Intake temperature sensor JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.G Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 1380 of 2199
(6) Remove accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
(7) Disconnect generator electrical connections.
(8) Unbolt the generator and move it away from
the intake manifold for clearance.
(9) Disconnect air conditioning compressor electri-
cal connections.
(10) Unbolt the air conditioning compressor and
move it away from the intake manifold for clearance.
(11) Disconnect left and right radio suppressor
straps.
(12) Disconnect and remove ignition coil towers
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/IGNITION CONTROL/
IGNITION COIL - REMOVAL).
(13) Remove top oil dipstick tube retaining bolt
and ground strap.
(14) Bleed pressure from fuel system (Refer to 14 -
FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
(15) Remove fuel rail (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYS-
TEM/FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL RAIL - REMOVAL).
(16) Remove throttle body assembly and mounting
bracket.
(17) Drain cooling system below coolant tempera-
ture level (Refer to 7 - COOLING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
(18) Remove coolant temperature sensor (Refer to
7 - COOLING/ENGINE/ENGINE COOLANT TEMP
SENSOR - REMOVAL).
(19) Remove cowl to hood seal. (Refer to 23 -
BODY/WEATHERSTRIP/SEALS/COWL WEATHER-
STRIP - REMOVAL).
(20) Remove right side engine lifting stud.
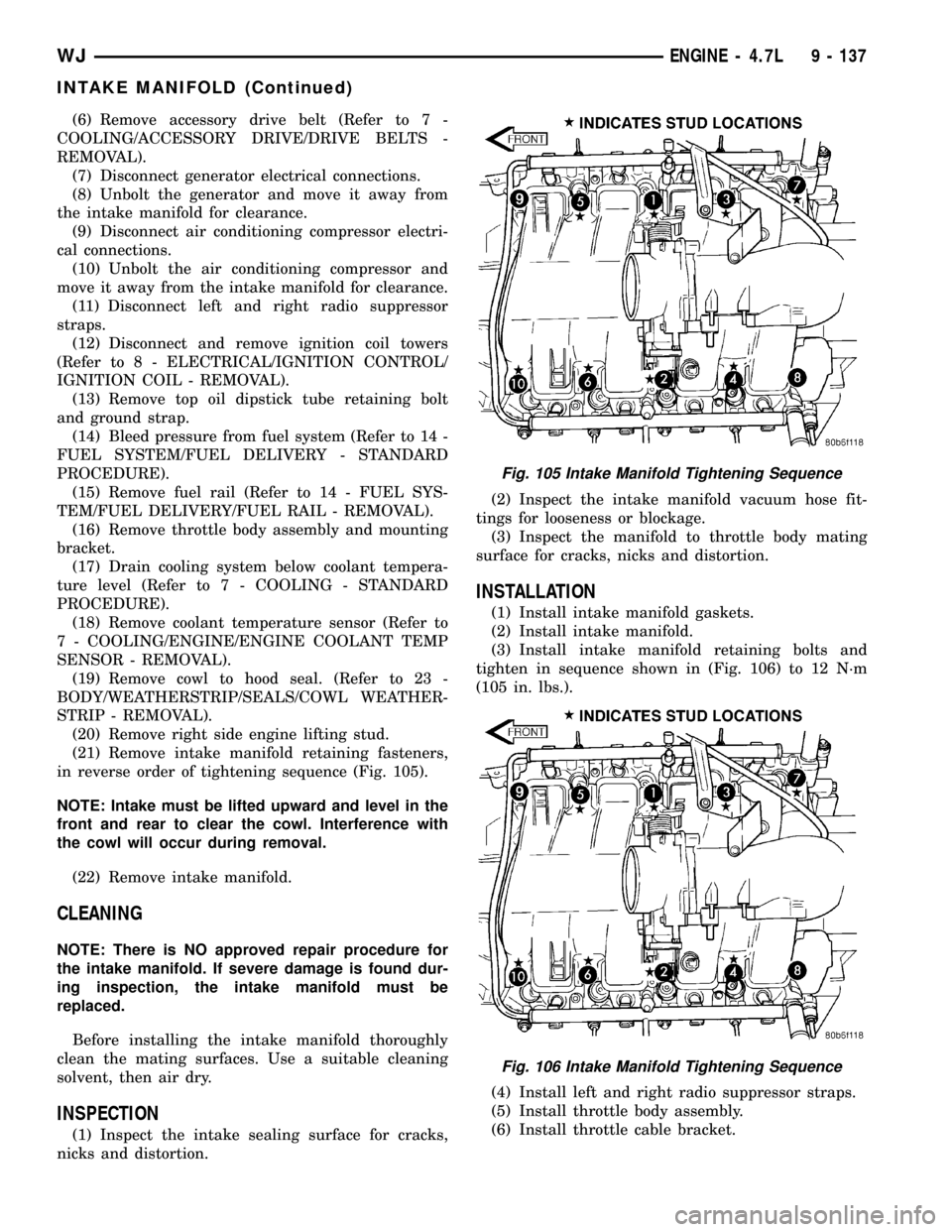
(21) Remove intake manifold retaining fasteners,
in reverse order of tightening sequence (Fig. 105).
NOTE: Intake must be lifted upward and level in the
front and rear to clear the cowl. Interference with
the cowl will occur during removal.
(22) Remove intake manifold.
CLEANING
NOTE: There is NO approved repair procedure for
the intake manifold. If severe damage is found dur-
ing inspection, the intake manifold must be
replaced.
Before installing the intake manifold thoroughly
clean the mating surfaces. Use a suitable cleaning
solvent, then air dry.
INSPECTION
(1) Inspect the intake sealing surface for cracks,
nicks and distortion.(2) Inspect the intake manifold vacuum hose fit-
