bleed JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.G Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 261 of 2199

REMOVAL
REMOVALÐ4.0L ENGINE
WARNING: DO NOT LOOSEN THE RADIATOR
DRAINCOCK WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND PRES-
SURIZED. SERIOUS BURNS FROM THE COOLANT
CAN OCCUR.
Do not waste reusable coolant. If the solution is
clean, drain the coolant into a clean container for
reuse.
(1) Drain the coolant from the radiator until the
level is below the thermostat housing (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
WARNING: CONSTANT TENSION HOSE CLAMPS
ARE USED ON MOST COOLING SYSTEM HOSES.
WHEN REMOVING OR INSTALLING, USE ONLY
TOOLS DESIGNED FOR SERVICING THIS TYPE OF
CLAMP, SUCH AS SPECIAL CLAMP TOOL (NUMBER
6094) (Fig. 52). SNAP-ON CLAMP TOOL (NUMBER
HPC-20) MAY BE USED FOR LARGER CLAMPS.
ALWAYS WEAR SAFETY GLASSES WHEN SERVIC-
ING CONSTANT TENSION CLAMPS.
CAUTION: A number or letter is stamped into the
tongue of constant tension clamps. If replacement
is necessary, use only an original equipment clamp
with matching number or letter.
(2) Remove radiator upper hose and heater hose at
thermostat housing.
(3) Disconnect wiring connector at engine coolant
temperature sensor.
(4) Remove thermostat housing mounting bolts,
thermostat housing, gasket and thermostat (Fig. 24).
Discard old gasket.
(5) Clean the gasket mating surfaces.
REMOVALÐ4.7L ENGINE
WARNING: DO NOT LOOSEN RADIATOR DRAIN-
COCK WITH SYSTEM HOT AND PRESSURIZED.
SERIOUS BURNS FROM COOLANT CAN OCCUR.
Do not waste reusable coolant. If solution is clean,
drain coolant into a clean container for reuse.
If thermostat is being replaced, be sure that
replacement is specified thermostat for vehicle model
and engine type.
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable at battery.
(2) Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(3) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(4) Remove splash shield.(5) Remove lower radiator hose clamp and lower
radiator hose at thermostat housing.
(6) Remove thermostat housing mounting bolts,
thermostat housing and thermostat (Fig. 25).
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATIONÐ4.0L ENGINE
(1) Install the replacement thermostat so that the
pellet, which is encircled by a coil spring, faces the
engine. All thermostats are marked on the outer
flange to indicate the proper installed position.
(a) Observe the recess groove in the engine cyl-
inder head (Fig. 26).
(b) Position thermostat in groove with arrow and
air bleed hole on outer flange pointing up.
(2) Install replacement gasket and thermostat
housing.
CAUTION: Tightening the thermostat housing
unevenly or with the thermostat out of its recess,
may result in a cracked housing.
(3) Tighten the housing bolts to 22 N´m (16 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(4) Install hoses to thermostat housing.
Fig. 24 Thermostat
1 - LONG BOLT
2 - GASKET
3 - THERMOSTAT
4 - THERMOSTAT HOUSING
5 - SHORT BOLT
7 - 38 ENGINEWJ
ENGINE COOLANT THERMOSTAT (Continued)
Page 267 of 2199

the radiator to flush the radiator and/or A/C con-
denser of debris.
INSPECTION
The radiator cooling fins should be checked for
damage or deterioration. Inspect cooling fins to make
sure they are not bent or crushed, these areas result
in reduced heat exchange causing the cooling system
to operate at higher temperatures. Inspect the plastic
end tanks for cracks, damage or leaks.
Inspect the radiator neck for damage or distortion.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Before installing the radiator or A/C con-
denser, be sure the radiator-to-body and radiator-to-
A/C condenser rubber air seals (Fig. 39) are
properly fastened to their original positions. These
are used at the top, bottom and sides of the radia-
tor and A/C condenser. To prevent overheating,
these seals must be installed to their original posi-
tions.
(1) Equipped with air conditioning: Gently lower
the radiator and fan shroud into the vehicle. Guide
the two radiator alignment dowels through the holes
in the rubber air seals first and then through the A/C
support brackets (Fig. 40). Continue to guide thealignment dowels into the rubber grommets located
in lower radiator crossmember. The holes in the
L-shaped brackets (located on bottom of A/C con-
denser) must be positioned between bottom of rubber
air seals and top of rubber grommets.
(2) Connect the radiator upper and lower hoses
and hose clamps to radiator.
CAUTION: The tangs on the hose clamps must be
positioned straight down.
(3) Install coolant reserve/overflow tank hose at
radiator.
(4) Connect both transmission cooler lines at the
radiator.
(5) Install both radiator mounting bolts.
(6) Install air inlet duct at grill.
(7) Attach electric connector for hydraulic fan con-
trol solenoid.
(8) Install the grill (Refer to 23 - BODY/EXTERI-
OR/GRILLE - INSTALLATION).
(9) Connect the two high pressure lines to the
hydraulic fan drive. Tighten
1¤2in. pressure line fit-
ting to 49 N´m (36 ft. lbs.). and the 3/8 in. pressure
line fitting to 29 N´m (21.5 ft. lbs.).
(10) Connect the low pressure hose to the hydrau-
lic fan drive. Position the spring clamp.
(11) Connect the power steering filter hoses to the
filter. Install new hose clamps.
(12) Rotate the fan blades (by hand) and check for
interference at fan shroud.
(13) Refill cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(14) Refill the power steering reservoir and bleed
air from system (Refer to 19 - STEERING/PUMP -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(15) Connect battery cable at battery.
