Engine JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 1783 of 2199

A solenoid can also be described by the method by
which it is controlled. Some of the possibilities
include variable force, pulse-width modulated, con-
stant ON, or duty cycle. The variable force and pulse-
width modulated versions utilize similar methods to
control the current flow through the solenoid to posi-
tion the solenoid plunger at a desired position some-
where between full ON and full OFF. The constant
ON and duty cycled versions control the voltage
across the solenoid to allow either full flow or no flow
through the solenoid's valve.
OPERATION
When an electrical current is applied to the sole-
noid coil, a magnetic field is created which produces
an attraction to the plunger, causing the plunger to
move and work against the spring pressure and the
load applied by the fluid the valve is controlling. The
plunger is normally directly attached to the valve
which it is to operate. When the current is removed
from the coil, the attraction is removed and the
plunger will return to its original position due to
spring pressure.
The plunger is made of a conductive material and
accomplishes this movement by providing a path for
the magnetic field to flow. By keeping the air gap
between the plunger and the coil to the minimum
necessary to allow free movement of the plunger, the
magnetic field is maximized.
TORQUE CONVERTER
DESCRIPTION
The torque converter (Fig. 109) is a hydraulic
device that couples the engine crankshaft to the
transmission. The torque converter consists of an
outer shell with an internal turbine, a stator, an
overrunning clutch, an impeller and an electronically
applied converter clutch. The converter clutch pro-vides reduced engine speed and greater fuel economy
when engaged. Clutch engagement also provides
reduced transmission fluid temperatures. The con-
verter clutch engages in third gear. The torque con-
verter hub drives the transmission oil (fluid) pump
and contains an o-ring seal to better control oil flow.
The torque converter is a sealed, welded unit that
is not repairable and is serviced as an assembly.
CAUTION: The torque converter must be replaced if
a transmission failure resulted in large amounts of
metal or fiber contamination in the fluid. If the fluid
is contaminated, flush the fluid cooler and lines.
Fig. 109 Torque Converter Assembly
1 - TURBINE ASSEMBLY
2-STATOR
3 - CONVERTER HUB
4 - O-RING
5 - IMPELLER ASSEMBLY
6 - CONVERTER CLUTCH PISTON
7 - TURBINE HUB
21 - 264 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFEWJ
SOLENOIDS (Continued)
Page 1784 of 2199

IMPELLER
The impeller (Fig. 110) is an integral part of the
converter housing. The impeller consists of curved
blades placed radially along the inside of the housing
on the transmission side of the converter. As the con-
verter housing is rotated by the engine, so is the
impeller, because they are one and the same and are
the driving members of the system.
Fig. 110 Impeller
1 - ENGINE FLEXPLATE 4 - ENGINE ROTATION
2 - OIL FLOW FROM IMPELLER SECTION INTO TURBINE
SECTION5 - ENGINE ROTATION
3 - IMPELLER VANES AND COVER ARE INTEGRAL
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 265
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1785 of 2199

TURBINE
The turbine (Fig. 111) is the output, or driven,
member of the converter. The turbine is mounted
within the housing opposite the impeller, but is not
attached to the housing. The input shaft is inserted
through the center of the impeller and splined into
the turbine. The design of the turbine is similar to
the impeller, except the blades of the turbine are
curved in the opposite direction.
Fig. 111 Turbine
1 - TURBINE VANE 4 - PORTION OF TORQUE CONVERTER COVER
2 - ENGINE ROTATION 5 - ENGINE ROTATION
3 - INPUT SHAFT 6 - OIL FLOW WITHIN TURBINE SECTION
21 - 266 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFEWJ
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1786 of 2199

STATOR
The stator assembly (Fig. 112) is mounted on a sta-
tionary shaft which is an integral part of the oil
pump. The stator is located between the impeller and
turbine within the torque converter case (Fig. 113).
The stator contains an over-running clutch, which
allows the stator to rotate only in a clockwise direc-
tion. When the stator is locked against the over-run-
ning clutch, the torque multiplication feature of the
torque converter is operational.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC)
The TCC (Fig. 114) was installed to improve the
efficiency of the torque converter that is lost to the
slippage of the fluid coupling. Although the fluid cou-
pling provides smooth, shock-free power transfer, it is
natural for all fluid couplings to slip. If the impeller
and turbine were mechanically locked together, a
zero slippage condition could be obtained. A hydraulic
piston with friction material was added to the tur-
bine assembly to provide this mechanical lock-up.
