sensor JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2003 WJ / 2.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: JEEP, Model Year: 2003, Model line: GRAND CHEROKEE, Model: JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2003 WJ / 2.GPages: 2199, PDF Size: 76.01 MB
Page 2086 of 2199

CONTROLS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
CONTROLS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - VACUUM
SYSTEM............................10
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH
DESCRIPTION.........................13
OPERATION...........................13
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COMPRESSOR
CLUTCH COIL........................13
STANDARD PROCEDURE - COMPRESSOR
CLUTCH BREAK-IN....................14
REMOVAL.............................14
INSPECTION..........................15
INSTALLATION.........................15
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH RELAY
DESCRIPTION.........................16
OPERATION...........................16
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C
COMPRESSOR CLUTCH RELAY..........16
REMOVAL.............................17
INSTALLATION.........................17
A/C HEATER CONTROL
DESCRIPTION.........................17
OPERATION...........................17
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AUTOMATIC
ZONE CONTROL SYSTEM..............18
REMOVAL.............................24
INSTALLATION.........................25
A/C PRESSURE TRANSDUCER
DESCRIPTION.........................25
OPERATION...........................25
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C PRESSURE
TRANSDUCER.......................26
REMOVAL.............................26
INSTALLATION.........................26
BLOWER MOTOR CONTROLLER
DESCRIPTION.........................26
OPERATION...........................26
REMOVAL.............................27
INSTALLATION.........................27
BLOWER MOTOR RESISTOR BLOCK
DESCRIPTION.........................27
OPERATION...........................27
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BLOWER
MOTOR RESISTOR BLOCK..............27
REMOVAL.............................28
INSTALLATION.........................28BLOWER MOTOR SWITCH
DESCRIPTION.........................28
OPERATION...........................28
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BLOWER
MOTOR SWITCH-MANUAL TEMPERATURE
CONTROL SYSTEM....................28
REMOVAL.............................29
IN-CAR TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................29
OPERATION...........................29
REMOVAL.............................29
BLEND DOOR ACTUATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................30
REMOVAL.............................30
INSTALLATION.........................30
MODE DOOR ACTUATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................30
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - HEAT/DEFROST - PANEL/
DEFROST DOOR ELECTRIC ACTUATOR . . . 31
REMOVAL - HEAT/DEFROST DOOR
VACUUM ACTUATOR..................31
REMOVAL - PANEL/DEFROST DOOR
VACUUM ACTUATOR..................32
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - HEAT/DEFROST -
PANEL/DEFROST DOOR ELECTRIC
ACTUATOR..........................32
INSTALLATION - HEAT/DEFROST DOOR
VACUUM ACTUATOR..................33
INSTALLATION - PANEL/DEFROST DOOR
VACUUM ACTUATOR..................33
RECIRCULATION DOOR ACTUATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................33
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - RECIRCULATION DOOR
VACUUM ACTUATOR..................33
REMOVAL - RECIRCULATION DOOR
ELECTRIC ACTUATOR.................33
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - RECIRCULATION DOOR
VACUUM ACTUATOR..................34
INSTALLATION - RECIRCULATION DOOR
ELECTRIC ACTUATOR.................34
VACUUM CHECK VALVE
DESCRIPTION.........................34
OPERATION...........................34
REMOVAL.............................34
INSTALLATION.........................34
WJCONTROLS 24 - 9
Page 2087 of 2199

VACUUM RESERVOIR
DESCRIPTION.........................34
OPERATION...........................34
REMOVAL.............................35
INSTALLATION.........................35EVAPORATOR TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................35
OPERATION...........................35
REMOVAL.............................35
INSTALLATION.........................35
CONTROLS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - VACUUM SYSTEM
Vacuum control is used to operate the mode doors
in the standard equipment manual temperature con-
trol system HVAC housing. Testing of the A/C Heater
mode control switch operation will determine if the
vacuum and electrical controls are functioning. How-
ever, it is possible that a vacuum control system that
operates perfectly at engine idle (high engine vac-
uum) may not function properly at high engine
speeds or loads (low engine vacuum). This can be
caused by leaks in the vacuum system, or a faulty
vacuum check valve.
A vacuum system test will help to identify the
source of poor vacuum system performance or vac-
uum system leaks. Before starting this test, stop the
engine and make certain that the problem isn't a dis-
connected vacuum supply tube at the engine intake
manifold vacuum tap or the vacuum reservoir.
