Vacuum system JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2003 WJ / 2.G Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2003, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2003 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 1265 of 2199

(12) Install the push rods, rocker arms, pivots and
bridges in the order they were removed (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/ROCKER ARM /
ADJUSTER ASSY - INSTALLATION).
(13) Install the engine cylinder head cover (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER
HEAD COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(14) Attach the air conditioner compressor mount-
ing bracket to the engine cylinder head and block.
Tighten the bolts to 40 N´m (30 ft. lbs.) torque.
(15) Attach the air conditioning compressor to the
bracket. Tighten the bolts to 27 N´m (20 ft. lbs.)
torque.
CAUTION: The serpentine drive belt must be routed
correctly. Incorrect routing can cause the water
pump to turn in the opposite direction causing the
engine to overheat.
(16) Install the serpentine drive belt. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION).
(17) Install the air cleaner and ducting.
(18) Connect the hoses to the engine thermostat
housing and fill the cooling system to the specified
level (Refer to 7 - COOLING - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE).
(19) The automatic transmission throttle linkage
and cable must be adjusted after completing the
engine cylinder head installation (Refer to 21 -
TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC - AW4/
THROTTLE VALVE CABLE - ADJUSTMENTS).
(20) Install the temperature sending unit and con-
nect the wire connector.
(21) If equipped with air conditioning, install A/C
compressor (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDI-
TIONING/PLUMBING/A/C COMPRESSOR -
INSTALLATION) and charge A/C system (Refer to 24
- HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(22) Connect negative cable to battery.
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING. DO NOT STAND IN DIRECT
LINE WITH THE FAN. DO NOT PUT HANDS NEAR
THE PULLEYS, BELTS OR FAN. DO NOT WEAR
LOOSE CLOTHING.
(23) Operate the engine with the radiator cap off.
Inspect for leaks and continue operating the engine
until the engine thermostat opens. Add coolant, if
required.CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S)
DESCRIPTION
The cylinder head cover (Fig. 11) is made of
stamped steel and incorporates the Crankcase Venti-
lation (CCV) Hoses and the oil fill opening.
REMOVAL
The cylinder head cover is isolated from the cylin-
der head via grommets and a reusable molded rubber
gasket. The grommet and limiter are retained in the
cylinder head cover.
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Disconnect the Crankcase Ventilation (CCV)
vacuum hose from engine cylinder head cover.
(3) Disconnect the fresh air inlet hose from the
engine cylinder head cover.
(4) Disconnect the accelerator, transmission, and
speed (if equipped) control cables from the throttle
body (Fig. 12).
(5) Remove the three bolts that fasten the control
cable bracket to the intake manifold.
(6) Remove control cables from cylinder head cover
clip.
(7) Position control cables and bracket away from
cylinder head cover secure with tie straps.
(8) Remove the engine cylinder head cover mount-
ing bolts.
(9) Remove the engine cylinder head cover and
gasket.
Fig. 11 Cylinder Head Cover
9 - 22 ENGINE - 4.0LWJ
CYLINDER HEAD (Continued)
Page 1300 of 2199

INSTALLATION
A gear-type oil pump is mounted at the underside
of the cylinder block opposite the No.4 main bearing.
(1) Install the oil pump on the cylinder block using
a replacement gasket. Tighten the bolts to 23 N´m
(17 ft. lbs.) torque.
(2) Install the oil pan (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LU-
BRICATION/OIL PAN - INSTALLATION).
(3) Fill the oil pan with oil to the specified level.
INTAKE MANIFOLD
DESCRIPTION
The intake manifold (Fig. 83) is made of cast alu-
minum and uses eleven bolts to mount to the cylin-
der head. This mounting style improves sealing and
reduces the chance of leaks.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - INTAKE
MANIFOLD LEAKAGE
An intake manifold air leak is characterized by
lower than normal manifold vacuum. Also, one or
more cylinders may not be functioning.
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING. DO NOT STAND IN A
DIRECT LINE WITH THE FAN. DO NOT PUT YOUR
HANDS NEAR THE PULLEYS, BELTS OR THE FAN.
DO NOT WEAR LOOSE CLOTHING.
(1) Start the engine.
(2) Spray a small stream of water at the suspected
leak area.
(3) If a change in RPM is observed the area of the
suspected leak has been found.
(4) Repair as required.
REMOVAL
NOTE: THE ENGINE INTAKE AND EXHAUST MANI-
FOLD MUST BE REMOVED AND INSTALLED
TOGETHER. THE MANIFOLDS USE A COMMON
GASKET AT THE CYLINDER HEAD.
(1) Disconnect the battery negative cable.
(2) Remove air cleaner inlet hose from the resona-
tor assembly.
(3) Remove the air cleaner assembly.
(4) Remove the throttle cable, vehicle speed control
cable (if equipped) and the transmission line pres-
sure cable (Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANS-
AXLE/AUTOMATIC - AW4/THROTTLE VALVE
CABLE - REMOVAL).
(5) Disconnect the following electrical connections
and secure their harness out of the way:
²Throttle Position Sensor
²Idle Air Control Motor
²Coolant Temperature Sensor (at thermostat
housing)
²Intake Air Temperature Sensor
²Oxygen Sensor
²Crank Position Sensor
²Six (6) Fuel Injector Connectors
²Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor.
