water leak JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2003 WJ / 2.G User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2003, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2003 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 270 of 2199

INSPECTION
The radiator cooling fins should be checked for
damage or deterioration. Inspect cooling fins to make
sure they are not bent or crushed, these areas result
in reduced heat exchange causing the cooling system
to operate at higher temperatures. Inspect the plastic
end tanks for cracks, damage or leaks.
Inspect the radiator neck for damage or distortion.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Before installing the radiator or A/C con-
denser, be sure the radiator-to-body and radiator-to-
A/C condenser rubber air seals (Fig. 39) are
properly fastened to their original positions. These
are used at the top, bottom and sides of the radia-
tor and A/C condenser. To prevent overheating,
these seals must be installed to their original posi-
tions.
(1) Equipped with air conditioning: Gently lower
the radiator into the vehicle. Guide the two radiator
alignment dowels through the holes in the rubber air
seals first and then through the A/C support brackets
(Fig. 40). Continue to guide the alignment dowels
into the rubber grommets located in lower radiator
crossmember. The holes in the L-shaped brackets
(located on bottom of A/C condenser) must be posi-
tioned between bottom of rubber air seals and top of
rubber grommets.
(2) Connect the radiator upper and lower hoses
and hose clamps to radiator (Fig. 41).
CAUTION: The tangs on the hose clamps must be
positioned straight down.
(3) Install coolant reserve/overflow tank hose at
radiator (Fig. 41).
(4) Connect both transmission cooler lines at the
radiator (Fig. 41).
(5) Install both radiator mounting bolts (Fig. 41).
(6) Install air inlet duct at grill.
(7) Attach electric fan harness to shroud, then con-
nect harness to connector (Fig. 41).
(8) Install the grill (Refer to 23 - BODY/EXTERI-
OR/GRILLE - INSTALLATION).
(9) Install the fan/viscous fan drive assembly to
the water pump.
(10) Rotate the fan blades (by hand) and check for
interference at fan shroud.
(11) Be sure of at least 25 mm (1.0 inch) between
tips of fan blades and fan shroud.
(12) Fill cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(13) Connect battery cable at battery.
(14) Start and warm engine. Check for leaks.
RADIATOR FAN MOTOR
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐELECTRIC
COOLING FAN
The powertrain control module (PCM) will enter a
diagnostic trouble code (DTC) in memory if it detects
a problem in the auxiliary cooling fan relay or circuit.
(Refer to 25 - EMISSIONS CONTROL - DESCRIP-
TION).
If the electric cooling fan is inoperative, check the
15A fuse in the junction block and the 40A fuse in
the Power Distribution Center (PDC) with a 12 volt
test lamp or DVOM. Refer to the inside of the PDC
cover for the exact location of the fuse. If fuses are
okay, refer to ELECTRICAL for cooling fan and relay
circuit schematic.
WATER PUMP - 4.7L
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTIONÐWATER PUMP
A centrifugal water pump circulates coolant
through the water jackets, passages, intake manifold,
radiator core, cooling system hoses and heater core.
The pump is driven from the engine crankshaft by a
single serpentine drive belt.
The water pump impeller is pressed onto the rear
of a shaft that rotates in bearings pressed into the
housing. The housing has two small holes to allow
seepage to escape. The water pump seals are lubri-
cated by the antifreeze in the coolant mixture. No
additional lubrication is necessary.
Both heater hoses are connected to fittings on the
timing chain front cover. The water pump is also
mounted directly to the timing chain cover and is
equipped with a non serviceable integral pulley (Fig.
42).
DESCRIPTIONÐWATER PUMP BYPASS
The 4.7L engine uses an internal water/coolant
bypass system. The design uses galleries in the tim-
ing chain cover to circulate coolant during engine
warm-up preventing the coolant from flowing
through the radiator. The thermostat uses a stub
shaft located at the rear of the thermostat (Fig. 43)
to control flow through the bypass gallery.
OPERATION
OPERATIONÐWATER PUMP
A centrifugal water pump circulates coolant
through the water jackets, passages, intake manifold,
WJENGINE 7 - 47
RADIATOR - 4.0L (Continued)
Page 272 of 2199

WARNING: DO NOT LOOSEN THE RADIATOR
DRAINCOCK WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER
PRESSURE. SERIOUS BURNS FROM THE COOL-
ANT CAN OCCUR.
(1) Drain sufficient coolant from the radiator to
decrease the level below the heater hose inlet. On
4.7L engines this requires complete draining.
(2) Remove the heater hose.
(3) Inspect the inlet for metal casting flash or
other restrictions.
NOTE: On 4.0L engines remove the pump from the
engine before removing restriction to prevent con-
tamination of the coolant with debris. . On 4.7L
engine remove the fitting from the timing chain
cover, If the restriction is in the timing chain cover,
remove the timing chain cover.
REMOVAL
The water pump on 4.7L engines is bolted directly
to the engine timing chain case/cover.
A gasket is used as a seal between the water pump
and timing chain case/cover.
The water pump can be removed without discharg-
ing the air conditioning system (if equipped).
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable from battery.
(2) Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE). Do not waste reusable
coolant. If solution is clean, drain coolant into a clean
container for reuse.
WARNING: CONSTANT TENSION HOSE CLAMPS
ARE USED ON MOST COOLING SYSTEM HOSES.
