evap temp JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.G Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 2168 of 2199
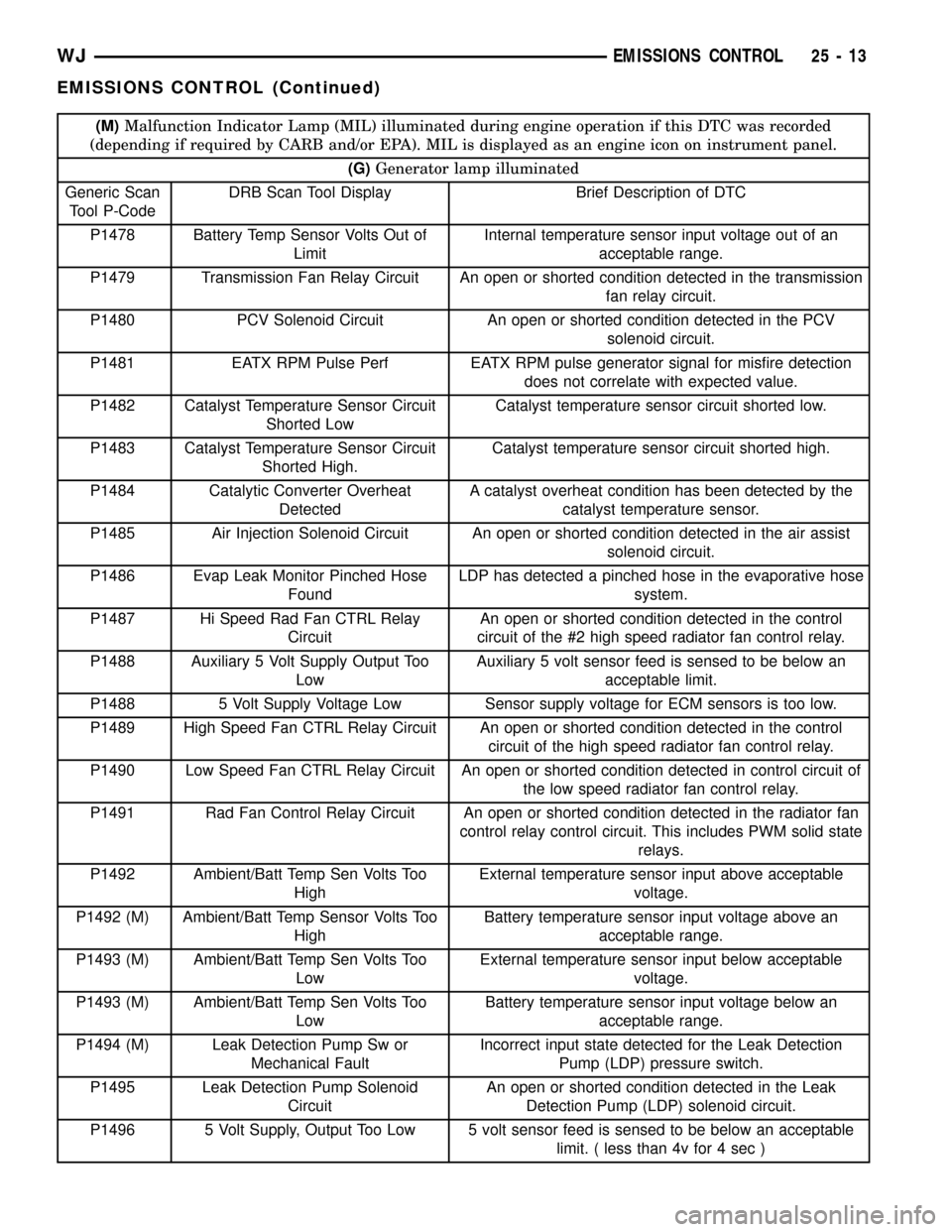
(M)Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) illuminated during engine operation if this DTC was recorded
(depending if required by CARB and/or EPA). MIL is displayed as an engine icon on instrument panel.
(G)Generator lamp illuminated
Generic Scan
Tool P-CodeDRB Scan Tool Display Brief Description of DTC
P1478 Battery Temp Sensor Volts Out of
LimitInternal temperature sensor input voltage out of an
acceptable range.
P1479 Transmission Fan Relay Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the transmission
fan relay circuit.
P1480 PCV Solenoid Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the PCV
solenoid circuit.
P1481 EATX RPM Pulse Perf EATX RPM pulse generator signal for misfire detection
does not correlate with expected value.
P1482 Catalyst Temperature Sensor Circuit
Shorted LowCatalyst temperature sensor circuit shorted low.
P1483 Catalyst Temperature Sensor Circuit
Shorted High.Catalyst temperature sensor circuit shorted high.
P1484 Catalytic Converter Overheat
DetectedA catalyst overheat condition has been detected by the
catalyst temperature sensor.
P1485 Air Injection Solenoid Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the air assist
solenoid circuit.
P1486 Evap Leak Monitor Pinched Hose
FoundLDP has detected a pinched hose in the evaporative hose
system.
P1487 Hi Speed Rad Fan CTRL Relay
CircuitAn open or shorted condition detected in the control
circuit of the #2 high speed radiator fan control relay.
P1488 Auxiliary 5 Volt Supply Output Too
LowAuxiliary 5 volt sensor feed is sensed to be below an
acceptable limit.
