Outlet JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2002, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2002 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 177 of 2199

INSTALLATION.........................23
MASTER CYLINDER
DESCRIPTION.........................23
OPERATION...........................24
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - MASTER
CYLINDER/POWER BOOSTER...........24
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MASTER
CYLINDER BLEEDING PROCEDURE......25
REMOVAL.............................25
INSTALLATION.........................25
PEDAL
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - STANDARD PEDAL.......25
DESCRIPTION - ADJUSTABLE PEDALS....25
OPERATION...........................26
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - NON-ADJUSTABLE PEDAL....26
REMOVAL - ADJUSTABLE PEDALS........27
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - NON-ADJUSTABLE PEDAL . 28
INSTALLATION - ADJUSTABLE PEDALS....28
PEDAL MOTOR
REMOVAL.............................28
INSTALLATION.........................28
POWER BRAKE BOOSTER
DESCRIPTION.........................29
OPERATION...........................29
REMOVAL.............................31
INSTALLATION.........................31
ROTORS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FRONT DISC
BRAKE ROTOR.......................31DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REAR DISC
BRAKE ROTOR.......................32
STANDARD PROCEDURE - DISC ROTOR
MACHINING..........................33
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - FRONT DISC BRAKE ROTOR . . 33
REMOVAL - REAR DISC BRAKE ROTOR . . . 33
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - FRONT DISC BRAKE
ROTOR .............................34
INSTALLATION - REAR DISC BRAKE
ROTOR .............................34
PARKING BRAKE
OPERATION...........................34
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PARKING BRAKE . 34
CABLES
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - FRONT PARKING BRAKE
CABLE..............................35
REMOVAL - REAR PARKING BRAKE
CABLES............................36
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - FRONT PARKING BRAKE
CABLE..............................37
INSTALLATION - REAR PARKING BRAKE
CABLES............................37
LEVER
REMOVAL.............................38
INSTALLATION.........................39
SHOES
REMOVAL.............................39
INSTALLATION.........................39
ADJUSTMENTS - PARKING BRAKE SHOE....40
BRAKES - BASE
DESCRIPTION
Dual piston disc brake calipers are used on the
front. Single piston disc brake calipers are used on
the rear. Ventilated disc brake rotors are used on the
front and solid rotors are used on the rear.
Power brake assist is supplied by a vacuum oper-
ated, dual diaphragm power brake booster. The mas-
ter cylinder used for all applications has an
aluminum body and nylon reservoir with single filler
cap. A fluid level indicator is mounted to the side of
the reservoir.
The braking force of the rear wheels is controlled
by electronic brake distribution (EBD). The EBD
functions like a rear proportioning valve. The EBD
system uses the ABS system to control the slip of the
rear wheels in partial braking range. The braking
force of the rear wheels is controlled electronically by
using the inlet and outlet valves located in the HCU.
Factory installed brake linings on all models con-
sists of organic base material combined with metallic
particles.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BASE BRAKE
SYSTEM
Base brake components consist of the brake shoes,
calipers, rear park brake drums/rotors, front brake
rotors, brake lines, master cylinder, booster, HCU
and parking brake shoes.
Brake diagnosis involves determining if the prob-
lem is related to a mechanical, hydraulic, electrical
or vacuum operated component.
The first diagnosis step is the preliminary check.
PRELIMINARY BRAKE CHECK
(1) Check condition of tires and wheels. Damaged
wheels and worn, damaged, or underinflated tires
can cause pull, shudder, vibration, and a condition
similar to grab.
5 - 2 BRAKES - BASEWJ
Page 200 of 2199

STANDARD PROCEDURE - MASTER CYLINDER
BLEEDING PROCEDURE
A new master cylinder should be bled before instal-
lation on the vehicle. Required bleeding tools include
bleed tubes and a wood dowel to stroke the pistons.
Bleed tubes can be fabricated from brake line.
(1) Mount master cylinder in vise with brass jaws.
(2) Attach bleed tubes to cylinder outlet ports.
Then position each tube end into the bottom of the
reservoir (Fig. 50).
(3) Fill reservoir with fresh brake fluid.
(4) Press cylinder pistons inward with wood dowel.
Then release pistons and allow them to return under
spring pressure. Continue bleeding operations until
air bubbles are no longer visible in fluid.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the wire connector from the brake fluid
level sensor.
