Power JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.G Manual Online
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 366 of 2199
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE - STARTER
DESCRIPTION N-m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Stater Motor (B+) Terminal
(Diesel)27 20
Stater Motor (B+) Terminal
(Except Diesel)11.3 100
Starter Motor Retaining Bolts
(Diesel)27 20
Starter Motor Retaining Bolt
(Forward Facing 4.0L)41 30
Starter Motor Retaining Bolt
(Forward Facing 4.7L)54 40
Starter Motor Retaining Bolt
(Rearward Facing 4.7L)54 40
STARTER MOTOR - GAS POWERED
Starter Motor and Solenoid
Manufacturer Mitsubishi
Engine Application 4.0L/4.7L
Power Rating 1.4 Kilowatt (1.9 Horsepower)
Voltage12 Volts
Number of Fields 4
Number of Poles 4
Number of Brushes 4
Drive Type Planetary Gear Reduction
Free Running Test Voltage 11.2 Volts
Free Running Test Maximum Amperage Draw 90 Amperes
Free Running Test Minimum Speed 2400 rpm
Solenoid Closing Maximum Voltage Required 7.8 Volts
*Cranking Amperage Draw Test 160 Amperes
*Test at operating temperature. Cold engine, tight (new) engine, or heavy oil will increase starter amperage draw.
STARTER MOTOR
DESCRIPTION
The starter motors used for both the 4.0L and the
4.7L engines available in this model are very similar,
but are not interchangeable. Both starter motors are
mounted with two screws to the automatic transmis-
sion torque converter housing and are located on the
right side of the engine.
Each of these starter motors incorporates several
of the same features to create a reliable, efficient,compact, lightweight and powerful unit. The electric
motors of both starters feature four electromagnetic
field coils wound around four pole shoes, and four
brushes contact the motor commutator. Both starter
motors are rated at 1.4 kilowatts (about 1.9 horse-
power) output at 12 volts.
Both of these starter motors are serviced only as a
unit with their starter solenoids, and cannot be
repaired. If either component is faulty or damaged,
the entire starter motor and starter solenoid unit
must be replaced.
WJSTARTING 8F - 35
STARTING (Continued)
Page 369 of 2199

(8) Remove the starter motor from the engine com-
partment.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the starter motor in the engine com-
partment.
(2) Reconnect the solenoid terminal wire harness
connector to the connector receptacle on the starter
solenoid. Always support the starter motor during
this process, do not let the starter motor hang from
the wire harness.
(3) Install the battery cable eyelet onto the sole-
noid battery terminal. Always support the starter
motor during this process, do not let the starter
motor hang from the wire harness.
(4) Install and tighten the nut that secures the
battery cable eyelet to the solenoid battery terminal.
Tighten the nut to 11.3 N´m (100 in. lbs.). Always
support the starter motor during this process, do not
let the starter motor hang from the wire harness.
(5) Position the starter motor to the front of the
automatic transmission torque converter housing and
loosely install both the upper and lower mounting
screws.
(6) Tighten the lower (forward facing) starter
motor mounting screw. On 4.0L engines, tighten the
screw to 41 N´m (30 ft. lbs.). On 4.7L engines, tighten
the screw to 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.).(7) Tighten the upper (rearward facing) starter
mounting screw. Tighten the screw to 54 N´m (40 ft.
lbs.).
(8) Lower the vehicle.
(9) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
STARTER MOTOR RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The starter relay is an electromechanical device
that switches battery current to the pull-in coil of the
starter solenoid when the ignition switch is turned to
the Start position. The starter relay is located in the
Power Distribution Center (PDC), in the engine com-
partment. See the fuse and relay layout label affixed
to the inside surface of the PDC cover for starter
relay identification and location.
The starter relay is a International Standards
Organization (ISO) micro-relay. Relays conforming to
the ISO specifications have common physical dimen-
sions, current capacities, terminal patterns, and ter-
minal functions. The ISO micro-relay terminal
functions are the same as a conventional ISO relay.
However, the ISO micro-relay terminal pattern (or
footprint) is different, the current capacity is lower,
and the physical dimensions are smaller than those
of the conventional ISO relay.
The starter relay cannot be repaired or adjusted
and, if faulty or damaged, it must be replaced.