P1488 5 Volt Supply Voltage Low Sensor supply voltage for ECM sensors is too low.
P1489 High Speed Fan CTRL Relay Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the control
circuit of the high speed radiator fan control relay.
P1490 Low Speed Fan CTRL Relay Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in control circuit of
the low speed radiator fan control relay.
P1491 Rad Fan Control Relay Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the radiator fan
control relay control circuit. This includes PWM solid state
relays.
P1492 Ambient/Batt Temp Sen Volts Too
HighExternal temperature sensor input above acceptable
voltage.
P1492 (M) Ambient/Batt Temp Sensor Volts Too
HighBattery temperature sensor input voltage above an
acceptable range.
P1493 (M) Ambient/Batt Temp Sen Volts Too
LowExternal temperature sensor input below acceptable
voltage.
P1493 (M) Ambient/Batt Temp Sen Volts Too
LowBattery temperature sensor input voltage below an
acceptable range.
P1494 (M) Leak Detection Pump Sw or
Mechanical FaultIncorrect input state detected for the Leak Detection
Pump (LDP) pressure switch.
P1495 Leak Detection Pump Solenoid
CircuitAn open or shorted condition detected in the Leak
Detection Pump (LDP) solenoid circuit.
P1496 5 Volt Supply, Output Too Low 5 volt sensor feed is sensed to be below an acceptable
limit. ( less than 4v for 4 sec )
WJEMISSIONS CONTROL 25 - 13
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2172 of 2199

DESCRIPTION - TASK MANAGER
The PCM is responsible for efficiently coordinating
the operation of all the emissions-related compo-
nents. The PCM is also responsible for determining if
the diagnostic systems are operating properly. The
software designed to carry out these responsibilities
is referred to as the 'Task Manager'.
DESCRIPTION - MONITORED SYSTEMS
There are new electronic circuit monitors that
check fuel, emission, engine and ignition perfor-
mance. These monitors use information from various
sensor circuits to indicate the overall operation of the
fuel, engine, ignition and emission systems and thus
the emissions performance of the vehicle.
The fuel, engine, ignition and emission systems
monitors do not indicate a specific component prob-
lem. They do indicate that there is an implied prob-
lem within one of the systems and that a specific
problem must be diagnosed.
If any of these monitors detect a problem affecting
vehicle emissions, the Malfunction Indicator Lamp
(MIL) will be illuminated. These monitors generate
Diagnostic Trouble Codes that can be displayed with
the MIL or a scan tool.
The following is a list of the system monitors:
²Misfire Monitor
²Fuel System Monitor
²Oxygen Sensor Monitor
²Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor
²Catalyst Monitor
²Leak Detection Pump Monitor (if equipped)
All these system monitors require two consecutive
trips with the malfunction present to set a fault.
Refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnos-
tics Procedures manual for diagnostic proce-
dures.
The following is an operation and description of
each system monitor:
OXYGEN SENSOR (O2S) MONITOR
Effective control of exhaust emissions is achieved
by an oxygen feedback system. The most important
element of the feedback system is the O2S. The O2S
is located in the exhaust path. Once it reaches oper-
ating temperature 300É to 350ÉC (572É to 662ÉF), the
sensor generates a voltage that is inversely propor-
tional to the amount of oxygen in the exhaust. The
information obtained by the sensor is used to calcu-
late the fuel injector pulse width. This maintains a
14.7 to 1 Air Fuel (A/F) ratio. At this mixture ratio,
the catalyst works best to remove hydrocarbons (HC),
carbon monoxide (CO) and nitrogen oxide (NOx) from
the exhaust.
The O2S is also the main sensing element for the
Catalyst and Fuel Monitors.The O2S can fail in any or all of the following
manners:
²slow response rate
²reduced output voltage
²dynamic shift
²shorted or open circuits
Response rate is the time required for the sensor to
switch from lean to rich once it is exposed to a richer
than optimum A/F mixture or vice versa. As the sen-
sor starts malfunctioning, it could take longer to
detect the changes in the oxygen content of the
exhaust gas.
The output voltage of the O2S ranges from 0 to 1
volt. A good sensor can easily generate any output
voltage in this range as it is exposed to different con-
centrations of oxygen. To detect a shift in the A/F
mixture (lean or rich), the output voltage has to
change beyond a threshold value. A malfunctioning
sensor could have difficulty changing beyond the
threshold value.
OXYGEN SENSOR HEATER MONITOR
If there is an oxygen sensor (O2S) shorted to volt-
age DTC, as well as a O2S heater DTC, the O2S
fault MUST be repaired first. Before checking the
O2S fault, verify that the heater circuit is operating
correctly.
Effective control of exhaust emissions is achieved
by an oxygen feedback system. The most important
element of the feedback system is the O2S. The O2S
is located in the exhaust path. Once it reaches oper-
ating temperature 300É to 350ÉC (572 É to 662ÉF), the
sensor generates a voltage that is inversely propor-
tional to the amount of oxygen in the exhaust. The
information obtained by the sensor is used to calcu-
late the fuel injector pulse width. This maintains a
14.7 to 1 Air Fuel (A/F) ratio. At this mixture ratio,
the catalyst works best to remove hydrocarbons (HC),
carbon monoxide (CO) and nitrogen oxide (NOx) from
the exhaust.