tings for looseness or blockage.
(3) Inspect the manifold to throttle body mating
surface for cracks, nicks and distortion.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install intake manifold gaskets.
(2) Install intake manifold.
(3) Install intake manifold retaining bolts and
tighten in sequence shown in (Fig. 106) to 12 N´m
(105 in. lbs.).
(4) Install left and right radio suppressor straps.
(5) Install throttle body assembly.
(6) Install throttle cable bracket.
Fig. 105 Intake Manifold Tightening Sequence
Fig. 106 Intake Manifold Tightening Sequence
WJENGINE - 4.7L 9 - 137
INTAKE MANIFOLD (Continued)
Page 1381 of 2199

(7) Connect throttle cable and speed control cable
to throttle body.
(8) Install fuel rail (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/
FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL RAIL - INSTALLATION).
(9) Install ignition coil towers (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION COIL -
INSTALLATION).
(10) Install coolant temperature sensor (Refer to 7
- COOLING/ENGINE/ENGINE COOLANT TEMP
SENSOR - INSTALLATION).
(11) Connect electrical connectors for the following
components:
²Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
²Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
²Throttle Position (TPS) Sensor
²Coolant Temperature (CTS) Sensor
²Idle Air Control (IAC) Motor
²Ignition coil towers
²Fuel injectors
(12) Install top oil dipstick tube retaining bolt and
ground strap.
(13) Install right side engine lifting stud.
(14) Install generator including electrical connec-
tions (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/CHARGING/GEN-
ERATOR - INSTALLATION).
(15) Connect Vapor purge hose, Brake booster
hose, Speed control servo hose, Positive crankcase
ventilation (PCV) hose.
(16) Install air conditioning compressor including
electrical connections.
(17) Fill cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(18) Install accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION).
(19) Install cowl to hood seal (Refer to 23 - BODY/
WEATHERSTRIP/SEALS/COWL WEATHERSTRIP -
INSTALLATION).
(20) Install air cleaner housing and throttle body
resonator. Tighten resonator bolts 4.5 N´m (40 in.
lbs.).
(21) Connect negative cable to battery.