OPERATION
The ISO relay consists of an electromagnetic coil, a
resistor or diode, and three (two fixed and one mov-
able) electrical contacts. The movable (common feed)
relay contact is held against one of the fixed contacts
(normally closed) by spring pressure. When the elec-
tromagnetic coil is energized, it draws the movable
contact away from the normally closed fixed contact,
and holds it against the other (normally open) fixed
contact.
When the electromagnetic coil is de-energized,
spring pressure returns the movable contact to the
normally closed position. The resistor or diode is con-
nected in parallel with the electromagnetic coil in the
relay, and helps to dissipate voltage spikes that are
produced when the coil is de-energized.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - STARTER RELAY
The starter relay (Fig. 13) is located in the Power
Distribution Center (PDC), in the engine compart-
ment. Refer to the fuse and relay layout label affixed
to the underside of the PDC cover for starter relay
identification and location. For complete circuit dia-
grams, refer toStarting Systemin the Contents of
Group 8W - Wiring Diagrams.
Fig. 12 Starter Wire Harness Remove/Install - 4.7L
Engine
1 - SOLENOID BATTERY TERMINAL EYELET
2 - NUT
3 - SOLENOID TERMINAL CONNECTOR
4 - BATTERY STARTER AND GENERATOR WIRE HARNESS
5 - RETAINERS
8F - 38 STARTINGWJ
STARTER MOTOR (Continued)
Page 370 of 2199

(1) Remove the starter relay from the PDC. Refer
toStarter Relayin the Removal and Installation
section of this group for the procedures.
(2) A relay in the de-energized position should
have continuity between terminals 87A and 30, and
no continuity between terminals 87 and 30. If OK, go
to Step 3. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
(3) Resistance between terminals 85 and 86 (elec-
tromagnet) should be 75 5 ohms. If OK, go to Step
4. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
(4) Connect a battery to terminals 85 and 86.
There should now be continuity between terminals
30 and 87, and no continuity between terminals 87A
and 30. If OK, perform the Relay Circuit Test that
follows. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
RELAY CIRCUIT TEST
(1) The relay common feed terminal cavity (30) is
connected to battery voltage and should be hot at all
times. If OK, go to Step 2. If not OK, repair the open
circuit to the fuse in the PDC as required.
(2) The relay normally closed terminal (87A) is
connected to terminal 30 in the de-energized position,
but is not used for this application. Go to Step 3.
(3) The relay normally open terminal (87) is con-
nected to the common feed terminal (30) in the ener-
gized position. This terminal supplies battery voltage
to the starter solenoid field coils. There should be
continuity between the cavity for relay terminal 87
and the starter solenoid terminal at all times. If OK,
go to Step 4. If not OK, repair the open circuit to the
starter solenoid as required.
(4) The coil battery terminal (86) is connected to
the electromagnet in the relay. It is energized when
the ignition switch is held in the Start position.
Check for battery voltage at the cavity for relay ter-
minal 86 with the ignition switch in the Start posi-tion, and no voltage when the ignition switch is
released to the On position. If OK, go to Step 5. If
not OK, check for an open or short circuit to the igni-
tion switch and repair, if required. If the circuit to
the ignition switch is OK, refer toIgnition Switch
and Key Lock Cylinderin the Diagnosis and Test-
ing section of Group 8D - Ignition System for testing
of the ignition switch.
(5) The coil ground terminal (85) is connected to
the electromagnet in the relay. It is grounded
through the park/neutral position switch only when
the gearshift selector lever is in the Park or Neutral
positions. Check for continuity to ground at the cav-
ity for relay terminal 85. If not OK, check for an
open or short circuit to the park/neutral position
switch and repair, if required. If the circuit to the
park/neutral position switch is OK, refer toPark/
Neutral Position Switchin the Diagnosis and
Testing section of Group 21 - Transmission for testing
of the park/neutral position switch.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the cover from the Power Distribution
Center (PDC) (Fig. 14) .
Fig. 13 Starter Relay
30 - COMMON FEED
85 - COIL GROUND
86 - COIL BATTERY
87 - NORMALLY OPEN
87A - NORMALLY CLOSED
Fig. 14 Power Distribution Center
1 - RIGHT FENDER
2 - BATTERY
3 - POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER
4 - COVER
WJSTARTING 8F - 39
STARTER MOTOR RELAY (Continued)
Page 374 of 2199

(1) Confirm that the ignition switch is in the On
position.