The voltage readings taken from the O2S sensor
are very temperature sensitive. The readings are not
accurate below 300ÉC. Heating of the O2S sensor is
done to allow the engine controller to shift to closed
loop control as soon as possible. The heating element
used to heat the O2S sensor must be tested to ensure
that it is heating the sensor properly.
The O2S sensor circuit is monitored for a drop in
voltage. The sensor output is used to test the heater
by isolating the effect of the heater element on the
O2S sensor output voltage from the other effects.
LEAK DETECTION PUMP MONITOR (IF EQUIPPED)
The leak detection assembly incorporates two pri-
mary functions: it must detect a leak in the evapora-
WJEMISSIONS CONTROL 25 - 17
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2173 of 2199

tive system and seal the evaporative system so the
leak detection test can be run.
The primary components within the assembly are:
A three port solenoid that activates both of the func-
tions listed above; a pump which contains a switch,
two check valves and a spring/diaphragm, a canister
vent valve (CVV) seal which contains a spring loaded
vent seal valve.
Immediately after a cold start, between predeter-
mined temperature thresholds limits, the three port
solenoid is briefly energized. This initializes the
pump by drawing air into the pump cavity and also
closes the vent seal. During non test conditions the
vent seal is held open by the pump diaphragm
assembly which pushes it open at the full travel posi-
tion. The vent seal will remain closed while the
pump is cycling due to the reed switch triggering of
the three port solenoid that prevents the diaphragm
assembly from reaching full travel. After the brief
initialization period, the solenoid is de-energized
allowing atmospheric pressure to enter the pump
cavity, thus permitting the spring to drive the dia-
phragm which forces air out of the pump cavity and
into the vent system. When the solenoid is energized
and de energized, the cycle is repeated creating flow
in typical diaphragm pump fashion. The pump is con-
trolled in 2 modes:
Pump Mode:The pump is cycled at a fixed rate to
achieve a rapid pressure build in order to shorten the
overall test length.
Test Mode:The solenoid is energized with a fixed
duration pulse. Subsequent fixed pulses occur when
the diaphragm reaches the Switch closure point.
The spring in the pump is set so that the system
will achieve an equalized pressure of about 7.5º
water. The cycle rate of pump strokes is quite rapid
as the system begins to pump up to this pressure. As
the pressure increases, the cycle rate starts to drop
off. If there is no leak in the system, the pump would
eventually stop pumping at the equalized pressure. If
there is a leak, it will continue to pump at a rate rep-
resentative of the flow characteristic of the size of the
leak. From this information we can determine if the
leak is larger than the required detection limit (cur-
rently set at .040º orifice by CARB). If a leak is
revealed during the leak test portion of the test, the
test is terminated at the end of the test mode and no
further system checks will be performed.
After passing the leak detection phase of the test,
system pressure is maintained by turning on the
LDP's solenoid until the purge system is activated.
Purge activation in effect creates a leak. The cycle
rate is again interrogated and when it increases due
to the flow through the purge system, the leak check
portion of the diagnostic is complete.The canister vent valve will unseal the system
after completion of the test sequence as the pump
diaphragm assembly moves to the full travel position.
Evaporative system functionality will be verified by
using the stricter evap purge flow monitor. At an
appropriate warm idle the LDP will be energized to
seal the canister vent. The purge flow will be clocked
up from some small value in an attempt to see a
shift in the 02 control system. If fuel vapor, indicated
by a shift in the 02 control, is present the test is
passed. If not, it is assumed that the purge system is
not functioning in some respect. The LDP is again
turned off and the test is ended.
MISFIRE MONITOR
Excessive engine misfire results in increased cata-
lyst temperature and causes an increase in HC emis-
sions. Severe misfires could cause catalyst damage.
To prevent catalytic convertor damage, the PCM
monitors engine misfire.
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) monitors
for misfire during most engine operating conditions
(positive torque) by looking at changes in the crank-
shaft speed. If a misfire occurs the speed of the
crankshaft will vary more than normal.
FUEL SYSTEM MONITOR
To comply with clean air regulations, vehicles are
equipped with catalytic converters. These converters
reduce the emission of hydrocarbons, oxides of nitro-
gen and carbon monoxide. The catalyst works best
when the Air Fuel (A/F) ratio is at or near the opti-
mum of 14.7 to 1.
The PCM is programmed to maintain the optimum
air/fuel ratio of 14.7 to 1. This is done by making
short term corrections in the fuel injector pulse width
based on the O2S sensor output. The programmed
memory acts as a self calibration tool that the engine
controller uses to compensate for variations in engine
specifications, sensor tolerances and engine fatigue
over the life span of the engine. By monitoring the
actual fuel-air ratio with the O2S sensor (short term)
and multiplying that with the program long-term
(adaptive) memory and comparing that to the limit,
it can be determined whether it will pass an emis-
sions test. If a malfunction occurs such that the PCM
cannot maintain the optimum A/F ratio, then the
MIL will be illuminated.
CATALYST MONITOR
To comply with clean air regulations, vehicles are
equipped with catalytic converters. These converters
reduce the emission of hydrocarbons, oxides of nitro-
gen and carbon monoxide.
Normal vehicle miles or engine misfire can cause a
catalyst to decay. This can increase vehicle emissions
25 - 18 EMISSIONS CONTROLWJ
EMISSIONS CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2183 of 2199

CCV HOSE
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CCV SYSTEM -
4.0L
Before attempting diagnosis, be sure locations of
fixed orifice fitting and air inlet fitting (Fig. 8) have
not been inadvertently exchanged. The fixed orifice
fitting is light grey in color and is located atrearof
valve cover. The air inlet fitting is black in color and
is located atfrontof valve cover.