(16) Start and warm engine. Check for leaks.
RADIATOR - 4.0L
DESCRIPTION
All vehicles are equipped with a cross flow type
radiator with plastic side tanks (Fig. 36).
Plastic tanks, while stronger than brass, are sub-
ject to damage by impact, such as from tools or
wrenches. Handle radiator with care.
REMOVAL
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE CYLINDER
BLOCK DRAIN PLUGS OR LOOSEN THE RADIATOR
DRAINCOCK WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER
PRESSURE. SERIOUS BURNS FROM COOLANT
CAN OCCUR. REFER TO COOLING SYSTEM DRAIN-
ING.
Fig. 35 Radiator Alignment Dowels - Typical
1 - RADIATOR
2 - ALIGNMENT DOWEL
3 - RADIATOR LOWER ISOLATOR
4 - RADIATOR LOWER CROSSMEMBER
7 - 44 ENGINEWJ
RADIATOR - 4.7L (Continued)
Page 586 of 2199

(8) Connect negative battery cable at battery.
(9) Before starting engine, operate accelerator
pedal to check for any binding.
SERVO
DESCRIPTION
The servo unit consists of a solenoid valve body,
and a vacuum chamber. The solenoid valve body con-
tains three solenoids:
²Vacuum
²Vent
²Dump
The vacuum chamber contains a diaphragm with a
cable attached to control the throttle linkage.
OPERATION
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) controls the
solenoid valve body. The solenoid valve body controls
the application and release of vacuum to the dia-
phragm of the vacuum servo. The servo unit cannot
be repaired and is serviced only as a complete assem-
bly.
Power is supplied to the servo's by the PCM
through the brake switch. The PCM controls the
ground path for the vacuum and vent solenoids.The dump solenoid is energized anytime it receives
power. If power to the dump solenoid is interrupted,
the solenoid dumps vacuum in the servo. This pro-
vides a safety backup to the vent and vacuum sole-
noids.
The vacuum and vent solenoids must be grounded
at the PCM to operate. When the PCM grounds the
vacuum servo solenoid, the solenoid allows vacuum
to enter the servo and pull open the throttle plate
using the cable. When the PCM breaks the ground,
the solenoid closes and no more vacuum is allowed to
enter the servo. The PCM also operates the vent sole-
noid via ground. The vent solenoid opens and closes a
passage to bleed or hold vacuum in the servo as
required.
The PCM duty cycles the vacuum and vent sole-
noids to maintain the set speed, or to accelerate and
decelerate the vehicle. To increase throttle opening,
the PCM grounds the vacuum and vent solenoids. To
decrease throttle opening, the PCM removes the
grounds from the vacuum and vent solenoids. When
the brake is released, if vehicle speed exceeds 30
mph to resume, 35 mph to set, and the RES/ACCEL
switch has been depressed, ground for the vent and
vacuum circuits is restored.
REMOVAL
The speed control servo is attached to a bracket.
The bracket and servo assembly are located below
the battery tray.
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable at battery.
(2) Disconnect positive battery cable at battery.
(3) Remove air cleaner housing at top of throttle
body and disconnect servo cable at throttle body.
Refer to Servo Cable Removal/Installation.
(4) Remove battery from battery tray.
(5) Disconnect wiring at battery tray.
(6) Disconnect positive battery cable at Power Dis-
tribution Center (PDC).
(7) Loosen PDC at battery tray.
(8) Remove 4 battery tray bolts. One of these bolts
attaches to speed control bracket flange that sup-
ports battery tray. While removing battery tray, dis-
connect battery temperature sensor electrical
connector at sensor.
(9) Disconnect vacuum line at servo vacuum hose
fitting (Fig. 5) .
(10) Disconnect electrical connector at servo (Fig.
5) .
If servo and mounting bracket are being removed
as one assembly, remove two mounting nuts (Fig. 5) .
These are located above right-front tire. Remove
inner fender clips and pry inner fender back slightly
to gain access to mounting nuts.
Fig. 4 Speed Control Cable at BracketÐ4.7L V-8
Engine
1 - PLASTIC CABLE MOUNT
2 - SPEED CONTROL CABLE
3 - BRACKET
4 - SLIDE FOR REMOVAL
WJSPEED CONTROL 8P - 5
CABLE (Continued)
Page 589 of 2199

(4) Install airbag module. Refer to Group 8M, Pas-
sive Restraint Systems.
(5) Connect negative battery cable.
VACUUM RESERVOIR
DESCRIPTION
The vacuum reservoir is a plastic storage tank con-
nected to an engine vacuum source by vacuum lines.
OPERATION
The vacuum reservoir is used to supply the vac-
uum needed to maintain proper speed control opera-
tion when engine vacuum drops, such as in climbing
a grade while driving. A one-way check valve is used
in the vacuum line between the reservoir and the
vacuum source. This check valve is used to trap
engine vacuum in the reservoir. On certain vehicle
applications, this reservoir is shared with the heat-
ing/air-conditioning system. The vacuum reservoir
cannot be repaired and must be replaced if faulty.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - VACUUM
RESERVOIR
(1) Disconnect vacuum hose at speed control servo
and install a vacuum gauge into the disconnected
hose.
(2) Start engine and observe gauge at idle. Vac-
uum gauge should read at least ten inches of mer-
cury.
(3) If vacuum is less than ten inches of mercury,
determine source of leak. Check vacuum line to
engine for leaks. Also check actual engine intake
manifold vacuum. If manifold vacuum does not meet
this requirement, check for poor engine performance
and repair as necessary.