(2) Ensure that the rear glass heating grid feed
and ground terminals are connected to the glass.
Confirm that the ground wire has continuity to
ground.
(3) Check the fused B(+) fuse in the Power Distri-
bution Center (PDC). The fuse must be tight in its
receptacles and all electrical connections must be
secure.
When the above steps have been completed and the
rear glass heating grid is still inoperative, one or
more of the following is faulty:
²Rear window defogger switch
²Rear window defogger relay
²Body Control Module (BCM)
²Rear window grid lines (all grid lines would
have to be broken or one of the feed wires discon-
nected for the entire system to be inoperative).
When the above steps have been completed and the
heated mirror glass heating grid is still inoperative,
one or more of the following is faulty:
²Body Control Module (BCM)
²Programmable Communications Interface (PCI)
data bus
²Driver Door Module (DDM) or Passenger Door
Module (PDM)
²Outside rear view mirror heating grids.
If turning the rear window defogger system on pro-
duces a severe voltmeter deflection, check for a short
circuit between the rear window defogger relay out-
put and the rear glass heating grid.
REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER
GRID
DESCRIPTION
The electrically heated rear window glass is stan-
dard equipment on this model. The liftgate flip-up
glass has two electrically conductive vertical bus bars
and a series of horizontal grid lines made of a silver-
ceramic material, which is baked on and bonded to
the inside surface of the glass. These grid lines and
the bus bars comprise a parallel electrical circuit. A
spade type terminal near the top of each bus bar
accept the connectors from the two coiled liftgate
wire harness take outs.
The grid lines and bus bars are highly resistant to
abrasion. However, it is possible for an open circuit
to occur in an individual grid line, resulting in no
current flow through the line. The grid lines can be
damaged or scraped off with sharp instruments. Care
should be taken when cleaning the glass or removing
foreign materials, decals, or stickers from the glass.Normal glass cleaning solvents or hot water used
with rags or toweling is recommended.
A repair kit is available to repair the grid lines and
bus bars, or to reinstall the heated glass terminals.
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/HEATED GLASS/REAR
WINDOW DEFOGGER GRID - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE)
OPERATION
The rear glass heating grid is energized and de-en-
ergized by the rear window defogger relay. The Body
Control Module (BCM) monitors the rear window
defogger switch. When the BCM receives an input
from the switch, it energizes or de-energizes the rear
window defogger relay through a hard wired control
output. The rear defogger relay switches fused bat-
tery current to the rear window grid lines through
the bus bars. The grid lines heat the rear window
glass to clear the surface of ice, snow or fog. Protec-
tion for the rear glass heating grid circuit is provided
by a fuse in the Power Distribution Center (PDC).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REAR WINDOW
DEFOGGER GRID
For complete circuit diagrams, (Refer to Appropri-
ate Wiring Information). To detect breaks in the rear
glass heating grid lines, the following procedure is
required:
(1) Turn the ignition switch to the On position.
Turn the rear window defogger system on. The rear
window defogger switch LED indicator should light.
If OK, go to Step 2. If not OK, (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/HEATED GLASS/REAR WINDOW DEFOG-
GER RELAY - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).
(2) Using a 12-volt DC voltmeter, contact the rear
glass heating grid vertical bus bar on the right side
of the vehicle with the negative lead. With the posi-
tive lead, contact the rear glass heating grid vertical
bus bar on the left side of the vehicle. The voltmeter
should read battery voltage. If OK, go to Step 3. If
not OK, repair the open rear window defogger relay
output circuit to the rear window defogger relay as
required.
(3) With the positive voltmeter lead still contacting
the rear glass heating grid vertical bus bar on the
left side of the vehicle, move the negative lead of the
voltmeter to a good body ground point. The voltage
reading should not change. If OK, go to Step 4. If not
OK, repair the ground circuit to ground as required.
(4) Connect the negative lead of the voltmeter to
the right side bus bar and touch each grid line at
midpoint C with the positive lead (Fig. 2). A reading
of approximately six volts indicates a line is good. A
reading of zero volts indicates a break in the grid
line between midpoint C and the left side rear glass
heating grid bus bar. A reading of ten to fourteen
WJHEATED GLASS 8G - 3
HEATED GLASS (Continued)
Page 376 of 2199

not attach the wire harness connectors until the cur-
ing process is complete.
(11) Check the operation of the rear glass heating
grid.
REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER
RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The rear window defogger relay is an electrome-
chanical device that switches fused battery current to
the rear glass heating grid and the Light-Emitting
Diode (LED) indicator of the rear window defogger
switch, when the Body Control Module (BCM) rear
window defogger timer and logic circuitry grounds
the relay coil. The rear window defogger relay is
located in the junction block, under the left end of
the instrument panel in the passenger compartment.
The rear window defogger relay is a International
Standards Organization (ISO) relay. Relays conform-
ing to the ISO specifications have common physical
dimensions, current capacities, terminal patterns,
and terminal functions.
The rear window defogger relay cannot be repaired
or adjusted and, if faulty or damaged, it must be
replaced.
OPERATION
The ISO relay consists of an electromagnetic coil, a
resistor or diode, and three (two fixed and one mov-
able) electrical contacts. The movable (common feed)
relay contact is held against one of the fixed contacts
(normally closed) by spring pressure. When the elec-
tromagnetic coil is energized, it draws the movable
contact away from the normally closed fixed contact,
and holds it against the other (normally open) fixed
contact.
When the electromagnetic coil is de-energized,
spring pressure returns the movable contact to the
normally closed position. The resistor or diode is con-
nected in parallel with the electromagnetic coil in the
relay, and helps to dissipate voltage spikes that are
produced when the coil is de-energized.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REAR WINDOW
DEFOGGER RELAY
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN AN ACCIDENTAL
AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
RELAY TEST
The rear window defogger relay (Fig. 4) is located
in the junction block, under the left end of the instru-
ment panel in the passenger compartment. Remove
the rear window defogger relay from the junction
block to perform the following tests:
(1) A relay in the de-energized position should
have continuity between terminals 87A and 30, and
no continuity between terminals 87 and 30. If OK, go
to Step 2. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
(2) Resistance between terminals 85 and 86 (elec-
tromagnet) should be 75 10 ohms. If OK, go to Step
3. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
(3) Connect a battery to terminals 85 and 86.
There should now be continuity between terminals
30 and 87, and no continuity between terminals 87A
and 30. If OK, refer to theRelay Circuit Test.If
not OK, replace the faulty relay.
RELAY CIRCUIT TEST
(1) The relay common feed terminal cavity (30) is
connected to battery voltage and should be hot at all
times. If OK, go to Step 2. If not OK, repair the open
fused B(+) circuit to the Power Distribution Center
(PDC) fuse as required.
(2) The relay normally closed terminal (87A) is
connected to terminal 30 in the de-energized position,
but is not used for this application. Go to Step 3.
Fig. 4 REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER RELAY
TERMINAL LEGEND
NUMBER IDENTIFICATION
30 COMMON FEED
85 COIL GROUND
86 COIL BATTERY
87 NORMALLY OPEN
87A NORMALLY CLOSED
WJHEATED GLASS 8G - 5
REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER GRID (Continued)
Page 379 of 2199

HEATED MIRRORS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
HEATED MIRRORS
DESCRIPTION..........................8
OPERATION............................8DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEATED
MIRRORS............................8
HEATED MIRRORS
DESCRIPTION
Electrically heated outside rear view mirrors are
optional equipment on this model. These mirrors fea-
ture an electric heating grid located behind the mir-
ror glass of each power operated outside rear view
mirror. These heating grids consist of a single resis-
tor wire routed in a grid-like pattern and captured
between two thin sheets of plastic. When electrical
current is passed through the resistor wire, it pro-
duces enough heat energy to clear the outside mirror
glass of ice, snow or fog. Battery current is directed
to the outside mirror heating grid only when the rear
window defogger switch is in the On position.
If the outside mirror heating grids and the rear
window heating grid are all inoperative, (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/HEATED GLASS - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING - REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER SYSTEM).
If the outside mirror heating grids are inoperative,
but the rear window heating grid is operating as
designed, (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/HEATED MIR-
RORS - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)
The heating grid behind each outside mirror glass
cannot be repaired and, if faulty or damaged, the
entire power mirror unit must be replaced. Refer to
Power Mirrors for the procedures.