(1) Pull fixed orifice fitting (Fig. 8) from valve
cover and leave tube attached.
(2) Start engine and bring to idle speed.
(3) If fitting is not plugged, a hissing noise will be
heard as air passes through fitting orifice. Also, a
strong vacuum should be felt with a finger placed at
fitting inlet.
(4) If vacuum is not present, remove fitting orifice
fitting from tube. Start engine. If vacuum can now be
felt, replace fixed orifice fitting. Do not attempt to
clean plastic fitting.
(5) If vacuum is still not felt at hose, check line/
hose for kinks or for obstruction. If necessary, clean
out intake manifold fitting at intake manifold. Do
this by turning a 1/4 inch drill (by hand) through the
fitting to dislodge any solid particles. Blow out thefitting with shop air. If necessary, use a smaller drill
to avoid removing any metal from the fitting.
(6) Return fixed orifice fitting to valve cover and
leave tube attached.
(7) Disconnect air inlet fitting and its attached
hose at front of valve cover (Fig. 8). Start engine and
bring to idle speed. Hold a piece of stiff paper (such
as a parts tag) loosely over the rubber grommet
(opening) of the disconnected air inlet fitting.
(8) The paper should be drawn against the rubber
grommet with noticeable force. This will be after
allowing approximately one minute for crankcase
pressure to reduce.
(9) If vacuum is not present, check breather hoses/
tubes/lines for obstructions or restrictions.
(10) After testing, reconnect all system hoses/
tubes/lines.
REMOVAL - FIXED ORIFICE FITTING
When installing fixed orifice fitting, be sure loca-
tions of fixed orifice fitting and air inlet fitting (Fig.
9) have not been inadvertently exchanged. The fixed
orifice fitting is light grey in color and is located at
rearof valve cover. The air inlet fitting is black in
color and is located atfrontof valve cover.
(1) Pull fixed orifice fitting (Fig. 9) from valve
cover grommet.
(2) Separate fitting from CCV breather tube.
Fig. 8 Fixed Orifice Fitting and CCV SystemÐ4.0L
Engine
1 - AIR INLET FITTING
2 - FIXED ORIFICE FITTING
3 - CCV BREATHER TUBE (REAR)
4 - INT. MAN. FITTING
5 - CCV BREATHER TUBE (FRONT)
Fig. 9 FIXED ORIFICE FITTING - 4.0L
1 - AIR INLET FITTING
2 - FIXED ORIFICE FITTING
3 - CCV BREATHER TUBE (REAR)
4 - INT. MAN. FITTING
5 - CCV BREATHER TUBE (FRONT)
25 - 28 EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONSWJ
Page 2184 of 2199

INSTALLATION - FIXED ORIFICE FITTING
When installing fixed orifice fitting, be sure loca-
tions of fixed orifice fitting and air inlet fitting (Fig.
9) have not been inadvertently exchanged. The fixed
orifice fitting is light grey in color and is located at
rearof valve cover. The air inlet fitting is black in
color and is located atfrontof valve cover.
(1) Connect fitting to CCV breather tube.
(2) Return fixed orifice fitting to valve cover grom-
met.
EVAP/PURGE SOLENOID
DESCRIPTION
The duty cycle EVAP canister purge solenoid (DCP)
regulates the rate of vapor flow from the EVAP can-
ister to the intake manifold. The Powertrain Control
Module (PCM) operates the solenoid.
OPERATION
During the cold start warm-up period and the hot
start time delay, the PCM does not energize the sole-
noid. When de-energized, no vapors are purged. The
PCM de-energizes the solenoid during open loop oper-
ation.
The engine enters closed loop operation after it
reaches a specified temperature and the time delay
ends. During closed loop operation, the PCM cycles
(energizes and de-energizes) the solenoid 5 or 10
times per second, depending upon operating condi-
tions. The PCM varies the vapor flow rate by chang-
ing solenoid pulse width. Pulse width is the amount
of time that the solenoid is energized. The PCM
adjusts solenoid pulse width based on engine operat-
ing condition.
REMOVAL
The duty cycle evaporative (EVAP) canister purge
solenoid is located in the engine compartment near
the brake master cylinder (Fig. 10).
(1) Disconnect electrical connector at solenoid.
(2) Disconnect vacuum lines at solenoid.
(3) Lift solenoid slot (Fig. 10) from mounting
bracket for removal.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position solenoid slot to mounting bracket.
(2) Connect vacuum lines to solenoid. Be sure vac-
uum lines are firmly connected and not leaking or
damaged. If leaking, a Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC) may be set with certain emission packages.
(3) Connect electrical connector to solenoid.
FUEL FILLER CAP
DESCRIPTION
The plastic fuel tank filler tube cap is threaded
onto the end of the fuel fill tube. Certain models are
equipped with a 1/4 turn cap.
OPERATION
The loss of any fuel or vapor out of fuel filler tube
is prevented by the use of a pressure-vacuum fuel fill
cap. Relief valves inside the cap will release fuel tank
pressure at predetermined pressures. Fuel tank vac-
uum will also be released at predetermined values.