WHEN REMOVING OR INSTALLING, USE ONLY
TOOLS DESIGNED FOR SERVICING THIS TYPE OF
CLAMP, SUCH AS SPECIAL CLAMP TOOL (NUMBER
6094). SNAP-ON CLAMP TOOL (NUMBER HPC-20)
MAY BE USED FOR LARGER CLAMPS. ALWAYS
WEAR SAFETY GLASSES WHEN SERVICING CON-
STANT TENSION CLAMPS.
CAUTION: A number or letter is stamped into the
tongue of constant tension clamps. If replacement
is necessary, use only an original equipment clamp
with matching number or letter.
(3) Remove accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
(4) Remove lower radiator hose clamp and remove
lower hose at water pump.
(5) Remove seven water pump mounting bolts and
one stud bolt.CAUTION: Do not pry water pump at timing chain
case/cover. The machined surfaces may be dam-
aged resulting in leaks.
(6) Remove water pump and gasket. Discard gas-
ket.
CLEANING
Clean the gasket mating surface. Use caution not
to damage the gasket sealing surface.
INSPECTION
Inspect the water pump assembly for cracks in the
housing, Water leaks from shaft seal, Loose or rough
turning bearing or Impeller rubbing either the pump
body or timing chain case/cover.
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean gasket mating surfaces.
(2) Using a new gasket, position water pump and
install mounting bolts as shown. (Fig. 44). Tighten
water pump mounting bolts to 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(3) Spin water pump to be sure that pump impel-
ler does not rub against timing chain case/cover.
(4) Connect radiator lower hose to water pump.
(5) Install accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS - INSTAL-
LATION).
Fig. 44 Water Pump Installation
1 - WATER PUMP
2 - TIMING CHAIN COVER
WJENGINE 7 - 49
WATER PUMP - 4.7L (Continued)
Page 273 of 2199

CAUTION: When installing the serpentine accessory
drive belt, belt must be routed correctly. If not,
engine may overheat due to water pump rotating in
wrong direction.
(6) Refill cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(7) Connect negative battery cable.
(8) Start and warm the engine. Check for leaks.
WATER PUMP - 4.0L
DESCRIPTION
CAUTION: All 4.0L 6-cylinder engines are equipped
with a reverse (counterclockwise) rotating water
pump and thermal viscous fan drive assembly.
REVERSE is stamped or imprinted on the cover of
the viscous fan drive and inner side of the fan. The
letter R is stamped into the back of the water pump
impeller. Engines from previous model years,
depending upon application, may have been
equipped with a forward (clockwise) rotating water
pump. Installation of the wrong water pump or vis-
cous fan drive will cause engine over heating.
A centrifugal water pump circulates coolant
through the water jackets, passages, intake manifold,
radiator core, cooling system hoses and heater core.
The pump is driven from the engine crankshaft by a
single serpentine drive belt.
The water pump impeller is pressed onto the rear
of a shaft that rotates in bearings pressed into the
housing. The housing has two small holes to allow
seepage to escape. The water pump seals are lubri-
cated by the antifreeze in the coolant mixture. No
additional lubrication is necessary (Fig. 45).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐWATER PUMP
LOOSE IMPELLER - 4.0L and 4.7L
NOTE: Due to the design of the 4.0L and 4.7L
engine water pumps, testing the pump for a loose
impeller must be done by verifying coolant flow in
the radiator. To accomplish this refer to the follow-
ing procedure.
DO NOT WASTE reusable coolant. If solution is
clean, drain coolant into a clean container for reuse.
(1) Drain coolant until the first row of cores is vis-
ible in the radiator (Refer to 7 - COOLING - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE) 4.7L Engine or (Refer to 7 -
COOLING - STANDARD PROCEDURE) 4.0L
Engine.(2) Leaving the radiator cap off, start the engine.
Run engine until thermostat opens.
(3) While looking into the radiator through the
radiator fill neck, raise engine rpm to 2000 RPM.
Observe the flow of coolant from the first row of
cores.
(4) If there is no flow or very little flow visable,
replace the water pump.
INSPECTING FOR INLET RESTRICTIONS
Inadequate heater performance may be caused by
a metal casting restriction in the heater hose inlet.
DO NOT WASTE reusable coolant. If solution is
clean, drain the coolant into a clean container for
reuse.
WARNING: DO NOT LOOSEN THE RADIATOR
DRAINCOCK WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER
PRESSURE. SERIOUS BURNS FROM THE COOL-
ANT CAN OCCUR.
(1) Drain sufficient coolant from the radiator to
decrease the level below the heater hose inlet. On
4.7L engines this requires complete draining.
(2) Remove the heater hose.
(3) Inspect the inlet for metal casting flash or
other restrictions.
Fig. 45 Water Pump
1 - HEATER HOSE FITTING BORE
2 - WATER PUMP
3 - WATER PUMP HUB
7 - 50 ENGINEWJ
WATER PUMP - 4.7L (Continued)
Page 275 of 2199

CLEANING
Clean the gasket mating surface. Use caution not
to damage the gasket sealing surface.
INSPECTION
Inspect the water pump assembly for cracks in the
housing, Water leaks from shaft seal, Loose or rough
turning bearing or Impeller rubbing either the pump
body or timing chain case/cover.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: If the water pump is replaced because of
mechanical damage, the fan blades and viscous fan
drive should also be inspected. These components
could have been damaged due to excessive vibra-
tion.