Use an adjustable vacuum test set (Special Tool
C-3707-B) and a suitable vacuum pump to test the
HVAC vacuum control system. With a finger placed
over the end of the vacuum test hose probe (Fig. 1),
adjust the bleed valve on the test set gauge to obtain
a vacuum of exactly 27 kPa (8 in. Hg.). Release and
block the end of the probe several times to verify that
the vacuum reading returns to the exact 27 kPa (8
in. Hg.) setting. Otherwise, a false reading will be
obtained during testing.
VACUUM CHECK VALVES
(1) Remove the vacuum check valve to be tested.
The valves are located in the (black) vacuum supply
tubes at either the engine intake manifold vacuum
tap, or on the bottom of the HVAC unit behind the
passenger front floor duct.
(2) Connect the test set vacuum supply hose to the
A/C Heater control side of the valve. When connected
to this side of the check valve, no vacuum should
pass and the test set gauge should return to the 27
kPa (8 in. Hg.) setting. If OK, go to Step 3. If not OK,
replace the faulty valve.
(3) Connect the test set vacuum supply hose to the
engine vacuum side of the valve. When connected to
this side of the check valve, vacuum should flow
through the valve without restriction. If not OK,
replace the faulty valve.
A/C HEATER CONTROL
(1) Connect the test set vacuum probe to the
HVAC vacuum supply (black) tube in the engine com-
partment. Position the test set gauge so that it can
be viewed from the passenger compartment.
(2) Place the A/C Heater mode control switch knob
in each mode position, one position at a time, and
pause after each selection. The test set gauge should
return to the 27 kPa (8 in. Hg.) setting shortly after
each selection is made. If not OK, a component or
vacuum line in the vacuum circuit of the selected
mode has a leak. See the procedure in Locating Vac-
uum Leaks.
CAUTION: Do not use lubricant on the switch ports
or in the holes in the plug, as lubricant will ruin the
vacuum valve in the switch. A drop of clean water
in the connector plug holes will help the connector
slide onto the switch ports.
Fig. 1 ADJUST VACUUM TEST BLEED VALVE -
TYPICAL
1 - VACUUM PUMP TOOL C-4289
2 - VACUUM TEST SET C-3707
3 - BLEED VALVE
4 - PROBE
24 - 10 CONTROLSWJ
Page 2094 of 2199

open circuit to the fuse in the junction block as
required.
(5) The coil ground terminal cavity (85) is switched
to ground through the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM). There should be continuity between this cav-
ity and the A/C compressor clutch relay control cir-
cuit cavity of the PCM wire harness connector C
(gray) at all times. If not OK, repair the open circuit
as required.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the cover from the Power Distribution
Center (PDC) (Fig. 11).
(3) Refer to the label on the PDC for compressor
clutch relay identification and location.
(4) Unplug the compressor clutch relay from the
PDC.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the compressor clutch relay by aligning
the relay terminals with the cavities in the PDC and
pushing the relay firmly into place.
(2) Install the PDC cover.
(3) Connect the battery negative cable.
(4) Test the relay operation.
A/C HEATER CONTROL
DESCRIPTION
The manual temperature control HVAC system
uses a combination of electrical, and vacuum con-trols. The Automatic Zone Control (AZC) HVAC sys-
tem uses only electrical controls. These controls
provide the vehicle operator with a number of setting
options to help control the climate and comfort
within the vehicle. Refer to the owner's manual in
the vehicle glove box for more information on the
suggested operation and use of these controls.
Both a/c heater control panels are located on the
instrument panel inboard of the steering column and
below the radio (Fig. 12). Both control panels contain
rotary-type temperature control knob(s), a rotary-
type mode control switch knob, a rotary-type blower
motor speed switch knob and an air conditioning
compressor push button switch. The rear window
defogger push button switch is also located on a/c
heater control panel. The AZC control panel also fea-
tures a recirculation push button switch and a vac-
uum fluorescent display area.
OPERATION
The AZC control module uses infrared sensing
technology to control occupant comfort levels, not the
actual passenger compartment air temperature. Dual
infrared sensors mounted in the face of the control
unit independently measure the surface temperature
to maintain customer-perceived comfort temperature
under changing conditions. Dual Zone temperature
control provides wide side-to-side variation in comfort
temperature to exceed the needs of either front seat
occupant. This sensing system replaces interior air
temperature and solar sensors used to approximate
direct sensing control through complex control pro-
grams.