EXHAUST MANIFOLD - LEFT
DESCRIPTION
The exhaust manifolds are log style with a pat-
ented flow enhancing design to maximize perfor-
mance. The exhaust manifolds are made of high
silicon molybdenum cast iron. A perforated core
graphite exhaust manifold gasket is used to improve
sealing to the cylinder head. The exhaust manifolds
are covered by a three layer laminated heat shield
for thermal protection and noise reduction. The heat
shields are fastened with a torque prevailing nutthat is backed off slightly to allow for the thermal
expansion of the exhaust manifold.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable for battery.
(2) Hoist vehicle.
(3) Disconnect exhaust pipe at manifold.
(4) Lower vehicle.
(5) Remove air cleaner housing and tube.
(6) Remove the front two exhaust heat shield
retaining fasteners. Raise vehicle and remove the
fasteners at rear of heat shield.
(7) Remove heat shield (Fig. 107).
(8) Lower vehicle and remove the upper exhaust
manifold retaining bolts (Fig. 107).
(9) Raise vehicle and remove the lower exhaust
manifold retaining bolts (Fig. 107).
(10) Remove exhaust manifold and gasket (Fig.
107). Manifold is removed from below the engine
compartment.
CLEANING
(1) Clean the exhaust manifold using a suitable
cleaning solvent, then allow to air dry.
(2) Clean all gasket residue from the manifold
mating surface.
INSPECTION
(1) Inspect the exhaust manifold for cracks in the
mating surface and at every mounting bolt hole.
(2) Using a straight edge and a feeler gauge, check
the mating surface for warp and twist.
(3) Inspect the manifold to exhaust pipe mating
surface for cracks, gouges, or other damage that
would prevent sealing.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install exhaust manifold and gasket from below
engine compartment.
(2) Install lower exhaust manifold fasteners (Fig.
107). DO NOT tighten until all fasteners are in
place.
(3) Lower vehicle and install upper exhaust mani-
fold fasteners (Fig. 107). Tighten all manifold bolts
starting at center and working outward to 25 N´m
(18 ft. lbs.).
CAUTION: Over tightening heat shield fasteners,
may cause shield to distort and/or crack.
(4) Install exhaust manifold heat shield (Fig. 107).
Tighten fasteners to 8 N´m (72 in. lbs.), then loosen
45 degrees.
(5) Install air cleaner housing and tube.
(6) Connect exhaust pipe to manifold.
(7) Connect negative cable to battery.
9 - 138 ENGINE - 4.7LWJ
INTAKE MANIFOLD (Continued)
Page 1450 of 2199

FUEL INJECTION
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
FUEL INJECTION
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
VISUAL INSPECTION..................32
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE - FUEL INJECTION.............39
ACCELERATOR PEDAL
REMOVAL.............................39
INSTALLATION.........................39
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - 4.0L...................40
DESCRIPTION - 4.7L...................40
OPERATION
OPERATION - 4.0L....................40
OPERATION - 4.7L....................41
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 4.0L......................41
REMOVAL - 4.7L......................41
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 4.0L..................42
INSTALLATION - 4.7L..................43
FUEL INJECTOR
DESCRIPTION.........................43
OPERATION
OPERATION.........................43
OPERATION - PCM OUTPUT............43
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL INJECTOR . 44
REMOVAL.............................44
INSTALLATION.........................44
FUEL PUMP RELAY
DESCRIPTION.........................44
OPERATION...........................44
IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR
DESCRIPTION.........................44
OPERATION...........................44
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 4.0L......................45
REMOVAL - 4.7L......................45
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 4.0L..................46
INSTALLATION - 4.7L..................46
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................46
OPERATION...........................46
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 4.0L......................46
REMOVAL - 4.7L......................46
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 4.0L..................47INSTALLATION - 4.7L..................47
MAP SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION........................48
DESCRIPTION - 4.7L...................48
OPERATION...........................48
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 4.0L......................48
REMOVAL - 4.7L......................49
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 4.0L..................49
INSTALLATION - 4.7L..................49
O2S HEATER RELAY
DESCRIPTION.........................49
OPERATION...........................49
REMOVAL.............................50
INSTALLATION.........................50
O2S SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................50
OPERATION...........................50
REMOVAL.............................51
INSTALLATION.........................51
THROTTLE BODY
DESCRIPTION.........................52
OPERATION...........................52
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 4.0L......................52
REMOVAL - 4.7L......................53
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 4.0L..................53
INSTALLATION - 4.7L..................54
THROTTLE CONTROL CABLE
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 4.0L......................54
REMOVAL - 4.7L......................55
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION ± 4.0L..................55
INSTALLATION - 4.7L..................56
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................56
OPERATION...........................56
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 4.0L......................57
REMOVAL - 4.7L......................57
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 4.0L..................58
INSTALLATION - 4.7L..................58
WJFUEL INJECTION 14 - 31
Page 1453 of 2199

(8) Inspect system body grounds for loose or dirty
connections. Refer to Group 8, Wiring for ground
locations.