(1) If pump is being replaced, install the heater
hose fitting to the pump. Use a sealant on the fitting
such as MopartThread Sealant With Teflon. Refer to
the directions on the package.
(2) Clean the gasket mating surfaces. If the origi-
nal pump is used, remove any deposits or other for-
eign material. Inspect the cylinder block and water
pump mating surfaces for erosion or damage from
cavitation.
(3) Install the gasket and water pump. The sili-
cone bead on the gasket should be facing the water
pump. Also, the gasket is installed dry. Tighten
mounting bolts to 30 N´m (22 ft. lbs.) torque. Rotate
the shaft by hand to be sure it turns freely.
(4) Connect the radiator and heater hoses to the
water pump.
(5) Position water pump pulley to water pump
hub. Tighten bolts 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.).
Install the idler pulley. Tighten the bolt 47 N´m (35
ft. lbs.).
Fig. 47 Hose Clamp Tool - Typical
1 - HOSE CLAMP TOOL 6094
2 - HOSE CLAMP
Fig. 48 Clamp - Typical
1 - TYPICAL CONSTANT TENSION HOSE CLAMP
2 - CLAMP NUMBER/LETTER LOCATION
3 - TYPICAL HOSE
Fig. 49 Water Pump Remove/Install - Typical
1 - HEATER HOSE FITTING
2 - PUMP GASKET
3 - WATER PUMP
4 - LONG BOLT
5 - BOLTS (4) SHORT
7 - 52 ENGINEWJ
WATER PUMP - 4.0L (Continued)
Page 276 of 2199

CAUTION: When installing the serpentine engine
accessory drive belt, the belt MUST be routed cor-
rectly. If not, the engine may overheat due to the
water pump rotating in the wrong direction. Refer to
the Belt Removal and Installtion in this group for
appropriate belt routing. You may also refer to the
Belt Routing Label in the vehicle engine compart-
ment.
Install accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS - INSTALLA-
TION).
(6) Install fan blade and viscous fan drive onto
water pump.
(7) Fill cooling system with coolant and check for
leaks. (Refer to 7 - COOLING - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE).
(8) Connect battery cable to battery.
(9) Start and warm the engine. Check for leaks.
RADIATOR PRESSURE CAP
DESCRIPTION
All radiators are equipped with a pressure cap
(Fig. 50). This cap releases pressure at some point
within a range of 124-to-145 kPa (18-to-21 psi). The
pressure relief point (in pounds) is engraved on top of
the cap
The cooling system will operate at pressures
slightly above atmospheric pressure. This results in a
higher coolant boiling point allowing increased radi-
ator cooling capacity. The cap contains a spring-
loaded pressure relief valve. This valve opens when
system pressure reaches the release range of 124-to-
145 kPa (18-to-21 psi).
A rubber gasket seals the radiator filler neck. This is
done to maintain vacuum during coolant cool-down and
to prevent leakage when system is under pressure.
OPERATION
A vent valve in the center of the cap will remain
shut as long as the cooling system is pressurized. As
the coolant cools, it contracts and creates a vacuum
in cooling system. This causes the vacuum valve to
open and coolant in reserve/overflow tank to be
drawn through connecting hose into radiator. If the
vacuum valve is stuck shut, or overflow hose is
kinked, radiator hoses will collapse on cool-down.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐRADIATOR
PRESSURE CAP
Remove cap from radiator. Be sure that sealing
surfaces are clean. Moisten rubber gasket with water
and install the cap on pressure tester (tool 7700 or
an equivalent) (Fig. 51).Operate the tester pump and observe the gauge
pointer at its highest point. The cap release pressure
should be 124 to 145 kPa (18 to 21 psi). The cap is
satisfactory when the pressure holds steady. It is also
good if it holds pressure within the 124 to 145 kPa
(18 to 21 psi) range for 30 seconds or more. If the
pointer drops quickly, replace the cap.
CAUTION: Radiator pressure testing tools are very
sensitive to small air leaks, which will not cause
cooling system problems. A pressure cap that does
not have a history of coolant loss should not be
replaced just because it leaks slowly when tested
with this tool. Add water to tool. Turn tool upside
down and recheck pressure cap to confirm that cap
needs replacement.CLEANING
Clean the radiator pressure cap using a mild soap
and water only.
Fig. 50 Radiator Pressure Cap - Typical
1 - FILLER NECK SEAL
2 - VACUUM VENT VALVE
3 - PRESSURE RATING
4 - PRESSURE VALVE
WJENGINE 7 - 53
WATER PUMP - 4.0L (Continued)
Page 277 of 2199

INSPECTION
Visually inspect the pressure valve gasket on the
cap. Replace cap if the gasket is swollen, torn or
worn. Inspect the area around radiator filler neck for
white deposits that indicate a leaking cap.
WATER PUMP INLET TUBE
REMOVAL
WARNING: CONSTANT TENSION HOSE CLAMPS
ARE USED ON MOST COOLING SYSTEM HOSES.
WHEN REMOVING OR INSTALLING, USE ONLY
TOOLS DESIGNED FOR SERVICING THIS TYPE OF
CLAMP, SUCH AS SPECIAL CLAMP TOOL (NUMBER
6094) (Fig. 52). SNAP-ON CLAMP TOOL (NUMBER
HPC-20) MAY BE USED FOR LARGER CLAMPS.