In order to reduce heat build-up in the transmission
and buffer the powertrain against torsional vibrations,
the TCM can duty cycle the L/R-CC Solenoid to achieve
a smooth application of the torque converter clutch.
This function, referred to as Electronically Modulated
Converter Clutch (EMCC) can occur at various times
depending on the following variables:
²Shift lever position
²Current gear range
²Transmission fluid temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²Input speed
²Throttle angle
²Engine speed
Fig. 112 Stator Components
1 - CAM (OUTER RACE)
2 - ROLLER
3 - SPRING
4 - INNER RACE
Fig. 113 Stator Location
1-STATOR
2 - IMPELLER
3 - FLUID FLOW
4 - TURBINE
Fig. 114 Torque Converter Clutch (TCC)
1 - IMPELLER FRONT COVER
2 - THRUST WASHER ASSEMBLY
3 - IMPELLER
4-STATOR
5 - TURBINE
6 - PISTON
7 - FRICTION DISC
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 267
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1787 of 2199
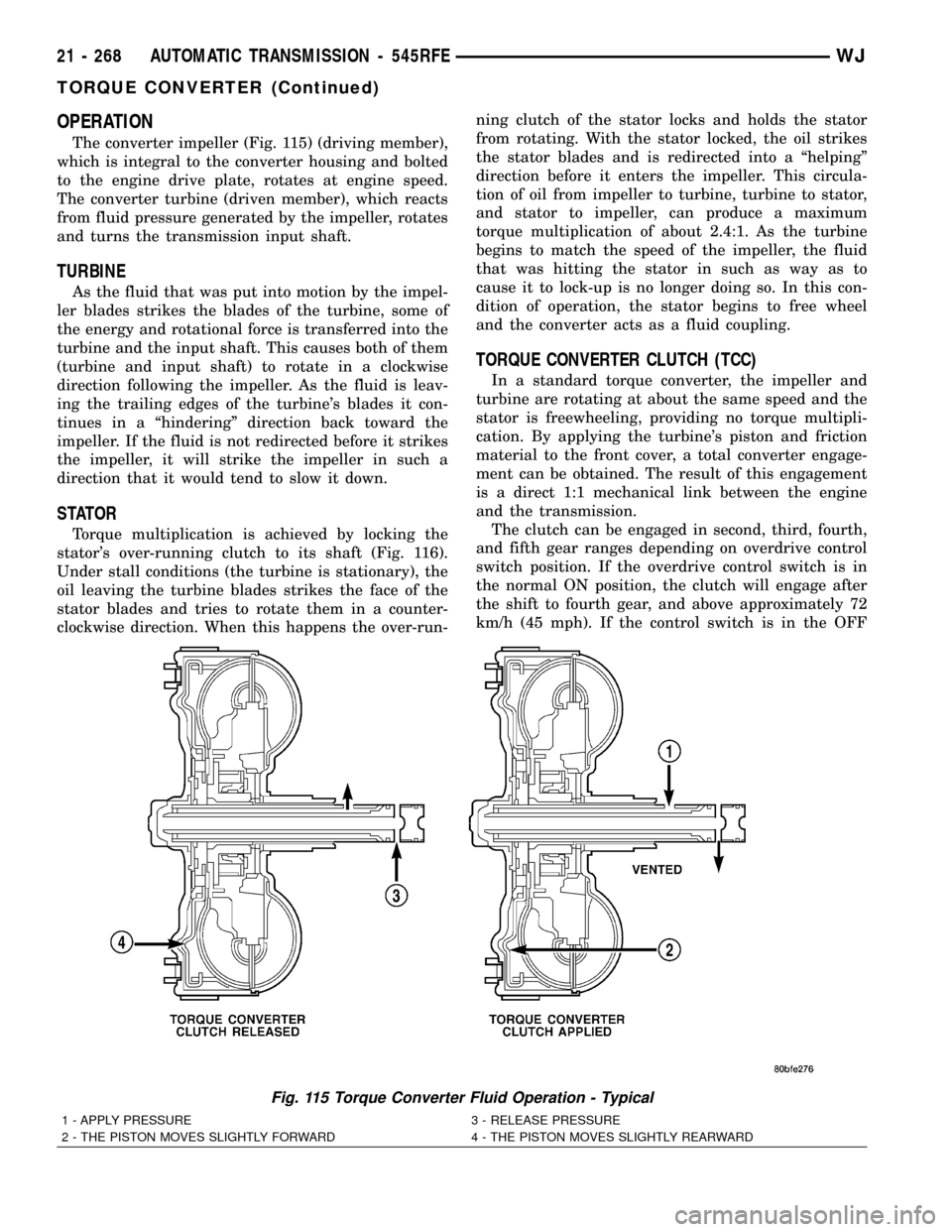
OPERATION
The converter impeller (Fig. 115) (driving member),
which is integral to the converter housing and bolted
to the engine drive plate, rotates at engine speed.