(6) Disconnect HVAC, and Brake Booster vacuum
supply hoses at the intake manifold.
(7) Perform the fuel pressure release procedure.
(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
(8) Disconnect and remove the fuel system supply
line from the fuel rail assembly.
(9) Remove the accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
(10) Remove the power steering pump from the
intake manifold and set aside.
(11) Raise the vehicle.
(12) Disconnect the exhaust pipes from the engine
exhaust manifolds.
(13) Lower the vehicle.
(14) Remove the intake manifold and exhaust
manifold bolts and manifolds (Fig. 84).
INSTALLATION
If the manifold is being replaced, ensure all the fit-
ting, etc. are transferred to the replacement mani-
fold.
(1) Install a new engine exhaust/intake manifold
gasket over the alignment dowels on the cylinder
head.
(2) Position the engine exhaust manifolds to the
cylinder head. Install fastener Number 3 and finger
tighten at this time (Fig. 84).
Fig. 83 Intake Manifold 4.0L Engine
WJENGINE - 4.0L 9 - 57
OIL PUMP (Continued)
Page 1301 of 2199
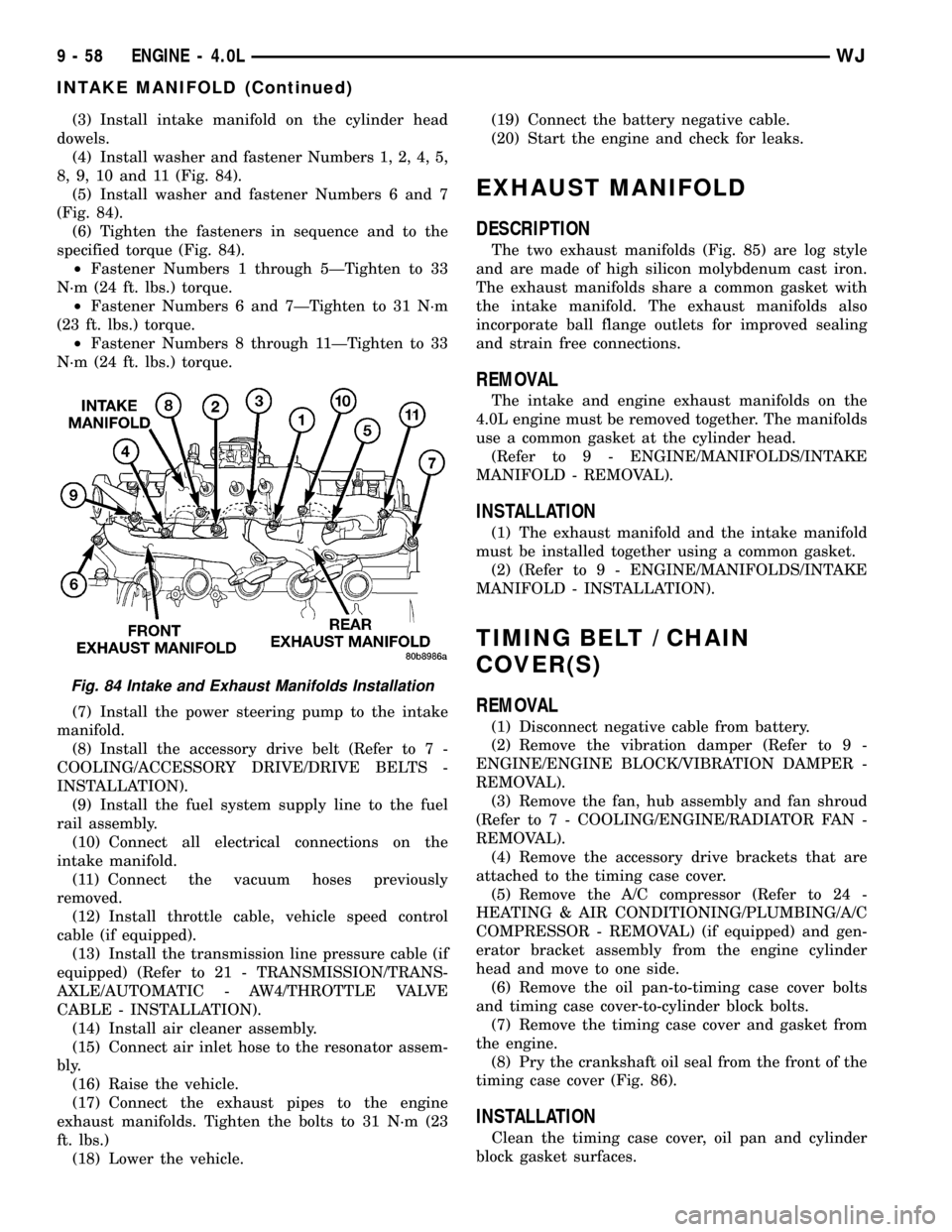
(3) Install intake manifold on the cylinder head
dowels.
(4) Install washer and fastener Numbers 1, 2, 4, 5,
8, 9, 10 and 11 (Fig. 84).
(5) Install washer and fastener Numbers 6 and 7
(Fig. 84).
