Lock cylinder JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2003 WJ / 2.G Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2003, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2003 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 309 of 2199
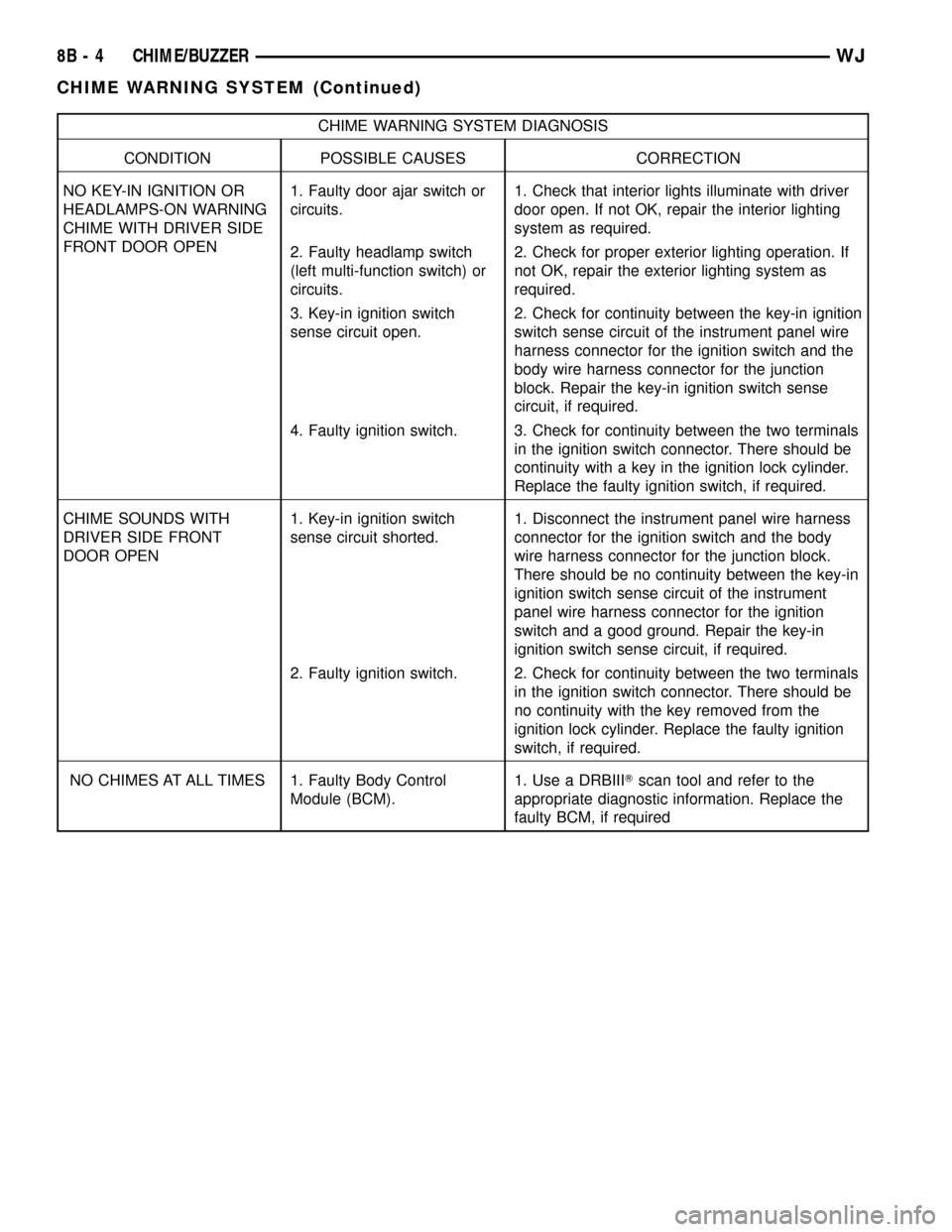
CHIME WARNING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
NO KEY-IN IGNITION OR
HEADLAMPS-ON WARNING
CHIME WITH DRIVER SIDE
FRONT DOOR OPEN1. Faulty door ajar switch or
circuits.1. Check that interior lights illuminate with driver
door open. If not OK, repair the interior lighting
system as required.
2. Faulty headlamp switch
(left multi-function switch) or
circuits.2. Check for proper exterior lighting operation. If
not OK, repair the exterior lighting system as
required.
3. Key-in ignition switch
sense circuit open.2. Check for continuity between the key-in ignition
switch sense circuit of the instrument panel wire
harness connector for the ignition switch and the
body wire harness connector for the junction
block. Repair the key-in ignition switch sense
circuit, if required.
4. Faulty ignition switch. 3. Check for continuity between the two terminals
in the ignition switch connector. There should be
continuity with a key in the ignition lock cylinder.