(2) Remove brake lines from master cylinder.
(3) Remove nuts that attach master cylinder to
booster studs (Fig. 51).
(4) Remove master cylinder from booster.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: Bleed new master cylinder on bench before
installation, refer to Service Procedures.
(1) Have an assistant depress the brake pedal
while guiding the master cylinder on the booster rod
and mounting studs.
CAUTION: Do not depress brake pedal too hard and
ensure the booster rod is in the master cylinder pis-
ton or booster/master cylinder damage will occur.(2) Install master cylinder mounting nuts and
tighten nuts to 25 N´m (18 lb. lbs.).
NOTE: Use original or factory replacement nuts only.
(3) Install brake lines and tighten to 16 N´m (144
in. lbs.).
(4) Install fluid level sensor connector.
(5) Fill and bleed brake system.
PEDAL
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - STANDARD PEDAL
A suspended-type brake pedal is used, the pedal
pivots on a shaft mounted in the pedal support
bracket. The bracket is attached to the dash panel.
The brake pedal assembly and pedal pad are the
only serviceable component.
DESCRIPTION - ADJUSTABLE PEDALS
The Adjustable Pedals System (APS) is designed to
enable the fore and aft repositioning of the brake and
accelerator pedals. This results in improved ergonom-
ics in relation to the steering wheel for taller and
shorter drivers. Being able to adjust the pedal posi-
Fig. 50 Master Cylinder Bleeding
1 - BLEEDING TUBES
2 - RESERVOIR
Fig. 51 Master Cylinder Mounting
1 - MOUNTING NUT
2 - SENSOR CONNECTOR
3 - MOUNTING NUT
4 - BRAKE LINES
WJBRAKES - BASE 5 - 25
MASTER CYLINDER (Continued)
Page 218 of 2199

ELECTRIC BRAKE
DESCRIPTION
The electronic brake distribution (EBD) functions
like a rear proportioning valve. The EBD system uses
the ABS system to control the slip of the rear wheels
in partial braking range. The braking force of the
rear wheels is controlled electronically by using the
inlet and outlet valves located in the HCU.
OPERATION
Upon entry into EBD the inlet valve for the rear
brake circuit is switched on so that the fluid supply
from the master cylinder is shut off. In order to
decrease the rear brake pressure the outlet valve for
the rear brake circuit is pulsed. This allows fluid to
enter the low pressure accumulator (LPA) in the
HCU resulting in a drop in fluid pressure to the rear
brakes. In order to increase the rear brake pressure
the outlet valve is switched off and the inlet valve is
pulsed. This increases the pressure to the rear
brakes. This will continue until the required slip dif-
ference is obtained. At the end of EBD braking (no
brake application) the fluid in the LPA drains back to
the master cylinder by switching on the outlet valve
and draining through the inlet valve check valve. At
the same time the inlet valve is switched on to pre-
vent a hydraulic short circiut in case of another
brake application.
The EBD will remain functional during many ABS
fault modes. If the red and amber warning lamps are
illuminated the EBD may have a fault.
FRONT WHEEL SPEED
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
A wheel speed sensor is used at each wheel. The
front sensors are mounted to the steering knuckles.
The rear sensors are mounted at the outboard end of
the axle. Tone wheels are mounted to the outboard
ends of the front and rear axle shafts. The gear type
tone wheel serves as the trigger mechanism for each
sensor.
OPERATION
The sensors convert wheel speed into a small digi-
tal signal. The CAB sends 12 volts to the sensors.
The sensor has an internal magneto resistance
bridge that alters the voltage and amperage of the
signal circuit. This voltage and amperage is changed
by magnetic induction when the toothed tone wheel
passes the wheel speed sensor. This digital signal issent to the CAB. The CAB measures the voltage and
amperage of the digital signal for each wheel.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support the vehicle.
(2) Remove the front wheel sensor mounting bolt
(Fig. 1).
(3) Remove the sensor from the steering knuckle.
(4) Disengage the sensor wire from the brackets
(Fig. 1)on the steering knuckle.
(5) Disconnect the sensor from the sensor harness
(Fig. 2)and (Fig. 3).
(6) Remove the sensor and wire.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the sensor on the steering knuckle.
