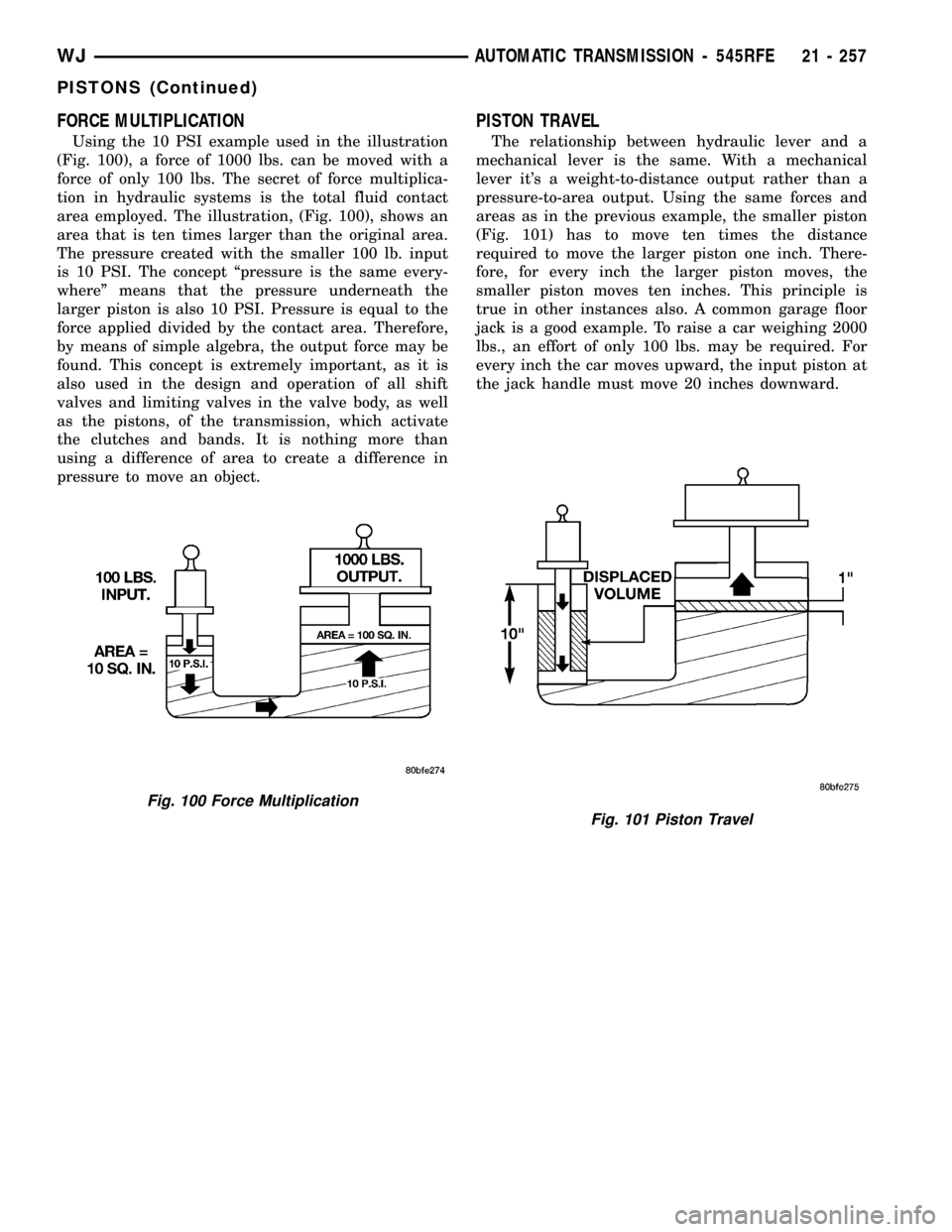
FORCE MULTIPLICATION
Using the 10 PSI example used in the illustration
(Fig. 100), a force of 1000 lbs. can be moved with a
force of only 100 lbs. The secret of force multiplica-
tion in hydraulic systems is the total fluid contact
area employed. The illustration, (Fig. 100), shows an
area that is ten times larger than the original area.
The pressure created with the smaller 100 lb. input
is 10 PSI. The concept ªpressure is the same every-
whereº means that the pressure underneath the
larger piston is also 10 PSI. Pressure is equal to the
force applied divided by the contact area. Therefore,
by means of simple algebra, the output force may be
found. This concept is extremely important, as it is
also used in the design and operation of all shift
valves and limiting valves in the valve body, as well
as the pistons, of the transmission, which activate
the clutches and bands. It is nothing more than
using a difference of area to create a difference in
pressure to move an object.