Fig. 11 POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER (PDC)
1 - TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE (TCM)
2 - NEGATIVE CABLE
3 - POSITIVE CABLE
4 - POWER DISTRIBUTION CENTER (PDC)
Fig. 12 A/C HEATER CONTROL PANELS
WJCONTROLS 24 - 17
A/C COMPRESSOR CLUTCH RELAY (Continued)
Page 2095 of 2199

Both the manual A/C Heater control panel and the
AZC control panel are serviced only as complete
units and cannot be repaired. If faulty or damaged,
the entire control panel unit must be replaced.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AUTOMATIC ZONE
CONTROL SYSTEM
The Automatic Zone Control (AZC) control module
has a system self-diagnostic mode which continuously
monitors various parameters during normal system
operation. If a system fault is detected, a current and
historical fault is recorded. When the current fault is
cleared, the historical fault remains until reset (man-
ually or automatically). Both the current and histor-
ical fault codes can be accessed through either the
front panel, or over the Programmable Communica-
tions Interface (PCI) bus using a DRBIIItscan tool,
and the appropriate diagnostic information.
The AZC control module is capable of three differ-
ent types of self-diagnostic tests, as follows:
²Fault Code Tests
²Input Circuit Tests
²Output Circuit/Actuator Tests
The information that follows describes:
²How to read the self-diagnostic display
²How to enter the AZC control module self-diag-
nostic test mode
²How to select the self-diagnostic test types
²How to perform the different tests
ENTERING THE AZC SELF-DIAGNOSTIC MODE
To enter the AZC self-diagnostic mode, perform the
following:
(1) Depress the a/c and recirc buttons at the same
time and hold. Rotate the left temperature control
knob clockwise (CW) one detent.
(2) If you continue to keep the a/c and recirc but-
tons depressed, the AZC control module will perform
a Segment Test of the Vacuum Fluorescent (VF) dis-
play. In the Segment Test you should see all of the
display segments illuminate as long as both buttons
are held. If a display segment fails to illuminate, the
vacuum fluorescent display is faulty and the a/c
heater control must be replaced.
(3) After viewing the Segment Test, release the
A/C and Recirc buttons and the display will clear
momentarily.Ifa0isdisplayed, then no faults
are set in the system.Should there be any faults,
either9current9or9historical9, all fault codes will be
displayed in ascending numerical sequence (note no
effort is made to display fault codes in chronological
order). Each fault code is displayed for one second
before the next code is displayed. Once all fault codes
have been displayed, the system will then repeat the
fault code numbers. This will continue until the left
side set temperature control is moved at least onedetent position in the CW direction or the ignition is
turned9OFF9.
FAULT CODE TESTS
Fault codes are two-digit numbers that identify a
circuit that is malfunctioning. There are two differ-
ent kinds of fault codes.
1.Current Fault Codes- Current means the
fault is present right now. There are two types of cur-
rent faults: input faults, and system faults.
2.Historical Fault Codes- Historical or stored
means that the fault occurred previously, but is not
present right now. A majority of historical fault codes
are caused by intermittent wire harness or wire har-
ness connector problems.
CURRENT FAULT CODES
Input faults 01 = IR thermister circuit
open
02 = IR thermister circuit
shorted
03 = Fan pot shorted
04 = Fan pot open
05 = Mode pot shorted
06 = Mode pot open
07 = IR sensor delta too
large
08 = Reserved
09 = Reserved
10 = One of four motor
drivers has drive9A9
shorted to ground
11 = Engine air intake
temperature Buss
message missing
12 = Country code Buss
message missing
24 - 18 CONTROLSWJ
A/C HEATER CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2097 of 2199

HISTORICAL FAULT CODES
Input faults 33 = IR thermister circuit was open
34 = IR thermister circuit was shorted
35 = Fan pot was shorted
36 = Fan pot was open
37 = Mode pot was shorted
38 = Mode pot was open
39 = IR sensor delta was too large
40 = Reserved
41 = Reserved
42 = One of four motor drivers had drive9A9shorted to
ground
43 = Engine air intake temperature Buss message
missing
44 = Country code Buss message missing
System Faults 45 = Mode motor was not responding
46 = AI (Recirc) motor was not responding
47 = Left temperature door was not responding
48 = Right temperature door was not responding
49 = Mode door travel range too small
50 = Mode door travel range too large
51 = AI (Recirc) door travel range too small
52 = AI (Recirc) door travel range too large
53 = Left temperature door travel too small
54 = Left temperature door travel too large
55 = Right temperature door travel too small
56 = Right temperature door travel too large
57 = Calibration check sum error
58 = Engine coolant temp bus message missing
59 = Vehicle speed bus message missing
60 = Engine RPM bus message missing
61 = OAT bus message missing
62 = Display intensity bus message missing
63 = VIN number bus message missing
64 = Raw OAT bus message was missing
65 = Reserved
66 = Reserved
67 = Reserved
NOTE: A battery disconnect will erase all faults
stored in Random Access Memory (RAM) of the
AZC control module. It is recommended that all
faults be recorded before they are erased.RETRIEVING FAULT CODES
(1) To begin the fault code tests, depress the A/C
and Recirc buttons at the same time and rotate the
left temperature control knob clockwise (CW) one
detent, then release the push-button.