(9) Verify crankcase ventilation (CCV) operation.
Refer to Emission Control System for additional
information.
(10) Inspect all fuel line quick-connect fittings for
damage or leaks.
(11) Verify hose connections to all ports of vacuum
fittings on intake manifold, and for emission system
are tight and not leaking.
(12) Inspect accelerator cable, transmission throt-
tle cable (if equipped) and speed control cable connec-
tions (if equipped). Check their connections to
throttle body linkage for any binding or restrictions.
(13) Verify vacuum booster hose is firmly con-
nected to fitting on intake manifold. Also check con-
nection to brake vacuum booster.(14) Inspect air cleaner inlet and air cleaner ele-
ment for dirt or restrictions.
(15) Inspect radiator grille area, radiator fins and
air conditioning condenser for restrictions.
(16) 4.0L Engine: Verify MAP, Intake Manifold Air
Temperature (IAT) sensor, TPS and Idle Air Control
(IAC) motor connectors are firmly connected (Fig. 9).
Be sure throttle body mounting bolts (Fig. 9)are
tight.
(17) 4.7L Engine: Verify Intake Manifold Air Tem-
perature (IAT) sensor, TPS and Idle Air Control (IAC)
motor connectors are firmly connected (Fig. 10). Be
sure throttle body mounting bolts (Fig. 10)are tight.
Fig. 8 Crankshaft Position SensorÐ4.7L V-8 Engine
1 - CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
2-STARTER
3 - ELEC. CONNECTOR
Fig. 9 IAT, MAP, IAC, TPS Sensor LocationsÐ4.0L
Engine
1 - MOUNTING BOLTS (4)
2 - THROTTLE BODY
3 - IAC MOTOR
4 - ELEC. CONN.
5 - TPS
6 - MAP SENSOR
7 - ELEC. CONN.
8 - IAT SENSOR
9 - ELEC. CONN.
14 - 34 FUEL INJECTIONWJ
FUEL INJECTION (Continued)
Page 1454 of 2199

(18) 4.0L Engine: Verify wire harness connector is
firmly connected to Engine Coolant Temperature
(ECT) sensor (Fig. 11).(19) 4.7L Engine: Verify MAP and Engine Coolant
Temperature (ECT) sensor electrical connectors are
firmly connected to sensors (Fig. 12).
(20) Verify fuel injector wire harness connectors
are firmly connected to injectors in correct order.
Each harness connector is numerically tagged with
injector number (INJ 1, INJ 2 etc.) of its correspond-
ing fuel injector and cylinder number.
(21) Raise and support vehicle.
(22) Verify all oxygen sensor wire connectors are
firmly connected to sensors. Inspect sensors and con-
nectors for damage (Fig. 13)or (Fig. 14).