(4) If vacuum line to engine is not leaking, check
for leak at vacuum reservoir. To locate and gain
access to reservoir, refer to Vacuum Reservoir Remov-
al/Installation in this group. Disconnect vacuum line
at reservoir and connect a hand-operated vacuum
pump to reservoir fitting. Apply vacuum. Reservoir
vacuum should not bleed off. If vacuum is being lost,
replace reservoir.
(5) Verify operation of one-way check valve and
check it for leaks.
(a) Locate one-way check valve. The valve is
located in vacuum line between vacuum reservoir
and engine vacuum source. Disconnect vacuum
hoses (lines) at each end of valve.
(b) Connect a hand-operated vacuum pump to
reservoir end of check valve. Apply vacuum. Vac-
uum should not bleed off. If vacuum is being lost,
replace one-way check valve.
(c) Connect a hand-operated vacuum pump to
vacuum source end of check valve. Apply vacuum.
Vacuum should flow through valve. If vacuum is
not flowing, replace one-way check valve. Seal the
fitting at opposite end of valve with a finger and
apply vacuum. If vacuum will not hold, diaphragm
within check valve has ruptured. Replace valve.
REMOVAL
The vacuum reservoir is located in the right/front
corner of the vehicle behind the front bumper fascia
(Fig. 8).
(1) Remove front bumper and grill assembly.
(2) Remove 1 support bolt near front of reservoir
(Fig. 8).
(3) Remove 2 reservoir mounting bolts.
(4) Remove reservoir from vehicle to gain access to
vacuum hose (Fig. 9). Disconnect vacuum hose from
reservoir fitting at rear of reservoir.
Fig. 7 Speed Control Switches
1 - MOUNTING SCREW
2 - SPEED CONTROL SWITCHES
8P - 8 SPEED CONTROLWJ
SWITCH (Continued)
Page 1380 of 2199
(6) Remove accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
(7) Disconnect generator electrical connections.
(8) Unbolt the generator and move it away from
the intake manifold for clearance.
(9) Disconnect air conditioning compressor electri-
cal connections.
(10) Unbolt the air conditioning compressor and
move it away from the intake manifold for clearance.
(11) Disconnect left and right radio suppressor
straps.
(12) Disconnect and remove ignition coil towers
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/IGNITION CONTROL/
IGNITION COIL - REMOVAL).
(13) Remove top oil dipstick tube retaining bolt
and ground strap.
(14) Bleed pressure from fuel system (Refer to 14 -
FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
(15) Remove fuel rail (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYS-
TEM/FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL RAIL - REMOVAL).
(16) Remove throttle body assembly and mounting
bracket.
(17) Drain cooling system below coolant tempera-
ture level (Refer to 7 - COOLING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
(18) Remove coolant temperature sensor (Refer to
7 - COOLING/ENGINE/ENGINE COOLANT TEMP
SENSOR - REMOVAL).
(19) Remove cowl to hood seal. (Refer to 23 -
BODY/WEATHERSTRIP/SEALS/COWL WEATHER-
STRIP - REMOVAL).
(20) Remove right side engine lifting stud.
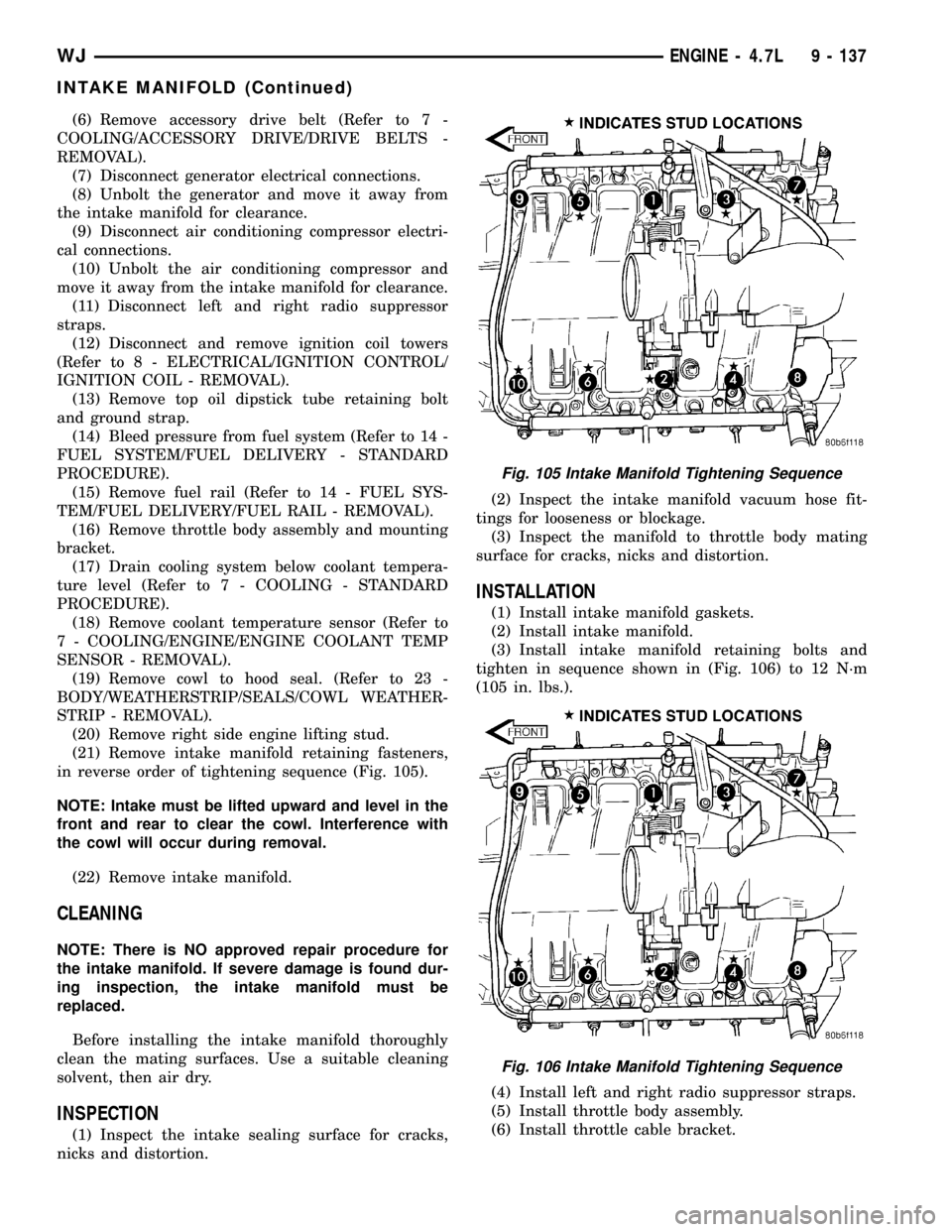
(21) Remove intake manifold retaining fasteners,
in reverse order of tightening sequence (Fig. 105).