(2) Apply Mopar Lock N' Seal or Loctitet242 to
the sensor mounting bolt. Use new sensor bolt if orig-
inal bolt is worn or damaged.
(3) Install the sensor mounting bolt and tighten
bolt to 12-14 N´m (106-124 in. lbs.).
(4) Engage the grommets on the sensor wire to the
steering knuckle brackets.
(5) Connect the sensor wire to the harness connec-
tor.
(6) Check the sensor wire routing. Be sure the
wire is clear of all chassis components and is not
twisted or kinked at any spot.
(7) Remove the support and lower vehicle.
Fig. 1 Sensor Location
1 - BRACKET
2 - BRACKET
3 - WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
4 - MOUNTING BOLT
WJBRAKES - ABS 5 - 43
Page 221 of 2199

INSTALLATION
(1) Insert the sensor through the backing plate
(Fig. 9).
(2) Apply Mopar Lock N' Seal or Loctite 242tto
the original sensor bolt. Use a new bolt if the original
is worn or damaged.
(3) Tighten the sensor bolt to 12-14 N´m (106-124
in. lbs.).
(4) Secure the sensor wire in the brackets and the
retainers on the rear brake lines. Verify that the sen-
sor wire is secure and clear of the rotating compo-
nents.
(5) Route the sensor wires to the rear seat area.
(6) Feed the sensor wires the through floorpan
access hole and seat the sensor grommets into the
floorpan.
(7) Remove the support and lower the vehicle.(8) Fold the rear seat and carpet forward for
access to the sensor wires and connectors.
(9) Connect the sensor wires to the harness con-
nectors.
(10) Reposition the carpet and fold the rear seat
down.
HCU (HYDRAULIC CONTROL
UNIT)
DESCRIPTION
The HCU consists of a valve body, pump motor,
and wire harness.
OPERATION
Accumulators in the valve body store extra fluid
released to the system for ABS mode operation. The
pump is used to clear the accumulator of brake fluid
and is operated by a DC type motor. The motor is
controlled by the CAB.
The valves modulate brake pressure during
antilock braking and are controlled by the CAB.
The HCU provides three channel pressure control
to the front and rear brakes. One channel controls
the rear wheel brakes in tandem. The two remaining
channels control the front wheel brakes individually.
During antilock braking, the solenoid valves are
opened and closed as needed. The valves are not
static. They are cycled rapidly and continuously to
modulate pressure and control wheel slip and decel-
eration.
During normal braking, the HCU solenoid valves
and pump are not activated. The master cylinder and
power booster operate the same as a vehicle without
an ABS brake system.
During antilock braking, solenoid valve pressure
modulation occurs in three stages, pressure increase,
pressure hold, and pressure decrease. The valves are
all contained in the valve body portion of the HCU.
PRESSURE DECREASE
The outlet valve is opened and the inlet valve is
closed during the pressure decrease cycle.
A pressure decrease cycle is initiated when speed
sensor signals indicate high wheel slip at one or
more wheels. At this point, the CAB closes the inlet
then opens the outlet valve, which also opens the
return circuit to the accumulators. Fluid pressure is
allowed to bleed off (decrease) as needed to prevent
wheel lock.
Once the period of high wheel slip has ended, the
CAB closes the outlet valve and begins a pressure
increase or hold cycle as needed.
Fig. 8 Sensor Mounting Bolt
1 - WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
2 - MOUNTING BOLT
Fig. 9 Wheel Speed Sensor
1 - WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
2 - BACKING PLATE
5 - 46 BRAKES - ABSWJ
REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR (Continued)
Page 222 of 2199

PRESSURE HOLD
Both solenoid valves are closed in the pressure
hold cycle. Fluid apply pressure in the control chan-
nel is maintained at a constant rate. The CAB main-
tains the hold cycle until sensor inputs indicate a
pressure change is necessary.
PRESSURE INCREASE
The inlet valve is open and the outlet valve is
closed during the pressure increase cycle. The pres-
sure increase cycle is used to counteract unequal
wheel speeds. This cycle controls re-application of
fluid apply pressure due to changing road surfaces or
wheel speed.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the negative battery cable from the
battery.
(2) Remove the air cleaner housing,(Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/AIR INTAKE SYSTEM/AIR CLEANER
HOUSING - REMOVAL).