ALWAYS WEAR SAFETY GLASSES WHEN SERVIC-
ING CONSTANT TENSION CLAMPS.
CAUTION: A number or letter is stamped into the
tongue of constant tension clamps (Fig. 53). If
replacement is necessary, use only an original
equipment clamp with matching number or letter.
(1) Partially drain cooling system .
(2) Do not waste reusable coolant. If solution is
clean, drain coolant into a clean container for reuse.(3) Loosen both bypass hose clamps (Fig. 52) and
position to center of hose. Remove hose from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position bypass hose clamps (Fig. 52) to center
of hose.
(2) Install bypass hose to engine.
(3) Secure both hose clamps (Fig. 52).
(4) Refill cooling system .
(5) Start and warm the engine. Check for leaks.
Fig. 51 Pressure Testing Radiator Pressure
CapÐTypical
1 - PRESSURE CAP
2 - TYPICAL COOLING SYSTEM PRESSURE TESTER
Fig. 52 Hose Clamp ToolÐTypical
1 - HOSE CLAMP TOOL 6094
2 - HOSE CLAMP
Fig. 53 Clamp Number/Letter Location
1 - TYPICAL CONSTANT TENSION HOSE CLAMP
2 - CLAMP NUMBER/LETTER LOCATION
3 - TYPICAL HOSE
7 - 54 ENGINEWJ
RADIATOR PRESSURE CAP (Continued)
Page 339 of 2199

diagnose the charging system after replenishing the
water in the battery for a low electrolyte condition
and before returning the vehicle to service. Refer to
Charging Systemfor additional information.
For battery maintenance schedules and jump start-
ing procedures, see the owner's manual in the vehicle
glove box. Optionally, refer toMaintenance Sched-
ulesandJump Starting, Towing and Hoistingin
the index of this service manual for the location of
the recommended battery maintenance schedules and
the proper battery jump starting procedures. While
battery charging can be considered a maintenance
procedure, the battery charging procedures and infor-
mation are located in the service procedures section
of this service manual. This was done because the
battery must be fully-charged before any battery
diagnosis or testing procedures can be performed.
Refer toStandard Proceduresin the index of this
service manual for the location of the proper battery
charging procedures.
OPERATION
The battery is designed to store electrical energy in
a chemical form. When an electrical load is applied to
the terminals of the battery, an electrochemical reac-
tion occurs. This reaction causes the battery to dis-
charge electrical current from its terminals. As the
battery discharges, a gradual chemical change takes
place within each cell. The sulfuric acid in the elec-
trolyte combines with the plate materials, causing
both plates to slowly change to lead sulfate. At the
same time, oxygen from the positive plate material
combines with hydrogen from the sulfuric acid, caus-
ing the electrolyte to become mainly water. The
chemical changes within the battery are caused by
the movement of excess or free electrons between the
positive and negative plate groups. This movement of
electrons produces a flow of electrical current
through the load device attached to the battery ter-
minals.
As the plate materials become more similar chem-
ically, and the electrolyte becomes less acid, the volt-
age potential of each cell is reduced. However, by
charging the battery with a voltage higher than that
of the battery itself, the battery discharging process
is reversed. Charging the battery gradually changes
the sulfated lead plates back into sponge lead and
lead dioxide, and the water back into sulfuric acid.
This action restores the difference in the electron
charges deposited on the plates, and the voltage
potential of the battery cells. For a battery to remain
useful, it must be able to produce high-amperage cur-
rent over an extended period. A battery must also be
able to accept a charge, so that its voltage potential
may be restored.The battery is vented to release excess hydrogen
gas that is created when the battery is being charged
or discharged. However, even with these vents,
hydrogen gas can collect in or around the battery. If
hydrogen gas is exposed to flame or sparks, it may
ignite. If the electrolyte level is low, the battery may
arc internally and explode. If the battery is equipped
with removable cell caps, add distilled water when-
ever the electrolyte level is below the top of the
plates. If the battery cell caps cannot be removed, the
battery must be replaced if the electrolyte level
becomes low.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BATTERY
The battery must be completely charged and the
terminals should be properly cleaned and inspected
before diagnostic procedures are performed. Refer to
Battery System Cleaning for the proper cleaning pro-
cedures, and Battery System Inspection for the
proper battery inspection procedures. Refer to Stan-
dard Procedures for the proper battery charging pro-
cedures.
MICRO 420 ELECTRICAL SYSTEM TESTER
The Micro420 automotive battery tester is designed
to help the dealership technicians diagnose the cause
of a defective battery. Follow the instruction manual
supplied with the tester to properly diagnose a vehi-
cle. If the instruction manual is not available refer to
the standard procedure in this section, which
includes the directions for using the Micro420 electri-
cal system tester.
WARNING: IF THE BATTERY SHOWS SIGNS OF
FREEZING, LEAKING OR LOOSE POSTS, DO NOT
TEST, ASSIST-BOOST, OR CHARGE. THE BATTERY
MAY ARC INTERNALLY AND EXPLODE. PERSONAL
INJURY AND/OR VEHICLE DAMAGE MAY RESULT.
WARNING: EXPLOSIVE HYDROGEN GAS FORMS IN
AND AROUND THE BATTERY. DO NOT SMOKE,
USE FLAME, OR CREATE SPARKS NEAR THE BAT-
TERY. PERSONAL INJURY AND/OR VEHICLE DAM-
AGE MAY RESULT.