The converter turbine (driven member), which reacts
from fluid pressure generated by the impeller, rotates
and turns the transmission input shaft.
TURBINE
As the fluid that was put into motion by the impel-
ler blades strikes the blades of the turbine, some of
the energy and rotational force is transferred into the
turbine and the input shaft. This causes both of them
(turbine and input shaft) to rotate in a clockwise
direction following the impeller. As the fluid is leav-
ing the trailing edges of the turbine's blades it con-
tinues in a ªhinderingº direction back toward the
impeller. If the fluid is not redirected before it strikes
the impeller, it will strike the impeller in such a
direction that it would tend to slow it down.
STATOR
Torque multiplication is achieved by locking the
stator's over-running clutch to its shaft (Fig. 116).
Under stall conditions (the turbine is stationary), the
oil leaving the turbine blades strikes the face of the
stator blades and tries to rotate them in a counter-
clockwise direction. When this happens the over-run-ning clutch of the stator locks and holds the stator
from rotating. With the stator locked, the oil strikes
the stator blades and is redirected into a ªhelpingº
direction before it enters the impeller. This circula-
tion of oil from impeller to turbine, turbine to stator,
and stator to impeller, can produce a maximum
torque multiplication of about 2.4:1. As the turbine
begins to match the speed of the impeller, the fluid
that was hitting the stator in such as way as to
cause it to lock-up is no longer doing so. In this con-
dition of operation, the stator begins to free wheel
and the converter acts as a fluid coupling.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC)
In a standard torque converter, the impeller and
turbine are rotating at about the same speed and the
stator is freewheeling, providing no torque multipli-
cation. By applying the turbine's piston and friction
material to the front cover, a total converter engage-
ment can be obtained. The result of this engagement
is a direct 1:1 mechanical link between the engine
and the transmission.
The clutch can be engaged in second, third, fourth,
and fifth gear ranges depending on overdrive control
switch position. If the overdrive control switch is in
the normal ON position, the clutch will engage after
the shift to fourth gear, and above approximately 72
km/h (45 mph). If the control switch is in the OFF
Fig. 115 Torque Converter Fluid Operation - Typical
1 - APPLY PRESSURE 3 - RELEASE PRESSURE
2 - THE PISTON MOVES SLIGHTLY FORWARD 4 - THE PISTON MOVES SLIGHTLY REARWARD
21 - 268 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFEWJ
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1788 of 2199

position, the clutch will engage after the shift to
third gear, at approximately 56 km/h (35 mph) at
light throttle.
The TCM controls the torque converter by way of
internal logic software. The programming of the soft-
ware provides the TCM with control over the L/R-CC
Solenoid. There are four output logic states that can
be applied as follows:
²No EMCC
²Partial EMCC
²Full EMCC
²Gradual-to-no EMCC
NO EMCC
Under No EMCC conditions, the L/R Solenoid is
OFF. There are several conditions that can result in
NO EMCC operations. No EMCC can be initiated
due to a fault in the transmission or because the
TCM does not see the need for EMCC under current
driving conditions.
PARTIAL EMCC
Partial EMCC operation modulates the L/R Sole-
noid (duty cycle) to obtain partial torque converter
clutch application. Partial EMCC operation is main-
tained until Full EMCC is called for and actuated.
During Partial EMCC some slip does occur. Partial
EMCC will usually occur at low speeds, low load and
light throttle situations.
FULL EMCC
During Full EMCC operation, the TCM increases
the L/R Solenoid duty cycle to full ON after PartialEMCC control brings the engine speed within the
desired slip range of transmission input speed rela-
tive to engine rpm.