NOTE: Intake must be lifted upward and level in the
front and rear to clear the cowl. Interference with
the cowl will occur during removal.
(22) Remove intake manifold.
CLEANING
NOTE: There is NO approved repair procedure for
the intake manifold. If severe damage is found dur-
ing inspection, the intake manifold must be
replaced.
Before installing the intake manifold thoroughly
clean the mating surfaces. Use a suitable cleaning
solvent, then air dry.
INSPECTION
(1) Inspect the intake sealing surface for cracks,
nicks and distortion.(2) Inspect the intake manifold vacuum hose fit-
tings for looseness or blockage.
(3) Inspect the manifold to throttle body mating
surface for cracks, nicks and distortion.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install intake manifold gaskets.
(2) Install intake manifold.
(3) Install intake manifold retaining bolts and
tighten in sequence shown in (Fig. 106) to 12 N´m
(105 in. lbs.).
(4) Install left and right radio suppressor straps.
(5) Install throttle body assembly.
(6) Install throttle cable bracket.
Fig. 105 Intake Manifold Tightening Sequence
Fig. 106 Intake Manifold Tightening Sequence
WJENGINE - 4.7L 9 - 137
INTAKE MANIFOLD (Continued)
Page 1384 of 2199

INSPECTION
(1) Inspect the exhaust manifold for cracks in the
mating surface and at every mounting bolt hole.
(2) Using a straight edge and a feeler gauge, check
the mating surface for warp and twist.
(3) Inspect the manifold to exhaust pipe mating
surface for cracks, gouges, or other damage that
would prevent sealing.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install exhaust manifold and gasket from below
engine compartment.
(2) Install lower exhaust manifold fasteners. DO
NOT tighten until all fasteners are in place.
(3) Lower vehicle and install upper exhaust mani-
fold fasteners. Tighten all manifold bolts starting at
center and working outward to 25 N´m (18 ft. lbs.).
CAUTION: Over tightening heat shield fasteners,
may cause shield to distort and/or crack.
(4) Install exhaust manifold heat shield. Tighten
fasteners to 8 N´m (72 in. lbs.), then loosen 45
degrees.
(5) Install starter and fasteners.
(6) Connect exhaust pipe to manifold.
(7) Connect heater hoses at engine.
(8) Install fastener attaching A/C accumulator.
(9) Install A/C compressor and fasteners.
(10) Install accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION).
(11) Install washer bottle and battery tray assem-
bly.
(12) Install PDC.
(13) Install battery and connect cables.
(14) Fill cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
VALVE TIMING
DESCRIPTION - TIMING DRIVE SYSTEM
The timing drive system has been designed to pro-
vide quiet performance and reliability to support a
non-free wheelingengine. Specifically the intake
valves are non-free wheeling and can be easily dam-
aged with forceful engine rotation if camshaft-to-
crankshaft timing is incorrect. The timing drive
system consists of a primary chain and two second-
ary timing chain drives (Fig. 109).
OPERATION - TIMING DRIVE SYSTEM
The primary timing chain is a single inverted tooth
type. The primary chain drives the large fifty tooth
idler sprocket directly from a 25 tooth crankshaftsprocket. Primary chain motion is controlled by a
pivoting leaf spring tensioner arm and a fixed guide.
The arm and the guide both use nylon plastic wear
faces for low friction and long wear. The primary
chain receives oil splash lubrication from the second-
ary chain drive and oil pump leakage. The idler
sprocket assembly connects the primary and second-
ary chain drives. The idler sprocket assembly con-
sists of two integral thirty tooth sprockets and a fifty
tooth sprocket that is splined to the assembly. The
spline joint is a non ± serviceable press fit anti rattle
type. A spiral ring is installed on the outboard side of
the fifty tooth sprocket to prevent spline disengage-
ment. The idler sprocket assembly spins on a station-
ary idler shaft. The idler shaft is press-fit into the
cylinder block. A large washer on the idler shaft bolt
and the rear flange of the idler shaft are used to con-
trol sprocket thrust movement. Pressurized oil is
routed through the center of the idler shaft to pro-
vide lubrication for the two bushings used in the
idler sprocket assembly.