Replace the faulty ignition switch, if required.
CHIME SOUNDS WITH
DRIVER SIDE FRONT
DOOR OPEN1. Key-in ignition switch
sense circuit shorted.1. Disconnect the instrument panel wire harness
connector for the ignition switch and the body
wire harness connector for the junction block.
There should be no continuity between the key-in
ignition switch sense circuit of the instrument
panel wire harness connector for the ignition
switch and a good ground. Repair the key-in
ignition switch sense circuit, if required.
2. Faulty ignition switch. 2. Check for continuity between the two terminals
in the ignition switch connector. There should be
no continuity with the key removed from the
ignition lock cylinder. Replace the faulty ignition
switch, if required.
NO CHIMES AT ALL TIMES 1. Faulty Body Control
Module (BCM).1. Use a DRBIIITscan tool and refer to the
appropriate diagnostic information. Replace the
faulty BCM, if required
8B - 4 CHIME/BUZZERWJ
CHIME WARNING SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 311 of 2199

(1) Turn the ignition switch to the On position
(transmission in Park/Neutral).
(2) Use the DRBIIItand select THEFT ALARM,
SKIM, then MISCELLANEOUS.
(3) Select PCM REPLACED (GAS ENGINE).
(4) Enter secured access mode by entering the
vehicle four-digit PIN.
(5) Select ENTER to update PCM VIN.
NOTE: If three attempts are made to enter secure
access mode using an incorrect PIN, secured
access mode will be locked out for one hour. To
exit this lockout mode, turn the ignition switch to
the ON position for one hour, then enter the correct
PIN. (Ensure all accessories are turned off. Also
monitor the battery state and connect a battery
charger if necessary).
(6) Press ENTER to transfer the secret key (the
SKIM will send the secret key to the PCM).
(7) Press Page Back to get to the Select System
menu and select ENGINE, MISCELLANEOUS, and
SRI MEMORY CHECK.
(8) The DRBIIItwill ask, ªIs odometer reading
between XX and XX?º Select the YES or NO button
on the DRBIIIt. If NO is selected, the DRBIIItwill
read, ªEnter Odometer Reading (From I.P. odome-
ter)º. Enter the odometer reading from the instru-
ment cluster and press ENTER.
PROGRAMMING THE SKIM
(1) Turn the ignition switch to the On position
(transmission in Park/Neutral).
(2) Use the DRBIIItand select THEFT ALARM,
SKIM, then MISCELLANEOUS.
(3) Select PCM REPLACED (GAS ENGINE).
(4) Program the vehicle four-digit PIN into SKIM.
(5) Select COUNTRY CODE and enter the correct
country.
NOTE: Be sure to enter the correct country code. If
the incorrect country code is programmed into
SKIM, it cannot be changed and the SKIM must be
replaced.
(6) Select YES to update VIN (the SKIM will learn
the VIN from the PCM).
(7) Press ENTER to transfer the secret key (the
PCM will send the secret key to the SKIM).
(8) Program ignition keys to the SKIM.
NOTE: If the PCM and the SKIM are replaced at the
same time, all vehicle ignition keys will need to be
replaced and programmed to the new SKIM.
PROGRAMMING IGNITION KEYS TO THE SKIM
(1) Turn the ignition switch to the On position
(transmission in Park/Neutral).
(2) Use the DRBIIItand select THEFT ALARM,
SKIM, then MISCELLANEOUS.
(3) Select PROGRAM IGNITION KEY'S.
(4) Enter secured access mode by entering the
vehicle four-digit PIN.
NOTE: A maximum of eight keys can be learned to
each SKIM. Once a key is learned to a SKIM it (the
key) cannot be transferred to another vehicle.
(5) Obtain ignition keys to be programmed from
the customer (8 keys maximum).
(6) Using the DRBIIIt, erase all ignition keys by
selecting MISCELLANEOUS, and ERASE ALL CUR-
RENT IGN. KEYS.
(7) Program all of the ignition keys.
If ignition key programming is unsuccessful, the
DRBIIItwill display one of the following messages:
²Programming Not Attempted- The DRBIIIt
attempts to read the programmed key status and
there are no keys programmed into SKIM memory.
²Programming Key Failed (Possible Used
Key From Wrong Vehicle)- SKIM is unable to pro-
gram an ignition key transponder due to one of the
following:
²The ignition key transponder is faulty.
²The ignition key transponder is or has been
already programmed to another vehicle.
²8 Keys Already Learned, Programming Not
Done- The SKIM transponder ID memory is full.
²Learned Key In Ignition- The ID for the igni-
tion key transponder currently in the ignition lock
cylinder is already programmed in SKIM memory.
ADJUSTABLE PEDALS
MODULE
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the negative battery cable.