This cap must be replaced by a similar unit if
replacement is necessary. This is in order for the sys-
tem to remain effective.
CAUTION: Remove fill cap before servicing any fuel
system component to relieve tank pressure. If
equipped with a California emissions package and a
Leak Detection Pump (LDP), the cap must be tight-
ened securely. If cap is left loose, a Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC) may be set.
REMOVAL
If replacement of the 1/4 turn fuel tank filler tube
cap is necessary, it must be replaced with an identi-
cal cap to be sure of correct system operation.
Fig. 10 EVAP/PURGE SOLENOID LOCATION
1 - BRAKE MASTER CYLINDER
2 - EVAP SOLENOID
3 - SLOT
4 - ELEC. CONNEC.
5 - VACUUM LINE CONNEC.
6 - TEST PORT
WJEVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS 25 - 29
CCV HOSE (Continued)
Page 2187 of 2199
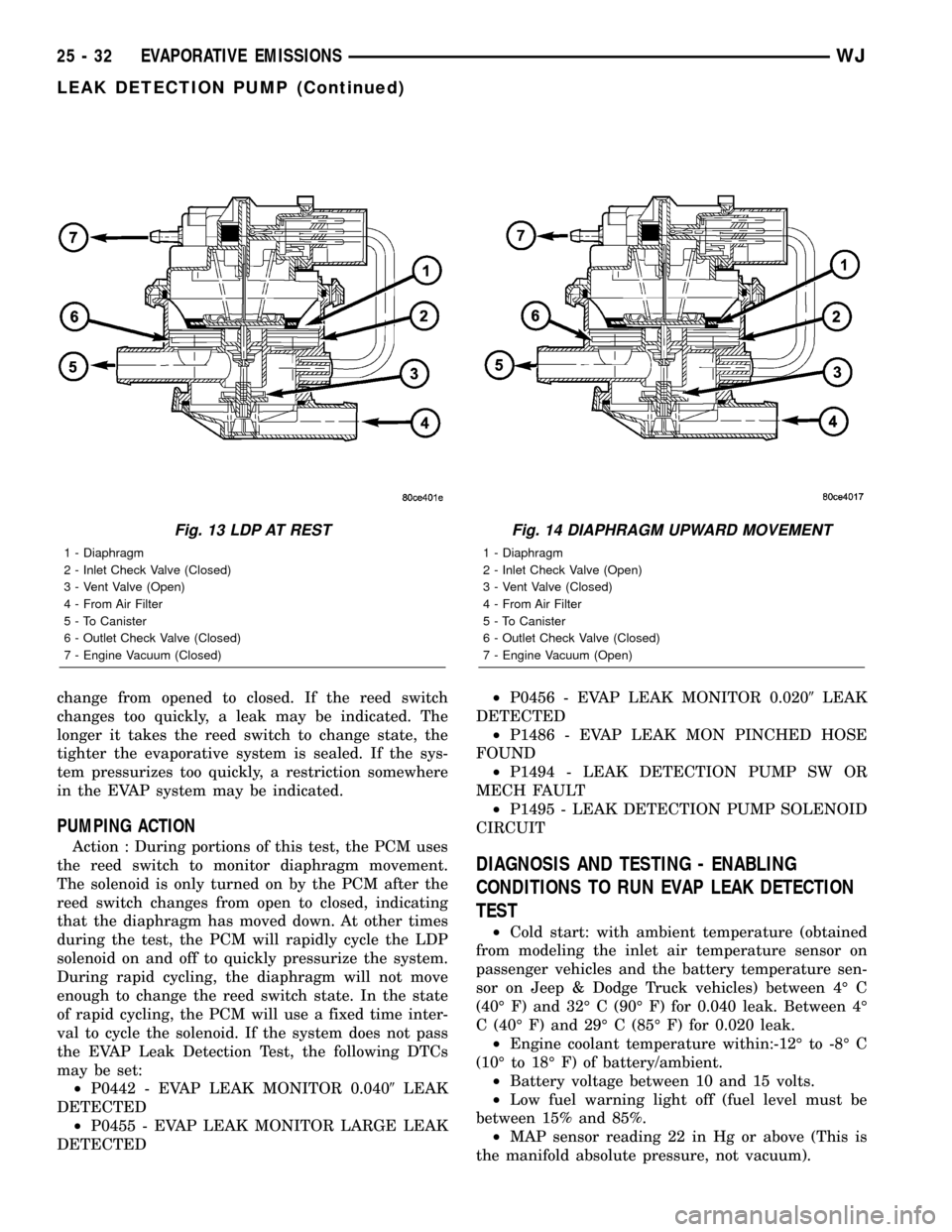

change from opened to closed. If the reed switch
changes too quickly, a leak may be indicated. The
longer it takes the reed switch to change state, the
tighter the evaporative system is sealed. If the sys-
tem pressurizes too quickly, a restriction somewhere
in the EVAP system may be indicated.
PUMPING ACTION
Action : During portions of this test, the PCM uses
the reed switch to monitor diaphragm movement.
The solenoid is only turned on by the PCM after the
reed switch changes from open to closed, indicating
that the diaphragm has moved down. At other times
during the test, the PCM will rapidly cycle the LDP
solenoid on and off to quickly pressurize the system.