(3) Pull the CAB harness connector release up and
remove connector (Fig. 10).(4) Remove the brake lines from the HCU.
(5) Remove the HCU/CAB side mounting bolt and
the two rear mounting bolts. (Fig. 11).
(6) Remove the HCU/CAB assembly from the vehi-
cle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install HCU/CAB assembly into the mounting
bracket and tighten mounting bolts to 12 N´m (9 ft.
lbs.).
(2) Install the brake lines to the HCU and tighten
to 16 N´m (12 ft. lbs.).
(3) Install CAB harness connector and push down
connector release.
(4) Install air cleaner housing,(Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/AIR INTAKE SYSTEM/AIR CLEANER
HOUSING - INSTALLATION).
(5) Install negative battery cable to the battery.
(6) Bleed base and ABS brake systems,(Refer to 5 -
BRAKES - STANDARD PROCEDURE) OR (Refer to
5 - BRAKES - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
Fig. 10 CAB Connector Release
1 - CONNECTOR RELEASE
2 - CAB
Fig. 11 HCU/CAB Assembly
1 - SIDE MOUNTING BOLT
2 - REAR MOUNTING BOLTS
WJBRAKES - ABS 5 - 47
HCU (HYDRAULIC CONTROL UNIT) (Continued)
Page 237 of 2199
corrosion inhibitors called HOAT, for Hybrid Organic
Additive Technology) is recommended. This coolant
offers the best engine cooling without corrosion when
mixed with 50% distilled water to obtain to obtain a
freeze point of -37ÉC (-35ÉF). If it loses color or
becomes contaminated, drain, flush, and replace with
fresh properly mixed coolant solution.
CAUTION: Do not use coolant additives that are
claimed to improve engine cooling.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - COOLING SYSTEM -
REVERSE FLUSHING
CAUTION: The cooling system normally operates at
97-to-124 kPa (14-to -18 psi) pressure. Exceeding
this pressure may damage the radiator or hoses.
Reverse flushing of the cooling system is the forc-
ing of water through the cooling system. This is done
using air pressure in the opposite direction of normal
coolant flow. It is usually only necessary with very
dirty systems with evidence of partial plugging.
CHEMICAL CLEANING
If visual inspection indicates the formation of
sludge or scaly deposits, use a radiator cleaner
(Mopar Radiator Kleen or equivalent) before flushing.
This will soften scale and other deposits and aid the
flushing operation.
CAUTION: Be sure instructions on the container are
followed.
REVERSE FLUSHING RADIATOR
Disconnect the radiator hoses from the radiator fit-
tings. Attach a section of radiator hose to the radia-
tor bottom outlet fitting and insert the flushing gun.
Connect a water supply hose and air supply hose to
the flushing gun.
CAUTION: The cooling system normally operates at
97-to-124 kPa (14- to-18 psi) pressure. Exceeding
this pressure may damage the radiator or hoses.
Allow the radiator to fill with water. When radiator
is filled, apply air in short blasts allowing radiator to
refill between blasts. Continue this reverse flushing
until clean water flows out through rear of radiator
cooling tube passages. For more information, refer to
operating instructions supplied with flushing equip-
ment. Have radiator cleaned more extensively by a
radiator repair shop.
REVERSE FLUSHING ENGINE
Drain the cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE). Remove the thermostat
housing and thermostat. Install the thermostat hous-
ing. Disconnect the radiator upper hose from the
radiator and attach the flushing gun to the hose. Dis-
connect the radiator lower hose from the water
pump. Attach a lead away hose to the water pump
inlet fitting.
CAUTION: Be sure that the heater control valve is
closed (heat off). This is done to prevent coolant
flow with scale and other deposits from entering
the heater core.
Connect the water supply hose and air supply hose
to the flushing gun. Allow the engine to fill with
water. When the engine is filled, apply air in short
blasts, allowing the system to fill between air blasts.
Continue until clean water flows through the lead
away hose. For more information, refer to operating
instructions supplied with flushing equipment.
Remove the lead away hose, flushing gun, water
supply hose and air supply hose. Remove the thermo-
stat housing (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/EN-
GINE COOLANT THERMOSTAT - REMOVAL).
Install the thermostat and housing with a replace-
ment gasket (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/EN-
GINE COOLANT THERMOSTAT -
INSTALLATION). Connect the radiator hoses. Refill
the cooling system with the correct antifreeze/water
mixture (Refer to 7 - COOLING - STANDARD PRO-
CEDURE).