Fig. 10 IAT, IAC, TPS Sensor LocationsÐ4.7L V-8
Engine
1 - MOUNTING BOLTS (3)
2 - THROTTLE BODY
3 - IAT SENSOR CONNECTOR
4 - IAC MOTOR CONNECTOR
5 - TPS CONNECTOR
Fig. 11 ECT Sensor LocationÐ4.0L Engine
1 - THERMOSTAT HOUSING
2 - ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
3 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
Fig. 12 MAP and ECT Sensor LocationsÐ4.7L V-8
Engine
1 - ECT SENSOR
2 - MOUNTING BOLTS (2)
3 - MAP SENSOR
4 - INTAKE MANIFOLD
WJFUEL INJECTION 14 - 35
FUEL INJECTION (Continued)
Page 1458 of 2199

SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE - FUEL INJECTION
DESCRIPTION N-m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Air Cleaner Housing Mount. Nuts 10 93
Air Cleaner Air Duct Clamps 4 35
Air Cleaner Resonator Bolts 4 35
Engine Coolant Temperature SensorÐ4.0L Engine 11 96
Engine Coolant Temperature SensorÐ4.7L Engine 11 96
Fuel Hose Clamps 1 10
IAC Motor-To-Throttle Body BoltsÐ4.0L Engine 7860
IAC Motor-To-Throttle Body BoltsÐ4.7L Engine 7 60
Intake Manifold Air Temp. SensorÐ4.0L Engine 28 20
Intake Manifold Air Temp. SensorÐ4.7L Engine 28 20
MAP Sensor Mounting ScrewsÐ4.0L Engine 3 25
MAP Sensor Mounting ScrewsÐ4.7L Engine 3 25
Oxygen SensorÐAll Engines 30 22
PCM-to-Mounting Bracket Screws 3 25
PCM-to-Mounting Bracket Screws 9 80
Radiator Cooling Fan Relay Bolts 3 25
Throttle Body Mounting BoltsÐ4.0L Engine 11 100
Throttle Body Mounting BoltsÐ4.7L Engine 12 105
TPS Mounting ScrewsÐ4.0L Engine 7 60
TPS Mounting ScrewsÐ4.7L Engine 7 60
ACCELERATOR PEDAL
REMOVAL
The accelerator pedal is connected to the throttle
body linkage by the throttle cable. The cable is pro-
tected by a plastic sheathing and is connected to the
throttle body linkage by a ball socket. It is connected
to the accelerator pedal arm by a plastic retainer
(clip) (Fig. 16). This retainer (clip) snaps into the top
of the accelerator pedal arm. A retainer clip (Fig. 16)
is also used to fasten cable to dash panel.
CAUTION: Be careful not to damage or kink the
cable core wire (within the cable sheathing) while
servicing accelerator pedal or throttle cable.
(1) From inside vehicle, hold up accelerator pedal.
Remove plastic cable retainer (clip) and throttle cable
core wire from upper end of pedal arm. Plastic cable
retainer (clip) snaps into pedal arm.
(2) Remove accelerator pedal bracket nuts. Remove
accelerator pedal assembly.
INSTALLATION
The accelerator pedal is connected to the throttle
body linkage by the throttle cable. The cable is pro-
tected by a plastic sheathing and is connected to the
throttle body linkage by a ball socket. It is connected
to the accelerator pedal arm by a plastic retainer
(clip) (Fig. 16) . This retainer (clip) snaps into the top
of the accelerator pedal arm. A retainer clip (Fig. 16)
is also used to fasten cable to dash panel.
(1) Place accelerator pedal assembly over studs
protruding from floor pan. Tighten mounting nuts to
12 N´m 2 N´m (105 in. lbs. 20 in. lbs.) torque.
(2) Slide throttle cable into opening in top of pedal
arm. Push plastic cable retainer (clip) into pedal arm
opening until it snaps into place.
(3) Before starting engine, operate accelerator
pedal to check for any binding.
WJFUEL INJECTION 14 - 39
Page 1465 of 2199

INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 4.0L
The IAC motor is located on the throttle body.