OPERATION
The outside mirror heating grids are energized and
de-energized by the Driver Door Module (DDM) and
the Passenger Door Module (PDM) based upon the
rear window defogger switch status. The Body Con-
trol Module (BCM) monitors the rear window defog-ger switch. When the BCM receives an input from
the switch, it sends a defogger switch status message
to the DDM and the PDM over the Programmable
Communications Interface data bus. The DDM and
PDM respond to the defogger switch status messages
by energizing or de-energizing the battery current
feed to their respective outside rear view mirror
heating grids.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEATED MIRRORS
For circuit descriptions and diagrams, (Refer to
Appropriate Wiring Information).
(1) If both mirror heaters are inoperative, check
for proper operation of the Rear Window Defogger
System. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/HEATED GLASS
- DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REAR WINDOW
DEFOGGER SYSTEM). If Rear Window Defogger
System operates correctly, or if only one mirror
heater is inoperative, go to Step 2.
(2) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable. Remove the front door trim panel on the side
of the inoperative mirror heater. Go to Step 3.
(3) Disconnect the door wire harness connector
from the door module connector receptacle. Check for
continuity between the mirror heater 12 volt supply,
and the mirror heater ground. There should be con-
tinuity. If OK, go to Step 4. If not OK, check for con-
tinuity of the individual circuits between the power
mirror and the door module, and of the mirror heater
grid right at the power mirror.
(4) Use a DRB IIItand (Refer to Appropriate
Diagnostic Information) to test the door module and
the PCI data bus.
8G - 8 HEATED MIRRORSWJ
Page 380 of 2199
HEATED SEAT SYSTEM
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
HEATED SEAT SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION..........................9
OPERATION...........................10
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEATED SEAT
SYSTEM............................10
DRIVER HEATED SEAT SWITCH
DESCRIPTION.........................11
OPERATION...........................11
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - DRIVER HEATED
SEAT SWITCH........................11
REMOVAL.............................12
INSTALLATION.........................13
HEATED SEAT ELEMENT
DESCRIPTION.........................13
OPERATION...........................13
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEATED SEAT
ELEMENT...........................14REMOVAL.............................14
INSTALLATION.........................14
HEATED SEAT SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................15
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEATED SEAT
SENSOR............................15
REMOVAL.............................15
PASSENGER HEATED SEAT SWITCH
DESCRIPTION.........................15
OPERATION...........................16
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PASSENGER
HEATED SEAT SWITCH.................16
REMOVAL.............................17
INSTALLATION.........................17
HEATED SEAT SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION
Individually controlled driver and passenger side