During rapid cycling, the diaphragm will not move
enough to change the reed switch state. In the state
of rapid cycling, the PCM will use a fixed time inter-
val to cycle the solenoid. If the system does not pass
the EVAP Leak Detection Test, the following DTCs
may be set:
²P0442 - EVAP LEAK MONITOR 0.0409LEAK
DETECTED
²P0455 - EVAP LEAK MONITOR LARGE LEAK
DETECTED²P0456 - EVAP LEAK MONITOR 0.0209LEAK
DETECTED
²P1486 - EVAP LEAK MON PINCHED HOSE
FOUND
²P1494 - LEAK DETECTION PUMP SW OR
MECH FAULT
²P1495 - LEAK DETECTION PUMP SOLENOID
CIRCUIT
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENABLING
CONDITIONS TO RUN EVAP LEAK DETECTION
TEST
²Cold start: with ambient temperature (obtained
from modeling the inlet air temperature sensor on
passenger vehicles and the battery temperature sen-
sor on Jeep & Dodge Truck vehicles) between 4É C
(40É F) and 32É C (90É F) for 0.040 leak. Between 4É
C (40É F) and 29É C (85É F) for 0.020 leak.
²Engine coolant temperature within:-12É to -8É C
(10É to 18É F) of battery/ambient.
²Battery voltage between 10 and 15 volts.
²Low fuel warning light off (fuel level must be
between 15% and 85%.
²MAP sensor reading 22 in Hg or above (This is
the manifold absolute pressure, not vacuum).
Fig. 13 LDP AT REST
1 - Diaphragm
2 - Inlet Check Valve (Closed)
3 - Vent Valve (Open)
4 - From Air Filter
5 - To Canister
6 - Outlet Check Valve (Closed)
7 - Engine Vacuum (Closed)
Fig. 14 DIAPHRAGM UPWARD MOVEMENT
1 - Diaphragm
2 - Inlet Check Valve (Open)
3 - Vent Valve (Closed)
4 - From Air Filter
5 - To Canister
6 - Outlet Check Valve (Closed)
7 - Engine Vacuum (Open)
25 - 32 EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONSWJ
LEAK DETECTION PUMP (Continued)
Page 2188 of 2199

²No engine stall during test.
NOTE: IF BATTERY VOLTAGE DROPS BELOW 10
VOLTS FOR MORE THAN 5 SECONDS DURING
ENGINE CRANKING, THE EVAP LEAK DETECTION
TEST WILL NOT RUN.
NOTE: THE FOLLOWING VALUES ARE APPROXI-
MATE AND VEHICLE SPECIFIC. USE THE VALUES
SEEN IN PRE TEST/MONITOR TEST SCREEN ON
THE DRB IIIT. SEE TSB 25-02-98 FOR MORE
DETAIL.
A DTC will not be set if a one-trip fault is set or if
the MIL is illuminated for any of the following:
²Purge Solenoid Electrical Fault
²All TPS Faults
²All Engine Controller Self Test Faults
²LDP Pressure Switch Fault
²All Cam and/or Crank Sensor Fault
²EGR Solenoid Electrical Fault
²All MAP Sensor Faults
²All Injector Faults
²Ambient/Battery Temperature Sensor Electrical
Faults²Baro Out of Range
²Vehicle Speed Faults
²All Coolant Sensor Faults
²LDP Solenoid Circuit
NOTE: IF BATTERY TEMPERATURE IS NOT WITHIN
RANGE, OR IF THE ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERA-
TURE IS NOT WITHIN A SPECIFIED RANGE OF THE
BATTERY TEMPERATURE, THE PCM WILL NOT
RUN TESTS FOR DTC P1494, P1486, P0442, P0455
AND P0441. THESE TEMPERATURE CALIBRATIONS
MAY BE DIFFERENT BETWEEN MODELS.
SECTION 1 - P1495 Leak Detection Pump
Solenoid Circuit-When the ignition key is turned
to9ON9, the LDP diaphragm should be in the down
position and the LDP reed switch should be closed. If
the EVAP system has residual pressure, the LDP dia-
phragm may be up. This could result in the LDP reed
switch being open when the key is turned to9ON9
and a P1494 fault could be set because the PCM is
expecting the reed switch to be closed.
After the key is turned9ON9, the PCM immedi-
ately tests the LDP solenoid circuit for electrical
faults. If a fault is detected, DTC P1495 will set, the
Fig. 15 DIAPHRAGM DOWNWARD MOVEMENT
1 - Diaphragm
2 - Inlet Check Valve (Closed)
3 - Vent Valve (Closed)
4 - From Air Filter
5 - To Canister
6 - Outlet Check Valve (Open)
7 - Engine Vacuum (Closed)EVAP LDP TEST SEQUENCE
1 - IGNITION SWITCH
2 - LDP DIAPHRAM
3 - LDP SWITCH
4 - LDP SOLENOID
5 - SECTION 1
6 - SECTION 2
7 - SECTION 3
8 - SECTION 4
9 - SECTION 5
10 - 3 TEST CYCLES TO TEST FOR BLOCKAGE
11- RAPID PUMP CYCLING FOR 70 CYCLES
WJEVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS 25 - 33
LEAK DETECTION PUMP (Continued)
Page 2189 of 2199

MIL will illuminate, and the remaining EVAP Leak
Detection Test is canceled.