(1) Install IAC motor to throttle body.
(2) Install and tighten two mounting bolts (screws)
to 7 N´m (60 in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Install electrical connector.
(4) Install air cleaner duct/air box to throttle body.
INSTALLATION - 4.7L
(1) Install IAC motor to throttle body.
(2) Install and tighten two mounting bolts (screws)
to 7 N´m (60 in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Install electrical connector.
(4) Install air duct/air box to throttle body.
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The 2±wire Intake Manifold Air Temperature (IAT)
sensor is installed in the intake manifold with the
sensor element extending into the air stream.
The IAT sensor is a two-wire Negative Thermal
Coefficient (NTC) sensor. Meaning, as intake mani-
fold temperature increases, resistance (voltage) in the
sensor decreases. As temperature decreases, resis-
tance (voltage) in the sensor increases.
OPERATION
The IAT sensor provides an input voltage to the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) indicating the
density of the air entering the intake manifold based
upon intake manifold temperature. At key-on, a
5±volt power circuit is supplied to the sensor from
the PCM. The sensor is grounded at the PCM
through a low-noise, sensor-return circuit.
The PCM uses this input to calculate the following:
²Injector pulse-width
²Adjustment of spark timing (to help prevent
spark knock with high intake manifold air-charge
temperatures)
The resistance values of the IAT sensor is the same
as for the Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 4.0L
The Intake Manifold Air Temperature (IAT) sensor
is installed into the intake manifold plenum near the
front of the throttle body (Fig. 27).
(1) Disconnect electrical connector from sensor.
(2) Remove sensor from intake manifold.
REMOVAL - 4.7L
The Intake Manifold Air Temperature (IAT) sensor
is located on the left side of the intake manifold.
Threaded Type Sensor
(1) Disconnect electrical connector from sensor.
(2) Remove sensor from intake manifold (Fig. 28).
Snap-In Type Sensor
(1) Disconnect electrical connector from IAT sen-
sor.
(2) Clean dirt from intake manifold at sensor base.
(3) Gently lift on small plastic release tab (Fig. 30)
or (Fig. 29) and rotate sensor about 1/4 turn counter-
clockwise for removal.
(4) Check condition of sensor o-ring.
Fig. 27 Intake Manifold Air Sensor LocationÐ4.0L
Engine
1 - MOUNTING BOLTS (4)
2 - THROTTLE BODY
3 - IAC MOTOR
4 - ELEC. CONN.
5 - TPS
6 - MAP SENSOR
7 - ELEC. CONN.
8 - IAT SENSOR
9 - ELEC. CONN.
14 - 46 FUEL INJECTIONWJ
IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR (Continued)
Page 1466 of 2199

INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 4.0L
The Intake Manifold Air Temperature (IAT) sensor
is installed into the intake manifold plenum near the
front of the throttle body (Fig. 27).
(1) Install sensor into intake manifold. Tighten
sensor to 28 N´m (20 ft. lbs.) torque.
(2) Connect electrical connector to sensor.
INSTALLATION - 4.7L
Threaded Type Sensor
(1) Install sensor (Fig. 28) into intake manifold.
Tighten sensor to 28 N´m (20 ft. lbs.) torque.
(2) Connect electrical connector to sensor.
Snap-In Type Sensor
(1) Check condition of sensor o-ring (Fig. 30).
(2) Clean sensor mounting hole in intake manifold.(3) Position sensor (Fig. 29) into intake manifold
and rotate clockwise until past release tab.
(4) Install electrical connector.
Fig. 28 IAT - 4.7L (THREADED TYPE)
1 - THROTTLE BODY
2 - TPS
3 - IAC MOTOR
4 - IAT SENSOR (THREADED TYPE)
5 - MOUNTING SCREWS
Fig. 29 IAT SENSOR - 4.7L (SNAP-IN TYPE)
1 - LEFT SIDE OF THROTTLE BODY
2 - ELEC. CONNECT.