(2) Remove the cluster bezel (Refer to 23 - BODY/
INSTRUMENT PANEL/CLUSTER BEZEL - REMOV-
AL).
(3) Remove the steering column opening cover
(Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/STEER-
ING COLUMN OPENING COVER - REMOVAL).
(4) Remove the adjustable pedal motor for accessi-
bility. (Refer to 5 - BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHAN-
ICAL/PEDAL - REMOVAL).
(5) Remove the two mounting clips from the mod-
ule (Fig. 1).
(6) Disconnect the electrical connector.
(7) Remove the adjustable pedal module.
8E - 2 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESWJ
ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES (Continued)
Page 313 of 2199

BCM programming then performs those tasks and
provides features through both PCI data bus commu-
nication with other electronic modules and hard
wired outputs to a number of relays. These relays
provide the BCM with the ability to control numer-
ous high current accessory systems in the vehicle.
The BCM circuitry operates on battery current
received through fuses in the Junction Block (JB) on a
non-switched fused B(+) circuit, a fused ignition switch
output (start-run) circuit, and a fused ignition switch
output (run-accessory) circuit. This arrangement allows
the BCM to provide some features regardless of the
ignition switch position. The BCM circuitry is grounded
through the chassis beneath the center console.
The BCM monitors its own internal circuitry as
well as many of its input and output circuits, and
will store a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) in elec-
tronic memory for any failure it detects. These DTCs
can be retrieved and diagnosed using a DRBIIItscan
tool. Refer to the appropriate diagnostic information.
HARD WIRED INPUTS
The hard wired inputs to the BCM include the fol-
lowing:
²A/C switch signal
²Ambient temperature sensor signal
²Body control module flash enable
²Coolant level switch sense
²Door ajar switch sense (two circuits - one left
rear, and one right rear)
²Driver seat heater switch mux
²Fog lamp switch sense
²Fused B(+)
²Fused ignition switch output (run-acc)
²Fused ignition switch output (st-run)
²Ground (five circuits - two Z1, and three Z2)
²Hazard switch sense
²Headlamp switch mux
²High beam switch sense
²Hood ajar switch sense (export)
²Key-in ignition switch sense
²Liftgate ajar switch sense
²Liftgate courtesy disable
²Liftgate flip-up ajar switch sense
²Panel lamps dimmer signal
²Park lamp relay output
²Passenger seat heater switch mux
²PCI bus
²Radio control mux
²Rear window defogger switch sense
²Seat belt switch sense
²Ultralight sensor signal
²Washer fluid switch sense
²Washer pump switch sense
²Windshield wiper switch mux
²Wiper park switch sense
MESSAGING
The BCM uses the following messages received
from other electronic modules over the PCI data bus:
²Accessory Delay Control (DDM/PDM)
²Battery Temperature (PCM)
²Chime Request (EMIC, EVIC, SKIM)
²Cylinder Lock Switch Status (DDM)
²Door Ajar Status/Front Doors (DDM/PDM)
²Door Lock Status (DDM/PDM)
²Engine Model (PCM)
²Engine RPM (PCM)
²Engine Temperature (PCM)
²English/Metric Default (EMIC)
²Fuel Tank Level (PCM)
²Fuel Used/Injector Pulses (PCM)
²Panic Control (PDM)
²Programmable Features Preferences/Audible &
Optical Chirps/Headlamp Delay (EVIC)
²RKE Status (PDM)
²Vehicle Identification Number (PCM)
²Vehicle Speed (PCM)
The BCM provides the following messages to other
electronic modules over the PCI data bus:
²A/C Switch Status (PCM)
²Ambient Temperature Data (AZC/EVIC/PCM)
²Average/Instantaneous Fuel Economy (EVIC)
²Country Code (EMIC)
²Courtesy Lamp Status (DDM/PDM)
²Distance To Empty (EVIC)
²Elapsed Ignition On Timer (EVIC)
²English/Metric Status (EMIC)
²Front & Rear Door Ajar Status (EVIC)
²Front & Rear Fog Lamp Status (EMIC)
²Heated Seat Switch Status (HSM/MHSM)
²High Beam Status (EMIC)
²Ignition Off Timer (EVIC)
²Ignition Switch Position (DDM/PDM)
²Key-In Ignition Status (DDM/PDM)
²Low Beam Status (EMIC)
²Panel Lamp Status (AZC/EMIC/Radio)
²Rear Window Defogger Relay Status (DDM/
PDM)
²Remote Radio Switch Status (Radio)
²Seatbelt Status (EMIC/MHSM/MSM)
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BODY CONTROL
MODULE
The hard wired inputs to and outputs from the
Body Control Module (BCM) may be diagnosed and
tested using conventional diagnostic tools and proce-
dures. Refer to the appropriate wiring information.