There are two secondary drive chains, both are
inverted tooth type, one to drive the camshaft in each
SOHC cylinder head. There are no shaft speed
changes in the secondary chain drive system. Each
secondary chain drives a thirty tooth cam sprocket
directly from the thirty tooth sprocket on the idler
sprocket assembly. A fixed chain guide and a hydrau-
lic oil damped tensioner are used to maintain tension
in each secondary chain system. The hydraulic ten-
sioners for the secondary chain systems are fed pres-
surized oil from oil reservoir pockets in the block.
Each tensioner also has a mechanical ratchet system
that limits chain slack if the tensioner piston bleeds
down after engine shut down. The tensioner arms
and guides also utilize nylon wear faces for low fric-
tion and long wear. The secondary timing chains
receive lubrication from a small orifice in the ten-
sioners. This orifice is protected from clogging by a
fine mesh screen which is located on the back of the
hydraulic tensioners.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE TIMING -
VERIFICATION
CAUTION: The 4.7L is a non free-wheeling design
engine. Therefore, correct engine timing is critical.
NOTE: Components referred to as left hand or right
hand are as viewed from the drivers position inside
the vehicle.
WJENGINE - 4.7L 9 - 141
EXHAUST MANIFOLD - RIGHT (Continued)
Page 1421 of 2199

FUEL DELIVERY
DESCRIPTION
The fuel delivery system consists of:
²the fuel pump module containing the electric
fuel pump, fuel gauge sending unit (fuel level sensor)
and a separate fuel filter located at bottom of pump
module
²a separate combination fuel filter/fuel pressure
regulator
²fuel tubes/lines/hoses
²quick-connect fittings
²fuel injector rail
²fuel injectors
²fuel tank
²fuel tank filler/vent tube assembly
²fuel tank filler tube cap
²accelerator pedal
²throttle cable
OPERATION
The fuel tank assembly consists of: the fuel tank,
fuel tank shield, fuel tank straps, fuel pump module
assembly, fuel pump module locknut/gasket, and fuel
tank check valve (refer to Emission Control System
for fuel tank check valve information).
A fuel filler/vent tube assembly using a pressure/
vacuum, 1/4 turn fuel filler cap is used. The fuel
filler tube contains a flap door located below the fuel
fill cap.
Also to be considered part of the fuel system is the
evaporation control system. This is designed to
reduce the emission of fuel vapors into the atmo-
sphere. The description and function of the Evapora-
tive Control System is found in Emission Control
Systems.
Both fuel filters (at bottom of fuel pump module
and within fuel pressure regulator) are designed for
extended service. They do not require normal sched-
uled maintenance. Filters should only be replaced if
a diagnostic procedure indicates to do so.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
FUEL PRESSURE LEAK DOWN TEST
Use this test in conjunction with the Fuel Pump
Pressure Test and Fuel Pump Capacity Test.
Check Valve Operation:The electric fuel pump
outlet contains a one-way check valve to prevent fuel
flow back into the tank and to maintain fuel supply
line pressure (engine warm) when pump is not oper-
ational. It is also used to keep the fuel supply line
full of gasoline when pump is not operational. After
the vehicle has cooled down, fuel pressure may drop
to 0 psi (cold fluid contracts), but liquid gasoline willremain in fuel supply line between the check valve
and fuel injectors.Fuel pressure that has
dropped to 0 psi on a cooled down vehicle
(engine off) is a normal condition.When the elec-
tric fuel pump is activated, fuel pressure should
immediately(1±2 seconds) rise to specification.
Abnormally long periods of cranking to restart a
hotengine that has been shut down for a short
period of time may be caused by:
²Fuel pressure bleeding past a fuel injector(s).
²Fuel pressure bleeding past the check valve in
the fuel pump module.
²A defective fuel filter/pressure regulator.
Two #6539, 5/16º, Fuel Line Pressure Test Adapter
Hose Tools are required for the following tests.
(1) Release fuel system pressure. Refer to Fuel
Pressure Release Procedure.
(2) Raise vehicle.
Fuel Line Identification:The fuel filter/pressure
regulator is located in front of the fuel tank and
above the rear axle. It is transversely mounted to a
chassis crossmember (left-to-right). The filter/regula-
tor is equipped with 3 fuel line fittings (2 at one end
and 1 at the other end). The single fitting facing the
left side of the vehicle is the supply line to the fuel
rail (Fig. 1) . The 2 fittings facing the right side of
the vehicle are connected to the fuel tank. Of these 2
fittings, the fitting towards thefrontis used for fuel
return to the fuel tank. The fitting towards therear
is a pressure line. Thisrearfitting must be discon-
nected for the following step.
(3) See previous step. Disconnect fuel pressure line
atrearof filter/regulator. This is a 5/169quick-con-
nect fitting (Fig. 1) . Refer to Quick-Connect Fittings
for procedures.
(4) Obtain correct Fuel Line Pressure Test Adapter
Hose Tool # 6539 for 5/16º fuel lines. Connect one
end of this Special Tool into the disconnected fuel
pressure line. Connect the other end of the Tool into
fitting on filter/regulator.
(5) Lower vehicle.
(6) Disconnect the fuel inlet line at fuel rail. Refer
to Quick-Connect Fittings for procedures. On some
engines, air cleaner housing removal may be neces-
sary before fuel line disconnection.
(7) Obtain a second Fuel Line Pressure Test
Adapter Hose Tool # 6539 for 5/16º fuel lines. Con-
nect this tool between disconnected fuel line and fuel
rail (Fig. 2) .