WARNING: THE BATTERY CONTAINS SULFURIC
ACID, WHICH IS POISONOUS AND CAUSTIC. AVOID
CONTACT WITH THE SKIN, EYES, OR CLOTHING.
IN THE EVENT OF CONTACT, FLUSH WITH WATER
AND CALL A PHYSICIAN IMMEDIATELY. KEEP OUT
OF THE REACH OF CHILDREN.
A battery that will not accept a charge is faulty,
and must be replaced. Further testing is not
required. A fully-charged battery must be load tested
8F - 8 BATTERY SYSTEMWJ
BATTERY (Continued)
Page 340 of 2199

to determine its cranking capacity. A battery that is
fully-charged, but does not pass the load test, is
faulty and must be replaced.
NOTE: Completely discharged batteries may take
several hours to accept a charge. Refer to Standard
Procedures for the proper battery charging proce-
dures.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - BATTERY
CHARGING
Battery charging is the means by which the bat-
tery can be restored to its full voltage potential. A
battery is fully-charged when:
²Micro 420 electrical system tester indicates bat-
tery is OK.
²All of the battery cells are gassing freely during
battery charging.
²Three hydrometer tests, taken at one-hour inter-
vals, indicate no increase in the temperature-cor-
rected specific gravity of the battery electrolyte.
²Open-circuit voltage of the battery is 12.4 volts
or above.
WARNING: NEVER EXCEED TWENTY AMPERES
WHEN CHARGING A COLD (-1É C [30É F] OR
LOWER) BATTERY. THE BATTERY MAY ARC INTER-
NALLY AND EXPLODE. PERSONAL INJURY AND/OR
VEHICLE DAMAGE MAY RESULT.
WARNING: IF THE BATTERY SHOWS SIGNS OF
FREEZING, LEAKING, LOOSE POSTS, DO NOT
TEST, ASSIST-BOOST, OR CHARGE. THE BATTERY
MAY ARC INTERNALLY AND EXPLODE. PERSONAL
INJURY AND/OR VEHICLE DAMAGE MAY RESULT.
WARNING: EXPLOSIVE HYDROGEN GAS FORMS IN
AND AROUND THE BATTERY. DO NOT SMOKE,
USE FLAME, OR CREATE SPARKS NEAR THE BAT-
TERY. PERSONAL INJURY AND/OR VEHICLE DAM-
AGE MAY RESULT.
WARNING: THE BATTERY CONTAINS SULFURIC
ACID, WHICH IS POISONOUS AND CAUSTIC. AVOID
CONTACT WITH THE SKIN, EYES, OR CLOTHING.
IN THE EVENT OF CONTACT, FLUSH WITH WATER
AND CALL A PHYSICIAN IMMEDIATELY. KEEP OUT
OF THE REACH OF CHILDREN.WARNING: IF THE BATTERY IS EQUIPPED WITH
REMOVABLE CELL CAPS, BE CERTAIN THAT EACH
OF THE CELL CAPS IS IN PLACE AND TIGHT
BEFORE THE BATTERY IS RETURNED TO SER-
VICE. PERSONAL INJURY AND/OR VEHICLE DAM-
AGE MAY RESULT FROM LOOSE OR MISSING
CELL CAPS.
CAUTION: Always disconnect and isolate the bat-
tery negative cable before charging a battery. Do
not exceed sixteen volts while charging a battery.
Damage to the vehicle electrical system compo-
nents may result.
CAUTION: Battery electrolyte will bubble inside the
battery case during normal battery charging. Elec-
trolyte boiling or being discharged from the battery
vents indicates a battery overcharging condition.
Immediately reduce the charging rate or turn off the
charger to evaluate the battery condition. Damage
to the battery may result from overcharging.
CAUTION: The battery should not be hot to the
touch. If the battery feels hot to the touch, turn off
the charger and let the battery cool before continu-
ing the charging operation. Damage to the battery
may result.
After the battery has been charged to 12.4 volts or
greater, perform a load test to determine the battery
cranking capacity. Refer to Standard Procedures for
the proper battery load test procedures. If the battery
will endure a load test, return the battery to service.
If the battery will not endure a load test, it is faulty
and must be replaced.
Clean and inspect the battery hold downs, tray,
terminals, posts, and top before completing battery
service. Refer to Battery System Cleaning for the
proper battery system cleaning procedures, and Bat-
tery System Inspection for the proper battery system
inspection procedures.
CHARGING A COMPLETELY DISCHARGED
BATTERY
The following procedure should be used to recharge
a completely discharged battery. Unless this proce-
dure is properly followed, a good battery may be
needlessly replaced.
(1) Measure the voltage at the battery posts with a
voltmeter, accurate to 1/10 (0.10) volt (Fig. 5). If the
reading is below ten volts, the battery charging cur-
rent will be low. It could take some time before the
battery accepts a current greater than a few milliam-
peres. Such low current may not be detectable on the
ammeters built into many battery chargers.