Conventional diagnostic methods may not prove
conclusive in the diagnosis of the BCM. In order to
obtain conclusive testing of the BCM, the Program-
mable Communications Interface (PCI) data bus net-
work and all of the electronic modules that provide
8E - 4 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESWJ
BODY CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 317 of 2199

Frequency (RF) Remote Keyless Entry (RKE)
receiver. The DDM and PDM control and integrate
many functions and features of the vehicle through
both hard wired outputs and messages over the PCI
data bus. The functions and features that the door
modules support or control include the following:
²Automatic Door Lock- The two door modules
provide an automatic door lock feature which locks
the doors when the vehicle is moving. This is a pro-
grammable feature.
²Automatic Door Unlock On Exit- The two
door modules provide an automatic door unlock on
exit feature. This feature will unlock all the doors if
they were locked via the automatic door lock feature
after the vehicle has stopped moving and the driver
door is opened. This is a programmable feature via
the EVIC.
²Customer Programmable Features- Each
door module provides support for certain customer
programmable features that are monitored on the
PCI bus.
²Cylinder Lock Switch Status- The DDM
monitors and transmits the status of the cylinder
lock switch on the driver side front door lock cylin-
der.
²Door Courtesy Lamp Control- Each door
module provides control of its own optional front
door-mounted courtesy lamp.
²Door Lock Inhibit- Each door module pro-
vides a door lock inhibit feature which prevents the
doors from being locked with a power lock switch ifthe key was left in the ignition and a front door is
open.
²Express-Down Window- The DDM provides
an express-down feature for the driver side front door
window only.
²Extended Window Operation- Both door
modules provide an extended power window opera-
tion feature that allows operation of the power win-
dows for 45 seconds following ignition Off or until a
front door is opened.
²Front Door Ajar Switch Status- Each door
module monitors and transmits the status of its own
front door ajar switch.
²Heated Mirrors- Each door module provides
control for its own optional heated outside rear view
mirror.
²Illuminated Entry- Each door module sup-
ports an illuminated entry feature through its own
optional front door-mounted courtesy lamp.
²Memory Mirrors- Each door module provides
control for its own optional memory outside rear view
mirror.
²Memory Switch- The DDM monitors the sta-
tus of the optional memory switch and controls the
illumination of the memory switch ªsetº Light Emit-
ting Diode (LED) indicator and illumination lamps.
²Memory System- The DDM transmits memory
set and recall messages based upon inputs from the
memory switch. If the optional RKE linked to mem-
ory feature is enabled, the DDM will also transmit
memory recall messages based upon memory
requests received from the Remote Keyless Entry
(RKE) system in the PDM. Certain memory system
features are programmable.
²Power Foldaway Mirrors - Export Only-
Each door module provides support for the optional
power foldaway outside mirrors. The DDM also
houses the control switch for this system.
²Power Lock Control- The DDM provides con-
trol for the driver side front door power lock motor,
while the PDM provides control for the power lock
motors of the three remaining doors and the liftgate.
²Power Lock Switch Status- Each door mod-
ule monitors and transmits the status of its own inte-
gral power lock switch.
²Power Window Control- Each door module
provides control for both the front and rear door
power window motors and the rear door power win-
dow switches on the same side of the vehicle.
²Power Window Switch Status- The DDM
monitors and transmits the status of its integral pas-
senger side front and rear power window switches.
²Remote Keyless Entry- The PDM monitors
and transmits the status of the Remote Keyless
Entry (RKE) system and provides support for the
RKE Lock (with the optional horn chirp and park
Fig. 7 Door Module
1 - FRONT DOOR TRIM PANEL
2 - SCREW (5)
3 - DOOR MODULE
8E - 8 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESWJ
DOOR MODULE (Continued)
Page 318 of 2199

lamp flash features), Unlock with the optional RKE
unlock, and Panic Mode functions. The optional RKE
features are programmable.
²Switch Illumination- Each door module pro-
vides control of the power window and power lock
switch illumination for the front and rear doors on
the same side of the vehicle. The DDM provides con-
trol of the power mirror switch illumination.
²Window Lockout- The DDM monitors and
transmits the status of its integral window lockout
switch to provide the power window lockout feature
and coordinate power window switch knob illumina-
tion.
The door modules are serviced only as complete
units. Many of the features in the vehicle controlled
or supported by the door modules are programmable
using either the Electronic Vehicle Information Cen-
ter (EVIC) user interface, or the DRBIIItscan tool. If
a door module is damaged or faulty, the entire door
module unit must be replaced.
OPERATION
The microprocessor-based DDM and PDM hard-
ware and software monitors integral and hard wired
external switch inputs as well as those resources it
shares with other electronic modules in the vehicle
through its communication over the PCI data bus
network. The internal programming and all of these
inputs allow the DDM or PDM microprocessor to
determine the tasks it needs to perform and their
priorities, as well as both the standard and optional
features that it should provide.