(6) Tighten the fasteners in sequence and to the
specified torque (Fig. 84).
²Fastener Numbers 1 through 5ÐTighten to 33
N´m (24 ft. lbs.) torque.
²Fastener Numbers 6 and 7ÐTighten to 31 N´m
(23 ft. lbs.) torque.
²Fastener Numbers 8 through 11ÐTighten to 33
N´m (24 ft. lbs.) torque.
(7) Install the power steering pump to the intake
manifold.
(8) Install the accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION).
(9) Install the fuel system supply line to the fuel
rail assembly.
(10) Connect all electrical connections on the
intake manifold.
(11) Connect the vacuum hoses previously
removed.
(12) Install throttle cable, vehicle speed control
cable (if equipped).
(13) Install the transmission line pressure cable (if
equipped) (Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANS-
AXLE/AUTOMATIC - AW4/THROTTLE VALVE
CABLE - INSTALLATION).
(14) Install air cleaner assembly.
(15) Connect air inlet hose to the resonator assem-
bly.
(16) Raise the vehicle.
(17) Connect the exhaust pipes to the engine
exhaust manifolds. Tighten the bolts to 31 N´m (23
ft. lbs.)
(18) Lower the vehicle.(19) Connect the battery negative cable.
(20) Start the engine and check for leaks.
EXHAUST MANIFOLD
DESCRIPTION
The two exhaust manifolds (Fig. 85) are log style
and are made of high silicon molybdenum cast iron.
The exhaust manifolds share a common gasket with
the intake manifold. The exhaust manifolds also
incorporate ball flange outlets for improved sealing
and strain free connections.
REMOVAL
The intake and engine exhaust manifolds on the
4.0L engine must be removed together. The manifolds
use a common gasket at the cylinder head.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE
MANIFOLD - REMOVAL).
INSTALLATION
(1) The exhaust manifold and the intake manifold
must be installed together using a common gasket.
(2) (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE
MANIFOLD - INSTALLATION).
TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S)
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove the vibration damper (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/VIBRATION DAMPER -
REMOVAL).
(3) Remove the fan, hub assembly and fan shroud
(Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR FAN -
REMOVAL).
(4) Remove the accessory drive brackets that are
attached to the timing case cover.
(5) Remove the A/C compressor (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/A/C
COMPRESSOR - REMOVAL) (if equipped) and gen-
erator bracket assembly from the engine cylinder
head and move to one side.
(6) Remove the oil pan-to-timing case cover bolts
and timing case cover-to-cylinder block bolts.
(7) Remove the timing case cover and gasket from
the engine.
(8) Pry the crankshaft oil seal from the front of the
timing case cover (Fig. 86).
INSTALLATION
Clean the timing case cover, oil pan and cylinder
block gasket surfaces.
Fig. 84 Intake and Exhaust Manifolds Installation
9 - 58 ENGINE - 4.0LWJ
INTAKE MANIFOLD (Continued)
Page 1308 of 2199
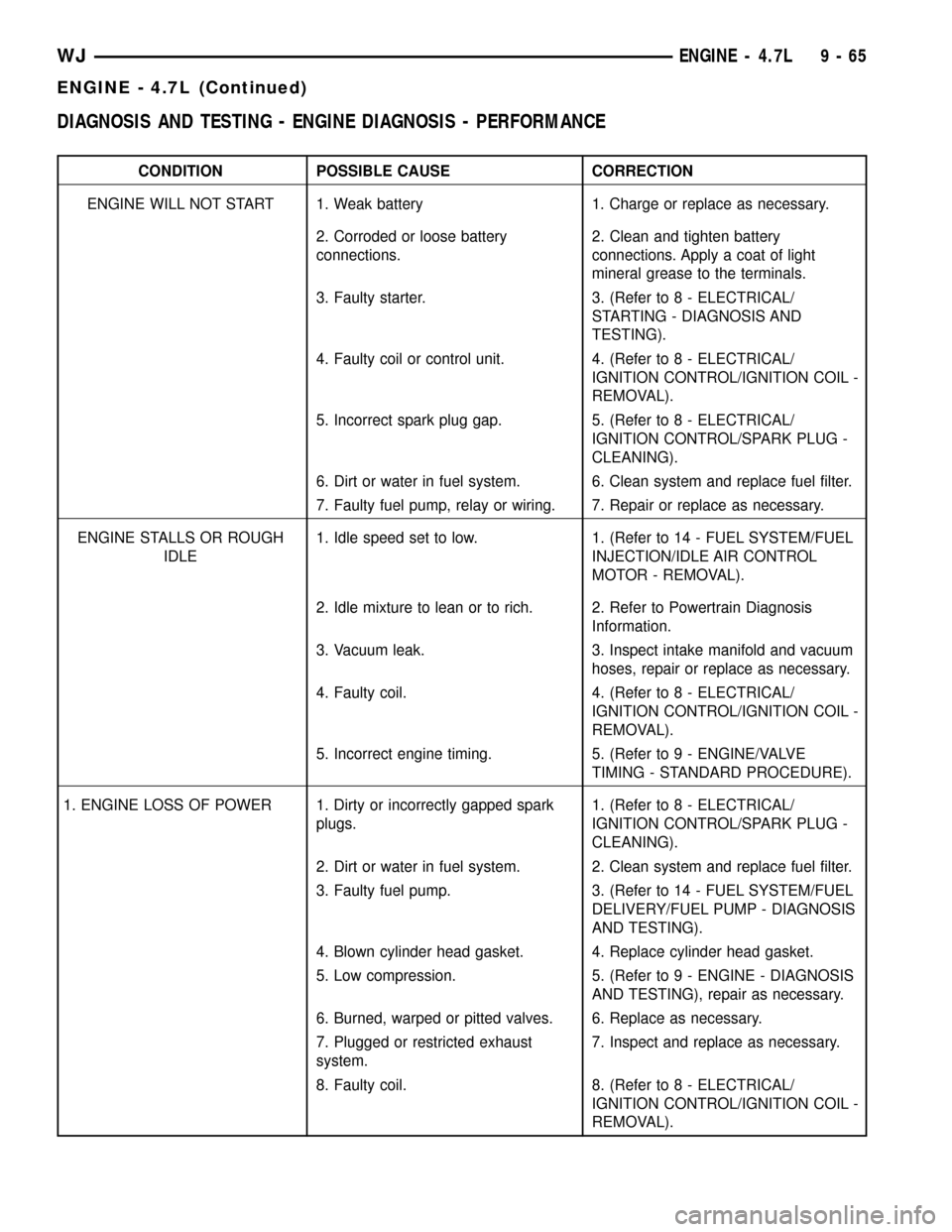
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE DIAGNOSIS - PERFORMANCE
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
ENGINE WILL NOT START 1. Weak battery 1. Charge or replace as necessary.
2. Corroded or loose battery
connections.2. Clean and tighten battery