WJBATTERY SYSTEM 8F - 9
BATTERY (Continued)
Page 782 of 2199
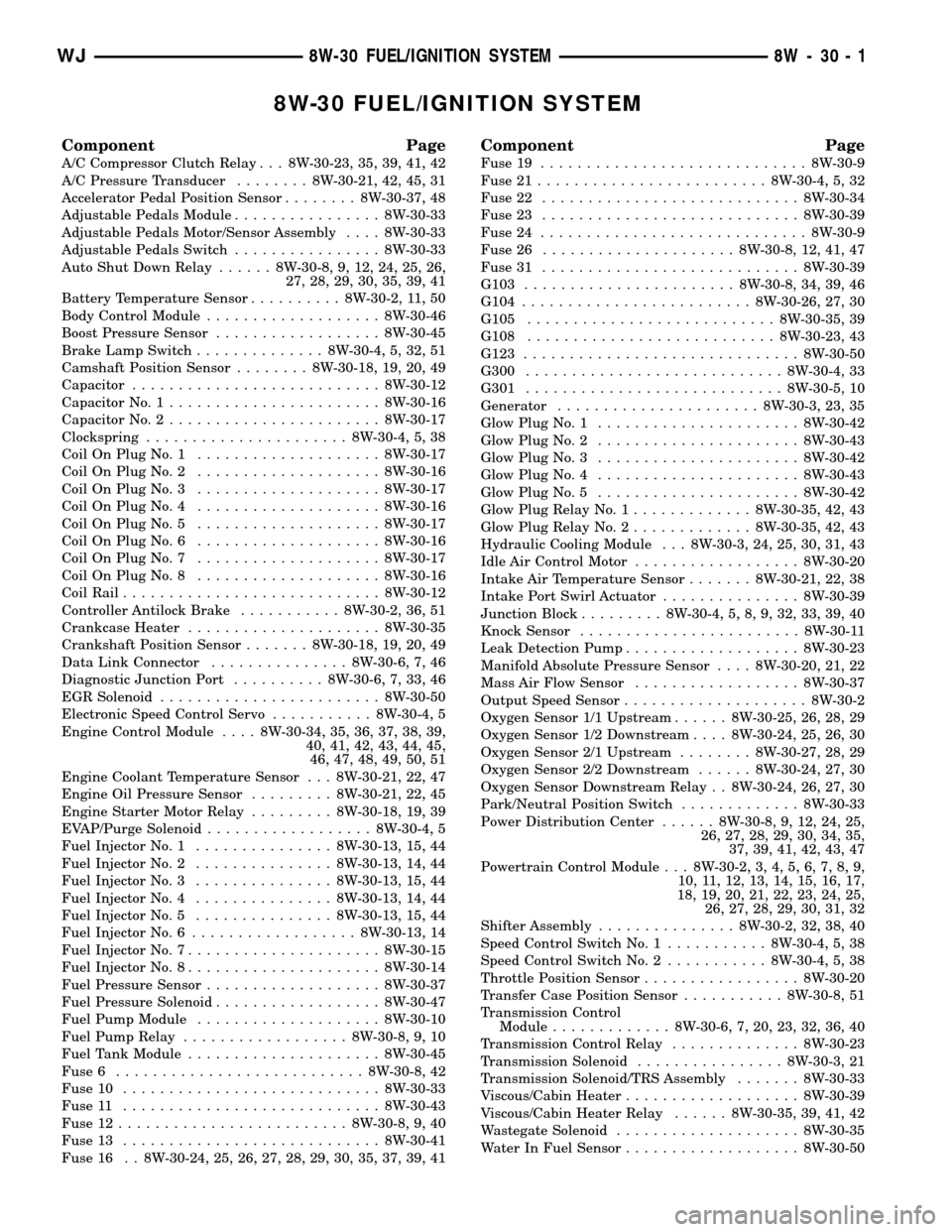
8W-30 FUEL/IGNITION SYSTEM
Component Page
A/C Compressor Clutch Relay . . . 8W-30-23, 35, 39, 41, 42
A/C Pressure Transducer........ 8W-30-21, 42, 45, 31
Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor........ 8W-30-37, 48
Adjustable Pedals Module................ 8W-30-33
Adjustable Pedals Motor/Sensor Assembly.... 8W-30-33
Adjustable Pedals Switch................ 8W-30-33
Auto Shut Down Relay...... 8W-30-8, 9, 12, 24, 25, 26,
27, 28, 29, 30, 35, 39, 41
Battery Temperature Sensor.......... 8W-30-2, 11, 50
Body Control Module................... 8W-30-46
Boost Pressure Sensor.................. 8W-30-45
Brake Lamp Switch.............. 8W-30-4, 5, 32, 51
Camshaft Position Sensor........ 8W-30-18, 19, 20, 49
Capacitor........................... 8W-30-12
Capacitor No. 1....................... 8W-30-16
Capacitor No. 2....................... 8W-30-17
Clockspring...................... 8W-30-4, 5, 38
Coil On Plug No. 1.................... 8W-30-17
Coil On Plug No. 2.................... 8W-30-16
Coil On Plug No. 3.................... 8W-30-17
Coil On Plug No. 4.................... 8W-30-16
Coil On Plug No. 5.................... 8W-30-17
Coil On Plug No. 6.................... 8W-30-16
Coil On Plug No. 7.................... 8W-30-17
Coil On Plug No. 8.................... 8W-30-16
Coil Rail............................ 8W-30-12
Controller Antilock Brake........... 8W-30-2, 36, 51
Crankcase Heater..................... 8W-30-35
Crankshaft Position Sensor....... 8W-30-18, 19, 20, 49
Data Link Connector............... 8W-30-6, 7, 46
Diagnostic Junction Port.......... 8W-30-6, 7, 33, 46
EGR Solenoid........................ 8W-30-50
Electronic Speed Control Servo........... 8W-30-4, 5
Engine Control Module.... 8W-30-34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39,
40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45,
46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor . . . 8W-30-21, 22, 47
Engine Oil Pressure Sensor......... 8W-30-21, 22, 45
Engine Starter Motor Relay......... 8W-30-18, 19, 39
EVAP/Purge Solenoid.................. 8W-30-4, 5
Fuel Injector No. 1............... 8W-30-13, 15, 44
Fuel Injector No. 2............... 8W-30-13, 14, 44
Fuel Injector No. 3............... 8W-30-13, 15, 44
Fuel Injector No. 4............... 8W-30-13, 14, 44
Fuel Injector No. 5............... 8W-30-13, 15, 44
Fuel Injector No. 6.................. 8W-30-13, 14
Fuel Injector No. 7..................... 8W-30-15
Fuel Injector No. 8..................... 8W-30-14
Fuel Pressure Sensor................... 8W-30-37
Fuel Pressure Solenoid.................. 8W-30-47
Fuel Pump Module.................... 8W-30-10
Fuel Pump Relay.................. 8W-30-8, 9, 10