SECTION 2 - P1494 Leak Detection Pump
Switch or Mechanical Fault-If DTC P1495 is not
set, the PCM will check for DTC P1494. If the LDP
reed switch was closed when the key was turned to
9ON9, the PCM energizes the LDP solenoid for up to
8 seconds and monitors the LDP switch. As the LDP
diaphragm is pulled up by engine vacuum, the LDP
reed switch should change from closed to open. If it
does not, the PCM sets a temporary fault (P1494) in
memory, and waits until the next time the Enabling
Conditions are met to run the test again. If this is
again detected, P1494 is stored and the MIL is illu-
minated. If the problem is not detected during the
next enabling cycle, the temporary fault will be
cleared.
However, if the PCM detects the reed switch open
when the key is turned to9ON9, the PCM must deter-
mine if this condition is due to residual pressure in
the EVAP system, or an actual fault. The PCM stores
information in memory on EVAP system purging
from previous engine run or drive cycles.
If little or no purging took place, residual pressure
could be holding the LDP diaphragm up, causing the
LDP switch to be open. Since this is not a malfunc-
tion, the PCM cancels the EVAP Leak Detection Test
without setting the temporary fault.
If there was sufficient purging during the previous
cycle to eliminate EVAP system pressure, the PCM
judges that this is a malfunction and sets a tempo-
rary fault in memory. The next time that the
Enabling Conditions are met, the test will run again.
If the fault is again detected, the MIL will illuminate
and DTC P1494 will be stored. If the fault is not
detected, the temporary fault will be cleared.
SECTION 3 - P1486 EVAP Leak Monitor
Pinched Hose Found-If no fault has been detected
so far, the PCM begins testing for possible blockage
in the EVAP system between the LDP and the fuel
tank. This is done by monitoring the time required
for the LDP to pump air into the EVAP system dur-
ing two to three pump cycles. If no blockage is
present, the LDP diaphragm is able to quickly pump
air out of the LDP each time the PCM turns off the
LDP solenoid. If a blockage is present, the PCM
detects that the LDP takes longer to complete each
pump cycle. If the pump cycles take longer than
expected (approximately 6 to 10 seconds) the PCM
will suspect a blockage. On the next drive when
Enabling Conditions are met, the test will run again.
If blockage is again detected, P1486 is stored, and
the MIL is illuminated.
SECTION4-NoDTCCanBeSetDuring This
Time-After the LDP blockage tests are completed,
the PCM then tests for EVAP system leakage. First,the PCM commands the LDP to rapidly pump for 20
to 50 seconds (depending on fuel level) to build pres-
sure in the EVAP system. This evaluates the system
J18-24-0 to see if it can be sufficiently pressurized.
This evaluation (rapid pump cycling) may occur sev-
eral times prior to leak checking. The LDP reed
switch does not close and open during rapid pumping
because the diaphragm does not travel through its
full range during this part of the test.
SECTION 5 - P0456, P0442, P0455 EVAP Leak
Monitor and Leak Detected-Next, the PCM per-
forms one or more test cycles by monitoring the time
required for the LDP reed switch to close (diaphragm
to drop) after the LDP solenoid is turned off.
If the switch does not close, or closes after a long
delay, it means that the system does not have any
significant leakage and the EVAP Leak Detection
Test is complete.
However, if the LDP reed switch closes quickly,
there may be a leak or the fuel level may be low
enough that the LDP must pump more to finish pres-
surizing the EVAP system. In this case, the PCM will
rapidly pump the LDP again to build pressure in the
EVAP system, and follow that by monitoring the time
needed for several LDP test cycles. This process of
rapid pumping followed by several LDP test cycles
may repeat several times before the PCM judges that
a leak is present.
When leaks are present, the LDP test cycle time
will be inversely proportional to the size of the leak.
The larger the leak, the shorter the test cycle time.
The smaller the leak, the longer the test cycle time.
DTC's may be set when a leak as small as 0.5 mm
(0.0209) diameter is present.
If the system detects a leak, a temporary fault will
be stored in PCM memory. The time it takes to detect
a .020, .040, or Large leak is based on calibrations
that vary from model to model. The important point
to remember is if a leak is again detected on the next
EVAP Leak Detection Test, the MIL will illuminate
and a DTC will be stored based on the size of leak
detected. If no leak is detected during the next test,
the temporary fault will be cleared.
DIAGNOSTIC TIPS During diagnosis, you can
compare the LDP solenoid activity with the monitor
sequence in Figure 6. If the PCM detects a problem
that could set a DTC, the testing is halted and LDP
solenoid activity will stop. As each section of the test
begins, it indicates that the previous section passed
successfully. By watching to see which tests complete,
you can see if any conditions are present that the
PCM considers abnormal.
For example, if the LDP solenoid is energized for
the test cycles to test for blockage (P1486), it means
that the LDP has already passed its test for P1494.
Then, if the PCM detects a possible blockage, it will
25 - 34 EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONSWJ
LEAK DETECTION PUMP (Continued)
Page 2190 of 2199

set a temporary fault without turning on the MIL
and continue the leak portion of the test. However,
the PCM will assume that the system is already
pressurized and skip the rapid pump cycles.
Always diagnose leaks, if possible, before discon-
necting connections. Disconnecting connections may
mask a leak condition.