connections. Apply a coat of light
mineral grease to the terminals.
3. Faulty starter. 3. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
STARTING - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
4. Faulty coil or control unit. 4. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION COIL -
REMOVAL).
5. Incorrect spark plug gap. 5. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG -
CLEANING).
6. Dirt or water in fuel system. 6. Clean system and replace fuel filter.
7. Faulty fuel pump, relay or wiring. 7. Repair or replace as necessary.
ENGINE STALLS OR ROUGH
IDLE1. Idle speed set to low. 1. (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL
INJECTION/IDLE AIR CONTROL
MOTOR - REMOVAL).
2. Idle mixture to lean or to rich. 2. Refer to Powertrain Diagnosis
Information.
3. Vacuum leak. 3. Inspect intake manifold and vacuum
hoses, repair or replace as necessary.
4. Faulty coil. 4. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION COIL -
REMOVAL).
5. Incorrect engine timing. 5. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE
TIMING - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
1. ENGINE LOSS OF POWER 1. Dirty or incorrectly gapped spark
plugs.1. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/SPARK PLUG -
CLEANING).
2. Dirt or water in fuel system. 2. Clean system and replace fuel filter.
3. Faulty fuel pump. 3. (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL
DELIVERY/FUEL PUMP - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING).
4. Blown cylinder head gasket. 4. Replace cylinder head gasket.
5. Low compression. 5. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING), repair as necessary.
6. Burned, warped or pitted valves. 6. Replace as necessary.
7. Plugged or restricted exhaust
system.7. Inspect and replace as necessary.
8. Faulty coil. 8. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/IGNITION COIL -
REMOVAL).
WJENGINE - 4.7L 9 - 65
ENGINE - 4.7L (Continued)
Page 1380 of 2199
(6) Remove accessory drive belt (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL).
(7) Disconnect generator electrical connections.
(8) Unbolt the generator and move it away from
the intake manifold for clearance.
(9) Disconnect air conditioning compressor electri-
cal connections.
(10) Unbolt the air conditioning compressor and
move it away from the intake manifold for clearance.
(11) Disconnect left and right radio suppressor
straps.
(12) Disconnect and remove ignition coil towers
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/IGNITION CONTROL/
IGNITION COIL - REMOVAL).
(13) Remove top oil dipstick tube retaining bolt
and ground strap.
(14) Bleed pressure from fuel system (Refer to 14 -
FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
(15) Remove fuel rail (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYS-
TEM/FUEL DELIVERY/FUEL RAIL - REMOVAL).
(16) Remove throttle body assembly and mounting
bracket.
(17) Drain cooling system below coolant tempera-
ture level (Refer to 7 - COOLING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE).
(18) Remove coolant temperature sensor (Refer to
7 - COOLING/ENGINE/ENGINE COOLANT TEMP
SENSOR - REMOVAL).
(19) Remove cowl to hood seal. (Refer to 23 -
BODY/WEATHERSTRIP/SEALS/COWL WEATHER-
STRIP - REMOVAL).
(20) Remove right side engine lifting stud.