Fuel Tank Module..................... 8W-30-45
Fuse 6........................... 8W-30-8, 42
Fuse 10............................ 8W-30-33
Fuse 11............................ 8W-30-43
Fuse 12......................... 8W-30-8, 9, 40
Fuse 13............................ 8W-30-41
Fuse 16 . . 8W-30-24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 35, 37, 39, 41
Component Page
Fuse 19............................. 8W-30-9
Fuse 21......................... 8W-30-4, 5, 32
Fuse 22............................ 8W-30-34
Fuse 23............................ 8W-30-39
Fuse 24............................. 8W-30-9
Fuse 26..................... 8W-30-8, 12, 41, 47
Fuse 31............................ 8W-30-39
G103....................... 8W-30-8, 34, 39, 46
G104......................... 8W-30-26, 27, 30
G105........................... 8W-30-35, 39
G108........................... 8W-30-23, 43
G123.............................. 8W-30-50
G300............................ 8W-30-4, 33
G301............................ 8W-30-5, 10
Generator...................... 8W-30-3, 23, 35
Glow Plug No. 1...................... 8W-30-42
Glow Plug No. 2...................... 8W-30-43
Glow Plug No. 3...................... 8W-30-42
Glow Plug No. 4...................... 8W-30-43
Glow Plug No. 5...................... 8W-30-42
Glow Plug Relay No. 1............. 8W-30-35, 42, 43
Glow Plug Relay No. 2............. 8W-30-35, 42, 43
Hydraulic Cooling Module . . . 8W-30-3, 24, 25, 30, 31, 43
Idle Air Control Motor.................. 8W-30-20
Intake Air Temperature Sensor....... 8W-30-21, 22, 38
Intake Port Swirl Actuator............... 8W-30-39
Junction Block......... 8W-30-4, 5, 8, 9, 32, 33, 39, 40
Knock Sensor........................ 8W-30-11
Leak Detection Pump................... 8W-30-23
Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor.... 8W-30-20, 21, 22
Mass Air Flow Sensor.................. 8W-30-37
Output Speed Sensor.................... 8W-30-2
Oxygen Sensor 1/1 Upstream...... 8W-30-25, 26, 28, 29
Oxygen Sensor 1/2 Downstream.... 8W-30-24, 25, 26, 30
Oxygen Sensor 2/1 Upstream........ 8W-30-27, 28, 29
Oxygen Sensor 2/2 Downstream...... 8W-30-24, 27, 30
Oxygen Sensor Downstream Relay . . 8W-30-24, 26, 27, 30
Park/Neutral Position Switch............. 8W-30-33
Power Distribution Center...... 8W-30-8, 9, 12, 24, 25,
26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 34, 35,
37, 39, 41, 42, 43, 47
Powertrain Control Module . . . 8W-30-2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17,
18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25,
26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32
Shifter Assembly............... 8W-30-2, 32, 38, 40
Speed Control Switch No. 1........... 8W-30-4, 5, 38
Speed Control Switch No. 2........... 8W-30-4, 5, 38