3 - IAT SENSOR
4 - RELEASE TAB
Fig. 30 IAT SENSOR TAB / O-RING - 4.7L (SNAP-IN
TYPE)
1 - IAT SENSOR
2 - SENSOR O-RING
3 - RELEASE TAB
WJFUEL INJECTION 14 - 47
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1467 of 2199

MAP SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION
On the 4.0L six-cylinder engine the MAP sensor is
mounted to the engine throttle body. On the 4.7L V-8
engine the MAP sensor is mounted to front of the
intake manifold.
DESCRIPTION - 4.7L
The MAP sensor is located on the front of the
intake manifold. An o-ring seals the sensor to the
intake manifold.
OPERATION
The MAP sensor is used as an input to the Power-
train Control Module (PCM). It contains a silicon
based sensing unit to provide data on the manifold
vacuum that draws the air/fuel mixture into the com-
bustion chamber. The PCM requires this information
to determine injector pulse width and spark advance.
When manifold absolute pressure (MAP) equals
Barometric pressure, the pulse width will be at max-
imum.
A 5 volt reference is supplied from the PCM and
returns a voltage signal to the PCM that reflects
manifold pressure. The zero pressure reading is 0.5V
and full scale is 4.5V. For a pressure swing of 0±15
psi, the voltage changes 4.0V. To operate the sensor,
it is supplied a regulated 4.8 to 5.1 volts. Ground is
provided through the low-noise, sensor return circuit
at the PCM.
The MAP sensor input is the number one contrib-
utor to fuel injector pulse width. The most important
function of the MAP sensor is to determine baromet-
ric pressure. The PCM needs to know if the vehicle is
at sea level or at a higher altitude, because the air
density changes with altitude. It will also help to cor-
rect for varying barometric pressure. Barometric
pressure and altitude have a direct inverse correla-
tion; as altitude goes up, barometric goes down. At
key-on, the PCM powers up and looks at MAP volt-
age, and based upon the voltage it sees, it knows the
current barometric pressure (relative to altitude).
Once the engine starts, the PCM looks at the voltage
again, continuously every 12 milliseconds, and com-
pares the current voltage to what it was at key-on.
The difference between current voltage and what it
was at key-on, is manifold vacuum.
During key-on (engine not running) the sensor
reads (updates) barometric pressure. A normal range
can be obtained by monitoring a known good sensor.
As the altitude increases, the air becomes thinner
(less oxygen). If a vehicle is started and driven to avery different altitude than where it was at key-on,
the barometric pressure needs to be updated. Any
time the PCM sees Wide Open Throttle (WOT), based
upon Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) angle and RPM,
it will update barometric pressure in the MAP mem-
ory cell. With periodic updates, the PCM can make
its calculations more effectively.
The PCM uses the MAP sensor input to aid in cal-
culating the following:
²Manifold pressure
²Barometric pressure
²Engine load
²Injector pulse-width
²Spark-advance programs
²Shift-point strategies (certain automatic trans-
missions only)
²Idle speed
²Decel fuel shutoff
The MAP sensor signal is provided from a single
piezoresistive element located in the center of a dia-
phragm. The element and diaphragm are both made
of silicone. As manifold pressure changes, the dia-
phragm moves causing the element to deflect, which
stresses the silicone. When silicone is exposed to
stress, its resistance changes. As manifold vacuum
increases, the MAP sensor input voltage decreases
proportionally. The sensor also contains electronics
that condition the signal and provide temperature
compensation.
The PCM recognizes a decrease in manifold pres-
sure by monitoring a decrease in voltage from the
reading stored in the barometric pressure memory
cell. The MAP sensor is a linear sensor; meaning as
pressure changes, voltage changes proportionately.
The range of voltage output from the sensor is usu-
ally between 4.6 volts at sea level to as low as 0.3
volts at 26 in. of Hg. Barometric pressure is the pres-
sure exerted by the atmosphere upon an object. At
sea level on a standard day, no storm, barometric
pressure is approximately 29.92 in Hg. For every 100
feet of altitude, barometric pressure drops .10 in. Hg.