electrically heated front seats are available factory-
installed optional equipment on this model, when it
is also equipped with the power seat option. The
heated seat system allows both the driver and the
front seat passenger the option to select one of two
seat heating ranges, Low or High, or to turn the indi-
vidual seat heaters Off using the heated seat
switches located in the center lower bezel near the
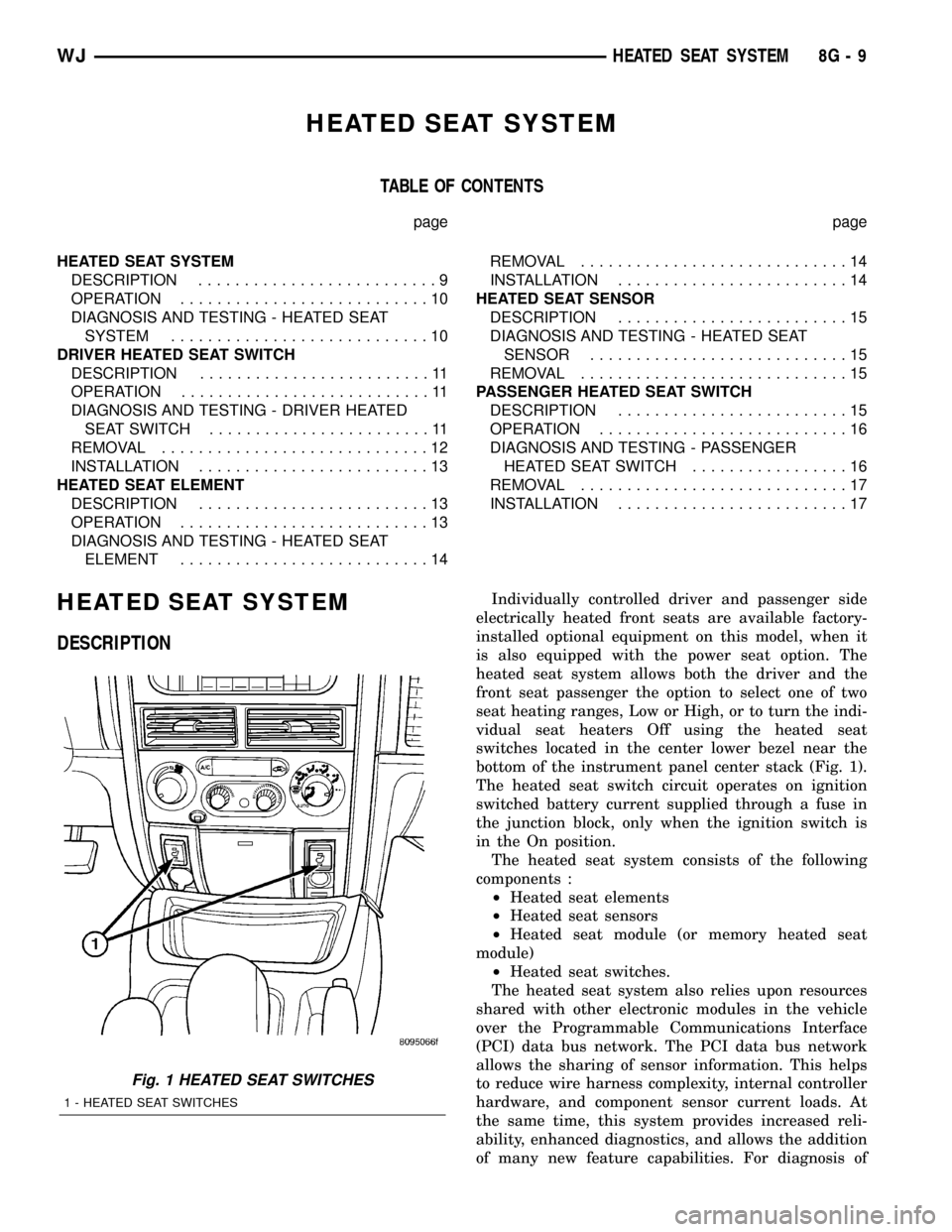
bottom of the instrument panel center stack (Fig. 1).
The heated seat switch circuit operates on ignition
switched battery current supplied through a fuse in
the junction block, only when the ignition switch is
in the On position.
The heated seat system consists of the following
components :
²Heated seat elements
²Heated seat sensors
²Heated seat module (or memory heated seat
module)
²Heated seat switches.
The heated seat system also relies upon resources
shared with other electronic modules in the vehicle
over the Programmable Communications Interface
(PCI) data bus network. The PCI data bus network
allows the sharing of sensor information. This helps
to reduce wire harness complexity, internal controller
hardware, and component sensor current loads. At
the same time, this system provides increased reli-
ability, enhanced diagnostics, and allows the addition
of many new feature capabilities. For diagnosis of
Fig. 1 HEATED SEAT SWITCHES
1 - HEATED SEAT SWITCHES
WJHEATED SEAT SYSTEM 8G - 9
Page 381 of 2199

these electronic modules or of the PCI data bus net-
work, the use of a DRBtscan tool and the proper
Diagnostic Procedures manual are recommended.
The electronic modules that may affect heated seat
system operation are as follows:
²Body Control Module (BCM)- Refer toBody
Control Modulein Electronic Control Modules for
more information.
²Heated Seat Module (HSM)- Refer toHeated
Seat Modulein Electronic Control Modules for more
information.
²Memory Heated Seat Module (MHSM)-If
the vehicle is equipped with the Memory System,
refer toMemory Seat Modulein Electronic Control
Modules for more information.
Refer toPower Seats Premium I/IIIin the Con-
tents of Wiring Diagrams for complete circuit dia-
grams. Following are general descriptions of the
major components in the heated seat system.
OPERATION
The heated seat system will only operate when the
ignition switch is in the On position, and the surface
temperature at the front seat heating element sen-
sors is below the designed temperature set points of
the system. The heated seat system will not operate
in ambient temperatures greater than about 41É C
(105É F). The front seat heating elements and sensors
are hard wired to the Heated Seat Module (HSM) or
the Memory Heated Seat Module (MHSM).
The heated seat switches are hard wired to the
Body Control Module (BCM). The BCM monitors the
heated seat switch inputs, then sends heated seat
switch status messages to the HSM or MHSM over
the Programmable Communications Interface (PCI)
data bus. The HSM or MHSM contains the control
logic for the heated seat system. The HSM or MHSM
responds to the heated seat switch status messages,
ignition switch status messages, and the front seat
heating element sensor inputs by controlling the out-
put to the front seat heating elements through inte-
gral solid-state relays.