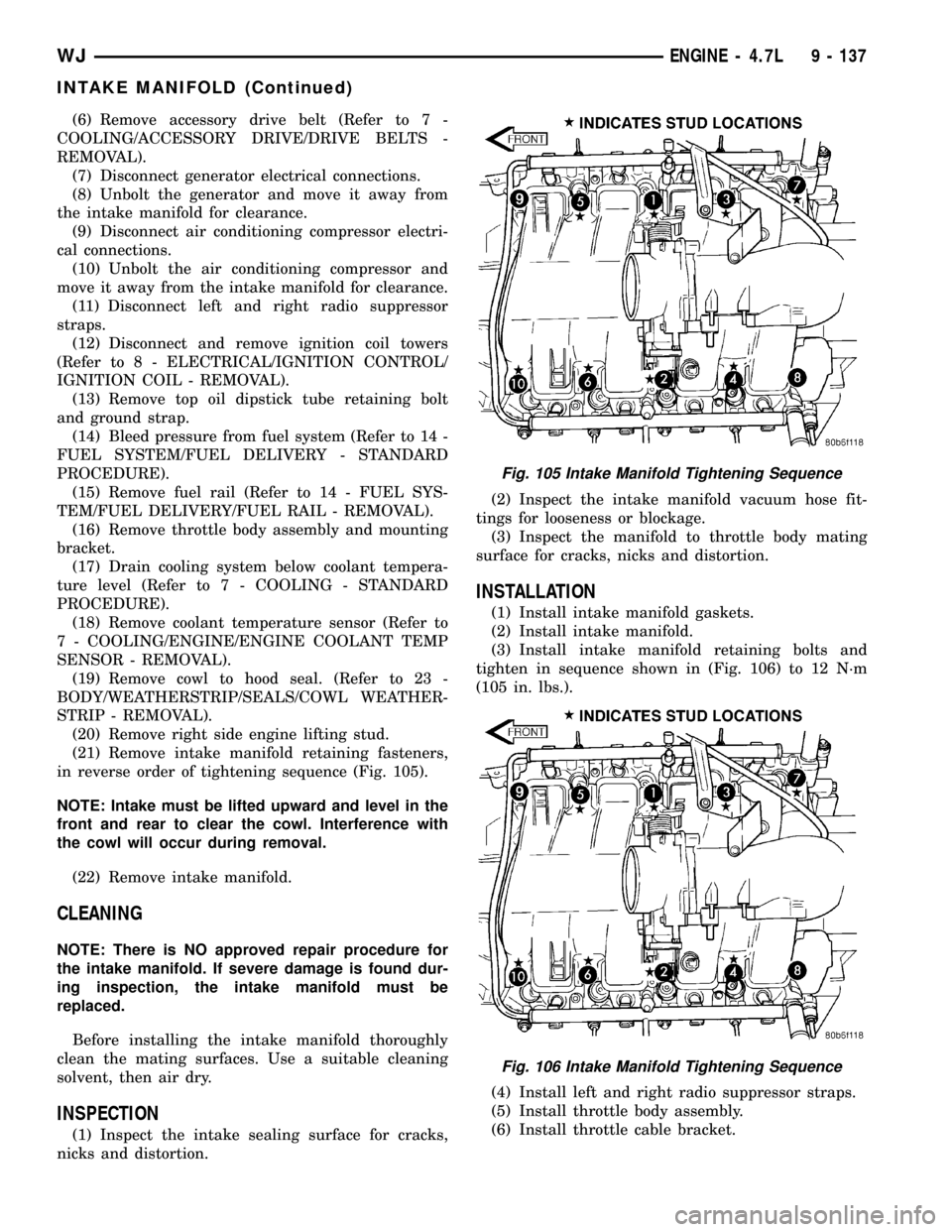
(21) Remove intake manifold retaining fasteners,
in reverse order of tightening sequence (Fig. 105).
NOTE: Intake must be lifted upward and level in the
front and rear to clear the cowl. Interference with
the cowl will occur during removal.
(22) Remove intake manifold.
CLEANING
NOTE: There is NO approved repair procedure for
the intake manifold. If severe damage is found dur-
ing inspection, the intake manifold must be
replaced.
Before installing the intake manifold thoroughly
clean the mating surfaces. Use a suitable cleaning
solvent, then air dry.
INSPECTION
(1) Inspect the intake sealing surface for cracks,
nicks and distortion.(2) Inspect the intake manifold vacuum hose fit-
tings for looseness or blockage.
(3) Inspect the manifold to throttle body mating
surface for cracks, nicks and distortion.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install intake manifold gaskets.
(2) Install intake manifold.
(3) Install intake manifold retaining bolts and
tighten in sequence shown in (Fig. 106) to 12 N´m
(105 in. lbs.).
(4) Install left and right radio suppressor straps.
(5) Install throttle body assembly.
(6) Install throttle cable bracket.
Fig. 105 Intake Manifold Tightening Sequence
Fig. 106 Intake Manifold Tightening Sequence
WJENGINE - 4.7L 9 - 137
INTAKE MANIFOLD (Continued)
Page 1421 of 2199

FUEL DELIVERY
DESCRIPTION
The fuel delivery system consists of:
²the fuel pump module containing the electric
fuel pump, fuel gauge sending unit (fuel level sensor)
and a separate fuel filter located at bottom of pump
module
²a separate combination fuel filter/fuel pressure
regulator
²fuel tubes/lines/hoses
²quick-connect fittings
²fuel injector rail
²fuel injectors
²fuel tank
²fuel tank filler/vent tube assembly
²fuel tank filler tube cap
²accelerator pedal
²throttle cable
OPERATION
The fuel tank assembly consists of: the fuel tank,
fuel tank shield, fuel tank straps, fuel pump module
assembly, fuel pump module locknut/gasket, and fuel
tank check valve (refer to Emission Control System
for fuel tank check valve information).