The DDM and PDM are powered by a fused bat-
tery circuit so that they can operate regardless of the
ignition switch position. The DDM and PDM cir-
cuitry is grounded to the chassis beneath the front
seat.
The DDM and PDM can be diagnosed using a
DRBIIItscan tool. Refer to the appropriate diagnos-
tic information.
HARD WIRED INPUTS
The hard wired inputs to the door modules include
the following:
²Door ajar switch sense
²Driver door key cylinder switch sense (DDM)
²Fused B(+)
²Ground
²Memory switch mux (DDM)
²Mirror horizontal position signal
²Mirror vertical position signal
²PCI bus
HARD WIRED OUTPUTS
The hard wired outputs of the door modules
include the following:
²Courtesy lamp driver
²Courtesy lamp ground
²Diagnostic out (DDM)
²Door/liftgate lock driver
²Door/liftgate unlock driver
²Door switch illumination (rear power window)
²Front window driver (down)
²Front window driver (up)
²Memory set indicator driver (DDM)
²Memory switch return (DDM)
²Mirror common driver
²Mirror heater ground
²Mirror heater 12V supply
²Rear window driver (down)
²Rear window driver (up)
²Mirror horizontal driver
²Mirror sensor ground
²Mirror vertical driver
²PCI bus
²Switch illumination driver (memory - DDM)
MESSAGING
The door modules use the following messages
received from other electronic modules over the PCI
data bus:
²Accessory Delay Control (PDM)
²Courtesy Lamp Status (BCM)
²Door Ajar Status/Rear Doors (BCM)
²Door Lock Status (DDM/PDM)
²Ignition Switch Position (BCM)
²Key-In Ignition Status (BCM)
²Programmable Features Preferences/Auto Lock/
Auto Unlock/RKE Unlock Sequence/RKE Link to
Memory (EVIC)
²Memory Recall (DDM)
²Rear Window Defogger Relay Status (BCM)
²Vehicle Speed (PCM)
The door modules provide the following messages
to other electronic modules over the PCI data bus:
²Cylinder Lock Switch Status (BCM)
²Door Ajar Status/Front Doors (BCM/DDM/PDM)
²Door Lock Status (DDM/PDM)
²Memory Recall (PDM/MHSM/MSM/Radio)
²Memory Set Switch Status (PDM/MHSM/MSM/
Radio)
²Panic Control (BCM)
²Power Window Switch Status (PDM)
²RKE Status (BCM/DDM)
²Window Lockout Switch Status (PDM)
WJELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES 8E - 9
DOOR MODULE (Continued)
Page 326 of 2199

(2) If equipped, remove Transmission Control Mod-
ule (TCM).
(3) Remove coolant reserve/overflow tank.
(4) Remove cover over electrical connectors. Cover
snaps onto PCM.
(5) Carefully unplug three 32±way connectors at
PCM.
(6) Remove three PCM bracket-to-body mounting
nuts (Fig. 13).
(7) Remove PCM/PCM bracket assembly from
vehicle.
(8) Remove 3 PCM-to-PCM bracket bolts (screws)
(Fig. 14).
INSTALLATION
USE THE DRBIIItSCAN TOOL TO REPRO-
GRAM THE NEW POWERTRAIN CONTROL
MODULE (PCM) WITH THE VEHICLES ORIGI-
NAL IDENTIFICATION NUMBER (VIN) AND
THE VEHICLES ORIGINAL MILEAGE. IF THIS
STEP IS NOT DONE, A DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE
CODE (DTC) MAY BE SET.
The PCM is located on the cowl panel in right/rear
side of engine compartment (Fig. 12).
(1) Check pins in three 32±way electrical connec-
tors for damage. Repair as necessary.
(2) Install PCM to its mounting bracket. Tighten
three mounting bolts to 3 N´m (25 in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Install PCM/PCM bracket to body. Install 3
nuts and tighten 9 N´m (80 in. lbs.) torque.
(4) Install three 32±way connectors.(5) Install cover over electrical connectors. Cover
snaps onto PCM.
(6) Install coolant reserve/overflow tank.
(7) If equipped, install Transmission Control Mod-
ule (TCM).
(8) Connect negative cable to battery.
(9) Use the DRBIIItscan tool to reprogram new
PCM with vehicles original Identification Number
(VIN) and original vehicle mileage.
SENTRY KEY IMMOBILIZER
MODULE
DESCRIPTION
The Sentry Key Immobilizer Module (SKIM) is the
primary component of the Sentry Key Immobilizer
System (SKIS) (Fig. 15). The SKIM is located in the
steering column, below the ignition lock cylinder
housing. The SKIM has an integral halo-like antenna
ring that extends from one side.