When a seat heater is turned on, the sensor
located on the seat cushion electric heater element
provides the HSM or MHSM with an input indicating
the surface temperature of the seat cushion. If the
surface temperature input is below the temperature
set point for the selected Low or High heated seat
switch position, the HSM or MHSM energizes the
integral solid-state relay, which supplies battery cur-
rent to the heating elements in the seat cushion and
back. When the sensor input indicates the correct
temperature set point has been achieved, the HSM or
MHSM de-energizes the solid-state relay. The HSM
or MHSM will continue to cycle the solid-state relay
as needed to maintain the temperature set point.The HSM or MHSM and the seat heater elements
operate on non-switched battery current supplied
through the power seat circuit breaker in the junc-
tion block. However, the HSM or MHSM will auto-
matically turn off the heating elements if it detects
an open or short in the sensor circuit, a short or open
in the heating element circuit causing an excessive
current draw, or when the ignition switch is turned
to the Off position.
See the owner's manual in the vehicle glove box for
more information on the features, use and operation
of the heated seat system.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEATED SEAT
SYSTEM
Following are tests that will help to diagnose the
components and circuits that are hard wired inputs
or outputs of the heated seat system. However, these
tests may not prove conclusive in the diagnosis of
this system. In order to obtain conclusive testing of
the heated seat system, the Programmable Commu-
nications Interface (PCI) data bus network and all of
the electronic modules that provide inputs to, or
receive outputs from the heated seat system compo-
nents must be checked.
The most reliable, efficient, and accurate means to
diagnose the heated seat system requires the use of a
DRB scan tool and the proper Diagnostic Procedures
manual. The DRBtscan tool can provide confirma-
tion that the PCI data bus is functional, that all of
the electronic modules are sending and receiving the
proper messages on the PCI data bus, and that the
Heated Seat Module (HSM) or Memory Heated Seat
Module (MHSM) is receiving the proper hard wired
inputs and relaying the proper hard wired outputs to
perform its heated seat system functions.
For complete circuit diagrams, refer toWiring
Diagrams.
NOTE: DO NOT ATTEMPT TO SWAP MEMORY OR
NON-MEMORY HEATED SEAT MODULES FROM
ONE VEHICLE TO ANOTHER. MOST OF THESE
MODULES ARE VEHICLE FEATURE SPECIFIC AND
THEREFORE NOT INTERCHANGEABLE. ALWAYS
USE THE CORRECT PART NUMBERED MODULE
WHEN DIAGNOSING OR REPLACING A MODULE.
WARNING: REFER TO THE RESTRAINTS SECTION
OF THIS MANUAL BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY
STEERING WHEEL, STEERING COLUMN, OR
INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS OR
SERVICE. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
8G - 10 HEATED SEAT SYSTEMWJ
HEATED SEAT SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 382 of 2199

PRELIMINARY TEST
Before testing the individual components in the
heated seat system, check the following:
²If the heated seat switch LED indicators do not
light with the ignition switch in the On position and
the heated seat switch in the Low or High position,
check the fused ignition switch output (run) fuse in
the junction block. If OK, refer toHeated Seat
Switch Diagnosis and Testingin this section. If
not OK, repair the shorted circuit or component as
required and replace the faulty fuse.
²If the heated seat switch LED indicators light,
but the heating elements do not heat, check the
power seat circuit breaker in the junction block. If
OK, refer toHeated Seat Element Diagnosis and
Testingin this section of the manual. If not OK,
replace the faulty power seat circuit breaker.
DRIVER HEATED SEAT
SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
The heated seat switches are mounted in the
instrument panel center lower bezel (Fig. 2), which is
located near the bottom of the instrument panel cen-
ter stack. The two three-position rocker-type
switches, one switch for each front seat, provide a
resistor multiplexed signal to the Body Control Mod-
ule (BCM) through separate hard wired circuits.Each switch has an Off, Low, and High position so
that both the driver and the front seat passenger can
select a preferred seat heating mode. Each switch
has two Light-Emitting Diodes (LED), one each for
the Low position and the High position, which light
to indicate that the heater for the seat that the
switch controls is turned on. Each switch is also back
lit by a replaceable incandescent bulb.