(8) Connect the 0-414 kPa (0-60 psi) fuel pressure
test gauge (from Gauge Set 5069) to the test port on
the appropriate Adaptor Tool.NOTE: The DRB III
Scan Tool along with the PEP module, the 500
psi pressure transducer, and the transducer-to-
test port adapter may also be used in place of
the fuel pressure gauge.
14 - 2 FUEL DELIVERYWJ
Page 1481 of 2199
LOOSE STEERING AND VEHICLE LEADS/DRIFTS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
EXCESSIVE PLAY IN STEERING
WHEEL1. Worn or loose suspension or
steering components.1. Repair as necessary.
2. Worn or loose wheel bearings. 2. Repair as necessary.
3. Steering gear mounting. 3. Tighten gear mounting bolts to
specification.
4. Gear out of adjustment. 4. Adjust gear to specification.
5. Worn or loose steering coupler. 5. Repair as necessary.
VEHICLE PULLS TO ONE SIDE
DURING BRAKING1. Tire Pressure. 1. Adjust tire pressure.
2. Air in brake hydrauliics system. 2. Bleed brake system.
3. Worn brake components. 3. Repair as necessary.
VEHICLE LEADS OR DRIFTS
FROM STRAIGHT AHEAD
DIRECTION ON UNCROWNED
ROAD.1. Tire pressure. 1. Adjust tire pressure.
2. Radial tire lead. 2. Cross front tires.
3. Brakes dragging. 3. Repair as necessary.
4. Wheel alignment. 4. Align vehicle.
5. Weak or broken spring. 5. Replace spring.
6. Loose or worn steering/
suspension components.6. Repair as necessary.
7. Cross caster out of spec. 7. Adjust or replace axle as
necessary.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - STEERING FLOW
AND PRESSURE
The following procedure is used to test the opera-
tion of the power steering system on the vehicle. This
test will provide the gallons per minute (GPM) or
flow rate of the power steering pump along with the
maximum relief pressure. Perform test any time a
power steering system problem is present. This test
will determine if the power steering pump or power
steering gear is not functioning properly. The follow-
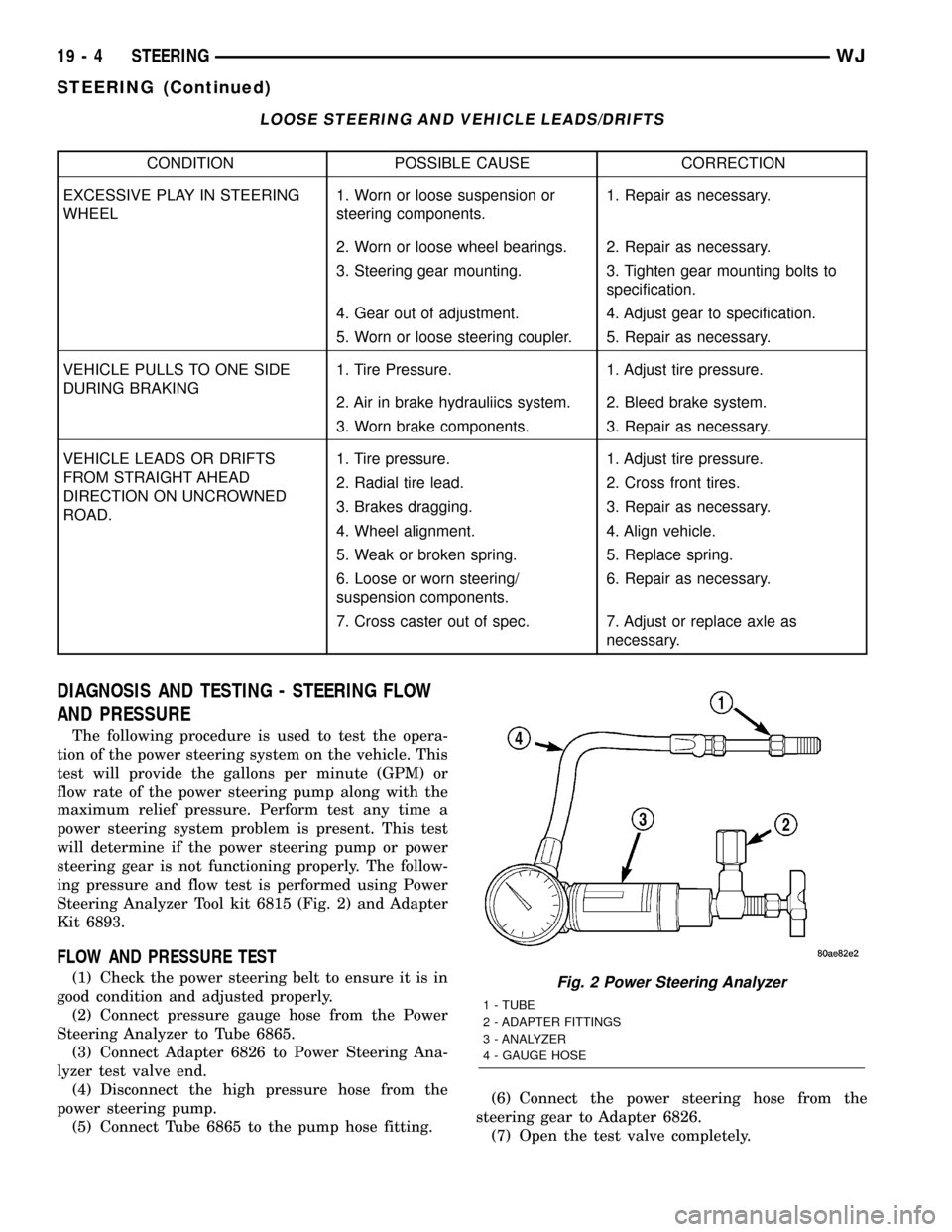
ing pressure and flow test is performed using Power
Steering Analyzer Tool kit 6815 (Fig. 2) and Adapter
Kit 6893.