PISTON TRAVEL
The relationship between hydraulic lever and a
mechanical lever is the same. With a mechanical
lever it's a weight-to-distance output rather than a
pressure-to-area output. Using the same forces and
areas as in the previous example, the smaller piston
(Fig. 101) has to move ten times the distance
required to move the larger piston one inch. There-
fore, for every inch the larger piston moves, the
smaller piston moves ten inches. This principle is
true in other instances also. A common garage floor
jack is a good example. To raise a car weighing 2000
lbs., an effort of only 100 lbs. may be required. For
every inch the car moves upward, the input piston at
the jack handle must move 20 inches downward.
Fig. 100 Force Multiplication
Fig. 101 Piston Travel
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 257
PISTONS (Continued)
Page 1782 of 2199

INSTALLATION
(1) Place the floor shifter lever in PARK position.
(2) Loosen the adjustment screw on the shift cable.
(3) Verify that the park lock cable adjustment tab
is pulled upward to the unlocked position.
(4) Install wiring harness to the shifter assembly
bracket. Engage any wire connectors removed from
the shifter assembly.
(5) Install the transfer case shift cable to the
shifter assembly bracket. Install clip to hold cable to
the bracket.
(6) Snap the transfer case shift cable, if equipped,
onto the transfer case shift lever pin.
(7) Install the park lock cable into the shifter
assembly bracket and into the shifter BTSI lever.(Re-
fer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTO-
MATIC/SHIFT INTERLOCK MECHANISM -
ADJUSTMENTS)
(8) Install the shift cable to the shifter assembly
bracket. Push cable into the bracket until secure.
(9) Install shifter assembly onto the shifter assem-
bly studs on the floor pan.
(10) Install the nuts to hold the shifter assembly
onto the floor pan. Tighten nuts to 28 N´m (250
in.lbs.).
(11) Snap the shift cable onto the shift lever pin.
(12) Verify that the shift lever is in the PARK posi-
tion.
(13) Tighten the adjustment screw to 7 N´m (65
in.lbs.).
(14) Place the key in the accessory position.
(15) Push downward on the park lock cable adjust-
ment tab to lock the adjustment.
(16) Verify correct shifter, park lock, and BTSI
operation.
(17) Install any console parts removed for access to
shift lever assembly and shift cables. (Refer to 23 -
BODY/INTERIOR/FLOOR CONSOLE - INSTALLA-
TION)
SOLENOID SWITCH VALVE
DESCRIPTION
The Solenoid Switch Valve (SSV) is located in the
valve body and controls the direction of the transmis-
sion fluid when the L/R-TCC solenoid is energized.
OPERATION
The Solenoid Switch Valve controls line pressure
from the LR-TCC solenoid. In 1st gear, the SSV will
be in the downshifted position, thus directing fluid to
the L/R clutch circuit. In 2nd, 3rd, 4th,and 5th gears,
the solenoid switch valve will be in the upshifted
position and directs the fluid into the torque con-
verter clutch (TCC) circuit.When shifting into 1st gear, a special hydraulic
sequence is performed to ensure SSV movement into
the downshifted position. The L/R pressure switch is
monitored to confirm SSV movement. If the move-
ment is not confirmed (the L/R pressure switch does
not close), 2nd gear is substituted for 1st. A DTC will
be set after three unsuccessful attempts are made to
get into 1st gear in one given key start.
SOLENOIDS
DESCRIPTION
The typical electrical solenoid used in automotive
applications is a linear actuator. It is a device that
produces motion in a straight line. This straight line
motion can be either forward or backward in direc-
tion, and short or long distance.
A solenoid is an electromechanical device that uses
a magnetic force to perform work. It consists of a coil
of wire, wrapped around a magnetic core made from
steel or iron, and a spring loaded, movable plunger,
which performs the work, or straight line motion.
The solenoids used in transmission applications
are attached to valves which can be classified asnor-
mally openornormally closed. Thenormally
opensolenoid valve is defined as a valve which
allows hydraulic flow when no current or voltage is
applied to the solenoid. Thenormally closedsole-
noid valve is defined as a valve which does not allow
hydraulic flow when no current or voltage is applied
to the solenoid. These valves perform hydraulic con-
trol functions for the transmission and must there-
fore be durable and tolerant of dirt particles. For
these reasons, the valves have hardened steel pop-
pets and ball valves. The solenoids operate the valves
directly, which means that the solenoids must have
very high outputs to close the valves against the siz-
able flow areas and line pressures found in current
transmissions. Fast response time is also necessary
to ensure accurate control of the transmission.
The strength of the magnetic field is the primary
force that determines the speed of operation in a par-
ticular solenoid design. A stronger magnetic field will
cause the plunger to move at a greater speed than a
weaker one. There are basically two ways to increase
the force of the magnetic field:
1. Increase the amount of current applied to the
coil or
2. Increase the number of turns of wire in the coil.
The most common practice is to increase the num-
ber of turns by using thin wire that can completely
fill the available space within the solenoid housing.
The strength of the spring and the length of the
plunger also contribute to the response speed possi-
ble by a particular solenoid design.
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 263
SHIFT MECHANISM (Continued)