GRADUAL-TO-NO EMCC
This operation is to soften the change from Full or
Partial EMCC to No EMCC. This is done at mid-
throttle by decreasing the L/R Solenoid duty cycle.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove transmission and torque converter
from vehicle.
(2) Place a suitable drain pan under the converter
housing end of the transmission.
CAUTION: Verify that transmission is secure on the
lifting device or work surface, the center of gravity
of the transmission will shift when the torque con-
verter is removed creating an unstable condition.
The torque converter is a heavy unit. Use caution
when separating the torque converter from the
transmission.
(3) Pull the torque converter forward until the cen-
ter hub clears the oil pump seal.
(4) Separate the torque converter from the trans-
mission.
INSTALLATION
Check converter hub and drive flats for sharp
edges, burrs, scratches, or nicks. Polish the hub and
flats with 320/400 grit paper or crocus cloth if neces-
sary. Verify that the converter hub o-ring is properly
installed and is free from debris. The hub must be
smooth to avoid damaging the pump seal at installa-
tion.
(1) Lubricate oil pump seal lip with transmission
fluid.
(2) Place torque converter in position on transmis-
sion.
CAUTION: Do not damage oil pump seal or con-
verter hub o-ring while inserting torque converter
into the front of the transmission.
(3) Align torque converter to oil pump seal open-
ing.
(4) Insert torque converter hub into oil pump.
(5) While pushing torque converter inward, rotate
converter until converter is fully seated in the oil
pump gears.
(6) Check converter seating with a scale and
straightedge (Fig. 117). Surface of converter lugs
should be at least 13 mm (1/2 in.) to rear of straight-
edge when converter is fully seated.
(7) If necessary, temporarily secure converter with
C-clamp attached to the converter housing.
Fig. 116 Stator Operation
1 - DIRECTION STATOR WILL FREE WHEEL DUE TO OIL
PUSHING ON BACKSIDE OF VANES
2 - FRONT OF ENGINE
3 - INCREASED ANGLE AS OIL STRIKES VANES
4 - DIRECTION STATOR IS LOCKED UP DUE TO OIL PUSHING
AGAINST STATOR VANES
WJAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFE 21 - 269
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)
Page 1791 of 2199

REMOVAL
(1) Remove the valve body from the transmission
(Fig. 119).
(2) Remove the screws holding the transmission
solenoid/TRS assembly onto the valve body (Fig. 120).
(3) Separate the transmission solenoid/TRS assem-
bly from the valve body.
INSTALLATION
(1) Place TRS selector plate in the PARK position.
(2) Position the transmission solenoid/TRS assem-
bly onto the valve body. Be sure that both alignment
dowels are fully seated in the valve body and that
the TRS switch contacts are properly positioned in
the selector plate
(3) Install the screws to hold the transmission
solenoid/TRS assembly onto the valve body.
(4) Tighten the solenoid assembly screws adjacent
to the arrows cast into the bottom of the valve body
first. Tighten the screws to 5.7 N´m (50 in.lbs.).
(5) Tighten the remainder of the solenoid assembly
screws to 5.7 N´m (50 in.lbs.).
(6) Install the valve body into the transmission.
TRANSMISSION
TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The transmission temperature sensor is a ther-
mistor that is integral to the Transmission Range
Sensor (TRS).
OPERATION
The transmission temperature sensor is used by
the TCM to sense the temperature of the fluid in the
sump. Since fluid temperature can affect transmis-
sion shift quality and convertor lock up, the TCM
requires this information to determine which shift
schedule to operate in.
Calculated Temperature
A failure in the temperature sensor or circuit will
result in calculated temperature being substituted for
actual temperature. Calculated temperature is a pre-
dicted fluid temperature which is calculated from a
combination of inputs:
²Battery (ambient) temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²In-gear run time since start-up
Fig. 119 Valve Body Bolts
1 - VALVE BODY TO CASE BOLT (6)
Fig. 120 Ttransmission Solenoid/TRS Assembly
Screws
1 - SOLENOID PACK BOLTS (15)
21 - 272 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 545RFEWJ
TRANSMISSION SOLENOID/TRS ASSEMBLY (Continued)
Page 1865 of 2199
TIRES
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - TIRES
Tires are designed and engineered for each specific
vehicle. They provide the best overall performance
for normal operation. The ride and handling charac-
teristics match the vehicle's requirements. With
proper care they will give excellent reliability, trac-
tion, skid resistance, and tread life.