Keep in mind that if the purge solenoid seat is
leaking, it could go undetected since the leak would
end up in the intake manifold. Disconnect the purge
solenoid at the manifold when leak checking. In addi-
tion, a pinched hose fault (P1486) could set if the
purge solenoid does not purge the fuel system prop-
erly (blocked seat). The purge solenoid must vent the
fuel system prior to the LDP system test. If the
purge solenoid cannot properly vent the system the
LDP cannot properly complete the test for P1486 and
this fault can set due to pressure being in the EVAP
system during the test sequence.
Multiple actuation's of the DRB IIItLeak Detec-
tion Pump (LDP) Monitor Test can hide a 0.020 leak
because of excess vapor generation. Additionally, any
source for additional vapor generation can hide a
small leak in the EVAP system. Excess vapor gener-
ation can delay the fall of the LDP diaphragm thus
hiding the small leak. An example of this condition
could be bringing a cold vehicle into a warm shop for
testing or high ambient temperatures.
Fully plugged and partially plugged underhood
vacuum lines have been known to set MIL condi-
tions. P1494 and P0456 can be set for this reason.
Always, thoroughly, check plumbing for pinches or
blockage before condemning components.
TEST EQUIPMENT The Evaporative Emission
Leak Detector (EELD) Miller Special Tool 8404 is
capable of visually detecting leaks in the evaporative
system and will take the place of the ultrasonic leak
detector 6917A. The EELD utilizes shop air and a
smoke generator to visually detect leaks down to
0.020 or smaller. The food grade oil used to make the
smoke includes an UV trace dye that will leave tell-
tale signs of the leak under a black light. This is
helpful when components have to be removed to
determine the exact leak location. For detailed test
instructions, follow the operators manual packaged
with the EELD.
NOTE: Be sure that the PCM has the latest software
update. Reprogram as indicated by any applicable
Technical Service Bulletin. After LDP repairs are
completed, verify the repair by running the DRB IIIT
Leak Detection Pump (LDP) Monitor Test as
described in Technical Service Bulletin 18-12-99.REMOVAL
The Leak Detection Pump (LDP) is located under
the left quarter panel behind the left/rear wheel (Fig.
16). It is attached to a two-piece support bracket
(Fig. 17). The LDP and LDP filter are replaced (ser-
viced) as one unit.
(1) Remove stone shield behind left/rear wheel
(Fig. 18). Drill out plastic rivets for removal.
(2) Remove 3 LDP mounting bolts (Fig. 19).
(3) Remove support bracket brace bolt (Fig. 17).
(4) Loosen, but do not remove 2 support bracket
nuts at frame rail (Fig. 19).
(5) To separate and lower front section of two-piece
support bracket, remove 3 attaching bolts on bottom
of support bracket (Fig. 17). While lowering support
bracket, disconnect LDP wiring clip (Fig. 20).
(6) Disconnect electrical connector at LDP (Fig.
20).
(7) Carefully remove vapor/vacuum lines at LDP
(Fig. 20).
(8) Remove LDP.
INSTALLATION
The LDP is located in the left quarter panel behind
the left/rear wheel. It is attached to a two-piece sup-
port bracket (Fig. 17). The LDP and LDP filter are
replaced (serviced) as one unit.
(1) Position LDP and carefully install vapor/vac-
uum lines to LDP and LDP filter.The vapor/vac-
uum lines and hoses must be firmly connected.
Fig. 16 LOCATION, LDP / EVAP CANISTER
1 - LEAK DETECTION PUMP
2 - EVAP CANISTER
WJEVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS 25 - 35
LEAK DETECTION PUMP (Continued)
Page 2193 of 2199

(8)Do not attempt to clean the old PCV valve.
(9) Return PCV valve back to oil filler tube by
placing valve locating tabs (Fig. 21) into cam lock.
Press PCV valve in and rotate valve upward. A slight
click will be felt when tabs have engaged cam lock.
Valve should be pointed towards rear of vehicle.
(10) Connect PCV line/hose and connecting rubber
hose to PCV valve.
(11) Disconnect rubber hose from fresh air fitting
at left side of air cleaner resonator box (Fig. 22).
Start engine and bring to idle speed. Hold a piece of
stiff paper (such as a parts tag) loosely over the
opening of the disconnected rubber hose.
(12) The paper should be drawn against the hose
opening with noticeable force. This will be after
allowing approximately one minute for crankcase
pressure to reduce.
(13) If vacuum is not present, disconnect each PCV
system hose at top of each breather (Fig. 22). Check
for obstructions or restrictions.(14) If vacuum is still not present, remove each
PCV system breather (Fig. 22) from each cylinder
head. Check for obstructions or restrictions. If
plugged, replace breather. Tighten breather to 12
N´m (106 in. lbs.) torque. Do not attempt to clean
breather
(15) If vacuum is still not present, disconnect each
PCV system hose at each fitting and check for
obstructions or restrictions.
Fig. 21 PCV Valve/Oil Filler TubeÐ4.7L V-8 Engine
1 - O-RING
2 - LOCATING TABS
3 - CAM LOCK
4 - OIL FILLER TUBE
5 - PCV LINE/HOSE
6 - P C V VA LV E
Fig. 22 PCV Breathers/Tubes/HosesÐ4.7L V-8
Engine
1 - FRESH AIR FITTING
2 - CONNECTING TUBES/HOSES
3 - CRANKCASE BREATHERS (2)
4 - RUBBER HOSE
5 - AIR CLEANER RESONATOR
25 - 38 EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONSWJ
PCV VALVE (Continued)