The SKIM cannot be adjusted or repaired. If faulty
or damaged, the entire SKIM unit must be replaced.
OPERATION
The Sentry Key Immobilizer Module (SKIM) con-
tains a Radio Frequency (RF) transceiver and a
microprocessor. The SKIM transmits RF signals to,
and receives RF signals from the Sentry Key tran-
Fig. 14 Powertrain Control Module (PCM) Mounting
Bracket
1 - PCM BRACKET
2 - PCM
3 - PCM-TO-BRACKET SCREWS (3)
Fig. 15 Sentry Key Immobilizer Module
1 - STEERING COLUMN
2 - SKIM
3 - MOUNTING SCREW
WJELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES 8E - 17
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 327 of 2199

sponder through a tuned antenna ring integral to the
SKIM housing. If this antenna ring is not mounted
properly around the ignition lock cylinder housing,
communication problems between the SKIM and the
transponder may arise. These communication prob-
lems will result in Sentry Key transponder-related
faults. The SKIM also communicates over the Pro-
grammable Communications Interface (PCI) data bus
with the Powertrain Control Module (PCM), the Elec-
troMechanical Instrument Cluster (EMIC), the Body
Control Module (BCM), and/or the DRBIIItscan tool.
The SKIM retains in memory the ID numbers of
any Sentry Key transponder that is programmed into
it. A maximum of eight transponders can be pro-
grammed into the SKIM. For added system security,
each SKIM is programmed with a unique Secret Key
code. This code is stored in memory, sent over the
PCI data bus to the PCM, and is encoded to the tran-
sponder of every Sentry Key that is programmed into
the SKIM. Another security code, called a PIN, is
used to gain access to the SKIM Secured Access
Mode. The Secured Access Mode is required during
service to perform the SKIS initialization and Sentry
Key transponder programming procedures. The
SKIM also stores the Vehicle Identification Number
(VIN) in its memory, which it learns through a PCI
data bus message from the PCM during SKIS initial-
ization.
In the event that a SKIM replacement is required,
the Secret Key code can be transferred to the new
SKIM from the PCM using the DRBIIItscan tool
and the SKIS replacement procedure. Proper comple-
tion of the SKIS initialization will allow the existing
Sentry Keys to be programmed into the new SKIM so
that new keys will not be required. In the event that
the original Secret Key code cannot be recovered,
SKIM replacement will also require new Sentry
Keys. The DRBIIItscan tool will alert the technician
during the SKIS replacement procedure if new Sen-
try Keys are required.
When the ignition switch is turned to the On posi-
tion, the SKIM transmits an RF signal to the tran-
sponder in the ignition key. The SKIM then waits for
an RF signal response from the transponder. If the
response received identifies the key as valid, the
SKIM sends a valid key message to the PCM over
the PCI data bus. If the response received identifies
the key as invalid, or if no response is received from
the key transponder, the SKIM sends an invalid key
message to the PCM. The PCM will enable or disable
engine operation based upon the status of the SKIM
messages. It is important to note that the default
condition in the PCM is an invalid key; therefore, if
no message is received from the SKIM by the PCM,
the engine will be disabled and the vehicle immobi-
lized after two seconds of running.The SKIM also sends indicator light status mes-
sages to the EMIC over the PCI data bus to tell the
EMIC how to operate the SKIS indicator. This indi-
cator light status message tells the EMIC to turn the
indicator on for about three seconds each time the
ignition switch is turned to the On position as a bulb
test. After completion of the bulb test, the SKIM
sends indicator light status messages to the EMIC to
turn the indicator off, turn the indicator on, or to
flash the indicator on and off. If the SKIS indicator
lamp flashes or stays on solid after the bulb test, it
signifies a SKIS fault. If the SKIM detects a system
malfunction and/or the SKIS has become inoperative,
the SKIS indicator will stay on solid. If the SKIM
detects an invalid key or if a key transponder-related
fault exists, the SKIS indicator will flash. If the vehi-
cle is equipped with the Customer Learn transponder
programming feature, the SKIM will also send mes-
sages to the EMIC to flash the SKIS indicator lamp,
and to the BCM to generate a single audible chime
tone whenever the Customer Learn programming
mode is being utilized. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
VEHICLE THEFT SECURITY - STANDARD PRO-
CEDURE - SENTRY KEY TRANSPONDER
PROGRAMMING).
The SKIS performs a self-test each time the igni-
tion switch is turned to the On position, and will
store fault information in the form of Diagnostic
Trouble Codes (DTC's) in SKIM memory if a system
malfunction is detected. The SKIM can be diagnosed,
and any stored DTC's can be retrieved using a
DRBIIItscan tool. Refer to the appropriate diagnos-
tic information.