24 - 20 CONTROLSWJ
A/C HEATER CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2099 of 2199
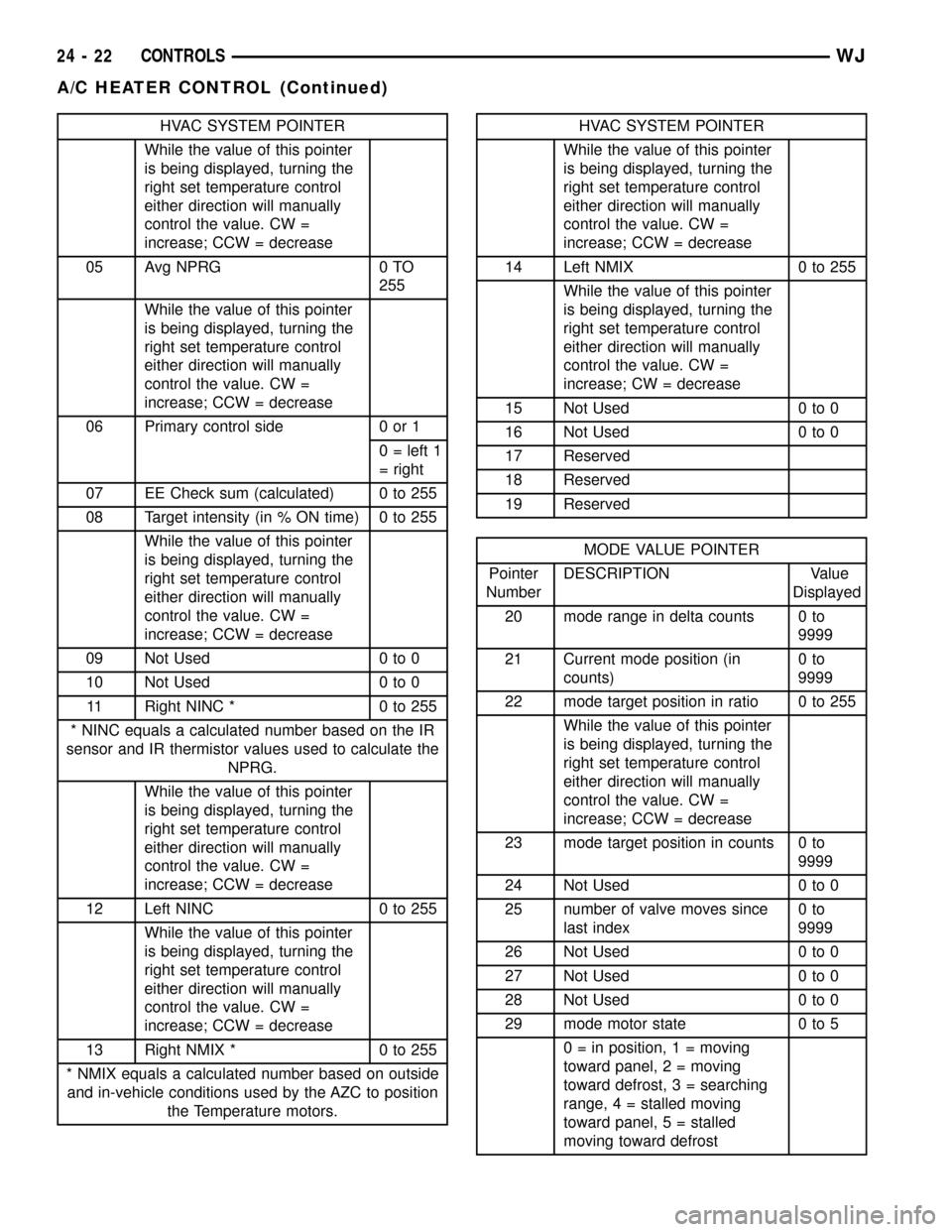
HVAC SYSTEM POINTER
While the value of this pointer
is being displayed, turning the
right set temperature control
either direction will manually
control the value. CW =
increase; CCW = decrease
05 Avg NPRG 0 TO
255
While the value of this pointer
is being displayed, turning the
right set temperature control
either direction will manually
control the value. CW =
increase; CCW = decrease
06 Primary control side 0 or 1
0 = left 1
= right
07 EE Check sum (calculated) 0 to 255
08 Target intensity (in % ON time) 0 to 255
While the value of this pointer
is being displayed, turning the
right set temperature control
either direction will manually
control the value. CW =
increase; CCW = decrease
09 Not Used 0 to 0
10 Not Used 0 to 0
11 Right NINC * 0 to 255
* NINC equals a calculated number based on the IR
sensor and IR thermistor values used to calculate the
NPRG.