A fuel filler/vent tube assembly using a pressure/
vacuum, 1/4 turn fuel filler cap is used. The fuel
filler tube contains a flap door located below the fuel
fill cap.
Also to be considered part of the fuel system is the
evaporation control system. This is designed to
reduce the emission of fuel vapors into the atmo-
sphere. The description and function of the Evapora-
tive Control System is found in Emission Control
Systems.
Both fuel filters (at bottom of fuel pump module
and within fuel pressure regulator) are designed for
extended service. They do not require normal sched-
uled maintenance. Filters should only be replaced if
a diagnostic procedure indicates to do so.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
FUEL PRESSURE LEAK DOWN TEST
Use this test in conjunction with the Fuel Pump
Pressure Test and Fuel Pump Capacity Test.
Check Valve Operation:The electric fuel pump
outlet contains a one-way check valve to prevent fuel
flow back into the tank and to maintain fuel supply
line pressure (engine warm) when pump is not oper-
ational. It is also used to keep the fuel supply line
full of gasoline when pump is not operational. After
the vehicle has cooled down, fuel pressure may drop
to 0 psi (cold fluid contracts), but liquid gasoline willremain in fuel supply line between the check valve
and fuel injectors.Fuel pressure that has
dropped to 0 psi on a cooled down vehicle
(engine off) is a normal condition.When the elec-
tric fuel pump is activated, fuel pressure should
immediately(1±2 seconds) rise to specification.
Abnormally long periods of cranking to restart a
hotengine that has been shut down for a short
period of time may be caused by:
²Fuel pressure bleeding past a fuel injector(s).
²Fuel pressure bleeding past the check valve in
the fuel pump module.
²A defective fuel filter/pressure regulator.
Two #6539, 5/16º, Fuel Line Pressure Test Adapter
Hose Tools are required for the following tests.
(1) Release fuel system pressure. Refer to Fuel
Pressure Release Procedure.
(2) Raise vehicle.
Fuel Line Identification:The fuel filter/pressure
regulator is located in front of the fuel tank and
above the rear axle. It is transversely mounted to a
chassis crossmember (left-to-right). The filter/regula-
tor is equipped with 3 fuel line fittings (2 at one end
and 1 at the other end). The single fitting facing the
left side of the vehicle is the supply line to the fuel
rail (Fig. 1) . The 2 fittings facing the right side of
the vehicle are connected to the fuel tank. Of these 2
fittings, the fitting towards thefrontis used for fuel
return to the fuel tank. The fitting towards therear
is a pressure line. Thisrearfitting must be discon-
nected for the following step.
(3) See previous step. Disconnect fuel pressure line
atrearof filter/regulator. This is a 5/169quick-con-
nect fitting (Fig. 1) . Refer to Quick-Connect Fittings
for procedures.
(4) Obtain correct Fuel Line Pressure Test Adapter
Hose Tool # 6539 for 5/16º fuel lines. Connect one
end of this Special Tool into the disconnected fuel
pressure line. Connect the other end of the Tool into
fitting on filter/regulator.
(5) Lower vehicle.
(6) Disconnect the fuel inlet line at fuel rail. Refer
to Quick-Connect Fittings for procedures. On some
engines, air cleaner housing removal may be neces-
sary before fuel line disconnection.
(7) Obtain a second Fuel Line Pressure Test
Adapter Hose Tool # 6539 for 5/16º fuel lines. Con-
nect this tool between disconnected fuel line and fuel
rail (Fig. 2) .
(8) Connect the 0-414 kPa (0-60 psi) fuel pressure
test gauge (from Gauge Set 5069) to the test port on
the appropriate Adaptor Tool.NOTE: The DRB III
Scan Tool along with the PEP module, the 500
psi pressure transducer, and the transducer-to-
test port adapter may also be used in place of
the fuel pressure gauge.
14 - 2 FUEL DELIVERYWJ
Page 1424 of 2199
SPECIAL TOOLS
FUEL SYSTEM
FUEL FILTER/PRESSURE
REGULATOR
DESCRIPTION
The combination fuel filter/pressure regulator is
located in front of the fuel tank and above the rear
axle (Fig. 3). It is transversely mounted to a chassis
crossmember (left-to-right).Fuel Line Identifica-
tion:The filter/regulator is equipped with 3 fuel line
fittings (2 at one end and 1 at the other end). The
single fitting facing the left side of the vehicle is the
supply line to the fuel rail (Fig. 3). The 2 fittings fac-
ing the right side of the vehicle are connected to the
fuel tank. Of these 2 fittings, the fitting towards the
frontis used for fuel return to the fuel tank. The fit-
ting towards therearis a pressure line.
OPERATION
Fuel Pressure Regulator Operation:The pres-
sure regulator is a mechanical device that is not con-
trolled by engine vacuum or the Powertrain Control
Module (PCM).