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. In.
Lbs. Lbs.
Automatic Belt Tensioner to
Mounting
BracketÐBolt
4.0L 28 Ð 250
4.7L 41 30 Ð
Automatic Belt Tensioner
PulleyÐ
Bolt
(4.7L) 61 45 Ð
Block HeaterÐBolt
7 - 14 COOLINGWJ
COOLING (Continued)
Page 238 of 2199

DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. In.
Lbs. Lbs.
4.0L 4 Ð 32
4.7L 2 Ð 17
Fan Blade Assy. to Viscous
DriveÐ
Bolts 4.0L 23 Ð 200
Generator MountingÐBolts
4.0L57 42 Ð
Radiator Upper Isolator to
CrossmemberÐNuts 3 Ð 20
Radiator Upper Isolator to
RadiatorÐ
Nuts 4 Ð 36
Radiator BraceÐBolts 10 Ð 90
Thermostat HousingÐBolts
4.0L 22 16 Ð
4.7L 13 Ð 115
Upper Radiator Crossmember
to
BodyÐBolts 10 Ð 90
Water PumpÐBolts
4.0L 23 17 Ð
4.7L 54 40 Ð
Water Pump Pulley to Water
PumpÐ
Bolts 4.0L 28 Ð 250
High Pressure Inlet Hose to
Hydraulic Fan DriveÐ1/2 inch
Fitting49 36 Ð
High Pressure Outlet Hose to
Steering GearÐ3/8 inch
Fitting29 21.5 Ð
Fan Shroud to Radiator
Mounting Bolts6Ð50SPECIAL TOOLS
COOLING
Pliers 6094
Pressure Tester 7700±A
WJCOOLING 7 - 15
COOLING (Continued)
Page 251 of 2199

²Fan control valve
²Two stage G-rotor hydraulic drive
The hydraulic fan and drive is not serviceable.
Therefore any failure of the fan blade, hydraulic fan
drive or fan shroud requires replacement of the fan
module because the fan blade and hydraulic fan drive
are matched and balanced as a system and servicing
either separately would disrupt this balance.
For hydraulic fluid routing information refer to
(Fig. 5).
CAUTION: Do not attempt to service the hydraulic
cooling fan or fan drive separately replace the cooling
module as an assembly. Failure to do so may cause
severe damage to the hydraulic cooling fan assembly.
OPERATION
The hydraulic radiator cooling fan used on the
Grand Cherokee with the 4.7L engine replaces both
the electric fan and the engine driven mechanical
fan. The use of this hydraulic fan provides the 4.7L
equipped Grand Cherokee with heavy trailer tow
capability while at the same time reducing unneces-
sary power drain on both the engine and the vehicles
electrical system.
HYDRAULIC FAN STRATEGY
The hydraulic radiator cooling fan is controlled by
the JTEC. A PWM (Pulse With Modulated) signal
from the JTEC controls the fan from 0 to 100% of the
available fan speed. There are four inputs to the
JTEC that determine what speed percentage of fan is
required by the vehicle. These inputs are:
²Engine Coolant Temperature
²Transmission Oil Temperature
²Battery Temperature
²A/C System Pressure
By monitoring these four parameters, the JTEC
can determine if cooling airflow is required. If airflow
is required, the JTEC will slowly ramp up (speed up)
the fan speed until the parameter(s) are under con-
trol. Once the temperature or pressure is reduced to
within operating parameters the fan will ramp up,
ramp down, or hold its speed to maintain the temper-
ature / pressure requirements.
NOTE: Even if the JTEC is not requesting fan on
operation the fan blade will usually spin between
100 and 500 RPM when the vehicle is at idle. This is
due to a controlled minimum oil flow requirement
through the fan drive motor.
ACTIVATING THE HYDRAULIC FAN WITH THE DRB
Under the Engine Systems test heading, there is a
subheading. ªHydraulic fan solenoid testº, that has
the selections, on /off. Activating the fan with the
DRB will run the fan at 100% duty cycle, which will
help troubleshoot any system problems, and also help
with the deaeration procedure.
NOTE: Engine must be running to activate the fan
with the DRB.