While the value of this pointer
is being displayed, turning the
right set temperature control
either direction will manually
control the value. CW =
increase; CCW = decrease
12 Left NINC 0 to 255
While the value of this pointer
is being displayed, turning the
right set temperature control
either direction will manually
control the value. CW =
increase; CCW = decrease
13 Right NMIX * 0 to 255
* NMIX equals a calculated number based on outside
and in-vehicle conditions used by the AZC to position
the Temperature motors.HVAC SYSTEM POINTER
While the value of this pointer
is being displayed, turning the
right set temperature control
either direction will manually
control the value. CW =
increase; CCW = decrease
14 Left NMIX 0 to 255
While the value of this pointer
is being displayed, turning the
right set temperature control
either direction will manually
control the value. CW =
increase; CW = decrease
15 Not Used 0 to 0
16 Not Used 0 to 0
17 Reserved
18 Reserved
19 Reserved
MODE VALUE POINTER
Pointer
NumberDESCRIPTION Value
Displayed
20 mode range in delta counts 0 to
9999
21 Current mode position (in
counts)0to
9999
22 mode target position in ratio 0 to 255
While the value of this pointer
is being displayed, turning the
right set temperature control
either direction will manually
control the value. CW =
increase; CCW = decrease
23 mode target position in counts 0 to
9999
24 Not Used 0 to 0
25 number of valve moves since
last index0to
9999
26 Not Used 0 to 0
27 Not Used 0 to 0
28 Not Used 0 to 0
29 mode motor state 0 to 5
0 = in position, 1 = moving
toward panel, 2 = moving
toward defrost, 3 = searching
range, 4 = stalled moving
toward panel, 5 = stalled
moving toward defrost
24 - 22 CONTROLSWJ
A/C HEATER CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2101 of 2199
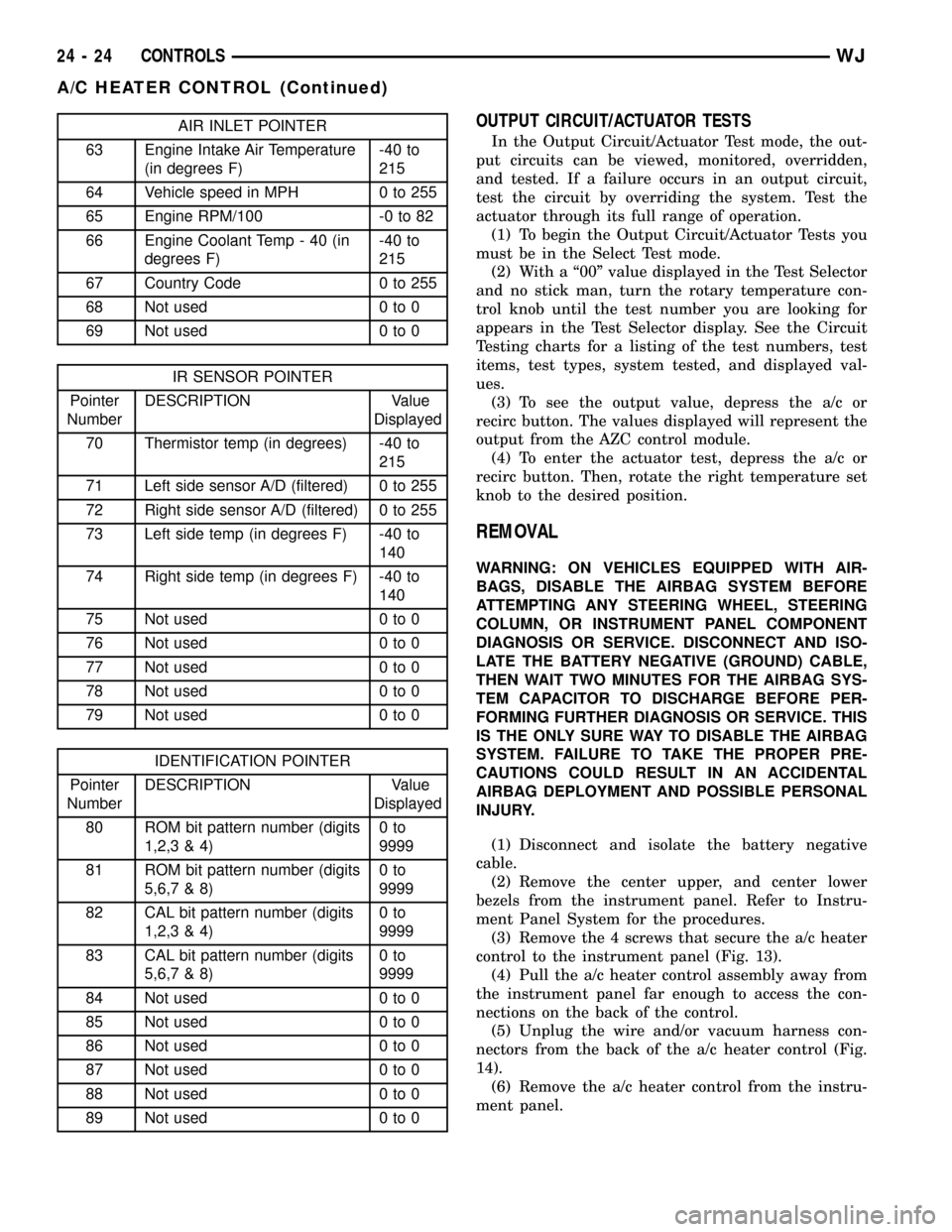
AIR INLET POINTER
63 Engine Intake Air Temperature
(in degrees F)-40 to
215
64 Vehicle speed in MPH 0 to 255
65 Engine RPM/100 -0 to 82
66 Engine Coolant Temp - 40 (in
degrees F)-40 to
215
67 Country Code 0 to 255
68 Not used 0 to 0
69 Not used 0 to 0
IR SENSOR POINTER
Pointer
NumberDESCRIPTION Value
Displayed
70 Thermistor temp (in degrees) -40 to
215
71 Left side sensor A/D (filtered) 0 to 255