FLOW AND PRESSURE TEST
(1) Check the power steering belt to ensure it is in
good condition and adjusted properly.
(2) Connect pressure gauge hose from the Power
Steering Analyzer to Tube 6865.
(3) Connect Adapter 6826 to Power Steering Ana-
lyzer test valve end.
(4) Disconnect the high pressure hose from the
power steering pump.
(5) Connect Tube 6865 to the pump hose fitting.(6) Connect the power steering hose from the
steering gear to Adapter 6826.
(7) Open the test valve completely.Fig. 2 Power Steering Analyzer
1 - TUBE
2 - ADAPTER FITTINGS
3 - ANALYZER
4 - GAUGE HOSE
19 - 4 STEERINGWJ
STEERING (Continued)
Page 1514 of 2199

INSTALLATION
(1) Position and install the power steering cooler
to the vehicle.
(2) Install the three mounting bracket bolts (Fig.
6).
(3) Reconnect the upper hose at cooler (Fig. 6).
(4) Reconnect the lower hose at cooler (Fig. 6).
(5) Connect negative battery cable to battery.
(6) Refill the power steering fluid and bleed the
system,(Refer to 19 - STEERING/PUMP - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE).
(7) Start engine and check for leaks.
(8) Install the grille opening reinforcement panel
(9) Install the front fascia grille,(Refer to 13 -
FRAMES & BUMPERS/BUMPERS/FRONT FASCIA
- INSTALLATION).
HOSES - 4.0L
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - PRESSURE LINE
The hose consists of two metal ends and rubber
center section that contains a tuning cable. The
pump end uses a quick connect fitting. Lubircation
must be used on the quick connect nut and o-ring
when installing.
DESCRIPTION - RETURN LINE
Power steering return line is a hose which is
clamped at the pump and the gear.
OPERATION
OPERATION - PRESSURE LINE
Power steering pressure line, is used to transfer
high pressure power steering fluid, from the power
steering pump to the power steering gear on the
4.0L. The 4.7L power steering pressure line, is used
to transfer high pressure power steering fluid, from
the power steering pump to the engine cooling fan
and the steering gear.
OPERATION - RETURN LINE
Power steering return line, is used to transfer low
pressure power steering fluid, from the power steer-
ing gear to the power steering pump.
REMOVAL
(1) Drain the power steering fluid from the reser-
voir.
(2) Remove the air box,(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/AIR
INTAKE SYSTEM/AIR CLEANER HOUSING -
REMOVAL).
(3) Disconnect the power steering pressure hose
from the power steering pump and then the power
steering gear (Fig. 7).
(4) Disconnect the power steering return hose from
the power steering cooler and the reservoir.
(5) Remove the hoses from the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the hoses to the vehicle.
(2) Reconnect the power steering return hose to
the power steering cooler and the reservoir.
(3) Reconnect the power steering pressure hose to
the power steering pump and then the power steer-
ing gear.
(4) Install the air box,(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/AIR
INTAKE SYSTEM/AIR CLEANER HOUSING -
INSTALLATION).
(5) Refill the power steering fluid and bleed the
system,(Refer to 19 - STEERING/PUMP - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE).
Fig. 7 POWER STEERING HOSES
1 - RETURN HOSE
2 - HIGH PRESSURE HOSE
3 - STEERING GEAR
WJPUMP 19 - 37
FLUID COOLER (Continued)
Page 1517 of 2199
(5) Disconnect the rubber hose from the power
steering reservoir (Fig. 12).
(6) Remove the hose from the vehicle.
REMOVAL - 3/8(GEAR OUTLET HOSE
(1) Drain the power steering fluid from the reser-
voir.
(2) Remove the air box,(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/AIR
INTAKE SYSTEM/AIR CLEANER HOUSING -
REMOVAL).
(3) Raise and support the vehicle.
(4) Disconnect the rubber hose from the steering
cooler inlet tube (Fig. 11).
(5) Disconnect the metal tube from the power
steering gear (Fig. 11).
(6) Remove the hose from the vehicle.
REMOVAL - INLET COOLER HOSE
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable at battery.
(2) Drain the power steering fluid out of the reser-
voir.
(3) Remove the air box,(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/AIR
INTAKE SYSTEM/AIR CLEANER HOUSING -
REMOVAL).
(4) Remove the front fascia grille assembly,(Refer
to 13 - FRAMES & BUMPERS/BUMPERS/FRONT
FASCIA - REMOVAL).
(5) Remove the grille opening reinforcement panel
(6) Place a drain pan under the cooler.
(7) Disconnect the lower hose at cooler (Fig. 6).
(8) Disconnect the cooler hose at the gear.