Driving habits have more effect on tire life than
any other factor. Careful drivers will obtain in most
cases, much greater mileage than severe use or care-
less drivers. A few of the driving habits which will
shorten the life of any tire are:
²Rapid acceleration
²Severe brake applications
²High speed driving
²Excessive speeds on turns
²Striking curbs and other obstacles
Radial-ply tires are more prone to irregular tread
wear. It is important to follow the tire rotation inter-
val shown in the section on Tire Rotation.(Refer to 22
- TIRES/WHEELS - STANDARD PROCEDURE),
This will help to achieve a greater tread life.
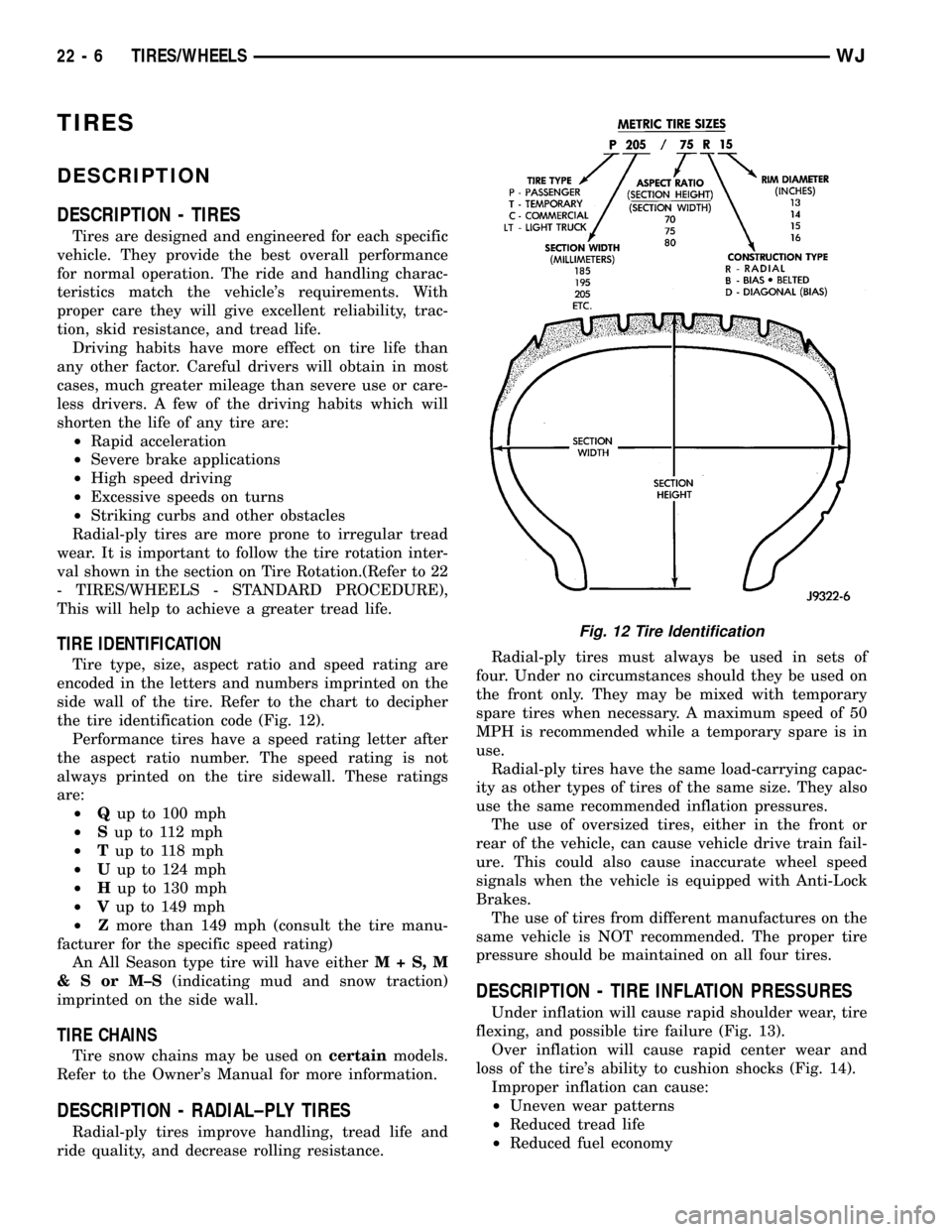
TIRE IDENTIFICATION
Tire type, size, aspect ratio and speed rating are
encoded in the letters and numbers imprinted on the
side wall of the tire. Refer to the chart to decipher
the tire identification code (Fig. 12).