72 Right side sensor A/D (filtered) 0 to 255
73 Left side temp (in degrees F) -40 to
140
74 Right side temp (in degrees F) -40 to
140
75 Not used 0 to 0
76 Not used 0 to 0
77 Not used 0 to 0
78 Not used 0 to 0
79 Not used 0 to 0
IDENTIFICATION POINTER
Pointer
NumberDESCRIPTION Value
Displayed
80 ROM bit pattern number (digits
1,2,3 & 4)0to
9999
81 ROM bit pattern number (digits
5,6,7 & 8)0to
9999
82 CAL bit pattern number (digits
1,2,3 & 4)0to
9999
83 CAL bit pattern number (digits
5,6,7 & 8)0to
9999
84 Not used 0 to 0
85 Not used 0 to 0
86 Not used 0 to 0
87 Not used 0 to 0
88 Not used 0 to 0
89 Not used 0 to 0
OUTPUT CIRCUIT/ACTUATOR TESTS
In the Output Circuit/Actuator Test mode, the out-
put circuits can be viewed, monitored, overridden,
and tested. If a failure occurs in an output circuit,
test the circuit by overriding the system. Test the
actuator through its full range of operation.
(1) To begin the Output Circuit/Actuator Tests you
must be in the Select Test mode.
(2) With a ª00º value displayed in the Test Selector
and no stick man, turn the rotary temperature con-
trol knob until the test number you are looking for
appears in the Test Selector display. See the Circuit
Testing charts for a listing of the test numbers, test
items, test types, system tested, and displayed val-
ues.
(3) To see the output value, depress the a/c or
recirc button. The values displayed will represent the
output from the AZC control module.
(4) To enter the actuator test, depress the a/c or
recirc button. Then, rotate the right temperature set
knob to the desired position.
REMOVAL
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN AN ACCIDENTAL
AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the center upper, and center lower
bezels from the instrument panel. Refer to Instru-
ment Panel System for the procedures.
(3) Remove the 4 screws that secure the a/c heater
control to the instrument panel (Fig. 13).
(4) Pull the a/c heater control assembly away from
the instrument panel far enough to access the con-
nections on the back of the control.
(5) Unplug the wire and/or vacuum harness con-
nectors from the back of the a/c heater control (Fig.
14).
(6) Remove the a/c heater control from the instru-
ment panel.