The heated seat switches and their LEDs cannot
be repaired. If either switch or LED is faulty or dam-
aged, the entire switch unit must be replaced. The
incandescent switch illumination bulb and bulb
holder units are available for service replacement.
OPERATION
There are three positions that can be selected with
each of the heated seat switches: Off, Low, or High.
When the top of the switch rocker is fully depressed,
the High position is selected and the high position
LED indicator illuminates. When the bottom of the
switch rocker is fully depressed, the Low position is
selected and the low position LED indicator illumi-
nates. When the switch rocker is moved to its neutral
position, Off is selected and both LED indicators are
extinguished.
Both switches provide separate resistor multi-
plexed hard wire inputs to the BCM to indicate the
selected switch position. The BCM monitors the
switch inputs and sends heated seat switch status
messages to the Heated Seat Module (HSM) or the
Memory Heated Seat Module (MHSM) over the Pro-
grammable Communications Interface (PCI) data
bus. The HSM or MHSM responds to the heated seat
switch status messages by controlling the output to
the seat heater elements of the selected seat. The
Low heat position set point is about 36É C (97É F),
and the High heat position set point is about 41É C
(105É F).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - DRIVER HEATED
SEAT SWITCH
For complete circuit diagrams, refer toWiring
Diagrams.
WARNING: REFER TO THE RESTRAINTS SECTION
OF THIS MANUAL BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY
STEERING WHEEL, STEERING COLUMN, OR
INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS OR
SERVICE. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
(1) Check the fused ignition switch output (run)
fuse in the junction block. If OK, go to Step 2. If not
Fig. 2 HEATED SEAT SWITCHES
1 - HEATED SEAT SWITCHES
WJHEATED SEAT SYSTEM 8G - 11
HEATED SEAT SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 384 of 2199

(2) Remove the center lower bezel from the instru-
ment panel. Refer toInstrument Panel Center
Lower Bezelin the Body section of this manual for
the procedure.
(3) Remove the four screws that secure the heated
seat switch to the back of the instrument panel cen-
ter lower bezel (Fig. 4).
(4) Remove the heated seat switch from the back
of the instrument panel center lower bezel.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the heated seat switch onto the back
of the instrument panel center lower bezel.
(2) Install and tighten the four screws that secure
the heated seat switch to the back of the instrument
panel center lower bezel. Tighten the screws to 1.5
N´m (13 in. lbs.).
(3) Install the center lower bezel onto the instru-
ment panel. Refer toInstrument Panel Center
Lower Bezelin the Body section of this manual for
the procedure.
(4) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
HEATED SEAT ELEMENT
DESCRIPTION
The heated seat system includes two seat heating ele-
ments in each front seat, one for the seat cushion (Fig.
5)and the other for the seat back. One type of heated
seat element is offered. All models use two resistor wire
heating elements for each seat that are connected in
series with the Heated Seat Module (HSM).
The seat heating elements are glued to the seat and
seat back cushions. The heated seat elements can be
replaced if faulty or damaged, service replacement seat
or seat back elements are available. Refer to the pro-
cedure in this section for detailed instructions.
OPERATION
The heated seat elements resist the flow of electri-
cal current. When battery current is passed through
the elements, the energy lost by the resistance of the
elements to the current flow is released in the form
of heat. The temperature sensor is a NTC thermistor.
When the temperature of the seat cushion cover
rises, the resistance of the sensor decreases. The
HSM or MHSM supplies a five-volt current to one
side of each sensor, and monitors the voltage drop
through the sensor on a return circuit. The MSM or
MHSM uses this temperature sensor input to moni-
tor the temperature of the seat, and regulates the
current flow to the seat heating elements accordingly.
Fig. 4 Heated Seat Switch Remove/Install
1 - HEATED SEAT SWITCHES
2 - SCREWS (4)
3 - CENTER LOWER BEZEL
4 - CIGAR LIGHTER
5 - ILLUMINATION LAMPS
6 - POWER OUTLET
Fig. 5 HEATING ELEMENT INSTALLED
1 - SEAT BACK WIRE HARNESS
2 - HEATED SEAT WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR
3 - HEATED SEAT CUSHION ELEMENT
WJHEATED SEAT SYSTEM 8G - 13
DRIVER HEATED SEAT SWITCH (Continued)