REMOVAL
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the steering column opening cover
from the instrument panel. (Refer to 23 - BODY/IN-
STRUMENT PANEL/STEERING COLUMN OPEN-
ING COVER - REMOVAL).
8E - 18 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESWJ
SENTRY KEY IMMOBILIZER MODULE (Continued)
Page 328 of 2199

(3) Disconnect the instrument panel wire harness
connector from the SKIM connector.
(4) Remove the screw that secures the SKIM to
the bottom of the steering column housing (Fig. 16).
(5) Disengage the antenna ring of the SKIM from
around the ignition lock cylinder housing.
(6) Remove the SKIM from the steering column.
INSTALLATION
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
(1) Position the SKIM to the underside of the
steering column (Fig. 16).
(2) Engage the antenna ring of the SKIM around
the ignition lock cylinder housing.
(3) Install and tighten the screw that secures the
SKIM to the bottom of the steering column hous-
ing.Tighten the screw to 3.4 N´m (30 in lbs.).
(4) Reconnect the instrument panel wire harness
connector to the SKIM connector.(5) Reinstall the steering column opening cover
onto the instrument panel. (Refer to 23 - BODY/IN-
STRUMENT PANEL/STEERING COLUMN OPEN-
ING COVER - INSTALLATION).
(6) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
(7) Perform the SKIS Replacement procedure
using the DRBIIIt.
(8) Perform the SKIS Initialization Procedure
using the DRBIIIt.
TRANSMISSION CONTROL
MODULE
DESCRIPTION
The Transmission Control Module (TCM) is located
in the engine compartment on the right (passenger)
side and is mounted to the inner fender (Fig. 17).
OPERATION
The Transmission Control Module (TCM) controls
all electronic operations of the transmission. The
TCM receives information regarding vehicle opera-
tion from both direct and indirect inputs, and selects
the operational mode of the transmission. Direct
inputs are hardwired to, and used specifically by the
TCM. Indirect inputs originate from other compo-
nents/modules, and are shared with the TCM via the
vehicle communication bus.
Some examples ofdirect inputsto the TCM are:
²Battery (B+) voltage
²Ignition ªONº voltage
²Transmission Control Relay (Switched B+)
²Throttle Position Sensor
²Crankshaft Position Sensor
²Transmission Range Sensor
Fig. 16
Fig. 17 Transmission Control Module Location
1 - TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE (TCM)
2 - 60±WAY CONNECTOR
WJELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES 8E - 19
SENTRY KEY IMMOBILIZER MODULE (Continued)
Page 349 of 2199

The battery cables (Fig. 17) or (Fig. 18) are large
gauge, stranded copper wires sheathed within a
heavy plastic or synthetic rubber insulating jacket.
The wire used in the battery cables combines excel-
lent flexibility and reliability with high electrical cur-
rent carrying capacity. Refer toWiring Diagrams
for battery cable wire gauge information.
A clamping type female battery terminal made of
soft lead is die cast onto one end of the battery cable
wire. A square headed pinch-bolt and hex nut are
installed at the open end of the female battery termi-
nal clamp. Large eyelet type terminals are crimped
onto the opposite end of the battery cable wire and
then solder-dipped. The battery positive cable wires
have a red insulating jacket to provide visual identi-
fication and feature a larger female battery terminal
clamp to allow connection to the larger battery posi-
tive terminal post. The battery negative cable wires
have a black insulating jacket and a smaller female
battery terminal clamp.
The battery cables cannot be repaired and, if dam-
aged or faulty they must be replaced. Both the bat-
tery positive and negative cables are available for
service replacement only as a unit with the battery
wire harness, which may include portions of the wir-
ing circuits for the generator and other components
on some models. Refer toWiring Diagramsfor more
information on the various wiring circuits included in
the battery wire harness for the vehicle being ser-
viced.
OPERATION
The battery cables connect the battery terminal
posts to the vehicle electrical system. These cables
also provide a path back to the battery for electrical
current generated by the charging system for restor-
ing the voltage potential of the battery. The female
battery terminal clamps on the ends of the battery
cable wires provide a strong and reliable connection
of the battery cable to the battery terminal posts.
The terminal pinch bolts allow the female terminal
clamps to be tightened around the male terminal
posts on the top of the battery. The eyelet terminals
secured to the opposite ends of the battery cable
wires from the female battery terminal clamps pro-
vide secure and reliable connection of the battery
cables to the vehicle electrical system.