24 - 24 CONTROLSWJ
A/C HEATER CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2102 of 2199

INSTALLATION
(1) Plug the wire harness and/or vacuum harness
connectors into the back of the a/c heater control.
(2) Position the a/c heater control in the instru-
ment panel and secure it with 4 screws. Tighten the
screws to 2.2 N´m (20 in. lbs.).
(3) Reinstall the center upper, and center lower
bezels onto the instrument panel. Refer to Instru-
ment Panel System for the procedures.
(4) Connect the battery negative cable.
A/C PRESSURE TRANSDUCER
DESCRIPTION
The A/C pressure transducer is installed on a fit-
ting located on the refrigerant discharge line near
the condenser. An internally threaded hex fitting on
the transducer connects it to the externally threaded
Schrader-type fitting on the discharge line. A rubber
O-ring seals the connection between the transducer
and the discharge line fitting. Three terminals within
a molded plastic connector receptacle on the top of
the transducer connect it to the vehicle electrical sys-
tem through a take out and connector of the head-
lamp and dash wire harness.
The A/C pressure transducer cannot be adjusted or
repaired and if faulty or damaged, it must be
replaced.
OPERATION
The A/C pressure transducer monitors the pres-
sures in the high side of the refrigerant system
through its connection to a fitting on the discharge
line. The transducer will change its internal resis-
tance in response to the pressures it monitors. The
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) provides a five
volt reference signal and a sensor ground to the
transducer, then monitors the output voltage of the
transducer on a sensor return circuit to determine
refrigerant pressure. The PCM is preporgrammed to
respond to this and other sensor inputs by controlling
the operation of the air conditioning compressor
clutch and the radiator cooling fan to help optimize
air conditioning system performance and to protect
the system components from damage. The A/C pres-
sure transducer input to the PCM will also prevent
the air conditioning compressor clutch from engaging
when the ambient temperatures are below about
0.556É C (33É F) due to the pressure/temperature
relationship of the refrigerant. The Schrader-type
valve in the liquid line fitting permits the A/C pres-
sure transducer to be removed or installed without
distrubing the refrigerant in the system. The A/C
pressure transducer is diagnosed using the DRBIIIt
scan tool. Refer to the appropriate diagnostic infor-
mation.
Fig. 13 A/C HEATER CONTROL REMOVE/INSTALL
1 - MOUNTING SCREW TABS
Fig. 14 A/C HEATER CONTROL CONNECTIONS
1 - MODE SWITCH
2 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTIONS
3 - VACUUM HARNESS
WJCONTROLS 24 - 25
A/C HEATER CONTROL (Continued)
Page 2103 of 2199

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C PRESSURE
TRANSDUCER
The A/C pressure transducer is tested using a
DRBIIItscan tool. Refer to the appropriate diagnos-
tic information. Before testing the A/C pressure
transducer, be certain that the transducer wire har-
ness connection is clean of corrosion and properly
connected. For the air conditioning system to operate,
an A/C pressure transducer voltage reading between0.7 and 4.56 volts is required. Voltage outside this
range indicate a low or high refrigerant system pres-
sure condition to the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM). The PCM is programmed to respond to a low
or high refrigerant system pressure by suppressing
operation of the compressor. Refer to the A/C Pres-
sure Transducer Voltage table for the possible condi-
tion indicated by the transducer voltage readings.
A/C PRESSURE TRANSDUCER VOLTAGE
VOLTAGE POSSIBLE INDICATION
0.0 1. NO SENSOR SUPPLY VOLTAGE FROM PCM.
2. SHORTED SENSOR CIRCUIT.
3. FAULTY TRANSDUCER
0.150 TO 0.450 1. AMBIENT TEMPERATURE BELOW 10É c (50É F).
2. LOW REFRIGERANT SYSTEM PRESSURE.
0.451 TO 4.519 1. NORMAL REFRIGERANT SYSTEM PRESSURE.
4.520 TO 4.850 1. HIGH REFRIGERANT SYSTEM PRESSURE.
5.0 1. OPEN SENSOR CIRCUIT.
2. FAULTY TRANSDUCER.
REMOVAL
WARNING: Transducer can be removed without
recoverying the system, but some loss of refriger-
ant can be expected(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - WARNING) and (Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
CAUTION).
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Disconnect the headlamp and dash wire har-
ness connector for the A/C pressure transducer from
the transducer connector receptacle.
(3) Using an open end wrench, unscrew the A/C
pressure transducer from the fitting on the discharge
line.
(4) Remove the seal from the A/C pressure trans-
ducer fitting and discard.
INSTALLATION
(1) Lubricate a new O-ring seal with clean refrig-
erant oil and install it on the A/C pressure trans-
ducer fitting.