Throttle Position Sensor................. 8W-30-20
Transfer Case Position Sensor........... 8W-30-8, 51
Transmission Control
Module............. 8W-30-6, 7, 20, 23, 32, 36, 40
Transmission Control Relay.............. 8W-30-23
Transmission Solenoid................ 8W-30-3, 21
Transmission Solenoid/TRS Assembly....... 8W-30-33
Viscous/Cabin Heater................... 8W-30-39
Viscous/Cabin Heater Relay...... 8W-30-35, 39, 41, 42
Wastegate Solenoid.................... 8W-30-35
Water In Fuel Sensor................... 8W-30-50
WJ8W-30 FUEL/IGNITION SYSTEM 8W - 30 - 1
Page 1248 of 2199
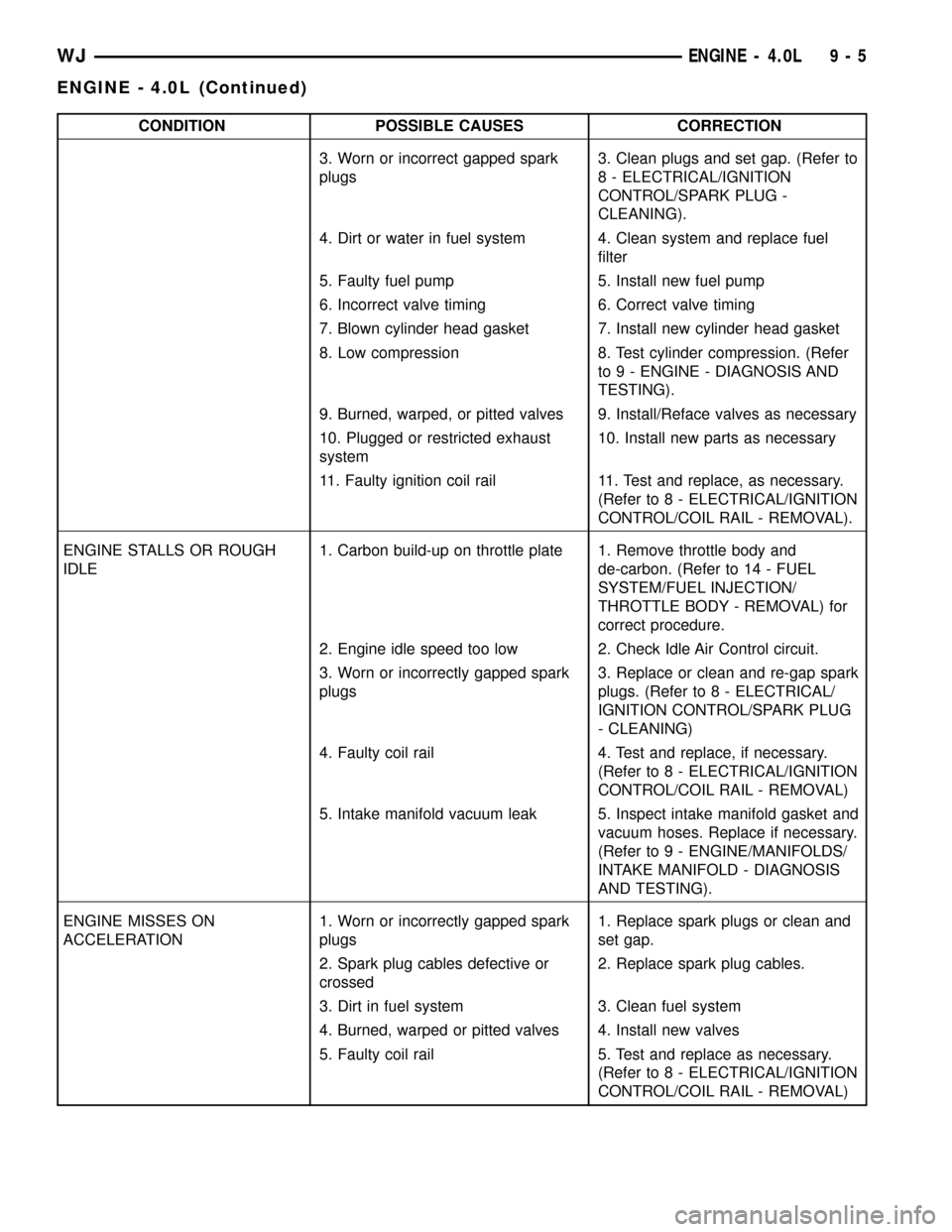
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
3. Worn or incorrect gapped spark
plugs3. Clean plugs and set gap. (Refer to
8 - ELECTRICAL/IGNITION
CONTROL/SPARK PLUG -
CLEANING).
4. Dirt or water in fuel system 4. Clean system and replace fuel
filter
5. Faulty fuel pump 5. Install new fuel pump
6. Incorrect valve timing 6. Correct valve timing
7. Blown cylinder head gasket 7. Install new cylinder head gasket
8. Low compression 8. Test cylinder compression. (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
9. Burned, warped, or pitted valves 9. Install/Reface valves as necessary
10. Plugged or restricted exhaust
system10. Install new parts as necessary
11. Faulty ignition coil rail 11. Test and replace, as necessary.
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/IGNITION
CONTROL/COIL RAIL - REMOVAL).
ENGINE STALLS OR ROUGH
IDLE1. Carbon build-up on throttle plate 1. Remove throttle body and
de-carbon. (Refer to 14 - FUEL
SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/
THROTTLE BODY - REMOVAL) for
correct procedure.
2. Engine idle speed too low 2. Check Idle Air Control circuit.
3. Worn or incorrectly gapped spark
plugs3. Replace or clean and re-gap spark
plugs. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG
- CLEANING)
4. Faulty coil rail 4. Test and replace, if necessary.
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/IGNITION
CONTROL/COIL RAIL - REMOVAL)
5. Intake manifold vacuum leak 5. Inspect intake manifold gasket and
vacuum hoses. Replace if necessary.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/
INTAKE MANIFOLD - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING).
ENGINE MISSES ON
ACCELERATION1. Worn or incorrectly gapped spark
plugs1. Replace spark plugs or clean and
set gap.
2. Spark plug cables defective or
crossed2. Replace spark plug cables.
3. Dirt in fuel system 3. Clean fuel system
4. Burned, warped or pitted valves 4. Install new valves
5. Faulty coil rail 5. Test and replace as necessary.
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/IGNITION
CONTROL/COIL RAIL - REMOVAL)
WJENGINE - 4.0L 9 - 5
ENGINE - 4.0L (Continued)