The battery positive cable terminal clamp is die
cast onto the ends of two wires. One wire has an eye-
let terminal that connects the battery positive cable
to the B(+) terminal stud of the Power Distribution
Center (PDC), and the other wire has an eyelet ter-
minal that connects the battery positive cable to the
B(+) terminal stud of the engine starter motor sole-
noid. The battery negative cable terminal clamp is
also die cast onto the ends of two wires. One wirehas an eyelet terminal that connects the battery neg-
ative cable to the vehicle powertrain through a stud
on the right side of the engine cylinder block. The
other wire has an eyelet terminal that connects the
battery negative cable to the vehicle body through a
ground screw on the right front fender inner shield,
near the battery.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BATTERY CABLES
A voltage drop test will determine if there is exces-
sive resistance in the battery cable terminal connec-
tions or the battery cable. If excessive resistance is
found in the battery cable connections, the connec-
tion point should be disassembled, cleaned of all cor-
rosion or foreign material, then reassembled.
Following reassembly, check the voltage drop for the
battery cable connection and the battery cable again
to confirm repair.
When performing the voltage drop test, it is impor-
tant to remember that the voltage drop is giving an
indication of the resistance between the two points at
which the voltmeter probes are attached.EXAM-
PLE:When testing the resistance of the battery pos-
itive cable, touch the voltmeter leads to the battery
positive cable terminal clamp and to the battery pos-
itive cable eyelet terminal at the starter solenoid
B(+) terminal stud. If you probe the battery positive
terminal post and the battery positive cable eyelet
terminal at the starter solenoid B(+) terminal stud,
you are reading the combined voltage drop in the
battery positive cable terminal clamp-to-terminal
post connection and the battery positive cable.
VOLTAGE DROP TEST
The following operation will require a voltmeter
accurate to 1/10 (0.10) volt. Before performing this
test, be certain that the following procedures are
accomplished:
²The battery is fully-charged and load tested.
Refer to Standard Procedures for the proper battery
charging and load test procedures.
²Fully engage the parking brake.
²If the vehicle is equipped with an automatic
transmission, place the gearshift selector lever in the
Park position. If the vehicle is equipped with a man-
ual transmission, place the gearshift selector lever in
the Neutral position and block the clutch pedal in the
fully depressed position.
²Verify that all lamps and accessories are turned
off.
²To prevent the engine from starting, remove the
Automatic Shut Down (ASD) relay. The ASD relay is
located in the Power Distribution Center (PDC), in
the engine compartment. See the fuse and relay lay-
out label affixed to the underside of the PDC cover
for ASD relay identification and location.
8F - 18 BATTERY SYSTEMWJ
BATTERY CABLE (Continued)
Page 356 of 2199

²a faulty or improperly adjusted switch that
allows a lamp to stay on. Refer to Ignition-Off Draw
Test in 8, Battery for more information.
INSPECTION
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) monitors
critical input and output circuits of the charging sys-
tem, making sure they are operational. A Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC) is assigned to each input and
output circuit monitored by the On-Board Diagnostic
(OBD) system. Some charging system circuits are
checked continuously, and some are checked only
under certain conditions.
Refer to Diagnostic Trouble Codes in; Powertrain
Control Module; Electronic Control Modules for more
DTC information. This will include a complete list of
DTC's including DTC's for the charging system.
To perform a complete test of the charging system,
refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic Proce-
dures service manual and the DRBtscan tool. Per-
form the following inspections before attaching the
scan tool.(1) Inspect the battery condition. Refer to 8, Bat-
tery for procedures.
(2) Inspect condition of battery cable terminals,
battery posts, connections at engine block, starter
solenoid and relay. They should be clean and tight.
Repair as required.
(3) Inspect all fuses in both the fuseblock and
Power Distribution Center (PDC) for tightness in
receptacles. They should be properly installed and
tight. Repair or replace as required.
(4) Inspect generator mounting bolts for tightness.
Replace or tighten bolts if required. Refer to the Gen-
erator Removal/Installation section of this group for
torque specifications.
(5) Inspect generator drive belt condition and ten-
sion. Tighten or replace belt as required. Refer to
Belt Tension Specifications in 7, Cooling System.
(6) Inspect automatic belt tensioner (if equipped).
Refer to 7, Cooling System for information.
(7) Inspect generator electrical connections at gen-
erator field, battery output, and ground terminal (if
equipped). Also check generator ground wire connec-
tion at engine (if equipped). They should all be clean
and tight. Repair as required.
SPECIFICATIONS
GENERATOR RATINGS - GAS POWERED
TYPE PART NUMBER RATED SAE AMPS ENGINES MINIMUM TEST AMPS
BOSCH 56041322 136 4.0L 6-Cylinder 100
DENSO 56041324 136 4.7L V-8 100
TORQUE - GAS POWERED
DESCRIPTION N-m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Generator Mounting Bolts-4.0L 55 41
Generator Vertical Mounting Bolt-4.7L 40 29
Generator (long) Horizontal Mounting
Bolt-4.7L55 41
Generator (short) Horizontal Mounting
Bolt-4.7L55 41
Generator B+ Terminal Nut 11 95
WJCHARGING 8F - 25
CHARGING (Continued)