(2) Using an open end wrench, install and tighten
the A/C pressure transducer onto the fitting on the
discharge line.
(3) Reconnect the headlamp and dash wire harness
connector for the A/C pressure transducer to the
transducer connector receptacle.(4) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
BLOWER MOTOR
CONTROLLER
DESCRIPTION
Models equipped with the optional Automatic Zone
Control (AZC) system have a blower motor controller.
The controller allows the selection of almost infi-
nitely variable blower motor speeds. The controller is
mounted to the HVAC housing, under the instrument
panel and just inboard of the blower motor, in the
same location used for the blower motor resistor on
manual temperature control systems. It can be
accessed without removing any other components.
OPERATION
The blower motor controller output to the blower
motor can be adjusted by the blower motor speed
switch knob on the AZC A/C Heater control panel, or
it can be adjusted automatically by the logic circuitry
and programming of the AZC control module. In
either case, the AZC control module sends the correct
pulse width modulated signal to the blower motor
controller to obtain the selected or programmed
blower motor speed.
The blower motor controller cannot be repaired
and, if faulty or damaged, it must be replaced.
24 - 26 CONTROLSWJ
A/C PRESSURE TRANSDUCER (Continued)
Page 2106 of 2199

WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN AN ACCIDENTAL
AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
(1) Check for battery voltage at the fuse in the
Power Distribution Center (PDC). If OK, go to Step
2. If not OK, repair the shorted circuit or component
as required and replace the faulty fuse.
(2) Turn the ignition switch to the Off position.
Disconnect and isolate the battery negative cable.
Remove the a/c heater control from the instrument
panel. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITION-
ING/CONTROLS/A/C HEATER CONTROL -
REMOVAL) Check for continuity between the ground
circuit cavity of the a/c heater control wire harness
connector and a good ground. There should be conti-
nuity. If OK, go to Step 3. If not OK, repair the open
circuit to ground as required.
(3) With the a/c heater control wire harness con-
nector unplugged, place the a/c heater mode control
switch knob in any position except the Off position.
Check for continuity between the ground circuit ter-
minal and each of the blower motor driver circuit ter-
minals of the a/c heater control as you move the
blower motor switch knob to each of the four speed
positions. There should be continuity at each driver
circuit terminal in only one blower motor switch
speed position. If OK, test and repair the blower
driver circuits between the a/c heater control connec-
tor and the blower motor resistor as required. If not
OK, replace the faulty a/c heater control unit.
REMOVAL
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM BEFORE
ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL, STEERING
COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT
DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCONNECT AND ISO-
LATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE (GROUND) CABLE,
THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIRBAG SYS-
TEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE BEFORE PER-
FORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. THIS
IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DISABLE THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN AN ACCIDENTALAIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
The blower motor switch cannot be adjusted or
repaired, and if faulty or damaged, the a/c heater
control must be replaced. (Refer to 24 - HEATING &
AIR CONDITIONING/CONTROLS/A/C HEATER
CONTROL - REMOVAL)
IN-CAR TEMPERATURE
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
Models equipped with the optional Automatic Zone
Control (AZC) system use automatic dual zone tem-
perature control with infrared sensing technology.
The temperature sensor is located in the center
instrument panel, between the dual temperature
knobs of the AZC.
OPERATION
The Automatic Zone Control uses infrared sensing
technology to control occupant comfort levels, not the
actual passenger compartment air temperature. Dual
infrared sensors mounted in the face of the control
unit independently measure the surface temperature
to maintain customer-perceived comfort temperature
under changing conditions. Dual Zone temperature
control provides wide side-to-side variation in comfort
temperature to exceed the needs of either front seat
occupant. This sensing system replaces interior air
temperature and solar sensors used to approximate
direct sensing control through complex control pro-
grams.
The infrared temperature sensor cannot be
adjusted or repaired and, if faulty or damaged, the
AZC head must be replaced.
NOTE: The infrared sensor window may be perma-
nently damaged if any type of cosmetic vinyl dress-
ings are allowed to contact the lens. Avoid spraying
or wiping this area with any cleaner or conditioner.
This may result in impaired temperature sensing
and control.
REMOVAL
The infrared temperature sensor cannot be
adjusted or repaired and, if faulty or damaged, the
AZC head must be replaced. (Refer to 24 - HEATING
& AIR CONDITIONING/CONTROLS/A/C HEATER
CONTROL - REMOVAL)
WJCONTROLS 24 - 29
BLOWER MOTOR SWITCH (Continued)