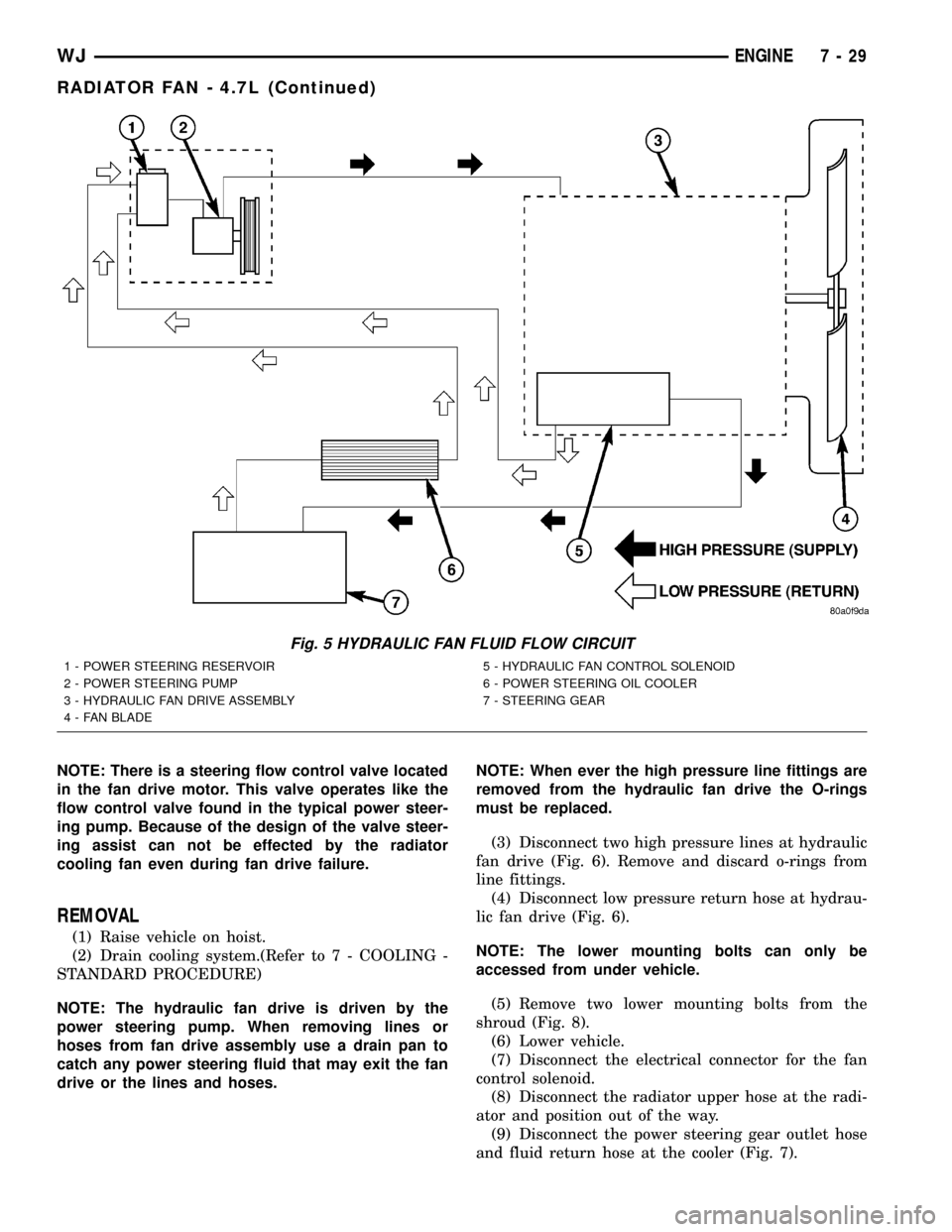
RADIATOR COOLING FAN HYDRAULIC FLUID PATH
Hydraulic fluid is pumped through the power
steering pump, from the pump the fluid travels
though a high pressure delivery line to the fan drive
motor. As fluid is diverted through the G-rotors, rota-
tional motion is created as fluid moves from the high-
pressure (inlet) side of the motor to the low-pressure
(outlet) side. Fluid exiting the drive motor is divided
into two paths. Path one continues through a high
pressure delivery line to the vehicles steering gear to
provide steering assist. and path two sends fluid
back to the power steering pump through a low pres-
sure line. Fluid exits the steering gear under low
pressure and travels through a low pressure line to
the power steering fluid cooler to be cooled before
being returned back the the power steering fluid res-
ervoir (Fig. 5).