Performance tires have a speed rating letter after
the aspect ratio number. The speed rating is not
always printed on the tire sidewall. These ratings
are:
²Qup to 100 mph
²Sup to 112 mph
²Tup to 118 mph
²Uup to 124 mph
²Hup to 130 mph
²Vup to 149 mph
²Zmore than 149 mph (consult the tire manu-
facturer for the specific speed rating)
An All Season type tire will have eitherM+S,M
&SorM±S(indicating mud and snow traction)
imprinted on the side wall.
TIRE CHAINS
Tire snow chains may be used oncertainmodels.
Refer to the Owner's Manual for more information.
DESCRIPTION - RADIAL±PLY TIRES
Radial-ply tires improve handling, tread life and
ride quality, and decrease rolling resistance.Radial-ply tires must always be used in sets of
four. Under no circumstances should they be used on
the front only. They may be mixed with temporary
spare tires when necessary. A maximum speed of 50
MPH is recommended while a temporary spare is in
use.
Radial-ply tires have the same load-carrying capac-
ity as other types of tires of the same size. They also
use the same recommended inflation pressures.
The use of oversized tires, either in the front or
rear of the vehicle, can cause vehicle drive train fail-
ure. This could also cause inaccurate wheel speed
signals when the vehicle is equipped with Anti-Lock
Brakes.
The use of tires from different manufactures on the
same vehicle is NOT recommended. The proper tire
pressure should be maintained on all four tires.
DESCRIPTION - TIRE INFLATION PRESSURES
Under inflation will cause rapid shoulder wear, tire
flexing, and possible tire failure (Fig. 13).
Over inflation will cause rapid center wear and
loss of the tire's ability to cushion shocks (Fig. 14).
Improper inflation can cause:
²Uneven wear patterns
²Reduced tread life
²Reduced fuel economy
Fig. 12 Tire Identification
22 - 6 TIRES/WHEELSWJ
Page 1867 of 2199

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PRESSURE
GAUGES
A quality air pressure gauge is recommended to
check tire pressure. After checking the air pressure,
replace valve cap finger tight.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TREAD WEAR
INDICATORS
Tread wear indicators are molded into the bottom
of the tread grooves. When tread depth is 1.6 mm
(1/16 in.), the tread wear indicators will appear as a
13 mm (1/2 in.) band (Fig. 15).
Tire replacement is necessary when indicators
appear in two or more grooves or if localized balding
occurs.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE WEAR
PATTERNS
Under inflation will cause wear on the shoulders of
tire. Over inflation will cause wear at the center of
tire.
Excessive camber causes the tire to run at an
angle to the road. One side of tread is then worn
more than the other (Fig. 16).
Excessive toe-in or toe-out causes wear on the
tread edges and a feathered effect across the tread
(Fig. 16).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TIRE NOISE OR
VIBRATION
Radial-ply tires are sensitive to force impulses
caused by improper mounting, vibration, wheel
defects, or possibly tire imbalance.
To find out if tires are causing the noise or vibra-
tion, drive the vehicle over a smooth road at varying
speeds. Note the noise level during acceleration and
deceleration. The engine, differential and exhaust
noises will change as speed varies, while the tire
noise will usually remain constant.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REPAIRING LEAKS
For proper repairing, a radial tire must be removed
from the wheel. Repairs should only be made if the
defect, or puncture, is in the tread area (Fig. 17). The
tire should be replaced if the puncture is located in
the sidewall.
Deflate tire completely before removing the tire
from the wheel. Use lubrication such as a mild soap
solution when dismounting or mounting tire. Use
tools free of burrs or sharp edges which could dam-
age the tire or wheel rim.
Before mounting tire on wheel, make sure all rust
is removed from the rim bead and repaint if neces-
sary.
Install wheel on vehicle, and tighten to proper
torque specification (Refer to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS/
WHEELS - SPECIFICATIONS).