If a storm goes through it can change barometric
pressure from what should be present for that alti-
tude. You should know what the average pressure
and corresponding barometric pressure is for your
area.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 4.0L
The MAP sensor is mounted to the side of the
throttle body (Fig. 40). An L-shaped rubber fitting is
used to connect the MAP sensor to throttle body (Fig.
31).
(1) Remove air cleaner duct and air resonator box
at throttle body.
14 - 48 FUEL INJECTIONWJ
Page 2087 of 2199

VACUUM RESERVOIR
DESCRIPTION.........................34
OPERATION...........................34
REMOVAL.............................35
INSTALLATION.........................35EVAPORATOR TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................35
OPERATION...........................35
REMOVAL.............................35
INSTALLATION.........................35
CONTROLS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - VACUUM SYSTEM
Vacuum control is used to operate the mode doors
in the standard equipment manual temperature con-
trol system HVAC housing. Testing of the A/C Heater
mode control switch operation will determine if the
vacuum and electrical controls are functioning. How-
ever, it is possible that a vacuum control system that
operates perfectly at engine idle (high engine vac-
uum) may not function properly at high engine
speeds or loads (low engine vacuum). This can be
caused by leaks in the vacuum system, or a faulty
vacuum check valve.
A vacuum system test will help to identify the
source of poor vacuum system performance or vac-
uum system leaks. Before starting this test, stop the
engine and make certain that the problem isn't a dis-
connected vacuum supply tube at the engine intake
manifold vacuum tap or the vacuum reservoir.
Use an adjustable vacuum test set (Special Tool
C-3707-B) and a suitable vacuum pump to test the
HVAC vacuum control system. With a finger placed
over the end of the vacuum test hose probe (Fig. 1),
adjust the bleed valve on the test set gauge to obtain
a vacuum of exactly 27 kPa (8 in. Hg.). Release and
block the end of the probe several times to verify that
the vacuum reading returns to the exact 27 kPa (8
in. Hg.) setting. Otherwise, a false reading will be
obtained during testing.
VACUUM CHECK VALVES
(1) Remove the vacuum check valve to be tested.
The valves are located in the (black) vacuum supply
tubes at either the engine intake manifold vacuum
tap, or on the bottom of the HVAC unit behind the
passenger front floor duct.
(2) Connect the test set vacuum supply hose to the
A/C Heater control side of the valve. When connected
to this side of the check valve, no vacuum should
pass and the test set gauge should return to the 27
kPa (8 in. Hg.) setting. If OK, go to Step 3. If not OK,
replace the faulty valve.
(3) Connect the test set vacuum supply hose to the
engine vacuum side of the valve. When connected to
this side of the check valve, vacuum should flow
through the valve without restriction. If not OK,
replace the faulty valve.
A/C HEATER CONTROL
(1) Connect the test set vacuum probe to the
HVAC vacuum supply (black) tube in the engine com-
partment. Position the test set gauge so that it can
be viewed from the passenger compartment.
(2) Place the A/C Heater mode control switch knob
in each mode position, one position at a time, and
pause after each selection. The test set gauge should
return to the 27 kPa (8 in. Hg.) setting shortly after
each selection is made. If not OK, a component or
vacuum line in the vacuum circuit of the selected
mode has a leak. See the procedure in Locating Vac-
uum Leaks.
CAUTION: Do not use lubricant on the switch ports
or in the holes in the plug, as lubricant will ruin the
vacuum valve in the switch. A drop of clean water
in the connector plug holes will help the connector
slide onto the switch ports.
Fig. 1 ADJUST VACUUM TEST BLEED VALVE -
TYPICAL
1 - VACUUM PUMP TOOL C-4289
2 - VACUUM TEST SET C-3707
3 - BLEED VALVE
4 - PROBE
24 - 10 CONTROLSWJ