Fig. 4 HYDRAULIC RADIATOR COOLING FAN AND
FAN DRIVE
1 - POWER STEERING FLUID COOLER
2 - RADIATOR
3 - HIGH PRESSURE LINE FROM STEERING GEAR PUMP TO
HYDRAULIC FAN MOTOR
4 - HYDRAULIC FAN MOTOR
5 - HIGH PRESSURE LINE FROM HYDRAULIC FAN MOTOR TO
STEERING GEAR
6 - FAN SHROUD
7 - 28 ENGINEWJ
RADIATOR FAN - 4.7L (Continued)
Page 252 of 2199

NOTE: There is a steering flow control valve located
in the fan drive motor. This valve operates like the
flow control valve found in the typical power steer-
ing pump. Because of the design of the valve steer-
ing assist can not be effected by the radiator
cooling fan even during fan drive failure.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(2) Drain cooling system.(Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE)
NOTE: The hydraulic fan drive is driven by the
power steering pump. When removing lines or
hoses from fan drive assembly use a drain pan to
catch any power steering fluid that may exit the fan
drive or the lines and hoses.NOTE: When ever the high pressure line fittings are
removed from the hydraulic fan drive the O-rings
must be replaced.
(3) Disconnect two high pressure lines at hydraulic
fan drive (Fig. 6). Remove and discard o-rings from
line fittings.
(4) Disconnect low pressure return hose at hydrau-
lic fan drive (Fig. 6).
NOTE: The lower mounting bolts can only be
accessed from under vehicle.
(5) Remove two lower mounting bolts from the
shroud (Fig. 8).
(6) Lower vehicle.
(7) Disconnect the electrical connector for the fan
control solenoid.
(8) Disconnect the radiator upper hose at the radi-
ator and position out of the way.
(9) Disconnect the power steering gear outlet hose
and fluid return hose at the cooler (Fig. 7).
Fig. 5 HYDRAULIC FAN FLUID FLOW CIRCUIT
1 - POWER STEERING RESERVOIR
2 - POWER STEERING PUMP
3 - HYDRAULIC FAN DRIVE ASSEMBLY
4 - FAN BLADE5 - HYDRAULIC FAN CONTROL SOLENOID
6 - POWER STEERING OIL COOLER
7 - STEERING GEAR
WJENGINE 7 - 29
RADIATOR FAN - 4.7L (Continued)
Page 253 of 2199

(10) Remove two upper mounting bolts from the
shroud (Fig. 8).
(11) Remove the shroud and fan drive from vehi-
cle.
CLEANING
Clean the fan blades using a mild soap and water.
Do not use an abrasive to clean the blades.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: There is an external ground wire con-
nected to the hydraulic fan drive located at the elec-
trical connector on the fan assembly. This ground
MUST remain connected at all times. Failure to
ensure ground wire is connected when engine is
operating can cause severe damage to the JTEC
module.
(1) Position fan drive and shroud in vehicle.
(2) Install fan shroud upper mounting bolts. Do
not tighten at this time.
(3) Install radiator upper hose onto radiator.
(4) Connect power steering cooler hoses.
(5) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(6) Install fan shroud lower mounting bolts.
Tighten to 6 N´m (50 in. lbs.).
Fig. 6 HYDRAULIC LINES/HOSES AND ELECTRICAL
CONNECTOR
1 - LOW PRESSURE RETURN HOSE
2 - HIGH PRESSURE LINE (OUTLET)
3 - HIGH PRESSURE LINE (INLET)
4 - HYDRAULIC FAN DRIVE
Fig. 7 POWER STEERING GEAR OUTLET AND
RETURN HOSES
1 - POWER STEERING COOLER RETURN HOSE
2 - POWER STEERING COOLER SUPPLY HOSE
Fig. 8 FAN SHROUD MOUNTING BOLT LOCATIONS
1 - FAN SHROUD UPPER MOUNTING BOLT LOCATIONS
2 - FAN SHROUD LOWER MOUNTING BOLT LOCATIONS
7 - 30 ENGINEWJ
RADIATOR FAN - 4.7L (Continued)