Fig. 15 Tread Wear Indicators
1 - TREAD ACCEPTABLE
2 - TREAD UNACCEPTABLE
3 - WEAR INDICATOR
22 - 8 TIRES/WHEELSWJ
Page 1875 of 2199

leak area. If the hose cannot be positioned without
being held, have someone help do the water test.
Some water leaks must be tested for a considerable
length of time to become apparent. When a leak
appears, find the highest point of the water track or
drop. The highest point usually will show the point of
entry. After leak point has been found, repair the
leak and water test to verify that the leak has
stopped.
Locating the entry point of water that is leaking
into a cavity between panels can be difficult. The
trapped water may splash or run from the cavity,
often at a distance from the entry point. Most water
leaks of this type become apparent after accelerating,
stopping, turning, or when on an incline.
MIRROR INSPECTION METHOD
When a leak point area is visually obstructed, use
a suitable mirror to gain visual access. A mirror can
also be used to deflect light to a limited-access area
to assist in locating a leak point.
BRIGHT LIGHT LEAK TEST METHOD
Some water leaks in the luggage compartment can
be detected without water testing. Position the vehi-
cle in a brightly lit area. From inside the darkened
luggage compartment inspect around seals and body
seams. If necessary, have a helper direct a drop light
over the suspected leak areas around the luggage
compartment. If light is visible through a normally
sealed location, water could enter through the open-
ing.
PRESSURIZED LEAK TEST METHOD
When a water leak into the passenger compart-
ment cannot be detected by water testing, pressurize
the passenger compartment and soap test exterior of
the vehicle. To pressurize the passenger compart-
ment, close all doors and windows, start engine, and
set heater control to high blower in HEAT position. If
engine can not be started, connect a charger to the
battery to ensure adequate voltage to the blower.
With interior pressurized, apply dish detergent solu-
tion to suspected leak area on the exterior of the
vehicle. Apply detergent solution with spray device or
soft bristle brush. If soap bubbles occur at a body
seam, joint, seal or gasket, the leak entry point could
be at that location.
WIND NOISE
Wind noise is the result of most air leaks. Air leaks
can be caused by poor sealing, improper body compo-
nent alignment, body seam porosity, or missing plugs
in the engine compartment or door hinge pillar areas.
All body sealing points should be airtight in normal
driving conditions. Moving sealing surfaces will notalways seal airtight under all conditions. At times,
side glass or door seals will allow wind noise to be
noticed in the passenger compartment during high
cross winds. Over compensating on door or glass
adjustments to stop wind noise that occurs under
severe conditions can cause premature seal wear and
excessive closing or latching effort. After a repair pro-
cedure has been performed, test vehicle to verify
noise has stopped before returning vehicle to use.
Wind noise can also be caused by improperly fitted
exterior moldings or body ornamentation. Loose
moldings can flutter, creating a buzzing or chattering
noise. An open cavity or protruding edge can create a
whistling or howling noise. Inspect the exterior of the
vehicle to verify that these conditions do not exist.
VISUAL INSPECTION BEFORE TESTS
Verify that floor and body plugs are in place and
body components are aligned and sealed. If compo-
nent alignment or sealing is necessary, refer to the
appropriate section of this group for proper proce-
dures.
ROAD TESTING WIND NOISE
(1) Drive the vehicle to verify the general location
of the wind noise.
(2) Apply 50 mm (2 in.) masking tape in 150 mm
(6 in.) lengths along weatherstrips, weld seams or
moldings. After each length is applied, drive the vehi-
cle. If noise goes away after a piece of tape is applied,
remove tape, locate, and repair defect.
POSSIBLE CAUSE OF WIND NOISE
²Moldings standing away from body surface can
catch wind and whistle.
²Gaps in sealed areas behind overhanging body
flanges can cause wind-rushing sounds.
²Misaligned movable components.
²Missing or improperly installed plugs in pillars.
²Weld burn through holes.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - BODY LUBRICATION
All mechanisms and linkages should be lubricated
when necessary. This will maintain ease of operation
and provide protection against rust and excessive
wear. The weatherstrip seals should be lubricated to
prolong their life as well as to improve door sealing.
All applicable exterior and interior vehicle operat-
ing mechanisms should be inspected and cleaned.
Pivot/sliding contact areas on the mechanisms should
then be lubricated.
(1) When necessary, lubricate the operating mech-
anisms with the specified lubricants.
23 - 2 BODYWJ
BODY (Continued)