Spanner WrenchÐ6856
FITTING, AIR METERING - 6714
Adapters, Fuel Pressure TestÐ6539 and/or 6631
O2S (Oxygen Sensor) Remover/InstallerÐC-4907
Test Kit, Fuel PressureÐ5069
Test Kit, Fuel PressureÐC-4799-B
Fuel Line Removal ToolÐ6782
WJFUEL DELIVERY 14 - 5
FUEL DELIVERY (Continued)
Page 1430 of 2199

(19) Disconnect test leads from relay cavities
immediately after testing.
FUEL PUMP PRESSURE TEST
Use this test in conjunction with other fuel system
tests. Refer to the Fuel Pump Capacity Test, Fuel
Pressure Leak Down Test and Fuel Pump Amperage
Test.
Check Valve Operation:The electric fuel pump
outlet contains a one-way check valve to prevent fuel
flow back into the tank and to maintain fuel supply
line pressure (engine warm) when pump is not oper-
ational. It is also used to keep the fuel supply line
full of gasoline when pump is not operational. After
the vehicle has cooled down, fuel pressure may drop
to 0 psi (cold fluid contracts), but liquid gasoline will
remain in fuel supply line between the check valve
and fuel injectors.Fuel pressure that has
dropped to 0 psi on a cooled down vehicle
(engine off) is a normal condition.When the elec-
tric fuel pump is activated, fuel pressure should
immediately(1±2 seconds) rise to specification.
The fuel system is equipped with a combination
fuel filter/fuel pressure regulator. The fuel pressure
regulator is not controlled by engine vacuum.
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER CON-
STANT FUEL PRESSURE EVEN WITH THE ENGINE
OFF. BEFORE DISCONNECTING FUEL LINE AT
FUEL RAIL, THIS PRESSURE MUST BE RELEASED.REFER TO THE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
RELEASE PROCEDURE.
(1) Remove pressure test port cap at fuel rail test
port (Fig. 12) or (Fig. 13) . Connect 0±414 kPa (0-60
psi) fuel pressure gauge (from gauge set 5069) to test
port pressure fitting on fuel rail (Fig. 14) .The DRB
III Scan Tool along with the PEP module, the
500 psi pressure transducer, and the transduc-
er-to-test port adapter may also be used in
place of the fuel pressure gauge.
(2) Start and warm engine and note pressure
gauge reading. The DRB scan tool may also be used
to power fuel pump. Fuel pressure should be 339 kPa
34 kPa (49.2 psi 5 psi) at idle.
(3) If engine runs, but pressure is below 44.2 psi,
determine if fuel pump or filter/regulator is defective.
Proceed to next step:
(a) Check for a kinked fuel supply line some-
where between fuel rail and fuel pump module.
Fig. 11 FUEL PUMP RELAY - TYPE 3
TERMINAL LEGEND
NUMBER IDENTIFICATION
1 COIL BATTERY
2 COIL GROUND
3 COMMON FEED
4 NORMALLY CLOSED
5 NORMALLY OPEN
Fig. 12 Test Port Cap LocationÐ4.0L Engine
1 - INJ. #1
2 - INJ. #2
3 - INJ. #3
4 - INJ. #4
5 - INJ. #5
6 - INJ. #6
7 - FUEL INJECTOR RAIL
8 - FUEL DAMPER
9 - PRESSURE TEST PORT CAP
10 - MOUNTING BOLTS (4)
11 - QUICK-CONNECT FITTING
WJFUEL DELIVERY 14 - 11
FUEL PUMP (Continued)
Page 1435 of 2199

CAUTION: The left and right fuel rails are replaced
as an assembly. Do not attempt to separate rail
halves at connector tube (Fig. 22). Due to design of
tube, it does not use any clamps. Never attempt to
install a clamping device of any kind to tube. When
removing fuel rail assembly for any reason, be care-
ful not to bend or kink tube.
(1) Remove fuel tank filler tube cap.
(2) Perform Fuel System Pressure Release Proce-
dure.
(3) Remove negative battery cable at battery.
(4) Remove air duct at throttle body air box.
(5) Remove air box at throttle body.
(6) Remove wiring at rear of generator.
(7) Disconnect fuel line latch clip and fuel line at
fuel rail. A special tool will be necessary for fuel line
disconnection. Refer to Quick-Connect Fittings.
(8) Remove vacuum lines at throttle body.(9) Disconnect electrical connectors at all 8 fuel
injectors. To remove connector refer to (Fig. 23). Push
red colored slider away from injector (1). While push-
ing slider, depress tab (2) and remove connector (3)
from injector. The factory fuel injection wiring har-
ness is numerically tagged (INJ 1, INJ 2, etc.) for
injector position identification. If harness is not
tagged, note wiring location before removal.
(10) Disconnect electrical connectors at throttle
body.
(11) Disconnect electrical connectors at MAP and
IAT sensors.