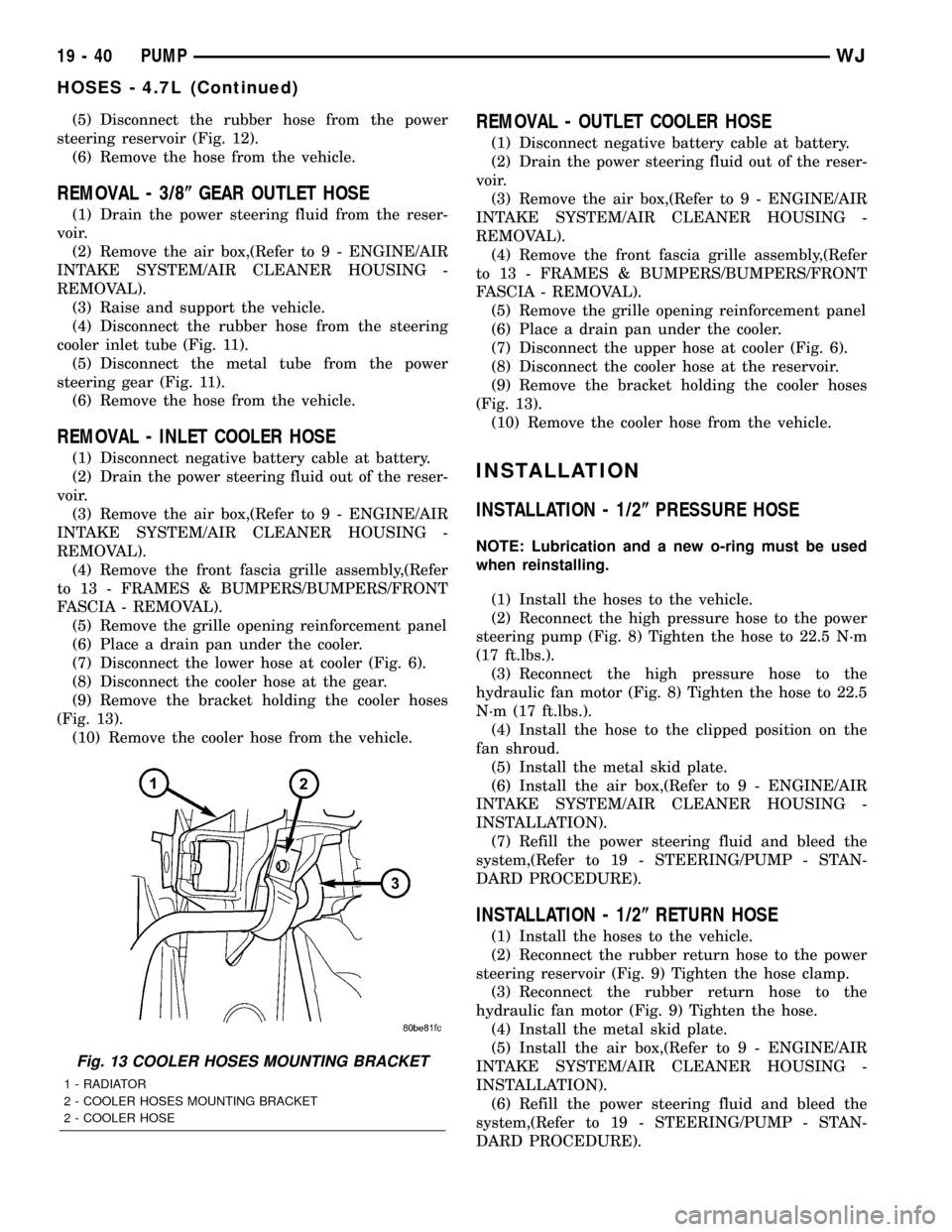
(9) Remove the bracket holding the cooler hoses
(Fig. 13).
(10) Remove the cooler hose from the vehicle.
REMOVAL - OUTLET COOLER HOSE
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable at battery.
(2) Drain the power steering fluid out of the reser-
voir.
(3) Remove the air box,(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/AIR
INTAKE SYSTEM/AIR CLEANER HOUSING -
REMOVAL).
(4) Remove the front fascia grille assembly,(Refer
to 13 - FRAMES & BUMPERS/BUMPERS/FRONT
FASCIA - REMOVAL).
(5) Remove the grille opening reinforcement panel
(6) Place a drain pan under the cooler.
(7) Disconnect the upper hose at cooler (Fig. 6).
(8) Disconnect the cooler hose at the reservoir.
(9) Remove the bracket holding the cooler hoses
(Fig. 13).
(10) Remove the cooler hose from the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 1/2(PRESSURE HOSE
NOTE: Lubrication and a new o-ring must be used
when reinstalling.
(1) Install the hoses to the vehicle.
(2) Reconnect the high pressure hose to the power
steering pump (Fig. 8) Tighten the hose to 22.5 N´m
(17 ft.lbs.).
(3) Reconnect the high pressure hose to the
hydraulic fan motor (Fig. 8) Tighten the hose to 22.5
N´m (17 ft.lbs.).
(4) Install the hose to the clipped position on the
fan shroud.
(5) Install the metal skid plate.
(6) Install the air box,(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/AIR
INTAKE SYSTEM/AIR CLEANER HOUSING -
INSTALLATION).
(7) Refill the power steering fluid and bleed the
system,(Refer to 19 - STEERING/PUMP - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE).
INSTALLATION - 1/2(RETURN HOSE
(1) Install the hoses to the vehicle.
(2) Reconnect the rubber return hose to the power
steering reservoir (Fig. 9) Tighten the hose clamp.
(3) Reconnect the rubber return hose to the
hydraulic fan motor (Fig. 9) Tighten the hose.
(4) Install the metal skid plate.
(5) Install the air box,(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/AIR
INTAKE SYSTEM/AIR CLEANER HOUSING -
INSTALLATION).
(6) Refill the power steering fluid and bleed the
system,(Refer to 19 - STEERING/PUMP - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE).
Fig. 13 COOLER HOSES MOUNTING BRACKET
1 - RADIATOR
2 - COOLER HOSES MOUNTING BRACKET
2 - COOLER HOSE
19 - 40 PUMPWJ
HOSES - 4.7L (Continued)