Fig. 21 Fuel Injector Rail/Fuel DamperÐ4.0L Engine
1 - INJ. #1
2 - INJ. #2
3 - INJ. #3
4 - INJ. #4
5 - INJ. #5
6 - INJ. #6
7 - FUEL INJECTOR RAIL
8 - FUEL DAMPER
9 - PRESSURE TEST PORT CAP
10 - MOUNTING BOLTS (4)
11 - QUICK-CONNECT FITTING
Fig. 22 FUEL INJECTOR RAIL - 4.7L V-8 EN
1 - MOUNTING BOLTS (4)
2 - INJ.#7
3 - INJ.#5
4 - QUICK-CONNECT FITTING
5 - INJ.#3
6 - FUEL INJECTOR RAIL
7 - INJ.#1
8 - CONNECTOR TUBE
9 - INJ.#2
10 - INJ.#4
11 - INJ.#6
12 - INJ.#8
13 - PRESSURE TEST PORT CAP
14 - 16 FUEL DELIVERYWJ
FUEL RAIL (Continued)
Page 1438 of 2199

(14) Install air tube (or duct) at top of throttle
body.
(15) Install fuel tank cap.
(16) Connect negative battery cable to battery.
(17) Start engine and check for fuel leaks.
FUEL TANK
DESCRIPTION
The fuel tank is constructed of a plastic material.
Its main functions are for fuel storage and for place-
ment of the fuel pump module and certain ORVR
components.
OPERATION
All models pass a full 360 degree rollover test
without fuel leakage. To accomplish this, fuel and
vapor flow controls are required for all fuel tank con-
nections.
A fuel tank check valve(s) is mounted into the top
of the fuel tank (or pump module). Refer to Fuel
Tank Check Valve for additional information.
An evaporation control system is connected to the
check valve(s) to reduce emissions of fuel vapors into
the atmosphere. When fuel evaporates from the fuel
tank, vapors pass through vent hoses or tubes to a
charcoal canister where they are temporarily held.
When the engine is running, the vapors are drawn
into the intake manifold. Certain models are also
equipped with a self-diagnosing system using a Leak
Detection Pump (LDP). Refer to Emission Control
System for additional information.
Refer to ORVR for On-Board Refueling Vapor
Recovery system information.
REMOVAL
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER CON-
STANT FUEL PRESSURE EVEN WITH ENGINE OFF.
PRESSURE MUST BE RELEASED BEFORE SERVIC-
ING FUEL TANK.
Two different procedures may be used to drain fuel
tank (through ORVR control valve opening at top of
fuel tank, or using DRB scan tool). The quickest is
draining through ORVR control valve opening at top
of fuel tank (Fig. 26).
As an alternative procedure, the electric fuel pump
may be activated allowing tank to be drained at fuel
rail connection. Refer to DRB scan tool for fuel pump
activation procedures. Before disconnecting fuel line
at fuel rail, release fuel pressure. Refer to the Fuel
System Pressure Release Procedure for procedures.
Attach end of Special Adapter Hose Tool number
6539 at fuel rail disconnection. Position opposite end
of 6539 to an approved gasoline draining station.Activate fuel pump with DRB and drain tank until
empty.
If electric fuel pump is not operating, tankMUST
be drained through ORVR control valve opening at
top of fuel tank (Fig. 26).
(1) Release fuel system pressure. Refer to Fuel
System Pressure Release Procedure.
(2) Disconnect negative battery cable at battery.
(3) Raise and support vehicle.
(4) Remove left rear wheel/tire.
CAUTION: HANDLE EVAP, LDP AND ORVR VAPOR /
VACUUM LINES VERY CAREFULLY. THESE LINES
AND HOSES MUST BE FIRMLY CONNECTED.
CHECK THE VAPOR/VACUUM LINES AT THE LDP,
LDP FILTER, EVAP CANISTER, EVAP CANISTER
PURGE SOLENOID AND ORVR COMPONENTS FOR
DAMAGE OR LEAKS. IF A LEAK IS PRESENT, A
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) MAY BE SET.
(5) Clean top of fuel tank at ORVR control valve
(Fig. 26) or (Fig. 27).
(6) Press release tab in direction of arrow in (Fig.
27) and remove ORVR control valve lock ring
(counter-clockwise). Lift up ORVR control slightly.
Using an approved gasoline draining station, drain
tank until empty through this opening.
(7) Remove stone shield behind left/rear wheel
(Fig. 28). Drill out plastic rivets for removal.
(8) Remove 3 LDP mounting bolts (Fig. 29).
(9) Remove support bracket brace bolt (Fig. 30).
(10) Loosen, but do not remove 2 support bracket
nuts at frame rail (Fig. 29).
(11) To separate and lower front section of two-
piece support bracket, remove 3 attaching bolts on
bottom of support bracket (Fig. 30). While lowering
support bracket, disconnect LDP wiring clip (Fig. 31).
(12) Remove hose clamp (Fig. 32) and remove fuel
fill hose from fuel fill tube.
(13) Cut and discard tie wrap from axle vent hose
(Fig. 32).
(14) Disconnect fuel vent hose from fuel vent tube
(Fig. 32).
(15) Disconnect ORVR hose elbow (Fig. 33) at top
of EVAP canister.
(16) Place hydraulic jack to bottom of fuel tank.
(17) Remove fuel tank-to-rear bumper fascia clips
(Fig. 34).
(18) Remove fuel tank heat shield mounting bolts
(Fig. 35).
CAUTION: To protect fuel tank from exhaust heat,
shield must re-installed after tank installation.
WARNING: PLACE SHOP TOWEL AROUND FUEL
LINES TO CATCH ANY EXCESS FUEL.
WJFUEL DELIVERY 14 - 19
FUEL RAIL (Continued)